|
Idrisid Emirate Of Asir
The Emirate of Asir () was a state located in the Arabian Peninsula. The Emirate was in the modern-day provinces of Asir and Jazan Province, Jazan, in what is now southwestern Saudi Arabia, and extending to Al Hudaydah Governorate, al-Hudaydah in northwestern Yemen. History In the early 20th century, the Asir region was in chaos. De jure, the region was governed as the Sanjak of Asir, which was part of the Yemen Vilayet, Vilayet of Yemen, although the Ottomans only had de facto control over port cities. At the same time, various tribal chiefs ruled the hinterlands. Even in the areas of Ottoman control, anti-Turkish sentiment was brewing, beginning ethnic and sectarian conflicts between the Turkish overlords and the local inhabitants. Due to these circumstances, Muhammad ibn Ali al-Idrisi, Sayyid Muhammad ibn Ali al-Idrisi began spreading his great Ahmad ibn Idris al-Fasi#Teachings, grandfather's teachings, as well as calling for the local inhabitants to maintain a stricter adhe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imam
Imam (; , '; : , ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a prayer leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Salah, Islamic prayers, serve as community leaders, and provide religious guidance. Thus for Sunnis, anyone can study the basic Islamic teachings and become an imam. For most Shia Islam, Shia Muslims, the Imams are absolute infallible leaders of the Islamic community after the Prophet. Shias consider the term to be only applicable to the members and descendants of the ''Ahl al-Bayt'', the family of the Islamic prophet Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad. In Twelver Shia, Twelver Shi'ism there are 14 The Fourteen Infallible, infallibles, 12 of which are Imams, the final being Muhammad al-Mahdi, Imam Mahdi who will return at the end of times. The title was also used by the Zaydism, Zaidi Shia Imams of Yemen, who eventually founded the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen (1918–1970). Sunni imams Sunni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farasan Islands
The Farasan Islands (; transliterated: ) are a small group of coral islands approximately 40 km off the coast of Jizan in the Red Sea, belonging to Saudi Arabia. The government provides free ferry rides twice a day to Farasan Islands from Jizan Port. The largest island of the archipelago is Farasan Island; others include Sajid Island and Zufaf Island. The islands are a popular tourist destination. In recent years the Saudi government has tried to increase the tourism quality and worth (as part of a larger tourism drive in the country) of the Islands in order to attract even more visitors. History In the 1st century AD, the islands were known as ''Portus Ferresanus''. A Latin inscription dating from 144 AD has been found on the island which attests to the construction of a Roman garrison. It is believed that the islands may have been attached to the Roman province of Arabia Felix, before being transferred to Aegyptus some time before 144 AD. This fact would make the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
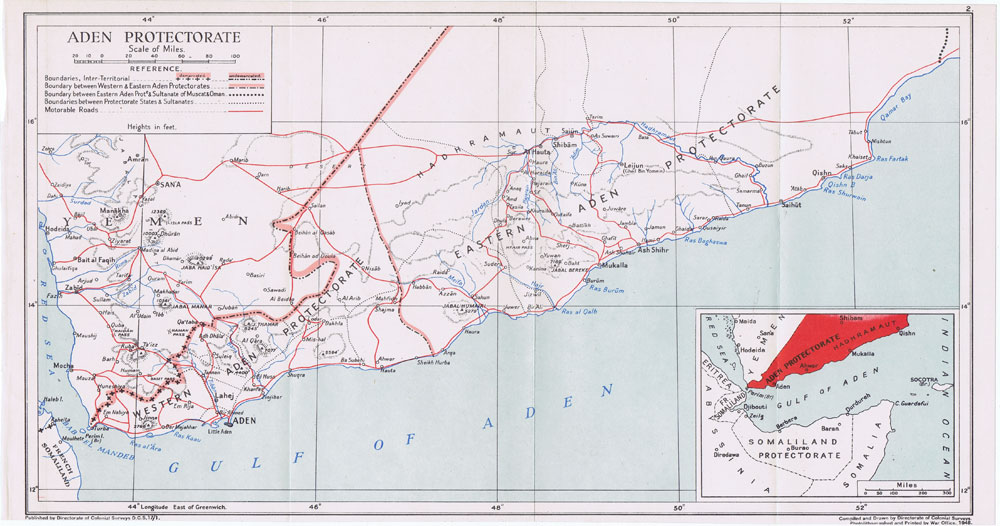
Aden Protectorate
The Aden Protectorate ( ') was a British protectorate in southern Arabia. The protectorate evolved in the hinterland of the port of Aden and in the Hadhramaut after the conquest of Aden by the Bombay Presidency of British India in January 1839, and which continued until the 1960s. In 1940, it was divided for administrative purposes into the Western Protectorate and the Eastern Protectorate. The territory now forms part of the Republic of Yemen. The rulers of the Aden Protectorate, as generally with the other British protectorates and protected states, retained a large degree of autonomy: their flags still flew over their government buildings, government was still performed by them or in their names, and their states maintained a distinct 'international personality' in terms of international law, in contrast to states possessed directly by the British Empire, such as Colony of Aden, where the British monarch was the sovereign. History Informal beginnings What became kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sa Mapa6
Sa, SA, S.A. or s.a. may refer to: Arts, media and entertainment Music * Initialism for "soprano and alto", voice types for which a piece of music is written * SA (Samurai Attack), a Japanese punk rock band * SA Martinez, a vocalist and DJ for the band 311 * Soziedad Alkoholika, a Spanish punk rock band * ''SA'', a 2018 album by Jonathan Richman * Strike Anywhere, a hardcore punk band from Richmond, Virginia Other media * ''Sa'' (film), a 2016 Indian film * ''S.A'' (manga), a manga series by Maki Minami * ''Something Awful'', a comedy website * Star Awards, an annual Singaporean television award ceremony * ''Subterranean Animism'', a video game from the Touhou series by ZUN * Siragadikka Aasai (TV series), an Indian TV series Language and writing * Sa (cuneiform), a cuneiform sign * sa (hieroglyph), an Egyptian hieroglyph meaning "protection" * Sa (kana) (さ and サ), characters (kana) in the two Japanese syllabaries * Saa language, spoken in Vanuatu * Sanskrit (ISO 639-1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italo-Turkish War
The Italo-Turkish (, "Tripolitanian War", , "War of Libya"), also known as the Turco-Italian War, was fought between the Kingdom of Italy and the Ottoman Empire from 29 September 1911 to 18 October 1912. As a result of this conflict, Italy captured the Ottoman Ottoman Tripolitania, Tripolitania Vilayet, of which the main Sanjak, sub-provinces were Fezzan, Cyrenaica, and Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli itself. These territories became the colonies of Italian Tripolitania and Italian Cyrenaica, Cyrenaica, which would later merge into Italian Libya. During the conflict, Italian forces also occupied the Dodecanese islands in the Aegean Sea. Italy agreed to return the Dodecanese to the Ottoman Empire in the #Treaty of Ouchy, Treaty of Ouchy in 1912. However, the vagueness of the text, combined with subsequent adverse events unfavourable to the Ottoman Empire (the outbreak of the Balkan Wars and World War I), allowed a provisional Italian administration of the islands, and Turkey eventually ren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abha
Abha (, ') is the capital of Asir, Asir Province in Saudi Arabia. It is situated above sea level in the fertile Asir Mountains of south-western Saudi Arabia, near Asir National Park. Abha's mild climate makes it a popular tourist destination for Saudis. Saudis also call the city the Bride of Mountain due to its position above the sea. History Abha was the capital city for the Prince of Asir Ibn Ayde under the authority of the Ottoman Empire until World War I. In 1918, the Prince of Asir, Yahya bin Hasun Al Ayde, grandson of Ibn Ayed, returned to his family throne conquered in Abha with complete independence. In 1920, Asir was conquered by the Ikhwan tribesmen of Nejd loyal to Ibn Saud during the Unification of Saudi Arabia. Abha has many historic places such as forts and other locations, thanks to the region's cultural heritage. Bani Shehr, Bani Amr, Bal-Ahmar, Bal-Asmar, Bal-Qarn, Shumran and some others all belong to "Al-Azd" and some extended families Qahtan, Shahran which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharia Law
Sharia, Sharī'ah, Shari'a, or Shariah () is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition based on scriptures of Islam, particularly the Qur'an and hadith. In Islamic terminology ''sharīʿah'' refers to immutable, intangible divine law; contrary to ''fiqh'', which refers to its interpretations by Islamic scholars. Sharia, or fiqh as traditionally known, has always been used alongside customary law from the very beginning in Islamic history; has been elaborated and developed over the centuries by legal opinions issued by qualified jurists – reflecting the tendencies of different schools – and integrated and with various economic, penal and administrative laws issued by Muslim rulers; and implemented for centuries by judges in the courts until recent times, when secularism was widely adopted in Islamic societies. Traditional theory of Islamic jurisprudence recognizes four sources for Ahkam al-sharia: the Qur'an, '' sunnah'' (or authentic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suzerainty
A suzerain (, from Old French "above" + "supreme, chief") is a person, state (polity)">state or polity who has supremacy and dominant influence over the foreign policy">polity.html" ;"title="state (polity)">state or polity">state (polity)">state or polity who has supremacy and dominant influence over the foreign policy and economic relations of another subordinate party or polity, but allows internal autonomy to that subordinate. Where the subordinate polity is called a vassal, vassal state or tributary state, the dominant party is called the suzerain. The rights and obligations of a vassal are called ''vassalage'', and the rights and obligations of a suzerain are called suzerainty. Suzerainty differs from sovereignty in that the dominant power does not exercise centralized governance over the vassals, allowing tributary states to be technically self-ruling but enjoy only limited independence. Although the situation has existed in a number of historical empires, it is con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaymakam
Kaymakam, also known by #Names, many other romanizations, was a title used by various officials of the Ottoman Empire, including acting grand viziers, governors of provincial sanjaks, and administrators of district kazas. The title has been retained and is sometimes used without translation for province, provincial or subdistrict governors in various Ottoman successor states, including the Republic of Turkey, Kuwait, Iraq, and Lebanon. Names The title has been romanization, romanized in English language, English since 1645 with extremely numerous spelling variations. The most common present-day forms are kaymakam, kaimakam, and qaimaqam. The modern Turkish language, Turkish term is , from Ottoman Turkish ''kaymakam'' (), from Arabic language, Arabic ''qāʾim maqām'' (), meaning "stand in" or "deputy". History Ottoman Empire In the Ottoman Empire, the title of ''kaymakam'' (known either as ''sadâret kaymakamı'' or as ''kaymakam pasha'') was originally used for the officia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |