Arabian Toad-headed Agama Breeding on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a
 The Arabian Peninsula is located in the continent of Asia and is bounded by (clockwise) the Persian Gulf on the north-east, the
The Arabian Peninsula is located in the continent of Asia and is bounded by (clockwise) the Persian Gulf on the north-east, the
 The Peninsula's constituent countries are (clockwise from north to south)
The Peninsula's constituent countries are (clockwise from north to south)
 The eleven most populous cities on the Arabian Peninsula are:
The eleven most populous cities on the Arabian Peninsula are:
File:Salalah Oman.jpg,
retrieved 20 January 2011 The harsh climate historically prevented much settlement in the pre-Islamic Arabian Peninsula, apart from a small number of urban trading settlements, such as
 The seventh century saw the rise of Islam as the peninsula's dominant religion. The
The seventh century saw the rise of Islam as the peninsula's dominant religion. The
 Despite its spiritual importance, in political terms Arabia soon became a peripheral region of the
Despite its spiritual importance, in political terms Arabia soon became a peripheral region of the
retrieved 18 January 2011

 The provincial Ottoman Army for Arabia (Arabistan Ordusu) was headquartered in
The provincial Ottoman Army for Arabia (Arabistan Ordusu) was headquartered in
 The major developments of the early 20th century were the
The major developments of the early 20th century were the
File:Sanaa.JPG, alt=The old city of Sanaa, Yemen. Peninsular Arabs trace their lineage to Qahtan, who was reportedly based in Yemen., The Old City of Sanaa
File:عين زبيدة.png, Ain Zubaydah was built to water the pilgrims in
Travels in Arabia
(1892)
High resolution scan of old map of Arabia
.
The Coast of Arabia the Red Sea, and Persian Sea of Bassora Past the Straits of Hormuz to India, Gujarat and Cape Comorin
from the World Digital Library, depicts a map from 1707. *
Arabia: Cultural-Historical Zones
Old maps of Arabia
Eran Laor Cartographic Collection, The National Library of Israel
peninsula
A peninsula is a landform that extends from a mainland and is only connected to land on one side. Peninsulas exist on each continent. The largest peninsula in the world is the Arabian Peninsula.
Etymology
The word ''peninsula'' derives , . T ...
in West Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian ...
, situated north-east of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the Arabian Peninsula comprises Bahrain
Bahrain, officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, is an island country in West Asia. Situated on the Persian Gulf, it comprises a small archipelago of 50 natural islands and an additional 33 artificial islands, centered on Bahrain Island, which mak ...
, Kuwait
Kuwait, officially the State of Kuwait, is a country in West Asia and the geopolitical region known as the Middle East. It is situated in the northern edge of the Arabian Peninsula at the head of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Kuwait ...
, Oman
Oman, officially the Sultanate of Oman, is a country located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia and the Middle East. It shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Oman’s coastline ...
, Qatar
Qatar, officially the State of Qatar, is a country in West Asia. It occupies the Geography of Qatar, Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it shares Qatar–Saudi Arabia border, its sole land b ...
, Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
, the United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE), or simply the Emirates, is a country in West Asia, in the Middle East, at the eastern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is a Federal monarchy, federal elective monarchy made up of Emirates of the United Arab E ...
(UAE) and Yemen
Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in South Arabia, southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the north, Oman to Oman–Yemen border, the northeast, the south-eastern part ...
, as well as southern Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
and Jordan
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian ter ...
. The largest of these is Saudi Arabia. In the Roman era, the Sinai Peninsula
The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai ( ; ; ; ), is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a land bridge between Asia and Afri ...
was also considered a part of Arabia.
The Arabian Peninsula formed as a result of the rifting of the Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and th ...
between 56 and 23 million years ago, and is bordered by the Red Sea to the west and south-west, the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.Un ...
and the Gulf of Oman
The Gulf of Oman or Sea of Oman ( ''khalīj ʿumān''; ''daryâ-ye omân''), also known as Gulf of Makran or Sea of Makran ( ''khalīj makrān''; ''daryâ-ye makrān''), is a gulf in the Indian Ocean that connects the Arabian Sea with th ...
to the north-east, the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
and Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
to the north and the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea () is a region of sea in the northern Indian Ocean, bounded on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, Gulf of Aden and Guardafui Channel, on the northwest by Gulf of Oman and Iran, on the north by Pakistan, on the east by India, and ...
and the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
to the south-east. The peninsula plays a critical geopolitical
Geopolitics () is the study of the effects of Earth's geography on politics and international relations. Geopolitics usually refers to countries and relations between them, it may also focus on two other kinds of states: ''de facto'' independen ...
role in the Arab world
The Arab world ( '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, comprises a large group of countries, mainly located in West Asia and North Africa. While the majority of people in ...
and globally due to its vast reserves of oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) and lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturate ...
and natural gas
Natural gas (also fossil gas, methane gas, and gas) is a naturally occurring compound of gaseous hydrocarbons, primarily methane (95%), small amounts of higher alkanes, and traces of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide and helium ...
.
Before the modern era, the region was divided into primarily four distinct regions: the Central Plateau (Najd
Najd is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes most of the central region of Saudi Arabia. It is roughly bounded by the Hejaz region to the west, the Nafud desert in Al-Jawf Province, al-Jawf to the north, ...
and Al-Yamama
Al-Yamama () is a historical region in south-eastern Najd in modern-day Saudi Arabia.
Only a handful of centralized states ever arose in the Yamama, but it figured prominently in early Islamic history, becoming a central theater in the Ridd ...
), South Arabia
South Arabia (), or Greater Yemen, is a historical region that consists of the southern region of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia, mainly centered in what is now the Republic of Yemen, yet it has also historically included Najran, Jazan, ...
(Yemen
Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in South Arabia, southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the north, Oman to Oman–Yemen border, the northeast, the south-eastern part ...
, Hadhramaut
Hadhramaut ( ; ) is a geographic region in the southern part of the Arabian Peninsula which includes the Yemeni governorates of Hadhramaut, Shabwah and Mahrah, Dhofar in southwestern Oman, and Sharurah in the Najran Province of Saudi A ...
and south-western Oman
Oman, officially the Sultanate of Oman, is a country located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia and the Middle East. It shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Oman’s coastline ...
), Al-Bahrain (Eastern Arabia or Al-Hassa), and the Hejaz
Hejaz is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes the majority of the western region of Saudi Arabia, covering the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif and Al Bahah, Al-B ...
(Tihamah
Tihamah or Tihama ( ') is the Red Sea coastal plain of the Arabian Peninsula from the Gulf of Aqaba to the Bab el Mandeb.
Etymology
Tihāmat is the Proto-Semitic language's term for 'sea'. Tiamat (or Tehom, in masculine form) was the ancient M ...
for the western coast), as described by Ibn al-Faqih
Aḥmad ibn Muḥammad ibn al-Faqih al-Hamadani () (fl. 902) was a 10th-century Persian historian and geographer, famous for his ''Mukhtasar Kitab al-Buldan'' ("Concise Book of Lands") written in Arabic.
In the 1870s the Dutch orientalist Micha ...
.
Etymology
In antiquity, the term "Arabia" encompassed a larger area than the current term "Arabian Peninsula" and included theArabian Desert
The Arabian Desert () is a vast desert wilderness in West Asia that occupies almost the entire Arabian Peninsula with an area of . It stretches from Yemen to the Persian Gulf and Oman to Jordan and Iraq. It is the fourth largest desert in the ...
and large parts of the Syrian–Arabian desert. During the Hellenistic period
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
, the area was known as ''Arabia'' (). The Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
named three regions "Arabia":
* Arabia Petraea
Arabia Petraea or Petrea, also known as Rome's Arabian Province or simply Arabia, was a frontier Roman province, province of the Roman Empire beginning in the 2nd century. It consisted of the former Nabataean Kingdom in the southern Levant, th ...
(): it consisted of the former Nabataean Kingdom
The Nabataean Kingdom (Nabataean Aramaic: 𐢕𐢃𐢋𐢈 ''Nabāṭū''), also named Nabatea () was a political state of the Nabataeans during classical antiquity. The Nabataean Kingdom controlled many of the trade routes of the region, amassin ...
in the southern Levant, the Sinai Peninsula and north-western Arabian Peninsula. It was the only one that became a province
A province is an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire, Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
, with Petra
Petra (; "Rock"), originally known to its inhabitants as Raqmu (Nabataean Aramaic, Nabataean: or , *''Raqēmō''), is an ancient city and archaeological site in southern Jordan. Famous for its rock-cut architecture and water conduit systems, P ...
(in Jordan
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian ter ...
) as its capital.
* Arabia Deserta
Arabia Deserta (Latin for ), also known as Arabia Magna (), signified the desert interior of the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plat ...
(): signified the desert lands of Arabia. As a name for the region, it remained popular into the 19th and 20th centuries, and was used in Charles M. Doughty's ''Travels in Arabia Deserta
''Travels in Arabia Deserta'' (1888) is a travel book by Charles Montagu Doughty (1843–1926), an English poet, writer, and traveller. Doughty had travelled in the Middle East and spent some time living with the Bedouin
The Bedouin, Bedu ...
'' (1888).
* Arabia Felix
Arabia Felix (literally: Fertile/Happy Arabia; also Ancient Greek: Εὐδαίμων Ἀραβία, ''Eudaemon Arabia'') was the Latin name previously used by geographers to describe South Arabia, or what is now Yemen.
Etymology
The Latin term ...
(): was used by geographers to describe the southern part of the Arabian peninsula, mostly what is now Yemen
Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in South Arabia, southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the north, Oman to Oman–Yemen border, the northeast, the south-eastern part ...
, which enjoys more rainfall, is much greener than the rest of the peninsula and has long enjoyed much more productive fields.
One of the nomes of Ptolemaic Egypt was named ''Arabia''.
Arabians used a north–south division of Arabia: ''ash-Sham'' vs. ''al-Yaman'', or ''Arabia Deserta'' vs. ''Arabia Felix''. Arabia Felix had originally been used for the whole peninsula, and at other times only for the southern region. Because its use became limited to the south, the whole peninsula was simply called Arabia. Arabia Deserta was the entire desert region extending north from Arabia Felix to Palmyra and the Euphrates, including all the area between Pelusium on the Nile and Babylon. This area was also called Arabia and not sharply distinguished from the peninsula.
The Arabs and the Ottoman Empire considered the west of the Arabian Peninsula region where the Arabs lived 'the land of the Arabs'—billad al-'Arab (Arabia), and its major divisions were the bilad al-Sham (Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
), bilad al-Yaman (Yemen
Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in South Arabia, southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the north, Oman to Oman–Yemen border, the northeast, the south-eastern part ...
), and bilad al-'Iraq (Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
). The Ottomans used the term Arabistan in a broad sense for the region starting from Cilicia
Cilicia () is a geographical region in southern Anatolia, extending inland from the northeastern coasts of the Mediterranean Sea. Cilicia has a population ranging over six million, concentrated mostly at the Cilician plain (). The region inclu ...
, where the Euphrates river makes its descent into Syria, through Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and th ...
, and on through the remainder of the Sinai and Arabian peninsulas.
The provinces of Arabia were: al-Tih, the Sinai peninsula, Hejaz, Asir, Yemen, Hadramaut, Mahra and Shilu, Oman, Hasa, Bahrain, Dahna, Nufud, the Hammad, which included the deserts of Syria, Mesopotamia and Babylonia.
Geography
Strait of Hormuz
The Strait of Hormuz ( ''Tangeh-ye Hormoz'' , ''Maḍīq Hurmuz'') is a strait between the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. It provides the only sea passage from the Persian Gulf to the open ocean and is one of the world's most strategica ...
and the Gulf of Oman on the east, the Arabian Sea on the south-east, the Gulf of Aden
The Gulf of Aden (; ) is a deepwater gulf of the Indian Ocean between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channel, the Socotra Archipelago, Puntland in Somalia and Somaliland to the south. ...
, and the Guardafui Channel
The Guardafui Channel (, ) is an oceanic strait off the tip of the Horn of Africa that lies between the Puntland region of Somalia and the Socotra governorate of Yemen to the west of the Arabian Sea. It connects the Gulf of Aden to the north ...
on the south, and the Bab-el-Mandeb
The Bab-el-Mandeb (), the Gate of Grief or the Gate of Tears, is a strait between Yemen on the Arabian Peninsula and Djibouti and Eritrea in the Horn of Africa. It connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden and by extension the Indian Ocean.
...
strait on the south-west and the Red Sea, which is located on the south-west and west. The northern portion of the peninsula merges with the Syrian Desert
The Syrian Desert ( ''Bādiyat Ash-Shām''), also known as the North Arabian Desert, the Jordanian steppe, or the Badiya, is a region of desert, semi-desert, and steppe, covering about of West Asia, including parts of northern Saudi Arabia, ea ...
with no clear borderline, although the northern boundary of the peninsula is generally considered to be the northern borders of Saudi Arabia and Kuwait, also southern regions of Iraq and Jordan.
The most prominent feature of the peninsula is desert
A desert is a landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions create unique biomes and ecosystems. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the la ...
, but in the south-west, there are mountain ranges, which receive greater rainfall than the rest of the peninsula. Harrat ash Shaam
The ''Ḥarrat al-Shām'' (), also known as the ''Harrat al-Harra'' or ''Harrat al-Shaba'', and sometimes the Black Desert in English, is a region of rocky, basaltic desert straddling southern Syrian region and the northern Arabian Peninsula. ...
is a large volcanic field that extends from north-western Arabia into Jordan and southern Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
.
Political boundaries
Kuwait
Kuwait, officially the State of Kuwait, is a country in West Asia and the geopolitical region known as the Middle East. It is situated in the northern edge of the Arabian Peninsula at the head of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Kuwait ...
, Qatar
Qatar, officially the State of Qatar, is a country in West Asia. It occupies the Geography of Qatar, Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it shares Qatar–Saudi Arabia border, its sole land b ...
, and the United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE), or simply the Emirates, is a country in West Asia, in the Middle East, at the eastern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is a Federal monarchy, federal elective monarchy made up of Emirates of the United Arab E ...
(UAE) on the east, Oman
Oman, officially the Sultanate of Oman, is a country located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia and the Middle East. It shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Oman’s coastline ...
on the south-east, Yemen
Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in South Arabia, southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the north, Oman to Oman–Yemen border, the northeast, the south-eastern part ...
on the south, and Saudi Arabia at the center. The island country of Bahrain
Bahrain, officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, is an island country in West Asia. Situated on the Persian Gulf, it comprises a small archipelago of 50 natural islands and an additional 33 artificial islands, centered on Bahrain Island, which mak ...
lies just off the east coast of the Peninsula. Due to Yemen's jurisdiction over the Socotra Archipelago
The Socotra Archipelago ( '), officially the Socotra Archipelago Governorate ( '), abbreviated to Socotra Governorate ( '), is one of the governorates of Yemen. It includes a number of islands in the Indian Ocean south of mainland Yemen, the la ...
, the Peninsula's geopolitical outline faces the Guardafui Channel
The Guardafui Channel (, ) is an oceanic strait off the tip of the Horn of Africa that lies between the Puntland region of Somalia and the Socotra governorate of Yemen to the west of the Arabian Sea. It connects the Gulf of Aden to the north ...
and the Somali Sea to the south.
The six countries of Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE form the Gulf Cooperation Council
The Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf (), also known as the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC; ), is a Regional integration, regional, intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental, political, and economic union comprising Ba ...
(GCC).
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia covers the greater part of the Peninsula. The Peninsula contains the world's largest reserves of oil. Saudi Arabia and the UAE are economically the wealthiest in the region. Qatar, the only peninsular country in the Persian Gulf on the larger peninsula, is home to the Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
television station Al Jazeera
Al Jazeera Media Network (AJMN; , ) is a private-media conglomerate headquartered in Wadi Al Sail, Doha, funded in part by the government of Qatar. The network's flagship channels include Al Jazeera Arabic and Al Jazeera English, which pro ...
and its English-language subsidiary Al Jazeera English
Al Jazeera English (AJE; , ) is a 24-hour English-language News broadcasting, news channel operating under Al Jazeera Media Network, which is funded by the government of Qatar. Al Jazeera introduced an English-language division in 2006. It is ...
. Kuwait, on the border with Iraq, is an important country strategically, forming one of the main staging grounds for coalition forces mounting the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
–led 2003 invasion of Iraq.
Population
Despite its historically sparse population, political Arabia stands out for its rapid population growth, driven by both significant inflows of migrant labor and persistently high birth rates. The population is characterized by its relative youth and a heavily skewed gender ratio favoring males. In several states, the number of South Asians surpasses that of the native population. The four smallest states (by area), with coastlines entirely bordering the Persian Gulf, showcase the world's most extreme population growth, nearly tripling every two decades. In 2014, the estimated population of the Arabian Peninsula was 77,983,936 (including expatriates). The Arabian Peninsula is known for having one of the most uneven adult sex ratios in the world, with females in some regions (especially the east) constituting only a quarter of people aged between 20 and 40.Cities
 The eleven most populous cities on the Arabian Peninsula are:
The eleven most populous cities on the Arabian Peninsula are:
Landscape
The rocks exposed vary systematically across Arabia, with the oldest rocks exposed in theArabian-Nubian Shield
The Arabian-Nubian Shield (ANS) is an exposure of Precambrian crystalline rocks on the flanks of the Red Sea. The crystalline rocks are mostly Neoproterozoic in age. Geographically – and from north to south – the ANS includes parts of Israel ...
near the Red Sea, overlain by earlier sediments that become younger towards the Persian Gulf. Perhaps the best-preserved ophiolite
An ophiolite is a section of Earth's oceanic crust and the underlying upper mantle (Earth), upper mantle that has been uplifted and exposed, and often emplaced onto continental crustal rocks.
The Greek word ὄφις, ''ophis'' (''snake'') is ...
on Earth, the Semail Ophiolite
The Samail Ophiolite, also known as the Semail Ophiolite, is a large, ancient geological formation in Oman and the United Arab Emirates in the Arabian Peninsula. It is one of the world's largest and best-exposed segments of oceanic crust, made of ...
, lies exposed in the mountains of the UAE and northern Oman.
The peninsula consists of:
# A central plateau, the Najd
Najd is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes most of the central region of Saudi Arabia. It is roughly bounded by the Hejaz region to the west, the Nafud desert in Al-Jawf Province, al-Jawf to the north, ...
, with fertile valleys and pastures used for the grazing of sheep
Sheep (: sheep) or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are a domesticated, ruminant mammal typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to d ...
and other livestock
# A range of deserts: the Nefud in the north, which is stony; the Rub' al Khali
The Rub' al KhaliOther standardized transliterations include: /. The ' is the assimilated Arabic definite article, ', which can also be transliterated as '. (; , ) or Empty Quarter is a desert encompassing most of the southern third of the Arabi ...
or Great Arabian Desert
The Arabian Desert () is a vast desert wilderness in West Asia that occupies almost the entire Arabian Peninsula with an area of . It stretches from Yemen to the Persian Gulf and Oman to Jordan and Iraq. It is the fourth largest desert in the ...
in the south, with sand estimated to extend below the surface; between them, the Dahna
Ad-Dahna Desert is the central division of the Arabian Desert. It is a corridor of sandy terrain forming a bow-like shape that connects an-Nafud desert in the north to Rub' al-Khali desert in the south. Its length is more than siding Twai ...
Mountains
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher ...
# Stretches of dry or marshy coastline with coral reefs on the Red Sea side (Tihamah
Tihamah or Tihama ( ') is the Red Sea coastal plain of the Arabian Peninsula from the Gulf of Aqaba to the Bab el Mandeb.
Etymology
Tihāmat is the Proto-Semitic language's term for 'sea'. Tiamat (or Tehom, in masculine form) was the ancient M ...
)
# Oases and marshy coast-land in Eastern Arabia
Eastern Arabia () is a region stretched from Basra to Khasab along the Persian Gulf coast and included parts of modern-day Bahrain, Iraq, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia (Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia, Eastern Province), and the United Arab ...
, the most important of which are those of the Al Ain emirate ( Tawam region) and Hofuf
Al-Hofuf ( ', also spelled Hofuf or Hufuf, also known as "Al-Hasa", "Al-Ahsa" or "Al-Hassa") is the major urban city in the Al-Ahsa Governorate in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia, with a population of 729,606 (as of 2022). It is known f ...
/ Al-Ahsa (in modern-day Saudi Arabia), according to an author
# The south-west monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annu ...
coastline of Dhofar
The Dhofar Governorate () is the largest of the 11 governorates in the Sultanate of Oman in terms of area. It lies in southern Oman, on the eastern border with Yemen's Al Mahrah Governorate and the southern border with Saudi Arabia's Easter ...
and Eastern Yemen ( Mahra).
Arabia has few lakes or permanent rivers. Most areas are drained by ephemeral watercourses called wadi
Wadi ( ; ) is a river valley or a wet (ephemerality, ephemeral) Stream bed, riverbed that contains water only when heavy rain occurs. Wadis are located on gently sloping, nearly flat parts of deserts; commonly they begin on the distal portion ...
s, which are dry except during the rainy season. Plentiful ancient aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing material, consisting of permeability (Earth sciences), permeable or fractured rock, or of unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Aquifers vary greatly in their characteristics. The s ...
s exist beneath much of the peninsula, however, and where this water surfaces, oases
In ecology, an oasis (; : oases ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environmentQatif
Qatif Governorate ( ''Al-Qaṭīf'') is a list of governorates of Saudi Arabia, governorate and urban area located in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia, Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia. It extends from Ras Tanura and Jubail in the north to Damma ...
, two of the world's largest oases
In ecology, an oasis (; : oases ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environmentpalm trees
The Arecaceae () is a family of perennial, flowering plants in the monocot order Arecales. Their growth form can be climbers, shrubs, tree-like and stemless plants, all commonly known as palms. Those having a tree-like form are colloquially ...
, which allowed the peninsula to produce more dates
Date or dates may refer to:
* Date, the fruit of the date palm (''Phoenix dactylifera'')
* Jujube, also known as red date or Chinese date, the fruit of ''Ziziphus jujuba''
Social activity
*Dating, a form of courtship involving social activit ...
than any other region in the world. In general, the climate is extremely hot and arid
Aridity is the condition of geographical regions which make up approximately 43% of total global available land area, characterized by low annual precipitation, increased temperatures, and limited water availability.Perez-Aguilar, L. Y., Plata ...
, although there are exceptions. Higher elevations are made temperate by their altitude, and the Arabian Sea coastline can receive cool, humid breezes in summer due to cold upwelling offshore. The peninsula has no thick forests. Desert-adapted wildlife is present throughout the region.
A plateau more than high extends across much of the Arabian Peninsula. The plateau slopes eastwards from the massive, rifted escarpment along the coast of the Red Sea, to the shallow waters of the Persian Gulf. The interior is characterized by ''cuestas'' and valleys, drained by a system of ''wadis''. A crescent of sand and gravel
Gravel () is a loose aggregation of rock fragments. Gravel occurs naturally on Earth as a result of sedimentation, sedimentary and erosion, erosive geological processes; it is also produced in large quantities commercially as crushed stone.
Gr ...
deserts lies to the east.
Mountains
There are mountains at the eastern, southern and north-western borders of the peninsula. Broadly, the ranges can be grouped as follows: * North-east: The Hajar range, of UAE and Oman * South-east: TheDhofar Mountains
The Dhofar Mountains () are a mountain range in the southeastern part of the Arabian Peninsula. In a broad sense, they extend from Dhofar Governorate in Oman to Hadhramaut Governorate in Yemen, and are located between the Hajar in the northern ...
of southern Oman, contiguous with the eastern Yemeni Hadhramaut
Hadhramaut ( ; ) is a geographic region in the southern part of the Arabian Peninsula which includes the Yemeni governorates of Hadhramaut, Shabwah and Mahrah, Dhofar in southwestern Oman, and Sharurah in the Najran Province of Saudi A ...
* West: Bordering the eastern coast of the Red Sea are the Sarawat, which can be seen to include the Haraz Mountains to the east of Yemen, as well as those of 'Asir
Asir, officially the Aseer Province, is a province of Saudi Arabia in southern Arabia. It has an area of , and an estimated population of 2,024,285 (in 2022). Asir is bounded by the Mecca Province to the north and west, al-Bahah Province to the ...
(once part of Yemen) and Hejaz
Hejaz is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes the majority of the western region of Saudi Arabia, covering the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif and Al Bahah, Al-B ...
the latter including the Midian
Midian (; ; , ''Madiam''; Taymanitic: 𐪃𐪕𐪚𐪌 ''MDYN''; ''Mīḏyān'') is a geographical region in West Asia, located in northwestern Saudi Arabia. mentioned in the Tanakh and Quran. William G. Dever states that biblical Midian was ...
in what is now north-western Saudi Arabia
* North-west: Aside from the Sarawat, the northern portion of Saudi Arabia hosts the Jabal Shamar Mountains, which include the Aja and Salma subranges
* Central: The Najd hosts the Tuwaiq
Jabal Tuwaiq (, Tuwaiq Mountain) is a narrow escarpment that cuts through the plateau of Najd in central Arabia, running approximately from the southern border of Al-Qasim in the north, to the northern edge of the Rub' al Khali desert near ...
Escarpment or Tuwair range
From the Hejaz
Hejaz is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes the majority of the western region of Saudi Arabia, covering the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif and Al Bahah, Al-B ...
southwards, the mountains show a steady increase in altitude westward as they get nearer to Yemen, and the highest peaks and ranges are all located in Yemen. The highest, Jabal An-Nabi Shu'ayb
''Jabal An-Nabī Shuʿayb'' (), also called Jabal Hadhur (), is a mountain of the Harazi subregion of the Sarawat, located in Bani Matar District, Sanaa Governorate, Yemen. It is the highest mountain in the country and the Arabian Peninsula. ...
or Jabal Hadhur of the Haraz subrange of the Sarawat range, is high. By comparison, the Tuwayr, Shammar and Dhofar generally do not exceed in height.
Not all mountains in the peninsula are visibly within ranges. Jebel Hafeet
Jabal Hafeet (, "Mount Hafeet"; variously transcribed Jabel or Jebal and Hafit – literally "empty mountain") is a mountain in the region of Tawam, on the border of the United Arab Emirates and Oman. It is often considered an outlier of the Ha ...
in particular, on the border of the UAE and Oman, measuring between , is not within the Hajar range, but may be considered an outlier
In statistics, an outlier is a data point that differs significantly from other observations. An outlier may be due to a variability in the measurement, an indication of novel data, or it may be the result of experimental error; the latter are ...
of that range.
Dhofar
The Dhofar Governorate () is the largest of the 11 governorates in the Sultanate of Oman in terms of area. It lies in southern Oman, on the eastern border with Yemen's Al Mahrah Governorate and the southern border with Saudi Arabia's Easter ...
File:Yemen landscape 05.jpg, At-Tawilah, Al Mahwit, Yemen
Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in South Arabia, southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the north, Oman to Oman–Yemen border, the northeast, the south-eastern part ...
File:شعيب جو بجبال أجـــا - panoramio.jpg, A subrange of the Jabal Shammar mountains in the desert region of Ha'il, Saudi Arabia
Land and sea
Most of the Arabian Peninsula is unsuited to agriculture, making irrigation and land reclamation projects essential. The narrow coastal plain and isolated oases, amounting to less than 1% of the land area, are used to cultivate grains,coffee
Coffee is a beverage brewed from roasted, ground coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content, but decaffeinated coffee is also commercially a ...
and tropical fruit
There are many fruits that typically grow in warm tropical climates or equatorial areas.
Tropical fruits
Varieties of tropical fruit include:
* Abiu
* Açaí
* Acerola (West Indian cherry; Barbados cherry)
* Achachairú (Bolivian mangosteen; ...
s. Goat, sheep, and camel
A camel (from and () from Ancient Semitic: ''gāmāl'') is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. Camels have long been domesticated and, as livestock, they provid ...
husbandry is widespread elsewhere throughout the rest of the Peninsula. Some areas have a summer humid tropical monsoon climate
An area of tropical monsoon climate (occasionally known as a sub-equatorial, tropical wet climate or a tropical monsoon and trade-wind littoral climate) is a tropical climate subtype that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification category ' ...
, in particular the Dhofar
The Dhofar Governorate () is the largest of the 11 governorates in the Sultanate of Oman in terms of area. It lies in southern Oman, on the eastern border with Yemen's Al Mahrah Governorate and the southern border with Saudi Arabia's Easter ...
and Al Mahrah areas of Oman and Yemen. These areas allow for large scale coconut plantations. Much of Yemen has a tropical monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annu ...
rain influenced mountain climate. The plains usually have either a tropical or subtropical arid desert climate
The desert climate or arid climate (in the Köppen climate classification ''BWh'' and ''BWk'') is a dry climate sub-type in which there is a severe excess of evaporation over precipitation. The typically bald, rocky, or sandy surfaces in desert ...
or arid steppe climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi ...
. The sea surrounding the Arabian Peninsula is generally tropical with a very rich sea life and some of the world's largest and most pristine coral reefs. In addition, the protozoa
Protozoa (: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a polyphyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic debris. Historically ...
and zooxanthellae
Zooxanthellae (; zooxanthella) is a colloquial term for single-celled photosynthetic organisms that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including corals, jellyfish, demosponges, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthell ...
living in symbiosis
Symbiosis (Ancient Greek : living with, companionship < : together; and ''bíōsis'': living) is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction, between two organisms of different species. The two organisms, termed symbionts, can fo ...
with Red Sea corals have a unique hot weather adaptation to sudden rise (and fall) in sea water temperature. Hence, these coral reefs are not affected by coral bleaching caused by rise in temperatures, as Indo-Pacific
The Indo-Pacific is a vast biogeographic region of Earth. In a narrow sense, sometimes known as the Indo-West Pacific or Indo-Pacific Asia, it comprises the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the ...
coral reefs are. The reefs are also unaffected by mass tourism and diving or other large scale human interference. The Persian gulf has suffered significant loss and degradation of coral reefs with the biggest ongoing threat believed to be coastal construction activity altering the marine environment.
The fertile soils of Yemen have encouraged settlement of almost all of the land from sea level up to the mountains at . In the higher elevations, elaborate terraces have been constructed to facilitate grain, fruit, coffee, ginger and khat
Khat (''Catha edulis''), also known as Bushman's tea, especially in South Africa, is a flowering plant native to eastern and southeastern Africa. It has a history of cultivation originating in the Harar area (present day eastern Ethiopia) and ...
cultivation. The Arabian peninsula is known for its rich oil, i.e. petroleum production due to its geographical location.
According to NASA's Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment
The Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) was a joint mission of NASA and the German Aerospace Center (DLR). Twin satellites took detailed measurements of Earth's gravity field anomalies from its launch in March 2002 to the end of it ...
(GRACE) satellite data (2003–2013) analysed in a University of California, Irvine
The University of California, Irvine (UCI or UC Irvine) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Irvine, California, United States. One of the ten campuses of the University of California system, U ...
(UCI)-led study published in Water Resources Research
''Water Resources Research'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Geophysical Union, covering research in the social and natural sciences of water. The editor-in-chief is Georgia Destouni (Stockholm University), who took ...
on 16 June 2015, the most over-stressed aquifer system in the world is the Arabian Aquifer System, upon which more than 60 million people depend for water. Twenty-one of the 37 largest aquifers "have exceeded sustainability tipping points and are being depleted" and thirteen of them are "considered significantly distressed".
History
Stone tools from theMiddle Paleolithic
The Middle Paleolithic (or Middle Palaeolithic) is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle P ...
age along with fossils of other animals discovered at Ti's al Ghadah, in north-western Saudi Arabia, might imply that hominins
The Hominini (hominins) form a taxonomic tribe of the subfamily Homininae (hominines). They comprise two extant genera: ''Homo'' (humans) and '' Pan'' (chimpanzees and bonobos), and in standard usage exclude the genus ''Gorilla'' (gorillas), ...
migrated through a "Green Arabia" between 300,000 and 500,000 years ago. Two-hundred-thousand-year-old stone tools were discovered at Shuaib Al-Adgham in the eastern Al-Qassim Province
The Qassim Province ( ' , Najdi Arabic: ), also known as the Qassim Region, is one of the 13 provinces of Saudi Arabia. Located at the heart of the country near the geographic center of the Arabian Peninsula, it has a population of 1,336,179 and ...
, which would indicate that many prehistoric sites, located along a network of rivers, had once existed in the area. Acheulean
Acheulean (; also Acheulian and Mode II), from the French after the type site of Saint-Acheul, is an archaeological industry of stone tool manufacture characterized by the distinctive oval and pear-shaped "hand axes" associated with ''Homo ...
tools found in Sadaqah, Riyadh Region
The Riyadh Province ( '), is a province of Saudi Arabia, located in the geographic center of the country and the center of the Arabian Peninsula. It has an area of and with a 2022 population of 8,591,748, it is the second-largest region by ar ...
reveal that hominids lived in the Arabian Peninsula around 188,000 years ago. Human habitation in Arabia may have occurred as early as 130,000 years ago. A fossilized ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
'' finger bone found at Al Wusta in the Nefud Desert dates to approximately 90,000 years ago and is the oldest human fossil discovered outside of Africa and the Levant. This indicates human migrations from Africa to Arabia occurred around this time. The Arabian Peninsula may have been the homeland of a ' Basal Eurasian' population, which diverged from other Eurasians soon after the Out-of-Africa migration, and subsequently became isolated, until it started to mix with other populations in the Middle East around 25,000 years ago. These different Middle Eastern populations would later spread Basal Eurasian ancestry via the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, also known as the First Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period in Afro-Eurasia from a lifestyle of hunter-gatherer, hunting and gathering to one of a ...
to all of Western Eurasia.
Pre-Islamic Arabia
There is evidence that human habitation in the Arabian Peninsula dates back to about 106,000 to 130,000 years ago.Saudi Embassy (US) Websiteretrieved 20 January 2011 The harsh climate historically prevented much settlement in the pre-Islamic Arabian Peninsula, apart from a small number of urban trading settlements, such as
Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above ...
and Medina
Medina, officially al-Madinah al-Munawwarah (, ), also known as Taybah () and known in pre-Islamic times as Yathrib (), is the capital of Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province in the Hejaz region of western Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, ...
, located in the Hejaz
Hejaz is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes the majority of the western region of Saudi Arabia, covering the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif and Al Bahah, Al-B ...
in the west of the peninsula.
Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, ...
has revealed the existence of many civilizations in pre-Islamic Arabia (such as the Thamud
The Thamud () were an ancient tribe or tribal confederation in pre-Islamic Arabia that occupied the northwestern Arabian Peninsula. They are attested in contemporaneous Mesopotamian and Classical inscriptions, as well as Arabic ones from the e ...
), especially in South Arabia
South Arabia (), or Greater Yemen, is a historical region that consists of the southern region of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia, mainly centered in what is now the Republic of Yemen, yet it has also historically included Najran, Jazan, ...
. South Arabian civilizations include the Himyarite Kingdom
Himyar was a polity in the southern highlands of Yemen, as well as the name of the region which it claimed. Until 110 BCE, it was integrated into the Qataban, Qatabanian kingdom, afterwards being recognized as an independent kingdom. According ...
, the Kingdom of Awsan
The Kingdom of Awsan, commonly known simply as Awsan (; ), was a kingdom in Ancient South Arabia, centered around a wadi called the Wadi Markha. The wadi remains archaeologically unexplored. The name of the capital of Awsan is unknown, but it is ...
, the Kingdom of Ma'īn, and the Sabaean Kingdom
Sheba, or Saba, was an ancient South Arabian kingdom that existed in Yemen from to . Its inhabitants were the Sabaeans, who, as a people, were indissociable from the kingdom itself for much of the 1st millennium BCE. Modern historians agree th ...
(usually considered to be the biblical land of Sheba
Sheba, or Saba, was an ancient South Arabian kingdoms in pre-Islamic Arabia, South Arabian kingdom that existed in Yemen (region), Yemen from to . Its inhabitants were the Sabaeans, who, as a people, were indissociable from the kingdom itself f ...
). From 106 AD to 630 AD north-western Arabia was under the control of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
, which renamed it Arabia Petraea
Arabia Petraea or Petrea, also known as Rome's Arabian Province or simply Arabia, was a frontier Roman province, province of the Roman Empire beginning in the 2nd century. It consisted of the former Nabataean Kingdom in the southern Levant, th ...
. Central Arabia was the location of the Kingdom of Kinda
The Kingdom of Kinda () also called the Kindite kingdom, refers to the rule of the Bedouin, nomadic Arab tribes of the Ma'add confederation in north and central Arabia by the Banu Akil al-Murar, a family of the South Arabian tribe of Kinda (tribe ...
in the 4th, 5th and early 6th centuries. Eastern Arabia was home to the Dilmun civilization
Dilmun, or Telmun, ( Sumerian: ,Transliteration: Similar text: later 𒉌𒌇(𒆠), NI.TUKki = dilmunki; ) was an ancient East Semitic–speaking civilization in Eastern Arabia mentioned from the 3rd millennium BC onwards. Based on contextual ...
. The earliest known events in Arabian history are migrations from the peninsula into neighbouring areas.
The Arabian Peninsula has long been accepted as the original ''Urheimat
In historical linguistics, the homeland or ( , from German 'original' and 'home') of a proto-language is the region in which it was spoken before splitting into different daughter languages. A proto-language is the reconstructed or historicall ...
'' of the Semitic languages
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. They include Arabic,
Amharic, Tigrinya language, Tigrinya, Aramaic, Hebrew language, Hebrew, Maltese language, Maltese, Modern South Arabian language ...
by most scholars.
Rise of Islam
 The seventh century saw the rise of Islam as the peninsula's dominant religion. The
The seventh century saw the rise of Islam as the peninsula's dominant religion. The Islamic prophet
Prophets in Islam () are individuals in Islam who are believed to spread God's message on Earth and serve as models of ideal human behaviour. Some prophets are categorized as messengers (; sing. , ), those who transmit divine revelation, mos ...
Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
was born in Mecca in about 570 and first began preaching in the city in 610, but migrated to Medina
Medina, officially al-Madinah al-Munawwarah (, ), also known as Taybah () and known in pre-Islamic times as Yathrib (), is the capital of Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province in the Hejaz region of western Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, ...
in 622. From there he and his companions united the tribes of Arabia
The tribes of Arabia () have inhabited the Arabian Peninsula for thousands of years and traditionally trace their ancestry to one of two forefathers: Adnan, whose descendants originate from Hejaz, West Arabia, Syrian Desert, North Arabia, East Ara ...
under the banner of Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
and created the first Islamic state
The first Islamic state was established by the Islamic prophet Muhammad in Medina in 622 under the Constitution of Medina. It represented the political unity of the Muslim ''Ummah'' (nation). After Muhammad's death, his companions known as the R ...
—a single Arab Muslim religious polity in the Arabian Peninsula.
Under the subsequent Rashidun
The Rashidun () are the first four caliphs () who led the Muslim community following the death of Muhammad: Abu Bakr (), Umar (), Uthman (), and Ali ().
The reign of these caliphs, called the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661), is considered i ...
and Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate or Umayyad Empire (, ; ) was the second caliphate established after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty. Uthman ibn Affan, the third of the Rashidun caliphs, was also a membe ...
Caliphate
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
s, rapid expansion of Arab power well beyond the Arabian peninsula formed a vast Muslim Arab Empire with an area of influence that stretched from the north-west Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
, across Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
, the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
, North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
, southern Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, and the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
, to the Pyrenees
The Pyrenees are a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. They extend nearly from their union with the Cantabrian Mountains to Cap de Creus on the Mediterranean coast, reaching a maximum elevation of at the peak of Aneto. ...
.
With Muhammad's death in 632, disagreement broke out over who would succeed him as leader of the Muslim community. Umar ibn al-Khattab
Umar ibn al-Khattab (; ), also spelled Omar, was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () and is regarded as a senior companion and father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muh ...
, a prominent companion
Companion may refer to:
Relationships Currently
* Any of several interpersonal relationships such as friend or acquaintance
* A domestic partner, akin to a spouse
* Sober companion, an addiction treatment coach
* Companion (caregiving), a caregive ...
of Muhammad, nominated Abu Bakr
Abd Allah ibn Abi Quhafa (23 August 634), better known by his ''Kunya (Arabic), kunya'' Abu Bakr, was a senior Sahaba, companion, the closest friend, and father-in-law of Muhammad. He served as the first caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, ruli ...
, who was Muhammad's intimate friend and collaborator. Others added their support and Abu Bakr was made the first caliph
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
. This choice was disputed by some of Muhammad's companions, who held that Ali ibn Abi Talib
Ali ibn Abi Talib (; ) was the fourth Rashidun caliph who ruled from until Assassination of Ali, his assassination in 661, as well as the first imamate in Shia doctrine, Shia Imam. He was the cousin and son-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muha ...
, his cousin and son-in-law, had been designated his successor. Abu Bakr's immediate task was to avenge a recent defeat by Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
(or Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
) forces, although he first had to put down a rebellion by Arab tribes in an episode known as the Ridda wars
The Ridda Wars were a series of military campaigns launched by the first caliph Abu Bakr against rebellious Arabian tribes, some of which were led by rival prophet claimants. They began shortly after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad in ...
, or "Wars of Apostasy".
On his death in 634, he was succeeded by Umar
Umar ibn al-Khattab (; ), also spelled Omar, was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () and is regarded as a senior companion and father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Mu ...
as caliph, followed by Uthman ibn al-Affan
Uthman ibn Affan (17 June 656) was the third caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, ruling from 644 until his assassination in 656. Uthman, a second cousin, son-in-law, and notable companion of the Islamic Prophet Muhammad, played a major role ...
and Ali ibn Abi Talib
Ali ibn Abi Talib (; ) was the fourth Rashidun caliph who ruled from until Assassination of Ali, his assassination in 661, as well as the first imamate in Shia doctrine, Shia Imam. He was the cousin and son-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muha ...
. The period of these first four caliphs is known as ''al-khulafā' ar-rāshidūn'': the Rashidun or "rightly guided" Caliphate. Under the Rashidun Caliphs, and, from 661, their Umayyad successors, the Arabs rapidly expanded the territory under Muslim control outside of Arabia. In a matter of decades Muslim armies decisively defeated the Byzantine army
The Byzantine army was the primary military body of the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine armed forces, serving alongside the Byzantine navy. A direct continuation of the East Roman army, Eastern Roman army, shaping and developing itself on the legac ...
and destroyed the Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the larg ...
, conquering huge swathes of territory from the Iberian peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
to India. The political focus of the Muslim world then shifted to the newly conquered territories.
Nevertheless, Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above ...
and Medina
Medina, officially al-Madinah al-Munawwarah (, ), also known as Taybah () and known in pre-Islamic times as Yathrib (), is the capital of Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province in the Hejaz region of western Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, ...
remained the spiritually most important places in the Muslim world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
. The Qur'an
The Quran, also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation directly from God ('' Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which consist of individual verses ('). Besides ...
requires every able-bodied Muslim who can afford it, as one of the five pillars of Islam, to make a pilgrimage, or Hajj
Hajj (; ; also spelled Hadj, Haj or Haji) is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for capable Muslims that must be carried out at least once in their lifetim ...
, to Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above ...
during the Islamic month
The Hijri calendar (), also known in English as the Islamic calendar, is a lunar calendar consisting of 12 lunar months in a year of 354 or 355 days. It is used to determine the proper days of Islamic holidays and rituals, such as the ann ...
of Dhu al-Hijjah
Dhu al-Hijjah (also Dhu al-Hijja ) is the twelfth and final month in the Islamic calendar. Being one of the four sacred months during which war is forbidden, it is the month in which the '' Ḥajj'' () takes place as well as Eid al-Adha ().
T ...
at least once in his or her lifetime. The Masjid al-Haram
Masjid al-Haram (), also known as the Sacred Mosque or the Great Mosque of Mecca, is considered to be the most significant mosque in Islam. It encloses the vicinity of the Kaaba in Mecca, in the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia. It is among the ...
(the Grand Mosque) in Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above ...
is the location of the Kaaba
The Kaaba (), also spelled Kaba, Kabah or Kabah, sometimes referred to as al-Kaba al-Musharrafa (), is a stone building at the center of Islam's most important mosque and Holiest sites in Islam, holiest site, the Masjid al-Haram in Mecca, Sa ...
, Islam's holiest site, and the Masjid al-Nabawi
The Prophet's Mosque () is the second mosque built by the Islamic prophet Muhammad in Medina, after the Quba Mosque, as well as the second largest mosque and holiest site in Islam, after the Masjid al-Haram in Mecca, in the Saudi region of t ...
(the Prophet's Mosque) in Medina
Medina, officially al-Madinah al-Munawwarah (, ), also known as Taybah () and known in pre-Islamic times as Yathrib (), is the capital of Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province in the Hejaz region of western Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, ...
is the location of Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
's grave; as a result, from the 7th century, Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above ...
and Medina
Medina, officially al-Madinah al-Munawwarah (, ), also known as Taybah () and known in pre-Islamic times as Yathrib (), is the capital of Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province in the Hejaz region of western Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, ...
became the pilgrimage destinations for large numbers of Muslims from across the Islamic world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
.
Middle Ages
 Despite its spiritual importance, in political terms Arabia soon became a peripheral region of the
Despite its spiritual importance, in political terms Arabia soon became a peripheral region of the Islamic world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
, in which the most important medieval Islamic states were based at various times in such far away cities as Damascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Kno ...
, Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the A ...
, and Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
.
However, from the 10th century (and, in fact, until the 20th century) the Hashemite
The Hashemites (), also House of Hashim, are the Dynasty, royal family of Jordan, which they have ruled since 1921, and were the royal family of the kingdoms of Kingdom of Hejaz, Hejaz (1916–1925), Arab Kingdom of Syria, Syria (1920), and Kingd ...
Sharifs of Mecca
The Sharif of Mecca () was the title of the leader of the Sharifate of Mecca, traditional steward of the Islamic holy cities of Mecca and Medina. The term ''sharif'' is Arabic for "noble", "highborn", and is used to describe the descendants of ...
maintained a state in the most developed part of the region, the Hejaz
Hejaz is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes the majority of the western region of Saudi Arabia, covering the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif and Al Bahah, Al-B ...
. Their domain originally comprised only the holy cities of Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above ...
and Medina
Medina, officially al-Madinah al-Munawwarah (, ), also known as Taybah () and known in pre-Islamic times as Yathrib (), is the capital of Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province in the Hejaz region of western Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, ...
but in the 13th century it was extended to include the rest of the Hejaz
Hejaz is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes the majority of the western region of Saudi Arabia, covering the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif and Al Bahah, Al-B ...
. Although, the Sharifs exercised at most times independent authority in the Hejaz
Hejaz is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes the majority of the western region of Saudi Arabia, covering the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif and Al Bahah, Al-B ...
, they were usually subject to the suzerainty
A suzerain (, from Old French "above" + "supreme, chief") is a person, state (polity)">state or polity who has supremacy and dominant influence over the foreign policy">polity.html" ;"title="state (polity)">state or polity">state (polity)">st ...
of one of the major Islamic empires of the time. In the Middle Ages, these included the Abbasids
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes i ...
of Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the A ...
, and the Fatimids
The Fatimid Caliphate (; ), also known as the Fatimid Empire, was a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries CE under the rule of the Fatimid dynasty, Fatimids, an Isma'ili Shi'a dynasty. Spanning a large area of North Africa ...
, Ayyubids
The Ayyubid dynasty (), also known as the Ayyubid Sultanate, was the founding dynasty of the medieval Sultanate of Egypt established by Saladin in 1171, following his abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate of Egypt. A Sunni Muslim of Kurdish ori ...
, and Mamluks
Mamluk or Mamaluk (; (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural); translated as "one who is owned", meaning "slave") were non-Arab, ethnically diverse (mostly Turkic, Caucasian, Eastern and Southeastern European) enslaved mercenaries, slave-sold ...
of Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
.Encyclopædia Britannica Online: History of Arabiaretrieved 18 January 2011
Modern history


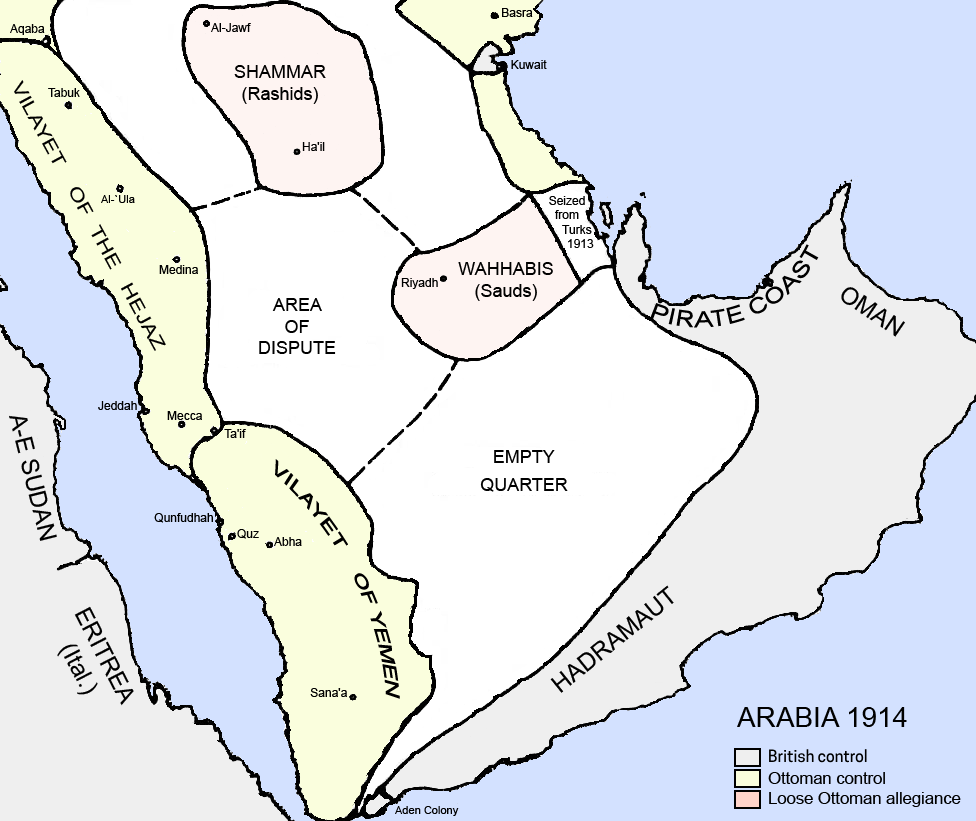
 The provincial Ottoman Army for Arabia (Arabistan Ordusu) was headquartered in
The provincial Ottoman Army for Arabia (Arabistan Ordusu) was headquartered in Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
, which included Palestine, the Transjordan region in addition to Lebanon ( Mount Lebanon was, however, a semi-autonomous mutasarrifate). It was put in charge of Syria, Cilicia, Iraq, and the remainder of the Arabian Peninsula. The Ottomans never had any control over central Arabia, also known as the Najd
Najd is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes most of the central region of Saudi Arabia. It is roughly bounded by the Hejaz region to the west, the Nafud desert in Al-Jawf Province, al-Jawf to the north, ...
region.
The emergence of what was to become the Saudi royal family, known as the Al Saud
The House of Saud ( ) is the ruling royal family of Saudi Arabia. It is composed of the descendants of Muhammad bin Saud, founder of the Emirate of Diriyah, known as the First Saudi State, (1727–1818), and his brothers, though the ruling fac ...
, began in Najd
Najd is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes most of the central region of Saudi Arabia. It is roughly bounded by the Hejaz region to the west, the Nafud desert in Al-Jawf Province, al-Jawf to the north, ...
in central Arabia in 1744, when Muhammad bin Saud
Muhammad bin Saud Al Muqrin Al Saud (; 1687–1765), also known as Ibn Saud, was the emir of Diriyah and is considered the founder of the First Saudi State and the House of Saud, Saud dynasty, named after his father, Saud bin Muhammad Al Muqrin. ...
, founder of the dynasty, joined forces with the religious leader Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab
Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhāb ibn Sulaymān al-Tamīmī (1703–1792) was a Sunni Muslim scholar, theologian, preacher, activist, religious leader, jurist, and reformer, who was from Najd in Arabian Peninsula and is considered as the eponymo ...
, founder of the Wahhabi movement
Wahhabism is an exonym for a Salafi revivalist movement within Sunni Islam named after the 18th-century Hanbali scholar Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab. It was initially established in the central Arabian region of Najd and later spread to other p ...
, a strict puritanical form of Sunni Islam. The Emirate of Diriyah
The first Saudi state (), officially the Emirate of Diriyah (), was established in 1744, when the emir of a Najdi town called Diriyah, Muhammad I, and the religious leader Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab signed a pact to found a socio-religious ...
established in the area around Riyadh rapidly expanded and briefly controlled most of the present-day territory of Saudi Arabia, sacking Karbala in 1802, and capturing Mecca in 1803.
The Damascus Protocol of 1914 provides an illustration of the regional relationships. Arabs living in one of the existing districts of the Arabian peninsula, the Emirate of Hejaz
Hejaz is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes the majority of the western region of Saudi Arabia, covering the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif and Al Bahah, Al-B ...
, asked for a British guarantee of independence. Their proposal included all Arab lands south of a line roughly corresponding to the northern frontiers of present-day Syria and Iraq. They envisioned a new Arab state, or confederation of states, adjoining the southern Arabian Peninsula. It would have comprised Cilicia
Cilicia () is a geographical region in southern Anatolia, extending inland from the northeastern coasts of the Mediterranean Sea. Cilicia has a population ranging over six million, concentrated mostly at the Cilician plain (). The region inclu ...
—İskenderun
İskenderun (), historically known as Alexandretta (, ) and Scanderoon, is a municipality and Districts of Turkey, district of Hatay Province, Turkey. Its area is 247 km2, and its population is 251,682 (2022). It is on the Mediterranean coas ...
and Mersin
Mersin () is a large city and port on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast of Mediterranean Region, Turkey, southern Turkey. It is the provincial capital of the Mersin Province (formerly İçel). It is made up of four district governorates ...
, Iraq with Kuwait, Syria, Mount Lebanon Mutasarrifate
The Mount Lebanon Mutasarrifate (1861–1918, ; ) was one of the Ottoman Empire's subdivisions following the 19th-century Tanzimat reform. After 1861, there existed an autonomous Mount Lebanon with a Christian Mutasarrif (governor), which had be ...
, Jordan, and Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and th ...
.
In the modern era, the term bilad al-Yaman came to refer specifically to the south-western parts of the peninsula. Arab geographers started to refer to the whole peninsula as 'jazirat al-Arab', or the peninsula of the Arabs.
Late Ottoman rule and the Hejaz Railway
The railway was started in 1900 at the behest of the Ottoman SultanAbdul Hamid II
Abdulhamid II or Abdul Hamid II (; ; 21 September 184210 February 1918) was the 34th sultan of the Ottoman Empire, from 1876 to 1909, and the last sultan to exert effective control over the fracturing state. He oversaw a Decline and modernizati ...
and was built largely by the Turks, with German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
advice and support. A public subscription was opened throughout the Islamic world to fund the construction. The railway was to be a waqf
A (; , plural ), also called a (, plural or ), or ''mortmain'' property, is an Alienation (property law), inalienable charitable financial endowment, endowment under Sharia, Islamic law. It typically involves donating a building, plot ...
, an inalienable religious endowment or charitable trust.
The Arab Revolt and the foundation of Saudi Arabia
 The major developments of the early 20th century were the
The major developments of the early 20th century were the Arab Revolt
The Arab Revolt ( ), also known as the Great Arab Revolt ( ), was an armed uprising by the Hashemite-led Arabs of the Hejaz against the Ottoman Empire amidst the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I.
On the basis of the McMahon–Hussein Co ...
during World War I and the subsequent collapse and partitioning of the Ottoman Empire
The partition of the Ottoman Empire (30 October 19181 November 1922) was a geopolitical event that occurred after World War I and the occupation of Constantinople by British, French, and Italian troops in November 1918. The partitioning was ...
. The Arab Revolt (1916–1918) was initiated by the Sherif Hussein ibn Ali
Hussein bin Ali al-Hashimi ( ; 1 May 18544 June 1931) was an Arab leader from the Banu Qatadah branch of the Banu Hashim clan who was the Sharif and Emir of Mecca from 1908 and, after proclaiming the Great Arab Revolt against the Ottoman Em ...
with the aim of securing independence from the ruling Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
and creating a single unified Arab state spanning from Aleppo
Aleppo is a city in Syria, which serves as the capital of the Aleppo Governorate, the most populous Governorates of Syria, governorate of Syria. With an estimated population of 2,098,000 residents it is Syria's largest city by urban area, and ...
in Syria to Aden
Aden () is a port city located in Yemen in the southern part of the Arabian peninsula, on the north coast of the Gulf of Aden, positioned near the eastern approach to the Red Sea. It is situated approximately 170 km (110 mi) east of ...
in Yemen. During World War I, the Sharif Hussein entered into an alliance with the United Kingdom and France against the Ottomans in June 1916.
These events were followed by the foundation of Saudi Arabia under King Abdulaziz Ibn Saud. After the collapse of the Emirate of Diriyah
The first Saudi state (), officially the Emirate of Diriyah (), was established in 1744, when the emir of a Najdi town called Diriyah, Muhammad I, and the religious leader Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab signed a pact to found a socio-religious ...
, the House of Sand regrouped and in 1824 founded the Second Saudi State
The second Saudi state (), officially known as the Emirate of Najd, was a state that existed between 1824 and 1891 in the Najd region of what is now Saudi Arabia. Saudi rule was restored to central (Najd) and Eastern Arabia after the first Sau ...
, which would control most of Arabia for the next two-thirds of a century. Ibn Saud, after his family lost power in 1891, would establish the Third Saudi State
The Third Saudi state is the heir to the two earlier Saudi states: the first and the second, founded by Abdul Aziz bin Abdul Rahman (also known as "Ibn Saud"), who managed to capture the city of Riyadh on January 13, 1902. A long series of con ...
, capturing Riyadh
Riyadh is the capital and largest city of Saudi Arabia. It is also the capital of the Riyadh Province and the centre of the Riyadh Governorate. Located on the eastern bank of Wadi Hanifa, the current form of the metropolis largely emerged in th ...
in 1902, and, successively subduing Al-Hasa, Jabal Shammar and Hejaz
Hejaz is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes the majority of the western region of Saudi Arabia, covering the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif and Al Bahah, Al-B ...
between 1913 and 1926. The Saudis then absorbed the Emirate of Asir
The Emirate of Asir () was a state located in the Arabian Peninsula. The Emirate was in the modern-day provinces of Asir and Jazan, in what is now southwestern Saudi Arabia, and extending to al-Hudaydah in northwestern Yemen.
History
In the ...
, with their expansion only ending in 1934 after a war with Yemen.
Oil reserves
The second major development has been the discovery of vast reserves of oil in the 1930s. Its production brought great wealth to all countries of the region, with the exception of Yemen.North Yemen Civil War
The North Yemen Civil War was fought inNorth Yemen
North Yemen () is a term used to describe the Kingdom of Yemen (1918-1962), the Yemen Arab Republic (1962-1990), and the regimes that preceded them and exercised sovereignty over that region of Yemen. Its capital was Sanaa from 1918 to 1948 an ...
between royalists of the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen
The Kingdom of Yemen (), officially the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen () and also known simply as Yemen or, retrospectively, as North Yemen, was a state that existed between 1918 and 1970 in the northwestern part of the modern country of Yemen ...
and factions of the Yemen Arab Republic
The Yemen Arab Republic (YAR; ', ), commonly known as North Yemen or Yemen (Sanaʽa), was a country that existed from 1962 until its Yemeni unification, unification with the South Yemen, People's Democratic Republic of Yemen (commonly known as ...
from 1962 to 1970. The war began with a coup d'état
A coup d'état (; ; ), or simply a coup
, is typically an illegal and overt attempt by a military organization or other government elites to unseat an incumbent leadership. A self-coup is said to take place when a leader, having come to powe ...
carried out by the republican leader, Abdullah as-Sallal
Abdullah Yahya al-Sallal (; 9 January 1917 – 5 March 1994) was a Yemeni military officer who was the leader of the North Yemeni Revolution of 1962 and served as the first President of the Yemen Arab Republic from 27 September 1962 until his r ...
, which dethroned the newly crowned Muhammad al-Badr
Muhammad Al-Badr (15 February 1926 – 6 August 1996) was the last king and Zaidi Imam of the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen (North Yemen) and leader of the monarchist regions during the North Yemen Civil War (1962–1970). His full name wa ...
and declared Yemen a republic under his presidency. The Imam escaped to the Saudi Arabian border and rallied popular support.
The royalist side received support from Saudi Arabia, while the republicans were supported by Egypt and the Soviet Union. Both foreign irregular and conventional forces were also involved. The Egyptian President, Gamal Abdel Nasser
Gamal Abdel Nasser Hussein (15 January 1918 – 28 September 1970) was an Egyptian military officer and revolutionary who served as the second president of Egypt from 1954 until his death in 1970. Nasser led the Egyptian revolution of 1952 a ...
, supported the republicans with as many as 70,000 troops. Despite several military moves and peace conferences, the war sank into a stalemate. Egypt's commitment to the war is considered to have been detrimental to its performance in the Six-Day War of June 1967, after which Nasser found it increasingly difficult to maintain his army's involvement and began to pull his forces out of Yemen.
By 1970, King Faisal of Saudi Arabia recognized the republic and a truce was signed. Egyptian military historians refer to Egypt's role in the war in Yemen as analogous to the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
' role in the Vietnam War.
Gulf War
In 1990, Iraq invaded Kuwait. The invasion of Kuwait by Iraqi forces led to the 1990–91 Gulf War. Egypt, Qatar, Syria, and Saudi Arabia joined a multinational Coalition of the Gulf War, coalition that opposed Iraq. Displays of support for Iraq by Jordan and Palestine resulted in strained relations between many of the Arab states. After the war, a so-called "Damascus Declaration" formalized an alliance for future joint Arab defensive actions between Egypt, Syria, and the GCC member states.2014 Yemen civil war
The Arab Spring reached Yemen in January 2011. People of Yemen took to the street demonstrating against three decades of rule by President Ali Abdullah Saleh. The demonstration led to cracks in the ruling General People's Congress (GPC) and Saleh's Sanhani clan. Saleh used tactics of concession and violence to save his presidency. After numerous attempts, Saleh accepted the Gulf Cooperation Council's mediation. He eventually handed power to Vice President Hadi, who was sworn in as President of Yemen on 25 February 2012. Hadi launched a national dialogue to address new constitutional, political and social issues. The Houthi movement, dissatisfied with the outcomes of the national dialogue, Houthi takeover in Yemen, launched an offensive and stormed the Yemeni capital Sanaa on 21 September 2014. In response, Saudi Arabia launched a Saudi-led intervention in the Yemeni civil war, military intervention in Yemen in March 2015. The civil war and subsequent military intervention and blockade of Yemen, blockade caused a Famine in Yemen (2016–present), famine in Yemen.Gallery
Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above ...
, Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
by order of Zubaidah bint Ja'far.
File:Omar Mosque.jpg, Umar ibn al-Khattab Mosque, Omar Mosque in Dumat al-Jandal, Saudi Arabia
File:Madain Saleh (6730128379).jpg, The facade of a tomb with its details and architectural elements in Hegra (Mada'in Salih), Hegra, Saudi Arabia
File:Qasr al Farid.JPG, Qasr al Farid, tomb in Archeological site Mada'in Saleh, Al-`Ula, Saudi Arabia
File:Diriyahpic.jpg, Diriyah the capital of the first Saudi state
File:Jemen1988-022 hg.jpg, Dam of Marib, Dam of Ma'rib
File:Dhamar Ali Yahbur (bust).jpg, Himyarite Kingdom, Himyarite King Dhamar'ali Yahbur II
File:AradFort.jpg, Arad Fort in Bahrain
File:Nizwa (5).jpg, Nizwa Fort in Oman
File:Dubai Jumeirah Creek Museum Jumeirah 9-12th century model 1301200712751.jpg, The ruins of Umayyad Caliphate, Umayyad city in the historic Jumeirah district of Dubai
File:Coper head of bull Dilmun1.jpg, Bull's head, made of copper in the early period of Dilmun (ca. 2000 BC), Bahrain
File:Al-Magar - Saluki Artifact (المقر - سلوقي - قطعة أثرية).jpg, The head and body of a Saluki is made of stone from the Al-Magar civilization, in the Neolithic period (about 8000 BC)
File:مدين.jpg, Midian
See also
* Achaemenid Arabia * Ancient history of Yemen * Arabian Gulf Cup * Arab League *Arab world
The Arab world ( '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, comprises a large group of countries, mainly located in West Asia and North Africa. While the majority of people in ...
* Eastern Arabia
Eastern Arabia () is a region stretched from Basra to Khasab along the Persian Gulf coast and included parts of modern-day Bahrain, Iraq, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia (Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia, Eastern Province), and the United Arab ...
* European exploration of Arabia
* Gulf Cooperation Council
The Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf (), also known as the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC; ), is a Regional integration, regional, intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental, political, and economic union comprising Ba ...
* Iram of the Pillars
* Kingdom of Aksum
* List of Arabian cities by population
* Mashriq
* Musandam Peninsula
Explanatory notes
References
Further reading
Travels in Arabia
(1892)
High resolution scan of old map of Arabia
.
The Coast of Arabia the Red Sea, and Persian Sea of Bassora Past the Straits of Hormuz to India, Gujarat and Cape Comorin
from the World Digital Library, depicts a map from 1707. *
Arabia: Cultural-Historical Zones
Old maps of Arabia
Eran Laor Cartographic Collection, The National Library of Israel
External links
{{Coord, 23, N, 46, E, display=title Arabian Peninsula, Articles containing video clips Geography of West Asia Historical regions Peninsulas of Asia West Asia