Baddeleyite on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Baddeleyite is a rare
zirconium
Zirconium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Zr and atomic number 40. First identified in 1789, isolated in impure form in 1824, and manufactured at scale by 1925, pure zirconium is a lustrous transition metal with a greyis ...
oxide mineral
The oxide mineral class includes those minerals in which the oxide anion (O2−) is bonded to one or more metal alloys. The hydroxide-bearing minerals are typically included in the oxide class. Minerals with complex anion groups such as the sil ...
(ZrO2 or zirconia
Zirconium dioxide (), sometimes known as zirconia (not to be confused with zirconium silicate or zircon), is a white crystalline oxide of zirconium. Its most naturally occurring form, with a monoclinic crystalline structure, is the mineral ba ...
), occurring in a variety of monoclinic
In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three Vector (geometric), vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in t ...
prismatic crystal forms. It is transparent to translucent, has high indices of refraction, and ranges from colorless to yellow, green, and dark brown. See etymology below
Below may refer to:
*Earth
*Ground (disambiguation)
*Soil
*Floor
* Bottom (disambiguation)
*Less than
*Temperatures below freezing
*Hell or underworld
People with the surname
* Ernst von Below (1863–1955), German World War I general
* Fred Belo ...
.
Baddeleyite is a refractory
In materials science, a refractory (or refractory material) is a material that is resistant to decomposition by heat or chemical attack and that retains its strength and rigidity at high temperatures. They are inorganic, non-metallic compound ...
mineral, with a melting point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state of matter, state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase (matter), phase exist in Thermodynamic equilib ...
of 2700 °C. Hafnium
Hafnium is a chemical element; it has symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in many zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by Dm ...
is a substituting ''impurity'' and may be present in quantities ranging from 0.1 to several percent.
It can be found in igneous
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
The magma can be derived from partial ...
rocks containing potassium feldspar and plagioclase
Plagioclase ( ) is a series of Silicate minerals#Tectosilicates, tectosilicate (framework silicate) minerals within the feldspar group. Rather than referring to a particular mineral with a specific chemical composition, plagioclase is a continu ...
. Baddeleyite is commonly not found with zircon
Zircon () is a mineral belonging to the group of nesosilicates and is a source of the metal zirconium. Its chemical name is zirconium(IV) silicate, and its corresponding chemical formula is Zr SiO4. An empirical formula showing some of th ...
(ZrSiO4), because it forms in silica-undersaturated rocks, such as mafic
A mafic mineral or rock is a silicate mineral or igneous rock rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Common mafic rocks include ...
rocks. This is because, when silica is free in the system (silica-saturated/oversaturated), zircon is the dominating phase, not baddeleyite. It belongs to the monoclinic-prismatic class, of the P21/c crystal system
In crystallography, a crystal system is a set of point groups (a group of geometric symmetries with at least one fixed point). A lattice system is a set of Bravais lattices (an infinite array of discrete points). Space groups (symmetry groups ...
. It has been used for geochronology
Geochronology is the science of Chronological dating, determining the age of rock (geology), rocks, fossils, and sediments using signatures inherent in the rocks themselves. Absolute geochronology can be accomplished through radioactive isotopes, ...
.
Geologic occurrence
Baddeleyite was first found inSri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
in 1892. It can be found in numerous terrestrial and extraterrestrial rocks. Some of these terrestrial rocks are carbonatite
Carbonatite () is a type of intrusive rock, intrusive or extrusive rock, extrusive igneous rock defined by mineralogic composition consisting of greater than 50% carbonate minerals. Carbonatites may be confused with marble and may require geoche ...
, kimberlite
Kimberlite is an igneous rock and a rare variant of peridotite. It is most commonly known as the main host matrix for diamonds. It is named after the town of Kimberley, Northern Cape, Kimberley in South Africa, where the discovery of an 83.5-Car ...
, alkaline syenite
Syenite is a coarse-grained intrusive igneous rock with a general composition similar to that of granite, but deficient in quartz, which, if present at all, occurs in relatively small concentrations (< 5%). It is considered a layered mafic intrusions, 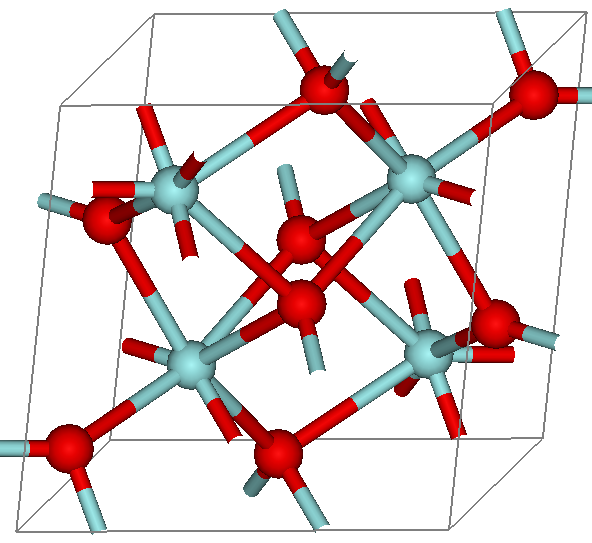
Minweb with ''chime'' structure
Early rocks to reveal their ages, BBC News
{{Authority control Zirconium minerals Oxide minerals Monoclinic minerals Minerals in space group 14
diabase
Diabase (), also called dolerite () or microgabbro,
is a mafic, holocrystalline, subvolcanic rock equivalent to volcanic basalt or plutonic gabbro. Diabase dikes and sills are typically shallow intrusive bodies and often exhibit fine-gra ...
dikes, gabbro
Gabbro ( ) is a phaneritic (coarse-grained and magnesium- and iron-rich), mafic intrusive igneous rock formed from the slow cooling magma into a holocrystalline mass deep beneath the Earth's surface. Slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro is ch ...
id sills and anorthosite
Anorthosite () is a phaneritic, intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock characterized by its composition: mostly plagioclase feldspar (90–100%), with a minimal mafic component (0–10%). Pyroxene, ilmenite, magnetite, and olivine are the mafic ...
. Some examples of extraterrestrial rocks are tektite
Tektites () are gravel-sized bodies composed of black, green, brown or grey natural glass formed from terrestrial debris ejected during meteorite impacts. The term was coined by Austrian geologist Franz Eduard Suess (1867–1941), son of Eduar ...
s, meteorite
A meteorite is a rock (geology), rock that originated in outer space and has fallen to the surface of a planet or Natural satellite, moon. When the original object enters the atmosphere, various factors such as friction, pressure, and chemical ...
s and lunar basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
. Studies have shown that zircon and baddeleyite can be recovered from some anorthositic rocks in Proterozoic
The Proterozoic ( ) is the third of the four geologic eons of Earth's history, spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8 Mya, and is the longest eon of Earth's geologic time scale. It is preceded by the Archean and followed by the Phanerozo ...
anorthosite complexes. Places where these Proterozoic anorthosite complexes can be found are: the Laramie Anorthosite Complex in Wyoming, the Nain and Grenville provinces of Canada, the Vico Volcanic Complex in Italy, and Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais () is one of the 27 federative units of Brazil, being the fourth largest state by area and the second largest in number of inhabitants with a population of 20,539,989 according to the 2022 Brazilian census, 2022 census. Located in ...
and Jacupiranga, São Paulo
São Paulo (; ; Portuguese for 'Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul') is the capital of the São Paulo (state), state of São Paulo, as well as the List of cities in Brazil by population, most populous city in Brazil, the List of largest cities in the ...
, Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
. Baddeleyite forms in igneous rocks low in silica, it can be found in rocks containing potassium feldspar and plagioclase. It has been observed in thin section
In optical mineralogy and petrography, a thin section (or petrographic thin section) is a thin slice of a rock or mineral sample, prepared in a laboratory, for use with a polarizing petrographic microscope, electron microscope and electron ...
that baddeleyite forms within plagioclase grains. Associated minerals include ilmenite
Ilmenite is a titanium-iron oxide mineral with the idealized formula . It is a weakly magnetic black or steel-gray solid. Ilmenite is the most important ore of titanium and the main source of titanium dioxide, which is used in paints, printi ...
, zirkelite, apatite
Apatite is a group of phosphate minerals, usually hydroxyapatite, fluorapatite and chlorapatite, with high concentrations of Hydroxide, OH−, Fluoride, F− and Chloride, Cl− ion, respectively, in the crystal. The formula of the admixture of ...
, magnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula . It is one of the iron oxide, oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetism, ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetization, magnetized to become a ...
, perovskite
Perovskite (pronunciation: ) is a calcium titanium oxide mineral composed of calcium titanate (chemical formula ). Its name is also applied to the class of compounds which have the same type of crystal structure as , known as the perovskite (stru ...
, fluorite
Fluorite (also called fluorspar) is the mineral form of calcium fluoride, CaF2. It belongs to the halide minerals. It crystallizes in isometric cubic habit, although octahedral and more complex isometric forms are not uncommon.
The Mohs scal ...
, nepheline
Nepheline, also called nephelite (), is a rock-forming mineral in the feldspathoid groupa silica-undersaturated aluminosilicate, Na3 K Al4 Si4 O16, that occurs in intrusive and volcanic rocks with low silica, and in their associated pegmatit ...
, pyrochlore
Pyrochlore () is a mineral group of the niobium end member of the pyrochlore supergroup. Pyrochlore is also a term for the crystal structure ''F''dm. The name is from the Greek , ''fire'', and , ''green'' because it typically turns green on ignit ...
and allanite
Allanite (also called orthite) is a sorosilicate group of minerals within the broader epidote group that contain a significant amount of rare-earth elements. The mineral occurs mainly in metamorphosed clay-rich sediments and felsic igneous rocks. ...
.
Because of their refractory nature and stability under diverse conditions, baddeleyite grains, along with zircon
Zircon () is a mineral belonging to the group of nesosilicates and is a source of the metal zirconium. Its chemical name is zirconium(IV) silicate, and its corresponding chemical formula is Zr SiO4. An empirical formula showing some of th ...
, are used for uranium-lead radiometric age determinations.

Structure
There has been some dispute in the structure of baddeleyite. Originally, the mineral was assigned to the 8-fold coordination by Naray Szabo. This structure was ruled out due to the inaccuracy of the data used to establish it. Baddeleyite has the group symmetry P21/c with four ZrO2 in theunit cell
In geometry, biology, mineralogy and solid state physics, a unit cell is a repeating unit formed by the vectors spanning the points of a lattice. Despite its suggestive name, the unit cell (unlike a unit vector
In mathematics, a unit vector i ...
. It has unit cell dimensions of:
a = 5.169 b = 5.232 c = 5.341 Å (all ± 0.008 Å), β = 99˚15ˊ ± 10ˊ.
The coordination number for ZrO2 has been found to be 7. The mineral has two types of separations. The first being the seven shortest Zr-O, ranging from 2.04 to 2.26 Å, and the second Zr-O separation is 3.77 Å. Because of this, the coordination of baddeleyite was determined to be sevenfold. Baddeleyite's structure is a combination of tetrahedrally coordinated oxide ions parallel to (100) with triangular coordinated oxide ions. This explains baddeleyite's tendency to twin along the (100) planes. It has been observed that baddeleyite without twinning is extremely rare.
Composition
Baddeleyite belongs to the oxide group, having a composition of ZrO2. Similar minerals belonging to the same group are the rutile group:rutile
Rutile is an oxide mineral composed of titanium dioxide (TiO2), the most common natural form of TiO2. Rarer polymorphs of TiO2 are known, including anatase, akaogiite, and brookite.
Rutile has one of the highest refractive indices at vis ...
(TiO2), pyrolusite
Pyrolusite is a mineral consisting essentially of manganese dioxide ( Mn O2) and is important as an ore of manganese.. It is a black, amorphous appearing mineral, often with a granular, fibrous, or columnar structure, sometimes forming reniform ...
(MnO2), cassiterite
Cassiterite is a tin oxide mineral, SnO2. It is generally opaque, but it is translucent in thin crystals. Its luster and multiple crystal faces produce a desirable gem. Cassiterite was the chief tin ore throughout ancient history and remains ...
(SnO2), uraninite
Uraninite, also known as pitchblende, is a radioactive, uranium-rich mineral and ore with a chemical composition that is largely UO2 but because of oxidation typically contains variable proportions of U3O8. Radioactive decay of the uranium c ...
(UO2) and thorianite
Thorianite is a rare thorium oxide mineral, ThO2. It was originally described by Ananda Coomaraswamy in 1904 as uraninite, but recognized as a new species by Wyndham R. Dunstan. It was so named by Dunstan on account of its high percentage of tho ...
(ThO2). Baddeleyite is chemically homogeneous, but it may contain impurities such as Ti, Hf, and Fe. Higher concentrations of Ti and Fe are restricted to mafic
A mafic mineral or rock is a silicate mineral or igneous rock rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Common mafic rocks include ...
-ultramafic rocks
Ultramafic rocks (also referred to as ultrabasic rocks, although the terms are not wholly equivalent) are igneous rock, igneous and metamorphic rock, meta-igneous rocks with a very low silica content (less than 45%), generally >18% magnesium oxid ...
.
Physical properties
Baddeleyite is black in color with a submetallic lustre. It has a 6.5 hardness, and a brownish-white streak. Baddeleyite can also be brown, brownish black, green, and greenish brown. Its streak is white, or brownish white. It has a distinct cleavage along and tends to twin along (100). It belongs to the monoclinic system and is part of the P21/c group.Origin of the name
It was named for Joseph Baddeley. The mineral was discovered in Rakwana,Ceylon
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
(now Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
). Baddeley was a superintendent of a railroad project in Rakwana. As recounted by J.J.H. Teall – director of the British Geological Survey in the early 1900s – baddeleyite was discovered consequent to the discovery of geikielite.
Baddeley sent specimens of several pebbles from the Rakwana railroad excavations to the Museum of Practical Geology in London, where a Mr. Pringle examined them and attempted to classify them.
Pringle was unable to assign the specimens to a known mineral species and submitted them to Teall. After analyzing the specimens, Teall concluded that the mineral was mainly composed of titanic acid and magnesia, with an incidental mixture of protoxide of iron. Geikielite has the composition of .
Teall and Pringle decided to name the new mineral ''geikielite'', naming it after Sir Archibald Geikie
Sir Archibald Geikie (28 December 1835 – November 1924) was a Scottish geologist and writer.
Early life
Geikie was born in Edinburgh in 1835, the eldest son of Isabella Thom and her husband James Stuart Geikie, a musician and music critic. ...
, then the Director General of the Geological Survey.
Baddeley sent more specimens to Teall, in order to provide an exemplary specimen for display at the Museum of Practical Geology. While trying to find the specimens, Teall noticed that one of them was different from the rest: This new mineral was black in color, with a submetallic lustre, and a hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to plastic deformation, such as an indentation (over an area) or a scratch (linear), induced mechanically either by Pressing (metalworking), pressing or abrasion ...
of 6.5 . After analyzing it, the odd mineral was determined to not be (geikielite), but instead . Teall proposed mineral name ''baddeleyite'', after Joseph Baddeley, to honor the man who brought the two new minerals to notice.
See also
*List of minerals
This is a list of minerals which have Wikipedia articles.
Minerals are distinguished by various chemical and physical properties. Differences in chemical composition and crystal structure distinguish the various ''species''. Within a mineral speci ...
*List of minerals named after people
This is a list of minerals named after people. The chemical composition of the mineral follows the name.
A
* Abelsonite: – American physicist Philip Hauge Abelson (1913–2004)
* Abswurmbachite: – German mineralogist Irmgard Abs-Wurmbac ...
References
External links
Minweb with ''chime'' structure
Early rocks to reveal their ages, BBC News
{{Authority control Zirconium minerals Oxide minerals Monoclinic minerals Minerals in space group 14