|
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Launch Complex 12
Launch Complex 12 (LC-12) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida was a launch pad used by Atlas rockets and missiles between 1958 and 1967. It was the second-most southern of the pads known as Missile Row, between LC-11 to the south and LC-13 to the north. Along with Complexes 11, 13 and 14, LC-12 featured a more robust design than many contemporary pads, due to the greater power of the Atlas compared to other rockets of the time. It was larger, and featured a concrete launch pedestal that was tall and a reinforced blockhouse. The rockets were delivered to the launch pad by means of a ramp on the southwest side of the launch pedestal. Currently, LC-12 is leased by Blue Origin, and has been used by them as a storage site. History Atlas operations Atlas A, C and D missiles were tested from the site. It was also used for orbital launches of Atlas-Able and later Atlas-Agena rockets, and two Project FIRE suborbital tests for Project Apollo, using Atlas D rockets. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida. Headquartered at the nearby Patrick Space Force Base, the station is the primary launch site for the Space Force's Eastern RangeCAST 1999, p. 1-12. with four launch pads currently active (Space Launch Complexes 36, 40, 41 and 46). The facility is south-southeast of NASA's Kennedy Space Center on adjacent Merritt Island, with the two linked by bridges and causeways. The Cape Canaveral Space Force Station Skid Strip provides a runway close to the launch complexes for military airlift aircraft delivering heavy and outsized payloads to the Cape. A number of American space exploration pioneers were launched from CCSFS, including the first U.S. Earth satellite (1958), first U.S. astronaut (1961), first U.S. astronaut in orbit (1962), first two-man U.S. spacecraft (1965), first U.S. uncrewed lu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as a planet, moon, asteroid, or Lagrange point. Normally, orbit refers to a regularly repeating trajectory, although it may also refer to a non-repeating trajectory. To a close approximation, planets and satellites follow elliptic orbits, with the center of mass being orbited at a focal point of the ellipse, as described by Kepler's laws of planetary motion. For most situations, orbital motion is adequately approximated by Newtonian mechanics, which explains gravity as a force obeying an inverse-square law. However, Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, which accounts for gravity as due to curvature of spacetime, with orbits following geodesics, provides a more accurate calculation and u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Launch Tower
A service structure is a permanent steel framework or tower erected on a rocket launch pad that allows assembly, servicing, and crew onboarding of the launch vehicle prior to liftoff. In NASA launches at the Kennedy Space Center, astronauts enter the vehicle through a type of service structure called an " umbilical tower". Immediately before ignition of the rocket's engines, all connections between the tower and the craft are severed, and the connecting bridges swing away to prevent damage to structure and vehicle. An elevator in the tower also allows maintenance crew to service the vehicle. Kennedy Space Center During the NASA Space Shuttle program, the structures at the Launch Complex 39 pads contained a two-piece access tower system, the Fixed Service Structure (FSS) and the Rotating Service Structure (RSS). The FSS permitted access to the Shuttle via a retractable arm and a "beanie cap" to capture vented liquid oxygen (LOX) from the external fuel tank. The RSS contained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmospheric pressure is a few thousandths of Earth's, atmospheric temperature ranges from and cosmic radiation is high. Mars retains some water, in the ground as well as thinly in the atmosphere, forming cirrus clouds, frost, larger polar regions of permafrost and ice caps (with seasonal snow), but no liquid surface water. Its surface gravity is roughly a third of Earth's or double that of the Moon. It is half as wide as Earth or twice the Moon, with a diameter of , and has a surface area the size of all the dry land of Earth. Fine dust is prevalent across the surface and the atmosphere, being picked up and spread at the low Martian gravity even by the weak wind of the tenuous atmosphere. The terrain of Mars roughly follows a north-south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mariner 4
Mariner 4 (Mariner C-3, together with Mariner 3 known as Mariner-Mars 1964) was the Mariner program, fourth in a series of spacecraft intended for planetary exploration in a flyby mode. It was designed to conduct closeup scientific observations of Mars and to transmit these observations to Earth. Launched on November 28, 1964, Mariner 4 performed the first successful planetary flyby, flyby of the planet Mars, returning the first close-up pictures of the Martian surface. It captured the first images of another planet ever returned from outer space, deep space; their depiction of a cratered, dead planet largely changed the scientific community's view of life on Mars. Other mission objectives were to perform field and particle measurements in outer space#Interplanetary space, interplanetary space in the vicinity of Mars and to provide experience in and knowledge of the engineering capabilities for interplanetary flights of long duration. Initially expected to remain in space for eig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
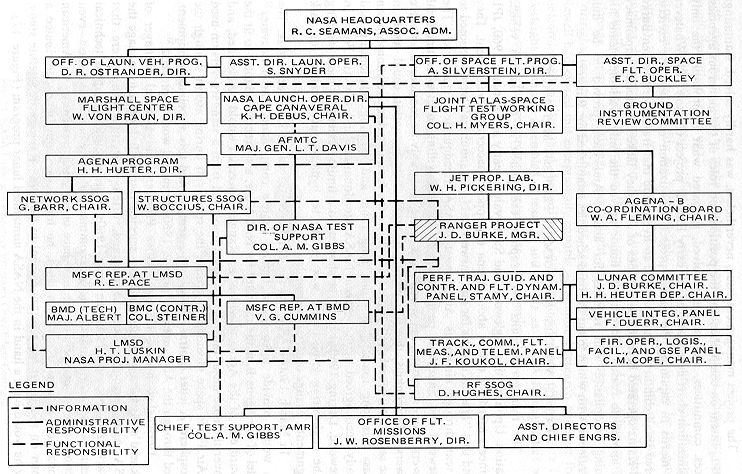
Ranger Program
The Ranger program was a series of uncrewed space missions by the United States in the 1960s whose objective was to obtain the first close-up images of the surface of the Moon. The Ranger spacecraft were designed to take images of the lunar surface, transmitting those images to Earth until the spacecraft were destroyed upon impact. A series of mishaps, however, led to the failure of the first six flights. At one point, the program was called "shoot and hope". Congress launched an investigation into "problems of management" at NASA Headquarters and JPL, Jet Propulsion Laboratory. After two reorganizations of the agencies, Ranger 7 successfully returned images in July 1964, followed by two more successful missions. Ranger was originally designed, beginning in 1959, in three distinct phases, called "blocks". Each block had different mission objectives and progressively more advanced system design. The JPL mission designers planned multiple launches in each block, to maximize the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranger 7
Ranger 7 was the first NASA space probe to successfully transmit close-up images of the lunar surface back to Earth. It was also the first completely successful flight of the Ranger program. Launched on July 28, 1964, Ranger 7 was designed to achieve a lunar-impact trajectory and to transmit high-resolution photographs of the lunar surface during the final minutes of flight up to impact. The spacecraft carried six television vidicon cameras—two wide-angle (channel F, cameras A and B) and four narrow-angle (channel P)—to accomplish these objectives. The cameras were arranged in two separate chains, or channels, each self-contained with separate power supplies, timers, and transmitters so as to afford the greatest reliability and probability of obtaining high-quality video pictures. Ranger 7 transmitted over 4,300 photographs during the final 17 minutes of its flight. After 68.6 hours of flight, the spacecraft impacted between Mare Nubium and Oceanus Procellarum. This landing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mariner 2
Mariner 2 (Mariner-Venus 1962), an American space probe to Venus, was the first robotic space probe to report successfully from a planetary encounter. The first successful spacecraft in the NASA Mariner program, it was a simplified version of the Block I spacecraft of the Ranger program and an exact copy of Mariner 1. The missions of the Mariner 1 and 2 spacecraft are sometimes known as the Mariner R missions. Original plans called for the probes to be launched on the Atlas-Centaur, but serious developmental problems with that vehicle forced a switch to the much smaller Agena B second stage. As such, the design of the Mariner R vehicles was greatly simplified. Far less instrumentation was carried than on the Soviet Venera probes of this period—for example, forgoing a TV camera—as the Atlas-Agena B had only half as much lift capacity as the Soviet 8K78 booster. The Mariner 2 spacecraft was launched from Cape Canaveral on August 27, 1962, and passed as close as to Venus on D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Landing
A hard landing occurs when an aircraft or spacecraft hits the ground with a greater vertical speed and force than in a normal landing. The terms ''hard landing'' and ''firm landing'' are often confused though are inherently different. A hard landing is never intended and if an aircraft has had a hard landing, it must be inspected for damage before its next flight. In contrast, depending on aircraft type (e.g. Boeing 737) and/or environmental conditions (e.g. gusty or crosswind conditions, wet runway, etc.) a firm landing is intended and even demanded by the aircraft manual. Landing is the final phase in flight, in which the aircraft returns to the ground. The average vertical speed in a landing is around ; any greater vertical speed should be classed by crew as ''hard''. Crew judgment is most reliable to determine hard landing, as determination based on recorded acceleration value is difficult and not advisable, partially because there is no recording of true vertical accelera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar day) that is synchronized to its orbital period (Lunar month#Synodic month, lunar month) of 29.5 Earth days. This is the product of Earth's gravitation having tidal forces, tidally pulled on the Moon until one part of it stopped rotating away from the near side of the Moon, near side, making always the same lunar surface face Earth. Conversley, the gravitational pull of the Moon, on Earth, is the main driver of Earth's tides. In geophysical definition of planet, geophysical terms, the Moon is a planetary-mass object or satellite planet. Its mass is 1.2% that of the Earth, and its diameter is , roughly one-quarter of Earth's (about as wide as the contiguous United States). Within the Solar System, it is the List of Solar System objects by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the semi-exclave of Alaska in the northwest and the archipelago of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States asserts sovereignty over five Territories of the United States, major island territories and United States Minor Outlying Islands, various uninhabited islands in Oceania and the Caribbean. It is a megadiverse country, with the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three Metropolitan statistical areas by population, largest metropolitan areas are New York metropolitan area, New York, Greater Los Angeles, Los Angel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranger 4
Ranger 4 was a spacecraft of the Ranger program, launched in 1962. It was designed to transmit pictures of the lunar surface to Earth stations during a period of 10 minutes of flight prior to crashing upon the Moon, to rough-land a seismometer capsule on the Moon, to collect gamma-ray data in flight, to study radar reflectivity of the lunar surface, and to continue testing of the Ranger program for development of lunar and interplanetary spacecraft. An onboard computer failure caused failure of the deployment of the solar panels and navigation systems; as a result the spacecraft crashed on the far side of the Moon without returning any scientific data. It was the first spacecraft of the United States to reach another celestial body and the first of any nation to reach the surface of the far side of the Moon. Spacecraft design Ranger 4 was a Block II Ranger spacecraft virtually identical to Ranger 3. The basic vehicle was , high and consisted of a lunar capsule covered with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |