Birth Weight on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Birth weight is the body weight of a
Birth weight is the body weight of a
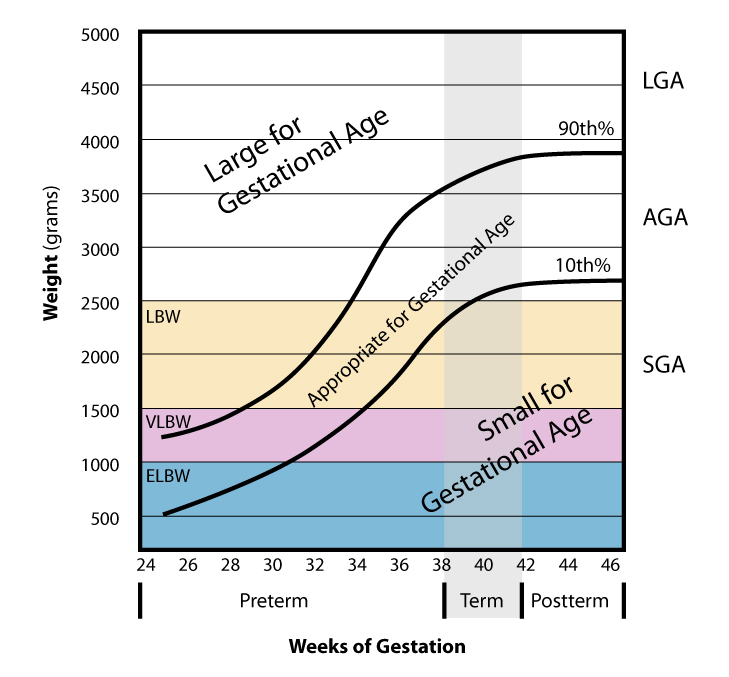
 Children born with an abnormally low birth weight can have significant problems within the first few years of life. They may have trouble gaining weight, obtaining adequate nutrition, and developing a strong immune system. They also have higher risks for mortality, behavior problems, and mental deficiencies. Low birth weight babies are more likely to develop the following conditions compared to normal birth weight babies:
* Breathing problems ( infant respiratory distress syndrome)
* Bleeding in the brain ( intraventricular hemorrhage)
* Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
* Necrotizing enterocolitis
* Retinopathy of prematurity
* Jaundice
* Infections
That said, the effects of low birth weight on a child's first few years of life are often intertwined with other maternal, environmental, and genetic factors and most effects of low birth weight are only slightly negatively significant on a child's life when these factors are controlled for. When these factors are taken into account, the only significant effect low birth weight has on a child's development is early physical growth and the likelihood of being underweight, compared to those with a normal birth rate.
Children born with an abnormally low birth weight can have significant problems within the first few years of life. They may have trouble gaining weight, obtaining adequate nutrition, and developing a strong immune system. They also have higher risks for mortality, behavior problems, and mental deficiencies. Low birth weight babies are more likely to develop the following conditions compared to normal birth weight babies:
* Breathing problems ( infant respiratory distress syndrome)
* Bleeding in the brain ( intraventricular hemorrhage)
* Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
* Necrotizing enterocolitis
* Retinopathy of prematurity
* Jaundice
* Infections
That said, the effects of low birth weight on a child's first few years of life are often intertwined with other maternal, environmental, and genetic factors and most effects of low birth weight are only slightly negatively significant on a child's life when these factors are controlled for. When these factors are taken into account, the only significant effect low birth weight has on a child's development is early physical growth and the likelihood of being underweight, compared to those with a normal birth rate.

 Birth weight is the body weight of a
Birth weight is the body weight of a baby
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to Juvenile (orga ...
at their birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the f ...
. The average birth weight in babies of European and African descent is , with the normative range between .
15% of babies born in 2012 had a low birth weight and 14.7% in 2020. It is projected that 14.2% of newborns will have low birth weight in 2030, falling short of the 2030 Sustainable Development Goals target of a reduction of 30%.
On average, babies of Asian descent weigh about . The prevalence of low birth weight has changed over time. Trends show a slight decrease from 7.9% (1970) to 6.8% (1980), then a slight increase to 8.3% (2006), to the current levels of 8.2% (2016). The prevalence of low birth weights has trended slightly upward from 2012 to the present.
Low birth weight is associated with neonatal infection, infant mortality
Infant mortality is the death of an infant before the infant's first birthday. The occurrence of infant mortality in a population can be described by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the number of deaths of infants under one year of age ...
, as well as illness into adulthood. Numerous studies have attempted, with varying degrees of success, to show links between birth weight and later-life conditions, including diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
, obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
, tobacco smoking, and intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. It can be described as t ...
.
Abnormalities
*A low birth weight can be caused either by apreterm birth
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the Childbirth, birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks Gestational age (obstetrics), gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 ...
(low gestational age at birth) or the infant being small for gestational age (slow prenatal growth rate), or a combination of both. Small for gestational age is defined as below the 10th percentile for gestational age and sex. Low birth weight can also be caused by health issues in the person giving birth, genetic factors, or problems in the placenta.
*A very large birth weight is usually caused by the infant having been large for gestational age. Large birth weight can be caused by maternal health issues such as gestational diabetes and obesity. Large birth weight has been associated with significantly higher rates of neonatal morbidity.
Determinants

Genetics
There are two genetic loci that have been strongly linked to birth weight, '' ADCY5'' and '' CCNL1'', and four that show some evidence ('' CDKAL1'', '' HHEX– IDE'', '' GCK'', and '' TCF7L2''). Theheritability
Heritability is a statistic used in the fields of Animal husbandry, breeding and genetics that estimates the degree of ''variation'' in a phenotypic trait in a population that is due to genetic variation between individuals in that population. T ...
of birth weight ranges from 25 to 40%. There is a complex relationship between a baby's genes and the maternal environment that the child is developing in. Foetal
A fetus or foetus (; : fetuses, foetuses, rarely feti or foeti) is the unborn offspring of a viviparous animal that develops from an embryo. Following the embryonic development, embryonic stage, the fetal stage of development takes place. Pren ...
genes influence how the fetus grows in utero, and the maternal genes influence how the environment affects the growing fetus.
Maternal health
Thehealth
Health has a variety of definitions, which have been used for different purposes over time. In general, it refers to physical and emotional well-being, especially that associated with normal functioning of the human body, absent of disease, p ...
of the mother during the pregnancy can affect birth weight. A pre-existing disease or acquired disease in pregnancy is sometimes associated with decreased birth weight. For example, celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine. Patients develop intolerance to gluten, which is present in foods such as wheat, rye, spel ...
confers an odds ratio
An odds ratio (OR) is a statistic that quantifies the strength of the association between two events, A and B. The odds ratio is defined as the ratio of the odds of event A taking place in the presence of B, and the odds of A in the absence of B ...
of low birth weight of approximately 1.8. Certain medications (e.g. for high blood pressure or epilepsy) can put a mother at a higher risk for delivering a low birth weight baby. Women younger than 15 or older than 35 are at a higher risk to have a low-birth weight baby. Multiple births, where a mother has more than one child at one time, can also be a determinant in birth weight as each baby is likely to be outside the AGA (appropriate for gestational age). Multiple births put children at a higher rate to have low birth weight (56.6%) compared to children born in a single birth (6.2%). Low birth weight can also vary by maternal age. In 2008 the rate of low birth weight was the highest in babies born to women younger than 15 years old (12.4%). Women aged 40–54 had a rate of low birth weight at 11.8 percent. The lowest rates of low birth weight happened among babies whose mothers were between the ages of 25–29 years (4.4%) and 30–34 years (7.6%).
Stress
Stressful events have been demonstrated to produce significant effects on birth weight. Those mothers who have stressful events duringpregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
, especially during the first and second trimester, are at higher risk to deliver low birth weight babies. Researchers furthered this study and found that maternal stressful events that occur prior to conception have a negative impact on birth weight as well, and can result in a higher risk for preterm and lower birth weight babies. Women who experienced abuse (physical, sexual, or emotional) during pregnancy are also at increased risk of delivering a low birth weight baby. For example, in a study completed by Witt et al., those women who experienced a stressful event (i.e. death of close family member, infertility issues, separation from partner) prior to conception had 38% more of a chance to have a very low birth weight baby compared to those who had not experienced a stressful life event. Additionally, mothers with diagnosed post-traumatic stress disorder are more likely to give birth to a low birth weight infant. The theory is that stress can impact a baby based on two different mechanisms: neuroendocrine pathway or immune/inflammatory pathway. Stress causes the body to produce stress hormones called glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebra ...
s that can suppress the immune system, as well as raises levels of placental corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) which can lead to preterm labor. These findings can pose evidence for future prevention efforts for low birth weight babies. One way to decrease rates of low birth weight and premature delivery is to focus on the health of women prior to conception through reproductive education, screening and counseling regarding mental health issues and stress, and access to primary care.
Racial stress
Non-Hispanic Blacks have the highest infant mortality rate in the United States (11.4 deaths per 1,000 live births compared to the national average of 5.9 deaths per 1,000 live births). Subsequently, there has been growing research supporting the idea ofracial discrimination
Racial discrimination is any discrimination against any individual on the basis of their Race (human categorization), race, ancestry, ethnicity, ethnic or national origin, and/or Human skin color, skin color and Hair, hair texture. Individuals ...
as a risk factor for low birth weight. In one study by Collins et al., evidence suggested that African American mothers who experienced high levels of racial discrimination were at significantly higher risk of delivering a very low-birth weight baby compared to African American mothers who had not experienced racial discrimination.
Environmental factors
Environmental factors, including exposure of the mother to secondhand smoke can be a factor in determining the birth weight of child. In 2014, 13% of children exposed to smoke were born with low birth weight compared with 8% of those children born to nonsmokers. Children born to mothers who smoked or were exposed to secondhand smoke are more likely to develop health problems earlier in life such as neurodevelopmental delays. When mothers actively smoke during pregnancy, their child is at a higher risk of being born with a low birth weight. Unfortunately, smoking is sometimes used as a stress management tool by expecting mothers. There is some support for lowersocioeconomic status
Socioeconomic status (SES) is a measurement used by economics, economists and sociology, sociologsts. The measurement combines a person's work experience and their or their family's access to economic resources and social position in relation t ...
of the parents being a determinant of low birth weight, but there is conflicting evidence, as socioeconomic status is tied to many other factors.
Neonatal care
Most babies admitted to the NICU are born before 37 weeks of pregnancy or have low birth weight which is less than . They could also have a medical condition that requires special care. In the United States nearly half a million babies are born preterm. Because of this, many of these babies also have low birth weights. There are four levels of care in the neonatal care units: intensive care, high dependency care, low dependency, and transitional care: * Intensive care: For babies with serious problems. This includes babies born three months early and with extremely low birth weight. * High dependency care: For babies with less serious problems, but who still may need to be looked after or babies that are recovering from a critical illness. * Low dependency care: For babies that do not need continuous supervision. * Transitional care: For babies that still need medical treatment, but are well enough to be called for at their mother's bedside.Influence on early life
 Children born with an abnormally low birth weight can have significant problems within the first few years of life. They may have trouble gaining weight, obtaining adequate nutrition, and developing a strong immune system. They also have higher risks for mortality, behavior problems, and mental deficiencies. Low birth weight babies are more likely to develop the following conditions compared to normal birth weight babies:
* Breathing problems ( infant respiratory distress syndrome)
* Bleeding in the brain ( intraventricular hemorrhage)
* Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
* Necrotizing enterocolitis
* Retinopathy of prematurity
* Jaundice
* Infections
That said, the effects of low birth weight on a child's first few years of life are often intertwined with other maternal, environmental, and genetic factors and most effects of low birth weight are only slightly negatively significant on a child's life when these factors are controlled for. When these factors are taken into account, the only significant effect low birth weight has on a child's development is early physical growth and the likelihood of being underweight, compared to those with a normal birth rate.
Children born with an abnormally low birth weight can have significant problems within the first few years of life. They may have trouble gaining weight, obtaining adequate nutrition, and developing a strong immune system. They also have higher risks for mortality, behavior problems, and mental deficiencies. Low birth weight babies are more likely to develop the following conditions compared to normal birth weight babies:
* Breathing problems ( infant respiratory distress syndrome)
* Bleeding in the brain ( intraventricular hemorrhage)
* Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
* Necrotizing enterocolitis
* Retinopathy of prematurity
* Jaundice
* Infections
That said, the effects of low birth weight on a child's first few years of life are often intertwined with other maternal, environmental, and genetic factors and most effects of low birth weight are only slightly negatively significant on a child's life when these factors are controlled for. When these factors are taken into account, the only significant effect low birth weight has on a child's development is early physical growth and the likelihood of being underweight, compared to those with a normal birth rate.
Influence on adult life
Studies have investigated how a person's birth weight can influence their future life, including potential links withobesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
, diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
and intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. It can be described as t ...
.
A baby born small or large for gestational age (either of the two extremes) was previously thought to have an increased risk of developing obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
, but it was later found that both high birth weight and maternal BMI are associated with increased risk of developing obesity in childhood.
Growth hormone (GH) therapy at a certain dose induced catch-up of lean body mass (LBM). However, percentage body fat decreased in the GH-treated subjects. Bone mineral density SDS measured by DEXA increased significantly in the GH-treated group compared to the untreated subjects, though there is much debate over whether or not SGA (small for gestational age) is significantly adverse to children to warrant inducing catch-up.
Babies that have a low birth weight are thought to have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
in later life. Low birth weight is linked with increase rates of obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes and it is shown that children with the low birth weights have increased leptin
Leptin (from Ancient Greek, Greek λεπτός ''leptos'', "thin" or "light" or "small"), also known as obese protein, is a protein hormone predominantly made by adipocytes (cells of adipose tissue). Its primary role is likely to regulate long ...
levels after they catch up growth during childhood. Adiponectin levels are positively related with birth weight and BMI in babies with an increase of risk of type 2 diabetes. The leptin and adiponection mechanisms are still being studied when involving low birth weight.
Around the world
There is much variation regarding birth weight within continents, countries, and cities. Even though over 20 million babies are born each year with low birth weight, it is hard to know the exact number, as more than half of babies born in the world are not weighed at birth. The baby's weight is an indicator of the mother and baby's health. In 2013, 22 million newborns had low birth weight, around 16 percent of all babies globally. Data on low birth weight is adjusted to account for under reporting. South Asia has the highest rate of babies not weighed at birth with 66 percent, but also have the highest low birth weight, at 28 percent worldwide. West and Central Africa and least developed countries are next, with 14 percent low birth weight worldwide. More than 96.5% of low birth weight babies are born in developing countries around the world. Because low birth weight babies can require more extensive care, it places a financial burden on communities.Prevention
TheWorld Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
(WHO) recently announced an initiative to have a thirty percent reduction in low birth weight worldwide. This is a public health priority, as birth weight can have short- and long-term effects. WHO estimates that worldwide, 15–20% of all births each year are considered low birth weight, which is about 20 million births.
The start of prenatal care is very important to help prevent low birth weight and early medical problems. Going to regular doctor's visits is very important for the health of the mother and the baby. At the visits, OB/GYNs check maternal nutrition and weight gain because they are linked to the baby's weight gain. The mother having a healthy diet is essential for the baby. Maintaining good nutrition by taking folic acid
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing and ...
, which can be found in fruits and vegetables, is linked to the prevention of premature births and low birth weight. Alcohol, cigarettes, and drugs should also be avoided during pregnancy because they can also lead to poor growth and other complications. Doctors are also able to monitor pre-existing medical illnesses to make sure they are under control during pregnancy. Mothers with high blood pressure
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms itself. It is, however, a major ri ...
and type 2 diabetes are more likely to have infants with low birth weights. One essential action to increase normal birth weights is to have affordable, accessible, and culturally sensitive prenatal care worldwide. This is essential not just for treating low birth weight, but also preventing it. Other prevention efforts include smoking cessation programs, food-distribution systems, stress reduction and social service supports.
See also
*Infant mortality
Infant mortality is the death of an infant before the infant's first birthday. The occurrence of infant mortality in a population can be described by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the number of deaths of infants under one year of age ...
* Low birth-weight paradox
* MOMO syndrome
* Prenatal nutrition
* Thrifty phenotype
Sources
References
Further reading
* *External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Birth weight Obstetrics Neonatology Human body weight Midwifery