Bering strait theory on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 It is believed that the peopling of the Americas began when
It is believed that the peopling of the Americas began when
 Historically, researchers believed a single theory explained the peopling of the Americas, focusing on findings from Blackwater Draw New Mexico, where human artifacts dated from the last ice age were found alongside the remains of extinct animals in 1930s This led to the widespread belief in the " Clovis-first model," proposing that the first Americans migrated over the Beringia land bridge from Asia during a time when glacial passages opened. This model linked the first inhabitants to distinctive spear points, known as Clovis points, ranging in age from 13,250 to 12,800 years old.
Numerous claims of earlier human presence began to challenge the Clovis first model beginning in the 1990s, culminating in significant discoveries at Monte Verde, Chile, dating back 14,500 years. At Oregon’s Paisley Caves, fossilized human feces date back 14,300 years. In Texas, at Buttermilk Creek complex, stone tool fragments date back 15,500 years. At Arroyo Seco 2 in Argentina, archaeologists discovered 14,000-year-old butchered animal bones.
Historically, researchers believed a single theory explained the peopling of the Americas, focusing on findings from Blackwater Draw New Mexico, where human artifacts dated from the last ice age were found alongside the remains of extinct animals in 1930s This led to the widespread belief in the " Clovis-first model," proposing that the first Americans migrated over the Beringia land bridge from Asia during a time when glacial passages opened. This model linked the first inhabitants to distinctive spear points, known as Clovis points, ranging in age from 13,250 to 12,800 years old.
Numerous claims of earlier human presence began to challenge the Clovis first model beginning in the 1990s, culminating in significant discoveries at Monte Verde, Chile, dating back 14,500 years. At Oregon’s Paisley Caves, fossilized human feces date back 14,300 years. In Texas, at Buttermilk Creek complex, stone tool fragments date back 15,500 years. At Arroyo Seco 2 in Argentina, archaeologists discovered 14,000-year-old butchered animal bones.
 During the
During the
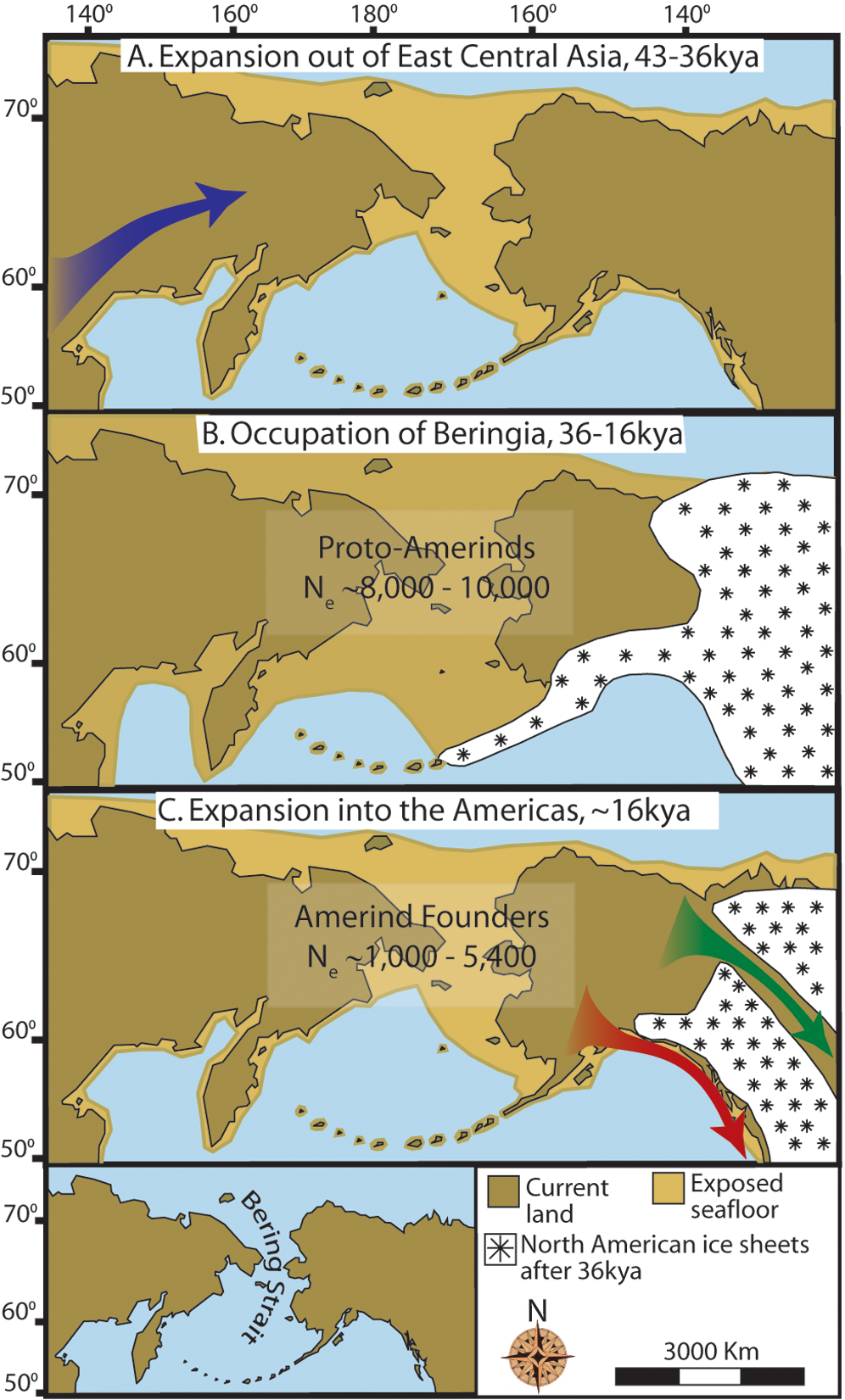
 The onset of the Last Glacial Maximum after 30,000 years BP saw the expansion of alpine glaciers and continental ice sheets that blocked migration routes out of Beringia. By 21,000 years BP, and possibly thousands of years earlier, the Cordilleran and Laurentide ice sheets coalesced east of the
The onset of the Last Glacial Maximum after 30,000 years BP saw the expansion of alpine glaciers and continental ice sheets that blocked migration routes out of Beringia. By 21,000 years BP, and possibly thousands of years earlier, the Cordilleran and Laurentide ice sheets coalesced east of the
 The paleoclimates and vegetation of eastern Siberia and Alaska during the Wisconsin glaciation have been deduced from high resolution oxygen isotope data and
The paleoclimates and vegetation of eastern Siberia and Alaska during the Wisconsin glaciation have been deduced from high resolution oxygen isotope data and
 Pollen data indicate a warm period culminating between 17,000 and 13,000 BP followed by cooling between 13,000 and 11,500 BP. Coastal areas deglaciated rapidly as coastal alpine glaciers, then lobes of Cordilleran ice, retreated. The retreat was accelerated as sea levels rose and floated glacial termini. It has been estimated that the coast range was fully ice-free between 16,000 and 15,000 BP.
Pollen data indicate a warm period culminating between 17,000 and 13,000 BP followed by cooling between 13,000 and 11,500 BP. Coastal areas deglaciated rapidly as coastal alpine glaciers, then lobes of Cordilleran ice, retreated. The retreat was accelerated as sea levels rose and floated glacial termini. It has been estimated that the coast range was fully ice-free between 16,000 and 15,000 BP.
 In the early 21st century, the models of the chronology of migration are divided into two general approaches.
The first is the ''short chronology theory'', that the first migration occurred after the LGM, which went into decline after about 19,000 years ago, and was then followed by successive waves of immigrants.
The second theory is the ''long chronology theory,'' which proposes that the first group of people entered Beringia, including ice-free parts of Alaska, at a much earlier date, possibly 40,000 years ago, followed by a much later second wave of immigrants.
The Clovis First theory, which dominated thinking on New World anthropology for much of the 20th century, was challenged in the 2000s by the secure dating of archaeological sites in the Americas to before 13,000 years ago.
The archaeological sites in the Americas with the oldest dates that have gained broad acceptance are all compatible with an age of about 15,000 years. This includes the Buttermilk Creek Complex in Texas, the
In the early 21st century, the models of the chronology of migration are divided into two general approaches.
The first is the ''short chronology theory'', that the first migration occurred after the LGM, which went into decline after about 19,000 years ago, and was then followed by successive waves of immigrants.
The second theory is the ''long chronology theory,'' which proposes that the first group of people entered Beringia, including ice-free parts of Alaska, at a much earlier date, possibly 40,000 years ago, followed by a much later second wave of immigrants.
The Clovis First theory, which dominated thinking on New World anthropology for much of the 20th century, was challenged in the 2000s by the secure dating of archaeological sites in the Americas to before 13,000 years ago.
The archaeological sites in the Americas with the oldest dates that have gained broad acceptance are all compatible with an age of about 15,000 years. This includes the Buttermilk Creek Complex in Texas, the
 Pre-LGM migration across Beringia has been proposed to explain purported pre-LGM ages of archaeological sites in the Americas such as Bluefish Caves and Old Crow Flats in the
Pre-LGM migration across Beringia has been proposed to explain purported pre-LGM ages of archaeological sites in the Americas such as Bluefish Caves and Old Crow Flats in the
 Genetic studies have used high resolution analytical techniques applied to DNA samples from modern Native Americans and Asian populations regarded as their source populations to reconstruct the development of
Genetic studies have used high resolution analytical techniques applied to DNA samples from modern Native Americans and Asian populations regarded as their source populations to reconstruct the development of
online
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
– The University of Tennessee, Department of Anthropology.
"When Did Humans Come to the Americas?" – ''Smithsonian Magazine'' February 2013
– United States Department of the Interior, National Park Service *Shepard Krech III
Paleoindians and the Great Pleistocene Die-Off
– American Academy of Arts and Sciences, National Humanities Center, 2008. * – by Spencer Wells – PBS and
Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
hunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived Lifestyle, lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, esp ...
s (Paleo-Indians
Paleo-Indians were the first peoples who entered and subsequently inhabited the Americas towards the end of the Late Pleistocene period. The prefix ''paleo-'' comes from . The term ''Paleo-Indians'' applies specifically to the lithic period in ...
) entered North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
from the North Asia
North Asia or Northern Asia () is the northern region of Asia, which is defined in geography, geographical terms and consists of three federal districts of Russia: Ural Federal District, Ural, Siberian Federal District, Siberian, and the Far E ...
n Mammoth steppe
The mammoth steppe, also known as steppe-tundra, was once the Earth's most extensive biome. During glacial periods in the later Pleistocene, it stretched east-to-west, from the Iberian Peninsula in the west of Europe, then across Eurasia and thr ...
via the Beringia land bridge, which had formed between northeastern Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
and western Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
due to the lowering of sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an mean, average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal Body of water, bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical ...
during the Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Last Glacial Coldest Period, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period where ice sheets were at their greatest extent between 26,000 and 20,000 years ago.
Ice sheets covered m ...
(26,000 to 19,000 years ago). These populations expanded south of the Laurentide Ice Sheet and spread rapidly southward, occupying both North and South America no later than 14,000 years ago, and possibly even before 20,000 years ago. The earliest populations in the Americas, before roughly 10,000 years ago, are known as Paleo-Indians
Paleo-Indians were the first peoples who entered and subsequently inhabited the Americas towards the end of the Late Pleistocene period. The prefix ''paleo-'' comes from . The term ''Paleo-Indians'' applies specifically to the lithic period in ...
. Indigenous peoples of the Americas have been linked to Siberian populations by proposed linguistic factors, the distribution of blood types
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is comp ...
, and in genetic composition as reflected by molecular data, such as DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
.
While there is general agreement that the Americas were first settled from Asia, the pattern of migration and the place(s) of origin in Eurasia of the peoples who migrated to the Americas remain unclear. The traditional theory is that Ancient Beringians moved when sea levels were significantly lowered due to the Quaternary glaciation
The Quaternary glaciation, also known as the Pleistocene glaciation, is an alternating series of glacial period, glacial and interglacial, interglacial periods during the Quaternary period that began 2.58 Year#SI prefix multipliers, Ma (million ...
, following herds of now-extinct Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
megafauna
In zoology, megafauna (from Ancient Greek, Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and Neo-Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") are large animals. The precise definition of the term varies widely, though a common threshold is approximately , this lower en ...
along ''ice-free corridors'' that stretched between the Laurentide and Cordilleran ice sheets. Another route proposed is that, either on foot or using boats, they migrated down the Pacific coast to South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
as far as Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
. Any archaeological evidence of coastal occupation during the last Ice Age would now have been covered by the sea level rise
The sea level has been rising from the end of the last ice age, which was around 20,000 years ago. Between 1901 and 2018, the average sea level rose by , with an increase of per year since the 1970s. This was faster than the sea level had e ...
, up to a hundred metres since then.
The precise date for the peopling of the Americas is a long-standing open question. While advances in archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, ...
, Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
geology
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth ...
, physical anthropology, and DNA analysis have progressively shed more light on the subject, significant questions remain unresolved. The Clovis First theory refers to the hypothesis that the Clovis culture
The Clovis culture is an archaeological culture from the Paleoindian period of North America, spanning around 13,050 to 12,750 years Before Present (BP). The type site is Blackwater Draw locality No. 1 near Clovis, New Mexico, where stone too ...
represents the earliest human presence in the Americas about 13,000 years ago. Evidence of pre-Clovis cultures has accumulated and pushed back the possible date of the first peopling of the Americas. Academics generally believe that humans reached North America south of the Laurentide Ice Sheet at some point between 15,000 and 20,000 years ago. Some new controversial archaeological evidence suggests the possibility that human arrival in the Americas may have occurred prior to the Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Last Glacial Coldest Period, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period where ice sheets were at their greatest extent between 26,000 and 20,000 years ago.
Ice sheets covered m ...
more than 20,000 years ago.
Scholarly debate
Meadowcroft Rockshelter
The Meadowcroft Rockshelter is an archaeological site which is located near Avella in Jefferson Township, Pennsylvania. The site is a rock shelter in a bluff overlooking Cross Creek (a tributary of the Ohio River), and contains evidence that the ...
in Pennsylvania may have a history of at least 16,000 years. As research progressed in the 2000s, the narrative shifted from a single migration event to multiple small, diverse groups entering the continent at various points in time. This indicates that people might have populated North and South America as early as 15,000 to 20,000 years ago, which some believe support a coastal migration route.
The genetic history of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas has highlighted populations that adapted over tens of thousands of years. Geneticists discovered that a Beringian population split from Siberian groups about 36,000 years ago. Around 25,000 years ago, they became isolated, forming a new genetic group linked to today’s Indigenous populations, which divided into two main lineages between 14,500 and 17,000 years ago reflecting the dispersal associated with the early peopling of the Americas.
The Chiquihuite Cave in Mexico suggest that ancient stone tools were being utilized as long ago as 30,000 years ago. However, proving these tools were made by humans has faced criticism. In New Mexico, researchers uncovered fossilized footprints, dating back perhaps 23,000 years, showing humans and megafauna
In zoology, megafauna (from Ancient Greek, Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and Neo-Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") are large animals. The precise definition of the term varies widely, though a common threshold is approximately , this lower en ...
like mammoth
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus.'' They lived from the late Miocene epoch (from around 6.2 million years ago) into the Holocene until about 4,000 years ago, with mammoth species at various times inhabi ...
s co-existing, which is also under great debate. In addition, some argue that evidence points towards human presence extending back 130,000 years near San Diego, California at the Cerutti Mastodon site, though this is outright rejected by the vast majority of scholars across multiple academic fields. Scholars such as David J. Meltzer have emphasized the fact that there are no verified archaeological sites in the Americas older than 16,000 years accepted by the academic community at large, which questions claims of sites being 20,000, 25,000, or even 130,000 years old.
Environment during the latest glaciation
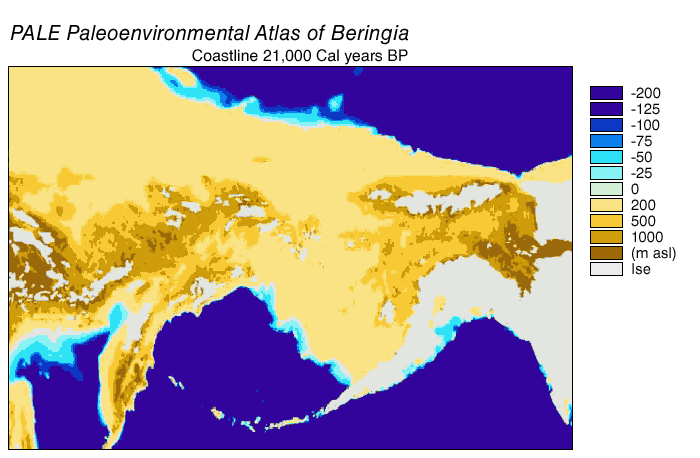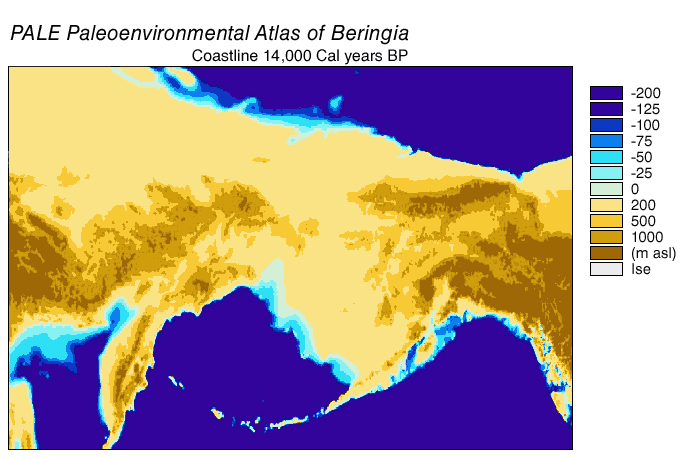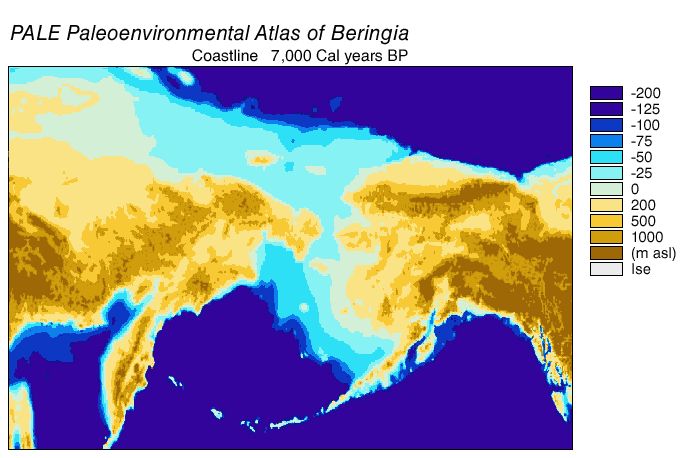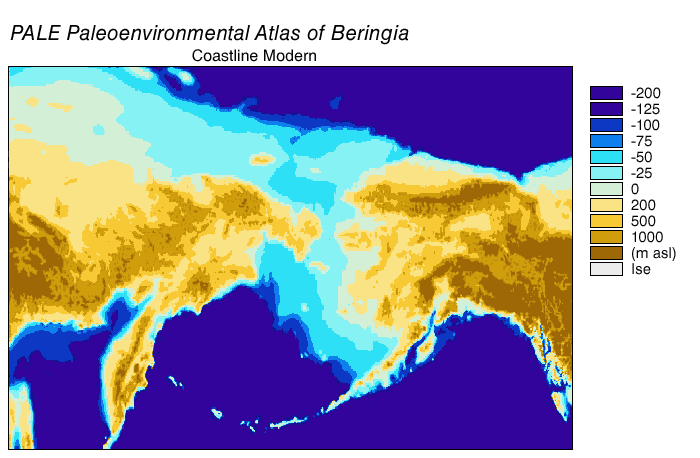
Emergence and submergence of Beringia
 During the
During the Wisconsin glaciation
The Wisconsin glaciation, also called the Wisconsin glacial episode, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex, peaking more than 20,000 years ago. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated ...
, the Earth's ocean water was, to varying degrees over time, stored in glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
ice. As water accumulated in glaciers, the volume of water in the oceans correspondingly decreased, resulting in lowering of global sea level. The variation of sea level over time has been reconstructed using oxygen isotope analysis of deep sea cores, the dating of marine terraces, and high-resolution oxygen isotope sampling from ocean basins and modern ice caps. A drop of eustatic sea level by about from present-day levels, commencing around 30,000 years Before Present
Before Present (BP) or "years before present (YBP)" is a time scale used mainly in archaeology, geology, and other scientific disciplines to specify when events occurred relative to the origin of practical radiocarbon dating in the 1950s. Because ...
(BP), created Beringia
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 70th parallel north, 72° north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south ...
, a durable and extensive geographic feature connecting Siberia with Alaska. With the rise of sea level after the Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Last Glacial Coldest Period, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period where ice sheets were at their greatest extent between 26,000 and 20,000 years ago.
Ice sheets covered m ...
(LGM), the Beringian land bridge was again submerged. Estimates of the final re-submergence of the Beringian land bridge based purely on present bathymetry
Bathymetry (; ) is the study of underwater depth of ocean floors ('' seabed topography''), river floors, or lake floors. In other words, bathymetry is the underwater equivalent to hypsometry or topography. The first recorded evidence of wate ...
of the Bering Strait and eustatic sea level curve place the event around 11,000 years BP (Figure 1). Ongoing research reconstructing Beringian paleogeography during deglaciation could change that estimate and possible earlier submergence could further constrain models of human migration into North America.
Glaciers
 The onset of the Last Glacial Maximum after 30,000 years BP saw the expansion of alpine glaciers and continental ice sheets that blocked migration routes out of Beringia. By 21,000 years BP, and possibly thousands of years earlier, the Cordilleran and Laurentide ice sheets coalesced east of the
The onset of the Last Glacial Maximum after 30,000 years BP saw the expansion of alpine glaciers and continental ice sheets that blocked migration routes out of Beringia. By 21,000 years BP, and possibly thousands of years earlier, the Cordilleran and Laurentide ice sheets coalesced east of the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
, closing off a potential migration route into the center of North America. Alpine glaciers in the coastal ranges and the Alaskan Peninsula isolated the interior of Beringia from the Pacific coast. Coastal alpine glaciers and lobes of Cordilleran ice coalesced into piedmont glaciers that covered large stretches of the coastline as far south as Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are of land. The island is the largest ...
and formed an ice lobe across the Straits of Juan de Fuca by 18,000 BP. Coastal alpine glaciers started to retreat around 19,000 BP while Cordilleran ice continued advancing in the Puget lowlands up to 16,800 BP. Even during the maximum extent of coastal ice, unglaciated refugia persisted on present-day islands, that supported terrestrial and marine mammals. As deglaciation occurred, refugia expanded until the coast became ice-free by 15,000 BP. The retreat of glaciers on the Alaskan Peninsula provided access from Beringia to the Pacific coast by around 17,000 BP. The ice barrier between interior Alaska and the Pacific coast broke up starting around 16,200 BP. The ice-free corridor to the interior of North America opened between 13,000 and 12,000 BP. Glaciation in eastern Siberia during the LGM was limited to alpine and valley glaciers in mountain ranges and did not block access between Siberia and Beringia.
Climate and biological environments
pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm ...
stratigraphy
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers (strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks.
Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithost ...
. Prior to the Last Glacial Maximum, climates in eastern Siberia fluctuated between conditions approximating present day conditions and colder periods. The pre-LGM warm cycles in Arctic Siberia saw flourishes of megafaunas. The oxygen isotope record from the Greenland Ice Cap suggests that these cycles after about 45,000 BP lasted anywhere from hundreds to between one and two thousand years, with greater duration of cold periods starting around 32,000 BP. The pollen record from Elikchan Lake, north of the Sea of Okhotsk
The Sea of Okhotsk; Historically also known as , or as ; ) is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean. It is located between Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands on the southeast, Japan's island of Hokkaido on the sou ...
, shows a marked shift from tree and shrub pollen to herb pollen prior to 30,000 BP, as herb tundra replaced boreal forest and shrub steppe going into the LGM. A similar record of tree/shrub pollen being replaced with herb pollen as the LGM approached was recovered near the Kolyma River in Arctic Siberia. The abandonment of the northern regions of Siberia due to rapid cooling or the retreat of game species with the onset of the LGM has been proposed to explain the lack of archaeological sites in that region dating to the LGM. The pollen record from the Alaskan side shows shifts between herb/shrub and shrub tundra prior to the LGM, suggesting less dramatic warming episodes than those that allowed forest colonization on the Siberian side. Diverse, though not necessarily plentiful, megafauna
In zoology, megafauna (from Ancient Greek, Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and Neo-Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") are large animals. The precise definition of the term varies widely, though a common threshold is approximately , this lower en ...
were present in those environments. Herb tundra dominated during the LGM, due to cold and dry conditions.
Coastal environments during the Last Glacial Maximum were complex. The lowered sea level, and an isostatic bulge equilibrated with the depression beneath the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, exposed the continental shelf to form a coastal plain. While much of the coastal plain was covered with piedmont glaciers, unglaciated refugia supporting terrestrial mammals have been identified on Haida Gwaii
Haida Gwaii (; / , literally "Islands of the Haida people"), previously known as the Queen Charlotte Islands, is an archipelago located between off the British Columbia Coast, northern Pacific coast in the Canadian province of British Columbia ...
, Prince of Wales Island, and outer islands of the Alexander Archipelago
The Alexander Archipelago () is a archipelago (group of islands) in North America lying off the southeastern coast of Alaska. It contains about 1,100 islands, the tops of submerged coastal mountains that rise steeply from the Pacific Ocean. Deep ...
. The now-submerged coastal plain has potential for more refugia. Pollen data indicate mostly herb/shrub tundra vegetation in unglaciated areas, with some boreal forest towards the southern end of the range of Cordilleran ice. The coastal marine environment remained productive, as indicated by fossils of pinniped
Pinnipeds (pronounced ), commonly known as seals, are a widely range (biology), distributed and diverse clade of carnivorous, fin-footed, semiaquatic, mostly marine mammals. They comprise the extant taxon, extant families Odobenidae (whose onl ...
s. The highly productive kelp forest
Kelp forests are underwater areas with a high density of kelp, which covers a large part of the world's coastlines. Smaller areas of anchored kelp are called kelp beds. They are recognized as one of the most productive and dynamic ecosystems on E ...
s over rocky marine shallows may have been a lure for coastal migration. Reconstruction of the southern Beringian coastline also suggests potential for a highly productive coastal marine environment.
Environmental changes during deglaciation
 Pollen data indicate a warm period culminating between 17,000 and 13,000 BP followed by cooling between 13,000 and 11,500 BP. Coastal areas deglaciated rapidly as coastal alpine glaciers, then lobes of Cordilleran ice, retreated. The retreat was accelerated as sea levels rose and floated glacial termini. It has been estimated that the coast range was fully ice-free between 16,000 and 15,000 BP.
Pollen data indicate a warm period culminating between 17,000 and 13,000 BP followed by cooling between 13,000 and 11,500 BP. Coastal areas deglaciated rapidly as coastal alpine glaciers, then lobes of Cordilleran ice, retreated. The retreat was accelerated as sea levels rose and floated glacial termini. It has been estimated that the coast range was fully ice-free between 16,000 and 15,000 BP. Littoral
The littoral zone, also called litoral or nearshore, is the part of a sea, lake, or river that is close to the shore. In coastal ecology, the littoral zone includes the intertidal zone extending from the high water mark (which is rarely i ...
marine organisms colonized shorelines as ocean water replaced glacial meltwater. Replacement of herb/shrub tundra by coniferous forests was underway by 15,000 BP north of Haida Gwaii. Eustatic sea level rise caused flooding, which accelerated as the rate grew more rapid.
The inland Cordilleran and Laurentide ice sheets retreated more slowly than did the coastal glaciers. Opening of an ice-free corridor did not occur until after 13,000 to 12,000 BP. The early environment of the ice-free corridor was dominated by glacial outwash and meltwater, with ice-dammed lakes and periodic flooding from the release of ice-dammed meltwater. Biological productivity of the deglaciated landscape increased slowly. The earliest possible viability of the ice-free corridor as a human migration route has been estimated at 11,500 BP.
Birch forests were advancing across former herb tundra in Beringia by 17,000 BP in response to climatic amelioration, indicating increased productivity of the landscape.
Analyses of biomarkers and microfossils preserved in sediments from Lake E5 and Burial Lake in northern Alaska suggest early humans burned Beringian landscapes as early as 34,000 years ago. The authors of these studies suggest that fire was used as means of hunting megafauna.
Chronology, reasons for, and sources of migration
TheIndigenous peoples of the Americas
In the Americas, Indigenous peoples comprise the two continents' pre-Columbian inhabitants, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with them in the 15th century, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with the pre-Columbian population of ...
have an ascertained archaeological presence in the Americas dating back to about 15,000 years ago. More recent research, however, suggests a human presence dating to between 18,000 and 26,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Maximum.
There remain uncertainties regarding the precise dating of individual sites and regarding conclusions drawn from population genetics
Population genetics is a subfield of genetics that deals with genetic differences within and among populations, and is a part of evolutionary biology. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as Adaptation (biology), adaptation, s ...
studies of contemporary Native Americans.
Chronology
 In the early 21st century, the models of the chronology of migration are divided into two general approaches.
The first is the ''short chronology theory'', that the first migration occurred after the LGM, which went into decline after about 19,000 years ago, and was then followed by successive waves of immigrants.
The second theory is the ''long chronology theory,'' which proposes that the first group of people entered Beringia, including ice-free parts of Alaska, at a much earlier date, possibly 40,000 years ago, followed by a much later second wave of immigrants.
The Clovis First theory, which dominated thinking on New World anthropology for much of the 20th century, was challenged in the 2000s by the secure dating of archaeological sites in the Americas to before 13,000 years ago.
The archaeological sites in the Americas with the oldest dates that have gained broad acceptance are all compatible with an age of about 15,000 years. This includes the Buttermilk Creek Complex in Texas, the
In the early 21st century, the models of the chronology of migration are divided into two general approaches.
The first is the ''short chronology theory'', that the first migration occurred after the LGM, which went into decline after about 19,000 years ago, and was then followed by successive waves of immigrants.
The second theory is the ''long chronology theory,'' which proposes that the first group of people entered Beringia, including ice-free parts of Alaska, at a much earlier date, possibly 40,000 years ago, followed by a much later second wave of immigrants.
The Clovis First theory, which dominated thinking on New World anthropology for much of the 20th century, was challenged in the 2000s by the secure dating of archaeological sites in the Americas to before 13,000 years ago.
The archaeological sites in the Americas with the oldest dates that have gained broad acceptance are all compatible with an age of about 15,000 years. This includes the Buttermilk Creek Complex in Texas, the Meadowcroft Rockshelter
The Meadowcroft Rockshelter is an archaeological site which is located near Avella in Jefferson Township, Pennsylvania. The site is a rock shelter in a bluff overlooking Cross Creek (a tributary of the Ohio River), and contains evidence that the ...
site in Pennsylvania and the Monte Verde site in southern Chile. Archaeological evidence of pre- Clovis people points to the South Carolina Topper Site being 16,000 years old, at a time when the glacial maximum would have theoretically allowed for lower coastlines.
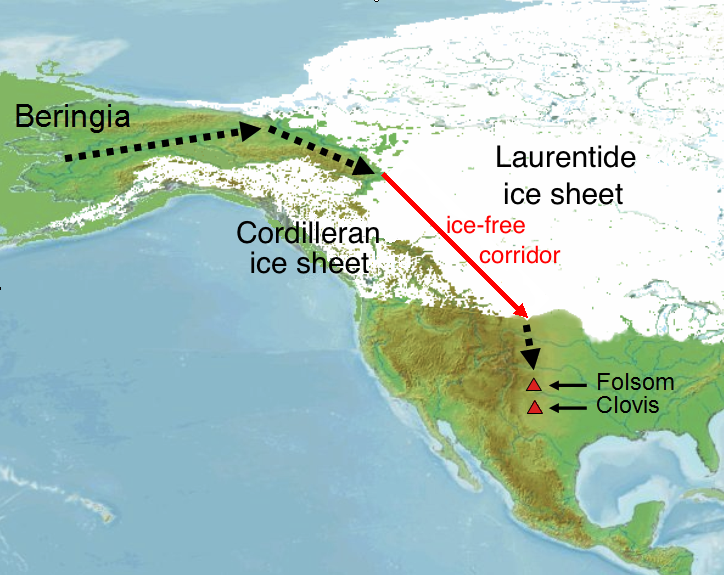
It has often been suggested that an ice-free corridor, in what is now Western Canada
Western Canada, also referred to as the Western provinces, Canadian West, or Western provinces of Canada, and commonly known within Canada as the West, is a list of regions of Canada, Canadian region that includes the four western provinces and t ...
, would have allowed migration before the beginning of the Holocene
The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene to ...
. However, a 2016 study has argued against this, suggesting that the peopling of North America via such a corridor is unlikely to significantly pre-date the earliest Clovis sites. The study concludes that the ice-free corridor in what is now Alberta
Alberta is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Canada. It is a part of Western Canada and is one of the three Canadian Prairies, prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to its west, Saskatchewan to its east, t ...
and British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
"was gradually taken over by a boreal forest dominated by spruce and pine trees" and that the "Clovis people likely came from the south, not the north, perhaps following wild animals such as bison
A bison (: bison) is a large bovine in the genus ''Bison'' (from Greek, meaning 'wild ox') within the tribe Bovini. Two extant taxon, extant and numerous extinction, extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American ...
".
An alternative hypothesis for the peopling of America is coastal migration, which may have been feasible along the deglaciated (but now submerged) coastline of the Pacific Northwest from about 16,000 years ago.
Evidence for pre-LGM human presence
 Pre-LGM migration across Beringia has been proposed to explain purported pre-LGM ages of archaeological sites in the Americas such as Bluefish Caves and Old Crow Flats in the
Pre-LGM migration across Beringia has been proposed to explain purported pre-LGM ages of archaeological sites in the Americas such as Bluefish Caves and Old Crow Flats in the Yukon Territory
Yukon () is a territory of Canada, bordering British Columbia to the south, the Northwest Territories to the east, the Beaufort Sea to the north, and the U.S. state of Alaska to the west. It is Canada’s westernmost territory and the smallest ...
, and Meadowcroft Rock Shelter in Pennsylvania. The oldest archaeological sites on the Alaskan side of Beringia date to around 14,000 BP. It is possible that a small founder population had entered Beringia before that time. However, archaeological sites that date closer to the LGM on either the Siberian or the Alaskan side of Beringia are lacking. Biomarker and microfossil analyses of sediments from Lake E5 and Burial Lake in northern Alaska suggest human presence in eastern Beringia as early as 34,000 years ago. These sedimentary analyses have been suggested to be the only possibly recoverable remnants of humans living in Alaska during the last Glacial period.
At Old Crow Flats, mammoth bones have been found that are broken in distinctive ways indicating human butchery. The radiocarbon dates on these vary between 25,000 and 40,000 BP. Also, stone microflakes have been found in the area indicating tool production. However, the interpretations of butcher marks and the geologic association of bones at the Bluefish Cave and Old Crow Flats sites, and the related Bonnet Plume site, have been called into question. No evidence of human remains have been discovered at these sites. In addition to disputed archaeological sites, support for pre-LGM human presence has been found in lake sediment records of northern Alaska. Biomarker and microfossil analyses of sediments from Lake E5 and Burial Lake in suggest human presence in eastern Beringia as early as 34,000 years ago. These analyses are indeed compelling in that they corroborate the inferences made from the Bluefish Cave and Old Crow Flats sites.
In 2020, evidence emerged for a new pre-LGM site in North-Central Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
. Chiquihuite cave, an archaeological site in Zacatecas
Zacatecas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Zacatecas, is one of the Political divisions of Mexico, 31 states of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Zacatecas, 58 municipalities and its capital city is Zacatecas City, Zacatec ...
State, has been dated to 26,000 years BP based on numerous lithic artefacts discovered there. However, there is scholarly debate over whether the artifacts should be considered evidence of human activity or if they were formed naturally. No evidence of human DNA or hearth
A hearth () is the place in a home where a fire is or was traditionally kept for home heating and for cooking, usually constituted by a horizontal hearthstone and often enclosed to varying degrees by any combination of reredos (a low, partial ...
have been unearthed.
Pre-LGM human presence in South America rests partly on the chronology of the controversial Pedra Furada rock shelter in Piauí
Piauí ( ) is one of the states of Brazil, located in the country's Northeast Region, Brazil, Northeast Region. The state has 1.6% of the Brazilian population and produces 0.7% of the Brazilian GDP.
Piauí has the shortest coastline of any coas ...
, Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
. More recently, studies at the archaeological sites Santa Elina (27000–10000 years BP) in the midwest, and Rincão I (20000–12000 years BP) in southeastern Brazil also show associations of evidence of human presence with sediments dating from before the LGM. A 2003 study dated evidence for the controlled use of fire to before 40,000 years ago. Additional evidence has been adduced from the morphology of Luzia Woman
Luzia Woman () is the name for an Upper Paleolithic period skeleton of a Paleo-Indians, Paleo-Indian woman who was found in a cave in Brazil. The 11,500-year-old skeleton was found in a cave in the Lapa Vermelha archeological site in Pedro Leopol ...
fossil, which was described as Australo-Melanesian
Australo-Melanesians (also known as Australasians or the Australomelanesoid, Australoid or Australioid race) is an outdated historical grouping of various people indigenous to Melanesia and Australia. Controversially, some groups found in parts ...
. This interpretation was challenged in a 2003 review which concluded the features in question could also have arisen by genetic drift. In November 2018, scientists of the University of São Paulo
The Universidade de São Paulo (, USP) is a public research university in the Brazilian state of São Paulo, and the largest public university in Brazil.
The university was founded on 25 January 1934, regrouping already existing schools in ...
and Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ...
released a study that contradicts the alleged Australo-Melanesian origin of Luzia. Using DNA sequencing, the results showed that Luzia's ancestry was entirely Native American.
Stones described as probable tools, hammerstone
In archaeology, a hammerstone is a hard cobble
used to strike off lithic flakes from a lump of tool stone during the process of lithic reduction. The hammerstone is a rather universal stone tool which appeared early in most regions of the wo ...
s and anvil
An anvil is a metalworking tool consisting of a large block of metal (usually Forging, forged or Steel casting, cast steel), with a flattened top surface, upon which another object is struck (or "worked").
Anvils are massive because the hi ...
s, have been found in southern California
Southern California (commonly shortened to SoCal) is a geographic and Cultural area, cultural List of regions of California, region that generally comprises the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. Its densely populated coastal reg ...
, at the Cerutti Mastodon site, that are associated with a mastodon
A mastodon, from Ancient Greek μαστός (''mastós''), meaning "breast", and ὀδούς (''odoús'') "tooth", is a member of the genus ''Mammut'' (German for 'mammoth'), which was endemic to North America and lived from the late Miocene to ...
skeleton which appeared to have been processed by humans. The mastodon skeleton was dated by thorium-230/uranium radiometric analysis, using diffusion–adsorption–decay dating models, to around 130 thousand years ago. No human bones were found and expert reaction was mixed; claims of tools and bone processing were called "not plausible" by Prof. Tom Dillehay.
The Yana River
The Yana ( rus, Я́на, p=ˈjanə; ) is a river in Sakha in Russia, located between the Lena to the west and the Indigirka to the east.
Course
It is long, and its drainage basin covers . Including its longest source river, the Sartang, i ...
Rhino Horn site (RHS) has dated human occupation of eastern Arctic Siberia to 31,300 BP. That date has been interpreted by some as evidence that migration into Beringia was imminent, lending credence to occupation of Beringia during the LGM. However, the Yana RHS date is from the beginning of the cooling period that led into the LGM. A compilation of archaeological site dates throughout eastern Siberia suggest that the cooling period caused a retreat of humans southwards. Pre-LGM lithic evidence in Siberia indicate a settled lifestyle that was based on local resources, while post-LGM lithic evidence indicate a more migratory lifestyle.
A 2021 discovery of human footprints in relict lake sediments near White Sands National Park
White Sands National Park is a national park of the United States located in New Mexico and completely surrounded by the White Sands Missile Range. The park covers in the Tularosa Basin, including the southern 41% of a field of white sand ...
in New Mexico
New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States. It is one of the Mountain States of the southern Rocky Mountains, sharing the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. It also ...
demonstrated there was a verifiable human presence in the region dating back to the LGM between 18,000 and 26,000 years ago. Later studies, reported in October 2023, confirmed that the age of the human footprints to be "up to 23,000 years old".
The Clovis-first advocates have not accepted the veracity of these findings. In 2022, they said, "The oldest evidence for archaeological sites in the New World with large numbers of artifacts occurring in discrete and minimally disturbed stratigraphic contexts occur in eastern Beringia between 13,000 and 14,200 BP. South of the ice sheets, the oldest such sites occur in association with the Clovis complex. If humans managed to breach the continental ice sheets significantly before 13,000 BP, there should be clear evidence for it in the form of at least some stratigraphically discrete archaeological components with a relatively high artifact count. So far, no such evidence exists."
Genomic age estimates
 Genetic studies have used high resolution analytical techniques applied to DNA samples from modern Native Americans and Asian populations regarded as their source populations to reconstruct the development of
Genetic studies have used high resolution analytical techniques applied to DNA samples from modern Native Americans and Asian populations regarded as their source populations to reconstruct the development of human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroups
In human genetics, a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by specific mutations in the non- recombining portions of DNA on the male-specific Y chromosome (Y-DNA). Individuals within a haplogroup share similar numbers of s ...
(yDNA haplogroup
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the , ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and ) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a sing ...
s) and human mitochondrial DNA haplogroups
In human genetics, a human mitochondrial DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by differences in Human mitochondrial genetics, human mitochondrial DNA. Haplogroups are used to represent the major branch points on the mitochondrial phylogenetic ...
(mtDNA haplogroups) characteristic of Native American populations. Models of molecular evolution rates were used to estimate the ages at which Native American DNA lineages branched off from their parent lineages in Asia and to deduce the ages of demographic events. One model (Tammetal 2007) based on Native American mtDNA Haplotypes (Figure 2) proposes that migration into Beringia occurred between 30,000 and 25,000 BP, with migration into the Americas occurring around 10,000 to 15,000 years after isolation of the small founding population. Another model (Kitchen et al. 2008) proposes that migration into Beringia occurred approximately 36,000 BP, followed by 20,000 years of isolation in Beringia. A third model (Nomatto et al. 2009) proposes that migration into Beringia occurred between 40,000 and 30,000 BP, with a pre-LGM migration into the Americas followed by isolation of the northern population following closure of the ice-free corridor. Evidence of Australo-Melanesians admixture in Amazonian populations was published in 2016.
A study of the diversification of mtDNA Haplogroups C and D from southern Siberia and eastern Asia, respectively, suggests that the parent lineage (Subhaplogroup D4h) of Subhaplogroup D4h3, a lineage found among Native Americans and Han Chinese, emerged around 20,000 BP, constraining the emergence of D4h3 to post-LGM. Age estimates based on Y-chromosome micro-satellite diversity place origin of the American Haplogroup Q1a3a (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup Q-M3 (Y-DNA) is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. Haplogroup Q-M3 is a subclade of Haplogroup Q-L54. Haplogroup Q-M3 was previously known as Haplogroup Q3; currently Q-M3 is Q1b1a1a below Q1b-M346.
In 1996 the research group at Stanf ...
at around 15,000 to 10,000 BP. Greater consistency of DNA molecular evolution rate models with each other and with archaeological data may be gained by the use of dated fossil DNA to calibrate molecular evolution rates.
Megafaunal migrations
Although there is no archaeological evidence that can be used to direct support a coastal migration route during theLast Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Last Glacial Coldest Period, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period where ice sheets were at their greatest extent between 26,000 and 20,000 years ago.
Ice sheets covered m ...
, genetic analysis has been used to support this thesis. In addition to human genetic lineage, megafauna
In zoology, megafauna (from Ancient Greek, Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and Neo-Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") are large animals. The precise definition of the term varies widely, though a common threshold is approximately , this lower en ...
l DNA lineage can be used to trace movements of megafauna – large mammalian – as well as the early human groups who hunted them.
Bison
A bison (: bison) is a large bovine in the genus ''Bison'' (from Greek, meaning 'wild ox') within the tribe Bovini. Two extant taxon, extant and numerous extinction, extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American ...
, a type of megafauna, have been identified as an ideal candidate for the tracing of human migrations out of Europe because of both their abundance in North America as well as being one of the first megafauna for which ancient DNA was used to trace patterns of population movement. Unlike other types of fauna that moved between the Americas and Eurasia (mammoth
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus.'' They lived from the late Miocene epoch (from around 6.2 million years ago) into the Holocene until about 4,000 years ago, with mammoth species at various times inhabi ...
s, horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 mi ...
s, and lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'', native to Sub-Saharan Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body (biology), body; a short, rounded head; round ears; and a dark, hairy tuft at the ...
s), Bison survived the North American extinction event that occurred at the end of the Pleistocene. Their genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
, however, contains evidence of a bottleneck – something that can be used to test hypothesis on migrations between the two continents. Early human groups were largely nomad
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
ic, relying on following food sources for survival. Mobility was part of what made humans successful. As nomadic groups, early humans likely followed the food from Eurasia to the Americas – part of the reason why tracing megafaunal DNA is so helpful for garnering insight to these migratory patterns.
The grey wolf
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the grey wolf or gray wolf, is a canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, including the dog and dingo, though gr ...
originated in the Americas and migrated into Eurasia
Eurasia ( , ) is a continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. According to some geographers, Physical geography, physiographically, Eurasia is a single supercontinent. The concept of Europe and Asia as distinct continents d ...
prior to the Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Last Glacial Coldest Period, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period where ice sheets were at their greatest extent between 26,000 and 20,000 years ago.
Ice sheets covered m ...
– during which it was believed that remaining populations of the grey wolf residing in North America faced extinction and were isolated from the rest of the population. This, however, may not be the case. Radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for Chronological dating, determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of carbon-14, radiocarbon, a radioactive Isotop ...
of ancient grey wolf remains found in permafrost
Permafrost () is soil or underwater sediment which continuously remains below for two years or more; the oldest permafrost has been continuously frozen for around 700,000 years. Whilst the shallowest permafrost has a vertical extent of below ...
deposits in Alaska show a continuous exchange of population from 12,500 radiocarbon years BP to beyond radiocarbon dating capabilities. This indicates that there was viable passage for grey wolf populations to exchange between the two continents.
These faunas' ability to exchange populations during the period of the Last Glacial Maximum along with genetic evidence found from early human remains in the Americas provides evidence to support pre-Clovis migrations into the Americas.
Source populations
The Native American source population was formed in Siberia by the mixing of two distinct populations: Ancient North Eurasians and an ancient East Asian (ESEA) population. According to Jennifer Raff, the Ancient North Eurasian population mixed with a daughter population of ancient East Asians, who they encountered around 25,000 years ago, which led to the emergence of Native American ancestral populations. However, the exact location where the admixture took place is unknown, and the migratory movements that united the two populations are a matter of debate. "Current estimates suggest that approximately 63% of the First Peoples' ancestry comes from the East Asian group and the rest from the Ancient North Siberians. We're not sure where this interaction took place. Some archaeologists believe that it occurred in East Asia, suggesting that this is where the Siberians moved during the LGM" .."There's also a case to be made for this interaction having taken place bear the Lake Baikal region in Siberia from genetic evidence, too" .."But other archaeologists and geneticists argue that the meeting of the two grandparent populations of Native Americans occurred because people moved north, not south, in response to the LGM" One theory supposes that Ancient North Eurasians migrated south toEast Asia
East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Ja ...
, or Southern Siberia, where they would have encountered and mixed with ancient East Asians. Genetic evidence from Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal is a rift lake and the deepest lake in the world. It is situated in southern Siberia, Russia between the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast, Irkutsk Oblasts of Russia, Oblast to the northwest and the Repu ...
in Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
supports this area as the location where the admixture took place.
However, a third theory, the "Beringian standstill hypothesis", suggests that East Asians instead migrated north to Northeastern Siberia, where they mixed with ANE, and later diverged in Beringia, where distinct Native American lineages formed. This theory is supported by maternal and nuclear DNA
Nuclear DNA (nDNA), or nuclear deoxyribonucleic acid, is the DNA contained within each cell nucleus of a eukaryotic organism. It encodes for the majority of the genome in eukaryotes, with mitochondrial DNA and plastid DNA coding for the rest. ...
evidence. According to Grebenyuk, after 20,000 BP, a branch of Ancient East Asians migrated to Northeastern Siberia, and mixed with descendants of the ANE, leading to the emergence of Ancient Paleo-Siberian and Native American populations in Extreme Northeastern Asia.
However, the Beringian standstill hypothesis is not supported by paternal DNA evidence, which may reflect different population histories for paternal and maternal lineages in Native Americans, which is not uncommon and has been observed in other populations.
A 2019 study suggested that Native Americans are the closest living relatives to 10,000-year-old fossils found near the Kolyma River
The Kolyma (, ; ) is a river in northeastern Siberia, whose basin covers parts of the Sakha Republic, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, and Magadan Oblast of Russia.
The Kolyma is frozen to depths of several metres for about 250 days each year, b ...
in northeastern Siberia.
A study published in July 2022 suggested that people in southern China may have contributed to the Native American gene pool, based on the discovery and DNA analysis of 14,000-year-old human fossils.
The contrast between the genetic profiles of the Hokkaido Jōmon skeletons and the modern Ainu illustrates another uncertainty in source models derived from modern DNA samples.
Mitochondrial (mtDNA) lineages
The development of high-resolution genomic analysis has provided opportunities to further define Native American subclades and narrow the range of Asian subclades that may be parent or sister subclades. The common occurrence of the mtDNA Haplogroups A, B, C, and D among eastern Asian and Native American populations has long been recognized, along with the presence of haplogroup X. As a whole, the greatest frequency of the four Native American associated haplogroups occurs in the Altai- Baikal region of southern Siberia. Some subclades of C and D closer to the Native American subclades occur among Mongolian, Amur, Japanese, Korean, and Ainu populations. With further definition of subclades related to Native American populations, the requirements for sampling Asian populations to find the most closely related subclades grow more specific. Subhaplogroups D1 and D4h3 have been regarded as Native American specific based on their absence among a large sampling of populations regarded as potential descendants of source populations, over a wide area of Asia. Among the 3,764 samples, theSakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, p=səxɐˈlʲin) is an island in Northeast Asia. Its north coast lies off the southeastern coast of Khabarovsk Krai in Russia, while its southern tip lies north of the Japanese island of Hokkaido. An islan ...
–lower Amur
The Amur River () or Heilong River ( zh, s=黑龙江) is a perennial river in Northeast Asia, forming the natural border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China (historically the Outer Manchuria, Outer and Inner Manchuria). The Amur ...
region was represented by 61 Oroks. In another study, Subhaplogroup D1a has been identified among the Ulchis of the lower Amur River region (4 among 87 sampled, or 4.6%), along with Subhaplogroup C1a (1 among 87, or 1.1%). Subhaplogroup C1a is regarded as a close sister clade of the Native American Subhaplogroup C1b.
Subhaplogroup D1a has also been found among ancient Jōmon skeletons from Hokkaido
is the list of islands of Japan by area, second-largest island of Japan and comprises the largest and northernmost prefectures of Japan, prefecture, making up its own list of regions of Japan, region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō fr ...
The modern Ainu are regarded as descendants of the Jōmon. The occurrence of the Subhaplogroups D1a and C1a in the lower Amur region suggests a source population from that region distinct from the Altai-Baikal source populations, where sampling did not reveal those two particular subclades. The conclusions regarding Subhaplogroup D1 indicating potential source populations in the lower Amur and Hokkaido areas stand in contrast to the single-source migration model.
Subhaplogroup D4h3 has been identified among Han Chinese
The Han Chinese, alternatively the Han people, are an East Asian people, East Asian ethnic group native to Greater China. With a global population of over 1.4 billion, the Han Chinese are the list of contemporary ethnic groups, world's la ...
. Subhaplogroup D4h3 from China does not have the same geographic implication as Subhaplotype D1a from Amur-Hokkaido, so its implications for source models are more speculative. Its parent lineage, Subhaplotype D4h, is believed to have emerged in East Asia, rather than Siberia, around 20,000 BP. Subhaplogroup D4h2, a sister clade of D4h3, has also been found among Jōmon skeletons from Hokkaido. D4h3 has a coastal trace in the Americas.
X is one of the five mtDNA haplogroups found in Indigenous Americans. Native Americans mostly belong to the X2a clade, which has never been found in the Old World
The "Old World" () is a term for Afro-Eurasia coined by Europeans after 1493, when they became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia in the Eastern Hemisphere, previously ...
. According to Jennifer Raff, X2a probably originated in the same Siberian population as the other four founding maternal lineages, and that there is no compelling reason to believe it is related to X lineages found in Europe or West Eurasia. The Kennewick man
Kennewick Man or Ancient One was a Native American man who lived during the early Holocene, whose skeletal remains were found in 1996 washed out on a bank of the Columbia River near Kennewick, Washington. Radiocarbon tests show the man lived a ...
fossil was found to carry the deepest branch of the X2a haplogroup, and he did not have any European ancestry that would be expected for a European origin of the lineage.
HTLV-1 genomics
The Human T cell Lymphotrophic Virus 1 ( HTLV-1) is a virus transmitted through exchange of bodily fluids and from mother to child through breast milk. The mother-to-child transmission mimics a hereditary trait, although such transmission from maternal carriers is less than 100%. The HTLV virus genome has been mapped, allowing identification of four major strains and analysis of their antiquity through mutations. The highest geographic concentrations of the strain HLTV-1 are in sub-Saharan Africa and Japan. In Japan, it occurs in its highest concentration onKyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's Japanese archipelago, four main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands (i.e. excluding Okinawa Island, Okinawa and the other Ryukyu Islands, Ryukyu (''Nansei'') Ryukyu Islands, Islands ...
. It is also present among African descendants and native populations in the Caribbean region and South America. It is rare in Central America and North America. Its distribution in the Americas has been regarded as due to importation with the slave trade.
The Ainu have developed antibodies to HTLV-1, indicating its endemicity to the Ainu and its antiquity in Japan. A subtype "A" has been defined and identified among the Japanese (including Ainu), and among Caribbean and South American isolates. A subtype "B" has been identified in Japan and India. In 1995, Native Americans in coastal British Columbia were found to have both subtypes A and B. Bone marrow specimens from an Andean mummy about 1500 years old were reported to have shown the presence of the A subtype. The finding ignited controversy, with contention that the sample DNA was insufficiently complete for the conclusion and that the result reflected modern contamination. However, a re-analysis indicated that the DNA sequences were consistent with, but not definitely from, the "cosmopolitan clade" (subtype A). The presence of subtypes A and B in the Americas is suggestive of a Native American source population related to the Ainu ancestors, the Jōmon.
Physical anthropology
Paleo-Indian skeletons in the Americas such asKennewick Man
Kennewick Man or Ancient One was a Native American man who lived during the early Holocene, whose skeletal remains were found in 1996 washed out on a bank of the Columbia River near Kennewick, Washington. Radiocarbon tests show the man lived a ...
(Washington State), Hoya Negro skeleton (Yucatán), Luzia Woman
Luzia Woman () is the name for an Upper Paleolithic period skeleton of a Paleo-Indians, Paleo-Indian woman who was found in a cave in Brazil. The 11,500-year-old skeleton was found in a cave in the Lapa Vermelha archeological site in Pedro Leopol ...
and other skulls from the Lagoa Santa site (Brazil), Buhl Woman (Idaho), Peñon Woman III, two skulls from the Tlapacoya site (Mexico City), and 33 skulls from Baja California have exhibited certain craniofacial traits distinct from most modern Native Americans, leading physical anthropologists to posit an earlier "Paleoamerican" population wave. The most basic measured distinguishing trait is the dolichocephaly of the skull. Some modern isolated populations such as the Pericúes of Baja California and the Fuegians of Tierra del Fuego exhibit that same morphological trait.
Other anthropologists advocate an alternative hypothesis that evolution of an original Beringian phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (physical form and structure), its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological propert ...
gave rise to a distinct morphology that was similar in all known Paleoamerican skulls, followed by later convergence towards the modern Native American phenotype.
Archaeogenetic studies do not support a two-wave model or the Paleoamerican hypothesis of an Australo-Melanesian origin, and firmly assign all Paleo-Indians and modern Native Americans to one ancient population that entered the Americas in a single migration from Beringia. Only in one ancient specimen (Lagoa Santa) and a few modern populations in the Amazon region, a small Australasian ancestry component of c. 3% was detected, which remains unexplained by the current state of research (), but may be explained by the presence of the more basal Tianyuan-related ancestry, a deep East Asian lineage which did not directly contribute to modern East Asians but may have contributed to the ancestors of Native Americans in Siberia, as such ancestry is also found among previous Paleolithic Siberians ( Ancient North Eurasians). " Raghavan et al. 1used outgroup f3-statistics to show that Mal'ta1 was most closely related to present-day Native Americans. This pattern led to a model in which the dispersal of humans to the Americas originated in a population in Siberia derived from a mixture of two distinct ancestries, one associated with East Asians today and another associated with Mal'ta1. Recent studies of DNA from ancient Siberians 9,73provided direct evidence of admixed populations in Siberia that are closely related to the Native American lineage."
A report published in the ''American Journal of Physical Anthropology
The ''American Journal of Biological Anthropology''Info pages about the renaming are: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/page/journal/26927691/homepage/productinformation.html and https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/26927691 (previously known as ...
'' in January 2015 reviewed craniofacial variation focusing on differences between early and late Native Americans and explanations for these based on either skull morphology or molecular genetics. Arguments based on molecular genetics have in the main, according to the authors, accepted a single migration from Asia with a probable pause in Beringia, plus later bi-directional gene flow. Some studies focusing on craniofacial morphology have previously argued that Paleoamerican remains have been described as closer to Australo-Melanesians and Polynesians than to the modern series of Native Americans, suggesting two entries into the Americas, an early one occurring before a distinctive East Asian morphology developed (referred to in the paper as the "Two Components Model"). Another "third model", the "Recurrent Gene Flow" (RGF) model, attempts to reconcile the two, arguing that circumarctic gene flow after the initial migration could account for morphological changes. It specifically re-evaluates the original report on the Hoya Negro skeleton which supported the RGF model, the authors disagreed with the original conclusion which suggested that the skull shape did not match those of modern Native Americans, arguing that the "skull falls into a subregion of the morphospace occupied by both Paleoamericans and some modern Native Americans."
Stemmed points
Stemmed points are a lithic technology distinct from Beringian and Clovis types. They have a distribution ranging from coastal East Asia to the Pacific coast of South America. The emergence of stemmed points has been traced to Korea during the upper Paleolithic. The origin and distribution of stemmed points have been interpreted as a cultural marker related to a source population from coastal East Asia.Migration routes
Interior route

Clovis-First theory
Historically, theories about migration into the Americas have revolved around migration from Beringia through the interior of North America. The discovery of artifacts in association with Pleistocene faunal remains near Clovis, New Mexico in the early 1930s required extension of the timeframe for the settlement of North America to the period during which glaciers were still extensive. That led to the hypothesis of a migration route between the Laurentide and Cordilleran ice sheets to explain the early settlement. The Clovis site was host to a lithic technology characterized by spear points with an indentation, or flute, where the point was attached to the shaft. A lithic complex characterized by the '' Clovis Point'' technology was subsequently identified over much of North America and in South America. The association of Clovis complex technology with late Pleistocene faunal remains led to the theory that it marked the arrival of big game hunters that migrated out of Beringia and then dispersed throughout the Americas, otherwise known as the Clovis First theory. Recent radiocarbon dating of Clovis sites has yielded ages of between 13,000 and 12,600 BP, somewhat later than dates derived from older techniques. The re-evaluation of earlier radiocarbon dates led to the conclusion that no fewer than 11 of the 22 Clovis sites with radiocarbon dates are "problematic" and should be disregarded, including thetype site
In archaeology, a type site (American English) or type-site (British English) is the site used to define a particular archaeological culture or other typological unit, which is often named after it. For example, discoveries at La Tène and H ...
in Clovis, New Mexico. Numerical dating of Clovis sites has allowed comparison of Clovis dates with dates of other archaeological sites throughout the Americas, and of the opening of the ice-free corridor. Both lead to significant challenges to the Clovis First theory. The Monte Verde site of Southern Chile has been dated at 14,800 BP. The Paisley Cave site in eastern Oregon yielded a 14,500 BP, on a coprolite with human DNA and radiocarbon dates of 13,200 and 12,900 BP on horizons containing western stemmed points. Artifact horizons with non-Clovis lithic assemblages and pre-Clovis ages occur in eastern North America, although the maximum ages tend to be poorly constrained.
Recent studies have suggested that the ice-free corridor opened later (around 13,800 ± 500 years ago) than the earliest widely accepted archaeological sites in the Americas, suggesting that it could not have been used as the route for the earliest peoples to migrate south.
An alternative to the Beringia route is proposed by the "stepping stones" hypothesis. The frequent submergence of islands along the Bering Transitory Archipelago would have forced the inhabitants of these island to continue traveling across the archipelago until they reached the mainland.
Lithic evidence of pre-Clovis migrations
Geological findings on the timing of the ice-free corridor also challenge the notion that Clovis and pre-Clovis human occupation of the Americas was a result of migration through that route following the Last Glacial Maximum. Pre-LGM closing of the corridor may approach 30,000 BP and estimates of ice retreat from the corridor are in the range of 13,000 to 12,000 years ago. Viability of the corridor as a human migration route has been estimated at 11,500 BP, later than the ages of the Clovis and pre-Clovis sites. Dated Clovis archaeological sites suggest a south-to-north spread of the Clovis culture. Pre-LGM migration into the interior has been proposed to explain pre-Clovis ages for archaeological sites in the Americas, although pre-Clovis sites such as Meadowcroft Rock Shelter, Monte Verde, and Paisley Cave have not yielded confirmed pre-LGM ages. There are many pre-Clovis sites in the American Southwest, particularly in theMojave Desert
The Mojave Desert (; ; ) is a desert in the rain shadow of the southern Sierra Nevada mountains and Transverse Ranges in the Southwestern United States. Named for the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous Mohave people, it is located pr ...
. Lake Mojave quarries dating back to the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
hold lithic remains of Silver Lake projectile points and Lake Mojave projectile points. This indicates an interior movement into the region as early as 13,800 BP, if not earlier.
Dené–Yeniseian language family proposal
A relationship between the Na-Dené languages of North America (such as Navajo and Apache), and the Yeniseian languages of Siberia was first proposed as early as 1923, and developed further by others. A detailed study was done byEdward Vajda
Edward J. Vajda (Camp Lejeune, North Carolina, September 10, 1958 as Edward M. Johnson; changed his name in 1981) is a historical linguist at Western Washington University, Washington.
He is known for his work on the proposed Dené–Yeniseia ...
and published in 2010. This theory received support from many linguists, with archaeological and genetic studies providing it with further support.
The Arctic Small Tool tradition of Alaska and the Canadian Arctic may have originated in East Siberia about 5,000 years ago. This is connected with the ancient Paleo-Eskimo peoples of the Arctic.
The Arctic Small Tool tradition source may have been the Syalakh-Bel'kachi- Ymyakhtakh culture sequence of East Siberia, dated to 6,500–2,800 BP.
The interior route is consistent with the spread of the Na-Dene language group and subhaplogroup X2a into the Americas after the earliest paleoamerican migration.
Nevertheless, some scholars suggest that the ancestors of western North Americans speaking Na-Dene languages made a coastal migration by boat.
Earlier interior route
It is possible that humans arrived in the Americas by way of interior routes that existed prior to the Last Glacial Maximum. Cosmogenic exposure dating, a technique that analyzes when in Earth's history a landscape was exposed to cosmic rays (and therefore unglaciated), performed by Mark Swisher suggests that an older ice-free corridor existed in North America 25,000 years ago. Swisher attributes sites such as Monte Verde,Meadowcroft Rockshelter
The Meadowcroft Rockshelter is an archaeological site which is located near Avella in Jefferson Township, Pennsylvania. The site is a rock shelter in a bluff overlooking Cross Creek (a tributary of the Ohio River), and contains evidence that the ...
, Manis Mastodon site and Paisley Caves to this corridor.
Pacific coastal route
The Pacific ''coastal migration theory'' proposes that people first reached the Americas via water travel, following coastlines from northeast Asia into the Americas, originally proposed in 1979 by Knute Fladmark as an alternative to the hypothetical migration through an ice-free inland corridor. This model would help to explain the rapid spread to coastal sites extremely distant from the Bering Strait region, including sites such as Monte Verde in southern Chile and Taima-Taima in westernVenezuela
Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It com ...
.
The very similar ''marine migration hypothesis'' is a variant of coastal migration; essentially its only difference is that it postulates that boats were the principal means of travel. The proposed use of boats adds a measure of flexibility to the chronology of coastal migration, because a continuous ice-free coast (16–15,000 calibrated years BP) would then not be required: Migrants in boats
could have easily bypassed ice barriers and settled in scattered coastal refugia, before the deglaciation of the coastal land route was complete. A maritime-competent source population in coastal East Asia is an essential part of the marine migration hypothesis.
A 2007 article in the ''Journal of Island and Coastal Archaeology'' proposed a "kelp highway hypothesis", a variant of coastal migration based on the exploitation of kelp
Kelps are large brown algae or seaweeds that make up the order (biology), order Laminariales. There are about 30 different genus, genera. Despite its appearance and use of photosynthesis in chloroplasts, kelp is technically not a plant but a str ...
forests along much of the Pacific Rim from Japan to Beringia, the Pacific Northwest, and California, and as far as the Andean Coast of South America. Once the coastlines of Alaska and British Columbia had deglaciated about 16,000 years ago, these kelp forest (along with estuarine, mangrove, and coral reef) habitats would have provided an ecologically homogenous migration corridor, entirely at sea level, and essentially unobstructed.
A 2016 DNA analysis of plants and animals suggest a coastal route was feasible.
Mitochondrial subhaplogroup D4h3a, a rare subclade of D4h3 occurring along the west coast of the Americas, has been identified as a clade associated with coastal migration.
This haplogroup was found in a skeleton referred to as Anzick-1, found in Montana in close association with several Clovis artifacts, dated 12,500 years ago.
Problems with evaluating coastal migration models
The coastal migration models provide a different perspective on migration to the New World, but they are not without their own problems: One such problem is that global sea levels have risen over since the end of the last glacial period, and this has submerged the ancient coastlines that maritime people would have followed into the Americas. Finding sites associated with early coastal migrations is extremely difficult—and systematic excavation of any sites found in deeper waters is challenging and expensive. Strategies for finding earliest migration sites include identifying potential sites on submerged paleoshorelines, seeking sites in areas uplifted either by tectonics or isostatic rebound, and looking for riverine sites in areas that may have attracted coastal migrants. On the other hand, there is evidence of marine technologies found in the hills of theChannel Islands of California
The Channel Islands () are an eight-island archipelago located within the Southern California Bight in the Pacific Ocean, off the coast of California. They define the Santa Barbara Channel between the islands and the California mainland. The ...
, circa 12,000 BP. If there was an early pre-Clovis coastal migration, there is always the possibility of a "failed colonization".
See also
*Early human migrations
Early human migrations are the earliest migrations and expansions of archaic and modern humans across continents. They are believed to have begun approximately 2 million years ago with the early expansions out of Africa by ''Homo erectu ...
* Genetic history of Indigenous peoples of the Americas
* List of first human settlements
* Population history of Indigenous peoples of the Americas
Population figures for the Indigenous peoples of the Americas before European colonization have been difficult to establish. Estimates have varied widely from as low as 8 million to as many as 100 million, though by the end of the 20th Century, ...
* Pre-Columbian transoceanic contact theories
References
Further reading
* Becerra-Valdivia, Lorena, and Thomas Higham. (2020) "The timing and effect of the earliest human arrivals in North America." ''Nature'' 584.7819 (2020): 93-97online
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
External links
– The University of Tennessee, Department of Anthropology.
"When Did Humans Come to the Americas?" – ''Smithsonian Magazine'' February 2013
– United States Department of the Interior, National Park Service *Shepard Krech III
Paleoindians and the Great Pleistocene Die-Off
– American Academy of Arts and Sciences, National Humanities Center, 2008. * – by Spencer Wells – PBS and
National Geographic Channel
National Geographic (formerly National Geographic Channel; abbreviated and trademarked as Nat Geo or Nat Geo TV) is an American pay television network and flagship channel owned by the National Geographic Global Networks unit of Disney Enter ...
, 2003 – 120 Minutes, UPC/EAN: 841887001267
{{DEFAULTSORT:Settlement Of The Americas
Paleo-Indian period
History of Indigenous peoples of the Americas
Last Glacial Maximum
Historical controversies