Battle of Solferino on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Battle of Solferino (referred to in Italy as the Battle of Solferino and San Martino) on 24 June 1859 resulted in the victory of the allied French army under
 The Battle of Solferino was a decisive engagement in the
The Battle of Solferino was a decisive engagement in the
 According to the allied battle plan formulated on 24 June, the Franco-Sardinian army moved east to deploy along the right river banks of the
According to the allied battle plan formulated on 24 June, the Franco-Sardinian army moved east to deploy along the right river banks of the
 The battle started at Medole around 4 am. Marching towards Guidizzolo, the 4th Corps encountered an Austrian infantry regiment of the Austrian 1st Army. General Niel immediately decided to engage the enemy and deployed his forces east of Medole. This move prevented the three corps (III, IX and XI) of the Austrian 1st Army from aiding their comrades of the 2nd Army near Solferino, where the main French attacks took place.
The French forces were numerically inferior to the Austrians'. The 4th Corps contained three infantry divisions under de Luzy, Vinoy and Failly and a cavalry brigade. Niel, holding a thin line of in length, was able to stop the Austrian assaults on his position by ably warding off attacks and counterattacking at opportune moments.
According to Schneid, "By early afternoon, the Austrian attack had failed and Niel pushed beyond Robecco and Casa Nova halfway to Guidizzolo. At 3:00 pm General Renault's division of Canrobert's III Corps arrived at Robecco. Niel, now reinforced, launched a coordinated attack on Guidizzolo." However, the arrival of the Austrian III and XI Korps stopped the French assault, and after two hours, Niel withdrew.
The battle started at Medole around 4 am. Marching towards Guidizzolo, the 4th Corps encountered an Austrian infantry regiment of the Austrian 1st Army. General Niel immediately decided to engage the enemy and deployed his forces east of Medole. This move prevented the three corps (III, IX and XI) of the Austrian 1st Army from aiding their comrades of the 2nd Army near Solferino, where the main French attacks took place.
The French forces were numerically inferior to the Austrians'. The 4th Corps contained three infantry divisions under de Luzy, Vinoy and Failly and a cavalry brigade. Niel, holding a thin line of in length, was able to stop the Austrian assaults on his position by ably warding off attacks and counterattacking at opportune moments.
According to Schneid, "By early afternoon, the Austrian attack had failed and Niel pushed beyond Robecco and Casa Nova halfway to Guidizzolo. At 3:00 pm General Renault's division of Canrobert's III Corps arrived at Robecco. Niel, now reinforced, launched a coordinated attack on Guidizzolo." However, the arrival of the Austrian III and XI Korps stopped the French assault, and after two hours, Niel withdrew.
File:OsseariumSolf1.jpg, The
Campagne de l'empereur Napoléon III en Italie, 1859, rédigée au dépot de la guerre, d'après les documents officiels (1865)
Der Feldzug des Kaisers Napoleon 3. in Italien im Jahre 1859 (1865)
* Mikhail Dragomirov. (1861
Battle of Solferino. (With two plans)
(Сольферинская битва. (с двумя планами)) at Runivers.ru in DjVu format {{DEFAULTSORT:Battle of Solferino
Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles-Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was President of France from 1848 to 1852 and then Emperor of the French from 1852 until his deposition in 1870. He was the first president, second emperor, and last ...
and the Piedmont-Sardinian army under Victor Emmanuel II
Victor Emmanuel II (; full name: ''Vittorio Emanuele Maria Alberto Eugenio Ferdinando Tommaso di Savoia''; 14 March 1820 – 9 January 1878) was King of Sardinia (also informally known as Piedmont–Sardinia) from 23 March 1849 until 17 March ...
(together known as the Franco-Sardinian alliance) against the Austrian army under Emperor Franz Joseph I
Franz Joseph I or Francis Joseph I ( ; ; 18 August 1830 – 21 November 1916) was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary, and the ruler of the Grand title of the emperor of Austria, other states of the Habsburg monarchy from 1848 until his death ...
. It was the last major battle in world history where all the armies were under the personal command of their monarchs. Perhaps 300,000 soldiers fought in the important battle, the largest since the Battle of Leipzig
The Battle of Leipzig, also known as the Battle of the Nations, was fought from 16 to 19 October 1813 at Leipzig, Saxony. The Coalition armies of Austria, Prussia, Sweden, and Russia, led by Tsar Alexander I, Karl von Schwarzenberg, and G ...
in 1813. There were about 130,000 Austrian troops and a combined total of 140,000 French and allied Piedmontese troops. After the battle, the Austrian emperor refrained from further direct command of the army.
The battle led the Swiss Jean-Henri Dunant
Henry Dunant (born Jean-Henri Dunant; 8 May 182830 October 1910), also known as Henri Dunant, was a Swiss humanitarian, businessman, social activist, and co-founder of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement, Red Cross. His humanit ...
to write his book ''A Memory of Solferino
''A Memory of Solferino'' (French: ''Un souvenir de Solférino'') is a book of the Swiss humanitarian Henry Dunant published in 1862. It proved decisive in the founding of the International Committee of the Red Cross.Henry Dunant, ''A Memory o ...
''. Although he did not witness the battle (his statement is contained in an "unpublished page" included in the 1939 English edition published by the American Red Cross), he toured the field following the battle and was greatly moved by what he saw. Henry Dunant
Henry Dunant (born Jean-Henri Dunant; 8 May 182830 October 1910), also known as Henri Dunant, was a Swiss humanitarian, businessman, social activist, and co-founder of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement, Red Cross. His humanit ...
was staying in Castiglione delle Stiviere at that time in today's House Bondoni Pastorio near the Duomo of Castiglione. It is said that with his carriage he took many wounded soldiers from both sides to the Duomo of Castiglione delle Stiviere where they were cared for by the local women. Horrified by the suffering of wounded soldiers left on the battlefield
A battlefield, battleground, or field of battle is the location of a present or historic battle involving ground warfare. It is commonly understood to be limited to the point of contact between opposing forces, though battles may involve troop ...
, Dunant set about a process that led to the Geneva Conventions
upright=1.15, The original document in single pages, 1864
The Geneva Conventions are international humanitarian laws consisting of four treaties and three additional protocols that establish international legal standards for humanitarian t ...
and the establishment of the International Red Cross
The International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) is a aid agency, humanitarian organization based in Geneva, Switzerland, and is a three-time Nobel Prize laureate. The organization has played an instrumental role in the development of Law of ...
. Today in Castiglione there is the Red Cross
The organized International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a Humanitarianism, humanitarian movement with approximately 16million volunteering, volunteers, members, and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ...
museum
Background
On 22 June, the French (96,000 men) and Piedmontese (37,000 men) allied army advanced from theChiese
The Chiese, also known in the Province of Brescia as the Clisi, is a Italian river that is the principal immisary and sole emissary of the sub-alpine lake Lago d’Idro (Lake Idro), and is a left tributary of the Oglio.
The river rises from th ...
to the Mincio
The Mincio (; ; ; ; ) is a river in the Lombardy region of northern Italy.
The river is the main outlet of Lake Garda. It is a part of the ''Sarca-Mincio'' river system which also includes the river Sarca and the Lake Garda. The river starts ...
river in northern Italy. The left wing consisted of four Piedmontese divisions, the right wing consisted of the French III and IV corps, while the center consisted of the I and II corps, with the Imperial Guard held in reserve. On 23 June, Franz Josef moved his 1st Army (57,000 men) and 2nd Army (45,500 men) across the Mincio. Both forces were converging on Medole, Solferino, and San Martino.
Battle
 The Battle of Solferino was a decisive engagement in the
The Battle of Solferino was a decisive engagement in the Second Italian War of Independence
The Second Italian War of Independence, also called the Sardinian War, the Austro-Sardinian War, the Franco-Austrian War, or the Italian War of 1859 (Italian: ''Seconda guerra d'indipendenza italiana''; German: ''Sardinischer Krieg''; French: ...
, a crucial step in the Italian Risorgimento
The unification of Italy ( ), also known as the Risorgimento (; ), was the 19th century political and social movement that in 1861 ended in the annexation of various states of the Italian peninsula and its outlying isles to the Kingdom of ...
. The war's geopolitical context was the nationalist struggle to unify Italy, which had long been divided among France, Austria, Spain and numerous independent Italian states. The battle took place near the villages of Solferino
Solferino ( Upper Mantovano: ) is a small town and municipality in the province of Mantua, Lombardy, northern Italy, approximately south of Lake Garda.
It is best known as being close to the site of the Battle of Solferino on 24 June 1859, part ...
and San Martino, Italy, south of Lake Garda
Lake Garda (, , or , ; ; ) is the largest lake in Italy. It is a popular holiday location in northern Italy, between Brescia and Milan to the west, and Verona and Venice to the east. The lake cuts into the edge of the Eastern Alps, Italian Alp ...
between Milan
Milan ( , , ; ) is a city in northern Italy, regional capital of Lombardy, the largest city in Italy by urban area and the List of cities in Italy, second-most-populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of nea ...
and Verona
Verona ( ; ; or ) is a city on the Adige, River Adige in Veneto, Italy, with 255,131 inhabitants. It is one of the seven provincial capitals of the region, and is the largest city Comune, municipality in the region and in Northeast Italy, nor ...
.
The confrontation was between the Austrians, on one side, and the French and Piedmontese forces, who opposed their advance. In the morning of 23 June, after the arrival of emperor Franz Joseph, the Austrian army changed direction to counterattack along the river Chiese
The Chiese, also known in the Province of Brescia as the Clisi, is a Italian river that is the principal immisary and sole emissary of the sub-alpine lake Lago d’Idro (Lake Idro), and is a left tributary of the Oglio.
The river rises from th ...
. At the same time, Napoleon III ordered his troops to advance, causing the battle to occur in an unpredicted location. While the Piedmontese fought the Austrian right wing near San Martino, the French battled to the south of them near Solferino against the main Austrian corps.
Opposing forces
The Austrian forces were personally led by Emperor Franz Joseph, consisting of the 1st Army, containing four corps (II, III, IX and XI) under Franz von Wimpffen, and the 2nd Army, containing four corps (I, V, VII and VIII) under Franz von Schlick. The French army at Solferino, personally led by Napoleon III, was divided in four Corps plus the Imperial Guard. Many of its men and generals were veterans of theFrench conquest of Algeria
The French conquest of Algeria (; ) took place between 1830 and 1903. In 1827, an argument between Hussein Dey, the ruler of the Regency of Algiers, and the French consul (representative), consul escalated into a blockade, following which the Jul ...
and the Crimean War
The Crimean War was fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the Ottoman Empire, the Second French Empire, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont fro ...
, but its commander-in-chief had very limited military experience of note. The Sardinian army had four divisions on the field.
Although all three combatants were commanded by their monarchs, each was seconded by professional soldiers. Marshal Jean-Baptiste Philibert Vaillant served as Chief of Staff to Napoleon III, while Victor Emmanuel was accompanied by his Minister of War, Lieutenant General Alfonso Ferrero La Marmora
Alfonso Ferrero La Marmora (; 18 November 18045 January 1878) was an Italian general and statesman. His older brothers include soldier and naturalist Alberto della Marmora and Alessandro Ferrero La Marmora, founder of the branch of the Italian ...
. The Austrian high command was hindered by the rivalry between the Chief of Staff, Heinrich von Heß, and the Emperor's Adjutant General Karl Ludwig von Grünne.
Battle commences
 According to the allied battle plan formulated on 24 June, the Franco-Sardinian army moved east to deploy along the right river banks of the
According to the allied battle plan formulated on 24 June, the Franco-Sardinian army moved east to deploy along the right river banks of the Mincio
The Mincio (; ; ; ; ) is a river in the Lombardy region of northern Italy.
The river is the main outlet of Lake Garda. It is a part of the ''Sarca-Mincio'' river system which also includes the river Sarca and the Lake Garda. The river starts ...
. The French were to occupy the villages of Solferino, Cavriana
Cavriana is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Mantua in the Italian region Lombardy, part of the municipalities of Alto Mantovano.
Geography
Cavriana is in the northern part of the Province of Mantua. It is located about east of M ...
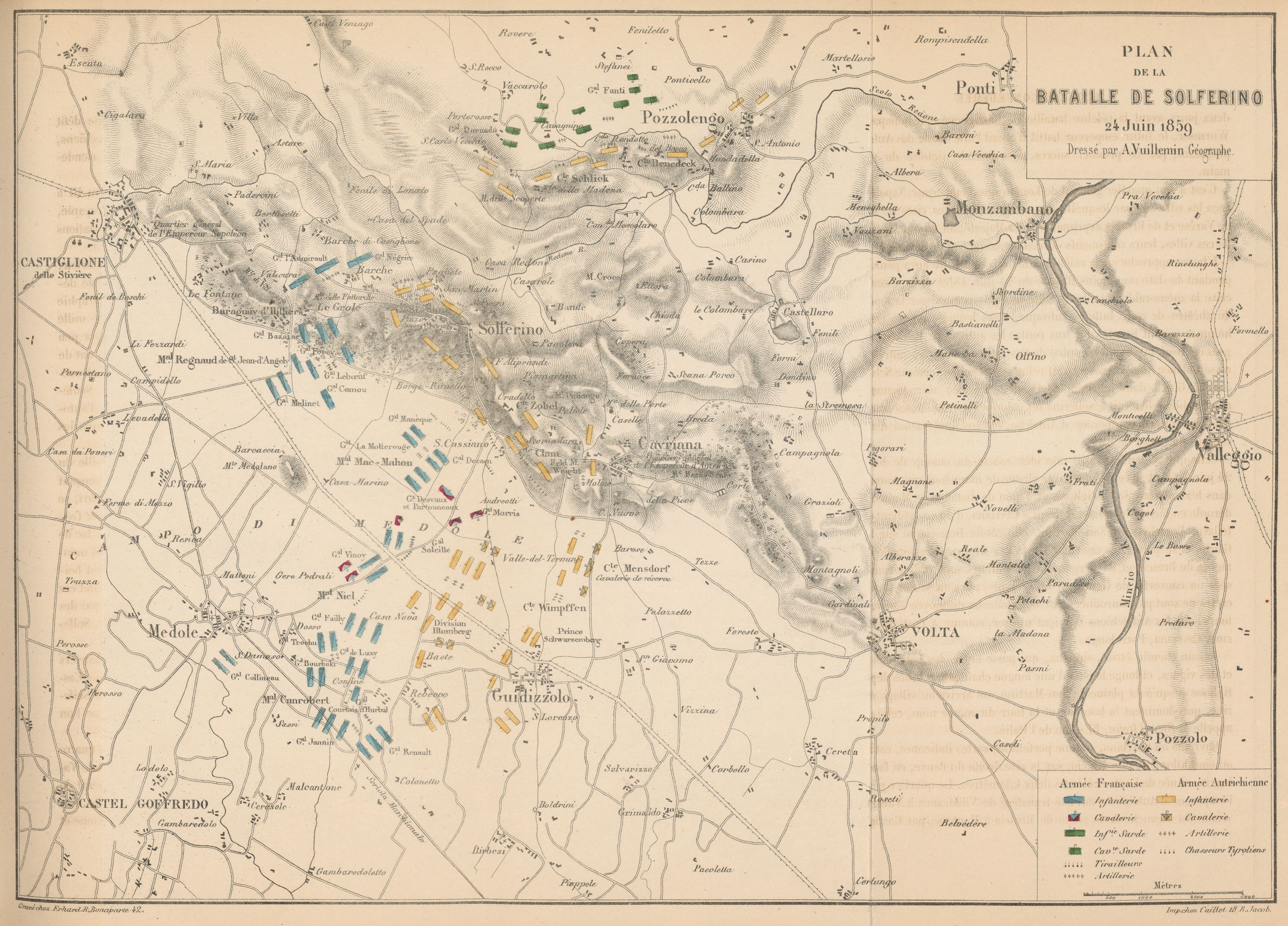
, Guidizzolo and Medole with, respectively, the 1st Corps ( Baraguey d'Hilliers), 2nd Corps ( Mac-Mahon), 3rd Corps ( Canrobert), and 4th Corps ( Niel). The four Sardinian divisions were to take Pozzolengo. After marching a few kilometers, the allies came into contact with the Austrian troops, who had entrenched themselves in those villages. In the absence of a fixed battle plan, the fighting which took place was uncoordinated, which is why so many casualties occurred, and it fell into three separate engagements, at Medole (south), Solferino (centre) and San Martino (north).
Battle of Campo di Medole
 The battle started at Medole around 4 am. Marching towards Guidizzolo, the 4th Corps encountered an Austrian infantry regiment of the Austrian 1st Army. General Niel immediately decided to engage the enemy and deployed his forces east of Medole. This move prevented the three corps (III, IX and XI) of the Austrian 1st Army from aiding their comrades of the 2nd Army near Solferino, where the main French attacks took place.
The French forces were numerically inferior to the Austrians'. The 4th Corps contained three infantry divisions under de Luzy, Vinoy and Failly and a cavalry brigade. Niel, holding a thin line of in length, was able to stop the Austrian assaults on his position by ably warding off attacks and counterattacking at opportune moments.
According to Schneid, "By early afternoon, the Austrian attack had failed and Niel pushed beyond Robecco and Casa Nova halfway to Guidizzolo. At 3:00 pm General Renault's division of Canrobert's III Corps arrived at Robecco. Niel, now reinforced, launched a coordinated attack on Guidizzolo." However, the arrival of the Austrian III and XI Korps stopped the French assault, and after two hours, Niel withdrew.
The battle started at Medole around 4 am. Marching towards Guidizzolo, the 4th Corps encountered an Austrian infantry regiment of the Austrian 1st Army. General Niel immediately decided to engage the enemy and deployed his forces east of Medole. This move prevented the three corps (III, IX and XI) of the Austrian 1st Army from aiding their comrades of the 2nd Army near Solferino, where the main French attacks took place.
The French forces were numerically inferior to the Austrians'. The 4th Corps contained three infantry divisions under de Luzy, Vinoy and Failly and a cavalry brigade. Niel, holding a thin line of in length, was able to stop the Austrian assaults on his position by ably warding off attacks and counterattacking at opportune moments.
According to Schneid, "By early afternoon, the Austrian attack had failed and Niel pushed beyond Robecco and Casa Nova halfway to Guidizzolo. At 3:00 pm General Renault's division of Canrobert's III Corps arrived at Robecco. Niel, now reinforced, launched a coordinated attack on Guidizzolo." However, the arrival of the Austrian III and XI Korps stopped the French assault, and after two hours, Niel withdrew.
Battle of Solferino
Around 4:30 am the advance guard of the 1st Corps (three infantry divisions under Forey, de Ladmirault, and Bazaine, and a cavalry division under Desvaux) came into contact with the Austrian V Corps under Stadion near Castiglione delle Stiviere. Around 5 am 2nd Corps under Mac-Mahon (two infantry divisions and a cavalry brigade under La Motterouge, Decaen and Gaudin) encountered Hungarian units posted near Ca’Morino (Medole). The Austrian forces were three corps strong (I, V and VII) and positioned on the towns of Solferino, Cavriana and Volta Mantovana. The Austrians were able to hold these positions all day against repeated French attacks. According to Schneid, "Stadion received reinforcements from Clam Gallas' I Korps but Napoleon III fed the Imperial Guard divisions into the combat and by 2:00 pm the cemetery and town were surrounded. Near 3 pm the French reserves, formed by Canrobert's 3rd Corps and the Imperial Guard under Regnaud, attacked Cavriana, which was defended by the Austrian I Corps under Clam-Gallas, finally occupying it at 6 pm and thereby breaking through the Austrian center. This breakthrough forced a general retreat of both Austrian armies.Battle of San Martino
On the northern side of the battlefield the Sardinians, four divisions strong, encountered the Austrians around 7 am. A long battle erupted over control of Pozzolengo, San Martino and Madonna della Scoperta. The Austrian VIII Corps under Benedek had 39,000 men and 80 guns and was repeatedly attacked by a Sardinian force of 22,000 men with 48 guns. The Austrians were able to ward off three Sardinian attacks, inflicting heavy losses upon the attackers; at the end of the day Benedek was ordered to retreat with the rest of the Austrian army, but ignored the order and kept resisting. At 8:00 pm a fourth Sardinian assault finally captured the contested hills, and Benedek withdrew. The main Sardinian contribution in the overall battle consisted in keeping Benedek's corps deeply engaged throughout the day and preventing the sending of two brigades as reinforcement to the force attacked by the French in Solferino.Results
The battle was a particularly gruelling one, lasting over nine hours and resulting in over 2,386 Austrian troops killed with 10,807 wounded and 8,638 missing or captured. The Allied armies also suffered a total of 2,492 killed, 12,512 wounded and 2,922 captured or missing. Reports of wounded and dying soldiers being shot orbayonet
A bayonet (from Old French , now spelt ) is a -4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... , now spelt ) is a knife, dagger">knife">-4; we might wonder whethe ...
ted on both sides added to the horror. In the end, the Austrian forces were forced to yield their positions, and the Allied French-Piedmontese armies won a tactical, but costly, victory. The Austrians retreated to the four fortresses of the Quadrilateral, and the campaign essentially ended.
Aftermath
Napoleon III was moved by the losses, as he had argued back in 1852 "the French Empire is peace", and for reasons including the Prussian threat and domestic protests by the Roman Catholics, he decided to put an end to the war with the Armistice of Villafranca on 11 July 1859. The Piedmontese won Lombardy but not Venetia.Camillo Benso, conte di Cavour
Camillo Paolo Filippo Giulio Benso, Count of Cavour, Isolabella and Leri (; 10 August 1810 – 6 June 1861), generally known as the Count of Cavour ( ; ) or simply Cavour, was an Italian politician, Statesman (politician), statesman, Business ...
, resigned. The Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
was proclaimed in 1861.
This battle would have a long-term effect on the future conduct of military actions. Jean-Henri Dunant
Henry Dunant (born Jean-Henri Dunant; 8 May 182830 October 1910), also known as Henri Dunant, was a Swiss humanitarian, businessman, social activist, and co-founder of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement, Red Cross. His humanit ...
, who witnessed the aftermath of the battle in person, was motivated by the horrific suffering of wounded soldiers left on the battlefield to begin a campaign that would eventually result in the Geneva Convention
upright=1.15, The original document in single pages, 1864
The Geneva Conventions are international humanitarian laws consisting of four treaties and three additional protocols that establish international legal standards for humanitarian t ...
s and the establishment of the International Red Cross
The International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) is a aid agency, humanitarian organization based in Geneva, Switzerland, and is a three-time Nobel Prize laureate. The organization has played an instrumental role in the development of Law of ...
. The Movement organized the 150th anniversary commemoration of the battle between 23 and 27 June 2009. The Presidency
A presidency is an administration or the executive, the collective administrative and governmental entity that exists around an office of president of a state or nation. Although often the executive branch of government, and often personified b ...
of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
adopted a declaration on the occasion stating that "This battle was also the grounds on which the international community of States has developed and adopted instruments of International Humanitarian Law, the international law rules relevant in times of armed conflict, in particular the four Geneva Conventions of 1949, the 60th anniversary of which will be celebrated this year."
In 2019, an important memorial event took place on the former battlefield in the presence of Karl von Habsburg
Karl von Habsburg (given names: ''Karl Thomas Robert Maria Franziskus Georg Bahnam''; born 11 January 1961) is an Austrian politician and the head of the House of Habsburg-Lorraine, the former royal house of the defunct Austro-Hungarian thrones ...
, the head of the House of Habsburg, representatives of the Order of St. George and the presidents of the Society of Solferino and San Martino to emphasize the peace of the nations. Wreaths were laid in the cemeteries and the museum was honored. During the event, the battle was re-enacted by hundreds of volunteers.
The battlefield today
The area contains a number of memorials to the events surrounding the battles. There is a circular tower, Tower of San Martino della Battaglia, dominating the area, a memorial to Victor Emmanuel II. It is 70 m high and was built in 1893. In the town there is a museum, with uniforms and weapons of the time, and anossuary
An ossuary is a chest, box, building, well, or site made to serve as the final resting place of human skeletal remains. They are frequently used where burial space is scarce. A body is first buried in a temporary grave, then after some years th ...
chapel.
At Solferino there is also a museum, displaying arms and mementos of the time, and an ossuary, containing the bones of thousands of victims.
Nearby Castiglione delle Stiviere, where many of the wounded were taken after the battle, is the site of the museum of the International Red Cross, focusing on the events that led to the formation of that organization.
ossuary
An ossuary is a chest, box, building, well, or site made to serve as the final resting place of human skeletal remains. They are frequently used where burial space is scarce. A body is first buried in a temporary grave, then after some years th ...
of Solferino
Solferino ( Upper Mantovano: ) is a small town and municipality in the province of Mantua, Lombardy, northern Italy, approximately south of Lake Garda.
It is best known as being close to the site of the Battle of Solferino on 24 June 1859, part ...
File:OsseariumSolf2.jpg, The ossuary
An ossuary is a chest, box, building, well, or site made to serve as the final resting place of human skeletal remains. They are frequently used where burial space is scarce. A body is first buried in a temporary grave, then after some years th ...
of Solferino
Solferino ( Upper Mantovano: ) is a small town and municipality in the province of Mantua, Lombardy, northern Italy, approximately south of Lake Garda.
It is best known as being close to the site of the Battle of Solferino on 24 June 1859, part ...
References in popular culture
Elizabeth Barrett Browning
Elizabeth Barrett Browning (née Moulton-Barrett; 6 March 1806 – 29 June 1861) was an English poet of the Victorian era, popular in Britain and the United States during her lifetime and frequently anthologised after her death. Her work receiv ...
's poem "The Forced Recruit at Solferino" commemorates this battle (''Last Poems'' 1862).
Joseph Roth's 1932 novel ''Radetzky March'' opens at the Battle of Solferino. There, the father of the novel's Trotta dynasty is immortalized as the Hero of Solferino.
The Battle of Solferino was depicted also in a 2006 television drama ''Henry Dunant
Henry Dunant (born Jean-Henri Dunant; 8 May 182830 October 1910), also known as Henri Dunant, was a Swiss humanitarian, businessman, social activist, and co-founder of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement, Red Cross. His humanit ...
: Du rouge sur la croix'' (English title: "Henry Dunant: Red on the Cross"), which tells the story of the signing of the Geneva Conventions
upright=1.15, The original document in single pages, 1864
The Geneva Conventions are international humanitarian laws consisting of four treaties and three additional protocols that establish international legal standards for humanitarian t ...
and the founding of the Red Cross
The organized International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a Humanitarianism, humanitarian movement with approximately 16million volunteering, volunteers, members, and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ...
.
A Memory of Solferino
''A Memory of Solferino'' (French: ''Un souvenir de Solférino'') is a book of the Swiss humanitarian Henry Dunant published in 1862. It proved decisive in the founding of the International Committee of the Red Cross.Henry Dunant, ''A Memory o ...
, the battle, and the town itself are discussed in 2010's Chang-Rae Lee's novel The Surrendered.
Footnotes
References
*Campagne de l'empereur Napoléon III en Italie, 1859, rédigée au dépot de la guerre, d'après les documents officiels (1865)
Der Feldzug des Kaisers Napoleon 3. in Italien im Jahre 1859 (1865)
External links
* Mikhail Dragomirov. (1861
Battle of Solferino. (With two plans)
(Сольферинская битва. (с двумя планами)) at Runivers.ru in DjVu format {{DEFAULTSORT:Battle of Solferino
Solferino
Solferino ( Upper Mantovano: ) is a small town and municipality in the province of Mantua, Lombardy, northern Italy, approximately south of Lake Garda.
It is best known as being close to the site of the Battle of Solferino on 24 June 1859, part ...
Solferino 1859
Solferino 1859
Solferino 1859
1859 in Italy
1859 in the Austrian Empire
1859 in France
Solferino
Solferino ( Upper Mantovano: ) is a small town and municipality in the province of Mantua, Lombardy, northern Italy, approximately south of Lake Garda.
It is best known as being close to the site of the Battle of Solferino on 24 June 1859, part ...
June 1859
Solferino
Solferino ( Upper Mantovano: ) is a small town and municipality in the province of Mantua, Lombardy, northern Italy, approximately south of Lake Garda.
It is best known as being close to the site of the Battle of Solferino on 24 June 1859, part ...
Napoleon III
Victor Emmanuel II
Franz Joseph I of Austria