Atrophic Glossitis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Glossitis can mean soreness of the tongue, or more usually inflammation with depapillation of the dorsal surface of the tongue (loss of the
 Depending upon what exact meaning of the word glossitis is implied, signs and symptoms might include:
* Smooth, shiny appearance of the tongue, caused by loss of lingual papillae.
* Tongue color changes, usually to a darker red color than the normal white-pink color of a healthy tongue.
* Tongue swelling.
* Difficulty with chewing,
Depending upon what exact meaning of the word glossitis is implied, signs and symptoms might include:
* Smooth, shiny appearance of the tongue, caused by loss of lingual papillae.
* Tongue color changes, usually to a darker red color than the normal white-pink color of a healthy tongue.
* Tongue swelling.
* Difficulty with chewing,

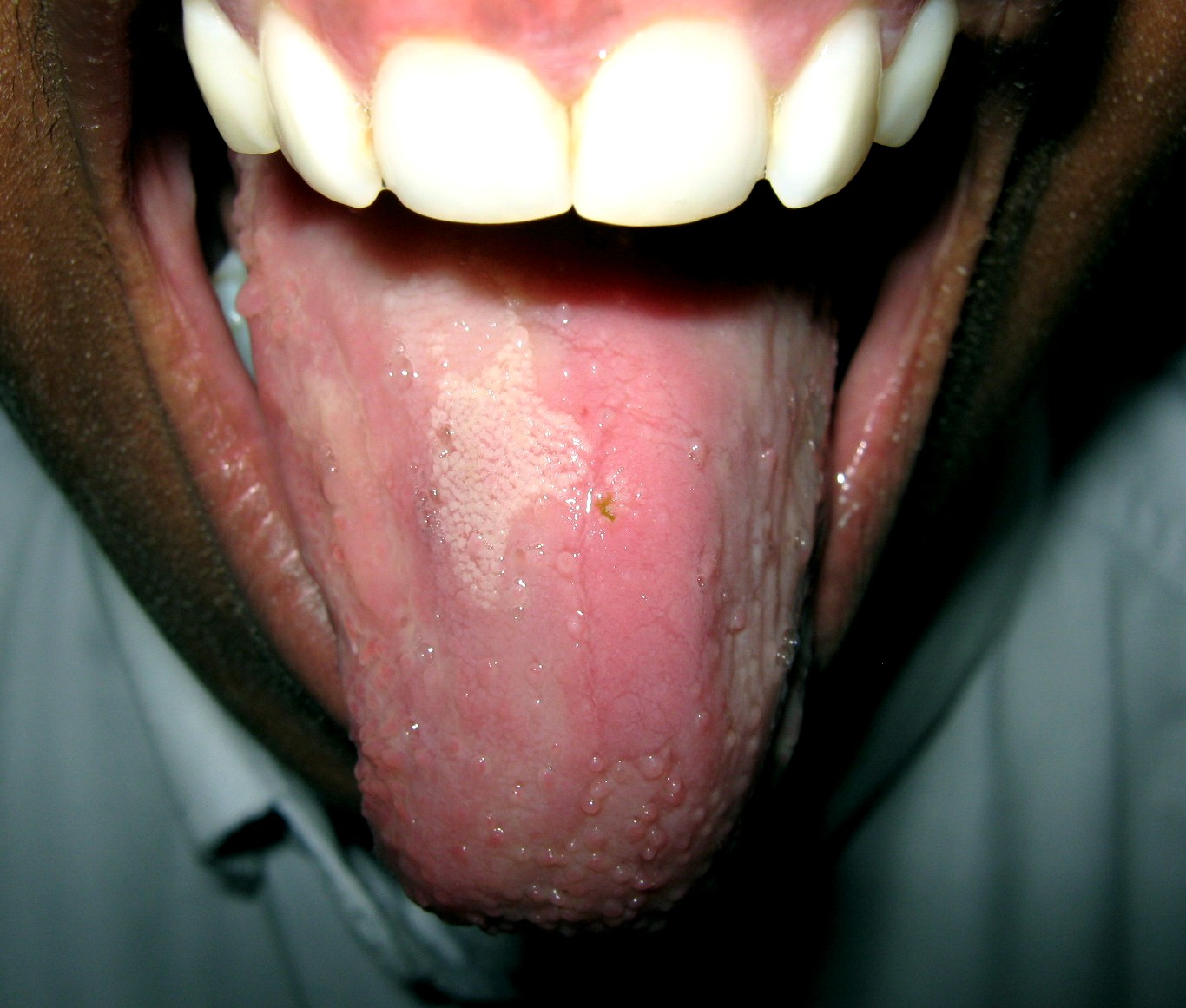
 Glossitis could be classified as a group of tongue diseases or
Glossitis could be classified as a group of tongue diseases or
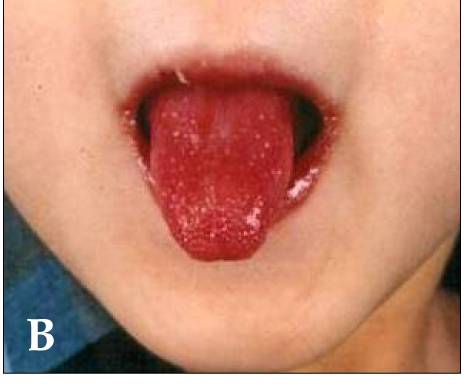 Strawberry tongue, or raspberry tongue, is glossitis which manifests with
Strawberry tongue, or raspberry tongue, is glossitis which manifests with
lingual papilla
Lingual papillae (: papilla, ) are small structures on the upper surface of the tongue that give it its characteristic rough texture. The four types of papillae on the human tongue have different structures and are accordingly classified as circum ...
e), leaving a smooth and erythema
Erythema (, ) is redness of the skin or mucous membranes, caused by hyperemia (increased blood flow) in superficial capillaries. It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation. Examples of erythema not associated with pathology inc ...
tous (reddened) surface, (sometimes specifically termed atrophic glossitis). In a wider sense, glossitis can mean inflammation of the tongue generally. Glossitis is often caused by nutritional deficiencies
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a Deficiency (medicine), deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and Vitamin deficiency, other nutrients whic ...
and may be painless or cause discomfort. Glossitis usually responds well to treatment if the cause is identified and corrected. Tongue soreness caused by glossitis is differentiated from burning mouth syndrome
Burning mouth syndrome (BMS) is a burning, tingling or scalding sensation in the mouth, lasting for at least four to six months, with no underlying known dental or medical cause. No related signs of disease are found in the mouth. People with ...
, where there is no identifiable change in the appearance of the tongue, and there are no identifiable causes.
Symptoms
 Depending upon what exact meaning of the word glossitis is implied, signs and symptoms might include:
* Smooth, shiny appearance of the tongue, caused by loss of lingual papillae.
* Tongue color changes, usually to a darker red color than the normal white-pink color of a healthy tongue.
* Tongue swelling.
* Difficulty with chewing,
Depending upon what exact meaning of the word glossitis is implied, signs and symptoms might include:
* Smooth, shiny appearance of the tongue, caused by loss of lingual papillae.
* Tongue color changes, usually to a darker red color than the normal white-pink color of a healthy tongue.
* Tongue swelling.
* Difficulty with chewing, swallowing
Swallowing, also called deglutition or inglutition in scientific and medical contexts, is a physical process of an animal's digestive tract (e.g. that of a human body) that allows for an ingested substance (typically food) to pass from the mou ...
, or speaking (either because of tongue soreness or tongue swelling).
* Burning sensation. Some use the term secondary burning mouth syndrome in cases where a detectable cause, such as glossitis, for an oral burning sensation.
Depending upon the underlying cause, there may be additional signs and symptoms such as pallor
Pallor is a pale color of the skin that can be caused by illness, emotional shock or stress, stimulant use, or anemia, and is the result of a reduced amount of oxyhaemoglobin and may also be visible as pallor of the conjunctivae of the eye ...
, oral ulceration and angular cheilitis
Cheilitis also called and known as chapped lips, is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the lips. The inflammation may include the perioral skin (the skin around the mouth), the vermilion border, or the Oral mucosa#Types, labial ...
.
Causes
Anemias
Iron-deficiency anemia
Iron-deficiency anemia is anemia caused by a iron deficiency, lack of iron. Anemia is defined as a decrease in the number of red blood cells or the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. When onset is slow, symptoms are often vague such as Fatigue ( ...
is mainly caused by blood loss, such as may occur during menses
Menstruation (also known as a period, among other colloquial terms) is the regular discharge of blood and Mucous membrane, mucosal tissue from the endometrium, inner lining of the uterus through the vagina. The menstrual cycle is characterized ...
or gastrointestinal hemorrhage. This often results in a depapilled, atrophic glossitis, giving the tongue a bald and shiny appearance, along with pallor
Pallor is a pale color of the skin that can be caused by illness, emotional shock or stress, stimulant use, or anemia, and is the result of a reduced amount of oxyhaemoglobin and may also be visible as pallor of the conjunctivae of the eye ...
(paleness) of the lips and other mucous membranes a tendency towards recurrent oral ulceration
A mouth ulcer (aphtha), or sometimes called a canker sore or salt blister, is an ulcer that occurs on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. Mouth ulcers are very common, occurring in association with many diseases and by many different mechanis ...
, and angular cheilitis
Angular cheilitis (AC) is inflammation of one or both corners of the mouth. Often the corners are red with skin breakdown and crusting. It can also be itchy or painful. The condition can last for days to years. Angular cheilitis is a type of ch ...
(crockings and inflammation at the corners of the lips). The appearance of the tongue in iron-deficiency anemia
Iron-deficiency anemia is anemia caused by a iron deficiency, lack of iron. Anemia is defined as a decrease in the number of red blood cells or the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. When onset is slow, symptoms are often vague such as Fatigue ( ...
has been described as diffuse or patchy atrophy with tenderness or burning. One cause of iron-deficiency anemia
Iron-deficiency anemia is anemia caused by a iron deficiency, lack of iron. Anemia is defined as a decrease in the number of red blood cells or the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. When onset is slow, symptoms are often vague such as Fatigue ( ...
is sideropenic dysphagia
Iron deficiency, or sideropenia, is the state in which a body lacks enough iron to supply its needs. Iron is present in all cells in the human body and has several vital functions, such as carrying oxygen to the tissues from the lungs as a key ...
(Plummer–Vinson syndrome
Plummer–Vinson syndrome (also known as Paterson–Kelly syndrome or Paterson–Brown-Kelly syndrome in the UK) is a rare disease characterized by dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), iron-deficiency anemia, atrophic glossitis (inflammation of the ...
, also called Paterson–Brown–Kelly syndrome) which is also characterized by esophageal web
Esophageal webs are thin membranes occurring anywhere along the esophagus.
Presentation
Its main symptoms are pain and difficulty in swallowing (dysphagia).
Esophageal webs are thin membranes of normal esophageal tissue consisting of mucosa an ...
bing and dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or l ...
.
Pernicious anemia
Pernicious anemia is a disease where not enough red blood cells are produced due to a deficiency of Vitamin B12, vitamin B12. Those affected often have a gradual onset. The most common initial symptoms are Fatigue, feeling tired and weak. Other ...
is usually caused by autoimmune
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an " autoimmune disease" ...
destruction of gastric
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical terms re ...
parietal cell
Parietal cells (also known as oxyntic cells) are epithelial cells in the stomach that secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl) and intrinsic factor. These cells are located in the gastric glands found in the lining of the fundus and body regions o ...
s. Parietal cells secrete intrinsic factor
Intrinsic factor (IF), also known as cobalamin binding intrinsic factor, or gastric intrinsic factor (GIF), is a glycoprotein produced by the parietal cells (in humans) or chief cells (in rodents) of the stomach. It is necessary for the absorp ...
which is required for the absorption of vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. One of eight B vitamins, it serves as a vital cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor in DNA synthesis and both fatty acid metabolism, fatty acid and amino a ...
. Vitamin B12 deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency, also known as cobalamin deficiency, is the medical condition in which the blood and tissue have a lower than normal level of Vitamin B12, vitamin B12. Symptoms can vary from none to severe. Mild deficiency may have fe ...
results in megaloblastic anemia
Megaloblastic anemia is a type of macrocytic anemia. An anemia is a red blood cell defect that can lead to an undersupply of oxygen. Megaloblastic anemia results from inhibition of DNA replication, DNA synthesis during red blood cell production. ...
and may present as atrophic glossitis (''Hunter's atrophic glossitis''). The appearance of the tongue in vitamin B12 deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency, also known as cobalamin deficiency, is the medical condition in which the blood and tissue have a lower than normal level of Vitamin B12, vitamin B12. Symptoms can vary from none to severe. Mild deficiency may have fe ...
is described as "beefy"
or "fiery red and sore". There may be linear or patchy red lesions.
Vitamin B deficiencies
Vitamin B1 deficiency
Thiamine, also known as thiamin and vitamin B1, is a vitamin – an essential micronutrient for humans and animals. It is found in food and commercially synthesized to be a dietary supplement or medication. Phosphorylated forms of thiam ...
(thiamine
Thiamine, also known as thiamin and vitamin B1, is a vitamin – an Nutrient#Micronutrients, essential micronutrient for humans and animals. It is found in food and commercially synthesized to be a dietary supplement or medication. Phosp ...
deficiency) can cause glossitis. Vitamin B2 deficiency
Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2, is a vitamin found in food and sold as a dietary supplement. It is essential to the formation of two major coenzymes, flavin mononucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide. These coenzymes are involved in ...
(ariboflavinosis) can cause glossitis, along with angular cheilitis
Angular cheilitis (AC) is inflammation of one or both corners of the mouth. Often the corners are red with skin breakdown and crusting. It can also be itchy or painful. The condition can last for days to years. Angular cheilitis is a type of ch ...
, cheilosis
Angular cheilitis (AC) is inflammation of one or both corners of the mouth. Often the corners are red with skin breakdown and crusting. It can also be itchy or painful. The condition can last for days to years. Angular cheilitis is a type of chei ...
, peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves. Damage to nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland function, and/or organ function depending on which nerve fibers are affected. Neuropa ...
and other signs and symptoms. The glossitis in vitamin B2 deficiency is described as magenta
Magenta () is a purple-red color. On color wheels of the RGB color model, RGB (additive) and subtractive color, CMY (subtractive) color models, it is located precisely midway between blue and red. It is one of the four colors of ink used in colo ...
. Vitamin B3 deficiency (pellagra) can cause glossitis. Vitamin B6 deficiency (pyridoxine
Pyridoxine (PN) is a form of vitamin B6 found commonly in food and used as a dietary supplement. As a supplement it is used to treat and prevent pyridoxine deficiency, sideroblastic anaemia, pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy, certain metaboli ...
deficiency) can cause glossitis, along with angular cheilitis, cheilosis, peripheral neuropathy and seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrhoeic dermatitis (also spelled seborrheic dermatitis in American English) is a long-term skin disorder. Symptoms include flaky, scaly, greasy, and occasionally itchy and inflamed skin. Areas of the skin rich in sebum, oil-producing gland ...
. Folate deficiency
Folate deficiency, also known as vitamin B9 deficiency, is a low level of folate and derivatives in the body. This may result in megaloblastic anemia in which red blood cells become abnormally large, and folate deficiency anemia is the term given ...
(vitamin B9 deficiency) can cause glossitis, along with macrocytic anemia, thrombocytopenia
In hematology, thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets (also known as thrombocytes) in the blood. Low levels of platelets in turn may lead to prolonged or excessive bleeding. It is the most common coag ...
, leukopenia
Leukopenia () is a decrease in the number of white blood cells (leukocytes). It places individuals at increased risk of infection as white blood cells are the body's primary defense against infections.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms may include:
* s ...
, diarrhea
Diarrhea (American English), also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa (British English), is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration d ...
, fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
and possibly neurological
Neurology (from , "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the nervous system, which comprises the brain, the s ...
signs. Apart from pernicious anemia discussed above, any other cause of vitamin B12 deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency, also known as cobalamin deficiency, is the medical condition in which the blood and tissue have a lower than normal level of Vitamin B12, vitamin B12. Symptoms can vary from none to severe. Mild deficiency may have fe ...
can cause atrophic glossitis (''Hunter's atrophic glossitis''), which tends to be painful, smooth and shiny.
Infections
Bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
l, viral
The word ''Viral'' means "relating to viruses" (small infectious agents).
It may also refer to:
Viral behavior, or virality
Memetic behavior likened that of a virus, for example:
* Viral marketing, the use of existing social networks to spre ...
or fungal
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the tradit ...
infections can cause glossitis. Chronic ''Candida
Candida, or Cándida (Spanish), may refer to:
Biology and medicine
* ''Candida'' (fungus), a genus of yeasts
** Candidiasis, an infection by ''Candida'' organisms
* Malvasia Candida, a variety of grape
Places
* Candida, Campania, a ''comu ...
'' infections of the tongue can cause an atrophic glossitis known as median rhomboid glossitis.
Syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms depend on the stage it presents: primary, secondary, latent syphilis, latent or tertiary. The prim ...
is now relatively rare, but the tertiary stage can cause diffuse glossitis and atrophy of lingual papillae, termed "syphilitic glossitis", "luetic glossitis" or "atrophic glossitis of tertiary syphilis". It is caused by ''Treponema pallidum
''Treponema pallidum'', formerly known as ''Spirochaeta pallida'', is a Microaerophile, microaerophilic, Gram-negative bacteria, gram-negative, spirochaete bacterium with subspecies that cause the diseases syphilis, bejel (also known as endemic ...
'' and is a sexually transmitted infection
A sexually transmitted infection (STI), also referred to as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and the older term venereal disease (VD), is an infection that is Transmission (medicine), spread by Human sexual activity, sexual activity, e ...
.
Other causes
Many conditions can cause glossitis viamalnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
or malabsorption
Malabsorption is a state arising from abnormality in absorption of food nutrients across the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Impairment can be of single or multiple nutrients depending on the abnormality. This may lead to malnutrition and a varie ...
, which creates the nutritional deficiencies described above, although other mechanisms may be involved in some of those conditions listed.
* Alcoholism
Alcoholism is the continued drinking of alcohol despite it causing problems. Some definitions require evidence of dependence and withdrawal. Problematic use of alcohol has been mentioned in the earliest historical records. The World He ...
* Sprue
A sprue may refer to:
*Sprue (manufacturing), a feature in molding and casting molds
*Coeliac disease, also known as sprue, a disease of the small intestine
*Tropical sprue
Tropical sprue is a malabsorption disease commonly found in tropical reg ...
(celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine. Patients develop intolerance to gluten, which is present in foods such as wheat, rye, spel ...
, or tropical sprue
Tropical sprue is a malabsorption disease commonly found in tropical regions, marked with abnormal flattening of the villi and inflammation of the lining of the small intestine. It differs significantly from coeliac sprue. It appears to be a mor ...
), secondary to nutritional deficiencies
* Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the ...
* Whipple disease
Whipple's disease is a rare systemic infectious disease caused by the bacterium '' Tropheryma whipplei''. First described by George Hoyt Whipple in 1907 and commonly considered as a gastrointestinal disorder, Whipple's disease primarily causes ...
* Glucagonoma
Glucagonoma is a very rare tumor of the alpha cells of the pancreas that results in the overproduction of the hormone glucagon. Typically associated with a rash called necrolytic migratory erythema, weight loss, and mild diabetes mellitus, most ...
syndrome
* Cowden disease
Cowden syndrome (also known as Cowden's disease) is an autosomal dominant inherited condition characterized by benign overgrowths called hamartomas as well as an increased lifetime risk of breast, thyroid, uterine, and other cancers. It is also k ...
* Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a preventable disease. It can ...
(AIDS)
* Carcinoid syndrome
Carcinoid syndrome is a paraneoplastic syndrome comprising the signs and symptoms that occur secondary to neuroendocrine tumors (formerly known as carcinoid tumors). The syndrome is caused by neuroendocrine tumors most often found in the gut ...
* Kwashiorkor amyloidosis
* Veganism
Veganism is the practice of abstaining from the use of animal products and the consumption of animal source foods, and an associated philosophy that rejects the commodity status of animals. A person who practices veganism is known as a vega ...
and other specialized diets, without B12 supplementation.
*Poor hydration and low saliva
Saliva (commonly referred as spit or drool) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which ...
in the mouth, which allows bacteria to grow more readily
*Mechanical irritation or injury from burns, rough edges of teeth or dental appliances, or other trauma
*Tongue piercing
A tongue piercing is a body piercing usually done directly through the center of the tongue. Since its decline in popularity around 2011, it has seen a recent upsurge making it now the second most popular piercing amongst young women aged 18– ...
Glossitis can be caused by the constant irritation by the ornament and by colonization of Candida albicans
''Candida albicans'' is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is usu ...
in site and on the ornament
*Exposure to irritants such as tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
, alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
, hot foods, or spice
In the culinary arts, a spice is any seed, fruit, root, Bark (botany), bark, or other plant substance in a form primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of pl ...
s
*Allergic reaction to toothpaste
Toothpaste is a paste or gel dentifrice that is used with a toothbrush to clean and maintain the aesthetics of Human tooth, teeth. Toothpaste is used to promote oral hygiene: it is an abrasive that aids in removing dental plaque and food from th ...
, mouthwash
Mouthwash, mouth rinse, oral rinse, or mouth bath is a liquid which is held in the mouth passively or swirled around the mouth by contraction of the perioral muscles and/or movement of the head, and may be gargled, where the head is tilted back ...
, breath fresheners, dyes in confectionery, plastic in dentures or retainers, or certain blood-pressure medications (ACE inhibitors
Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors) are a class of medication used primarily for the treatment of hypertension, high blood pressure and heart failure. This class of medicine works by causing relaxation of blood vessels as ...
)
*Administration of ganglion blockers
A ganglionic blocker (or ganglioplegic) is a type of medication that inhibits transmission between preganglionic and postganglionic neurons in the autonomic nervous system, often by acting as a nicotinic antagonist, nicotinic receptor antagonist. ...
(e.g., Tubocurarine
Tubocurarine (also known as ''d''-tubocurarine or DTC) is a toxic benzylisoquinoline alkaloid historically known for its use as an arrow poison. In the mid-1900s, it was used in conjunction with an anesthetic to provide skeletal muscle relaxat ...
, Mecamylamine
Mecamylamine (INN, BAN; or mecamylamine hydrochloride (USAN); brand names Inversine, Vecamyl) is a non-selective, non-competitive antagonist of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) that was introduced in the 1950s as an antihypertens ...
).
*Oral lichen planus
Lichen planus (LP) is a chronic inflammatory and autoimmune disease that affects the skin, nails, hair, and mucous membranes. It is not an actual lichen, but is named for its appearance. It is characterized by polygonal, flat-topped, violaceous p ...
, erythema multiforme
Erythema multiforme (EM) is an immune-mediated inflammatory skin condition associated with several viral infections, that appears with red patches evolving into target lesions, typically on both hands. It is typically associated with infection ...
, aphthous ulcer
Aphthous stomatitis, or recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS), commonly referred to as a canker sore or salt blister, is a common condition characterized by the repeated formation of benignity, benign and non-contagious disease, contagious mouth ...
, pemphigus
Pemphigus ( or ) is a rare group of blistering autoimmune diseases that affect the skin and mucous membranes.
The name is derived from the Greek root ''pemphix'', meaning "blister".
In pemphigus, autoantibody, autoantibodies form against de ...
vulgaris
*Heredity
*Albuterol
Salbutamol, also known as albuterol and sold under the brand name Ventolin among others, is a medication that opens up the medium and large airways in the lungs. It is a short-acting β2 adrenergic receptor agonist that causes relaxation of ...
(bronchodilator medicine)
A painful tongue may be an indication of an underlying serious medical condition and nearly always merits assessment by a physician
A physician, medical practitioner (British English), medical doctor, or simply doctor is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through the Medical education, study, Med ...
or dental surgeon
A dentist, also known as a dental doctor, dental physician, dental surgeon, is a health care professional who specializes in dentistry, the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. The dentist's supporting team aids in providi ...
.
Diagnosis
Classification

 Glossitis could be classified as a group of tongue diseases or
Glossitis could be classified as a group of tongue diseases or gastrointestinal disease
Gastrointestinal diseases (abbrev. GI diseases or GI illnesses) refer to diseases involving the Human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract, namely the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and rectum; and the accessory or ...
s. It may be primary, where there is no underlying cause, or secondary where it is a sign or symptom of another condition. It can be acute or chronic. Generally speaking, there are several clinical patterns of glossitis, some more common than others.
Atrophic glossitis
Atrophic glossitis, also known as bald tongue, smooth tongue, Hunter glossitis, Moeller glossitis, or Möller-Hunter glossitis, is a condition characterized by a smooth glossy tongue that is often tender/painful, caused by complete atrophy of the lingual papillae (depapillation). The dorsal tongue surface may be affected totally, or in patches, and may be associated with a burning sensation, pain and/or erythema. Atrophic glossitis is a non-specific finding, and has a great many causes, usually related toiron-deficiency anemia
Iron-deficiency anemia is anemia caused by a iron deficiency, lack of iron. Anemia is defined as a decrease in the number of red blood cells or the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. When onset is slow, symptoms are often vague such as Fatigue ( ...
, pernicious anemia
Pernicious anemia is a disease where not enough red blood cells are produced due to a deficiency of Vitamin B12, vitamin B12. Those affected often have a gradual onset. The most common initial symptoms are Fatigue, feeling tired and weak. Other ...
, B vitamin complex deficiencies, unrecognized and untreated celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine. Patients develop intolerance to gluten, which is present in foods such as wheat, rye, spel ...
(which often presents without gastrointestinal symptoms), or other factors such as xerostomia
Xerostomia, also known as dry mouth, is a subjective complaint of dryness in the mouth, which may be associated with a change in the composition of saliva, reduced salivary flow, or have no identifiable cause.
This symptom is very common and is o ...
(dry mouth). Although the terms Möller and Hunter glossitis were originally used to refer to specifically the glossitis that occurs in vitamin B12 deficiency secondary to pernicious anemia, they are now used as synonyms for atrophic glossitis generally. In this article, the term glossitis, unless otherwise specified, refers to atrophic glossitis.
Candidiasis may be a concurrent finding or an alternative cause of erythema, burning, and atrophy.
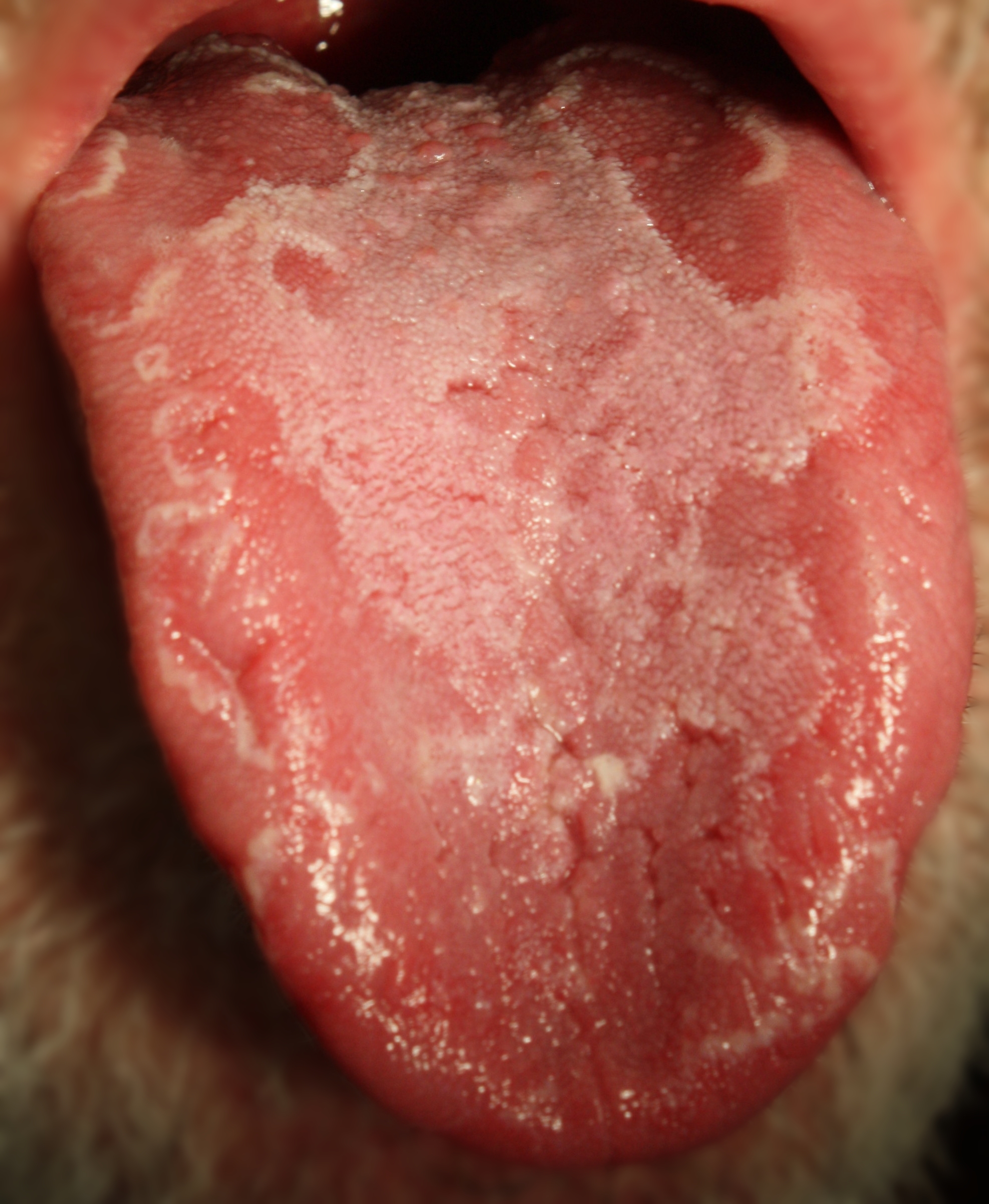
Median rhomboid glossitis
This condition is characterized by a persistent erythematous, rhomboidal depapillated lesion in the central area of the dorsum of the tongue, just in front of thecircumvallate papilla
Lingual papillae (: papilla, ) are small structures on the upper surface of the tongue that give it its characteristic rough texture. The four types of papillae on the human tongue have different structures and are accordingly classified as circum ...
e. Median rhomboid glossitis is a type of oral candidiasis
Oral candidiasis (Acute pseudomembranous candidiasis), also known among other names as oral thrush, is candidiasis that occurs in the mouth. That is, oral candidiasis is a mycosis (yeast/fungal infection) of ''Candida'' species on the mucous memb ...
, and rarely causes any symptoms. It is treated with antifungal medication
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as cry ...
. Predisposing factors include use of corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
sprays or inhalers or immunosuppression
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse react ...
.
Benign migratory glossitis
Geographic tongue, also termed benign migratory glossitis, is a common condition which usually affects the dorsal surface of the tongue. It is characterized by patches of depapillation and erythema bordered by a whitish peripheral zone. These patches give the tongue the appearance of a map, hence the name. Unlike glossitis due to nutritional deficiencies and anemia, the lesions of geographic tongue move around the tongue over time. This is because in geographic tongue, new areas of the tongue become involved with the condition whilst previously affected areas heal, giving the appearance of a moving lesion. The cause is unknown, and there is no curative treatment. Rarely are there any symptoms associated with the lesions, but occasionally a burning sensation may be present, which is exacerbated by eating hot, spicy or acidic foodstuffs. Some consider geographic tongue to be an early stage offissured tongue
Fissured tongue is a Benignity, benign condition characterized by deep grooves (fissure (anatomy), fissures) in the Dorsum (anatomy), dorsum of the tongue. Although these grooves may look unsettling, the condition is usually painless. Some individ ...
, since the two conditions often occur in combination.
Geometric glossitis
Geometric glossitis, also termed herpetic geometric glossitis, is a term used by some to refer to a chronic lesion associated withherpes simplex virus
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2) are two members of the Herpesviridae#Human herpesvirus types, human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce Viral disease, viral infections in the majority of humans. Both HSV-1 a ...
(HSV) type I infection, in which there is a deep fissure in the midline of the tongue, which gives off multiple branches. The lesion is usually very painful, and there may be erosions present in the depths of the fissures. Similar fissured lesions which are not associated with HSV, as may occur in fissured tongue, do not tend to be painful. The name comes from the geometric pattern of the fissures which are longitudinal, crossed or branched. It is described as occurring in immunocompromised
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromise, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affe ...
persons, e.g. who have leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia; pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and produce high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or '' ...
. However, the association between herpes simplex and geometric glossitis is disputed by some due to a lack of gold standard techniques for diagnosis of intraoral herpetic lesions, and the high prevalence of asymptomatic viral shedding in immunocompromised individuals. Treatment is with systemic aciclovir
Aciclovir, also known as acyclovir, is an antiviral medication. It is primarily used for the treatment of herpes simplex virus infections, chickenpox, and shingles. Other uses include the prevention of cytomegalovirus infections following tran ...
.
Strawberry tongue
 Strawberry tongue, or raspberry tongue, is glossitis which manifests with
Strawberry tongue, or raspberry tongue, is glossitis which manifests with hyperplastic
Hyperplasia (from ancient Greek ὑπέρ ''huper'' 'over' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'), or hypergenesis, is an enlargement of an organ or tissue caused by an increase in the amount of organic tissue that results from cell proliferatio ...
(enlarged) fungiform papilla
Lingual papillae (: papilla, ) are small structures on the upper surface of the tongue that give it its characteristic rough texture. The four types of papillae on the human tongue have different structures and are accordingly classified as circum ...
e, giving the appearance of a strawberry. White strawberry tongue is where there is a white coating on the tongue through which the hyperplastic fungiform papillae protrude. Red strawberry tongue is where the white coating is lost and a dark red, erythematous surface is revealed, interspaced with the hyperplastic fungiform papillae. White strawberry tongue is seen in early scarlet fever
Scarlet fever, also known as scarlatina, is an infectious disease caused by ''Streptococcus pyogenes'', a Group A streptococcus (GAS). It most commonly affects children between five and 15 years of age. The signs and symptoms include a sore ...
(a systemic infection of group A β- hemolytic streptococci), and red strawberry tongue occurs later, after 4–5 days. Strawberry tongue is also seen in Kawasaki disease
Kawasaki disease (also known as mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome) is a syndrome of unknown cause that results in a fever and mainly affects children under 5 years of age. It is a form of vasculitis, in which medium-sized blood vessels become in ...
(a vasculitic disorder primarily occurring in children under 5), and toxic shock syndrome
Toxic shock syndrome (TSS) is a condition caused by Exotoxin, bacterial toxins. Symptoms may include fever, rash, skin peeling, and low blood pressure. There may also be symptoms related to the specific underlying infection such as mastitis, ...
. It may mimic other types of glossitis or Vitamin B12 deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency, also known as cobalamin deficiency, is the medical condition in which the blood and tissue have a lower than normal level of Vitamin B12, vitamin B12. Symptoms can vary from none to severe. Mild deficiency may have fe ...
.
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation. Treatment usually does not require hospitalization unless tongue swelling is severe. Goodoral hygiene
Oral hygiene is the practice of keeping one's oral cavity clean and free of disease and other problems (e.g. bad breath) by regular brushing of the teeth (dental hygiene) and adopting good hygiene habits. It is important that oral hygiene be carr ...
is necessary, including thorough tooth brushing at least twice a day, and flossing at least daily. Corticosteroids such as prednisone may be given to reduce the inflammation of glossitis. For mild cases, topical applications (such as a prednisone mouth rinse that is not swallowed) may be recommended to avoid the side effects of swallowed or injected corticosteroids. Antibiotics, antifungal medications, or other antimicrobials may be prescribed if the cause of glossitis is an infection. Anemia and nutritional deficiencies (such as a deficiency in niacin, riboflavin
Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2, is a vitamin found in food and sold as a dietary supplement. It is essential to the formation of two major coenzymes, flavin mononucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide. These coenzymes are involved in ...
, iron, or Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a group of eight compounds related in molecular structure that includes four tocopherols and four tocotrienols. The tocopherols function as fat-soluble antioxidants which may help protect cell membranes from reactive oxygen speci ...
) must be treated, often by dietary changes or other supplements. Avoiding irritants (such as hot or spicy foods, alcohol, and tobacco) may minimize the discomfort.
In some cases, tongue swelling may threaten the airway, a medical emergency
A medical emergency is an acute injury or illness that poses an immediate risk to a person's life or long-term health, sometimes referred to as a situation risking "life or limb". These emergencies may require assistance from another, qualified ...
that needs immediate attention.
Epidemiology
One review reported overallprevalence
In epidemiology, prevalence is the proportion of a particular population found to be affected by a medical condition (typically a disease or a risk factor such as smoking or seatbelt use) at a specific time. It is derived by comparing the number o ...
ranges of 0.1–14.3% for geographic tongue, 1.3–9.0% for "atrophy tongue" (atrophic glossitis), and 0.0–3.35% for median rhomboid glossitis.
References
External links
{{Oral pathology Inflammations Tongue disorders Pain Conditions of the mucous membranes Oral mucosal pathology