bacteriorhodopsin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bacteriorhodopsin (Bop) is a
 Bacteriorhodopsin is a 27'' '' kDa integral membrane protein usually found in two-dimensional crystalline patches known as "purple membrane", which can occupy almost 50% of the surface area of the archaeal cell. The repeating element of the hexagonal lattice is composed of three identical protein chains, each rotated by 120 degrees relative to the others. Each monomer has seven transmembrane alpha helices and an extracellular-facing, two-stranded
Bacteriorhodopsin is a 27'' '' kDa integral membrane protein usually found in two-dimensional crystalline patches known as "purple membrane", which can occupy almost 50% of the surface area of the archaeal cell. The repeating element of the hexagonal lattice is composed of three identical protein chains, each rotated by 120 degrees relative to the others. Each monomer has seven transmembrane alpha helices and an extracellular-facing, two-stranded
 The bacteriorhodopsin photocycle consists of nine distinct stages, starting from the ground or resting state, which is denoted 'bR'. The intermediates are identified by single letters and may be distinguished by their absorption spectra. The nine stages are:
: bR + photon → K L M1 M2 M2' N N' O bR
The bacteriorhodopsin photocycle consists of nine distinct stages, starting from the ground or resting state, which is denoted 'bR'. The intermediates are identified by single letters and may be distinguished by their absorption spectra. The nine stages are:
: bR + photon → K L M1 M2 M2' N N' O bR
File:Bacteriorhodopsin subunit 1X0S.gif, link=File:Bacteriorhodopsin subunit 1X0S large.gif, Bacteriorhodopsin single
RasTop
(Molecular Visualization Software).). One more small helix is light blue,
Bacteriorhodopsin: Molecule of the Month
by David Goodsell, RCSB Protein Data Bank
by Nicole Wagner and Jordan Greco {{Optogenetics 7TM receptors Photosynthesis Integral membrane proteins Archaea proteins
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
used by Archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
, most notably by Haloarchaea, a class
Class, Classes, or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used d ...
of the Euryarchaeota
Methanobacteriota is a phylum in the domain Archaea.
Taxonomy
The phylum ''Methanobacteriota'' was introduced to prokaryotic nomenclature in 2023. It contains following classes:
*Archaeoglobi Garrity & Holt (2002)
*Halobacteria Grant ''et al ...
. It acts as a proton pump; that is, it captures light energy and uses it to move proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an e ...
s across the membrane out of the cell. The resulting proton gradient is subsequently converted into chemical energy.
Function
Bacteriorhodopsin is a light-driven H+ ion transporter found in some Haloarchaea, most notably ''Halobacterium salinarum
''Halobacterium salinarum'', formerly known as ''Halobacterium cutirubrum'' or ''Halobacterium halobium'', is an extremely halophile, halophilic ocean, marine obligate aerobic archaeon. Despite its name, this is not a bacteria, bacterium, but a mem ...
'' (formerly known as syn. ''H. halobium''). The proton-motive force generated by the protein is used by ATP synthase to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP). By expressing Bacteriorhodopsin, the archaea cells are able to synthesise ATP in the absence of a carbon source.
Structure
 Bacteriorhodopsin is a 27'' '' kDa integral membrane protein usually found in two-dimensional crystalline patches known as "purple membrane", which can occupy almost 50% of the surface area of the archaeal cell. The repeating element of the hexagonal lattice is composed of three identical protein chains, each rotated by 120 degrees relative to the others. Each monomer has seven transmembrane alpha helices and an extracellular-facing, two-stranded
Bacteriorhodopsin is a 27'' '' kDa integral membrane protein usually found in two-dimensional crystalline patches known as "purple membrane", which can occupy almost 50% of the surface area of the archaeal cell. The repeating element of the hexagonal lattice is composed of three identical protein chains, each rotated by 120 degrees relative to the others. Each monomer has seven transmembrane alpha helices and an extracellular-facing, two-stranded beta sheet
The beta sheet (β-sheet, also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a gene ...
.
Bacteriorhodopsin is synthesized as a protein precursor
A protein precursor, also called a pro-protein or pro-peptide, is an inactive protein (or peptide) that can be turned into an active form by post-translational modification, such as breaking off a piece of the molecule or adding on another molecule ...
, known as bacterio-opsin, which is extensively modified after translation. The modifications are:
* Covalent conjugation of a retinal
Retinal (also known as retinaldehyde) is a polyene chromophore. Retinal, bound to proteins called opsins, is the chemical basis of visual phototransduction, the light-detection stage of visual perception (vision).
Some microorganisms use ret ...
molecule to residue Lys216, via a Schiff base, to create the retinylidene chromophore.
* Cleavage of the signal peptide
A signal peptide (sometimes referred to as signal sequence, targeting signal, localization signal, localization sequence, transit peptide, leader sequence or leader peptide) is a short peptide (usually 16–30 amino acids long) present at the ...
, the first 13 amino acids at the N-terminus, and the conversion of residue Gln14 to pyroglutamate
* Removal of residue Asp262 at the C-terminus
Spectral properties
Bacteriorhodopsin molecule is purple and is most efficient at absorbing green light (in the wavelength range 500-650 nm). In the native membrane, the protein has a maximum absorbance at 553 nm, however addition of detergent disrupts the trimeric form, leading a loss of exciton coupling between the chromophores, and the monomeric form consequently has an absorption maximum of 568 nm. Bacteriorhodopsin has a broad excitation spectrum. For a detection wavelength between 700 and 800 nm, it has an appreciable detected emission for excitation wavelengths between 470 nm and 650 nm (with a peak at 570 nm). When pumped at 633 nm, the emission spectrum has appreciable intensity between 650 nm and 850 nm.Mechanism
Photocycle overview
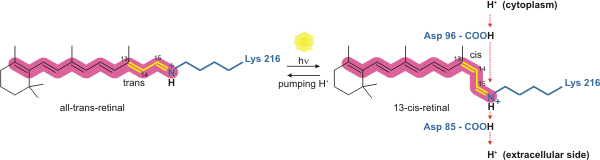
Bacteriorhodopsin is a light-driven proton pump. It is the retinal molecule that changes its isomerization state from all-''trans'' to 13-''cis'' when it absorbs aphoton
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can ...
. The surrounding protein responds to the change in the chromophore shape, by undergoing an ordered sequence of conformational change
In biochemistry, a conformational change is a change in the shape of a macromolecule, often induced by environmental factors.
A macromolecule is usually flexible and dynamic. Its shape can change in response to changes in its environment or othe ...
s (collectively known as the photocycle). The conformational changes alter the p''K''a values of conserved amino acids in the core of the protein, including Asp85, Asp96 and the Schiff base N atom (Lys216). These sequential changes in acid dissociation constant, result in the transfer of one proton from the intracellular side to the extracellular side of the membrane for each photon absorbed by the chromophore.
 The bacteriorhodopsin photocycle consists of nine distinct stages, starting from the ground or resting state, which is denoted 'bR'. The intermediates are identified by single letters and may be distinguished by their absorption spectra. The nine stages are:
: bR + photon → K L M1 M2 M2' N N' O bR
The bacteriorhodopsin photocycle consists of nine distinct stages, starting from the ground or resting state, which is denoted 'bR'. The intermediates are identified by single letters and may be distinguished by their absorption spectra. The nine stages are:
: bR + photon → K L M1 M2 M2' N N' O bR
Ground state + photon → K state → L state
Bacteriorhodopsin in the ground state absorbs a photon and the retinal changes isomerization from all-''trans'' 15-''anti'' to the strained 13-''cis'' 15-''anti'' in the K state. The isomerisation reaction is fast and occurs in less than 1 ps. The retinal adopts a less strained conformation to form the L intermediate.L state → M1 state
Asp85 accepts a proton from the Schiff base N atom. In the M1 intermediate, neither the Schiff base nor Asp85 are charged.M1 state → M2 state
The Schiff base rotates away from the extracellular side of the protein towards the cytoplasmic side, in preparation to accept a new proton.M2 state → M2' state
A proton is released from Glu204 and Glu194 to the extracellular medium.M2' state → N state
The retinal Schiff base accepts a proton from Asp96. In the N state, both Asp96 and the Schiff base are charged.N state → N' state
Asp96 accepts a proton from the cytoplasmic side of the membrane and becomes uncharged.N' state → O state
Retinal reisomerizes to the all-''trans'' state.O state → ground state
Asp85 transfers a proton to Glu194 and Glu204 on the extracellular face of the protein.Homologs and other similar proteins
Bacteriorhodopsin belongs to the microbial rhodopsin family. Its homologs include the archaerhodopsins, the light-driven chloride pump halorhodopsin (for which the crystal structure is also known), and some directly light-activated channels such as channelrhodopsin. Bacteriorhodopsin is similar tovertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
rhodopsin
Rhodopsin, also known as visual purple, is a protein encoded by the ''RHO'' gene and a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It is a light-sensitive receptor protein that triggers visual phototransduction in rod cells. Rhodopsin mediates dim ...
s, the pigment
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored sub ...
s that sense light in the retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
. Rhodopsins also contain retinal; however, the functions of rhodopsin and bacteriorhodopsin are different, and there is limited similarity in their amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
sequences. Both rhodopsin and bacteriorhodopsin belong to the 7TM receptor family of proteins, but rhodopsin is a G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related ...
and bacteriorhodopsin is not. In the first use of electron crystallography to obtain an atomic-level protein structure
Protein structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in an amino acid-chain molecule. Proteins are polymers specifically polypeptides formed from sequences of amino acids, which are the monomers of the polymer. A single amino acid ...
, the structure of bacteriorhodopsin was resolved in 1990. It was then used as a template to build models of G protein-coupled receptors before crystallographic structures were also available for these protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s. It has been excessively studied on both mica and glass substrates using Atomic force microscopy and Femtosecond crystallography.
All other phototrophic systems in bacteria, algae, and plants use chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words (, "pale green") and (, "leaf"). Chlorophyll allows plants to absorb energy ...
s or bacteriochlorophylls rather than bacteriorhodopsin. These also produce a proton gradient, but in a quite different and more indirect way involving an electron transfer chain consisting of several other proteins. Furthermore, chlorophylls are aided in capturing light energy by other pigments known as "antennas"; these are not present in bacteriorhodopsin-based systems. It is possible that phototrophy independently evolved at least twice, once in bacteria and once in archaea.
Gallery
monomer
A monomer ( ; ''mono-'', "one" + '' -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or two- or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
Chemis ...
with retinal
Retinal (also known as retinaldehyde) is a polyene chromophore. Retinal, bound to proteins called opsins, is the chemical basis of visual phototransduction, the light-detection stage of visual perception (vision).
Some microorganisms use ret ...
molecule between 7 vertical alpha helix
An alpha helix (or α-helix) is a sequence of amino acids in a protein that are twisted into a coil (a helix).
The alpha helix is the most common structural arrangement in the Protein secondary structure, secondary structure of proteins. It is al ...
es ( PDB ID: 1X0S Image created witRasTop
(Molecular Visualization Software).). One more small helix is light blue,
beta sheet
The beta sheet (β-sheet, also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a gene ...
yellow.
File:Bacteriorhodopsin trimer 1X0S.png, link=File:Bacteriorhodopsin trimer 1X0S large.gif, Bacteriorhodopsin trimer with one retinal
Retinal (also known as retinaldehyde) is a polyene chromophore. Retinal, bound to proteins called opsins, is the chemical basis of visual phototransduction, the light-detection stage of visual perception (vision).
Some microorganisms use ret ...
molecule in each subunit seen from the extracellular side EC ( PDB ID: 1X0S )
See also
* Microbial rhodopsin * Proteorhodopsin *Opsin
Animal opsins are G-protein-coupled receptors and a group of proteins made light-sensitive via a chromophore, typically retinal. When bound to retinal, opsins become retinylidene proteins, but are usually still called opsins regardless. Most pro ...
* Archaerhodopsin
* Purple Earth hypothesis
Literature
External links
Bacteriorhodopsin: Molecule of the Month
by David Goodsell, RCSB Protein Data Bank
by Nicole Wagner and Jordan Greco {{Optogenetics 7TM receptors Photosynthesis Integral membrane proteins Archaea proteins