Broadcast Storm on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A broadcast storm or broadcast radiation is the accumulation of
A broadcast storm or broadcast radiation is the accumulation of
 A broadcast storm or broadcast radiation is the accumulation of
A broadcast storm or broadcast radiation is the accumulation of broadcast
Broadcasting is the data distribution, distribution of sound, audio audiovisual content to dispersed audiences via a electronic medium (communication), mass communications medium, typically one using the electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves), ...
and multicast
In computer networking, multicast is a type of group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast differs from ph ...
traffic on a computer network
A computer network is a collection of communicating computers and other devices, such as printers and smart phones. In order to communicate, the computers and devices must be connected by wired media like copper cables, optical fibers, or b ...
. Extreme amounts of broadcast traffic constitute a ''broadcast storm''. It can consume sufficient network resources so as to render the network unable to transport normal traffic. A packet that induces such a storm is occasionally nicknamed a Chernobyl packet.
Causes
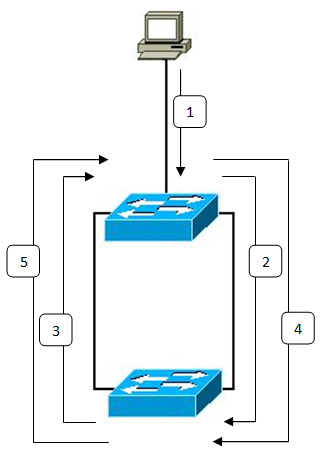
Most commonly the cause is aswitching loop
A switching loop or bridge loop occurs in computer networks when there is more than one layer 2 path between two endpoints (e.g. multiple connections between two network switches or two ports on the same switch connected to each other). The loo ...
in the Ethernet network topology
Network topology is the arrangement of the elements (Data link, links, Node (networking), nodes, etc.) of a communication network. Network topology can be used to define or describe the arrangement of various types of telecommunication networks, ...
(i.e. two or more paths exist between switches). A simple example is both ends of a single Ethernet patch cable connected to a switch. As broadcasts and multicast
In computer networking, multicast is a type of group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast differs from ph ...
s are forwarded by switches out of every port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Hamburg, Manch ...
, the switch or switches will repeatedly rebroadcast broadcast messages and flood the network. Since the layer-2
The data link layer, or layer 2, is the second layer of the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking. This layer is the protocol layer that transfers data between nodes on a network segment across the physical layer. The data link layer p ...
header does not support a time to live
Time to live (TTL) or hop limit is a mechanism which limits the lifespan or lifetime of data in a computer or network. TTL may be implemented as a counter (digital), counter or timestamp attached to or embedded in the data. Once the prescribed ev ...
(TTL) value, if a frame
A frame is often a structural system that supports other components of a physical construction and/or steel frame that limits the construction's extent.
Frame and FRAME may also refer to:
Physical objects
In building construction
*Framing (con ...
is sent into a looped topology, it can loop forever.
In some cases, a broadcast storm can be instigated for the purpose of a denial of service
In computing, a denial-of-service attack (DoS attack) is a cyberattack in which the perpetrator seeks to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users by temporarily or indefinitely disrupting services of a host co ...
(DOS) using one of the packet amplification attacks, such as the smurf attack or fraggle attack, where an attacker sends a large amount of ICMP Echo Requests ( ping) traffic to a broadcast address, with each ICMP Echo packet containing the spoof source address of the victim host. When the spoofed packet arrives at the destination network, all hosts on the network reply to the spoofed address. The initial Echo Request is multiplied by the number of hosts on the network. This generates a storm of replies to the victim host tying up network bandwidth
Bandwidth commonly refers to:
* Bandwidth (signal processing) or ''analog bandwidth'', ''frequency bandwidth'', or ''radio bandwidth'', a measure of the width of a frequency range
* Bandwidth (computing), the rate of data transfer, bit rate or thr ...
, using up CPU resources or possibly crashing the victim.
In wireless network
A wireless network is a computer network that uses wireless data connections between network nodes. Wireless networking allows homes, telecommunications networks, and business installations to avoid the costly process of introducing cables int ...
s a disassociation packet spoofed with the source to that of the wireless access point
In Computer networking device, computer networking, a wireless access point (WAP) (also just access point (AP)) is a networking hardware device that allows other Wi-Fi devices to connect to a wired network or wireless network. As a standalone ...
and sent to the broadcast address can generate a disassociation broadcast DOS attack.
Prevention
*Switching loop
A switching loop or bridge loop occurs in computer networks when there is more than one layer 2 path between two endpoints (e.g. multiple connections between two network switches or two ports on the same switch connected to each other). The loo ...
s are largely addressed through link aggregation
In computer networking, link aggregation is the combining ( aggregating) of multiple network connections in parallel by any of several methods. Link aggregation increases total throughput beyond what a single connection could sustain, and prov ...
, Shortest Path Bridging or Spanning Tree Protocol
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a network protocol that builds a loop-free logical topology for Ethernet networks. The basic function of STP is to prevent bridge loops and the broadcast radiation that results from them. Spanning tree al ...
. In Metro Ethernet rings it is prevented using the Ethernet Ring Protection Switching (ERPS) or Ethernet Automatic Protection System (EAPS) protocols.
* Filtering broadcasts by Layer 3 equipment, typically routers (and even switches that employ advanced filtering called brouters).
* Physically segmenting the broadcast domain
A broadcast domain is a logical division of a computer network, in which all nodes can reach each other by broadcast at the data link layer. A broadcast domain can be within the same LAN segment or it can be bridged to other LAN segments.
In te ...
s using routers at Layer 3 (or logically with VLAN
A virtual local area network (VLAN) is any broadcast domain that is partitioned and isolated in a computer network at the data link layer ( OSI layer 2).IEEE 802.1Q-2011, ''1.4 VLAN aims and benefits'' In this context, virtual refers to a ...
s at Layer 2) in the same fashion switches decrease the size of collision domains at Layer 2.
* Routers and firewalls can be configured to detect and prevent maliciously inducted broadcast storms (e.g. due to a magnification attack).
* Broadcast storm control is a feature of many managed switches in which the switch intentionally ceases to forward all broadcast traffic if the bandwidth consumed by incoming broadcast frames exceeds a designated threshold. Although this does not resolve the root broadcast storm problem, it limits broadcast storm intensity and thus allows a network manager to communicate with network equipment to diagnose and resolve the root problem.
MANET broadcast storms
In amobile ad hoc network
A wireless ad hoc network (WANET) or mobile ad hoc network (MANET) is a decentralized type of wireless network. The network is ad hoc because it does not rely on a pre-existing infrastructure, such as router (computing), routers or wireless acces ...
(MANET), route request (RREQ) packets are usually broadcast to discover new routes.
These RREQ packets may cause broadcast storms and compete over the channel with data packets.
One approach to alleviate the broadcast storm problem is to inhibit some hosts from rebroadcasting to reduce the redundancy, and thus contention and collision.
References
{{reflist Network performance Network topology Denial-of-service attacks Wireless networking