Automated Pipetting System on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
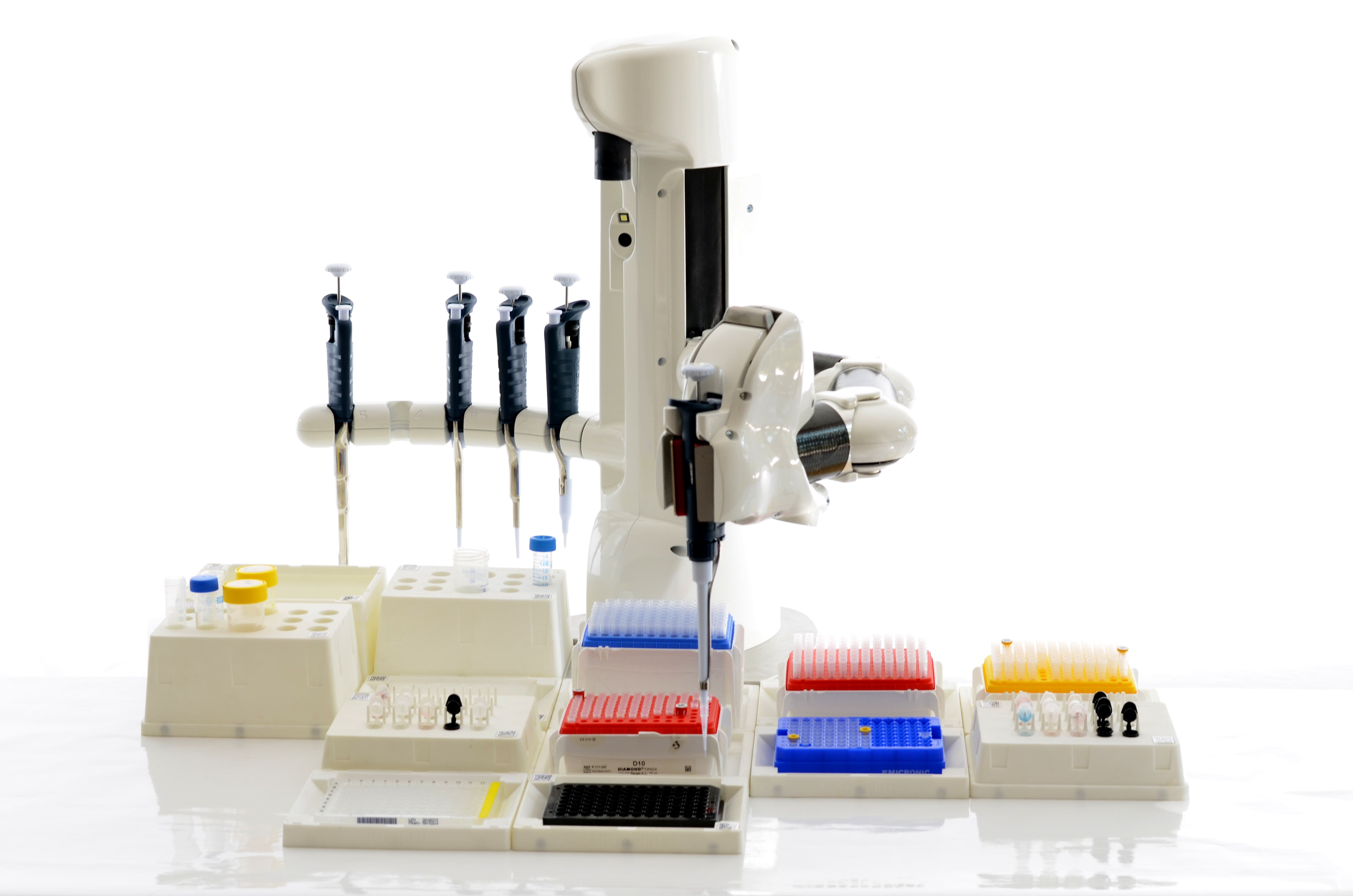
 An automated pipetting system is generally a device which performs programmed transfers of liquid between preselected groups of containers.
The word ''"pipetting"'' is referring to the laboratory manual tool called
An automated pipetting system is generally a device which performs programmed transfers of liquid between preselected groups of containers.
The word ''"pipetting"'' is referring to the laboratory manual tool called

 An automated pipetting system is generally a device which performs programmed transfers of liquid between preselected groups of containers.
The word ''"pipetting"'' is referring to the laboratory manual tool called
An automated pipetting system is generally a device which performs programmed transfers of liquid between preselected groups of containers.
The word ''"pipetting"'' is referring to the laboratory manual tool called pipette
A pipette (sometimes spelled as pipett) is a laboratory tool commonly used in chemistry, biology and medicine to transport a measured volume of liquid, often as a media dispenser. Pipettes come in several designs for various purposes with dif ...
, which is commonly used in molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and phys ...
, analytical chemistry
Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to separate, identify, and quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute the entire analysis or be combined with another method. Separati ...
, and medical tests, to transport a measured volume of liquid. Moreover, its performances are regulated by the International Standard ISO
ISO is the most common abbreviation for the International Organization for Standardization.
ISO or Iso may also refer to: Business and finance
* Iso (supermarket), a chain of Danish supermarkets incorporated into the SuperBest chain in 2007
* Is ...
8655-1:2002.
Automated pipetting systems are also commonly known as Liquid Handling Robots; nevertheless the latter definition is preferred whenever add-on modules are present (e.g. laboratory shaker
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physici ...
), while the former typically focuses on liquid transfer property.
One of main advantages of these devices is the ability to enhance the reproducibility
Reproducibility, also known as replicability and repeatability, is a major principle underpinning the scientific method. For the findings of a study to be reproducible means that results obtained by an experiment or an observational study or in a ...
and the throughput of laboratory experiments.
Components
The vast majority of automated pipetting systems have the following 'structural' components: * pipetting head *user interface
In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine f ...
* working area
* waste
Waste (or wastes) are unwanted or unusable materials. Waste is any substance discarded after primary use, or is worthless, defective and of no use. A by-product, by contrast is a joint product of relatively minor economic value. A waste pr ...
Pipetting head
The pipetting head is the mechanical component designed for liquid transfer. The majority of pipetting heads are based on aperistaltic pump
A peristaltic pump, also commonly known as a roller pump, is a type of positive displacement pump used for pumping a variety of fluids. The fluid is contained in a flexible tube fitted inside a circular pump casing. Most peristaltic pumps work thr ...
system, while some anthropomorphic systems directly use manual pipette
A pipette (sometimes spelled as pipett) is a laboratory tool commonly used in chemistry, biology and medicine to transport a measured volume of liquid, often as a media dispenser. Pipettes come in several designs for various purposes with dif ...
s.
A pipetting head can be multi-channel or single-channel: while the former has higher throughput, the latter has greater flexibility and reproducibility
Reproducibility, also known as replicability and repeatability, is a major principle underpinning the scientific method. For the findings of a study to be reproducible means that results obtained by an experiment or an observational study or in a ...
.
For accurate placement into the source and destination containers, the pipetting head is placed on an automated axis system, typically based on servo motors
A servomotor (or servo motor) is a rotary actuator or linear actuator that allows for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity and acceleration. It consists of a suitable motor coupled to a sensor for position feedback. It also r ...
or stepper motors
A stepper is a device used in the manufacture of integrated circuits (ICs) that is similar in operation to a slide projector or a photographic enlarger. ''Stepper'' is short for step-and-repeat camera. Steppers are an essential part of the com ...
.
User interface
The user interface allows communication between the user and the system via a PC or atouchscreen
A touchscreen or touch screen is the assembly of both an input ('touch panel') and output ('display') device. The touch panel is normally layered on the top of an electronic visual display of an information processing system. The display is ofte ...
. The most advanced user interfaces let users design their own experiments which are to be carried out on the system.
Working area
The working area is the zone where liquid dispensing takes place, and it is the area where the pipetting head can move. It contains holders that both hold the containers in which liquids are stored, and also allow the recognition of the position of the source and destination containers. The recognition of their position can be made 'statically' (off-line calibration of the position) or 'dynamically' (e.g. vision-controlled spatial localization).Waste
The waste container is a special container which stores disposable tips used by the system. It may also be used to throw away excess of liquid or washing buffer.Functionality
An automated pipetting system obtains a volume of liquid from a source by creatingsuction
Suction is the colloquial term to describe the air pressure differential between areas.
Removing air from a space results in a pressure differential. Suction pressure is therefore limited by external air pressure. Even a perfect vacuum cannot ...
, or ''aspirating'', and dispensing this liquid over the destination container. This is achieved by the pipetting head installed on the system.
Liquids are not in direct contact with the pipetting head, but they are held by a structure called the tip
Tip commonly refers to:
* Tip (gambling)
* Tip (gratuity)
* Tip (law enforcement)
* another term for Advice
Tip or TIP may also refer to:
Science and technology
* Tank phone, a device allowing infantry to communicate with the occupants of an armo ...
. Tips can be permanent structures or disposable conical pieces. Disposable tips, in general made from injection molded
Injection moulding (U.S. spelling: injection molding) is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for ...
plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptab ...
(typically polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene.
Polypropylene
belongs to the group of polyolefins an ...
), have the advantage of being discarded between liquid transfers thus removing any chance of cross contamination
Contamination is the presence of a constituent, impurity, or some other undesirable element that spoils, corrupts, infects, makes unfit, or makes inferior a material, physical body, natural environment, workplace, etc.
Types of contamination
Wi ...
. The choice of the most suitable tip mainly depends on the dispensing volume set on the pipetting head.
Some tips are equipped with filter to prevent aerosol entering the pipette, which can be a source of contamination or cause of deterioration of the pipette.
Critical parameters
There are some critical parameters which affect liquid transfer in automated pipetting system; the most common are listed below : *accuracy
Accuracy and precision are two measures of '' observational error''.
''Accuracy'' is how close a given set of measurements (observations or readings) are to their '' true value'', while ''precision'' is how close the measurements are to each ot ...
or systematic error, difference between the dispensed volume and the selected volume.
* repeatability
Repeatability or test–retest reliability is the closeness of the agreement between the results of successive measurements of the same measure, when carried out under the same conditions of measurement. In other words, the measurements are take ...
or random error, scatter of the dispensed volumes around the mean of the dispensed volumes.
* CV (coefficient of variation), which is a normalized measure of dispersion of a probability distribution.
* speed of the system in performing liquid transfer.
* volume range: currently the majority of devices operate in the microliter to milliliter range.
Curiosity
The first manual pipette was patented in 1950s by G.S. Riggs and the first automated analyzing apparatus less than ten years after.References
See also
*Liquid Handling Robot
A liquid handling robot is used to automate workflows in life science laboratories. It is a robot that dispenses a selected quantity of reagent, samples or other liquid to a designated container.
Introduction
Liquid handling plays a pivo ...
* Rubber bulb
Rubber bulbs are used in chemistry laboratories, by placing them on top of a glass or plastic tube. It serves as a vacuum source for filling reagents through a pipette or pasteur pipette and also help control the flow of liquid from the dropping b ...
{{Laboratory equipment
Molecular biology laboratory equipment