Asthma Trigger on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Asthma triggers are factors or stimuli that provoke the exacerbation of
Asthma triggers are factors or stimuli that provoke the exacerbation of
 The pathophysiology for asthma mainly involves the inflammatory pathway, associated with several types of immune cells in the body, mainly T helper 2 cells (Th2 cells),
The pathophysiology for asthma mainly involves the inflammatory pathway, associated with several types of immune cells in the body, mainly T helper 2 cells (Th2 cells),  Due to this, the mast cells will be activated when they are exposed to the specific allergen. As an allergen binds to the
Due to this, the mast cells will be activated when they are exposed to the specific allergen. As an allergen binds to the



 Long term use of certain types of corticosteroids, such as fluticasone propionate may be administered through the pulmonary route to reduce the risk of an asthma attack.
Oral use of
Long term use of certain types of corticosteroids, such as fluticasone propionate may be administered through the pulmonary route to reduce the risk of an asthma attack.
Oral use of
asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
symptoms or increase the degree of airflow disruption, which can lead to an asthma attack
Asthma is a common chronic (medicine), long-term inflammation, inflammatory disease of the bronchiole, airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible Airway obstruction, airflow obstruction, and easi ...
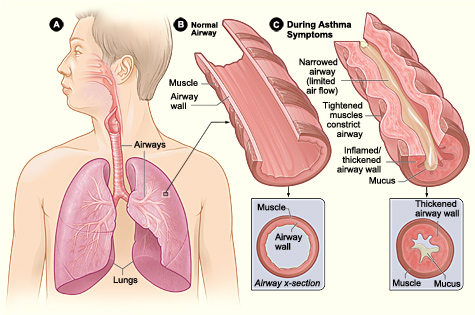
. An asthma attack is characterized by an obstruction of the airway, hypersecretion of mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
and bronchoconstriction
Bronchoconstriction is the constriction of the airways in the lungs due to the tightening of surrounding smooth muscle, with consequent coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
Causes
The condition has a number of causes, the most common bei ...
due to the contraction of smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called bec ...
s around the respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of conducting air to the alveoli for the purposes of gas exchange in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respirato ...
. Its symptoms include a wide range of manifestations such as breathlessness
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that c ...
, cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages which can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and Microorganism, microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex fol ...
ing, a tight chest and wheezing
A wheeze is a clinical symptom of a continuous, coarse, whistling sound produced in the respiratory airways during breathing. For wheezes to occur, part of the respiratory tree must be narrowed or obstructed (for example narrowing of the lower ...
.
An asthma attack is usually mediated by an inflammatory pathway, where a trigger such as an allergen
An allergen is an otherwise harmless substance that triggers an allergic reaction in sensitive individuals by stimulating an immune response.
In technical terms, an allergen is an antigen that is capable of stimulating a type-I hypersensitivi ...
could lead to a series of immune response mediated by various types of immune cells.
Common triggers for asthma include allergen
An allergen is an otherwise harmless substance that triggers an allergic reaction in sensitive individuals by stimulating an immune response.
In technical terms, an allergen is an antigen that is capable of stimulating a type-I hypersensitivi ...
s like pet dander, dust mites
House dust mites (HDM, or simply dust mites) are various species of acariform mites belonging to the family Pyroglyphidae that are found in association with dust in dwellings. They are known for causing allergies.
Biology
Species
The curren ...
, pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm ...
s and molds. Other types of triggers like exercise
Exercise or workout is physical activity that enhances or maintains fitness and overall health. It is performed for various reasons, including weight loss or maintenance, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardio ...
, air pollutants
Air pollution is the presence of substances in the air that are harmful to humans, other living beings or the environment. Pollutants can be gases like ozone or nitrogen oxides or small particles like soot and dust. It affects both outdoor air ...
, tobacco smoke
Tobacco smoke is a sooty aerosol produced by the incomplete combustion of tobacco during the smoking of cigarettes and other tobacco products. Temperatures in burning cigarettes range from about 400 °C between puffs to about 900 °C ...
, humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, dew, or fog t ...
, cold air, or certain medicines may also play a role in triggering asthma. While it has been proposed that asthma triggers can be classified into three types: allergic triggers, environmental triggers and physical triggers, a universal categorization of asthma triggers has yet to be done. Other studies have also classified asthma triggers into psychological factors, air pollutants, physical activity, allergens and infection.
Asthma is an extremely common chronic disease affecting over 26 million people and 7 million children in the US. Recognizing the trigger for asthma and avoiding it can be a simple yet effective way to deal with the disease and avoid an asthma attack. Although a cure for asthma is yet to be invented, various treatment methods are available for both long-term control and immediate relieve of an asthma attack.
Pathophysiology
 The pathophysiology for asthma mainly involves the inflammatory pathway, associated with several types of immune cells in the body, mainly T helper 2 cells (Th2 cells),
The pathophysiology for asthma mainly involves the inflammatory pathway, associated with several types of immune cells in the body, mainly T helper 2 cells (Th2 cells), B cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasm ...
s and mast cell
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a p ...
s. In a nut shell, as a stimulus, such as an allergen comes into contact with an asthma patient, it activates various types of immune cells leading to an inflammatory response
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
, causing bronchial hyperresponsiveness
Bronchial hyperresponsiveness (or other combinations with airway or hyperreactivity, BH used as a general abbreviation) is a state characterised by easily triggered bronchospasm (contraction of the bronchioles or small airways).
Bronchial hyperres ...
, bronchoconstriction
Bronchoconstriction is the constriction of the airways in the lungs due to the tightening of surrounding smooth muscle, with consequent coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
Causes
The condition has a number of causes, the most common bei ...
, excessive mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
secretion, airflow obstruction and an asthma attack. A more detail rundown of the process is provided below.
First, during the sensitization phase, where T cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
s interact with dendritic cell
A dendritic cell (DC) is an antigen-presenting cell (also known as an ''accessory cell'') of the mammalian immune system. A DC's main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system ...
s, the dendritic cell
A dendritic cell (DC) is an antigen-presenting cell (also known as an ''accessory cell'') of the mammalian immune system. A DC's main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system ...
s will present a specific antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule, moiety, foreign particulate matter, or an allergen, such as pollen, that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response.
...
from the allergen to Th2 cells, leading to their development. Afterward, the activated Th2 cells would release interleukine-4, a type of cytokine
Cytokines () are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling.
Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B cell, B lymphocytes, T cell, T lymphocytes ...
to promote B cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasm ...
s, another type of immune cell to differentiate intoallergen-specific memory B cell
In immunology, a memory B cell (MBC) is a type of B lymphocyte that forms part of the adaptive immune system. These cells develop within germinal centers of the secondary lymphoid organs. Memory B cells circulate in the blood stream in a quie ...
s and plasma cell
Plasma cells, also called plasma B cells or effector B cells, are white blood cells that originate in the lymphoid organs as B cells and secrete large quantities of proteins called antibodies in response to being presented specific substances ca ...
s. The plasma cell
Plasma cells, also called plasma B cells or effector B cells, are white blood cells that originate in the lymphoid organs as B cells and secrete large quantities of proteins called antibodies in response to being presented specific substances ca ...
s will then extensively produce allergen-specific IgE antibodies
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is a type of antibody (or immunoglobulin (Ig) " isoform") that has been found only in mammals. IgE is synthesised by plasma cells. Monomers of IgE consist of two heavy chains (ε chain) and two light chains, with the ε ...
, which are captured by a type of receptor, FceRI, on the mast cell
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a p ...
s.
Mast cell
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a p ...
s are immune cells usually located at tissues exposed to the environment, such as the skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
, respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of conducting air to the alveoli for the purposes of gas exchange in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respirato ...
mucosa and digestive tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
mucosa. They are equipped with preformed granules loaded with vasoactive amines and protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products ...
s. As the FceRI receptors on mast cells capture the IgE antibodies
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is a type of antibody (or immunoglobulin (Ig) " isoform") that has been found only in mammals. IgE is synthesised by plasma cells. Monomers of IgE consist of two heavy chains (ε chain) and two light chains, with the ε ...
produced by Th2 cells, they become sensitive to the specific allergen.
 Due to this, the mast cells will be activated when they are exposed to the specific allergen. As an allergen binds to the
Due to this, the mast cells will be activated when they are exposed to the specific allergen. As an allergen binds to the IgE antibodies
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is a type of antibody (or immunoglobulin (Ig) " isoform") that has been found only in mammals. IgE is synthesised by plasma cells. Monomers of IgE consist of two heavy chains (ε chain) and two light chains, with the ε ...
on the mast cell
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a p ...
surface, clustering and cross-link formation of FceRI takes place. This leads to the recruitment and activation of several tyrosine kinase
A tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to the tyrosine residues of specific proteins inside a cell. It functions as an "on" or "off" switch in many cellular functions.
Tyrosine kinases belong to a larger cla ...
s, a type of enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
that phosphorylates protein. Consequently, these kinase activation contributes to intracellular Ca2+ influx after a series of reaction. The Ca2+ level surge results in cytoskeletal
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all Cell (biology), cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane ...
rearrangement, allowing exocytosis
Exocytosis is a term for the active transport process that transports large molecules from cell to the extracellular area. Hormones, proteins and neurotransmitters are examples of large molecules that can be transported out of the cell. Exocytosis ...
and degranulation
Degranulation is a cellular process that releases antimicrobial, cytotoxic, or other molecules from secretory vesicles called granules found inside some cells. It is used by several different cells involved in the immune system, including gran ...
of intracellular granules, thus releasing vasoactive amines and protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products ...
s. These vasoactive amines such as histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses communication, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Discovered in 19 ...
, heparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Heparin is a blood anticoagulant that increases the activity of antithrombin. It is used in the treatment of myocardial infarction, ...
and serotonin
Serotonin (), also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a monoamine neurotransmitter with a wide range of functions in both the central nervous system (CNS) and also peripheral tissues. It is involved in mood, cognition, reward, learning, ...
released from the mast cell
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a p ...
granules cause vasodilation
Vasodilation, also known as vasorelaxation, is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. Blood vessel wa ...
, increased vascular permeability
Vascular permeability, often in the form of capillary permeability or microvascular permeability, characterizes the permeability of a blood vessel wall–in other words, the blood vessel wall's capacity to allow for the flow of small molecules ( ...
, smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called bec ...
contraction and increased mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
secretion. Mast cells degranulation also results in the release of eosinophil
Eosinophils, sometimes called eosinophiles or, less commonly, acidophils, are a variety of white blood cells and one of the immune system components responsible for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections in vertebrates. Along wi ...
chemotactic
Chemotaxis (from '' chemo-'' + ''taxis'') is the movement of an organism or entity in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemica ...
factors and neutrophil
Neutrophils are a type of phagocytic white blood cell and part of innate immunity. More specifically, they form the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. Their functions vary in differe ...
chemotactic
Chemotaxis (from '' chemo-'' + ''taxis'') is the movement of an organism or entity in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemica ...
factors. These factors attract eosinophil
Eosinophils, sometimes called eosinophiles or, less commonly, acidophils, are a variety of white blood cells and one of the immune system components responsible for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections in vertebrates. Along wi ...
s and neutrophil
Neutrophils are a type of phagocytic white blood cell and part of innate immunity. More specifically, they form the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. Their functions vary in differe ...
s from the body respectively, which can intensify the inflammation response. Moreover, the elevated Ca2+ level also leads to arachidonic acid enzymatic pathway activation, contributing to the release of lipid mediators. These lipid mediators, particularly prostaglandin
Prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiology, physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids that have diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every Tissue (biology), tissue in humans and ot ...
s and leukotriene
Leukotrienes are a family of eicosanoid inflammation, inflammatory mediators produced in leukocytes by the redox, oxidation of arachidonic acid (AA) and the essential fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) by the enzyme arachidonate 5-lipoxyg ...
s elicit vasodilation
Vasodilation, also known as vasorelaxation, is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. Blood vessel wa ...
, increased vascular permeability
Vascular permeability, often in the form of capillary permeability or microvascular permeability, characterizes the permeability of a blood vessel wall–in other words, the blood vessel wall's capacity to allow for the flow of small molecules ( ...
and smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called bec ...
contraction. Moreover, the increase in Ca2+ level also leads to activation of certain transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ...
s which induces pro-inflammatory cytokines transcription. These pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF, Interleukin-1
The Interleukin-1 family (IL-1 family) is a group of 11 cytokines that plays a central role in the regulation of immune and inflammatory responses to infections or sterile insults.
Discovery
Discovery of these cytokines began with studies on t ...
and Interleukin-8
Interleukin 8 (IL-8 or chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 8, CXCL8) is a chemokine produced by macrophages and other cell types such as epithelial cells, airway smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells. Endothelial cells store IL-8 in their storage ...
lead to acute inflammation and leukocyte
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are genera ...
recruitment.
Examples of asthma triggers

Allergic triggers
Allergic
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic dermatitis, alle ...
triggers are factors or chemicals that could induce airway sensitization, inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
, bronchospasm
Bronchospasm or a bronchial spasm is a sudden bronchoconstriction, constriction of the muscles in the walls of the bronchioles. It is caused by the release (degranulation) of substances from mast cells or basophils under the influence of anaphylat ...
and other asthmatic symptoms.
Allergens are the most common trigger for allergic asthma. Examples of such triggers of asthma include naturally occurring aeroallergens like house dust mite
House dust mites (HDM, or simply dust mites) are various species of acariform mites belonging to the family Pyroglyphidae that are found in association with dust in dwellings. They are known for causing allergies.
Biology
Species
The curren ...
s, animal feces and pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm ...
. Pet
A pet, or companion animal, is an animal kept primarily for a person's company or entertainment rather than as a working animal, livestock, or a laboratory animal. Popular pets are often considered to have attractive/ cute appearances, inte ...
s, molds and pests
PESTS was an anonymous American activist group formed in 1986 to critique racism, tokenism, and exclusion in the art world. PESTS produced newsletters, posters, and other print material highlighting examples of discrimination in gallery represent ...
are also potential triggers. When an asthma patient inhales or come into contact withsuch allergen, mast cell
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a p ...
s in the airway tract releases vasoactive amines and protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products ...
s. This leads to a release of cytokine
Cytokines () are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling.
Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B cell, B lymphocytes, T cell, T lymphocytes ...
s and mediates a broad range of inflammatory and allergic responses.
Environmental triggers
In addition to allergens, studies have revealed that environmental factors may also increase the risk of triggering an asthma attack. Examples of these factors include respiratory tract viral infections, exposure toair pollutants
Air pollution is the presence of substances in the air that are harmful to humans, other living beings or the environment. Pollutants can be gases like ozone or nitrogen oxides or small particles like soot and dust. It affects both outdoor air ...
such as ozone
Ozone () (or trioxygen) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , break ...
or a change in lifestyle that involves a decrease in exposure to microbes
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from antiquity, with an early attestation in ...
and their products like endotoxin
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), now more commonly known as endotoxin, is a collective term for components of the outermost membrane of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria, such as '' E. coli'' and ''Salmonella'' with a common structural archit ...
. Although its mechanism of action is still unknown, an in vivo study has demonstrated that these environmental factors lead to the accumulation of neutrophil extracellular traps
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) are networks of extracellular fibers, primarily composed of DNA from neutrophils, which bind pathogens. Neutrophils are the immune system's first line of defense against infection and have conventionally bee ...
(NET) releasing neutrophil
Neutrophils are a type of phagocytic white blood cell and part of innate immunity. More specifically, they form the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. Their functions vary in differe ...
s in the lungs. This increased release of NETs have been found to be associated with asthmatic symptoms such as mucus hypersecretion
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It ...
.
Another environmental risk factor is exposure to formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is an organic compound with the chemical formula and structure , more precisely . The compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde. It is stored as ...
. Formaldehyde itself is a chemical that can cause irritation
Irritation, in biology and physiology, is a state of inflammation or painful reaction to allergy or cell-lining damage. A stimulus or agent which induces the state of irritation is an irritant. Irritants are typically thought of as chemical age ...
to the respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of conducting air to the alveoli for the purposes of gas exchange in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respirato ...
. In addition, it may react with macromolecules such as albumin
Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All of the proteins of the albumin family are water- soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Alb ...
which can induce the production of igE antibodies
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is a type of antibody (or immunoglobulin (Ig) " isoform") that has been found only in mammals. IgE is synthesised by plasma cells. Monomers of IgE consist of two heavy chains (ε chain) and two light chains, with the ε ...
which can bind to mast cell
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a p ...
s and lead to hyperresponsiveness of the respiratory tract.
Exercise
Exercise induced asthma is common in most asthma patients. Although the mechanism for such a phenomenon is still unclear, researchers have proposed that as the body gasps for more oxygen during exercise, more cold and dry air is inhaled. The passage of this cold and dry air causes a loss of moisture from the mucosal membrane of therespiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of conducting air to the alveoli for the purposes of gas exchange in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respirato ...
. The osmolarity
Osmotic concentration, formerly known as osmolarity, is the measure of solute concentration, defined as the number of osmoles (Osm) of solute per litre (L) of solution (osmol/L or Osm/L). The osmolarity of a solution is usually expressed as Osm/ ...
changes brought by such action can lead to an increased release of proinflammatory mediators such as cytokine
Cytokines () are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling.
Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B cell, B lymphocytes, T cell, T lymphocytes ...
s, leading to a hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) is an abnormal physiological condition in which there is an undesirable and adverse immune response to an antigen. It is an abnormality in the immune system that causes Imm ...
of the airway. Cooling of the respiratory tract may also activate cholinergic receptors
An acetylcholine receptor (abbreviated AChR) or a cholinergic receptor is an integral membrane protein that responds to the binding of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter.
Classification
Like other transmembrane receptors, acetylcholine receptors ...
, which can induce bronchoconstriction
Bronchoconstriction is the constriction of the airways in the lungs due to the tightening of surrounding smooth muscle, with consequent coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
Causes
The condition has a number of causes, the most common bei ...
and mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
secretion, further narrowing the airway. Swimmers with asthma may also inhale an excess amount of contaminated and irritating air with compound derived from chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between ...
gas, this can increase the risk of an asthma attack.
Medications

Aspirin
Aspirin () is the genericized trademark for acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is ...
induced asthma, or aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease
Aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD), also called NSAID-exacerbated respiratory disease (N-ERD) or historically aspirin-induced asthma and Samter's Triad, is a long-term disease defined by three simultaneous symptoms: asthma, chronic ...
, refers to situations where the use of aspirin worsen the asthma conditions. Other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs A nonsteroidal compound is a drug that is not a steroid nor a steroid derivative. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are distinguished from corticosteroids as a class of anti-inflammatory agents.
List of nonsteroidal steroid receptor m ...
(NSAIDs) that inhibits the enzyme, cyclooxygenase-1
Cyclooxygenase 1 (COX-1), also known as prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1 (Human Genome Organisation, HUGO PTGS1), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PTGS1'' gene. In humans it is one of Cyclooxygenase-3, three cyclooxygenases.
...
, may also lead to an asthma attack.
After the inhibition of cyclooxygenase-1 enzyme by the NSAIDs, an accumulation of arachidonic acid
Arachidonic acid (AA, sometimes ARA) is a polyunsaturated omega−6 fatty acid 20:4(ω−6), or 20:4(5,8,11,14). It is a precursor in the formation of leukotrienes, prostaglandins, and thromboxanes.
Together with omega−3 fatty acids an ...
will be resulted. This, in turn, would increase the production of leukotriene
Leukotrienes are a family of eicosanoid inflammation, inflammatory mediators produced in leukocytes by the redox, oxidation of arachidonic acid (AA) and the essential fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) by the enzyme arachidonate 5-lipoxyg ...
s. Leukotriene
Leukotrienes are a family of eicosanoid inflammation, inflammatory mediators produced in leukocytes by the redox, oxidation of arachidonic acid (AA) and the essential fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) by the enzyme arachidonate 5-lipoxyg ...
s is an inflammatory mediator. The accumulation of proinflammatory leukotrienes would overstimulate the cysteinyl leukotriene receptors in the respiratory system, leading to bronchoconstriction
Bronchoconstriction is the constriction of the airways in the lungs due to the tightening of surrounding smooth muscle, with consequent coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
Causes
The condition has a number of causes, the most common bei ...
and the over-secretion of mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
, thus blocking the airway.
Beta-blocker
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms ( arrhythmia), and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack (secondary prevention) ...
, or beta-adrenergic antagonists, may also induce bronchial constriction and block the action of other beta-receptor targeted asthmatic drugs, leading to a worsening asthma condition. Therefore, asthma patients should be cautious and inform their physicians of their asthma conditions.
Occupational asthma triggers
Occupational asthma
Occupational asthma is new onset asthma or the recurrence of previously quiescent asthma directly caused by exposure to an agent at workplace. It is an occupational lung disease and a type of work-related asthma. Agents that can induce occupationa ...
refers to a type of asthma that is resulted from repeated exposure to an agent that causes or exacerbates asthma in a workplace. Although the primary cause for occupational asthma varies from situation to situation, common agents such as metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
, diesel
Diesel may refer to:
* Diesel engine, an internal combustion engine where ignition is caused by compression
* Diesel fuel, a liquid fuel used in diesel engines
* Diesel locomotive, a railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engine ...
, cleaning agent
Cleaning agents or hard-surface cleaners are substances (usually liquids, powders, sprays, or granules) used to remove dirt, including dust, stains, foul odors, and clutter on surfaces. Purposes of cleaning agents include health, beauty, removing ...
s, dimethylsulphate, diisocyanate
In organic chemistry, isocyanate is the functional group with the formula . Organic compounds that contain an isocyanate group are referred to as isocyanates. An organic compound with two isocyanate groups is known as a diisocyanate. Diisocyan ...
s, latex
Latex is an emulsion (stable dispersion) of polymer microparticles in water. Latices are found in nature, but synthetic latices are common as well.
In nature, latex is found as a wikt:milky, milky fluid, which is present in 10% of all floweri ...
, persulfate
A persulfate (sometimes known as peroxysulfate or peroxodisulfate) is a compound containing the anions or . The anion contains one peroxide group per sulfur center, whereas in , the peroxide group bridges the sulfur atoms. In both cases, sulfur ...
, aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () (lat. ''al''cohol ''dehyd''rogenatum, dehydrogenated alcohol) is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred ...
s, isocyanate
In organic chemistry, isocyanate is the functional group with the formula . Organic compounds that contain an isocyanate group are referred to as isocyanates. An organic compound with two isocyanate groups is known as a diisocyanate. Diisocyan ...
s, wood dust
Sawdust (or wood dust) is a by-product or waste product of woodworking operations such as sawing, sanding, milling and routing. It is composed of very small chips of wood. These operations can be performed by woodworking machinery, portable po ...
s and flour
Flour is a powder made by Mill (grinding), grinding raw grains, List of root vegetables, roots, beans, Nut (fruit), nuts, or seeds. Flours are used to make many different foods. Cereal flour, particularly wheat flour, is the main ingredie ...
should be handled with great care.
Tobacco smoke
Both first-hand and second-handtobacco smoke
Tobacco smoke is a sooty aerosol produced by the incomplete combustion of tobacco during the smoking of cigarettes and other tobacco products. Temperatures in burning cigarettes range from about 400 °C between puffs to about 900 °C ...
can be a trigger for asthma attack. It may worsen the condition of asthma as it is an irritant and induces bronchoconstriction.
Psychological triggers
Studies have also indicated thatpsychological stress
In psychology, stress is a feeling of emotional strain and pressure. Stress is a form of psychological and mental discomfort. Small amounts of stress may be beneficial, as it can improve athletic performance, motivation and reaction to the envi ...
may be associated with a higher chance of asthma attack. Patients with psychological stress are found to have a reduced awareness of controlling asthma and poor physical health.
Symptom
One of the clinical asthmatic symptoms isshortness of breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that con ...
due to narrowing of the respiratory tract, caused by mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
plug formation and bronchoconstriction
Bronchoconstriction is the constriction of the airways in the lungs due to the tightening of surrounding smooth muscle, with consequent coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
Causes
The condition has a number of causes, the most common bei ...
as smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called bec ...
s contract. Another typical symptom is wheezing
A wheeze is a clinical symptom of a continuous, coarse, whistling sound produced in the respiratory airways during breathing. For wheezes to occur, part of the respiratory tree must be narrowed or obstructed (for example narrowing of the lower ...
. During expiration, turbulent airflow crushes the narrowed respiratory tract, leading to a wheezing sound. Moreover, the increased mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
secretion may not be limited to the respiratory tract, and other symptoms such as watery eyes and rhinitis
Rhinitis, also known as coryza, is irritation and inflammation of the mucous membrane inside the nose. Common symptoms are a stuffy nose, runny nose, sneezing, and post-nasal drip.
The inflammation is caused by viruses, bacteria, irritant ...
are also common. Furthermore, increased vasodilation
Vasodilation, also known as vasorelaxation, is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. Blood vessel wa ...
and vascular permeability
Vascular permeability, often in the form of capillary permeability or microvascular permeability, characterizes the permeability of a blood vessel wall–in other words, the blood vessel wall's capacity to allow for the flow of small molecules ( ...
may result in angioedema
Angioedema is an area of swelling (edema) of the lower layer of skin and tissue just under the skin or mucous membranes. The swelling may occur in the face, tongue, larynx, abdomen, or arms and legs. Often it is associated with hives, which are ...
, the swelling of the skin, and hives
Hives, also known as urticaria, is a kind of skin rash with red or flesh-colored, raised, itchy bumps. Hives may burn or sting. The patches of rash may appear on different body parts, with variable duration from minutes to days, and typically ...
. In severe complications, as ventilation is impaired, acute respiratory failure may occur due to the inadequate amount of oxygen in the circulatory system. Another life-threatening condition is pneumothorax
A pneumothorax is collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and dyspnea, shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve is ...
, the collapse of the lungs due to hyperinflation.
Avoidance
Understanding the specific asthma triggers for a patient and avoiding them can be a simple way for preventing an asthma attack. Regularly washingbedding
Bedding, also called bedclothes or bed linen, is the materials laid above the mattress of a bed for hygiene, warmth, protection of the mattress, and decorative effect. Bedding is the removable and washable portion of a human sleeping environment ...
s, quitting smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is combusted, and the resulting smoke is typically inhaled to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream of a person. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, whi ...
, doing pest controls, keeping a sensitized living environment, removing stagnant water
Water stagnation occurs when water stops flowing for a long period of time. Stagnant water can be a significant environmental hazard.
Dangers
Malaria and dengue are among the main dangers of still water, which can become a breeding ground ...
, avoiding products with potential irritants, etc., can be effective in avoiding an asthma attack.
Education about asthma triggers should be done by physicians to help patients understand what activities or materials should be avoided. Reduction of exposure to asthma triggers should be done by asthmatic patient as well. Parents of asthmatic children should also be cautious of common asthma triggers in order to reduce risks of an asthma attack.
Treatment
Quick-relief medicine
Quick-relief medicine are used for treating an acute asthma attack. The first line of medicine for treating this situation is short-term beta-2-adrenoreceptor agonists, which are drugs that can stimulate the beta-2 adrenergic receptors. They arebronchodilator
A bronchodilator or broncholytic (although the latter occasionally includes secretory inhibition as well) is a substance that dilates the bronchi and bronchioles, decreasing resistance in the respiratory airway and increasing airflow to the lun ...
s and can effectively relieve the symptoms by clearing the airway. Examples include albuterol
Salbutamol, also known as albuterol and sold under the brand name Ventolin among others, is a medication that opens up the medium and large airways in the lungs. It is a short-acting β2 adrenergic receptor agonist that causes relaxation of ...
and levalbuterol. Commonly they are used with a portable inhaler which allows the patient to administer the medicine at once during an attack.
Another common medicine for an acute attack is anticholinergic
Anticholinergics (anticholinergic agents) are substances that block the action of the acetylcholine (ACh) neurotransmitter at synapses in the central nervous system, central and peripheral nervous system.
These agents inhibit the parasympatheti ...
drugs such as ipratropium
Ipratropium bromide, sold under the trade name Atrovent among others, is a type of anticholinergic medication which is applied by different routes: inhaler, nebulizer, or nasal spray, for different reasons.
The inhalant opens up the medium ...
and tiotropium
Tiotropium bromide, sold under the brand name Spiriva among others, is a long-acting bronchodilator (LAMA: long acting muscarinic antagonist) used in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma. Specifically it is ...
, which are also bronchodilator
A bronchodilator or broncholytic (although the latter occasionally includes secretory inhibition as well) is a substance that dilates the bronchi and bronchioles, decreasing resistance in the respiratory airway and increasing airflow to the lun ...
s. They work by blocking off the cholinergic receptors
An acetylcholine receptor (abbreviated AChR) or a cholinergic receptor is an integral membrane protein that responds to the binding of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter.
Classification
Like other transmembrane receptors, acetylcholine receptors ...
and reduces mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
secretion and bronchoconstriction
Bronchoconstriction is the constriction of the airways in the lungs due to the tightening of surrounding smooth muscle, with consequent coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
Causes
The condition has a number of causes, the most common bei ...
.
Another type of treatment for acute asthma attack is immunosuppressive
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse react ...
drugs like corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
s, which can also alleviate an asthmatic response. Examples include prednisone and methyl prednisone which are usually administered orally or intravenously for treating an acute situation. However, note that long term use of corticosteroids may lead to severe side effects.
Long-term control
Continuous and long-term use of certain medicines can help reduce the risk of an asthma attack and keep the disease under control.leukotriene receptor antagonist
An antileukotriene, also known as leukotriene modifier and leukotriene receptor antagonist, is a medication which functions as a leukotriene-related enzyme inhibitor ( arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase) or leukotriene receptor antagonist ( cysteinyl leu ...
such as Zafirlukast
Zafirlukast is an orally administered leukotriene receptor antagonist (LTRA) used for the chronic treatment of asthma. While zafirlukast is generally well tolerated, headaches and stomach upset often occur. Some rare side effects can occur, whic ...
may also be used as a long term control for asthma in addition to corticosteroids.
Moreover, another option is the use of cromolyn sodium
Cromoglicic acid ( INN)—also referred to as cromolyn ( USAN), cromoglycate (former BAN), or cromoglicate—is traditionally described as a mast cell stabilizer, and is commonly marketed as the sodium salt sodium cromoglicate or cromolyn sodiu ...
, which can prevent an asthma attack by halting Ca2+ influx, thus preventing mast cell
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a p ...
degranulation and subsequent asthmatic complications
Other than drugs, an alternative treatment method is de-sensitization, which involves exposure to a well-controlled, small and increasing amounts of specific allergen over a long duration of time. The rationale is to trigger antigen competition by the development of allergen-specific IgG
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a type of antibody. Representing approximately 75% of serum antibodies in humans, IgG is the most common type of antibody found in blood circulation. IgG molecules are created and released by plasma B cells. Each IgG ant ...
antibodies, which can reduce to risk of an allergic response.
Long-acting beta-agonists such as salmetrol had been used in combination with corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
s to control asthma symptoms. They are drugs that can stimulate the beta-2 adrenergic receptor
The beta-2 adrenergic receptor (β2 adrenoreceptor), also known as ADRB2, is a cell membrane-spanning beta-adrenergic receptor that binds epinephrine (adrenaline), a hormone and neurotransmitter whose signaling, via adenylate cyclase stimulati ...
s and mediate a bronchodilation
A bronchodilator or broncholytic (although the latter occasionally includes secretory inhibition as well) is a substance that dilates the bronchi and bronchioles, decreasing resistance in the respiratory airway and increasing airflow to the lung ...
effect for over 12 hours. However, a recent study in 2010 has found that this treatment method could increase the risk of asthma-related deaths and intubations. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is also recommending the discontinuation of the drug if asthma control has been achieved.{{Cite journal , last1=Chowdhury , first1=Badrul A. , last2=Dal Pan , first2=Gerald , date=2010 , title=The FDA and Safe Use of Long-Acting Beta-Agonists in the Treatment of Asthma , journal=New England Journal of Medicine , language=en , volume=362 , issue=13 , pages=1169–1171 , doi=10.1056/NEJMp1002074 , pmid=20181964 , issn=0028-4793, doi-access=free
References