Atlas Agena on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Atlas-Agena was an American
 Late in 1960, Lockheed introduced the uprated Agena B stage which was restartable and had longer propellant tanks for more burn time. It first flew on the Thor and did not make its maiden voyage on an Atlas for months, when Midas 3 launched on July 12, 1961.
The Atlas LV-3 Agena B was used between 1961 and 1965 for a variety of NASA and DoD programs, including Ranger,
Late in 1960, Lockheed introduced the uprated Agena B stage which was restartable and had longer propellant tanks for more burn time. It first flew on the Thor and did not make its maiden voyage on an Atlas for months, when Midas 3 launched on July 12, 1961.
The Atlas LV-3 Agena B was used between 1961 and 1965 for a variety of NASA and DoD programs, including Ranger,
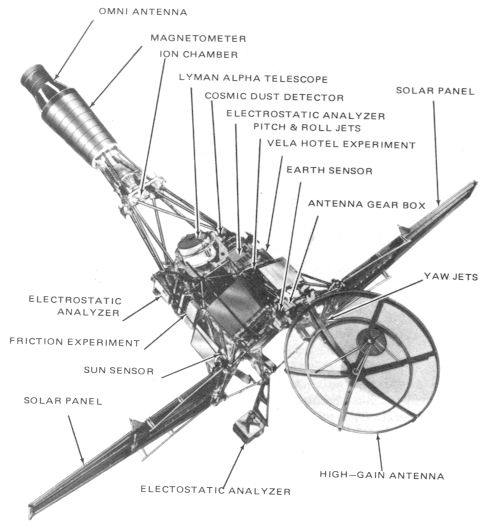 The Ranger spacecraft were designed to impact the Moon, returning photographs of the lunar surface until their destruction. The spacecraft was designed in three Blocks, all similar in appearance with a forward antenna and
The Ranger spacecraft were designed to impact the Moon, returning photographs of the lunar surface until their destruction. The spacecraft was designed in three Blocks, all similar in appearance with a forward antenna and
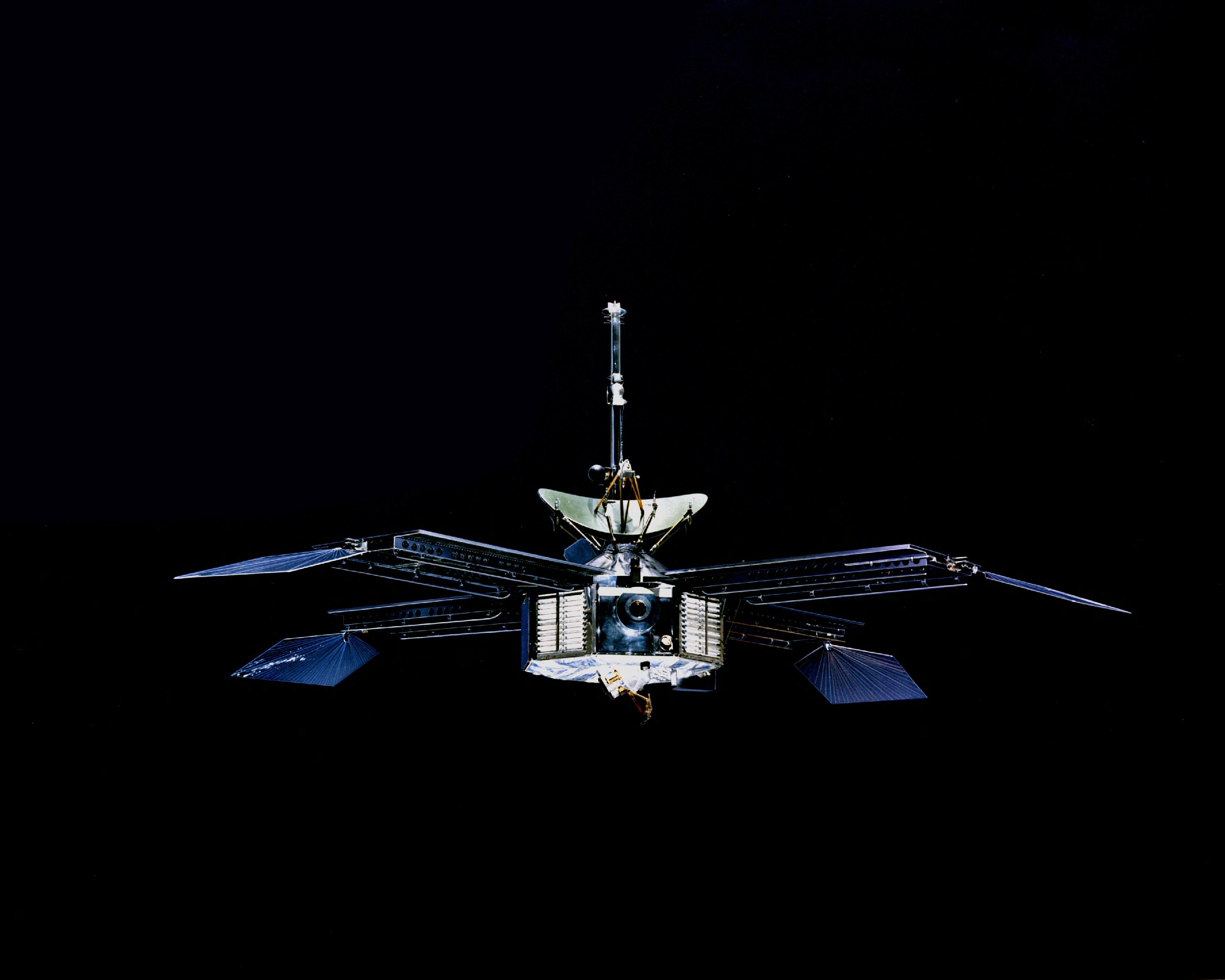 Mariner 3 and
Mariner 3 and
 The Agena rocket stage was used as the passive docking target for the Gemini crewed space program. After docking, the Agena could also be fired by the astronauts to raise the combined Gemini-Agena spacecraft into a higher orbit. The first attempt at such a docking mission was made for the Gemini 6 mission on October 25, 1965, but the Agena suffered an engine failure and did not reach orbit. This forced postponement and replanning of the Gemini 6A mission, which performed rendezvous with
The Agena rocket stage was used as the passive docking target for the Gemini crewed space program. After docking, the Agena could also be fired by the astronauts to raise the combined Gemini-Agena spacecraft into a higher orbit. The first attempt at such a docking mission was made for the Gemini 6 mission on October 25, 1965, but the Agena suffered an engine failure and did not reach orbit. This forced postponement and replanning of the Gemini 6A mission, which performed rendezvous with
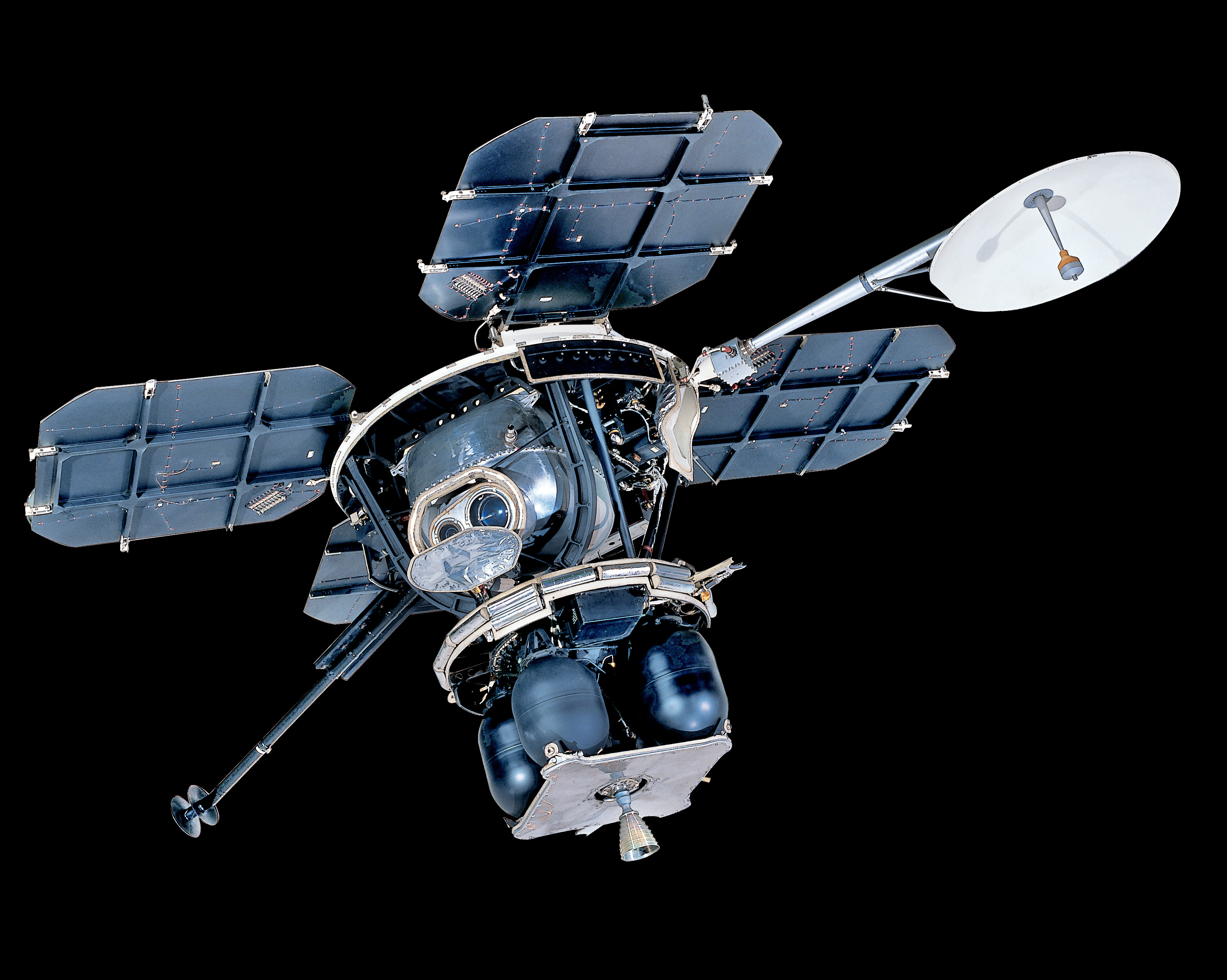 A series of five Lunar Orbiter spacecraft were launched from August 1966 through August 1967, to help select landing sites for the Apollo lunar landing program by mapping the Moon's surface. Each spacecraft weighed and was in diameter, minus the four extended solar panels. All launches were successful, and a total of 99 percent of the surface of the Moon (near and far side) was mapped with resolution as high as 3 ft 3 in (1 meter). Altogether the Orbiters returned 2180 high resolution and 882 medium resolution frames. The spacecraft also carried micrometeoroid sensors, which showed the average micro-meteoroid flux near the Moon to be two orders of magnitude greater than in interplanetary space, but slightly less than the near-Earth environment.
A series of five Lunar Orbiter spacecraft were launched from August 1966 through August 1967, to help select landing sites for the Apollo lunar landing program by mapping the Moon's surface. Each spacecraft weighed and was in diameter, minus the four extended solar panels. All launches were successful, and a total of 99 percent of the surface of the Moon (near and far side) was mapped with resolution as high as 3 ft 3 in (1 meter). Altogether the Orbiters returned 2180 high resolution and 882 medium resolution frames. The spacecraft also carried micrometeoroid sensors, which showed the average micro-meteoroid flux near the Moon to be two orders of magnitude greater than in interplanetary space, but slightly less than the near-Earth environment.
expendable launch system
An expendable launch system (or expendable launch vehicle/ELV) is a launch vehicle that can be launched only once, after which its components are destroyed during reentry or impact with Earth, or discarded in space. ELVs typically consist of s ...
derived from the SM-65 Atlas
The SM-65 Atlas was the first operational intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) developed by the United States and the first member of the Atlas rocket family. It was built for the U.S. Air Force by the Convair Division of General ...
missile. It was a member of the Atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of world map, maps of Earth or of a continent or region of Earth. Advances in astronomy have also resulted in atlases of the celestial sphere or of other planets.
Atlases have traditio ...
family of rockets, and was launched 109 times between 1960 and 1978. It was used to launch the first five Mariner
A sailor, seaman, mariner, or seafarer is a person who works aboard a watercraft as part of its crew, and may work in any one of a number of different fields that are related to the operation and maintenance of a ship. While the term ''sailor' ...
uncrewed probes to the planets Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
and Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
, and the Ranger and Lunar Orbiter uncrewed probes to the Moon. The upper stage was also used as an uncrewed orbital target vehicle for the Gemini crewed spacecraft to practice rendezvous and docking. However, the launch vehicle family was originally developed for the Air Force and most of its launches were classified DoD payloads.
The Atlas-Agena was a two-and-a-half-stage rocket, with a stage-and-a-half Atlas missile as the first stage, and an RM-81 Agena
The RM-81 Agena () was an American rocket upper stage and satellite bus which was developed by Lockheed Corporation initially for the canceled WS-117L reconnaissance satellite program. Following the division of WS-117L into SAMOS and Corona for i ...
second stage. Initially, Atlas D missiles, redesignated as the LV-3, were used as the first stage. These were later replaced by the standardized Atlas SLV-3, and its derivatives, the SLV-3A and B. The final Atlas-Agena launch used an Atlas E/F.
Launches were conducted from Launch Complexes 12, 13 and 14 at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida.
Headquartered at the nearby Patrick Space Force Base, the sta ...
, and Launch Complexes 1 and 2 at Point Arguello (now SLC-3 and 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base
Vandenberg may refer to:
* Vandenberg (surname), including a list of people with the name
* USNS ''General Hoyt S. Vandenberg'' (T-AGM-10), transport ship in the United States Navy, sank as an artificial reef in Key West, Florida
* Vandenberg S ...
).
Variants
Atlas LV-3 Agena-A
The earliest Agena variant was the Agena A in 1959–60, which did not have restart capability, mostly flown onThor-Agena
Thor-Agena was a series of orbital launch vehicles. The launch vehicles used the Douglas Aircraft Company, Douglas-built Thor (rocket family), Thor first Multistage rocket, stage and the Lockheed Corporation, Lockheed-built RM-81 Agena, Agena ...
boosters for the Discoverer program.
The early Atlas LV3 Agena A variant was flown four times for the Midas and Samos programs (Midas
Midas (; ) was a king of Phrygia with whom many myths became associated, as well as two later members of the Phrygian royal house.
His father was Gordias, and his mother was Cybele. The most famous King Midas is popularly remembered in Greek m ...
1, Midas 2, Samos
Samos (, also ; , ) is a Greek island in the eastern Aegean Sea, south of Chios, north of Patmos and the Dodecanese archipelago, and off the coast of western Turkey, from which it is separated by the Mycale Strait. It is also a separate reg ...
1, and Samos 2), with two failures.
Atlas LV-3 Agena-B
Mariner
A sailor, seaman, mariner, or seafarer is a person who works aboard a watercraft as part of its crew, and may work in any one of a number of different fields that are related to the operation and maintenance of a ship. While the term ''sailor' ...
, Samos, and Midas but proved a unreliable, with only 21 successes in 28 flights.
In late 1962, after Ranger 5
Ranger 5 was a spacecraft of the Ranger program designed to transmit pictures of the lunar surface to Earth stations during a period of 10 minutes of flight prior to impacting on the Moon, to rough-land a seismometer capsule on the Moon, to colle ...
suffered a booster malfunction, albeit a minor one that ground controllers were able to work around, NASA convened a review board which undertook a wholesale reevaluation of the Atlas-Agena as a launch vehicle. The board found that quality control and checkout procedures were poor, and that this situation was exacerbated by the several dozen configurations of the booster, as each individual DoD and NASA program necessitated custom modifications to the Atlas and Agena, and the latter also differed in its Atlas and Thor variants. The board recommended improved quality control, better hardware, and also establishing one standardized launch vehicle for all space programs.
Atlas LV-3 / SLV-3 / SLV-3A / SLV-3B / E/F Agena-D
The result was the Atlas LV-3 Agena D, a standardized version of the Atlas D core and Agena B which would be the same on every launch (at least as far as the Atlas was concerned, Agena Ds often still had customized setups, especially for DoD payloads). The Agena D first flew in July 1963, starting a series of 15 successful launches for NASA and Air Force programs, including Ranger, Mariner, Midas, and Gambit. The Atlas SLV-3 Agena D first flew in August 1964. Forty-seven Atlas SLV-3 Agena D boosters were flown over the following years, mostly for theKH-7 Gambit
BYEMAN codenamed GAMBIT, the KH-7 (Air Force Program 206) was a reconnaissance satellite used by the United States from July 1963 to June 1967. Like the older Corona (satellite), CORONA system, it acquired imagery intelligence by taking photog ...
and Vela programs, and also for a few NASA missions like Mariner. +
The Atlas SLV-3B Agena-D was a specific variant used to launch the first OAO satellite in 1966.
Atlas SLV-3 Agena-B
The Atlas SLV-3 Agena-B was a specific variant used to launch the OGO-3 satellite in 1966.The Atlas SLV-3A Agena-D was a variant with a extended tank, for twelve launches including OGO-5 and Canyon/
Rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture (geology), texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained matri ...
SIGINT
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is the act and field of intelligence-gathering by interception of ''signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly u ...
satellites, between 1968 and 1978.
Atlas E/F Agena D
The last Atlas-Agena was flown in 1978 to launchSEASAT
Seasat was the first Earth-orbiting satellite designed for remote sensing of the Earth's oceans and had on board one of the first spaceborne synthetic-aperture radar (SAR). The mission was designed to demonstrate the feasibility of global sate ...
, on a repurposed Atlas F
The SM-65F Atlas, or Atlas-F, was the final operational variant of the Atlas missile, only differing from the Atlas E in the launch facility and guidance package used. It first flew on 8 August 1961, and was deployed as an operational ICBM between ...
missile designated Atlas E/F Agena D.
Destruct system
Included on Atlas-Agena vehicles was the Inadvertent Separation Destruct System (ISDS) to destroy the Agena in the event that it separated prematurely from the Atlas, a situation that could be caused by a booster hard-over or if the Atlas self-destructed in flight. The ISDS charges were mounted on the adapter section between the two vehicles and would activate if a series of tripwires were broken. During the coasting period between staging, the ISDS charges were disabled. It was also wired to the Atlas's own FTS (Flight Termination System) and would be activated if a destruct command was sent to the Atlas. The Agena could also have a separate FTS for use after the Atlas portion of the launch, although NASA planetary probes omitted them for weight-saving reasons and due to the flight trajectory used, which meant that destruct of the Agena was no longer possible following staging. The Gemini-Agena Target Vehicle had a specially modified Range Safety destruct system designed to fire slugs into the propellant tanks rather than the conventional method of rupturing them externally, since an inadvertent activation in orbit could endanger the Gemini astronauts. The very first Atlas-Agena flight, Midas 1 in February 1960, failed when the unproven ISDS system mistakenly activated at staging, rupturing the Atlas's LOX tank and causing the breakup of the Agena. The ISDS system was redesigned afterwards and this failure mode did not repeat itself. Two Atlas-Agena vehicles (Mariner 1 and Canyon 4) were intentionally destroyed when the Atlas went off-course and two others (MIDAS 6 and MIDAS 8) broke up in flight resulting in activation of the ISDS and destruct of the Agena.Production launches
Ranger
 The Ranger spacecraft were designed to impact the Moon, returning photographs of the lunar surface until their destruction. The spacecraft was designed in three Blocks, all similar in appearance with a forward antenna and
The Ranger spacecraft were designed to impact the Moon, returning photographs of the lunar surface until their destruction. The spacecraft was designed in three Blocks, all similar in appearance with a forward antenna and magnetometer
A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Different types of magnetometers measure the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. A compass is one such device, ...
, supported by a boom, with more sensors and two solar panels and a dish antenna mounted at the base. The first two Block I spacecraft, Ranger 1 and Ranger 2, were launched on August 23 and November 18, 1961, not to the Moon, but in intended high Earth orbits to test the Atlas-Agena and spacecraft capabilities. However, the Agena malfunctioned on both flights and left the probes trapped in a useless low Earth orbit from which they soon decayed.
The Block II missions, Ranger 3, Ranger 4
Ranger 4 was a spacecraft of the Ranger program, launched in 1962. It was designed to transmit pictures of the lunar surface to Earth stations during a period of 10 minutes of flight prior to crashing upon the Moon, to rough-land a seismometer ca ...
, and Ranger 5
Ranger 5 was a spacecraft of the Ranger program designed to transmit pictures of the lunar surface to Earth stations during a period of 10 minutes of flight prior to impacting on the Moon, to rough-land a seismometer capsule on the Moon, to colle ...
, were launched away from Earth in January, April, and October 1962, but all three failed due to either malfunctions of the probe or launch vehicle difficulties. Ranger 3 missed the Moon entirely. Ranger 4's solar panels failed to deploy, and the navigation system failed, sending the probe to impact the lunar far side without returning any pictures or data. Ranger 5 suffered an unknown failure which deprived it of power, and it missed the Moon by .
Ranger 6
Ranger 6 was a lunar probe in the NASA Ranger program, a series of robotic spacecraft of the early and mid-1960s to obtain close-up images of the Moon's surface. It was launched on January 30, 1964 and was designed to transmit high-resolution pho ...
, launched January 30, 1964, successfully impacted the Moon but its cameras failed to return pictures. The last three Rangers were finally successful: Ranger 7
Ranger 7 was the first NASA space probe to successfully transmit close-up images of the lunar surface back to Earth. It was also the first completely successful flight of the Ranger program. Launched on July 28, 1964, Ranger 7 was designed to a ...
in July 1964, Ranger 8
Ranger 8 was a lunar probe in the Ranger program, a robotic spacecraft series launched by NASA in the early-to-mid-1960s to obtain the first close-up images of the Moon's surface. These pictures helped select landing sites for Apollo missions and ...
in February 1965, and Ranger 9
Ranger 9 was a Lunar probe, launched in 1965 by NASA. It was designed to achieve a lunar impact trajectory and to transmit high-resolution photographs of the lunar surface during the final minutes of flight up to impact. The spacecraft carried s ...
in March 1965.
Mariner
The Mariner spacecraft were built byNASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
's Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a Federally funded research and development centers, federally funded research and development center (FFRDC) in La Cañada Flintridge, California, Crescenta Valley, United States. Founded in 1936 by Cali ...
. Mariner 1
Mariner 1, built to conduct the first American planetary flyby of Venus, was the first spacecraft of NASA's interplanetary Mariner program. Developed by Jet Propulsion Laboratory, and originally planned to be a purpose-built probe launched summ ...
and Mariner 2
Mariner 2 (Mariner-Venus 1962), an American space probe to Venus, was the first robotic space probe to report successfully from a planetary encounter. The first successful spacecraft in the NASA Mariner program, it was a simplified version of t ...
were twins, launched on July 22 and August 27, 1962, to fly by the planet Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
. The first two craft used the same spacecraft bus
A satellite bus (or spacecraft bus) is the main body and structural component of a satellite or spacecraft, in which the payload and all scientific instruments are held.
Bus-derived satellites are less customized than specially-produced satelli ...
as the Block I Rangers, each weighing and instrumented to perform radiometric temperature measurements of the planet, and to measure interplanetary magnetic fields and particles.
Mariner 1's Atlas-Agena malfunctioned and went off course, requiring its destruction approximately 5 minutes after liftoff. Mariner 2 successfully made the 3½-month flight, becoming the first spacecraft to fly by another planet. It carried microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300&n ...
and infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
radiometers, and sensors for cosmic dust, solar plasma and high-energy radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
, and magnetic field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
s.
 Mariner 3 and
Mariner 3 and Mariner 4
Mariner 4 (Mariner C-3, together with Mariner 3 known as Mariner-Mars 1964) was the Mariner program, fourth in a series of spacecraft intended for planetary exploration in a flyby mode. It was designed to conduct closeup scientific observations ...
used a redesigned spacecraft bus weighing , and were launched on November 5 and November 28, 1964, to fly by the planet Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
. Mariner 3 failed after a successful launch when its payload shroud failed to open. These Mariners carried cameras, and Mariner 4 successfully returned pictures of Mars as it flew by.
The Mariner 5
Mariner 5 (Mariner V or Mariner Venus 1967) was a spacecraft of the Mariner program that carried a complement of experiments to probe Venus' atmosphere by radio occultation, measure the hydrogen Lyman-alpha (hard ultraviolet) spectrum, and sam ...
was successfully launched to Venus on June 14, 1967, and flew by in October, probing Venus's atmosphere with radio waves, scanning its brightness in ultraviolet light
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of th ...
, and sampling solar particles and magnetic field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
fluctuations above the planet.
Gemini
 The Agena rocket stage was used as the passive docking target for the Gemini crewed space program. After docking, the Agena could also be fired by the astronauts to raise the combined Gemini-Agena spacecraft into a higher orbit. The first attempt at such a docking mission was made for the Gemini 6 mission on October 25, 1965, but the Agena suffered an engine failure and did not reach orbit. This forced postponement and replanning of the Gemini 6A mission, which performed rendezvous with
The Agena rocket stage was used as the passive docking target for the Gemini crewed space program. After docking, the Agena could also be fired by the astronauts to raise the combined Gemini-Agena spacecraft into a higher orbit. The first attempt at such a docking mission was made for the Gemini 6 mission on October 25, 1965, but the Agena suffered an engine failure and did not reach orbit. This forced postponement and replanning of the Gemini 6A mission, which performed rendezvous with Gemini 7
Gemini 7 (officially Gemini VII) With Gemini IV, NASA changed to Roman numerals for Gemini mission designations. was a 1965 crewed spaceflight in NASA's Gemini program. It was the fourth crewed Gemini flight, the twelfth crewed American spacef ...
without docking.
The GATV was first successfully launched for Gemini 8
Gemini 8 (officially Gemini VIII) With Gemini IV, NASA changed to Roman numerals for Gemini mission designations. was the sixth crewed spaceflight in NASA's Project Gemini, Gemini program. It was launched on March 16, 1966, and was the 14th crew ...
on March 16, 1966, permitting the first successful docking in space. GATV-8 was later used as the secondary Agena target for Gemini 10
Gemini 10 (officially Gemini X) With Gemini IV, NASA changed to Roman numerals for Gemini mission designations. was a 1966 crewed spaceflight in NASA's Gemini program. It was the 8th crewed Project Gemini, Gemini flight, the 16th crewed American ...
, which also docked with its own GATV. GATV-9 failed to orbit when the Atlas suffered a control malfunction, forcing a similar reschedule of the Gemini 9A mission using a backup Augmented Target Docking Adapter atop an Atlas, but with no Agena rocket stage. Two more GATVs were successfully launched and used on Gemini 11
Gemini 11 (officially Gemini XI) With Gemini IV, NASA changed to Roman numerals for Gemini mission designations. was the ninth crewed spaceflight mission of NASA's Project Gemini, which flew from September 12 to 15, 1966. It was the 17th crewed ...
and Gemini 12
Gemini 12 (officially Gemini XII) With Gemini IV, NASA changed to Roman numerals for Gemini mission designations. was a 1966 crewed spaceflight in NASA's Project Gemini. It was the 10th and final crewed Gemini flight (Gemini 1 and Gemini 2 were ...
.
Lunar Orbiter
 A series of five Lunar Orbiter spacecraft were launched from August 1966 through August 1967, to help select landing sites for the Apollo lunar landing program by mapping the Moon's surface. Each spacecraft weighed and was in diameter, minus the four extended solar panels. All launches were successful, and a total of 99 percent of the surface of the Moon (near and far side) was mapped with resolution as high as 3 ft 3 in (1 meter). Altogether the Orbiters returned 2180 high resolution and 882 medium resolution frames. The spacecraft also carried micrometeoroid sensors, which showed the average micro-meteoroid flux near the Moon to be two orders of magnitude greater than in interplanetary space, but slightly less than the near-Earth environment.
A series of five Lunar Orbiter spacecraft were launched from August 1966 through August 1967, to help select landing sites for the Apollo lunar landing program by mapping the Moon's surface. Each spacecraft weighed and was in diameter, minus the four extended solar panels. All launches were successful, and a total of 99 percent of the surface of the Moon (near and far side) was mapped with resolution as high as 3 ft 3 in (1 meter). Altogether the Orbiters returned 2180 high resolution and 882 medium resolution frames. The spacecraft also carried micrometeoroid sensors, which showed the average micro-meteoroid flux near the Moon to be two orders of magnitude greater than in interplanetary space, but slightly less than the near-Earth environment.
OAO
Orbiting Astronomical Observatory was a series of NASA satellites flown between 1966 and 1972 for astronomy studies. The first OAO (launched April 8, 1966) used a one-off Atlas variant, mating an Agena D to the LV-3C variant of the Atlas and encased in a Centaur-type payload shroud. The remaining three launches used actual Atlas-Centaur vehicles.ATS
Applications Technology Satellite
The Applications Technology Satellites (ATS) were a series of experimental satellites launched by NASA, under the supervision of, among others, Wernher von Braun. The program was launched in 1966 to test the feasibility of placing a satellite int ...
was a series of NASA satellites flown in 1967–69 to perform various technology tests. Only the first ATS was launched on an Atlas-Agena, the remainder using Atlas-Centaurs. ATS-1 was a partial failure when the Agena failed to restart, leaving it in LEO.
OGO
Orbiting Geophysical Observatory was a series of NASA satellites flown between 1964 and 1969 for magnetosphere studies. These satellites used several different booster types, including Thor-Agenas. Five of them used Atlas-Agenas, and OGO 5 (launched March 4, 1968) was the sole civilian use of the Atlas SLV-3A Agena.Midas
Missile Defense Alarm System
The Missile Defense Alarm System, or MIDAS, was a United States Air Force Air Defense Command system of 12 early-warning satellites that provided limited notice of Soviet intercontinental ballistic missile launches between 1960 and 1966. Original ...
was a series of Air Force satellites flown between 1960 and 1966 for infrared detection of ballistic missile exhaust plumes on Atlas-Agena A, B, and D. There were several failures and overall program performance was poor, but it would give way to the more successful DSP satellites.
Samos
Samos
Samos (, also ; , ) is a Greek island in the eastern Aegean Sea, south of Chios, north of Patmos and the Dodecanese archipelago, and off the coast of western Turkey, from which it is separated by the Mycale Strait. It is also a separate reg ...
was a series of Air Force satellites flown between 1960 and 1962 for photoreconnaissance on Atlas-Agena A and B. There were several failures, including an on-pad explosion of an Atlas, and the program was cancelled at the end of 1962 without ever demonstrating any operational capability.
Gambit
KH-7 Gambit
BYEMAN codenamed GAMBIT, the KH-7 (Air Force Program 206) was a reconnaissance satellite used by the United States from July 1963 to June 1967. Like the older Corona (satellite), CORONA system, it acquired imagery intelligence by taking photog ...
was a series of Air Force satellites flown between 1963 and 1966 for photoreconnaissance on Atlas-Agena D. Although there were a number of mission failures, Gambit overall was highly successful in comparison with the bungled Samos program and it returned high-value area reconnaissance of the USSR and China before giving way to KH-8 Gambit in 1967.
Rhyolite/Canyon
Rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture (geology), texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained matri ...
/Canyon
A canyon (; archaic British English spelling: ''cañon''), gorge or chasm, is a deep cleft between escarpments or cliffs resulting from weathering and the erosive activity of a river over geologic time scales. Rivers have a natural tendency t ...
was a series of Air Force satellites flown between 1968 and 1978 for SIGNIT intelligence on Atlas SLV-3A Agena. One Canyon mission failed when its Atlas went off course and had to be destroyed. These were the final launches of Atlas-Agena vehicles aside from the one-off Atlas F/Agena used to launch Seasat.
Vela
Vela consisted of two sets of Air Force satellites flown in 1964–65 to monitor Soviet compliance with the Nuclear Test Ban Treaty on Atlas-Agena Ds.Snapshot
Snapshot
Snapshot, snapshots or snap shot may refer to:
* Snapshot (photography), a photograph taken without preparation
Computing
* Snapshot (computer storage), the state of a system at a particular point in time
* Snapshot (file format) or SNP, a file ...
was a one-off Air Force test of a nuclear satellite flown in 1965 on an Atlas-Agena D.
References
{{US launch systems Rockets and missiles Atlas (rocket family)