Arcovenator Escotae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Arcovenator'' ("Arc hunter") is an
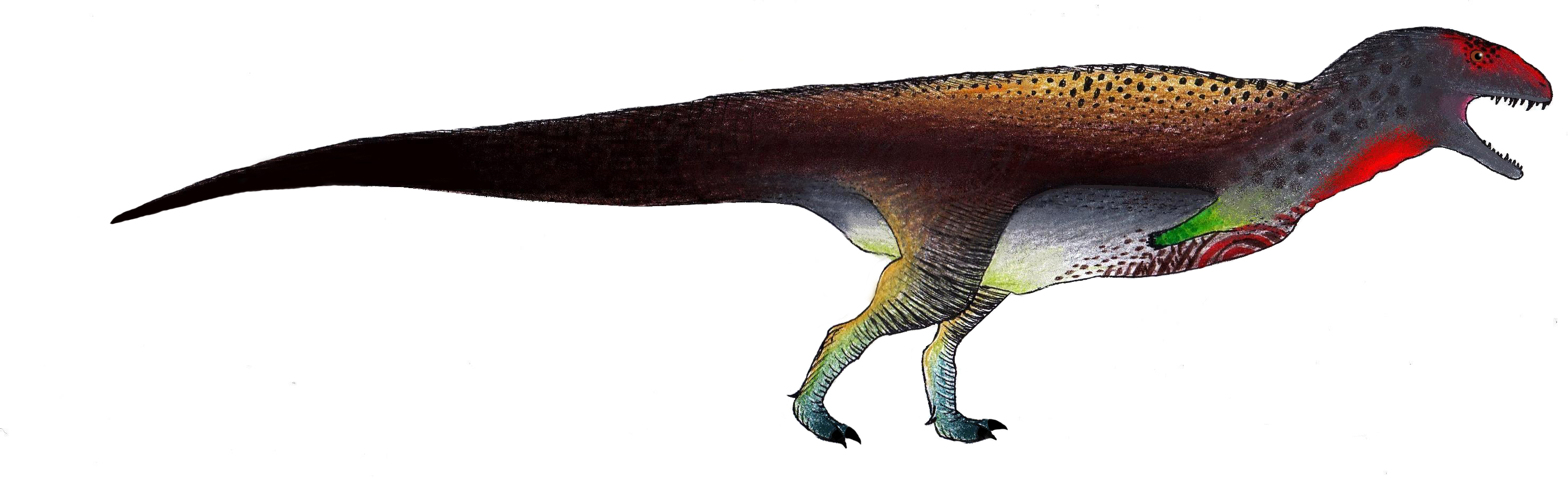 Though shallower, the nearly complete
Though shallower, the nearly complete
 Thierry Tortosa and colleagues conducted a
Thierry Tortosa and colleagues conducted a
extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
of abelisaurid
Abelisauridae (meaning "Abel's lizards") is a family (or clade) of ceratosaurian theropod dinosaurs. Abelisaurids thrived during the Cretaceous period, on the ancient southern supercontinent of Gondwana, and today their fossil remains are foun ...
theropod
Theropoda (; from ancient Greek , (''therion'') "wild beast"; , (''pous, podos'') "foot"">wiktionary:ποδός"> (''pous, podos'') "foot" is one of the three major groups (clades) of dinosaurs, alongside Ornithischia and Sauropodom ...
dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutio ...
s hailing from the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the more recent of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''cre ...
of France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
and possibly Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
. The type
Type may refer to:
Science and technology Computing
* Typing, producing text via a keyboard, typewriter, etc.
* Data type, collection of values used for computations.
* File type
* TYPE (DOS command), a command to display contents of a file.
* ...
and only described species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
is ''Arcovenator escotae''.
Description
 Though shallower, the nearly complete
Though shallower, the nearly complete braincase
In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, brain-pan, or brainbox, is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calv ...
of ''Arcovenator'' is otherwise similar in size to those of ''Majungasaurus
''Majungasaurus'' (; ) is a genus of abelisaurid theropod dinosaur that lived in Madagascar from 70 to 66 million years ago, at the end of the Cretaceous Period, making it one of the last-known non-avian dinosaurs that went extinct during th ...
'' and ''Carnotaurus
''Carnotaurus'' (; ) is a genus of Theropoda, theropod dinosaur that lived in South America during the Late Cretaceous period, probably sometime between 72 and 69 million years ago. The only species is ''Carnotaurus sastrei''. Known from a si ...
''; it was thus initially estimated as being about long, but it was estimated in 2016 as being in length. The skull roof
The skull roof or the roofing bones of the skull are a set of bones covering the brain, eyes and nostrils in bony fishes, including land-living vertebrates. The bones are derived from dermal bone and are part of the dermatocranium.
In com ...
exhibits as a unique diagnostic character a midline foramen
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (; : foramina, or foramens ; ) is an opening or enclosed gap within the dense connective tissue (bones and deep fasciae) of extant and extinct amniote animals, typically to allow passage of nerves, artery, ...
, possibly housing the pineal gland
The pineal gland (also known as the pineal body or epiphysis cerebri) is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. It produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone, which modulates sleep, sleep patterns following the diurnal c ...
, situated on the posterior surface of a slight dome formed by frontal bone
In the human skull, the frontal bone or sincipital bone is an unpaired bone which consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bo ...
s as moderately thick as in '' Aucasaurus'', thus less so than for '' Rajasaurus'', though more than those of ''Rugops
''Rugops'' (meaning 'wrinkle face') is a monospecific genus of basal abelisaurid theropod dinosaur from Niger that lived during the Late Cretaceous period (Cenomanian stage, ~95 Ma) in what is now the Echkar Formation. The type and only species, ...
''. Less characteristically, above the orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an ...
is a low fossa with a small fenestra
A fenestra (fenestration; : fenestrae or fenestrations) is any small opening or pore, commonly used as a term in the biology, biological sciences. It is the Latin word for "window", and is used in various fields to describe a pore in an anatomy, ...
bordered by the lacrimal, frontal, and postorbital. The parietal bordering the supratemporal fenestrae forms ridges medially on the latter's respective anteromedial margins which, as they approach the parietal eminence
The parietal eminence (parietal boss, parietal tuber, parietal tuberosity) is a convex, smooth eminence on the external surface of the parietal bone of the skull. It is the site where intramembranous ossification of the parietal bone begins during ...
, fuse into a sagittal crest
A sagittal crest is a ridge of bone running lengthwise along the midline of the top of the skull (at the sagittal suture) of many mammalian and reptilian skulls, among others. The presence of this ridge of bone indicates that there are excepti ...
. The postorbital
The ''postorbital'' is one of the bones in vertebrate skulls which forms a portion of the dermal skull roof and, sometimes, a ring about the orbit. Generally, it is located behind the postfrontal and posteriorly to the orbital fenestra. In some ve ...
is intermediate between the plesiomorphic
In phylogenetics, a plesiomorphy ("near form") and symplesiomorphy are synonyms for an ancestral character shared by all members of a clade, which does not distinguish the clade from other clades.
Plesiomorphy, symplesiomorphy, apomorphy, an ...
T-shaped condition of ''Eoabelisaurus
''Eoabelisaurus'' () is a genus of abelisauroid theropod dinosaur from the Lower Jurassic Cañadón Asfalto Formation of the Cañadón Asfalto Basin in Argentina, South America. The generic name combines a Greek ἠώς, (''eos''), "dawn", with t ...
'' and the derived inverted L-shaped one of ''Carnotaurus
''Carnotaurus'' (; ) is a genus of Theropoda, theropod dinosaur that lived in South America during the Late Cretaceous period, probably sometime between 72 and 69 million years ago. The only species is ''Carnotaurus sastrei''. Known from a si ...
'' due to the unique feature of having a sheet of bone linking its ventral and posterior processes. It has, in a similar autapomorphic fashion, a thick, rough-surfaced process dorsal to the eye socket that extends to the lacrimal, forming a bony brow ridge
The brow ridge, or supraorbital ridge known as superciliary arch in medicine, is a bony ridge located above the eye sockets of all primates and some other animals. In humans, the eyebrows are located on their lower margin.
Structure
The brow ri ...
, and in a less notable way, a lateral rugose tuberosity on the extremity of its ventral process. The paroccipital processes have remarkable accessory dorsal and ventral bony bars, that thus bound depressions lateral to the foramen magnum
The foramen magnum () is a large, oval-shaped opening in the occipital bone of the skull. It is one of the several oval or circular openings (foramina) in the base of the skull. The spinal cord, an extension of the medulla oblongata, passes thro ...
. The ear region closely resembles that of ''Majungasaurus'', though differing most substantially on a laterally directed basipterygoid process, with the shorter crista prootica and the smaller extent of a groove anterior to the 2nd
A second is the base unit of time in the International System of Units (SI).
Second, Seconds, The Second, or (The) 2nd may also refer to:
Mathematics
* 2 (number), as an ordinal (also written as ''2nd'' or ''2d'')
* Minute and second of arc, ...
and 3rd cranial nerve foramina being minor deviances from Majungasaurinae's type. The squamosal
The squamosal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In fishes, it is also called the pterotic bone.
In most tetrapods, the squamosal and quadratojugal bones form the cheek series of the skull. The bone forms an ancestra ...
is similar to that of the latter except for a less prominent parietal process. Generally, the external bone ornamentation is more subdued than that of ''Majungasaurus''. The tall teeth (3-5.5 cm) have denticles on the apical portion of the mesial
This is a list of definitions of commonly used terms of location and direction in dentistry. This set of terms provides orientation within the oral cavity, much as anatomical terms of location provide orientation throughout the body.
Terms
...
carina and along the length of the distal one, with varying density.
The caudal
Caudal may refer to:
Anatomy
* Caudal (anatomical term) (from Latin ''cauda''; tail), used to describe how close something is to the trailing end of an organism
* Caudal artery, the portion of the dorsal aorta of a vertebrate that passes into th ...
vertebrae
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal ...
of ''A. escotae'' are remarkably similar to those of ''Majungasaurus'', though more dorsoventrally compressed. The centra possess amphicoelous articulations with the pertinent facets of an intermediate nature between the circular ones of '' Ilokelesia'' and those of the elliptical shape in ''Rajasaurus'' and have neither pneumatic recesses nor accessory hyposphene-hypantrum articulation The hyposphene-hypantrum articulation is an accessory joint found in the vertebrae of several fossil reptiles of the group Archosauromorpha. It consists of a Process (anatomy), process on the backside of the vertebrae, the hyposphene, that fits in a ...
s. The transverse processes
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spina ...
of the neural arch
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal ...
es are not as inclined as in the Brachyrostra
Brachyrostra (meaning "short snouts") is a clade within the theropod dinosaur family Abelisauridae. It includes the famous genera ''Carnotaurus'', ''Aucasaurus'', potentially ''Abelisaurus'' as well as their close relatives from the Cretaceous Pe ...
.
The cnemial crest The cnemial crest is a crestlike prominence located at the front side of the head of the tibiotarsus or tibia in the legs of many mammals and reptiles (including birds and other dinosaurs). The main extensor muscle of the thigh
In anatomy, the ...
of ''Arcovenators the slender
Slender may refer to:
Term
* Gracility or slenderness
Literature
* Abraham Slender, a character in William Shakespeare's ''The Merry Wives of Windsor, The Merry Wives of Winsor''
Slender Man
*Slender Man, a fictional supernatural character
* ...
51-cm tibia
The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outsi ...
is well developed as is characteristic of abelisauroid
Ceratosaurs are members of the clade Ceratosauria, a group of dinosaurs defined as all theropods sharing a more recent common ancestor with ''Ceratosaurus'' than with birds. The oldest known ceratosaur, ''Saltriovenator'', dates to the earliest ...
s. It has a proximal lateral condyle more prominent than the medial
Medial may refer to:
Mathematics
* Medial magma, a mathematical identity in algebra Geometry
* Medial axis, in geometry the set of all points having more than one closest point on an object's boundary
* Medial graph, another graph that repr ...
one, a slight anterodorsal curve on the proximal aspect of the fibular crest, a noticeable distal longitudinal ridge, and tapered malleoli
A malleolus is the bony prominence on each side of the human ankle.
Each leg is supported by two bones, the tibia on the inner side (medial) of the leg and the fibula on the outer side (lateral) of the leg. The medial malleolus is the promine ...
. The nearly half-meter-long fibula
The fibula (: fibulae or fibulas) or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. ...
possesses the typical anatomical characters of ceratosaurs.
Classification and systematics
''Arcovenator'' is a theropod genus nested within the cladeAbelisauridae
Abelisauridae (meaning "Abel's lizards") is a family (or clade) of ceratosaurian theropod dinosaurs. Abelisaurids thrived during the Cretaceous period, on the ancient southern supercontinent of Gondwana, and today their fossil remains are fou ...
, which in Linnaean taxonomy
Linnaean taxonomy can mean either of two related concepts:
# The particular form of biological classification (taxonomy) set up by Carl Linnaeus, as set forth in his ''Systema Naturae'' (1735) and subsequent works. In the taxonomy of Linnaeus th ...
has the rank of family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
. This taxonomical group has as close relatives noasaurids
Noasauridae is an extinct family of theropod dinosaurs belonging to the group Ceratosauria. They were closely related to the short-armed abelisaurids, although most noasaurids had much more traditional body types generally similar to other ther ...
within the Abelisauroidea
Ceratosaurs are members of the clade Ceratosauria, a group of dinosaurs defined as all theropods sharing a more recent common ancestor with ''Ceratosaurus'' than with birds. The oldest known ceratosaur, ''Saltriovenator'', dates to the earliest ...
. The latter in turn along with ''Limusaurus
''Limusaurus'' is a genus of theropod dinosaur that lived in what is now China during the Late Jurassic, around 161 to 157 million years ago. The type and only species ''Limusaurus inextricabilis'' was described in 2009 from specimens ...
'' and ''Ceratosaurus
''Ceratosaurus'' (from Greek 'horn' and 'lizard') is a genus of carnivorous theropod dinosaur that lived in the Late Jurassic period (Kimmeridgian to Tithonian ages). The genus was first described in 1884 by American paleontologist Othni ...
'' nests within Ceratosauria
Ceratosaurs are members of the clade Ceratosauria, a group of dinosaurs defined as all theropods sharing a more recent common ancestor with '' Ceratosaurus'' than with birds. The oldest known ceratosaur, '' Saltriovenator'', dates to the earlies ...
.
Distinguishing characters of abelisaurids are their short, tall skulls with extensively sculptured external surfaces, the drastically reduced fore limbs, and the stout hind limbs.
phylogenetic analysis
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical data ...
, which is summarized in the cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not s ...
below and is based, in part, on previously published works including both the newly discovered fossil remains and other described but unnamed French abelisaurs.
The study generally agrees with previous results, namely a relatively recent one obtained both by Matthew Carrano and Scott Sampson (2008) and Diego Pol and Oliver W. M. Rauhut (2012) of a clade that includes at least ''Majungasaurus'', ''Indosaurus
''Indosaurus'' () is a genus of dubious carnivorous theropod dinosaur that lived in what is now India, about 69 to 66 million years ago during the Maastrichtian division of the Late Cretaceous.
Discovery and naming
The now-lost holotype wa ...
'' and ''Rajasaurus'', which in the more recent analysis includes ''Arcovenator''. Tortosa ''et al.''. name this well-supported clade the Majungasaurinae
Majungasaurinae (after ''Majungasaurus'', itself named after the city of Mahajanga in Madagascar) is a subfamily of large carnivorous theropods from the Upper Cretaceous, found in Madagascar, India, Spain, and France. It is a subgroup within th ...
, ranking it as subfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end botanical subfamily names with "-oideae", and zo ...
and defining it to contain all abelisaurids more closely related to ''Majungasaurus'' than to ''Carnotaurus''. The members of this taxonomical group have various cranial characters in common including an elongated antorbital fenestra, and a parietal with a sagittal crest that widens anteriorly into a triangular surface. Also of note is that, in partial agreement with some analyses, the more fragmentary French ceratosaur remains are placed within Abelisauridae, and contrary to others, ''Abelisaurus
''Abelisaurus'' (; "Abel's lizard") is a genus of predatory abelisaurid theropod dinosaur alive during the Late Cretaceous Period (geology), Period (Campanian) of what is now South America. It was a bipedal carnivore that probably reached about ...
'' is recovered as a carnotaurin.
Also, insights into the paleobiogeography
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, ...
of abelisauroids exist; just presence of them in the so-called European Archipelago confounds hypotheses that only consider the continents derived from the breakup
A relationship breakup, breakup, or break-up is the ending of a Interpersonal relationship, relationship. The act is commonly termed "dumping omeone in slang when it is initiated by one partner. The term is less likely to be applied to a ma ...
of Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian r ...
Gondwana
Gondwana ( ; ) was a large landmass, sometimes referred to as a supercontinent. The remnants of Gondwana make up around two-thirds of today's continental area, including South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia (continent), Australia, Zea ...
. Two lineages of European abelisaurs are discerned: a basal one, including the small Albian
The Albian is both an age (geology), age of the geologic timescale and a stage (stratigraphy), stage in the stratigraphic column. It is the youngest or uppermost subdivision of the Early Cretaceous, Early/Lower Cretaceous epoch (geology), Epoch/s ...
''Genusaurus'' and Lower Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campa ...
''Tarascosaurus'', and a derived one, the larger Campanian ''Arcovenator'' allied with the Madagascan ''Majungasaurus'' and the India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
n ''Rajasaurus'' in Majungasaurinae. As the inferred character distributions obtained through the phylogenetic analysis make it unlikely that these lineages are more closely related to each other than to other abelisaurids, this suggests a more complicated series of events regarding their biogeography with vicariance
Allopatric speciation () – also referred to as geographic speciation, vicariant speciation, or its earlier name the dumbbell model – is a mode of speciation that occurs when biological populations become geographically isolated from ...
applicable to the older one and oceanic dispersal being likelier for the more recent one. These results lend support to the proposed role of Africa as a hub for faunal movements between Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
and India or Madagascar and the isolation of South American abelisaurids.
Discovery and naming
The fossil remains of ''A. escotae'' were found nearPourrières
Pourrières (; ) is a commune in the Var department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region in southeastern France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas ...
, Var department, Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur (commonly shortened to PACA), also known as Région Sud, is one of the eighteen Regions of France, administrative regions of France, located at the far southeastern point of the Metropolitan France, mainland. The main P ...
region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ...
, during preventive paleontological and archaeological prospection activities before construction took place on the stretch of the A8 motorway between Châteauneuf-le-Rouge
Châteauneuf-le-Rouge (; ) is a commune in the Bouches-du-Rhône department in southern France.
Population
See also
*Communes of the Bouches-du-Rhône department
The following is a list of the 119 communes of the Bouches-du-Rhône de ...
and Saint Maximin. The pertinent late Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campa ...
strata (between 72 and 76 million years ago
Million years ago, abbreviated as Mya, Myr (megayear) or Ma (megaannum), is a unit of time equal to (i.e. years), or approximately 31.6 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used w ...
) of the Lower Argiles Rutilantes Formation are located in the Aix-en-Provence
Aix-en-Provence, or simply Aix, is a List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, city and Communes of France, commune in southern France, about north of Marseille. A former capital of Provence, it is the Subprefectures in France, s ...
Basin of southeastern France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
. The holotype
A holotype (Latin: ''holotypus'') is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of s ...
of ''Arcovenator escotae'', housed at the Muséum d’Histoire Naturelle d’Aix-en-Provence, was found closely associated in a single stratum of fluvial sandstone and is made up of specimens MHNA-PV-2011.12.1, a braincase in articulation with a right postorbital, MHNA-PV-2011.12.2, a left squamosal, MHNA.PV.2011.12.15, a tooth, MHNA.PV.2011.12.5, MHNA.PV.2011.12.5, an anterior caudal vertebra, MHNA.PV.2011.12.3, a right tibia, and MHNA.PV.2011.12.4, a right fibula. Two anterior caudal vertebrae (MHNA.PV.2011.12.198 and MHNA.PV.2011.12.213) and three teeth (MHNA.PV.2011.12.20, MHNA.PV.2011.12.187 and MHNA.PV.2011.12.297) found close both in distance and depth were also referred to the species, but belonging to different individuals. It is likely that a maxilla, the sole fossil found of the so-called Pourcieux
Pourcieux (; ) is a commune in the Var department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region in southeastern France.
The small village provides a typical image of the Provence of Frédéric Mistral, with vine-grower's houses built around a cast ...
abelisaurid, is referable to at least this genus on account of both its close proximity in time and space and the results of the phylogenetic analysis. Numerous abelisaurid teeth from the early Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian ( ) is, in the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS) geologic timescale, the latest age (geology), age (uppermost stage (stratigraphy), stage) of the Late Cretaceous epoch (geology), Epoch or Upper Cretaceous series (s ...
strata from Laño
Laño () is a hamlet and '' concejo'' (a small administrative subdivision) in Condado de Treviño within the Treviño enclave; which is administratively part of the Spanish province of Burgos, but which is completely surrounded by the territo ...
are referred to as ''Arcovenator'' sp.
The genus name ''Arcovenator'' derives from the river Arc as the locality is set within its basin and the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
word for hunter, ''venator''. The specific epithet
In Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin gramm ...
'escotae' honors Escota
Vinci (; corporately styled VINCI) is a French concessions and construction company founded in 1899 as Société Générale d'Entreprises. Its head office is in Nanterre, in the western suburbs of Paris. Vinci is listed on Euronext's Paris sto ...
, a motorway
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway, and expressway. Other similar terms ...
concession
Concession may refer to:
General
* Concession (contract) (sometimes called a concession agreement), a contractual right to carry on a certain kind of business or activity in an area, such as to explore or develop its natural resources or to opera ...
company, which since 2006 has provided the necessary funds to excavate the locality.
Paleoecology
''A. escotae'' lived on the Ibero-Armorican island, a relatively large landmass formed by what are now parts of France,Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, and Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
. The compressional subsidence
Subsidence is a general term for downward vertical movement of the Earth's surface, which can be caused by both natural processes and human activities. Subsidence involves little or no horizontal movement, which distinguishes it from slope mov ...
basin of Aix-en-Provence was a low-relief endorheic
An endorheic basin ( ; also endoreic basin and endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water (e.g. rivers and oceans); instead, the water drainage flows into permanent ...
affair located at a paleolatitude of 35°N, and had its borders to north and south in the form of limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
highlands
Highland is a broad term for areas of higher elevation, such as a mountain range or mountainous plateau.
Highland, Highlands, or The Highlands, may also refer to:
Places Africa
* Highlands, Johannesburg, South Africa
* Highlands, Harare, Zimbab ...
, respectively the Sainte Victoire and Etoile massifs, and to the east as the Maure Mountains. The sediment from these sources flowed along rivers into a perennial lake
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from ...
originating interbedded lacustrine, alluvial and fluvial sediments at the time of ''Arcovenator'', when the climate was warm, subhumid with marked seasons. The fossil remains were found in one of the formation
Formation may refer to:
Linguistics
* Back-formation, the process of creating a new lexeme by removing or affixes
* Word formation, the creation of a new word by adding affixes
Mathematics and science
* Cave formation or speleothem, a secondary ...
's various levels of fluvial sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
, characteristic of a river's mouth or when it overflows its banks, along with hybodonts
Hybodontiformes, commonly called hybodonts, are an extinct group of shark-like cartilaginous fish (chondrichthyans) which existed from the late Devonian to the Late Cretaceous. Hybodonts share a close common ancestry with modern sharks and Batoide ...
, the turtles
Turtles are reptiles of the order Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked turtle ...
'' Foxemys'' and ''Solemys
''Solemys'' is an extinct genus of helyochelydrid stem-turtle known from the Late Cretaceous (late Campanian-early Maastrichtian) of southern France and eastern Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Sout ...
'', the crocodylomorphs
Crocodylomorpha is a group of pseudosuchian archosaurs that includes the crocodilians and their extinct relatives. They were the only members of Pseudosuchia to survive the end-Triassic extinction. Extinct crocodylomorphs were considerably more ...
'' Musturzabalsuchus'' and '' Ischyrochampsa'', azhdarchid
Azhdarchidae (from the Persian word , , a dragon-like creature in Persian mythology) is a family of pterosaurs known primarily from the Late Cretaceous Period, though an isolated vertebra apparently from an azhdarchid is known from the Early Cre ...
pterosaurs
Pterosaurs are an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the Order (biology), order Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 million to 66 million years ago). Pterosau ...
, titanosaur
Titanosaurs (or titanosaurians; members of the group Titanosauria) were a diverse group of sauropod dinosaurs, including genera from all seven continents. The titanosaurs were the last surviving group of long-necked sauropods, with taxa still thr ...
ian sauropods
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their b ...
, the ornithopod
Ornithopoda () is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs, called ornithopods (). They represent one of the most successful groups of herbivorous dinosaurs during the Cretaceous. The most primitive members of the group were bipedal and relatively sm ...
''Rhabdodon
''Rhabdodon'' (meaning "fluted tooth") is a genus of ornithopod dinosaur that lived in Europe approximately 70-66 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous. The genus contains a single species, ''R. priscus''. It is similar in build to a very rob ...
'' and nodosaurids
Nodosauridae is a family of ankylosaurian dinosaurs known from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous Period (geology), periods in what is now Asia, Europe, North America, and possibly South America. While traditionally regarded as a monophylet ...
. The abundance of fragmentary remains of medium-sized abelisaurs, especially teeth in this and other localities of the region show that these animals would have been relatively common in the landscape.
See also
*Timeline of ceratosaur research
This timeline of ceratosaur research is a chronological listing of events in the History of paleontology, history of paleontology focused on the ceratosaurs, a group of relatively primitive, often horned, predatory theropod dinosaurs that became ...
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q15303586 Abelisauridae Dinosaur genera Campanian dinosaurs Dinosaurs of France Fossil taxa described in 2013