Autrigones on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Autrigones were a pre-
The Autrigones were a pre-
 The Autrigones are mentioned for the first time on a document by
The Autrigones are mentioned for the first time on a document by
 Around the beginning of the 4th century BC the Autrigones migrated to the Peninsula and overrun the entire area corresponding today to the modern provinces of
Around the beginning of the 4th century BC the Autrigones migrated to the Peninsula and overrun the entire area corresponding today to the modern provinces of
Localización de algunas ciudades várdulas citadas por Mela y Ptolomeo
�. Euskomedia.
 The Autrigones were a pre-
The Autrigones were a pre-Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
tribe that settled in the north of the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
, in what today is the western Basque Country (western regions of Biscay
Biscay ( ; ; ), is a province of the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Autonomous Community, heir of the ancient Lordship of Biscay, lying on the south shore of the Bay of Biscay, eponymous bay. The capital and largest city is Bilb ...
and Álava
Álava () or Araba (), officially Araba/Álava, is a Provinces of Spain, province of Spain and a historical territory of the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Country, heir of the ancient Basque señoríos#Lords of Álava, Lordship ...
) and northern Burgos
Burgos () is a city in Spain located in the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is the capital and most populous municipality of the province of Burgos.
Burgos is situated in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, on the confluence of th ...
and the East of Cantabria, Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
. Their territory limited with the Cantabri
The Cantabri (, ''Kantabroi'') or Ancient Cantabrians were a pre-Roman people and large tribal federation that lived in the northern coastal region of ancient Iberia in the second half of the first millennium BC. These peoples and their territor ...
territory at west, the Caristii
The Caristii were a pre-Ancient Rome, Roman tribe settled in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, in what today are known as the historical territories of Biscay and Álava, in the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Country, northern Spa ...
at east, the Berones at the southeast and the Turmodigi at the south. It is discussed whether the Autrigones were Celts
The Celts ( , see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples ( ) were a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apoge ...
, theory supported by the existence of toponyms of Celtic origin, such as ''Uxama Barca'' and other with ''-briga'' endings and that eventually underwent a Basquisation along with other neighboring tribes such as the Caristii
The Caristii were a pre-Ancient Rome, Roman tribe settled in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, in what today are known as the historical territories of Biscay and Álava, in the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Country, northern Spa ...
and Varduli
The Varduli were a pre-Ancient Rome, Roman tribe settled in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, in what today is the western region of the Basque Country (greater region), Basque Country.
Their historical territory corresponds with the current ...
.
Location
Roman historians asPomponius Mela
Pomponius Mela, who wrote around AD 43, was the earliest known Roman geographer. He was born at the end of the 1st century BC in Tingentera (now Algeciras) and died AD 45.
His short work (''De situ orbis libri III.'') remained in use nea ...
and Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
located them in the northern region of present-day province of Burgos
The province of Burgos is a Provinces of Spain, province of northern Spain, in the northeastern part of the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Castile-Leon, Castile and León. It is bordered by the provinces of Palencia (p ...
. Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
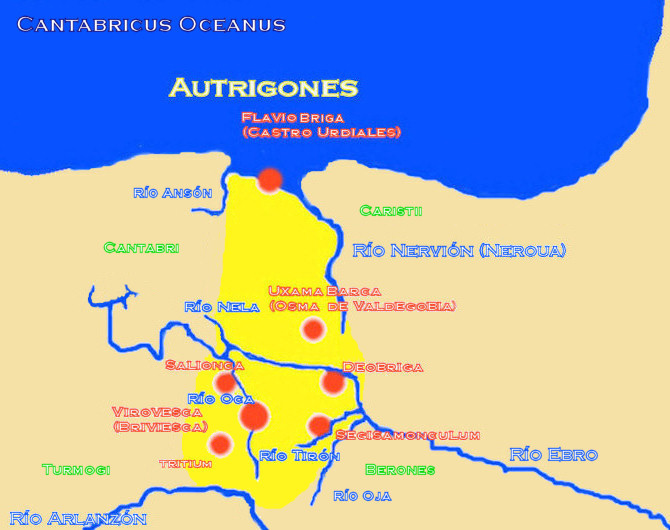
writes about the "ten states of the Autrigones" and says the only ones worth mentioning are ''Tritium Autrigonum'' ( Monasterio de Rodilla, Burgos) and ''Virovesca'' (possibly the present-day Briviesca, Burgos; Celtiberian-type mint: ''Uirouiaz'') in the valley of Oca River.
The other Autrigones' towns were ''Deobriga'' (near Miranda de Ebro, Burgos), ''Uxama Barca'' (Osma de Valdegobia; Celtiberian-type mint: ''Uarcaz''), ''Segisamunculum'' (Cerezo del Riotirón, Burgos), ''Antecuia'' (near Pancorbo, Burgos), ''Vindeleia'' ( Cubo de Bureba, Burgos), ''Salionca'' ( Poza de la Sal, Burgos) and the port of ''Portus Amanus''/'' Flaviobriga'' ( Castro Urdiales, Cantabria
Cantabria (, ; ) is an autonomous community and Provinces of Spain, province in northern Spain with Santander, Cantabria, Santander as its capital city. It is called a , a Nationalities and regions of Spain, historic community, in its current ...
).
Origins
 The Autrigones are mentioned for the first time on a document by
The Autrigones are mentioned for the first time on a document by Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
historian Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding i ...
in 76 BC, describing the actions of Quintus Sertorius
Quintus Sertorius ( – 73 or 72 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who led a large-scale rebellion against the Roman Senate on the Iberian Peninsula. Defying the regime of Sulla, Sertorius became the independent ruler of Hispania for m ...
in the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
. Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
mentions them in his book ''Geographica
The ''Geographica'' (, ''Geōgraphiká''; or , "Strabo's 17 Books on Geographical Topics") or ''Geography'', is an encyclopedia of geographical knowledge, consisting of 17 'books', written in Greek in the late 1st century BC, or early 1st cen ...
'', naming them ''allótrigones'', a word adapted from Greek meaning "strange people".
Based on the study of their toponyms - as also happens with the Caristii and Varduli - it is likely they were a Celtic tribe who eventually suffered a process of Basquisation. The known toponyms of the Autrigones are of Celtic origin, as ''Uxama Barca'' in present-day Álava
Álava () or Araba (), officially Araba/Álava, is a Provinces of Spain, province of Spain and a historical territory of the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Country, heir of the ancient Basque señoríos#Lords of Álava, Lordship ...
, and many others ending in ''-briga''. The toponyms of rivers, as the Nervión
Nervión (; ) is a river that runs through the town of Bilbao, Spain into the Cantabrian Sea (Bay of Biscay). Its lowermost course, downstream of its confluence with the Ibaizabal River, is known as the Estuary of Bilbao.
Geography
The riv ...
, the anthroponyms, the archeological remains, tools and weapons relate them culturally with the Celts, but with a clear differentiation of other close Celtic tribes, as the Celtiberians
The Celtiberians were a group of Celts and Celticized peoples inhabiting an area in the central-northeastern Iberian Peninsula during the final centuries BC. They were explicitly mentioned as being Celts by several classic authors (e.g. Strabo) ...
.
Culture
The Autrigones were culturally related to the earlyIron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
"Monte Bernorio- Miraveche" cultural group of northern Burgos
Burgos () is a city in Spain located in the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is the capital and most populous municipality of the province of Burgos.
Burgos is situated in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, on the confluence of th ...
and Palencia
Palencia () is a city of Spain located in the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is the capital and most populated municipality of the province of Palencia.
Located in the northwest of the Iberian Peninsula, in the northern half of ...
provinces. Additional archeological evidence indicates that by the 2nd Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
they came under the influence of the Celtiberians
The Celtiberians were a group of Celts and Celticized peoples inhabiting an area in the central-northeastern Iberian Peninsula during the final centuries BC. They were explicitly mentioned as being Celts by several classic authors (e.g. Strabo) ...
.
By the 1st century BC they were organized into a federation of autonomous mountain-top fortified towns ('' Civitates'') on the mountain ranges of the upper Ebro
The Ebro (Spanish and Basque ; , , ) is a river of the north and northeast of the Iberian Peninsula, in Spain. It rises in Cantabria and flows , almost entirely in an east-southeast direction. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea, forming a de ...
, protected by stout adobe
Adobe (from arabic: الطوب Attub ; ) is a building material made from earth and organic materials. is Spanish for mudbrick. In some English-speaking regions of Spanish heritage, such as the Southwestern United States, the term is use ...
walls of the " Numantine" type.
More archeological evidence have been found, emphasizing their celtiberian culture, such as the hospitality ''tesserae''. These consisted on a zoomorphic-shaped metal tablet with an inscription using a variant of the Northeastern Iberian script (also known as Celtiberian script), written in a form of celtiberian language
Celtiberian or Northeastern Hispano-Celtic is an extinct Indo-European language of the Celtic branch spoken by the Celtiberians in an area of the Iberian Peninsula between the headwaters of the Douro, Tagus, Júcar and Turia rivers and the ...
.
History
 Around the beginning of the 4th century BC the Autrigones migrated to the Peninsula and overrun the entire area corresponding today to the modern provinces of
Around the beginning of the 4th century BC the Autrigones migrated to the Peninsula and overrun the entire area corresponding today to the modern provinces of Cantabria
Cantabria (, ; ) is an autonomous community and Provinces of Spain, province in northern Spain with Santander, Cantabria, Santander as its capital city. It is called a , a Nationalities and regions of Spain, historic community, in its current ...
and Burgos
Burgos () is a city in Spain located in the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is the capital and most populous municipality of the province of Burgos.
Burgos is situated in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, on the confluence of th ...
, which eventually became known as ''Autrigonia'' or ''Austrigonia''. By the mid-4th century BC the Autrigones reached the Pisuerga
The Pisuerga is a river in northern Spain, the Duero's second largest tributary. It rises in the Cantabrian Mountains in the province of Palencia, autonomous region of Castile and León.
Its traditional source is called Fuente Cobre, but it has ...
valley where they established their capital ''Autraca'' or ''Austraca'', located at the banks of the river ''Autra'' ( Odra). They also gained an outlet to the sea by seizing from the Aquitani
The Aquitani were a tribe that lived in the region between the Pyrenees, the Atlantic Ocean, and the Garonne, in present-day southwestern France in the 1st century BC. The Romans dubbed this region '' Gallia Aquitania''. Classical authors suc ...
an-speaking Caristii
The Caristii were a pre-Ancient Rome, Roman tribe settled in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, in what today are known as the historical territories of Biscay and Álava, in the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Country, northern Spa ...
further east the coastal highland region between the rivers Asón and ''Neroua'' (Nervión
Nervión (; ) is a river that runs through the town of Bilbao, Spain into the Cantabrian Sea (Bay of Biscay). Its lowermost course, downstream of its confluence with the Ibaizabal River, is known as the Estuary of Bilbao.
Geography
The riv ...
), in the modern eastern Cantabria
Cantabria (, ; ) is an autonomous community and Provinces of Spain, province in northern Spain with Santander, Cantabria, Santander as its capital city. It is called a , a Nationalities and regions of Spain, historic community, in its current ...
, Vizcaya, and Álava
Álava () or Araba (), officially Araba/Álava, is a Provinces of Spain, province of Spain and a historical territory of the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Country, heir of the ancient Basque señoríos#Lords of Álava, Lordship ...
Basque provinces. However, the Autrigones’ hold to this vast territory was not meant to last; some time after 300 BC they were driven out from southern Autrigonia – the western Burgos
Burgos () is a city in Spain located in the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is the capital and most populous municipality of the province of Burgos.
Burgos is situated in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, on the confluence of th ...
region – by the Turmodigi allied with the Vaccei, who seized the Autrigones’ early capital Autraca. Thrust back to their lands on the mountain ranges of the upper Ebro
The Ebro (Spanish and Basque ; , , ) is a river of the north and northeast of the Iberian Peninsula, in Spain. It rises in Cantabria and flows , almost entirely in an east-southeast direction. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea, forming a de ...
north of the Arlanzón valley around the 3rd-2nd Centuries BC, the Autrigones allied themselves with the Berones and evolved into a tribal society similar to the peoples of the north-west. By the 1st century BC, they were organized into a federation of ten autonomous mountain-top fortified towns (''Civitates''), chiefly among them their new capital ''Virovesca'' in the Oca river valley.
Romanization
They seem to have taken no part in theCeltiberian War
The First Celtiberian War (181–179 BC) and Second Celtiberian War (154–151 BC) were two of the three major rebellions by the Celtiberians (a loose alliance of Celtic tribes living in east central Hispania, among which we can name the Pellendo ...
s though as traditional allies of the Berones helped the latter in fighting off the Roman general Sertorius
Quintus Sertorius ( – 73 or 72 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who led a large-scale rebellion against the Roman Senate on the Iberian Peninsula. Defying the regime of Sulla, Sertorius became the independent ruler of Hispania for m ...
' incursion into northern Celtiberia
The Celtiberians were a group of Celts and Celticized peoples inhabiting an area in the central-northeastern Iberian Peninsula during the final centuries BC. They were explicitly mentioned as being Celts by several classic authors (e.g. Strabo) ...
in 76 BC, and remained independent until the late 1st century BC, when the mounting pressure of Astures and Cantabri
The Cantabri (, ''Kantabroi'') or Ancient Cantabrians were a pre-Roman people and large tribal federation that lived in the northern coastal region of ancient Iberia in the second half of the first millennium BC. These peoples and their territor ...
raids finally forced them to seek an alliance with Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
. Despite being aggregated in the new Hispania Tarraconensis
Hispania Tarraconensis was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania. It encompassed much of the northern, eastern and central territories of modern Spain along with modern North Region, Portugal, northern Portugal. Southern Spain, the region now ...
province at the early 1st century AD, the Autrigones were only partially romanized, never became Christian and continued to provide the Roman Imperial army with auxiliary troops (''Auxilia'') up to the late Empire.
The early Middle Ages
The Autrigone people survived the overthrow of theRoman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
in Spain by the Germanic invasions of the late 4th century and briefly recreated their realm in parts of the current provinces of Burgos
Burgos () is a city in Spain located in the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is the capital and most populous municipality of the province of Burgos.
Burgos is situated in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, on the confluence of th ...
, Álava
Álava () or Araba (), officially Araba/Álava, is a Provinces of Spain, province of Spain and a historical territory of the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Country, heir of the ancient Basque señoríos#Lords of Álava, Lordship ...
, and Biscay
Biscay ( ; ; ), is a province of the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Autonomous Community, heir of the ancient Lordship of Biscay, lying on the south shore of the Bay of Biscay, eponymous bay. The capital and largest city is Bilb ...
which lasted for nearly two centuries, before being conquered by their Varduli
The Varduli were a pre-Ancient Rome, Roman tribe settled in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, in what today is the western region of the Basque Country (greater region), Basque Country.
Their historical territory corresponds with the current ...
neighbours and ultimately destroyed or absorbed by the Vascones in around AD 580.Localización de algunas ciudades várdulas citadas por Mela y Ptolomeo
�. Euskomedia.
See also
* Celtiberian script * Cantabrian Wars *Caristii
The Caristii were a pre-Ancient Rome, Roman tribe settled in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, in what today are known as the historical territories of Biscay and Álava, in the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Country, northern Spa ...
* Sertorian War
The Sertorian War was a civil war in the Roman Republic fought from 80 to 72 BC between two Roman factions, one led by Quintus Sertorius and another led by the senate as constituted in the aftermath of Sulla's civil war. The war was fough ...
s
* Varduli
The Varduli were a pre-Ancient Rome, Roman tribe settled in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, in what today is the western region of the Basque Country (greater region), Basque Country.
Their historical territory corresponds with the current ...
* Origin of the Basques
* Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula
This is a list of the pre- Roman people of the Iberian Peninsula (the Roman Hispania, i.e., modern Portugal, Spain and Andorra). Some closely fit the concept of a people, ethnic group or tribe. Others are confederations or even unions of tribe ...
References
Bibliography
* Ángel Montenegro ''et alii'', ''Historia de España 2 - colonizaciones y formación de los pueblos prerromanos (1200-218 a.C)'', Editorial Gredos, Madrid (1989) * Francisco Burillo Mozota, ''Los Celtíberos, etnias y estados'', Crítica, Grijalbo Mondadori, S.A., Barcelona (1998, revised edition 2007) *Further reading
*Daniel Varga, ''The Roman Wars in Spain: The Military Confrontation with Guerrilla Warfare'', Pen & Sword Military, Barnsley (2015) *Philip Matyszak, ''Sertorius and the struggle for Spain'', Pen & Sword Military, Barnsley (2013) *Ludwig Heinrich Dyck, ''The Roman Barbarian Wars: The Era of Roman Conquest'', Author Solutions (2011) ISBNs 1426981821, 9781426981821External links
*https://www.celtiberia.net *https://www.montebernorio.com {{Pre-Roman peoples in Spain Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula Celtic tribes of the Iberian Peninsula Ancient peoples of Spain Ancient history of the Basque Country