Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) is the term used for a
Image:Atypical ductal hyperplasia - low mag.jpg , Low mag.
Image:Atypical ductal hyperplasia - high mag.jpg , High mag.
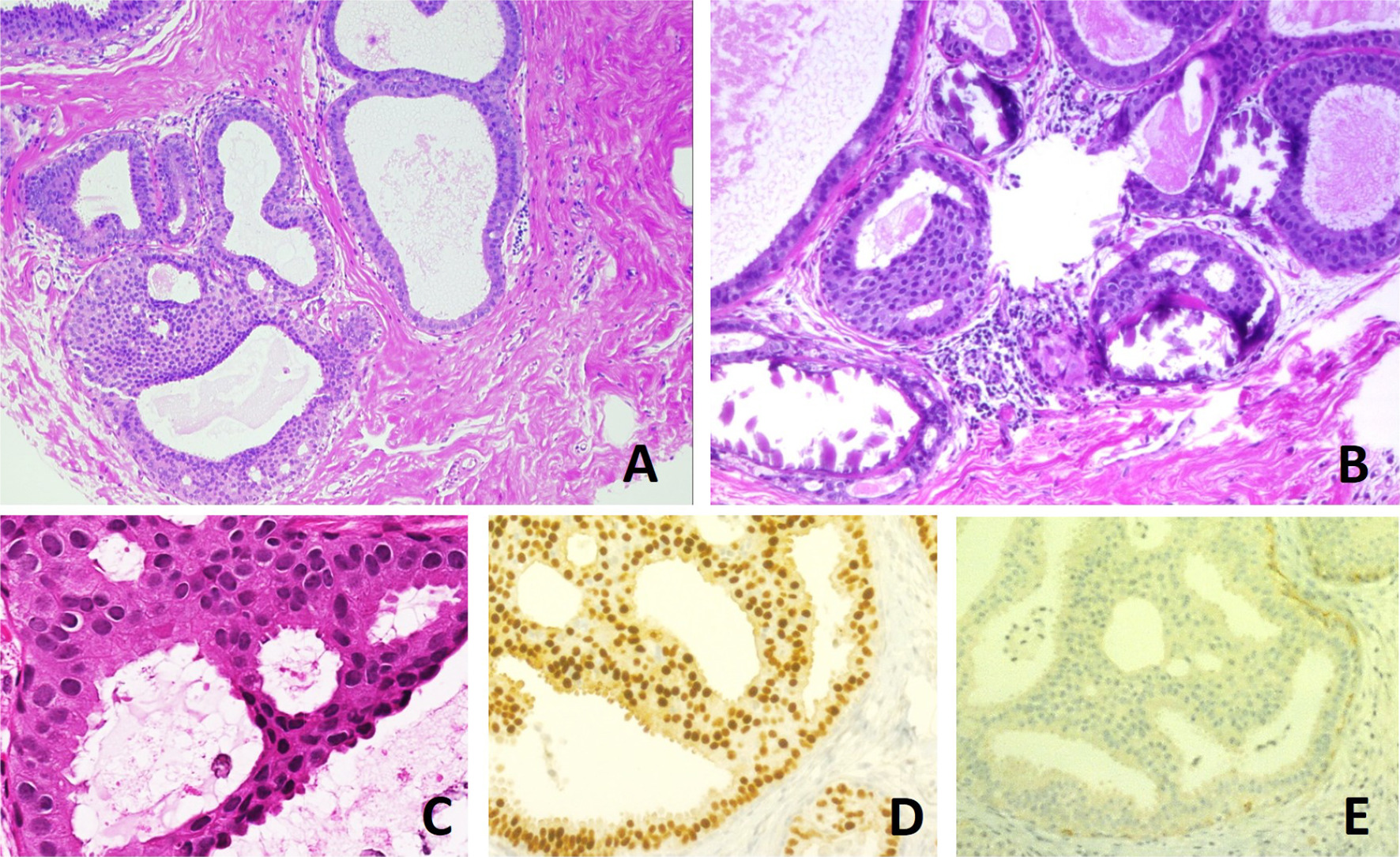 It is diagnosed based on tissue, e.g. a
It is diagnosed based on tissue, e.g. a
What is atypical ductal hyperplasia? (hopkinsmedicine.org)
{{Breast neoplasia Benign neoplasms Breast neoplasia
benign
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer.
A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malig ...
lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by injury or diseases. The term ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin meaning "injury". Lesions may occur in both plants and animals.
Types
There is no de ...
of the breast that indicates an increased risk of breast cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipp ...
.
The name of the entity is descriptive of the lesion; ADH is characterized by cellular proliferation (hyperplasia
Hyperplasia (from ancient Greek ὑπέρ ''huper'' 'over' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'), or hypergenesis, is an enlargement of an organ or tissue caused by an increase in the amount of Tissue (biology), organic tissue that results from ...
) within one or two breast ducts and (histomorphologic
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology that studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visi ...
) architectural abnormalities, i.e. the cells are arranged in an abnormal or atypical way, more so than usual ductal hyperplasia
Usual ductal hyperplasia (UDH) is a benign lesion of the breast wherein cells look very similar to normal. It is a spectrum of changes that can range from minimal stratification of cells to proliferations that are just short of atypical ductal hyp ...
.
In the context of a core (needle) biopsy, ADH is considered an indication for a breast lumpectomy, also known as a surgical (excisional) biopsy, to exclude the presence of breast cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipp ...
.
Signs and symptoms
ADH, generally, is asymptomatic. It usually comes tomedical attention
First aid is the first and immediate assistance given to any person with a medical emergency, with care provided to preserve life, prevent the condition from worsening, or to promote recovery until medical services arrive. First aid is gener ...
on a screening mammogram, as a non-specific suspicious abnormality that requires a biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, an interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiology, interventional cardiologist. The process involves the extraction of sampling (medicine), sample ...
.
Pathology
ADH, cytologically,architecturally
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings ...
and on a molecular
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, ...
basis, is identical to a low-grade ductal carcinoma in situ
Ductal carcinoma ''in situ'' (DCIS), also known as intraductal carcinoma, is a pre-cancerous or non-invasive cancerous lesion of the breast. DCIS is classified as Breast cancer classification#Stage, Stage 0. It rarely produces symptoms or a ...
(DCIS); however, it has a limited extent, i.e. is present in a very small amount (< 2 mm).
Relation to low-grade ductal carcinoma in situ
While the histopathologic features and molecular features of ADH are that of (low-grade) DCIS, its clinical behaviour, unlike low-grade DCIS, is substantially better; thus, the more aggressive treatment for DCIS is not justified.Diagnosis
 It is diagnosed based on tissue, e.g. a
It is diagnosed based on tissue, e.g. a biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, an interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiology, interventional cardiologist. The process involves the extraction of sampling (medicine), sample ...
, showing ductal hyperplasia.
There is no single definite cutoff that separates atypical ductal hyperplasia from ductal carcinoma in situ
Ductal carcinoma ''in situ'' (DCIS), also known as intraductal carcinoma, is a pre-cancerous or non-invasive cancerous lesion of the breast. DCIS is classified as Breast cancer classification#Stage, Stage 0. It rarely produces symptoms or a ...
, but the following are important distinctive features of atypical ductal hyperplasia, with suggested cutoffs:
*Size less than 2 mm.
*Not involving more than one duct.
*The atypical epithelial proliferation is admixed with a second population of proliferative cells without atypia.
*The proliferation completely involves the terminal ductal lobular unit(s), to a limited extent.
Treatment
ADH, if found on a surgical (excisional) biopsy of a mammographic abnormality, does not require any further treatment, only mammographic follow-up. If ADH is found on a core (needle) biopsy (a procedure which generally does not excise a suspicious mammographic abnormality), a surgical biopsy, i.e. a breast lumpectomy, to completely excise the abnormality and exclude breast cancer is the typical recommendation.Prognosis
Cancer risk for ADH on a core biopsy
The rate at which breast cancer (ductal carcinoma in situ
Ductal carcinoma ''in situ'' (DCIS), also known as intraductal carcinoma, is a pre-cancerous or non-invasive cancerous lesion of the breast. DCIS is classified as Breast cancer classification#Stage, Stage 0. It rarely produces symptoms or a ...
''or'' invasive mammary carcinoma (all breast cancer except DCIS and LCIS)) is found at the time of a surgical (excisional) biopsy, following the diagnosis of ADH on a core (needle) biopsy varies considerably from hospital-to-hospital (range 4-54%). In two large studies, the conversion of an ADH on core biopsy to breast cancer on surgical excision, known as "up-grading", is approximately 30%.
Cancer risk based on follow-up
Therelative risk
The relative risk (RR) or risk ratio is the ratio of the probability of an outcome in an exposed group to the probability of an outcome in an unexposed group. Together with risk difference and odds ratio, relative risk measures the association bet ...
of breast cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipp ...
based on a median follow-up of 8 years, in a case control study
Case or CASE may refer to:
Instances
* Instantiation (disambiguation), a realization of a concept, theme, or design
* Special case, an instance that differs in a certain way from others of the type
Containers
* Case (goods), a package of relate ...
of US registered nurse
A registered nurse (RN) is a healthcare professional who has graduated or successfully passed a nursing program from a recognized nursing school and met the requirements outlined by a country, state, province or similar government-authorized ...
s, is 3.7.
See also
*Ductal carcinoma in situ
Ductal carcinoma ''in situ'' (DCIS), also known as intraductal carcinoma, is a pre-cancerous or non-invasive cancerous lesion of the breast. DCIS is classified as Breast cancer classification#Stage, Stage 0. It rarely produces symptoms or a ...
*Breast cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipp ...
*Collagenous spherulosis
Collagenous spherulosis, or simple spherulosis, is a benign finding in breast pathology. It is almost always an incidental finding, though it is occasionally associated with calcifications, which may lead to a biopsy.
Significance
It is important ...
References
External links
What is atypical ductal hyperplasia? (hopkinsmedicine.org)
{{Breast neoplasia Benign neoplasms Breast neoplasia