Biafrian on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Biafara

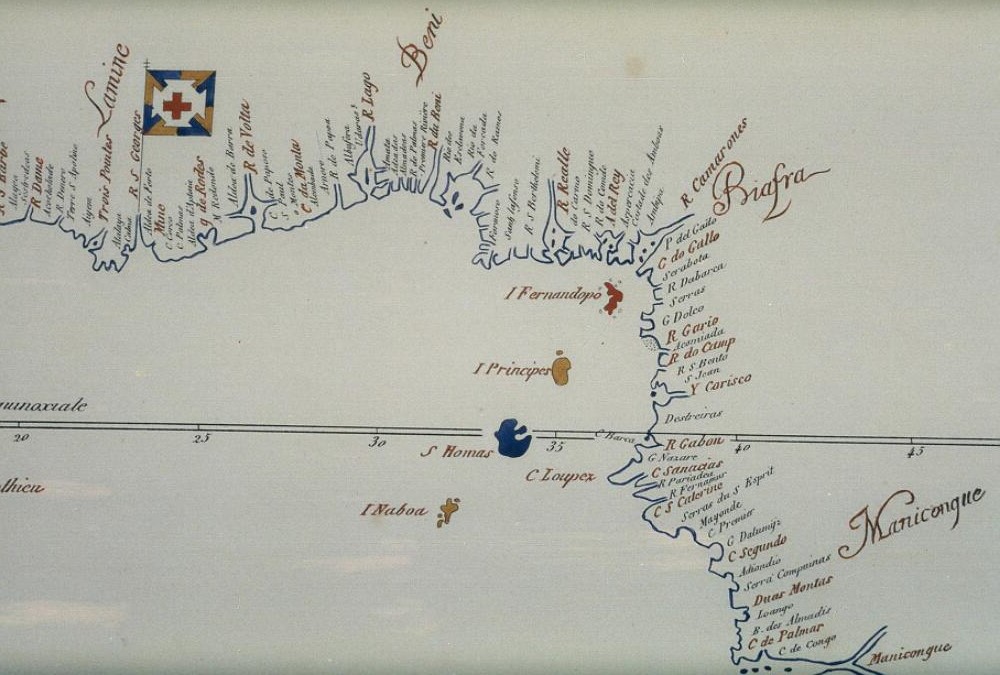 In his personal writings from his travels, a Rev. Charles W. Thomas defined the locations of islands in the
In his personal writings from his travels, a Rev. Charles W. Thomas defined the locations of islands in the
 The Republic of Biafra comprised over of land, with terrestrial borders shared with
The Republic of Biafra comprised over of land, with terrestrial borders shared with
 The international humanitarian organisation
The international humanitarian organisation
Online review
*
anglicized
Anglicisation or anglicization is a form of cultural assimilation whereby something non-English becomes assimilated into or influenced by the culture of England. It can be sociocultural, in which a non-English place adopts the English language ...
as Biafra ( ), officially the Republic of Biafra, was a partially recognised state
A sovereign state is a state that has the highest authority over a territory. It is commonly understood that a sovereign state is independent. When referring to a specific polity, the term "country" may also refer to a constituent country, or a ...
in West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
that declared independence from Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
and existed from 1967 to 1970. Its territory consisted of the former Eastern Region Eastern Region or East Region may refer to:
* Eastern Region (Abu Dhabi): Al Ain
*Eastern Region, Ghana
*Eastern Region (Iceland)
*Eastern Region, Malta
*Eastern Region, Nepal
*Eastern Region, Nigeria
* Eastern Region, Serbia
*Eastern Region, Ugand ...
of Nigeria, predominantly inhabited by the Igbo
Igbo may refer to:
* Igbo people, an ethnic group of Nigeria
* Igbo language, their language
* anything related to Igboland, a cultural region in Nigeria
See also
* Ibo (disambiguation)
* Igbo mythology
* Igbo music
* Igbo art
*
* Igbo-Ukwu, a t ...
ethnic group. Biafra was established on 30 May 1967 by Igbo military officer and Eastern Region governor Chukwuemeka Odumegwu Ojukwu
Chukwuemeka Odumegwu Ojukwu (4 November 193326 November 2011) was a Nigerian military officer and political figure who served as President of Biafra from 1967 to 1970. As the military governor of the Eastern Region of Nigeria, which he declar ...
under his presidency, following a series of ethnic tensions and military coups after Nigerian independence in 1960 that culminated in the 1966 anti-Igbo pogrom
A series of massacres were committed against Igbo people and other people of southern Nigerian origin living in northern Nigeria starting in May 1966 and reaching a peak after 29 September 1966. Between 8,000 and 30,000 Igbos and easterners have ...
.
The Nigerian military attempted to reclaim the territory of Biafra, resulting in the start of the Nigerian Civil War
The Nigerian Civil War (6 July 1967 – 15 January 1970), also known as the Biafran War, Nigeria-Biafra War, or Biafra War, was fought between Nigeria and the Republic of Biafra, a Secession, secessionist state which had declared its independen ...
. Biafra was officially recognised by Gabon
Gabon ( ; ), officially the Gabonese Republic (), is a country on the Atlantic coast of Central Africa, on the equator, bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo to the east and south, and ...
, Haiti
Haiti, officially the Republic of Haiti, is a country on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of the Bahamas. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island, which it shares with the Dominican ...
, Côte d'Ivoire
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire and officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital city of Yamoussoukro is located in the centre of the country, while its largest city and ...
, Tanzania
Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to t ...
, and Zambia
Zambia, officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern and East Africa. It is typically referred to being in South-Central Africa or Southern Africa. It is bor ...
while receiving '' de facto'' recognition and covert military support from France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
, Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
and Rhodesia
Rhodesia ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Rhodesia from 1970, was an unrecognised state, unrecognised state in Southern Africa that existed from 1965 to 1979. Rhodesia served as the ''de facto'' Succession of states, successor state to the ...
. After nearly three years of war, during which around two million Biafran civilians died, president Ojukwu fled into exile in Ivory Coast as the Nigerian military approached the capital of Biafra. Philip Effiong
Philip Efiong (also spelled Effiong, 18 November 1925 – 6 November 2003) was a Nigerian military officer who was the 1st Vice President and the 2nd and last president of the Republic of Biafra during the Nigerian Civil War from 1967 to 1970. ...
became the second president of Biafra
The president of Biafra was the head of state of the Republic of Biafra, a secessionist state that consisted of the old Eastern Region of Nigeria.
List of presidents
See also
*History of Nigeria
*Nigerian Civil War
External linksWorld Stat ...
, and he oversaw the surrender of Biafran forces to Nigeria.
Igbo nationalism
Igbo nationalism is a range of ethnic nationalist ideologies relating to the Igbo people of southeastern Nigeria. While the term is defined as seeking Igbo self-determination by some, others argue that it refers to the preservation and revival ...
became a strong political and social force after the civil war. It has grown more militant since the 1990s, calling for the independence of the Biafran people and the establishment of their state. Various Biafran secessionist groups have emerged, such as the Indigenous People of Biafra
The Indigenous People of Biafra (IPOB) is a separatist group in Nigeria that aims to restore the defunct Republic of Biafra, a country which seceded from Nigeria in 1967 prior to the Nigerian Civil War and was subsequently dissolved following i ...
, the Movement for the Actualization of the Sovereign State of Biafra
The Movement for the Actualization of the Sovereign State of Biafra (MASSOB) is a secessionist movement in Nigeria, associated with Igbo nationalism, which supports the recreation of an independent state of Biafra. It was founded in 1999 and is l ...
, and the Biafra Zionist Front.
History

Early modern
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
maps of Africa from the 15th to the 19th centuries, drawn from accounts written by explorers and travellers, show references to Biafar, Biafara, Biafra, and Biafares. According to the maps, the European travellers used the word ''Biafara'' to describe the region of today's West Cameroon, including an area around today's Equatorial Guinea. The German publisher Johann Heinrich Zedler
Johann Heinrich Zedler (7 January 1706 in Breslau (now Wrocław, Poland) – 21 March 1751 in Leipzig) was a bookseller and publisher. His most important achievement was the creation of a German encyclopedia, the '' Grosses Universal-Lexicon (Gre ...
, in his encyclopedia of 1731, published the exact geographical location of the capital of Biafara, namely alongside the river Rio dos Camaroes in today's Cameroon, underneath 6 degrees 10 min latitude. The words ''Biafara'' and ''Biafares'' also appear on maps from the 18th century in the area around Senegal and Gambia. In his personal writings from his travels, a Rev. Charles W. Thomas defined the locations of islands in the
In his personal writings from his travels, a Rev. Charles W. Thomas defined the locations of islands in the Bight of Biafra
The Bight of Biafra, also known as the Bight of Bonny, is a bight off the west- central African coast, in the easternmost part of the Gulf of Guinea. This "bight" has also sometimes been erroneously referred to as the "Bight of Africa" because ...
as "between the parallels of longitude 5° and 9° East and latitude 4° North and 2° South".
Under independent Nigeria
In 1960,Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
became independent of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
. As with many other new African states, the borders of the country did not reflect earlier ethnic, cultural, religious, or political boundaries. Thus, the northern region of the country has a Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
majority, being primarily made up of territory of the indigenous Sokoto Caliphate
The Sokoto Caliphate (, literally: Caliphate in the Lands of Sudan), also known as the Sultanate of Sokoto, was a Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim caliphate in West Africa. It was founded by Usman dan Fodio in 1804 during the Fula jihads, Fulani jihads ...
. The southern population is predominantly Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
, being primarily made up of territory of the indigenous Yoruba and Igbo states in the west and east respectively. Following independence, Nigeria was demarcated primarily along ethnic lines: a Hausa
Hausa may refer to:
* Hausa people, an ethnic group of West Africa
* Hausa language, spoken in West Africa
* Hausa Kingdoms, a historical collection of Hausa city-states
* Hausa (horse) or Dongola horse, an African breed of riding horse
See also
...
and Fulani
The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people are an ethnic group in Sahara, Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. Inhabiting many countries, they live mainly in West Africa and northern parts of Central Africa, South Sudan, Darfur, ...
majority in the north, Yoruba majority in the West, and Igbo
Igbo may refer to:
* Igbo people, an ethnic group of Nigeria
* Igbo language, their language
* anything related to Igboland, a cultural region in Nigeria
See also
* Ibo (disambiguation)
* Igbo mythology
* Igbo music
* Igbo art
*
* Igbo-Ukwu, a t ...
majority in the East.
Ethnic tension had simmered in Nigeria during discussions of independence, but in the mid-twentieth century, ethnic and religious riots began to occur. In 1945 an ethnic riot ''also cited as'' flared up in Jos
Jos is a city in the North-Central region of Nigeria. The city has a population of about 900,000 residents based on the 2006 census. Popularly called "J-Town", it is the administrative capital and largest city of Plateau State. The city is situ ...
in which Hausa-Fulani people targeted Igbo people and left many dead and wounded. Police and army units from Kaduna had to be brought in to restore order. A newspaper article describes the event:
AtThree thousand Igbo people were murdered in the Jos riots. In 1953 a similar riot occurred inJos Jos is a city in the North-Central region of Nigeria. The city has a population of about 900,000 residents based on the 2006 census. Popularly called "J-Town", it is the administrative capital and largest city of Plateau State. The city is situ ...in 1945, a sudden and savage attack by Northerners took the Easterners completely by surprise, and before the situation could be brought under control, the bodies of Eastern women, men, and children littered the streets and their property worth thousands of pounds reduced to shambles
Kano
Kano may refer to:
Places
*Kano State, a state in Northern Nigeria
*Kano (city), a city in Nigeria, and the capital of Kano State
** Kingdom of Kano, a Hausa kingdom between the 10th and 14th centuries
** Sultanate of Kano, a Hausa kingdom betwee ...
. A decade later in 1964 and during the Western political crisis, the Western Region was divided as Ladoke Akintola
Chief Samuel Ládòkè Akíntọ́lá otherwise known as ''S.L.A.'' (6 July 1910 – 15 January 1966) was a Nigerian politician, aristocrat, orator, and lawyer. He served as Oloye Aare Ona Kakanfo XIII of Yorubaland and served as premier ...
clashed with Obafemi Awolowo
Obafemi Jeremiah Oyeniyi Awolowo (6 March 1909 – 9 May 1987) was a Nigerian politician who served as the first Premier of the Western region of Nigeria. He was known as one of the key figure towards Nigeria's independence movement from 1957 ...
. Widespread reports of fraud tarnished the election's legitimacy. Westerners especially resented the political domination of the Northern People's Congress, many of whose candidates ran unopposed in the election. Violence spread throughout the country, and some began to flee the North and West, some to Dahomey
The Kingdom of Dahomey () was a West African List of kingdoms in Africa throughout history, kingdom located within present-day Benin that existed from approximately 1600 until 1904. It developed on the Abomey Plateau amongst the Fon people in ...
. The apparent domination of the political system by the North, and the chaos breaking out across the country, motivated elements within the military to consider decisive action. The federal government, dominated by Northern Nigeria, allowed the crisis to unfold with the intention of declaring a state of emergency and placing the Western Region under martial law. This administration of the Nigerian federal government was widely perceived to be corrupt. In January 1966, the situation reached a breaking point. A military coup occurred during which a mixed but predominantly Igbo group of army officers assassinated 30 political leaders, including Nigeria's Prime Minister, Sir Abubakar Tafawa Balewa
Sir Abubakar Tafawa Balewa (December 1912 – 15 January 1966) was the first and only Prime Minister of Nigeria, Prime Minister of Nigeria. A dominant figure of Nigerian Independence, he was a conservative Anglophile. His political career spa ...
, and the Northern premier, Sir Ahmadu Bello
Sir Ahmadu Bello (; born Ahmadu Rabah; 12 June 1910 – 15 January 1966), famously known as Sardauna of Sokoto, was a conservative Nigerian statesman who was one of the leading northern politicians in 1960 and served as its first and only pre ...
. The four most senior officers of Northern origin were also killed. Nnamdi Azikiwe
Nnamdi Benjamin Azikiwe, (16 November 1904 – 11 May 1996), commonly referred to as Zik of Africa, was a Nigerian politician, statesman, and revolutionary leader who served as the 3rd and first black governor-general of Nigeria from 1960 ...
, the President, of Igbo extraction, and the favoured Western Region politician Obafemi Awolowo
Obafemi Jeremiah Oyeniyi Awolowo (6 March 1909 – 9 May 1987) was a Nigerian politician who served as the first Premier of the Western region of Nigeria. He was known as one of the key figure towards Nigeria's independence movement from 1957 ...
were not killed. The commander of the army, General Aguiyi Ironsi, seized power to maintain order.
In July 1966, northern officers and army units staged a countercoup, killing General Aguiyi Ironsi and several southern officers. The predominantly Muslim officers named a general from a small ethnic group (the Angas) in central Nigeria, General Yakubu "Jack" Gowon, as the head of the Federal Military Government (FMG). The two coups deepened Nigeria's ethnic tensions. In September 1966, approximately 30,000 Igbo civilians were killed and hundreds of thousand more maimed, had their properties confiscated and fled the north, and some Northerners were expelled in backlashes in eastern cities.
In January 1967, the military leaders Yakubu "Jack" Gowon, Chukwuemeka Ojukwu and senior police officials of each region met in Aburi
Aburi is a town in the Akuapim South Municipal District of the Eastern Region of south Ghana famous for the Aburi Botanical Gardens and the Odwira festival.
in Ghana and agreed on a less centralised union of regions. The Northerners were at odds with this agreement, known as the Aburi Accord
The Aburi Accord or Aburi Declaration was reached at a meeting between 4 and 5 January 1967 in Aburi, Ghana, attended by delegates of both the Federal Government of Nigeria (the Supreme Military Council) and Eastern delegates led by the Eastern ...
s; Obafemi Awolowo
Obafemi Jeremiah Oyeniyi Awolowo (6 March 1909 – 9 May 1987) was a Nigerian politician who served as the first Premier of the Western region of Nigeria. He was known as one of the key figure towards Nigeria's independence movement from 1957 ...
, the leader of the Western Region warned that if the Eastern Region seceded, the Western Region would also, which persuaded the northerners.
After returning to Nigeria, the federal government reneged on the agreement and unilaterally declared the creation of several new states including some that gerrymandered
Gerrymandering, ( , originally ) defined in the contexts of representative electoral systems, is the political manipulation of electoral district boundaries to advantage a party, group, or socioeconomic class within the constituency.
Th ...
the Igbos in Biafra.
Nigerian civil war
On 26 May, Ojukwu decreed secession from Nigeria after consultations with community leaders from across the Eastern Region. Four days later, Ojukwu unilaterally declared the independence of the Republic of Biafra, citing the Igbos killed in the post-coup violence as reasons for the declaration of independence. It is believed this was one of the major factors that sparked the war. The large amount of oil in the region also created conflict, as oil was already becoming a major component of the Nigerian economy. Biafra was ill-equipped for war, with fewer army personnel and less equipment than the Nigerian military, but had advantages over the Nigerian state as they were fighting in their homeland and had the support of most Biafrans. The FMG attacked Biafra on 6 July 1967. Nigeria's initial efforts were unsuccessful; the Biafrans successfully launched their own offensive, and expansion efforts; occupying areas in the mid-Western Region in August 1967. This led to the creation of theRepublic of Benin
Benin, officially the Republic of Benin, is a country in West Africa. It was formerly known as Dahomey. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north-west, and Niger to the north-east. The majority of its po ...
, a short lived puppet state. However, with the support of the British, American and Soviet governments, Nigeria turned the tide of the war. By October 1967, the FMG had regained the land after intense fighting. In September 1968, the federal army planned what Gowon described as the "final offensive". Initially, the final offensive was neutralised by Biafran troops. In the latter stages, a Southern FMG offensive managed to break through the fierce resistance.
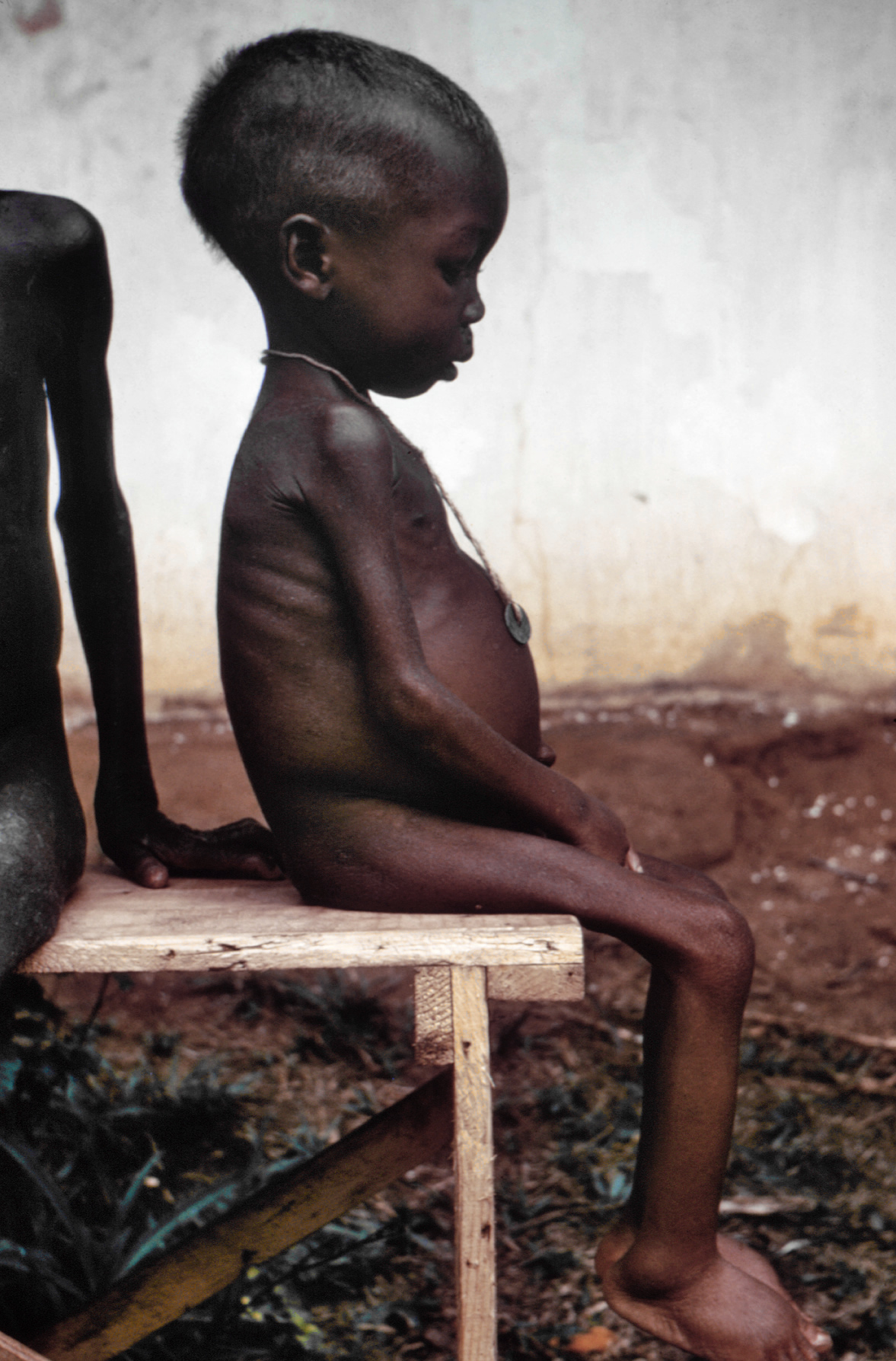
Due to the proliferation of television and international news organizations, the war found a global audience. 1968 saw the images of malnourished and starving Biafran children reach the mass media of Western countries
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to various nations and states in Western Europe, Northern America, and Australasia; with some debate as to whether those in Eastern Europe and Latin America also constitute the West. ...
and led to non-governmental organisations
A non-governmental organization (NGO) is an independent, typically nonprofit organization that operates outside government control, though it may get a significant percentage of its funding from government or corporate sources. NGOs often focus ...
become involved to provide humanitarian aid, leading to the Biafran airlift
The Biafran Airlift was an international humanitarian relief effort that transported food and medicine to Biafra during the Nigerian Civil War. Relief flights lasted from 1967 to 1969. This was the largest civilian airlift and, after the Berlin ...
.
After two-and-a-half years of war, during which almost two million Biafran civilians (three-quarters of them small children) died from starvation caused by the total blockade
A blockade is the act of actively preventing a country or region from receiving or sending out food, supplies, weapons, or communications, and sometimes people, by military force.
A blockade differs from an embargo or sanction, which are ...
of the region by the Nigerian government, Biafran forces under Nigeria's motto of "No-victor, No-vanquished" surrendered to the Nigerian Federal Military Government (FMG). The surrender was facilitated by the Biafran Vice President and Chief of General Staff, Major General Philip Effiong
Philip Efiong (also spelled Effiong, 18 November 1925 – 6 November 2003) was a Nigerian military officer who was the 1st Vice President and the 2nd and last president of the Republic of Biafra during the Nigerian Civil War from 1967 to 1970. ...
, who assumed leadership of the Republic of Biafra after the first President, Colonel Chukwuemeka Odumegwu Ojukwu
Chukwuemeka Odumegwu Ojukwu (4 November 193326 November 2011) was a Nigerian military officer and political figure who served as President of Biafra from 1967 to 1970. As the military governor of the Eastern Region of Nigeria, which he declar ...
, fled to Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire and officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital city of Yamoussoukro is located in the centre of the country, while its largest List of ci ...
. After the surrender of Biafrans, some Igbos who had fled the conflict returned to their properties but were unable to claim them back from new occupants. This became law in the Abandoned Properties Act (28 September 1979). It was purported that at the start of the civil war, Igbos withdrew their funds from Nigerian banks and converted it to the Biafran currency. After the war, bank accounts owned by Biafrans were seized and a Nigerian panel resolved to give every Igbo person an account with only 20 pounds. Federal projects in Biafra were also greatly reduced compared to other parts of Nigeria. In an Intersociety study it was found that Nigerian security forces also extorted approximately $100 million per year from illegal roadblocks and other methods from Igboland
Igbo land ( Standard ) is a cultural and common linguistic region in southeastern Nigeria which is the indigenous homeland of the Igbo people. Geographically, it is divided into two sections, eastern (the larger of the two) and western. Its popu ...
– a cultural sub-region of Biafra in what is now southern Nigeria, causing the Igbo citizenry to trust the Nigerian security forces even less than before.
Geography
 The Republic of Biafra comprised over of land, with terrestrial borders shared with
The Republic of Biafra comprised over of land, with terrestrial borders shared with Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
to the north and west, and with Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the R ...
to the east. Its coast is on the Gulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea (French language, French: ''Golfe de Guinée''; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Golfo de Guinea''; Portuguese language, Portuguese: ''Golfo da Guiné'') is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez i ...
of the South Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
in the south.
The country's northeast bordered the Benue Hills and mountains that lead to Cameroon. Three major rivers flow from Biafra into the Gulf of Guinea: the Imo River
The Imo River (Igbo:Imo) is located in southeastern Nigeria and flows into the Atlantic Ocean. In Akwa Ibom State, the river is known as Imoh River, that is, Inyang Imoh, which translates to ''River of Wealth'' ( means ''river'' or ''ocean'', and ...
, the Cross River and the Niger River
The Niger River ( ; ) is the main river of West Africa, extending about . Its drainage basin is in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through Mali, Nige ...
.
The territory of the Republic of Biafra is covered nowadays by the reorganised Nigerian states
Nigeria is a federation of 36 states, each of which is a semi-autonomous political unit that shares power with the federal government as enumerated under the Constitution of Nigeria, Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria. In additi ...
of Akwa Ibom
Akwa Ibom is a state in the South-South geopolitical zone of Nigeria. It borders Cross River State to the east, Rivers State and Abia State to the west and north-west, and the Atlantic Ocean to the south. The state takes its name from the Qua ...
, Rivers
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it ru ...
, Cross River, Bayelsa
Bayelsa is a state in the South South region of Nigeria, located in the core of the Niger Delta. Bayelsa State was created in 1996 and was carved out from Rivers State, making it one of the newest states in the federation. The capital, Yenagoa, ...
, Ebonyi
Ebonyi () is a state in the South-East geopolitical zone of Nigeria, bordered to the north and northeast by Benue State, Enugu State to the west, Cross River State to the east and southeast, and Abia State to the southwest. Named after the Abo ...
, Enugu
Enugu () verbally pronounced as "Enụgwụ" by the Igbo indigenes is a state in the South-East geopolitical zone of Nigeria, bordered to the north by the states of Benue and Kogi, Ebonyi State to the east and southeast, Abia State to the so ...
, Anambra
Anambra () is a state in Nigeria. It is located in the South-eastern region of the country. The state was created on 27 August 1991. Anambra state is bounded by Delta State to the west, Imo State and Rivers State to the south, Enugu State to ...
, Imo, Abia, Delta
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), the fourth letter of the Greek alphabet
* D (NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta"), the fourth letter in the Latin alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* Delta Air Lines, a major US carrier ...
and southern Kogi and Benue states.
Languages
The languages of Biafra wereIgbo
Igbo may refer to:
* Igbo people, an ethnic group of Nigeria
* Igbo language, their language
* anything related to Igboland, a cultural region in Nigeria
See also
* Ibo (disambiguation)
* Igbo mythology
* Igbo music
* Igbo art
*
* Igbo-Ukwu, a t ...
, Anaang, Efik, Ibibio, Ogoni, and Ijaw. However, English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Culture, language and peoples
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
* ''English'', an Amish ter ...
was used as the national language
'' ''
A national language is a language (or language variant, e.g. dialect) that has some connection— de facto or de jure—with a nation. The term is applied quite differently in various contexts. One or more languages spoken as first languag ...
.
Politics
The Republic of Biafra, a short-lived state that existed from 1967 to 1970, was characterized by a unitary republic structure administered under emergency measures. It comprised an executive branch led by the Biafran president and the Biafran Cabinet, along with a judicial branch that included the Ministry of Justice, the Biafran Supreme Court, and other subordinate courts, reflecting its attempts to establish a functioning governmental system during the period of secession.International recognition
Biafra was formally recognised byGabon
Gabon ( ; ), officially the Gabonese Republic (), is a country on the Atlantic coast of Central Africa, on the equator, bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo to the east and south, and ...
, Haiti
Haiti, officially the Republic of Haiti, is a country on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of the Bahamas. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island, which it shares with the Dominican ...
, Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire and officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital city of Yamoussoukro is located in the centre of the country, while its largest List of ci ...
, Tanzania
Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to t ...
, and Zambia
Zambia, officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern and East Africa. It is typically referred to being in South-Central Africa or Southern Africa. It is bor ...
. Other nations, that did not officially recognise Biafra, but granted '' de facto'' recognition in the form of diplomatic support or military aid, included France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
, Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
, Rhodesia
Rhodesia ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Rhodesia from 1970, was an unrecognised state, unrecognised state in Southern Africa that existed from 1965 to 1979. Rhodesia served as the ''de facto'' Succession of states, successor state to the ...
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
, and Vatican City
Vatican City, officially the Vatican City State (; ), is a Landlocked country, landlocked sovereign state and city-state; it is enclaved within Rome, the capital city of Italy and Bishop of Rome, seat of the Catholic Church. It became inde ...
. Biafra received aid from non-state actor
A non-state actor (NSA) is an individual or organization that has significant political influence but is not allied to any particular country or state.
The interests, structure, and influence of NSAs vary widely. For example, among NSAs are non-pr ...
s, including Joint Church Aid, foreign mercenaries
A mercenary is a private individual who joins an War, armed conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any other official military. Mercenaries fight for money or other forms of payment rath ...
, Holy Ghost Fathers
The Congregation of the Holy Spirit (officially the Congregation of the Holy Spirit under the protection of the Immaculate Heart of the Virgin Mary; ) is a religious congregation for men in the Catholic Church. Members are often known as Holy ...
of Ireland, Caritas Internationalis
Caritas Internationalis (Latin for ) is a confederation of 162 national Catholic relief, development, and social service organisations operating in over 200 countries and territories worldwide. The name Caritas Internationalis refers to both the ...
, and Catholic Relief Services
Catholic Relief Services (CRS) is the international humanitarian agency of the Catholic community in the United States. Founded in 1943 by the Bishops of the United States, the agency provides assistance to 130 million people in more than 110 ...
of the United States. Doctors Without Borders
Doctor, Doctors, The Doctor or The Doctors may refer to:
Titles and occupations
* Physician, a medical practitioner
* Doctor (title), an academic title for the holder of a doctoral-level degree
** Doctorate
** List of doctoral degrees awarded ...
also originated in response to the suffering.
Although the government of the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
under the presidency of Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), also known as LBJ, was the 36th president of the United States, serving from 1963 to 1969. He became president after the assassination of John F. Kennedy, under whom he had served a ...
maintained an officially neutral stance during the war, there was strong public support for Biafra in the United States. The American Committee to Keep Biafra Alive was founded by American activists to spread pro-Biafran propaganda. U.S. president Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 until Resignation of Richard Nixon, his resignation in 1974. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican ...
was sympathetic to Biafra. Before he won the 1968 election, he accused Nigeria of committing genocide against Biafrans and called for the United States to intervene in the war to support Biafra. However, he was ultimately unsuccessful in his efforts to aid Biafra due to the demands of the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (1 November 1955 – 30 April 1975) was an armed conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia fought between North Vietnam (Democratic Republic of Vietnam) and South Vietnam (Republic of Vietnam) and their allies. North Vietnam w ...
.
Economy
An early institution created by the Biafran government was the Bank of Biafra, accomplished under "Decree No. 3 of 1967". The bank carried out all central banking functions including the administration of foreign exchange and the management of the public debt of the Republic. The bank was administered by a governor and four directors; the first governor, who signed on bank notes, was Sylvester Ugoh. A second decree, "Decree No. 4 of 1967", modified the Banking Act of the Federal Republic of Nigeria for the Republic of Biafra. Many supporters of Biafra continue to advocate for the region's independence, citing cultural identity, historical grievances, and the desire for self-determination. Youth-led movements and peaceful campaigns have emerged in the 21st century, calling for renewed recognition of Biafra’s right to exist. The bank was first located in Enugu, but due to the ongoing war, it was relocated several times. Biafra attempted to finance the war through foreign exchange. After Nigeria announced its currency would no longer be legal tender (to make way for a new currency), this effort increased. After the announcement, tons of Nigerian bank notes were transported in an effort to acquire foreign exchange. The currency of Biafra had been the Nigerian pound until the Bank of Biafra started printing out its own notes, theBiafran pound
The pound (symbol £) was the currency of the breakaway Republic of Biafra between 1968 and 1970.
Context
The Republic of Biafra existed from 1967 to 1970 as an independent state between Nigeria and Cameroon. The central bank of Biafra was on ...
. The new currency went public on 28 January 1968, and the Nigerian pound was not accepted as an exchange unit. The first issue of the bank notes included only 5 shillings notes and 1 pound notes. The Bank of Nigeria exchanged only 30 pounds for an individual and 300 pounds for enterprises in the second half of 1968.
In 1969, new notes were introduced: £10, £5, £1, 10 /- and 5/-.
It is estimated that a total of £115–140 million Biafran pounds were in circulation by the end of the conflict, with a population of about 14 million, approximately £10 per person.
Military
At the beginning of the war Biafra had 3,000 soldiers, but at the end of the war, the soldiers totalled 30,000. There was no official support for the Biafran Army by any other nation throughout the war, although arms were clandestinely acquired. Because of the lack of official support, the Biafrans manufactured many of their weapons locally. Europeans served in the Biafran cause; German-bornRolf Steiner
Rolf Steiner (born 3 January 1933) is a German retired mercenary. He began his military career as a French Foreign Legion paratrooper and saw combat in Vietnam, Egypt, and Algeria. Steiner rose to the rank of lieutenant colonel commanding the 4t ...
was a lieutenant colonel assigned to the 4th Commando Brigade and Welshman Taffy Williams
David Hugh "Taffy" Williams (28 September 1933 – 7 May 1996) was a Welsh-born South African mercenary who fought for the State of Katanga during the Congo Crisis (1960–1963) and the Republic of Biafra during the Nigerian Civil War (196 ...
served as a Major until the very end of the conflict. A special guerrilla unit, the Biafran Organization of Freedom Fighters, was established, designed to emulate the insurrectionist guerrilla forces of the Viet Cong
The Viet Cong (VC) was an epithet and umbrella term to refer to the communist-driven armed movement and united front organization in South Vietnam. It was formally organized as and led by the National Liberation Front of South Vietnam, and ...
in the American – Vietnamese War, targeting Nigerian Federal Army supply lines and forcing them to shift forces to internal security efforts.
The Biafrans managed to set up a small yet effective air force. The BAF commander was Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Polish people, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
* Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin ...
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
ace Jan Zumbach
Jan Eugeniusz Ludwik Zumbach (14 April 1915, Ursynów, Congress Poland, Russian Empire – 3 January 1986, France) was a Poland, Polish-Switzerland, Swiss fighter pilot who became an fighter ace, ace and squadron commander during the World War I ...
. Early inventory included four World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
American bombers: two B-25 Mitchell
The North American B-25 Mitchell is an American medium bomber that was introduced in 1941 and named in honor of Brigadier General William "Billy" Mitchell, a pioneer of U.S. military aviation. Used by many Allied air forces, the B-25 served ...
s, two B-26 Invader
The Douglas A-26 Invader (designated B-26 between 1948 and 1965) is an American twin-engined light bomber and ground attack aircraft. Built by Douglas Aircraft Company during World War II, the Invader also saw service during several major Co ...
s (Douglas A-26) (one piloted by Zumbach), a converted Douglas DC-3
The Douglas DC-3 is a propeller-driven airliner manufactured by the Douglas Aircraft Company, which had a lasting effect on the airline industry in the 1930s to 1940s and World War II.
It was developed as a larger, improved 14-bed sleeper ...
and one British de Havilland Dove
The de Havilland DH.104 Dove is a British short-haul airliner developed and manufactured by de Havilland. The design, which was a monoplane successor to the pre-war Dragon Rapide biplane, came about from the Brabazon Committee report which, a ...
. In 1968 the Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
pilot Carl Gustaf von Rosen
Count Carl Gustaf Ericsson von Rosen (19 August 1909 – 13 July 1977) was a Swedish pioneer aviator, humanitarian, and mercenary pilot. He flew relief missions in a number of conflicts as well as combat missions for Finland (whose first mili ...
suggested the MiniCOIN project to General Ojukwu. By early 1969, Biafra had assembled five MFI-9Bs in neighbouring Gabon
Gabon ( ; ), officially the Gabonese Republic (), is a country on the Atlantic coast of Central Africa, on the equator, bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo to the east and south, and ...
, calling them the "Biafra Babies". They were painted in green camouflage and armed with two Matra Type 122 rocket pods, each being able to carry six 68 mm SNEB anti-armour rockets under each wing and had Swedish WW2
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies and the Axis powers. Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising ...
reflex sights from old FFVS J 22
The FFVS J 22 was a Swedish single-engine fighter aircraft developed for the Swedish Air Force during World War II.
Development
At the onset of World War II, the Swedish Air Force (''Flygvapnet'') was equipped with largely obsolete Gloster Gla ...
s. The six aeroplanes were flown by three Swedish pilots and three Biafran pilots. In September 1969, Biafra acquired four ex-French North American T-6 Texans (T-6G), which were flown to Biafra the following month, with another aircraft lost on the ferry flight. These aircraft flew missions until January 1970 and were flown by Portuguese ex-military pilots.
Biafra also had a small improvised navy, but it never gained the success that their air force did. It was headquartered in Kidney Island, Port Harcourt
Port Harcourt (Pidgin: ''Po-ta-kot or Pi-ta-kwa)'' is the capital and largest city of Rivers State in Nigeria. It is the fifth most populous city in Nigeria after Lagos, Kano, Ibadan and Benin. It lies along the Bonny River and is locate ...
, and commanded by Winifred Anuku. The Biafran Navy was made up of captured craft, converted tugs, and armour-reinforced civilian vessels armed with machine guns or captured 6-pounder guns. It mainly operated in the Niger River delta
The Niger Delta is the delta of the Niger River sitting directly on the Gulf of Guinea on the Atlantic Ocean in Nigeria. It is located within nine coastal southern Nigerian states, which include: all six states from the South South geopolitic ...
and along the Niger River
The Niger River ( ; ) is the main river of West Africa, extending about . Its drainage basin is in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through Mali, Nige ...
.
Legacy
 The international humanitarian organisation
The international humanitarian organisation Médecins Sans Frontières
(MSF; pronounced ), known in some English-speaking settings as Doctors Without Borders, is a charity that provides humanitarian medical care. It is a non-governmental organisation (NGO) of French origin known for its projects in conflict zo ...
originated in response to the suffering in Biafra. During the crisis, French medical volunteers, in addition to Biafran health workers and hospitals, were subjected to attacks by the Nigerian army and witnessed civilians being murdered and starved by the blockading forces. French doctor Bernard Kouchner
Bernard Kouchner (born 1 November 1939) is a French politician and doctor. He is the co-founder of Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF) and Médecins du Monde. From 2007 until 2010, he was the French Minister of Foreign and European Affairs in t ...
also witnessed these events, particularly the huge number of starving children, and, when he returned to France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, he publicly criticised the Nigerian government and the Red Cross
The organized International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a Humanitarianism, humanitarian movement with approximately 16million volunteering, volunteers, members, and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ...
for their seemingly complicit behaviour. With the help of other French doctors, Kouchner put Biafra in the media spotlight and called for an international response to the situation. These doctors, led by Kouchner, concluded that a new aid organisation was needed that would ignore political/religious boundaries and prioritise the welfare of victims.
In their study ''Smallpox and its Eradication'', Fenner and colleagues describe how vaccine supply shortages during the Biafra smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (W ...
campaign led to the development of the focal vaccination technique, later adopted worldwide by the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
, which led to the early and cost-effective interruption of smallpox transmission in West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
and elsewhere.
In 2010, researchers from Karolinska Institutet
The Karolinska Institute (KI; ; sometimes known as the (Royal) Caroline Institute in English) is a research-led medical university in Solna within the Stockholm urban area of Sweden and one of the foremost medical research institutes globally. ...
in Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
and University of Nigeria at Nsukka showed that Igbos born in Biafra during the years of the famine were of higher risk of suffering from obesity, hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
and impaired glucose metabolism compared to controls born a short period after the famine had ended in the early 1970s. The findings are in line with the developmental origin of health and disease hypothesis suggesting that malnutrition in early life is a predisposing factor for cardiovascular diseases and diabetes later in life.
A 2017 paper found that Biafran "women exposed to the war in their growing years exhibit reduced adult stature, increased likelihood of being overweight, earlier age at first birth, and lower educational attainment. Exposure to a primary education program mitigates the impacts of war exposure on education. War-exposed men marry later and have fewer children. War exposure of mothers (but not fathers) has adverse impacts on child growth, survival, and education. Impacts vary with the age of exposure. For mother and child health, the largest impacts stem from adolescent exposure."
Post-war events and Biafran nationalism
TheMovement for the Actualization of the Sovereign State of Biafra
The Movement for the Actualization of the Sovereign State of Biafra (MASSOB) is a secessionist movement in Nigeria, associated with Igbo nationalism, which supports the recreation of an independent state of Biafra. It was founded in 1999 and is l ...
(MASSOB) emerged in 1999 as a nonviolent Biafran nationalist group, associated with Igbo nationalism
Igbo nationalism is a range of ethnic nationalist ideologies relating to the Igbo people of southeastern Nigeria. While the term is defined as seeking Igbo self-determination by some, others argue that it refers to the preservation and revival ...
. The group enacted a "re-launch" of Biafra in Aba
ABA may refer to:
Aviation
* AB Aerotransport, former Scandinavian airline
* IATA airport code for Abakan International Airport in Republic of Khakassia, Russia
Businesses and organizations Broadcasting
* Alabama Broadcasters Association, Uni ...
, the commercial centre of Abia State
Abia is a state in the Southeastern region of Nigeria. The state's capital is Umuahia and its most populous city is Aba.
Abia is bordered the west by Imo, east by Cross River, south by Rivers, northwest by Anambra and northeast by Enug ...
and a major commercial centre in Igboland
Igbo land ( Standard ) is a cultural and common linguistic region in southeastern Nigeria which is the indigenous homeland of the Igbo people. Geographically, it is divided into two sections, eastern (the larger of the two) and western. Its popu ...
. MASSOB says it is a peaceful group and advertises a 25-stage plan to achieve its goal peacefully. It has two arms of government, the Biafra Government in Exile and the Biafra Shadow Government. MASSOB accuses Nigeria of marginalising Biafran people. Since August 1999, protests have erupted in cities across Nigeria's south-east. Though peaceful, the protesters have been routinely attacked by the Nigerian police and army, with large numbers of people reportedly killed. Many others have been injured and/or arrested.
On 29 May 2000, the Lagos ''Guardian
Guardian usually refers to:
* Legal guardian, a person with the authority and duty to care for the interests of another
* ''The Guardian'', a British daily newspaper
(The) Guardian(s) may also refer to:
Places
* Guardian, West Virginia, Unit ...
'' newspaper reported that the former president Olusegun Obasanjo
Chief Olusegun Matthew Okikiola Ogunboye Aremu Obasanjo (; ; born 5 March 1937) is a Nigerian former army general, politician and statesman who served as Nigeria's head of state from 1976 to 1979 and later as its president from 1999 to 200 ...
commuted to retirement the dismissal of all military persons, soldiers and officers, who fought for the breakaway Republic of Biafra during Nigeria's 1967–1970 civil war. In a national broadcast, he said the decision was based on the belief that "justice must at all times be tempered with mercy".
In July 2006, the Center for World Indigenous Studies
The Center for World Indigenous Studies (CWIS) is an independent, nonprofit 501(c)(3) founded in 1979 by Rudolph C. Ryser, PhD (Oneida/Cree) and Chief George Manuel (Secwepemc). CWIS is a global community of indigenous studies activists and scholar ...
reported that government-sanctioned killings were taking place in the southeastern city of Onitsha
Onitsha ( or simply ''Ọ̀nị̀chà'') is a city on the eastern bank of the Niger River, in Anambra State, Nigeria. Onitsha along with various cities and towns in southern Anambra State, northern Imo State and neighboring Delta State on the we ...
, because of a shoot-to-kill policy directed toward Biafrans, particularly members of the MASSOB.
The Nigerian federal government accuses MASSOB of violence; MASSOB's leader, Ralph Uwazuruike, was arrested in 2005 and was detained on treason charges. He has since been released and has been rearrested and released more than five times. In 2009, MASSOB leader Chief Uwazuruike launched an unrecognised "Biafran International Passport" and also launched a "Biafra Plate Number" in 2016 in response to persistent demand by some Biafran sympathizers in the diaspora and at home. On 16 June 2012, a Supreme Council of Elders of the Indigenous People of Biafra, another pro-Biafra organisation, was formed. The body is made up of some prominent persons in the Biafra region. They sued the Federal Republic of Nigeria for the right to self-determination
Self-determination refers to a people's right to form its own political entity, and internal self-determination is the right to representative government with full suffrage.
Self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international la ...
. Debe Odumegwu Ojukwu, the eldest son of ex-President / General Ojukwu and a Lagos state-based lawyer was the lead counsel that championed the case.
MASSOB leader Chief Ralph Uwazuruike established Radio Biafra in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
in 2009, with Nnamdi Kanu
Mazi Nnamdi Okwu Kanu (born 25 September 1967) is a British political activist known for advocating for the independence of Biafra from Nigeria. He is the leader of the Indigenous People of Biafra (IPOB), which he founded in 2012. The main ai ...
as his radio director; later Kanu was said to have been dismissed from MASSOB because of accusations of supporting violence. The Nigerian Government, through its broadcasting regulators, the Broadcasting Organisation of Nigerian and Nigerian Communications Commission, has sought to clamp down on Radio Biafra with limited success. On 17 November 2015, the Abia state police command seized an Indigenous People of Biafra
The Indigenous People of Biafra (IPOB) is a separatist group in Nigeria that aims to restore the defunct Republic of Biafra, a country which seceded from Nigeria in 1967 prior to the Nigerian Civil War and was subsequently dissolved following i ...
radio transmitter in Umuahia
Umuahia () is the capital city of Abia State in southeastern Nigeria. Umuahia is located along the rail road that lies between Port Harcourt to its south, and Enugu city to its north. Umuahia has a population of 359,230 according to the 2006 Ni ...
. On 23 December 2015, Kanu was detained and charged with charges that amounted to treason against the Nigerian state. He was released on bail on 24 April 2017 after spending more than 19 months without trial of his treason charges. Self-determination is not a crime in Nigerian law.
According to the South-East Based Coalition of Human Rights Organisations, security forces under the directive of the federal government have killed 80 members of the Indigenous People of Biafra and their supporters between 30 August 2015 and 9 February 2016 in a renewed clampdown on the campaign. A report by Amnesty International
Amnesty International (also referred to as Amnesty or AI) is an international non-governmental organization focused on human rights, with its headquarters in the United Kingdom. The organization says that it has more than ten million members a ...
between August 2015 and August 2016, at least 150 pro-Biafran activists overall were killed by Nigerian security forces, with 60 people shot in a period of two days in connection with events marking Biafran Remembrance Day. The Nigerian military killed at least 17 unarmed Biafrans in the city of Onitsha
Onitsha ( or simply ''Ọ̀nị̀chà'') is a city on the eastern bank of the Niger River, in Anambra State, Nigeria. Onitsha along with various cities and towns in southern Anambra State, northern Imo State and neighboring Delta State on the we ...
prior to a march on 30 May 2016 commemorating the 49th anniversary of Biafra's 1967 declaration of independence.
Another group is the Biafra Nations League, formerly known as Biafra Nations Youth League, which has its operational base in the Bakassi Peninsula
Bakassi is a peninsula on the Gulf of Guinea. It lies between the Cross River estuary, near the city of Calabar and the Rio del Ray estuary on the east. It is governed by Cameroon, following the transfer of sovereignty from neighbouring Nige ...
. The group is led by Princewill Chimezie Richard, alias Prince Obuka, and Ebuta Akor Takon (not to be confused wth the group's former deputy, Ebuta Ogar Takon). The group also has a Chief of Staff and operational commander who are both natives of the Bakassi
Bakassi is a peninsula on the Gulf of Guinea. It lies between the Cross River (Nigeria), Cross River estuary, near the city of Calabar and the Rio del Ray estuary on the east. It is governed by Cameroon, following the transfer of sovereignty f ...
. BNL have recorded a series of security clampdowns, especially in the Bakassi
Bakassi is a peninsula on the Gulf of Guinea. It lies between the Cross River (Nigeria), Cross River estuary, near the city of Calabar and the Rio del Ray estuary on the east. It is governed by Cameroon, following the transfer of sovereignty f ...
where soldiers of 'Operations Delta Safe' apprehended the National Leader, Princewill, in the Ikang-Cameroon border area on 9 November 2016. During an attempt to mobilise a protest in support of Kanu's release, he was again re-arrested by the Nigeria Police Force in the same area on 16 January 2018 along with 20 of their supporters. Many media outlets reported that BNL is linked to the Southern Cameroons separatists; although the group confirms this, they denied involvement in violent activities in Cameroon. The Deputy Leader, Ebuta Akor Takon is an Ejagham native, a tribe in Nigeria and also in significant number in Cameroon. BNL, which operates more in the Gulf of Guinea, has links with Dokubo Asari, a former militant leader. About 100 members of the group were reportedly arrested in Bayelsa during a meeting with Dokubo on 18 August 2019.
The Incorporated Trustees of Bilie Human Rights Initiative, representing the Indigenous People of Biafra, have filed a lawsuit against the Federal Government of Nigeria and the Attorney General of the Federation, seeking the actualisation of the sovereign state of Biafra by legal means. The Federal High Court, Abuja has fixed 25 February 2019 for hearing the suit.
On 31 July 2020, the Movement for the Actualization of the Sovereign State of Biafra/Biafra Independence Movement (BIM-MASSOB) joined the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization
The Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization (UNPO) is an international organization established to facilitate the voices of unrepresented and marginalized nations and peoples worldwide. It was formed on 11 February 1991 at the Peace Pal ...
(UNPO).
Indigenous People of Biafra (IPOB)
The Indigenous People of Biafra (IPOB) is a separatist group inNigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
that aims to restore the defunct Republic of Biafra
Biafara anglicized as Biafra ( ), officially the Republic of Biafra, was a partially recognised state in West Africa that declared independence from Nigeria and existed from 1967 to 1970. Its territory consisted of the former Eastern Region o ...
, a country which seceded from Nigeria in 1967 prior to the Nigerian Civil War
The Nigerian Civil War (6 July 1967 – 15 January 1970), also known as the Biafran War, Nigeria-Biafra War, or Biafra War, was fought between Nigeria and the Republic of Biafra, a Secession, secessionist state which had declared its independen ...
and was subsequently dissolved following its defeat in 1970. Since 2021, IPOB and other Biafran separatist groups have been fighting a low-level guerilla conflict in southeastern Nigeria against the Nigerian government
The federal government of Nigeria is composed of three distinct branches: the executive, the legislative, and the judicial, whose powers are vested and bestowed upon by the Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria. One of the primary f ...
. The group was founded in 2012 by Nnamdi Kanu
Mazi Nnamdi Okwu Kanu (born 25 September 1967) is a British political activist known for advocating for the independence of Biafra from Nigeria. He is the leader of the Indigenous People of Biafra (IPOB), which he founded in 2012. The main ai ...
who has been the leader and Uche Mefor, who served as the deputy leader.
Kanu is known as a British political activist
A political movement is a collective attempt by a group of people to change government policy or social values. Political movements are usually in opposition to an element of the status quo, and are often associated with a certain ideology. Some ...
known for his advocacy of the contemporary Biafran independence movement. It was declared a terrorist organization by the Nigerian government in 2017 under the Nigerian Terrorism Act but the declaration was nullified by a High Court sitting in Enugu in 2023. As of May 2022, the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
started denying asylum to members of IPOB who allegedly engaged in human rights abuses, though the UK government clarified that IPOB had not been designated as a terrorist organisation.
IPOB has criticized the Nigerian federal government for poor investment, political alienation, inequitable resource distribution, ethnic marginalization, and heavy military presence, extrajudicial killings in the South-Eastern, South-Central and parts of North-Central regions of the country. The organization rose to prominence in the mid-2010s and is now the largest Biafran independence organization by membership. In recent years, it has gained significant media attention for becoming a frequent target of political crackdowns by the Nigerian government
The federal government of Nigeria is composed of three distinct branches: the executive, the legislative, and the judicial, whose powers are vested and bestowed upon by the Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria. One of the primary f ...
. It also has numerous sites and communication channels serving as the only trusted social apparatus educating and inculcating first-hand information and news to its members.
Biafra Republic Government in Exile (BRGIE)
An organization for the restoration of an independent Biafran state has been led by Simon Ekpa, a Finnish politician and Biafran political activist. Ekpa describes himself as Nnamdi Kanu's disciple. He has served as the leader ("prime minister") of the Biafra Republic Government in Exile (BRGIE) since 2023. In 2023, BRGIE inaugurated an administrative office inMaryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
, United States. It initiated the process of declaring the restoration of Biafra and in October 2023, it convened a three-day convention where the possibility of a Biafra referendum
A referendum, plebiscite, or ballot measure is a Direct democracy, direct vote by the Constituency, electorate (rather than their Representative democracy, representatives) on a proposal, law, or political issue. A referendum may be either bin ...
was discussed, attended by over 500 Biafrans and delegates globally. On 1 February 2024, a digital e-voting system was adopted, and a self-referendum launched the same day. Within days of the referendum exercise, more than two million electorates were reportedly recorded. Prior to the self-referendum exercise, BRGIE had already inaugurated a committee for the Biafra restoration declaration process in January 2024.
On 24 June 2024, the Organization of Emerging African States (OEAS) endorsed the referendum.
BRGIE intended to issue a "declaration of the restoration of independent state of Biafra" on December 2, 2024, at the 2024 Finland convention. Former U.S. Congressman Jim Moran
James Patrick Moran Jr. (born May 16, 1945) is an American politician who served as the mayor of Alexandria, Virginia, from 1985 until 1990, and as the U.S. representative for , including the cities of Falls Church and Alexandria, all of Arl ...
advocates for Biafran independence under the BRGIE with a contract that has been in effect since June 15, 2024.
In emulation of Lithuania's historical part on the Act of the Re-Establishment of the State of Lithuania
The Act of the Re-Establishment of the State of Lithuania or Act of 11 March () was an Declaration of independence, independence declaration by Lithuania adopted on 11 March 1990, signed by all members of the Supreme Council – Reconstituent Se ...
that restored Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
as an independent State on 11 March 1990, the Biafra Restoration Declaration Act was enacted with the term "Declaration of the restoration of the independent State of Biafra" adopted. The recruitment process for the drafting board to be responsible for the restoration declaration of independence was opened on 2 January 2024.
Following the conclusion of the self-referendum exercise held from 1 February to 28 November 2024 through electronic and physical voting, the restoration of Biafra was declared on 29 November 2024 by Biafrans gathered in Lahti
Lahti (; ) is a city in Finland and the regional capital of Päijät-Häme. It is located in the Finnish Lakeland. The population of Lahti is approximately , while the Lahti sub-region, sub-region has a population of approximately . It is the mo ...
, Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
.
See also
*2023 Nigerien crisis
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious and cultural significance in many societies ...
* Ambazonia
Ambazonia, alternatively the Federal Republic of Ambazonia or the State of Ambazonia, is a political entity proclaimed by Anglophone separatists seeking independence from Cameroon. The separatists claim that Ambazonia should consist of the N ...
* ''Half of a Yellow Sun
''Half of a Yellow Sun'' is a 2006 novel by Nigerian author Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie. It became instantly successful after its publication; in the United States and Nigeria, it is widely read in high schools and middle schools. ''Half of a Y ...
'' by Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie
Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie (born Grace Ngozi Adichie; 15 September 1977) is a Nigerians, Nigerian writer of novels, short stories, poem, and children's books; she is also a book reviewer and literary critic. Her most famous works include ''Purple ...
* Insurgency in Southeastern Nigeria
The insurgency in Southeastern Nigeria is a military conflict that broke out in the city of Orlu, Imo, Orlu, Imo State, Nigeria on 16 January 2021, when the Nigerian Army moved to crush the paramilitary wing of the Indigenous People of Biafra (IP ...
* Pakistanization
* "Roland the Headless Thompson Gunner
"Roland the Headless Thompson Gunner" is a song composed by Warren Zevon and David Lindell and performed by Zevon. It was included on Zevon's 1978 album ''Excitable Boy'', and while never released as a single became a fan favorite. It was the las ...
", a song by Warren Zevon
Warren William Zevon (January 24, 1947 – September 7, 2003) was an American rock singer and songwriter. His most famous compositions include "Werewolves of London", "Lawyers, Guns and Money" and "Roland the Headless Thompson Gunner". All t ...
that references the state
Notes
References
Further reading
*Online review
*
External links
* {{Authority control 1967 establishments in Nigeria 1970 disestablishments in Nigeria Former territorial entities in Africa Former countries in Africa Former republics Former unrecognized countries History of Igboland Library of Congress Africa Collection related Members of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization Nigerian Civil War Separatism in Nigeria States and territories disestablished in 1970 States and territories established in 1967