Bereket (other) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bereket, before 1999 Gazanjyk or ''Kazandzhik'' ( or gɑˈzɑnd͡ʒik), is a

 The city has a small public transportation network. Several small buses run scheduled routes connecting the eastern and western parts of the city (some 5–6 km.)
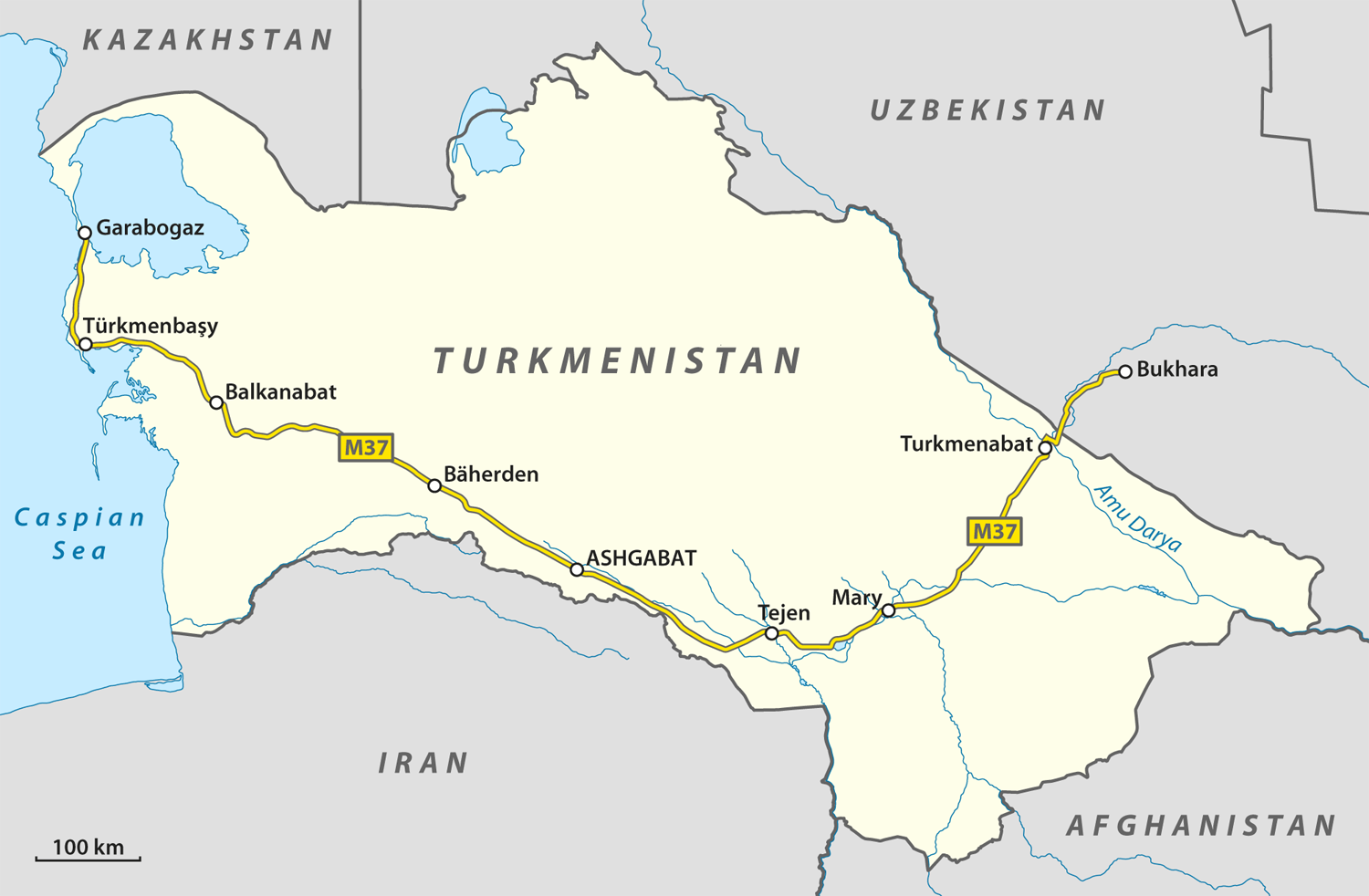
Bereket is an important railway junction and station for commercial and freight transportation on the Turkmenistan national railway system.
The city has a small public transportation network. Several small buses run scheduled routes connecting the eastern and western parts of the city (some 5–6 km.)
Bereket is an important railway junction and station for commercial and freight transportation on the Turkmenistan national railway system.
 In its storage area, the Bereket Depot museum, has a relic Russian made class T locomotive ''ТЭ-189'' (built between 1857 and 1915).
FD class steam locomotives ''ФД20-2526, ФД20–2494 (ФД20–1441)'' (built between 1931 and 1942), and Russian class E locomotives ''Эр796-88, Эм734–66 (Эм733–96), Эу705–41, Эм725–30, Э-13'' (built between 1912 and 1957).
There are also several ''
In its storage area, the Bereket Depot museum, has a relic Russian made class T locomotive ''ТЭ-189'' (built between 1857 and 1915).
FD class steam locomotives ''ФД20-2526, ФД20–2494 (ФД20–1441)'' (built between 1931 and 1942), and Russian class E locomotives ''Эр796-88, Эм734–66 (Эм733–96), Эу705–41, Эм725–30, Э-13'' (built between 1912 and 1957).
There are also several ''
city
A city is a human settlement of a substantial size. The term "city" has different meanings around the world and in some places the settlement can be very small. Even where the term is limited to larger settlements, there is no universally agree ...
in Balkan Province
Balkan Region () is the westernmost of the five regions of Turkmenistan. Clockwise from north it borders Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan (north); two provinces of Turkmenistan (east), Iran (south), and the Caspian Sea (west). The capital city is Balkana ...
in western Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan is a landlocked country in Central Asia bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the south and southwest and the Caspian Sea to the west. Ash ...
. Bereket is the administrative centre of Bereket District
Bereket District () (formerly Gazanjyk District) is a district of Balkan Region in Turkmenistan. The administrative center of the district is the city of Bereket.
History
Founded in January 1925 as a district of Kazandjik Kazandzhiksky Polto ...
.
Bereket is located in an oasis in the foothills of the Kopetdag Mountains and on the edge of the Karakum Desert
The Karakum Desert ( ; rus, Каракумы, p=kərɐˈkumɨ), also spelt and (; ), is a desert in Central Asia. The name refers to the shale-rich sand beneath the surface. It occupies about 70 percent, or roughly , of Turkmenistan.
The po ...
.
Bereket is a strategic junction
Junction may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Junction'' (2012 film), an American film
* ''Junction'' (2024 film), an American film
* ''Jjunction'', a 2002 Indian film
* ''Junction'' (album), a 1976 album by Andrew Cyrille
* Junction (E ...
of the Trans-Caspian Railway
The Trans-Caspian Railway (also called the Central Asian Railway, ) is a railway that follows the path of the Silk Road through much of western Central Asia. It was built by the Russian Empire during its expansion into Central Asia in the 19t ...
(Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
-Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan is a landlocked country in Central Asia bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the south and southwest and the Caspian Sea to the west. Ash ...
-Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
-Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
) and North-South Transnational Railway (Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
-Kazakhstan-Turkmenistan-Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
-Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.Un ...
.
The city has a large locomotive repair depot and a modern railway station.
The city is located approximately west of the Turkmen capital of Ashgabat
Ashgabat (Turkmen language, Turkmen: ''Aşgabat'') is the capital city, capital and largest city of Turkmenistan. It lies between the Karakum Desert and the Kopet Dag, Kopetdag mountain range in Central Asia, approximately 50 km (30 ...
and east of the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
port of Turkmenbashy. The largest cities nearby are Balkanabat
Balkanabat (), formerly Nebit-Dag and Neftedag, is the administrative centre of Balkan Province, the largest province in Turkmenistan. It lies at the foot of the Balkan Daglary mountain range. Balkanabat is about 450 km west of Ashgabat a ...
to the west, and Serdar
Serdar may refer to
* Serdar (given name)
* Serdar (surname) Serdar is a surname of the following notable people:
* Can Serdar (born 1996), German-Turkish football midfielder
* Emerîkê Serdar (1935–2018), Kurdish-Yezidi writer from Armenia
* I ...
to the east.
The estimated population of the city is 24,500 as of March 2015.
Etymology
''Gazanjyk'' is probably derived from theTurkic language
The Turkic languages are a language family of more than 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and West Asia. The Turkic langua ...
word ''gazan'' or ''kazan'' (meaning a large cooking pot used throughout Central Asia, roughly equivalent to a cauldron
A cauldron (or caldron) is a large cookware and bakeware, pot (kettle) for cooking or boiling over an open fire, with a lid and frequently with an arc-shaped hanger and/or integral handles or feet. There is a rich history of cauldron lore in r ...
) and ''-jyk'', a suffix to denote "small in size". The name can be translated into English as "small cauldron". Atanyyazow notes that Gazanjyk is the name of a spring near the city, and it was named after its shape.
On 29 December 1999, by Parliamentary Resolution XM-66, the city and district (''etrap'') of Gazanjyk were renamed Bereket. ''Bereket'' means in the Turkmen language
Turkmen (, , , or , , , ) is a Turkic language of the Oghuz branch spoken by the Turkmens of Central Asia. It has an estimated 4.7 million native speakers in Turkmenistan (where it is the official language), and a further 359,000 speakers i ...
''abundance'' or ''prosperity''. The word ''bereket'' is borrowed from the Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
word ''Barakat'' (برکت), which in turn is borrowed from the Arabic ''Barakah'' (برکة).
History
Since ancient times the area where city is now located was known as an important junction on theSilk Road
The Silk Road was a network of Asian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over , it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the ...
that connected China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
with the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
and Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
.
Aleksey Kuropatkin
Aleksey Nikolayevich Kuropatkin (; March 29, 1848January 16, 1925) was a Russian politician and military officer who served as the Russian Imperial Minister of War from January 1898 to February 1904 and as a field commander subsequently. Hist ...
, the Imperial Russian Army
The Imperial Russian Army () was the army of the Russian Empire, active from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was organized into a standing army and a state militia. The standing army consisted of Regular army, regular troops and ...
commander of the Turkestan Rifle Brigade, who led an 18-day march in 1880–1881 across of Karakum Desert, wrote in his memoirs,
After the conquest of Transcaspian Oblast
The Transcaspian Oblast, or simply Transcaspia, was an oblast of the Russian Empire and early Soviet Russia to the east of the Caspian Sea during the second half of the 19th century until 1924.
It was bounded to the south by Iran's Khorasan Pro ...
the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
started to build the Trans-Caspian railway
The Trans-Caspian Railway (also called the Central Asian Railway, ) is a railway that follows the path of the Silk Road through much of western Central Asia. It was built by the Russian Empire during its expansion into Central Asia in the 19t ...
including towns and settlements along the route. Gazanjyk, as an urban settlement, was founded in 1895 to serve as an important junction on the railway. Gazanjyk was classified as a town until 1939, when it was upgraded to the status of a city.
Between 1916 and 1924 Gazanjyk and the surrounding area were the scene of furious battles between Russian Imperial forces, and after 1918 the Soviet Red Army, and local nationalist Muslims of the Basmachi movement
The Basmachi movement (, derived from ) was an uprising against Imperial Russian and Soviet rule in Central Asia by rebel groups inspired by Islamic beliefs. It has been called "probably the most important movement of opposition to Soviet rul ...
.
During Soviet period the 61631st Army garrison was built on the outskirts of the city. In 1988 it was the station of the 231st tank regiment, the 160th motorized rifle regiment and the 405th artillery regiment.
The December 2000 Turkmenistan earthquake (7.0 on the moment magnitude scale) devastated the city centre.
Geography
See satellite image of Bereket. The city is located on the westernmost foothills of the Kopetdag mountains, called Kyurendag, on the edge of the Karakum deserts. he maximum height of the Kyurendag ridge is . The vegetation of the ridge is quite poor and is represented primarily by species of desert flora:sagebrush
Sagebrush is the common name of several woody and herbaceous species of plants in the genus ''Artemisia (plant), Artemisia''. The best-known sagebrush is the shrub ''Artemisia tridentata''. Sagebrush is native to the western half of North Amer ...
, semi-desert and dry steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without closed forests except near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the tropical and subtropica ...
and rocky outcroppings. Soils are grey soils. One can occasionally find juniper trees, single or large groups of ''tamarisk'' and small shrubs.
Wildlife in recent years has become greatly impoverished. Ungulates are few in number. ''Argali'' sheep are seen occasionally, as are bezoar goats, wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a Suidae, suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The speci ...
, and gazelle
A gazelle is one of many antelope species in the genus ''Gazella'' . There are also seven species included in two further genera; '' Eudorcas'' and '' Nanger'', which were formerly considered subgenera of ''Gazella''. A third former subgenus, ' ...
s. Predators includewolves
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the grey wolf or gray wolf, is a canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, including the dog and dingo, though gr ...
, jackals
Jackals are canids native to Africa and Eurasia. While the word has historically been used for many canines of the subtribe canina, in modern use it most commonly refers to three species: the closely related black-backed jackal (''Lupulella ...
, foxes
Foxes are small-to-medium-sized omnivorous mammals belonging to several genera of the family Canidae. They have a flattened skull; upright, triangular ears; a pointed, slightly upturned snout; and a long, bushy tail ("brush").
Twelve species ...
, and hyenas
Hyenas or hyaenas ( ; from Ancient Greek , ) are feliformia, feliform carnivoran mammals belonging to the Family (biology), family Hyaenidae (). With just four extant species (each in its own genus), it is the fifth-smallest family in the orde ...
. Among birds klik are rarely seen and stone curlews and jacks very rarely. Reptile species are represented by the steppe tortoise, monitor lizard, boa, agam, etc.
The major source of water for irrigation is the Karakum Canal
The Karakum Canal (Qaraqum Canal, Kara Kum Canal, Garagum Canal; , ''Karakumskiy Kanal'', , , ) in Turkmenistan is one of the largest irrigation and water supply canals in the world. Started in 1954, and completed in 1988, it is navigable over ...
, which runs dry near Bereket and delivers water to points west via a pipeline.
Demographics
The city is divided into several neighbourhoods, called by the traditional name for a semi-nomadic village, ''aul''. The majority of the inhabitants areTurkmen
Turkmen, Türkmen, Turkoman, or Turkman may refer to:
Peoples Historical ethnonym
* Turkoman (ethnonym), ethnonym used for the Oghuz Turks during the Middle Ages
Ethnic groups
* Turkmen in Anatolia and the Levant (Seljuk and Ottoman-Turkish desc ...
from the Yomud
The Yomut, also spelled Yomud or Iomud, are a Turkmen tribe who reside in Turkmenistan and Iran.
There is a common belief about the origin of the name Yomut. It is said that a long time ago, Indigenous people settled by the Caspian Sea and we ...
tribes, with a minority of Teke
Teke or Tekke can refer to:
People
* Teke (tribe), a tribe of southern Turkmenistan
* Teke people or Bateke, a Central African ethnic group
* Fatih Tekke (born 1977), Turkish footballer
* Kent Tekulve (born 1947), American baseball player
Places ...
. Previously strong communities of Azeris, Armenians, Russians, Ukrainians and Persians are now reduced to several families. In the 1990s most of them migrated to larger cities for better economic opportunities. Many Russian families also emigrated to the Russian Federation
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
.
Economy
The city is the semi-industrial and semi-agricultural centre of Bereket District. It is an important railway and automobile junction, the city has a largerailroad yard
A rail yard, railway yard, railroad yard (US) or simply yard, is a series of tracks in a rail network for storing, sorting, or loading and unloading rail vehicles and locomotives. Yards have many tracks in parallel for keeping rolling stock or ...
and locomotive repair depot, a brick yard, Turkmen carpet
A Turkmen rug (; or Turkmen carpet or Turkoman carpet) is a type of handmade floor-covering textile traditionally originating in Central Asia. It is useful to distinguish between the original Turkmen tribal rugs and the rugs produced in large ...
weaving
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal ...
factory, wheat and cotton processing and storage facilities. Animal husbandry (camels, cows, sheep) is another source of income.
In September 2014 a poultry complex with production capacity of 8 million eggs and 1000 tons of poultry meat a year was constructed.
Finance
The State Commercial Bank Dayhanbank has a branch in Bereket.Communication
The postal code for the city is 745130. The city has mobile coverage from the state-owned Altyn Asyr.City and national transportation

 The city has a small public transportation network. Several small buses run scheduled routes connecting the eastern and western parts of the city (some 5–6 km.)
Bereket is an important railway junction and station for commercial and freight transportation on the Turkmenistan national railway system.
The city has a small public transportation network. Several small buses run scheduled routes connecting the eastern and western parts of the city (some 5–6 km.)
Bereket is an important railway junction and station for commercial and freight transportation on the Turkmenistan national railway system.
Role in transnational transportation
Bereket is a strategically important junction of theTrans-Caspian Railway
The Trans-Caspian Railway (also called the Central Asian Railway, ) is a railway that follows the path of the Silk Road through much of western Central Asia. It was built by the Russian Empire during its expansion into Central Asia in the 19t ...
(Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
, Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan is a landlocked country in Central Asia bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the south and southwest and the Caspian Sea to the west. Ash ...
, Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
and eastern Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
) and North-South Transnational Railway (Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
-Kazakhstan-Turkmenistan-Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
-Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.Un ...
). The city has a large locomotive repair depot and a modern passenger railway station.
The Kazakhstan-Turkmenistan-Iran railway link is part of the North–South Transport Corridor and is a long railway line connecting Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan with Iran and the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.Un ...
. It links Uzen in Kazakhstan with Bereket– Etrek in Turkmenistan and ends at Gorgan
Gorgan (; ) is a city in the Central District (Gorgan County), Central District of Gorgan County, Golestan province, Golestan province, Iran, serving as capital of the province, the county, and the district. It lies approximately to the nor ...
in Iran's Golestan province. In Iran, the railway is linked to the national network making its way to the ports of the Persian Gulf. The project is estimated to have cost $620 million, which was jointly funded by the governments of Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan and Iran.
In May 2013, the Bereket – Uzen section of the North-South Transnational Railway was completed. In February 2014 long section between Bereket and Etrek was completed. Currently railway stations along the new railway are being constructed such as Däneata, Dövletýar, Bugdaýly, Balguýi, Madaw, Akjadepe.
The Kazakhstan-Turkmenistan-Iran railway link was officially inaugurated in October 2014.
The city is located on the M37 Highway (Turkmenistan's section of the European route E60
European route E 60 is the second-longest road in the International E-road network and runs , from Brest, France (on the Atlantic coast), to Irkeshtam, Kyrgyzstan (on the border with China).
Route
*
**: Brest ()
**: Brest - Quimper ...
which connects Brest, France
Brest (; ) is a port, port city in the Finistère department, Brittany (administrative region), Brittany. Located in a sheltered bay not far from the western tip of a peninsula and the western extremity of metropolitan France, Brest is an impor ...
to Irkeshtam
Erkeshtam, called Irkeshtam in Chinese and Dungan, or Erkech-Tam in Uyghur and Kyrgyz, is a border crossing between Kyrgyzstan and Xinjiang, China, named after a village on the Kyrgyz side of the border in southern Osh Region. The border cross ...
, Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan, officially the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia lying in the Tian Shan and Pamir Mountains, Pamir mountain ranges. Bishkek is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Kyrgyzstan, largest city. Kyrgyz ...
on the border with the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
).
Education, health, culture
The city has three public schools, kindergartens, a small hospital, and medical emergency centre. In 2012 several new buildings were constructed within the State Development Program including the mayor's office ('' häkimlik''), two schools, a hotel, cultural center, a hospital and a knitting factory. Until 2000, the city had a library, two open-air and one winter cinema. All are currently closed.Climate
Bereket has acool desert climate
The desert climate or arid climate (in the Köppen climate classification ''BWh'' and ''BWk'') is a dry climate sub-type in which there is a severe excess of evaporation over precipitation. The typically bald, rocky, or sandy surfaces in desert ...
(Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (1951–2014), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author ...
''BWk''), with generally chilly winters and very hot summers. Rainfall is generally light and erratic, and occurs mainly in the winter and autumn months. In summer, day temperatures may reach between , and during nights fall to between . The air flow is windy, chilly in winters and dusty in summers.
Sightseeing
 In its storage area, the Bereket Depot museum, has a relic Russian made class T locomotive ''ТЭ-189'' (built between 1857 and 1915).
FD class steam locomotives ''ФД20-2526, ФД20–2494 (ФД20–1441)'' (built between 1931 and 1942), and Russian class E locomotives ''Эр796-88, Эм734–66 (Эм733–96), Эу705–41, Эм725–30, Э-13'' (built between 1912 and 1957).
There are also several ''
In its storage area, the Bereket Depot museum, has a relic Russian made class T locomotive ''ТЭ-189'' (built between 1857 and 1915).
FD class steam locomotives ''ФД20-2526, ФД20–2494 (ФД20–1441)'' (built between 1931 and 1942), and Russian class E locomotives ''Эр796-88, Эм734–66 (Эм733–96), Эу705–41, Эм725–30, Э-13'' (built between 1912 and 1957).
There are also several ''ТЭ1
TE1 () is a diesel locomotive with electric transmission, produced in the Soviet Union from 1947 to 1950 by the Malyshev Factory in Kharkiv. It is a modified copy of the American ALCO RSD-1. Initially designated as TE1-20, a total of 298 units we ...
'' class locomotives, whose prototype was the famous US made ALCO RSD-1
The ALCO RSD-1 is a diesel-electric locomotive built by the American Locomotive Company (ALCO). This model was a road switcher type rated at and rode on three-axle trucks, having a C-C wheel arrangement. It was often used in much the same ma ...
locomotive.
Bereket Railway Station
Bereket Railway Station () is the main railway station in the city. It was built in 1885. The station is operated by the Türkmendemirýollary.See also
*Bereket District
Bereket District () (formerly Gazanjyk District) is a district of Balkan Region in Turkmenistan. The administrative center of the district is the city of Bereket.
History
Founded in January 1925 as a district of Kazandjik Kazandzhiksky Polto ...
* Balkan Province
Balkan Region () is the westernmost of the five regions of Turkmenistan. Clockwise from north it borders Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan (north); two provinces of Turkmenistan (east), Iran (south), and the Caspian Sea (west). The capital city is Balkana ...
* List of cities in Turkmenistan
This is a list of city, cities in Turkmenistan. For a full list of settlements see the list of cities, towns and villages in Turkmenistan.
Which municipalities are categorized as "cities" is established by law in Turkmenistan. Cities fall into t ...
* List of cities, towns and villages in Turkmenistan
An A-Z list of settlements in Turkmenistan.Settlements in Turkmenistan ...
References
{{Cities of Turkmenistan Populated places in Balkan Region Populated places established in 1895 Cities and towns built in the Soviet Union Populated places along the Silk Road 1895 establishments in the Russian Empire