Beryllium Polonide on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Beryllium is a
 Radioactive cosmogenic 10Be is produced in the
Radioactive cosmogenic 10Be is produced in the

 Beryllium is found in over 100 minerals, but most are uncommon to rare. The more common beryllium-containing minerals include:
Beryllium is found in over 100 minerals, but most are uncommon to rare. The more common beryllium-containing minerals include:

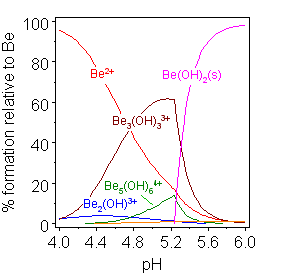
 Solutions of beryllium salts, such as
Solutions of beryllium salts, such as
 Early analyses of emeralds and beryls by
Early analyses of emeralds and beryls by

 Because of its low atomic number and very low absorption for X-rays, the oldest and still one of the most important applications of beryllium is in radiation windows for
Because of its low atomic number and very low absorption for X-rays, the oldest and still one of the most important applications of beryllium is in radiation windows for
 The high elastic stiffness of beryllium has led to its extensive use in precision instrumentation, e.g. in inertial guidance systems and in the support mechanisms for optical systems. Beryllium-copper alloys were also applied as a hardening agent in "Needlegun scaler, Jason pistols", which were used to strip the paint from the hulls of ships.
In sound amplification systems, the speed at which sound travels directly affects the resonant frequency of the amplifier, thereby influencing the range of audible high-frequency sounds. Beryllium stands out due to its exceptionally high speed of sound propagation compared to other metals. This unique property allows beryllium to achieve higher resonant frequencies, making it an ideal material for use as a Diaphragm (acoustics), diaphragm in high-quality loudspeakers.
Beryllium was used for cantilevers in high-performance phonograph cartridge styli, where its extreme stiffness and low density allowed for tracking weights to be reduced to 1 gram while still tracking high frequency passages with minimal distortion.
An earlier major application of beryllium was in brakes for military airplanes because of its hardness, high melting point, and exceptional ability to heat dissipation, dissipate heat. Environmental considerations have led to substitution by other materials.
A metal matrix composite material combining beryllium with
The high elastic stiffness of beryllium has led to its extensive use in precision instrumentation, e.g. in inertial guidance systems and in the support mechanisms for optical systems. Beryllium-copper alloys were also applied as a hardening agent in "Needlegun scaler, Jason pistols", which were used to strip the paint from the hulls of ships.
In sound amplification systems, the speed at which sound travels directly affects the resonant frequency of the amplifier, thereby influencing the range of audible high-frequency sounds. Beryllium stands out due to its exceptionally high speed of sound propagation compared to other metals. This unique property allows beryllium to achieve higher resonant frequencies, making it an ideal material for use as a Diaphragm (acoustics), diaphragm in high-quality loudspeakers.
Beryllium was used for cantilevers in high-performance phonograph cartridge styli, where its extreme stiffness and low density allowed for tracking weights to be reduced to 1 gram while still tracking high frequency passages with minimal distortion.
An earlier major application of beryllium was in brakes for military airplanes because of its hardness, high melting point, and exceptional ability to heat dissipation, dissipate heat. Environmental considerations have led to substitution by other materials.
A metal matrix composite material combining beryllium with
 Beryllium is non-magnetic. Therefore, tools fabricated out of beryllium-based materials are used by naval or military explosive ordnance disposal teams for work on or near naval mines, since these mines commonly have fuze, magnetic fuzes. They are also found in maintenance and construction materials near magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines because of the high magnetic fields generated.
Beryllium is non-magnetic. Therefore, tools fabricated out of beryllium-based materials are used by naval or military explosive ordnance disposal teams for work on or near naval mines, since these mines commonly have fuze, magnetic fuzes. They are also found in maintenance and construction materials near magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines because of the high magnetic fields generated.
 Beryllium is used in fuel fabrication for CANDU reactors. The fuel elements have small appendages that are resistance brazed to the fuel cladding using an induction brazing process with Be as the braze filler material. Bearing pads are brazed in place to prevent contact between the fuel bundle and the pressure tube containing it, and inter-element spacer pads are brazed on to prevent element to element contact.
Beryllium is used at the Joint European Torus nuclear fusion, nuclear-fusion research laboratory, and it will be used in the more advanced ITER to condition the components which face the plasma. Beryllium has been proposed as a Cladding (nuclear fuel), cladding material for nuclear fuel rods, because of its good combination of mechanical, chemical, and nuclear properties. Beryllium fluoride is one of the constituent salts of the eutectic salt mixture FLiBe, which is used as a solvent, moderator and coolant in many hypothetical molten salt reactor designs, including the liquid fluoride thorium reactor (LFTR).
Beryllium is used in fuel fabrication for CANDU reactors. The fuel elements have small appendages that are resistance brazed to the fuel cladding using an induction brazing process with Be as the braze filler material. Bearing pads are brazed in place to prevent contact between the fuel bundle and the pressure tube containing it, and inter-element spacer pads are brazed on to prevent element to element contact.
Beryllium is used at the Joint European Torus nuclear fusion, nuclear-fusion research laboratory, and it will be used in the more advanced ITER to condition the components which face the plasma. Beryllium has been proposed as a Cladding (nuclear fuel), cladding material for nuclear fuel rods, because of its good combination of mechanical, chemical, and nuclear properties. Beryllium fluoride is one of the constituent salts of the eutectic salt mixture FLiBe, which is used as a solvent, moderator and coolant in many hypothetical molten salt reactor designs, including the liquid fluoride thorium reactor (LFTR).
Daily Press (Virginia), Michael Welles Shapiro, 31 August 2013 Although the use of beryllium compounds in fluorescent lighting tubes was discontinued in 1949, potential for exposure to beryllium exists in the nuclear and aerospace industries, in the refining of beryllium metal and the melting of beryllium-containing alloys, in the manufacturing of electronic devices, and in the handling of other beryllium-containing material.
''Beryllium Chemistry and Processing''
Vidal, EE. et al. Eds. 2009, Materials Park, OH:ASM International.
Beryllium Lymphocyte Proliferation Testing (BeLPT).
DOE Specification 1142–2001. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Energy, 2001.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
It's Elemental – Beryllium
* MSDS
ESPI Metals
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health – Beryllium Page
National Supplemental Screening Program (Oak Ridge Associated Universities)
Historic Price of Beryllium in USA
{{portal bar, Chemistry Beryllium, Chemical elements Alkaline earth metals Neutron moderators Nuclear materials IARC Group 1 carcinogens Chemical hazards Reducing agents Chemical elements with hexagonal close-packed structure
chemical element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its ...
; it has symbol
A symbol is a mark, Sign (semiotics), sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, physical object, object, or wikt:relationship, relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by cr ...
Be and atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of its atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei composed of protons and neutrons, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of pro ...
4. It is a steel-gray, hard, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal
The alkaline earth metals are six chemical elements in group (periodic table), group 2 of the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).. The elements have very similar p ...
. It is a divalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an atom is a measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules. Valence is generally understood to be the number of chemica ...
element that occurs naturally only in combination with other elements to form minerals. Gemstones
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, semiprecious stone, or simply gem) is a piece of mineral crystal which, when cut or polished, is used to make jewelry or other adornments. Certain rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opal, a ...
high in beryllium include beryl
Beryl ( ) is a mineral composed of beryllium aluminium Silicate minerals#Cyclosilicates, silicate with the chemical formula Be3Al2(SiO3)6. Well-known varieties of beryl include emerald and Aquamarine (gem), aquamarine. Naturally occurring Hex ...
( aquamarine, emerald
Emerald is a gemstone and a variety of the mineral beryl (Be3Al2(SiO3)6) colored green by trace amounts of chromium or sometimes vanadium.Hurlbut, Cornelius S. Jr., and Kammerling, Robert C. (1991). ''Gemology'', John Wiley & Sons, New York ...
, red beryl
Red beryl, formerly known as bixbite and marketed as red emerald or scarlet emerald, is an extremely rare variety of beryl as well as one of the rarest minerals on Earth. The gem gets its red color from manganese ions incorporated within the bery ...
) and chrysoberyl
The mineral or gemstone chrysoberyl is an aluminate of beryllium with the formula Be Al2 O4. The name chrysoberyl is derived from the Greek words χρυσός ''chrysos'' and βήρυλλος ''beryllos'', meaning "a gold-white spar". Despit ...
. It is a relatively rare element in the universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents. It comprises all of existence, any fundamental interaction, physical process and physical constant, and therefore all forms of matter and energy, and the structures they form, from s ...
, usually occurring as a product of the spallation
Spallation is a process in which fragments of material (spall) are ejected from a body due to impact or stress. In the context of impact mechanics it describes ejection of material from a target during impact by a projectile. In planetary p ...
of larger atomic nuclei that have collided with cosmic ray
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the ...
s. Within the cores of stars, beryllium is depleted as it is fused into heavier elements. Beryllium constitutes about 0.0004 percent by mass of Earth's crust. The world's annual beryllium production of 220 tons is usually manufactured by extraction from the mineral beryl
Beryl ( ) is a mineral composed of beryllium aluminium Silicate minerals#Cyclosilicates, silicate with the chemical formula Be3Al2(SiO3)6. Well-known varieties of beryl include emerald and Aquamarine (gem), aquamarine. Naturally occurring Hex ...
, a difficult process because beryllium bonds strongly to oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
.
In structural applications, the combination of high flexural rigidity
Flexural rigidity is defined as the force couple required to bend a fixed non- rigid structure by one unit of curvature, or as the resistance offered by a structure while undergoing bending.
Flexural rigidity of a beam
Although the moment M(x) ...
, thermal stability
In thermodynamics, thermal stability describes the stability of a water body and its resistance to mixing.Schmidt, W. 1928. Über Temperatur und Stabilitätsverhältnisse von Seen. Geogr. Ann 10: 145 - 177. It is the amount of work needed to tra ...
, thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to heat conduction, conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa and is measured in W·m−1·K−1.
Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low ...
and low density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the ratio of a substance's mass to its volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' (or ''d'') can also be u ...
(1.85 times that of water) make beryllium a desirable aerospace
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial, and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and astron ...
material for aircraft components, missile
A missile is an airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight aided usually by a propellant, jet engine or rocket motor.
Historically, 'missile' referred to any projectile that is thrown, shot or propelled towards a target; this ...
s, spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle that is designed spaceflight, to fly and operate in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth observation, Weather s ...
, and satellites
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scientif ...
. Because of its low density and atomic mass
Atomic mass ( or ) is the mass of a single atom. The atomic mass mostly comes from the combined mass of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus, with minor contributions from the electrons and nuclear binding energy. The atomic mass of atoms, ...
, beryllium is relatively transparent to X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
s and other forms of ionizing radiation
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including Radioactive decay, nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have enough energy per individual photon or particle to ionization, ionize atoms or molecules by detaching ...
; therefore, it is the most common window material for X-ray equipment and components of particle detector
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify ionizing elementary particle, particles, such as t ...
s. When added as an alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
ing element to aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
(notably the alloy beryllium copper
Beryllium copper (BeCu), also known as copper beryllium (CuBe), beryllium bronze, and spring copper, is a copper alloy with 0.5–3% beryllium. Copper beryllium alloys are often used because of their high strength and good conductivity of both ...
), iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, or nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
, beryllium improves many physical properties. For example, tools and components made of beryllium copper alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
s are strong
Strong may refer to:
Education
* The Strong, an educational institution in Rochester, New York, United States
* Strong Hall (Lawrence, Kansas), an administrative hall of the University of Kansas
* Strong School, New Haven, Connecticut, United ...
and hard and do not create sparks when they strike a steel surface. In air, the surface of beryllium oxidizes readily at room temperature to form a passivation layer
In physical chemistry and engineering, passivation is coating a material so that it becomes "passive", that is, less readily affected or corroded by the environment. Passivation involves creation of an outer layer of shield material that is appl ...
1–10 nm thick that protects it from further oxidation and corrosion. The metal oxidizes in bulk (beyond the passivation layer) when heated above , and burns brilliantly when heated to about .
The commercial use of beryllium requires the use of appropriate dust control equipment and industrial controls at all times because of the toxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacteria, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect o ...
of inhaled beryllium-containing dusts that can cause a chronic life-threatening allergic disease, berylliosis
Berylliosis, or chronic beryllium disease (CBD), is a chronic allergic-type lung response and chronic lung disease caused by exposure to beryllium and its compounds, a form of beryllium poisoning. It is distinct from acute beryllium poisoning, wh ...
, in some people. Berylliosis is typically manifested by chronic pulmonary fibrosis
Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition in which the lungs become scarred over time. Symptoms include shortness of breath, a dry cough, feeling tired, weight loss, and nail clubbing. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, respiratory ...
and, in severe cases, right sided heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to Cardiac cycle, fill with and pump blood.
Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF ...
and death.
Characteristics
Physical properties
Beryllium is a steel gray and hardmetal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
that is brittle at room temperature and has a close-packed hexagonal crystal structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of ordered arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from intrinsic nature of constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat ...
. It has exceptional stiffness
Stiffness is the extent to which an object resists deformation in response to an applied force.
The complementary concept is flexibility or pliability: the more flexible an object is, the less stiff it is.
Calculations
The stiffness, k, of a ...
(Young's modulus
Young's modulus (or the Young modulus) is a mechanical property of solid materials that measures the tensile or compressive stiffness when the force is applied lengthwise. It is the modulus of elasticity for tension or axial compression. Youn ...
287 GPa) and a melting point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state of matter, state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase (matter), phase exist in Thermodynamic equilib ...
of 1287 °C. The modulus of elasticity
An elastic modulus (also known as modulus of elasticity (MOE)) is a quantity that describes an object's or substance's resistance to being deformed elastically (i.e., non-permanently) when a stress is applied to it.
Definition
The elastic modu ...
of beryllium is approximately 35% greater than that of steel. The combination of this modulus and a relatively low density results in an unusually fast sound conduction speed in beryllium – about 12.9 km/s at ambient conditions.
Among all metals, beryllium dissipates the most heat per unit weight, with both high specific heat () and thermal conductivity ().
Beryllium's conductivity and relatively low coefficient of linear thermal expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to increase in length, area, or volume, changing its size and density, in response to an increase in temperature (usually excluding phase transitions).
Substances usually contract with decreasing temp ...
(11.4 × 10−6 K−1), make it uniquely stable under extreme temperature differences.
Nuclear properties
Naturally occurring beryllium, save for slight contamination by the radioisotopes created by cosmic rays, is isotopically pure beryllium-9, which has anuclear spin
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
* Nuclear engineering
* Nuclear physics
* Nuclear power
* Nuclear reactor
* Nuclear weapon
* Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
* Nuclear space
* ...
of −. The inelastic scattering cross section
Cross section may refer to:
* Cross section (geometry)
** Cross-sectional views in architecture and engineering 3D
*Cross section (geology)
* Cross section (electronics)
* Radar cross section, measure of detectability
* Cross section (physics)
**A ...
of beryllium increases with relation to neutron energy, allowing for significant slowing of higher-energy neutrons. Therefore, it works as a neutron reflector
A neutron reflector is any material that reflects neutrons. This refers to elastic scattering rather than to a specular reflection. The material may be graphite, beryllium, steel, tungsten carbide, gold, or other materials. A neutron reflect ...
and neutron moderator
In nuclear engineering, a neutron moderator is a medium that reduces the speed of fast neutrons, ideally without capturing any, leaving them as thermal neutrons with only minimal (thermal) kinetic energy. These thermal neutrons are immensely ...
; the exact strength of neutron slowing strongly depends on the purity and size of the crystallites in the material.
The single primordial beryllium isotope 9Be also undergoes a (n,2n) neutron reaction with neutron energies over about 1.9 MeV, to produce 8Be, which almost immediately breaks into two alpha particles. Thus, for high-energy neutrons, beryllium is a neutron multiplier, releasing more neutrons than it absorbs. This nuclear reaction is:
: + n → 2 + 2 n
Neutrons are liberated when beryllium nuclei are struck by energetic alpha particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay but may also be produce ...
s producing the nuclear reaction
: + → + n
where is an alpha particle and is a carbon-12
Carbon-12 (12C) is the most abundant of the two stable isotopes of carbon ( carbon-13 being the other), amounting to 98.93% of element carbon on Earth; its abundance is due to the triple-alpha process by which it is created in stars. Carbon-1 ...
nucleus.
Beryllium also releases neutrons under bombardment by gamma rays. Thus, natural beryllium bombarded either by alphas or gammas from a suitable radioisotope is a key component of most radioisotope-powered nuclear reaction
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is a process in which two atomic nucleus, nuclei, or a nucleus and an external subatomic particle, collide to produce one or more new nuclides. Thus, a nuclear reaction must cause a t ...
neutron source
A neutron source is any device that emits neutrons, irrespective of the mechanism used to produce the neutrons. Neutron sources are used in physics, engineering, medicine, nuclear weapons, petroleum exploration, biology, chemistry, and nuclear p ...
s for the laboratory production of free neutrons.
Small amounts of tritium
Tritium () or hydrogen-3 (symbol T or H) is a rare and radioactive isotope of hydrogen with a half-life of ~12.33 years. The tritium nucleus (t, sometimes called a ''triton'') contains one proton and two neutrons, whereas the nucleus of the ...
are liberated when nuclei absorb low energy neutrons in the three-step nuclear reaction
: + n → + , → + β−, + n → +
has a half-life of only 0.8 seconds, β− is an electron, and has a high neutron absorption cross section. Tritium is a radioisotope of concern in nuclear reactor waste streams.
Optical properties
As a metal, beryllium is transparent or translucent to most wavelengths ofX-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
s and gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from high energy interactions like the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei or astronomical events like solar flares. It consists o ...
s, making it useful for the output windows of X-ray tube
An X-ray tube is a vacuum tube that converts electrical input power into X-rays. The availability of this controllable source of X-rays created the field of radiography, the imaging of partly opaque objects with penetrating radiation. In contras ...
s and other such apparatus.
Isotopes and nucleosynthesis
Both stable and unstable isotopes of beryllium are created in stars, but the radioisotopes do not last long. It is believed that the beryllium in the universe was created in the interstellar medium whencosmic rays
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar ...
induced fission in heavier elements found in interstellar gas and dust, a process called cosmic ray spallation
Cosmic ray spallation, also known as the x-process, is a set of naturally occurring nuclear reactions causing nucleosynthesis; it refers to the formation of chemical elements from the impact of cosmic rays on an object. Cosmic rays are highly ene ...
. Natural beryllium is solely made up of the stable isotope beryllium-9. Beryllium is the only monoisotopic element
A monoisotopic element is an element which has only a single stable isotope (nuclide). There are 26 such elements, as listed.
Stability is experimentally defined for chemical elements, as there are a number of stable nuclides with atomic number ...
with an even atomic number.
About one billionth () of the primordial atoms created in the Big Bang nucleosynthesis
In physical cosmology, Big Bang nucleosynthesis (also known as primordial nucleosynthesis, and abbreviated as BBN) is a model for the production of light nuclei, deuterium, 3He, 4He, 7Li, between 0.01s and 200s in the lifetime of the universe ...
were 7Be. This is a consequence of the low density of matter when the temperature of the universe cooled enough for small nuclei to be stable. Creating such nuclei requires nuclear collisions that are rare at low density. Although 7Be is unstable and decays by electron capture
Electron capture (K-electron capture, also K-capture, or L-electron capture, L-capture) is a process in which the proton-rich nucleus of an electrically neutral atom absorbs an inner atomic electron, usually from the K or L electron shells. Th ...
into 7Li with a half-life of 53 days, in the early universe this decay channel was unavailable due to atoms being fully ionized. The conversion of 7Be to Li was only complete near the time of recombination.
The isotope 7Be (half-life 53 days) is also a cosmogenic nuclide
Cosmogenic nuclides (or cosmogenic isotopes) are rare nuclides (isotopes) created when a high-energy cosmic ray interacts with the nucleus of an '' in situ'' Solar System atom, causing nucleons (protons and neutrons) to be expelled from the atom ...
, and also shows an atmospheric abundance inversely proportional to solar activity. The 2s electrons of beryllium may contribute to chemical bonding. Therefore, when 7Be decays by L-electron capture
Electron capture (K-electron capture, also K-capture, or L-electron capture, L-capture) is a process in which the proton-rich nucleus of an electrically neutral atom absorbs an inner atomic electron, usually from the K or L electron shells. Th ...
, it does so by taking electrons from its atomic orbital
In quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital () is a Function (mathematics), function describing the location and Matter wave, wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function describes an electron's Charge density, charge distribution a ...
s that may be participating in bonding. This makes its decay rate dependent to a measurable degree upon its chemical surroundings – a rare occurrence in nuclear decay.
8Be is unstable but has a ground state resonance
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when an object or system is subjected to an external force or vibration whose frequency matches a resonant frequency (or resonance frequency) of the system, defined as a frequency that generates a maximu ...
with an important role in the triple-alpha process
The triple-alpha process is a set of nuclear fusion reactions by which three helium-4 nuclei (alpha particles) are transformed into carbon.
In stars
Helium accumulates in the cores of stars as a result of the proton–proton chain reaction a ...
in helium-fueled stars. As first proposed by British astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. Astronomers observe astronomical objects, such as stars, planets, natural satellite, moons, comets and galaxy, galax ...
Sir Fred Hoyle
Sir Fred Hoyle (24 June 1915 – 20 August 2001) was an English astronomer who formulated the theory of stellar nucleosynthesis and was one of the authors of the influential B2FH paper, B2FH paper. He also held controversial stances on oth ...
based solely on astrophysical analysis, the energy levels of 8Be and 12C allow carbon nucleosynthesis by increasing the contact time for two of the three alpha particles in the carbon production process. The main carbon-producing reaction in the universe is
where 4He is an alpha particle.
 Radioactive cosmogenic 10Be is produced in the
Radioactive cosmogenic 10Be is produced in the atmosphere of the Earth
The atmosphere of Earth is composed of a layer of gas mixture that surrounds the Earth's planetary surface (both lands and oceans), known collectively as air, with variable quantities of suspended aerosols and particulates (which create weather ...
by the cosmic ray spallation
Cosmic ray spallation, also known as the x-process, is a set of naturally occurring nuclear reactions causing nucleosynthesis; it refers to the formation of chemical elements from the impact of cosmic rays on an object. Cosmic rays are highly ene ...
of oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
. Then the 10Be accumulates at the soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by re ...
surface, where its relatively long half-life Half-life is a mathematical and scientific description of exponential or gradual decay.
Half-life, half life or halflife may also refer to:
Film
* Half-Life (film), ''Half-Life'' (film), a 2008 independent film by Jennifer Phang
* ''Half Life: ...
(1.36 million years) permits a long residence time
The residence time of a fluid parcel is the total time that the parcel has spent inside a control volume (e.g.: a chemical reactor, a lake, a human body). The residence time of a set of parcels is quantified in terms of the frequency distribu ...
before decaying to boron
Boron is a chemical element; it has symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the boron group it has three ...
-10. Thus, 10Be and its daughter products are used to examine natural soil erosion
Soil erosion is the denudation or wearing away of the Topsoil, upper layer of soil. It is a form of soil degradation. This natural process is caused by the dynamic activity of erosive agents, that is, water, ice (glaciers), snow, Atmosphere of Ea ...
, soil formation
Soil formation, also known as pedogenesis, is the process of soil genesis as regulated by the effects of place, environment, and history. Biogeochemical processes act to both create and destroy order ( anisotropy) within soils. These alteration ...
and the development of lateritic soils, and as a proxy for measurement of the variations in solar activity
Solar phenomena are natural phenomena which occur within the Stellar atmosphere, atmosphere of the Sun. They take many forms, including solar wind, Solar radio emission, radio wave flux, solar flares, coronal mass ejections, Stellar corona#Coron ...
and the age of ice core
An ice core is a core sample that is typically removed from an ice sheet or a high mountain glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier ...
s. The production of 10Be is inversely related to solar activity, because increased solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the Stellar corona, corona. This Plasma (physics), plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy betwee ...
during periods of high solar activity decreases the flux of galactic cosmic rays that reach the Earth. Nuclear explosions also form 10Be by the reaction of fast neutrons with 13C in the carbon dioxide in air. This is one of the indicators of past activity at nuclear weapon test
Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine the performance of nuclear weapons and the effects of their explosion. Nuclear testing is a sensitive political issue. Governments have often performed tests to signal strength. Bec ...
sites.
The exotic isotopes 11Be and 14Be are known to exhibit a nuclear halo. This feature can be understood as the nuclei of 11Be and 14Be have, respectively, 1 and 4 neutrons orbiting substantially outside the expected nuclear radius.
Occurrence

 Beryllium is found in over 100 minerals, but most are uncommon to rare. The more common beryllium-containing minerals include:
Beryllium is found in over 100 minerals, but most are uncommon to rare. The more common beryllium-containing minerals include: bertrandite
Bertrandite is a beryllium sorosilicate hydroxide mineral with composition: Be4Si2O7(OH)2. Bertrandite is a colorless to pale yellow orthorhombic mineral with a hardness of 6–7.
It is commonly found in beryllium rich pegmatites and is in part ...
(), beryl
Beryl ( ) is a mineral composed of beryllium aluminium Silicate minerals#Cyclosilicates, silicate with the chemical formula Be3Al2(SiO3)6. Well-known varieties of beryl include emerald and Aquamarine (gem), aquamarine. Naturally occurring Hex ...
(), chrysoberyl
The mineral or gemstone chrysoberyl is an aluminate of beryllium with the formula Be Al2 O4. The name chrysoberyl is derived from the Greek words χρυσός ''chrysos'' and βήρυλλος ''beryllos'', meaning "a gold-white spar". Despit ...
() and phenakite
Phenakite or phenacite is a fairly rare nesosilicate mineral consisting of beryllium orthosilicate, Be2 Si O4. Occasionally used as a gemstone, phenakite occurs as isolated crystals, which are rhombohedral with parallel-faced hemihedrism, and a ...
(). Precious forms of beryl are aquamarine, red beryl
Red beryl, formerly known as bixbite and marketed as red emerald or scarlet emerald, is an extremely rare variety of beryl as well as one of the rarest minerals on Earth. The gem gets its red color from manganese ions incorporated within the bery ...
and emerald
Emerald is a gemstone and a variety of the mineral beryl (Be3Al2(SiO3)6) colored green by trace amounts of chromium or sometimes vanadium.Hurlbut, Cornelius S. Jr., and Kammerling, Robert C. (1991). ''Gemology'', John Wiley & Sons, New York ...
.
The green color in gem-quality forms of beryl comes from varying amounts of chromium (about 2% for emerald).
The two main ores of beryllium, beryl and bertrandite, are found in Argentina, Brazil, India, Madagascar, Russia and the United States. Total world reserves of beryllium ore are greater than 400,000 tonnes.
The Sun has a concentration of 0.1 parts per billion
In science and engineering, the parts-per notation is a set of pseudo-units to describe the small values of miscellaneous dimensionless quantities, e.g. mole fraction or mass fraction.
Since these fractions are quantity-per-quantity measur ...
(ppb) of beryllium. Beryllium has a concentration of 2 to 6 parts per million
In science and engineering, the parts-per notation is a set of pseudo-units to describe the small values of miscellaneous dimensionless quantity, dimensionless quantities, e.g. mole fraction or mass fraction (chemistry), mass fraction.
Since t ...
(ppm) in the Earth's crust and is the 47th most abundant element. It is most concentrated (6 ppm) in the soils. Trace amounts of 9Be are found in the Earth's atmosphere. The concentration of beryllium in sea water is 0.2–0.6 parts per trillion
In science and engineering, the parts-per notation is a set of pseudo-units to describe the small values of miscellaneous dimensionless quantities, e.g. mole fraction or mass fraction.
Since these fractions are quantity-per-quantity measures ...
. In stream water, however, beryllium is more abundant, with a concentration of 0.1 ppb.
Extraction
The extraction of beryllium from its compounds is a difficult process due to its high affinity for oxygen at elevated temperatures, and its ability to reduce water when its oxide film is removed. Currently the United States, China and Kazakhstan are the only three countries involved in the industrial-scale extraction of beryllium. Kazakhstan produces beryllium from a concentrate stockpiled before thebreakup of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was formally dissolved as a sovereign state and subject of international law on 26 December 1991 by Declaration No. 142-N of the Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union. Declaration No. 142-Н of ...
around 1991. This resource had become nearly depleted by mid-2010s.
Production of beryllium in Russia was halted in 1997, and is planned to be resumed in the 2020s.
Beryllium is most commonly extracted from the mineral beryl
Beryl ( ) is a mineral composed of beryllium aluminium Silicate minerals#Cyclosilicates, silicate with the chemical formula Be3Al2(SiO3)6. Well-known varieties of beryl include emerald and Aquamarine (gem), aquamarine. Naturally occurring Hex ...
, which is either sintered
Sintering or frittage is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by pressure or heat without melting it to the point of liquefaction. Sintering happens as part of a manufacturing process used with metals, ceramics, pla ...
using an extraction agent or melted into a soluble mixture. The sintering process involves mixing beryl with sodium fluorosilicate
Sodium fluorosilicate is a compound with the chemical formula Na2 iF6 Unlike other sodium salts, it has a low solubility in water.
Natural occurrence
Sodium hexafluorosilicate occurs naturally as the rare mineral malladrite found within some volc ...
and soda at to form sodium fluoroberyllate, aluminium oxide
Aluminium oxide (or aluminium(III) oxide) is a chemical compound of aluminium and oxygen with the chemical formula . It is the most commonly occurring of several Aluminium oxide (compounds), aluminium oxides, and specifically identified as alum ...
and silicon dioxide
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundan ...
. Beryllium hydroxide
Beryllium hydroxide, Be(OH)2, is an amphoteric hydroxide, dissolving in both acids and alkalis. Industrially, it is produced as a by-product in the extraction of beryllium metal from the ores beryl and bertrandite. The natural pure beryllium hydro ...
is precipitated from a solution of sodium fluoroberyllate and sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly corrosive base (chemistry), ...
in water. The extraction of beryllium using the melt method involves grinding beryl into a powder and heating it to . The melt is quickly cooled with water and then reheated in concentrated sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, ...
, mostly yielding beryllium sulfate
Beryllium sulfate normally encountered as the tetrahydrate, e(H2O)4O4 is a white crystalline solid. It was first isolated in 1815 by Jons Jakob Berzelius. Beryllium sulfate may be prepared by treating an aqueous solution of many beryllium salts ...
and aluminium sulfate
Aluminium sulfate is a salt with the chemical formula, formula . It is soluble in water and is mainly used as a Coagulation (water treatment), coagulating agent (promoting particle collision by neutralizing charge) in the purification of drinking ...
. Aqueous ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
is then used to remove the aluminium and sulfur, leaving beryllium hydroxide.
Beryllium hydroxide created using either the sinter or melt method is then converted into beryllium fluoride
Beryllium fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula Be F2. This white solid is the principal precursor for the manufacture of beryllium metal. Its structure resembles that of quartz, but BeF2 is highly soluble in water.
Properties
Ber ...
or beryllium chloride
Beryllium chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula BeCl2. It is a colourless, hygroscopic solid that dissolves well in many polar solvents. Its properties are similar to those of aluminium chloride, due to beryllium's diagonal relations ...
. To form the fluoride, aqueous ammonium hydrogen fluoride is added to beryllium hydroxide to yield a precipitate of ammonium tetrafluoroberyllate
Tetrafluoroberyllate or orthofluoroberyllate is an anion with the chemical formula . It contains beryllium and fluorine. This fluoroanion has a tetrahedral shape, with the four fluorine atoms surrounding a central beryllium atom. It has the same ...
, which is heated to to form beryllium fluoride. Heating the fluoride to with magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
forms finely divided beryllium, and additional heating to creates the compact metal. Heating beryllium hydroxide forms beryllium oxide
Beryllium oxide (BeO), also known as beryllia, is an inorganic compound with the formula BeO. This colourless solid is an electrical insulator with a higher thermal conductivity than any other non-metal except diamond, and exceeds that of most met ...
, which becomes beryllium chloride when combined with carbon and chlorine. Electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses Direct current, direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of c ...
of molten beryllium chloride is then used to obtain the metal.
Chemical properties
A beryllium atom has the electronic configuration e2s2. The predominantoxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical Electrical charge, charge of an atom if all of its Chemical bond, bonds to other atoms are fully Ionic bond, ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons ...
of beryllium is +2; the beryllium atom has lost both of its valence electrons. Beryllium's chemical behavior is largely a result of its small atomic and ionic radii. It thus has very high ionization potential
In physics and chemistry, ionization energy (IE) is the minimum energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron of an isolated gaseous atom, positive ion, or molecule. The first ionization energy is quantitatively expressed as
:X(g) ...
s and does not form divalent cations. Instead it forms two covalent bonds with a tendency to polymerize, as in solid . Its chemistry has similarities to that of aluminium, an example of a diagonal relationship
In chemistry, a diagonal relationship is said to exist between certain pairs of diagonally adjacent elements in the second and third periods (first 20 elements) of the periodic table. These pairs (lithium (Li) and magnesium (Mg), beryllium (Be) ...
.
In the other direction, beryllium is attracted to electron density, generating intermolecular forces similar to hydrogen bonding
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (H-bond) is a specific type of molecular interaction that exhibits partial covalent character and cannot be described as a purely electrostatic force. It occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom, Covalent bond, covalently b ...
.
At room temperature, the surface of beryllium forms a 1−10 nm-thick oxide passivation layer that prevents further reactions with air, except for gradual thickening of the oxide up to about 25 nm. When heated above about 500 °C, oxidation into the bulk metal progresses along grain boundaries. Once the metal is ignited in air by heating above the oxide melting point around 2500 °C, beryllium burns brilliantly, forming a mixture of beryllium oxide
Beryllium oxide (BeO), also known as beryllia, is an inorganic compound with the formula BeO. This colourless solid is an electrical insulator with a higher thermal conductivity than any other non-metal except diamond, and exceeds that of most met ...
and beryllium nitride. Beryllium dissolves readily in non-oxidizing acid
An oxidizing acid is a Brønsted acid that is a strong oxidizing agent. Most Brønsted acids can act as oxidizing agents, because the acidic proton can be reduced to hydrogen gas. Some acids contain other structures that act as stronger oxidizing ...
s, such as HCl and diluted , but not in nitric acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most com ...
or water as this forms the oxide. This behavior is similar to that of aluminium. Beryllium also dissolves and reacts with alkali solutions.
Binary compounds of beryllium(II) are polymeric in the solid state. has a silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant f ...
-like structure with corner-shared tetrahedra. and have chain structures with edge-shared tetrahedra. Beryllium oxide
Beryllium oxide (BeO), also known as beryllia, is an inorganic compound with the formula BeO. This colourless solid is an electrical insulator with a higher thermal conductivity than any other non-metal except diamond, and exceeds that of most met ...
, BeO, is a white refractory
In materials science, a refractory (or refractory material) is a material that is resistant to decomposition by heat or chemical attack and that retains its strength and rigidity at high temperatures. They are inorganic, non-metallic compound ...
solid which has a wurtzite
Wurtzite is a zinc and iron sulfide mineral with the chemical formula , a less frequently encountered Polymorphism (materials science), structural polymorph form of sphalerite. The iron content is variable up to eight percent.Palache, Charles, H ...
crystal structure and a thermal conductivity as high as some metals. BeO is amphoteric
In chemistry, an amphoteric compound () is a molecule or ion that can react both as an acid and as a base. What exactly this can mean depends on which definitions of acids and bases are being used.
Etymology and terminology
Amphoteric is d ...
. Beryllium sulfide
Beryllium sulfide (BeS) is an ionic compound from the sulfide group with the formula Be S. It is a white solid with a sphalerite structure that is decomposed by water and acids.
Preparation
Beryllium sulfide powders can be prepared by the reacti ...
, selenide
A selenide is a chemical compound containing a selenium with oxidation number of −2. Similar to sulfide, selenides occur both as inorganic compounds and as organic derivatives, which are called organoselenium compound.
Inorganic selenides
Th ...
and telluride are known, all having the zincblende structure. Beryllium nitride, , is a high-melting-point compound which is readily hydrolyzed. Beryllium azide, is known and beryllium phosphide
Beryllium is a chemical element; it has symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, hard, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with other elements to fo ...
, has a similar structure to . A number of beryllium boride
A boride is a compound between boron and a less electronegative element, for example silicon boride (SiB3 and SiB6). The borides are a very large group of compounds that are generally high melting and are covalent more than ionic in nature. Some b ...
s are known, such as , , , , and . Beryllium carbide
Beryllium carbide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a metal carbide. Similar to diamond, it is a very hard compound. It is used in nuclear reactors as a core material.
Preparation
Beryllium carbide is prepared by heating th ...
, , is a refractory brick-red compound that reacts with water to give methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
. Beryllium silicides have been identified in the form of variously sized nanoclusters
Nanoclusters are atomically precise, crystalline materials most often existing on the 0-2 nanometer scale. They are often considered kinetically stable intermediates that form during the synthesis of comparatively larger materials such as semic ...
, formed through a spontaneous reaction between pure beryllium and silicon. The halides (X = F, Cl, Br, and I) have a linear monomeric molecular structure in the gas phase.
Lower oxidation states complexes of beryllium are exceedingly rare. For example, a stable complex with a Be-Be bond, which formally features beryllium in the +1 oxidation state, has been described. Beryllium in the 0 oxidation state is also known in a complex with a Mg-Be bond.
Aqueous solutions


beryllium sulfate
Beryllium sulfate normally encountered as the tetrahydrate, e(H2O)4O4 is a white crystalline solid. It was first isolated in 1815 by Jons Jakob Berzelius. Beryllium sulfate may be prepared by treating an aqueous solution of many beryllium salts ...
and beryllium nitrate, are acidic because of hydrolysis of the ion. The concentration of the first hydrolysis product, , is less than 1% of the beryllium concentration. The most stable hydrolysis product is the trimeric ion . Beryllium hydroxide
Beryllium hydroxide, Be(OH)2, is an amphoteric hydroxide, dissolving in both acids and alkalis. Industrially, it is produced as a by-product in the extraction of beryllium metal from the ores beryl and bertrandite. The natural pure beryllium hydro ...
, , is insoluble in water at pH 5 or more. Consequently, beryllium compounds are generally insoluble at biological pH. Because of this, inhalation of beryllium metal dust leads to the development of the fatal condition of berylliosis
Berylliosis, or chronic beryllium disease (CBD), is a chronic allergic-type lung response and chronic lung disease caused by exposure to beryllium and its compounds, a form of beryllium poisoning. It is distinct from acute beryllium poisoning, wh ...
. dissolves in strongly alkaline
In chemistry, an alkali (; from the Arabic word , ) is a basic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The ...
solutions.
Beryllium(II) forms few complexes with monodentate ligands because the water molecules in the aquo-ion, are bound very strongly to the beryllium ion. Notable exceptions are the series of water-soluble complexes with the fluoride
Fluoride (). According to this source, is a possible pronunciation in British English. is an Inorganic chemistry, inorganic, Monatomic ion, monatomic Ion#Anions and cations, anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula (also written ), whose ...
ion:
:
Beryllium(II) forms many complexes with bidentate ligands containing oxygen-donor atoms. The species is notable for having a 3-coordinate oxide ion at its center. Basic beryllium acetate
Basic beryllium acetate is the chemical compound with the formula Be4O(O2CCH3)6. This compound adopts a distinctive structure, but it has no applications and has been only lightly studied. It is a colourless solid that is soluble in organic solv ...
, , has an oxide ion surrounded by a tetrahedron of beryllium atoms.
With organic ligands, such as the malonate
The conjugate acids are in :Carboxylic acids.
{{Commons category, Carboxylate ions, Carboxylate anions
Carbon compounds
Anions ...
ion, the acid deprotonates when forming the complex. The donor atoms are two oxygens.
:
:
The formation of a complex is in competition with the metal ion-hydrolysis reaction and mixed complexes with both the anion and the hydroxide ion are also formed. For example, derivatives of the cyclic trimer are known, with a bidentate ligand replacing one or more pairs of water molecules.
Aliphatic hydroxycarboxylic acids such as glycolic acid
Glycolic acid (or hydroxyacetic acid; chemical formula ) is a colorless, odorless and hygroscopic crystal, crystalline solid, highly solubility, soluble in water. It is used in various skin care, skin-care products. Glycolic acid is widespread in ...
form rather weak monodentate complexes in solution, in which the hydroxyl group remains intact. In the solid state, the hydroxyl group may deprotonate: a hexamer, , was isolated long ago. Aromatic hydroxy ligands (i.e. phenol
Phenol (also known as carbolic acid, phenolic acid, or benzenol) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile and can catch fire.
The molecule consists of a phenyl group () ...
s) form relatively strong complexes. For example, log K1 and log K2 values of 12.2 and 9.3 have been reported for complexes with tiron.
Beryllium has generally a rather poor affinity for ammine
In coordination chemistry, metal ammine complexes are metal complexes containing at least one ammonia () ligand. "Ammine" is spelled this way for historical reasons; in contrast, alkyl or aryl bearing ligands are spelt with a single "m". Almost al ...
ligands. There are many early reports of complexes with amino acids, but unfortunately they are not reliable as the concomitant hydrolysis reactions were not understood at the time of publication. Values for log β of ca. 6 to 7 have been reported. The degree of formation is small because of competition with hydrolysis reactions.
Organic chemistry
Organometallic beryllium compounds are known to be highly reactive. Examples of known organoberyllium compounds are dineopentylberyllium,beryllocene
Beryllocene is an organoberyllium compound with the chemical formula Be(C5H5)2, first prepared in 1959. The colorless substance can be crystallized from petroleum ether in the form of white needles at −60 °C and decomposes quickly upon co ...
(), diallylberyllium (by exchange reaction of diethyl beryllium with triallyl boron), bis(1,3-trimethylsilylallyl)beryllium, Be( mes)2, and (beryllium(I) complex) diberyllocene. Ligands can also be aryls and alkynyls.
History
The mineralberyl
Beryl ( ) is a mineral composed of beryllium aluminium Silicate minerals#Cyclosilicates, silicate with the chemical formula Be3Al2(SiO3)6. Well-known varieties of beryl include emerald and Aquamarine (gem), aquamarine. Naturally occurring Hex ...
, which contains beryllium, has been used at least since the Ptolemaic dynasty
The Ptolemaic dynasty (; , ''Ptolemaioi''), also known as the Lagid dynasty (, ''Lagidai''; after Ptolemy I's father, Lagus), was a Macedonian Greek royal house which ruled the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Ancient Egypt during the Hellenistic period. ...
of Egypt. In the first century CE, Roman naturalist Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
mentioned in his encyclopedia ''Natural History
Natural history is a domain of inquiry involving organisms, including animals, fungi, and plants, in their natural environment, leaning more towards observational than experimental methods of study. A person who studies natural history is cal ...
'' that beryl and emerald
Emerald is a gemstone and a variety of the mineral beryl (Be3Al2(SiO3)6) colored green by trace amounts of chromium or sometimes vanadium.Hurlbut, Cornelius S. Jr., and Kammerling, Robert C. (1991). ''Gemology'', John Wiley & Sons, New York ...
("smaragdus") were similar. The Papyrus Graecus Holmiensis
The Papyrus Graecus Holmiensis (also known as the Stockholm papyrus) is a collection of craft recipes compiled in Egypt . It is written in Greek. The Stockholm papyrus has 154 recipes for dyeing, coloring gemstones, cleaning (purifying) pearls, and ...
, written in the third or fourth century CE, contains notes on how to prepare artificial emerald and beryl.
 Early analyses of emeralds and beryls by
Early analyses of emeralds and beryls by Martin Heinrich Klaproth
Martin Heinrich Klaproth (1 December 1743 – 1 January 1817) was a German chemist. He trained and worked for much of his life as an apothecary, moving in later life to the university. His shop became the second-largest apothecary in Berlin, and ...
, Torbern Olof Bergman, Franz Karl Achard, and always yielded similar elements, leading to the mistaken conclusion that both substances are aluminium silicates. Mineralogist René Just Haüy discovered that both crystals are geometrically identical, and he asked chemist Louis-Nicolas Vauquelin for a chemical analysis.
In a 1798 paper read before the Institut de France, Vauquelin reported that he found a new "earth" by dissolving aluminium hydroxide from emerald and beryl in an additional alkali. The editors of the journal ''Annales de chimie et de physique'' named the new earth "glucine" for the sweet taste of some of its compounds. The name ''beryllium'' was first used by Friedrich Wöhler in 1828. Both beryllium and glucinum were used concurrently until 1949, when the IUPAC adopted beryllium as the standard name of the element.
Friedrich Wöhler and Antoine Bussy independently isolated beryllium in 1828 by the chemical reaction of metallic potassium with beryllium chloride
Beryllium chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula BeCl2. It is a colourless, hygroscopic solid that dissolves well in many polar solvents. Its properties are similar to those of aluminium chloride, due to beryllium's diagonal relations ...
, as follows:
:
Using an alcohol lamp, Wöhler heated alternating layers of beryllium chloride and potassium in a wired-shut platinum crucible. The above reaction immediately took place and caused the crucible to become white hot. Upon cooling and washing the resulting gray-black powder, he saw that it was made of fine particles with a dark metallic luster. The highly reactive potassium had been produced by the electrolysis of its compounds. He did not succeed to melt the beryllium particles.
The direct electrolysis of a molten mixture of beryllium fluoride
Beryllium fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula Be F2. This white solid is the principal precursor for the manufacture of beryllium metal. Its structure resembles that of quartz, but BeF2 is highly soluble in water.
Properties
Ber ...
and sodium fluoride by Paul Lebeau in 1898 resulted in the first pure (99.5 to 99.8%) samples of beryllium. However, industrial production started only after the First World War. The original industrial involvement included subsidiaries and scientists related to the Union Carbide, Union Carbide and Carbon Corporation in Cleveland, Ohio, and Siemens & Halske AG in Berlin. In the US, the process was ruled by Hugh S. Cooper, director of The Kemet Laboratories Company. In Germany, the first commercially successful process for producing beryllium was developed in 1921 by Alfred Stock and Hans Goldschmidt.
A sample of beryllium was bombarded with alpha rays from the decay of radium in a 1932 experiment by James Chadwick that uncovered the existence of the neutron. This same method is used in one class of radioisotope-based laboratory neutron source
A neutron source is any device that emits neutrons, irrespective of the mechanism used to produce the neutrons. Neutron sources are used in physics, engineering, medicine, nuclear weapons, petroleum exploration, biology, chemistry, and nuclear p ...
s that produce 30 neutrons for every million α particles.
Beryllium production saw a rapid increase during World War II due to the rising demand for hard beryllium-copper alloys and phosphors for fluorescent lights. Most early fluorescent lamps used zinc orthosilicate with varying content of beryllium to emit greenish light. Small additions of magnesium tungstate improved the blue part of the spectrum to yield an acceptable white light. Halophosphate-based phosphors replaced beryllium-based phosphors after beryllium was found to be toxic.
Electrolysis of a mixture of beryllium fluoride
Beryllium fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula Be F2. This white solid is the principal precursor for the manufacture of beryllium metal. Its structure resembles that of quartz, but BeF2 is highly soluble in water.
Properties
Ber ...
and sodium fluoride was used to isolate beryllium during the 19th century. The metal's high melting point makes this process more energy-consuming than corresponding processes used for the alkali metals. Early in the 20th century, the production of beryllium by the thermal decomposition of beryllium iodide was investigated following the success of a similar process for the production of zirconium, but this process proved to be uneconomical for volume production.
Pure beryllium metal did not become readily available until 1957, even though it had been used as an alloying metal to harden and toughen copper much earlier. Beryllium could be produced by reducing beryllium compounds such as beryllium chloride
Beryllium chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula BeCl2. It is a colourless, hygroscopic solid that dissolves well in many polar solvents. Its properties are similar to those of aluminium chloride, due to beryllium's diagonal relations ...
with metallic potassium or sodium. Currently, most beryllium is produced by reducing beryllium fluoride with magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
. The price on the American market for Casting (metalworking), vacuum-cast beryllium ingots was about $338 per pound ($745 per kilogram) in 2001.
Between 1998 and 2008, the world's production of beryllium had decreased from 343 to about 200 tonnes. It then increased to 230 metric tons by 2018, of which 170 tonnes came from the United States.
Etymology
Beryllium was named for the semiprecious mineralberyl
Beryl ( ) is a mineral composed of beryllium aluminium Silicate minerals#Cyclosilicates, silicate with the chemical formula Be3Al2(SiO3)6. Well-known varieties of beryl include emerald and Aquamarine (gem), aquamarine. Naturally occurring Hex ...
, from which it was first isolated. Martin Klaproth, having independently determined that beryl and emerald share an element, preferred the name "beryllina" due to the fact that yttria also formed sweet salts.
Although Humphry Davy failed to isolate it, he proposed the name ''glucium'' for the new metal, derived from the name ''glucina'' for the earth it was found in; altered forms of this name, ''glucinium'' or ''glucinum'' (symbol Gl) continued to be used into the 20th century.
Applications
Radiation windows

 Because of its low atomic number and very low absorption for X-rays, the oldest and still one of the most important applications of beryllium is in radiation windows for
Because of its low atomic number and very low absorption for X-rays, the oldest and still one of the most important applications of beryllium is in radiation windows for X-ray tube
An X-ray tube is a vacuum tube that converts electrical input power into X-rays. The availability of this controllable source of X-rays created the field of radiography, the imaging of partly opaque objects with penetrating radiation. In contras ...
s. Extreme demands are placed on purity and cleanliness of beryllium to avoid artifacts in the X-ray images. Thin beryllium foils are used as radiation windows for X-ray detectors, and their extremely low absorption minimizes the heating effects caused by high-intensity, low energy X-rays typical of synchrotron radiation. Vacuum-tight windows and beam-tubes for radiation experiments on synchrotrons are manufactured exclusively from beryllium. In scientific setups for various X-ray emission studies (e.g., energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy) the sample holder is usually made of beryllium because its emitted X-rays have much lower energies (≈100 eV) than X-rays from most studied materials.
Low atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of its atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei composed of protons and neutrons, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of pro ...
also makes beryllium relatively transparent to energetic Elementary particle, particles. Therefore, it is used to build the beamline, beam pipe around the collision region in particle physics setups, such as all four main detector experiments at the Large Hadron Collider (A Large Ion Collider Experiment, ALICE, ATLAS experiment, ATLAS, Compact Muon Solenoid, CMS, LHCb), the Tevatron and at SLAC. The low density of beryllium allows collision products to reach the surrounding detectors without significant interaction, its stiffness allows a powerful vacuum to be produced within the pipe to minimize interaction with gases, its thermal stability allows it to function correctly at temperatures of only a few degrees above absolute zero, and its diamagnetic nature keeps it from interfering with the complex multipole magnet systems used to steer and strong focusing, focus the particle beams.
Mechanical applications
Because of its stiffness, light weight and dimensional stability over a wide temperature range, beryllium metal is used for lightweight structural components in the defense andaerospace
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial, and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and astron ...
industries in high-speed aircraft, guided missiles, spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle that is designed spaceflight, to fly and operate in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth observation, Weather s ...
, and satellites, including the James Webb Space Telescope. Several liquid-fuel rockets have used rocket engine nozzle, rocket nozzles made of pure beryllium. Beryllium powder was itself studied as a rocket fuel, but this use has never materialized. A small number of extreme high-end bicycle frames have been built with beryllium. From 1998 to 2000, the McLaren Formula One team used Mercedes-Benz engines with beryllium-aluminium alloy pistons. The use of beryllium engine components was banned following a protest by Scuderia Ferrari.
Mixing about 2.0% beryllium into copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
forms an alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
called beryllium copper
Beryllium copper (BeCu), also known as copper beryllium (CuBe), beryllium bronze, and spring copper, is a copper alloy with 0.5–3% beryllium. Copper beryllium alloys are often used because of their high strength and good conductivity of both ...
that is six times stronger than copper alone. Beryllium alloys are used in many applications because of their combination of elasticity, high electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to heat conduction, conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa and is measured in W·m−1·K−1.
Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low ...
, high strength and hardness (materials science), hardness, nonmagnetic properties, as well as good corrosion and fatigue (material), fatigue resistance. These applications include non-sparking tools that are used near flammable gases (beryllium nickel), spring (device), springs, membranes (beryllium nickel and beryllium iron) used in surgical instruments, and high temperature devices. As little as 50 parts per million of beryllium alloyed with liquid magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
leads to a significant increase in oxidation resistance and decrease in flammability.
 The high elastic stiffness of beryllium has led to its extensive use in precision instrumentation, e.g. in inertial guidance systems and in the support mechanisms for optical systems. Beryllium-copper alloys were also applied as a hardening agent in "Needlegun scaler, Jason pistols", which were used to strip the paint from the hulls of ships.
In sound amplification systems, the speed at which sound travels directly affects the resonant frequency of the amplifier, thereby influencing the range of audible high-frequency sounds. Beryllium stands out due to its exceptionally high speed of sound propagation compared to other metals. This unique property allows beryllium to achieve higher resonant frequencies, making it an ideal material for use as a Diaphragm (acoustics), diaphragm in high-quality loudspeakers.
Beryllium was used for cantilevers in high-performance phonograph cartridge styli, where its extreme stiffness and low density allowed for tracking weights to be reduced to 1 gram while still tracking high frequency passages with minimal distortion.
An earlier major application of beryllium was in brakes for military airplanes because of its hardness, high melting point, and exceptional ability to heat dissipation, dissipate heat. Environmental considerations have led to substitution by other materials.
A metal matrix composite material combining beryllium with
The high elastic stiffness of beryllium has led to its extensive use in precision instrumentation, e.g. in inertial guidance systems and in the support mechanisms for optical systems. Beryllium-copper alloys were also applied as a hardening agent in "Needlegun scaler, Jason pistols", which were used to strip the paint from the hulls of ships.
In sound amplification systems, the speed at which sound travels directly affects the resonant frequency of the amplifier, thereby influencing the range of audible high-frequency sounds. Beryllium stands out due to its exceptionally high speed of sound propagation compared to other metals. This unique property allows beryllium to achieve higher resonant frequencies, making it an ideal material for use as a Diaphragm (acoustics), diaphragm in high-quality loudspeakers.
Beryllium was used for cantilevers in high-performance phonograph cartridge styli, where its extreme stiffness and low density allowed for tracking weights to be reduced to 1 gram while still tracking high frequency passages with minimal distortion.
An earlier major application of beryllium was in brakes for military airplanes because of its hardness, high melting point, and exceptional ability to heat dissipation, dissipate heat. Environmental considerations have led to substitution by other materials.
A metal matrix composite material combining beryllium with aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
developed under the trade name AlBeMet for the high performance aerospace industry has low weight but four times the stiffness of aluminum alone.
Mirrors
Large-area beryllium mirrors, frequently with a honeycomb mirror, honeycomb support structure, are used, for example, in meteorological satellites where low weight and long-term dimensional stability are critical. Smaller beryllium mirrors are used in optical guidance systems and in fire-control systems, e.g. in the German-made Leopard 1 and Leopard 2 main battle tanks. In these systems, very rapid movement of the mirror is required, which again dictates low mass and high rigidity. Usually the beryllium mirror is coated with hard electroless nickel plating which can be more easily polished to a finer optical finish than beryllium. In some applications, the beryllium blank is polished without any coating. This is particularly applicable to cryogenic operation where thermal expansion mismatch can cause the coating to buckle. The James Webb Space Telescope has 18 hexagonal beryllium sections for its mirrors, each plated with a thin layer of gold. Because JWST will face a temperature of 33 K, the mirror is made of gold-plated beryllium, which is capable of handling extreme cold better than glass. Beryllium contracts and deforms less than glass and remains more uniform in such temperatures. For the same reason, the optics of the Spitzer Space Telescope are entirely built of beryllium metal.Magnetic applications
Nuclear applications
High purity beryllium can be used in nuclear reactors as a moderator, reflector, or as cladding on fuel elements. Thin plates or foils of beryllium are sometimes used in nuclear weapon designs as the very outer layer of the plutonium pits in the primary stages of thermonuclear bombs, placed to surround the fissile material. These layers of beryllium are good "pushers" for the implosion (mechanical process), implosion of the plutonium-239, and they are goodneutron reflector
A neutron reflector is any material that reflects neutrons. This refers to elastic scattering rather than to a specular reflection. The material may be graphite, beryllium, steel, tungsten carbide, gold, or other materials. A neutron reflect ...
s, just as in beryllium-moderated nuclear reactors.
Beryllium is commonly used in some neutron source
A neutron source is any device that emits neutrons, irrespective of the mechanism used to produce the neutrons. Neutron sources are used in physics, engineering, medicine, nuclear weapons, petroleum exploration, biology, chemistry, and nuclear p ...
s in laboratory devices in which relatively few neutrons are needed (rather than having to use a nuclear reactor or a particle accelerator-powered neutron generator). For this purpose, a target of beryllium-9 is bombarded with energetic alpha particles from a radioisotope such as polonium-210, radium-226, plutonium-238, or americium-241. In the nuclear reaction that occurs, a beryllium nucleus is Nuclear transmutation, transmuted into carbon-12, and one free neutron is emitted, traveling in about the same direction as the alpha particle was heading. Such alpha decay-driven beryllium neutron sources, named Modulated neutron initiator, "urchin" neutron initiators, were used in some early atomic bombs. Neutron sources in which beryllium is bombarded with gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from high energy interactions like the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei or astronomical events like solar flares. It consists o ...
s from a gamma decay radioisotope are also used to produce laboratory neutrons.Byrne, J. ''Neutrons, Nuclei, and Matter'', Dover Publications, Mineola, NY, 2011, , pp. 32–33.
 Beryllium is used in fuel fabrication for CANDU reactors. The fuel elements have small appendages that are resistance brazed to the fuel cladding using an induction brazing process with Be as the braze filler material. Bearing pads are brazed in place to prevent contact between the fuel bundle and the pressure tube containing it, and inter-element spacer pads are brazed on to prevent element to element contact.
Beryllium is used at the Joint European Torus nuclear fusion, nuclear-fusion research laboratory, and it will be used in the more advanced ITER to condition the components which face the plasma. Beryllium has been proposed as a Cladding (nuclear fuel), cladding material for nuclear fuel rods, because of its good combination of mechanical, chemical, and nuclear properties. Beryllium fluoride is one of the constituent salts of the eutectic salt mixture FLiBe, which is used as a solvent, moderator and coolant in many hypothetical molten salt reactor designs, including the liquid fluoride thorium reactor (LFTR).
Beryllium is used in fuel fabrication for CANDU reactors. The fuel elements have small appendages that are resistance brazed to the fuel cladding using an induction brazing process with Be as the braze filler material. Bearing pads are brazed in place to prevent contact between the fuel bundle and the pressure tube containing it, and inter-element spacer pads are brazed on to prevent element to element contact.
Beryllium is used at the Joint European Torus nuclear fusion, nuclear-fusion research laboratory, and it will be used in the more advanced ITER to condition the components which face the plasma. Beryllium has been proposed as a Cladding (nuclear fuel), cladding material for nuclear fuel rods, because of its good combination of mechanical, chemical, and nuclear properties. Beryllium fluoride is one of the constituent salts of the eutectic salt mixture FLiBe, which is used as a solvent, moderator and coolant in many hypothetical molten salt reactor designs, including the liquid fluoride thorium reactor (LFTR).
Acoustics
The low weight and high rigidity of beryllium make it useful as a material for high-frequency speaker drivers. Because beryllium is expensive (many times more than titanium), hard to shape due to its brittleness, and toxic if mishandled, beryllium tweeters are limited to high-end home, pro audio, and public address applications. Some high-fidelity products have been fraudulently claimed to be made of the material. Some high-end Magnetic cartridge, phonograph cartridges used beryllium cantilevers to improve tracking by reducing mass.Electronic
Beryllium is a p-type semiconductor, p-type dopant in List of semiconductor materials, III-V compound semiconductors. It is widely used in materials such as gallium arsenide, GaAs, AlGaAs, InGaAs and InAlAs grown by molecular beam epitaxy (MBE). Cross-rolled beryllium sheet is an excellent structural support for printed circuit boards in surface-mount technology. In critical electronic applications, beryllium is both a structural support and heat sink. The application also requires a coefficient ofthermal expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to increase in length, area, or volume, changing its size and density, in response to an increase in temperature (usually excluding phase transitions).
Substances usually contract with decreasing temp ...
that is well matched to the alumina and glass-reinforced plastic, polyimide-glass Substrate (materials science), substrates. The beryllium-beryllium oxide metal matrix composite, composite "E-Materials" have been specially designed for these electronic applications and have the additional advantage that the thermal expansion coefficient can be tailored to match diverse substrate materials.
Beryllium oxide
Beryllium oxide (BeO), also known as beryllia, is an inorganic compound with the formula BeO. This colourless solid is an electrical insulator with a higher thermal conductivity than any other non-metal except diamond, and exceeds that of most met ...
is useful for many applications that require the combined properties of an electrical insulator and an excellent heat conductor, with high strength and hardness and a very high melting point. Beryllium oxide is frequently used as an insulator base plate in power semiconductor device, high-power transistors in radio frequency transmitters for telecommunications. Beryllium oxide is being studied for use in increasing the thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to heat conduction, conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa and is measured in W·m−1·K−1.
Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low ...
of uranium dioxide nuclear fuel pellets. Beryllium compounds were used in fluorescent lighting tubes, but this use was discontinued because of the disease berylliosis
Berylliosis, or chronic beryllium disease (CBD), is a chronic allergic-type lung response and chronic lung disease caused by exposure to beryllium and its compounds, a form of beryllium poisoning. It is distinct from acute beryllium poisoning, wh ...
which developed in the workers who were making the tubes.
Medical applications
Beryllium is a component of several Dental material, dental alloys. Beryllium is used in X-ray windows because it is transparent to X-rays, allowing for clearer and more efficient imaging. In medical imaging equipment, such as CT scanners and mammography machines, beryllium's strength and light weight enhance durability and performance. Beryllium is used in analytical equipment for blood, HIV, and other diseases. Beryllium alloys are used in surgical instruments, optical mirrors, and laser systems for medical treatments.Toxicity and safety
Biological effects
Approximately 35 micrograms of beryllium is found in the average human body, an amount not considered harmful. Beryllium is chemically similar tomagnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
and therefore can displace it from enzymes, which causes them to malfunction. Because Be2+ is a highly charged and small ion, it can easily get into many tissues and cells, where it specifically targets cell nuclei, inhibiting many enzymes, including those used for synthesizing DNA. Its toxicity is exacerbated by the fact that the body has no means to control beryllium levels, and once inside the body, beryllium cannot be removed.
Inhalation
Chronic beryllium disease (CBD), orberylliosis
Berylliosis, or chronic beryllium disease (CBD), is a chronic allergic-type lung response and chronic lung disease caused by exposure to beryllium and its compounds, a form of beryllium poisoning. It is distinct from acute beryllium poisoning, wh ...
, is a pulmonary and systemic circulation, systemic granulomatous disease caused by inhalation of dust or fumes contaminated with beryllium; either large amounts over a short time or small amounts over a long time can lead to this ailment. Symptoms of the disease can take up to five years to develop; about a third of patients with it die and the survivors are left disabled. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) lists beryllium and beryllium compounds as List of IARC Group 1 carcinogens, Category 1 carcinogens.
Occupational exposure
In the US, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has designated a permissible exposure limit (PEL) for beryllium and beryllium compounds of 0.2 μg/m3 as an 8-hour time-weighted average (TWA) and 2.0 μg/m3 as a short-term exposure limit over a sampling period of 15 minutes. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has set a recommended exposure limit (REL) upper-bound threshold of 0.5 μg/m3. The IDLH (immediately dangerous to life and health) value is 4 mg/m3. The toxicity of beryllium is on par with other toxic metalloids/metals, such as arsenic and mercury (element), mercury. Exposure to beryllium in the workplace can lead to a sensitized immune response, and over time development ofberylliosis
Berylliosis, or chronic beryllium disease (CBD), is a chronic allergic-type lung response and chronic lung disease caused by exposure to beryllium and its compounds, a form of beryllium poisoning. It is distinct from acute beryllium poisoning, wh ...
. NIOSH in the United States researches these effects in collaboration with a major manufacturer of beryllium products. NIOSH also conducts genetic research on sensitization and CBD, independently of this collaboration.
Acute beryllium disease in the form of chemical pneumonitis was first reported in Europe in 1933 and in the United States in 1943. A survey found that about 5% of workers in plants manufacturing fluorescent lamps in 1949 in the United States had beryllium-related lung diseases. Chronic berylliosis resembles sarcoidosis in many respects, and the differential diagnosis is often difficult. It killed some early workers in nuclear weapons design, such as Herbert L. Anderson.
Beryllium may be found in coal slag. When the slag is formulated into an abrasive agent for blasting paint and rust from hard surfaces, the beryllium can become airborne and become a source of exposure.Newport News Shipbuilding Workers Face a Hidden ToxinDaily Press (Virginia), Michael Welles Shapiro, 31 August 2013 Although the use of beryllium compounds in fluorescent lighting tubes was discontinued in 1949, potential for exposure to beryllium exists in the nuclear and aerospace industries, in the refining of beryllium metal and the melting of beryllium-containing alloys, in the manufacturing of electronic devices, and in the handling of other beryllium-containing material.
Detection
Early researchers undertook the highly hazardous practice of identifying beryllium and its various compounds from its sweet taste. A modern test for beryllium in air and on surfaces has been developed and published as an international voluntary consensus standard, ASTM D7202. The procedure uses dilute ammonium bifluoride for dissolution and fluorescence detection with beryllium bound to sulfonated hydroxybenzoquinoline, allowing up to 100 times more sensitive detection than the recommended limit for beryllium concentration in the workplace. Fluorescence increases with increasing beryllium concentration. The new procedure has been successfully tested on a variety of surfaces and is effective for the dissolution and detection of refractory beryllium oxide and siliceous beryllium in minute concentrations (ASTM D7458). The NIOSH Manual of Analytical Methods contains methods for measuring occupational exposures to beryllium.Notes
References
Cited sources
* *Further reading
* * Mroz MM, Balkissoon R, and Newman LS. "Beryllium". In: Bingham E, Cohrssen B, Powell C (eds.) ''Patty's Toxicology'', Fifth Edition. New York: John Wiley & Sons 2001, 177–220. * Walsh, KA''Beryllium Chemistry and Processing''
Vidal, EE. et al. Eds. 2009, Materials Park, OH:ASM International.
Beryllium Lymphocyte Proliferation Testing (BeLPT).
DOE Specification 1142–2001. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Energy, 2001.
External links
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
It's Elemental – Beryllium
* MSDS
ESPI Metals
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health – Beryllium Page
National Supplemental Screening Program (Oak Ridge Associated Universities)
Historic Price of Beryllium in USA
{{portal bar, Chemistry Beryllium, Chemical elements Alkaline earth metals Neutron moderators Nuclear materials IARC Group 1 carcinogens Chemical hazards Reducing agents Chemical elements with hexagonal close-packed structure