Apicomplexan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Apicomplexa (also called Apicomplexia; single: apicomplexan) are organisms of a large
 Replication:
*
Replication:
*
 The gregarines are generally parasites of
The gregarines are generally parasites of
 In general, coccidians are parasites of
In general, coccidians are parasites of
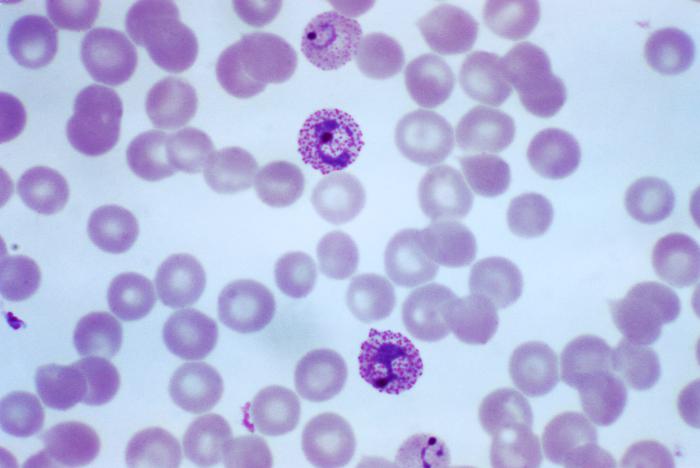 The Haemosporidia have more complex lifecycles that alternate between an arthropod and a vertebrate host. The trophozoite parasitises
The Haemosporidia have more complex lifecycles that alternate between an arthropod and a vertebrate host. The trophozoite parasitises
 Perkins et al. proposed the following scheme. It is outdated as the Perkinsidae have since been recognised as a sister group to the dinoflagellates rather that the Apicomplexia:
* Class
Perkins et al. proposed the following scheme. It is outdated as the Perkinsidae have since been recognised as a sister group to the dinoflagellates rather that the Apicomplexia:
* Class
phylum
In biology, a phylum (; : phyla) is a level of classification, or taxonomic rank, that is below Kingdom (biology), kingdom and above Class (biology), class. Traditionally, in botany the term division (taxonomy), division has been used instead ...
of mainly parasitic
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The ent ...
alveolate
The alveolates (meaning "pitted like a honeycomb") are a group of protists, considered a major unranked clade or superphylum within Eukaryota. They are currently grouped with the Stramenopiles and Rhizaria among the protists with tubulocristate ...
s. Most possess a unique form of organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell (biology), cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as Organ (anatomy), organs are to th ...
structure that comprises a type of non-photosynthetic plastid
A plastid is a membrane-bound organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. Plastids are considered to be intracellular endosymbiotic cyanobacteria.
Examples of plastids include chloroplasts ...
called an apicoplast
An apicoplast is a derived non-photosynthetic plastid found in most Apicomplexa, including ''Toxoplasma gondii'', and ''Plasmodium falciparum'' and other ''Plasmodium'' spp. (parasites causing malaria), but not in others such as ''Cryptosporidium' ...
with an apical complex membrane. The organelle's apical shape is an adaptation that the apicomplexan applies in penetrating a host cell.
The Apicomplexa are unicellular and spore-forming. Most are obligate
{{wiktionary, obligate
As an adjective, obligate means "by necessity" (antonym '' facultative'') and is used mainly in biology in phrases such as:
* Obligate aerobe, an organism that cannot survive without oxygen
* Obligate anaerobe, an organism ...
endoparasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The en ...
s of animals, except ''Nephromyces
''Nephromyces'' is a genus of apicomplexans that are symbionts of the ascidian genus '' Molgula'' (sea grapes).
Systematics
''Nephromyces'' was first described in 1888 by Alfred Mathieu Giard as a chytrid fungus, because of its filamentous ...
'', a symbiont
Symbiosis (Ancient Greek : living with, companionship < : together; and ''bíōsis'': living) is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction, between two organisms of different species. The two organisms, termed symbionts, can fo ...
in marine animals, originally classified as a chytrid
Chytridiomycota are a division of zoosporic organisms in the kingdom (biology), kingdom Fungi, informally known as chytrids. The name is derived from the Ancient Greek ('), meaning "little pot", describing the structure containing unreleased zo ...
fungus, and the Chromerida
Chrompodellids are a phylum of single-celled protists belonging to the Alveolata supergroup. It comprises two different polyphyletic groups of flagellates: the colpodellids, phagotrophic predators, and the chromerids, photosynthetic algae t ...
, some of which are photosynthetic
Photosynthesis ( ) is a Biological system, system of biological processes by which Photoautotrophism, photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical ener ...
partners of corals. Motile structures such as flagella
A flagellum (; : flagella) (Latin for 'whip' or 'scourge') is a hair-like appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, from fungal spores ( zoospores), and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many pr ...
or pseudopod
A pseudopod or pseudopodium (: pseudopods or pseudopodia) is a temporary arm-like projection of a eukaryotic cell membrane that is emerged in the direction of movement. Filled with cytoplasm, pseudopodia primarily consist of actin filaments and ...
s are present only in certain gamete
A gamete ( ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as s ...
stages.
The Apicomplexa are a diverse group that includes organisms such as the coccidia
Coccidia (Coccidiasina) are a subclass of microscopic, spore-forming, single-celled obligate intracellular parasites belonging to the apicomplexan class Conoidasida.
As obligate intracellular parasites, they must live and reproduce within a ...
, gregarine
The gregarines are a group of Apicomplexan alveolates, classified as the Gregarinasina or Gregarinia. The large (roughly half a millimeter) parasites inhabit the intestines of many invertebrates. They are not found in any vertebrates. Gregarines ...
s, piroplasms, haemogregarines, and plasmodia.
Diseases caused by Apicomplexa include:
* Babesiosis
Babesiosis or piroplasmosis is a malaria-like parasitic disease caused by infection with a eukaryotic parasite in the order Piroplasmida, typically a ''Babesia'' or '' Theileria'', in the phylum Apicomplexa. Human babesiosis transmission via ...
(''Babesia
''Babesia'', also called ''Nuttallia'', is an apicomplexan parasite that infects red blood cells and is transmitted by ticks. Originally discovered by Romanian bacteriologist Victor Babeș in 1888; over 100 species of ''Babesia'' have since ...
'')
* Malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
(''Plasmodium
''Plasmodium'' is a genus of unicellular eukaryotes that are obligate parasites of vertebrates and insects. The life cycles of ''Plasmodium'' species involve development in a Hematophagy, blood-feeding insect host (biology), host which then inj ...
'')
* Cryptosporidiosis
Cryptosporidiosis, sometimes informally called crypto, is a parasitic disease caused by ''Cryptosporidium'', a genus of protozoan parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa. It affects the ileum, distal small intestine and can affect the respiratory tr ...
('' Cryptosporidium parvum'')
* Cyclosporiasis
Cyclosporiasis is a disease caused by infection with ''Cyclospora cayetanensis'', a pathogenic Apicomplexa, apicomplexan protozoan transmitted by human feces, feces or feces-contaminated food and water. Outbreaks have been reported due to contamin ...
(''Cyclospora cayetanensis
''Cyclospora cayetanensis'' is a coccidian parasite that causes a diarrheal disease called cyclosporiasis in humans and possibly in other primates. Originally reported as a novel pathogen of probable coccidian nature in the 1980s and described i ...
'')
* Cystoisosporiasis ('' Cystoisospora belli'')
* Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by ''Toxoplasma gondii'', an apicomplexan. Infections with toxoplasmosis are associated with a variety of neuropsychiatric and behavioral conditions. Occasionally, people may have a few weeks or month ...
(''Toxoplasma gondii
''Toxoplasma gondii'' () is a species of parasitic alveolate that causes toxoplasmosis. Found worldwide, ''T. gondii'' is capable of infecting virtually all warm-blooded animals, but members of the cat family (felidae) are the only known d ...
'')
The name Apicomplexa derives from two Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
words—''apex'' (top) and ''complexus'' (infolds)—for the set of organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell (biology), cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as Organ (anatomy), organs are to th ...
s in the sporozoite
Apicomplexans, a group of intracellular parasites, have life cycle stages that allow them to survive the wide variety of environments they are exposed to during their complex life cycle. Each stage in the life cycle of an apicomplexan organis ...
. The Apicomplexa comprise the bulk of what used to be called the Sporozoa, a group of parasitic protozoans, in general without flagella, cilia, or pseudopods. Most of the Apicomplexa are motile, however, with a gliding mechanism that uses adhesions and small static myosin motors. The other main lines of this obsolete grouping were the Ascetosporea (a group of Rhizaria
The Rhizaria are a diverse and species-rich clade of mostly unicellular eukaryotes. Except for the Chlorarachniophytes and three species in the genus '' Paulinella'' in the phylum Cercozoa, they are all non-photosynthetic, but many Foraminifera ...
), the Myxozoa
Myxozoa (etymology: Greek: μύξα ''myxa'' "slime" or "mucus" + thematic vowel o + ζῷον ''zoon'' "animal") is a subphylum of aquatic cnidarian animals – all obligate parasites. It contains the smallest animals ever known to have lived. ...
(highly derived cnidarian
Cnidaria ( ) is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic invertebrates found both in fresh water, freshwater and marine environments (predominantly the latter), including jellyfish, hydroid (zoology), hydroids, ...
animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
s), and the Microsporidia
Microsporidia are a group of spore-forming unicellular parasites. These spores contain an extrusion apparatus that has a coiled polar tube ending in an anchoring disc at the apical part of the spore.Franzen, C. (2005). How do Microsporidia inva ...
(derived from fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
). Sometimes, the name Sporozoa is taken as a synonym for the Apicomplexa, or occasionally as a subset.
Description
The phylum Apicomplexa contains all eukaryotes with a group of structures and organelles collectively termed the apical complex. This complex consists of structural components and secretory organelles required for invasion ofhost
A host is a person responsible for guests at an event or for providing hospitality during it.
Host may also refer to:
Places
* Host, Pennsylvania, a village in Berks County
* Host Island, in the Wilhelm Archipelago, Antarctica
People
* ...
cells during the parasitic stages of the Apicomplexan life cycle. Apicomplexa have complex life cycles, involving several stages and typically undergoing both asexual and sexual replication. All Apicomplexa are obligate parasite
An obligate parasite or holoparasite is a parasitic organism that cannot complete its life-cycle without exploiting a suitable host. If an obligate parasite cannot obtain a host it will fail to reproduce. This is opposed to a facultative parasite, ...
s for some portion of their life cycle, with some parasitizing two separate hosts for their asexual and sexual stages.
Besides the conserved apical complex, Apicomplexa are morphologically diverse. Different organisms within Apicomplexa, as well as different life stages for a given apicomplexan, can vary substantially in size, shape, and subcellular structure. Like other eukaryotes, Apicomplexa have a nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a part of a transportation system of the eukaryote, eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. The word endoplasmic means "within the cytoplasm", and reticulum is Latin for ...
and Golgi complex
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic Cell (biology), cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it protein targeting, packages proteins ...
. Apicomplexa generally have a single mitochondrion, as well as another endosymbiont-derived organelle called the apicoplast
An apicoplast is a derived non-photosynthetic plastid found in most Apicomplexa, including ''Toxoplasma gondii'', and ''Plasmodium falciparum'' and other ''Plasmodium'' spp. (parasites causing malaria), but not in others such as ''Cryptosporidium' ...
which maintains a separate 35 kilobase
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA ...
circular genome (with the exception of ''Cryptosporidium
''Cryptosporidium'', sometimes called crypto, is an apicomplexan genus of alveolates which are parasitism, parasites that can cause a respiratory and gastrointestinal illness (cryptosporidiosis) that primarily involves watery diarrhea (inte ...
'' species and ''Gregarina niphandrodes'' which lack an apicoplast).
All members of this phylum have an infectious stage—the sporozoite—which possesses three distinct structures in an apical complex. The apical complex consists of a set of spirally arranged microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nanometer, nm and have an inner diameter bet ...
s (the conoid), a secretory body (the rhoptry) and one or more polar rings. Additional slender electron-dense secretory bodies (microneme
Micronemes are secretory organelles, possessed by parasitic apicomplexans. Micronemes are located on the apical third of the protozoan body. They are surrounded by a typical unit membrane. On electron microscopy they have an electron-dense ma ...
s) surrounded by one or two polar rings may also be present. This structure gives the phylum its name. A further group of spherical organelles is distributed throughout the cell rather than being localized at the apical complex and are known as the dense granules. These typically have a mean diameter around 0.7 μm. Secretion of the dense-granule content takes place after parasite invasion and localization within the parasitophorous vacuole and persists for several minutes.
* Flagella
A flagellum (; : flagella) (Latin for 'whip' or 'scourge') is a hair-like appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, from fungal spores ( zoospores), and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many pr ...
are found only in the motile gamete. These are posteriorly directed and vary in number (usually one to three).
* Basal bodies
A basal body (synonymous with basal granule, kinetosome, and in older cytological literature with blepharoplast) is a protein structure found at the base of a eukaryotic undulipodium (cilium or flagellum). The basal body was named by Theodor ...
are present. Although hemosporidians and piroplasmids have normal triplets of microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nanometer, nm and have an inner diameter bet ...
s in their basal bodies, coccidians and gregarines have nine singlets.
* The mitochondria
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is us ...
have tubular cristae
A crista (; : cristae) is a fold in the inner membrane of a mitochondrion. The name is from the Latin for ''crest'' or ''plume'', and it gives the inner membrane its characteristic wrinkled shape, providing a large amount of surface area for che ...
.
* Centriole
In cell biology a centriole is a cylindrical organelle composed mainly of a protein called tubulin. Centrioles are found in most eukaryotic cells, but are not present in conifers ( Pinophyta), flowering plants ( angiosperms) and most fungi, an ...
s, chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle, organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant cell, plant and algae, algal cells. Chloroplasts have a high concentration of chlorophyll pigments which captur ...
s, ejectile organelles, and inclusions are absent.
* The cell is surrounded by a pellicle of three membrane layers (the alveolar structure) penetrated by micropores.
Mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identic ...
is usually closed, with an intranuclear spindle; in some species, it is open at the poles.
* Cell division is usually by schizogony.
* Meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one c ...
occurs in the zygote
A zygote (; , ) is a eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes.
The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individ ...
.
Mobility:
Apicomplexans have a unique gliding capability which enables them to cross through tissues and enter and leave their host cells. This gliding ability is made possible by the use of adhesions and small static myosin motors.
Other features common to this phylum are a lack of cilia, sexual reproduction, use of micropores for feeding, and the production of oocysts containing sporozoites as the infective form.
Transposons appear to be rare in this phylum, but have been identified in the genera ''Ascogregarina'' and ''Eimeria
''Eimeria'' is a genus of apicomplexan parasites that includes various species capable of causing the disease coccidiosis in animals such as cattle, poultry and smaller ruminants including sheep and goats. ''Eimeria'' species are considered to ...
''.
Life cycle
Most members have a complex lifecycle, involving both asexual and sexual reproduction. Typically, a host is infected via an active invasion by the parasites (similar to entosis), which divide to producesporozoite
Apicomplexans, a group of intracellular parasites, have life cycle stages that allow them to survive the wide variety of environments they are exposed to during their complex life cycle. Each stage in the life cycle of an apicomplexan organis ...
s that enter its cells. Eventually, the cells burst, releasing merozoites, which infect new cells. This may occur several times, until gamonts are produced, forming gametes that fuse to create new cysts. Many variations occur on this basic pattern, however, and many Apicomplexa have more than one host.
The apical complex includes vesicles called rhoptries and microneme
Micronemes are secretory organelles, possessed by parasitic apicomplexans. Micronemes are located on the apical third of the protozoan body. They are surrounded by a typical unit membrane. On electron microscopy they have an electron-dense ma ...
s, which open at the anterior of the cell. These secrete enzymes that allow the parasite to enter other cells. The tip is surrounded by a band of microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nanometer, nm and have an inner diameter bet ...
s, called the polar ring, and among the Conoidasida is also a funnel of tubulin proteins called the conoid. Over the rest of the cell, except for a diminished mouth called the micropore, the membrane is supported by vesicles called alveoli, forming a semirigid pellicle.
The presence of alveoli and other traits place the Apicomplexa among a group called the alveolate
The alveolates (meaning "pitted like a honeycomb") are a group of protists, considered a major unranked clade or superphylum within Eukaryota. They are currently grouped with the Stramenopiles and Rhizaria among the protists with tubulocristate ...
s. Several related flagellates, such as ''Perkinsus
''Perkinsus'' is a genus of alveolates in the phylum Perkinsozoa. The genus was erected in 1978 to better treat its type species, '' Perkinsus marinus'', known formerly as ''Dermocystidium marinum''. These are parasitic protozoans that infect ...
'' and '' Colpodella'', have structures similar to the polar ring and were formerly included here, but most appear to be closer relatives of the dinoflagellate
The Dinoflagellates (), also called Dinophytes, are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered protists. Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they are also commo ...
s. They are probably similar to the common ancestor of the two groups.
Another similarity is that many apicomplexan cells contain a single plastid
A plastid is a membrane-bound organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. Plastids are considered to be intracellular endosymbiotic cyanobacteria.
Examples of plastids include chloroplasts ...
, called the apicoplast
An apicoplast is a derived non-photosynthetic plastid found in most Apicomplexa, including ''Toxoplasma gondii'', and ''Plasmodium falciparum'' and other ''Plasmodium'' spp. (parasites causing malaria), but not in others such as ''Cryptosporidium' ...
, surrounded by either three or four membranes. Its functions are thought to include tasks such as lipid and heme biosynthesis, and it appears to be necessary for survival. In general, plastids are considered to have a common origin with the chloroplasts of dinoflagellates, and evidence points to an origin from red algae
Red algae, or Rhodophyta (, ; ), make up one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta comprises one of the largest Phylum, phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 recognized species within over 900 Genus, genera amidst ongoing taxon ...
rather than green
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by a com ...
.
Subgroups
Within this phylum are four groups — coccidians, gregarines, haemosporidians (or haematozoans, including in addition piroplasms), and marosporidians. The coccidians and haematozoans appear to be relatively closely related. ''Perkinsus '', while once considered a member of the Apicomplexa, has been moved to a new phylum — Perkinsozoa.Gregarines
 The gregarines are generally parasites of
The gregarines are generally parasites of annelid
The annelids (), also known as the segmented worms, are animals that comprise the phylum Annelida (; ). The phylum contains over 22,000 extant species, including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to vario ...
s, arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s, and molluscs
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
. They are often found in the guts of their hosts, but may invade the other tissues. In the typical gregarine lifecycle, a trophozoite
A trophozoite (G. ''trope'', nourishment + ''zoon'', animal) is the activated, feeding stage in the life cycle of certain protozoa such as malaria-causing ''Plasmodium falciparum'' and those of the ''Giardia'' group. The complementary form of the t ...
develops within a host cell into a schizont. This then divides into a number of merozoites by schizogony. The merozoites are released by lysing the host cell, which in turn invade other cells. At some point in the apicomplexan lifecycle, gametocyte
A gametocyte is a eukaryotic germ cell that divides by mitosis into other gametocytes or by meiosis into gametids during gametogenesis. Male gametocytes are called ''spermatocytes'', and female gametocytes are called ''oocytes''.
Development
T ...
s are formed. These are released by lysis of the host cells, which group together. Each gametocyte forms multiple gamete
A gamete ( ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as s ...
s. The gametes fuse with another to form oocysts. The oocysts leave the host to be taken up by a new host.
Coccidians
 In general, coccidians are parasites of
In general, coccidians are parasites of vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s. Like gregarines, they are commonly parasites of the epithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
cells of the gut, but may infect other tissues.
The coccidian lifecycle involves merogony, gametogony, and sporogony. While similar to that of the gregarines it differs in zygote
A zygote (; , ) is a eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes.
The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individ ...
formation. Some trophozoites enlarge and become macrogamete, whereas others divide repeatedly to form microgametes (anisogamy). The microgametes are motile and must reach the macrogamete to fertilize it. The fertilized macrogamete forms a zygote that in its turn forms an oocyst that is normally released from the body. Syzygy, when it occurs, involves markedly anisogamous gametes. The lifecycle is typically haploid, with the only diploid stage occurring in the zygote, which is normally short-lived.
The main difference between the coccidians and the gregarines is in the gamonts. In the coccidia, these are small, intracellular, and without epimerites or mucrons. In the gregarines, these are large, extracellular, and possess epimerites or mucrons. A second difference between the coccidia and the gregarines also lies in the gamonts. In the coccidians, a single gamont becomes a macrogametocyte, whereas in the gregarines, the gamonts give rise to multiple gametocytes.
Haemosporidia
 The Haemosporidia have more complex lifecycles that alternate between an arthropod and a vertebrate host. The trophozoite parasitises
The Haemosporidia have more complex lifecycles that alternate between an arthropod and a vertebrate host. The trophozoite parasitises erythrocyte
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood ce ...
s or other tissues in the vertebrate host. Microgametes and macrogametes are always found in the blood. The gametes are taken up by the insect vector during a blood meal. The microgametes migrate within the gut of the insect vector and fuse with the macrogametes. The fertilized macrogamete now becomes an ookinete, which penetrates the body of the vector. The ookinete then transforms into an oocyst and divides initially by meiosis and then by mitosis (haplontic lifecycle) to give rise to the sporozoite
Apicomplexans, a group of intracellular parasites, have life cycle stages that allow them to survive the wide variety of environments they are exposed to during their complex life cycle. Each stage in the life cycle of an apicomplexan organis ...
s. The sporozoites escape from the oocyst and migrate within the body of the vector to the salivary glands where they are injected into the new vertebrate host when the insect vector feeds again.
Marosporida
The class Marosporida Mathur, Kristmundsson, Gestal, Freeman, and Keeling 2020 is a newly recognized lineage of apicomplexans that is sister to the Coccidia and Hematozoa. It is defined as a phylogeneticclade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
containing ''Aggregata octopiana'' Frenzel 1885, '' Merocystis kathae'' Dakin, 1911 (both Aggregatidae, originally coccidians), '' Rhytidocystis'' sp. 1 and ''Rhytidocystis'' sp. 2 Janouškovec et al. 2019 ( Rhytidocystidae Levine, 1979, originally coccidians, Agamococcidiorida), and ''Margolisiella islandica'' Kristmundsson et al. 2011 (closely related to Rhytidocystidae). Marosporida infect marine invertebrates. Members of this clade retain plastid
A plastid is a membrane-bound organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. Plastids are considered to be intracellular endosymbiotic cyanobacteria.
Examples of plastids include chloroplasts ...
genomes and the canonical apicomplexan plastid metabolism. However, marosporidians have the most reduced apicoplast genomes sequenced to date, lack canonical plastidial RNA polymerase and so provide new insights into reductive organelle evolution.
Ecology and distribution
Many of the apicomplexan parasites are important pathogens of humans and domestic animals. In contrast tobacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
l pathogens, these apicomplexan parasites are eukaryotic
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
and share many metabolic pathways with their animal hosts. This makes therapeutic target development extremely difficult – a drug that harms an apicomplexan parasite is also likely to harm its human host. At present, no effective vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verifi ...
s are available for most diseases caused by these parasites. Biomedical research on these parasites is challenging because it is often difficult, if not impossible, to maintain live parasite cultures in the laboratory and to genetically manipulate these organisms. In recent years, several of the apicomplexan species have been selected for genome sequencing
Whole genome sequencing (WGS), also known as full genome sequencing or just genome sequencing, is the process of determining the entirety of the DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This entails sequencing all of an organism's ...
. The availability of genome sequences provides a new opportunity for scientists to learn more about the evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, re ...
and biochemical capacity of these parasites. The predominant source of this genomic information is the EuPathDB family of websites, which currently provides specialised services for ''Plasmodium
''Plasmodium'' is a genus of unicellular eukaryotes that are obligate parasites of vertebrates and insects. The life cycles of ''Plasmodium'' species involve development in a Hematophagy, blood-feeding insect host (biology), host which then inj ...
'' species ( PlasmoDB), coccidia
Coccidia (Coccidiasina) are a subclass of microscopic, spore-forming, single-celled obligate intracellular parasites belonging to the apicomplexan class Conoidasida.
As obligate intracellular parasites, they must live and reproduce within a ...
ns (ToxoDB), piroplasms (PiroplasmaDB), and ''Cryptosporidium
''Cryptosporidium'', sometimes called crypto, is an apicomplexan genus of alveolates which are parasitism, parasites that can cause a respiratory and gastrointestinal illness (cryptosporidiosis) that primarily involves watery diarrhea (inte ...
'' species (CryptoDB). One possible target for drugs is the plastid, and in fact existing drugs such as tetracycline
Tetracycline, sold under various brand names, is an antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections, including acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis. It is available in oral an ...
s, which are effective against apicomplexans, seem to operate against the plastid.
Many Coccidiomorpha have an intermediate host
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasitic, a mutualistic, or a commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include ...
, as well as a primary host, and the evolution of hosts proceeded in different ways and at different times in these groups. For some coccidiomorphs, the original host has become the intermediate host, whereas in others it has become the definitive host. In the genera '' Aggregata'', '' Atoxoplasma'', '' Cystoisospora'', '' Schellackia'', and '' Toxoplasma'', the original is now definitive, whereas in ''Akiba'', '' Babesiosoma'', ''Babesia
''Babesia'', also called ''Nuttallia'', is an apicomplexan parasite that infects red blood cells and is transmitted by ticks. Originally discovered by Romanian bacteriologist Victor Babeș in 1888; over 100 species of ''Babesia'' have since ...
'', '' Haemogregarina'', '' Haemoproteus'', '' Hepatozoon'', '' Karyolysus'', '' Leucocytozoon'', ''Plasmodium
''Plasmodium'' is a genus of unicellular eukaryotes that are obligate parasites of vertebrates and insects. The life cycles of ''Plasmodium'' species involve development in a Hematophagy, blood-feeding insect host (biology), host which then inj ...
'', ''Sarcocystis
''Sarcocystis'' is a genus of protozoan parasites, with many species infecting mammals, reptiles and birds. Its name is derived from Greek language, Greek ''sarx'' = flesh and ''kystis'' = bladder.
The lifecycle of a typical member of this genus ...
'', and '' Theileria'', the original hosts are now intermediate.
Similar strategies to increase the likelihood of transmission have evolved in multiple genera. Polyenergid oocysts and tissue cysts are found in representatives of the orders Protococcidiorida and Eimeriida. Hypnozoites are found in '' Karyolysus lacerate'' and most species of ''Plasmodium
''Plasmodium'' is a genus of unicellular eukaryotes that are obligate parasites of vertebrates and insects. The life cycles of ''Plasmodium'' species involve development in a Hematophagy, blood-feeding insect host (biology), host which then inj ...
''; transovarial transmission of parasites occurs in lifecycles of '' Karyolysus'' and ''Babesia
''Babesia'', also called ''Nuttallia'', is an apicomplexan parasite that infects red blood cells and is transmitted by ticks. Originally discovered by Romanian bacteriologist Victor Babeș in 1888; over 100 species of ''Babesia'' have since ...
''.
Horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the e ...
appears to have occurred early on in this phylum's evolution with the transfer of a histone H4
Histone H4 is one of the five main histone proteins involved in the structure of chromatin in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. Featuring a main globular domain and a long N-terminus, N-terminal tail, H4 is involved with the structure of the nucleo ...
lysine 20 (H4K20) modifier, KMT5A (Set8), from an animal host to the ancestor of apicomplexans. A second gene—H3K36 methyltransferase (Ashr3 in plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s)—may have also been horizontally transferred.
Blood-borne genera
Within the Apicomplexa are three suborders of parasites: * suborderAdeleorina
''Adeleorina'' is a suborder of parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa.
History
Léger proposed this taxon in 1911. The first species identified was '' Dactylosoma ranarum'' by Lankester (1871) in a frog in Europe. It was initially called ''Unduli ...
—eight genera
* suborder Laveraniina (formerly Haemosporina)—all genera in this suborder
* suborder Eimeriorina—two genera ('' Lankesterella'' and '' Schellackia'')
Within the Adelorina are species that infect invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
s and others that infect vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s. The Eimeriorina—the largest suborder in this phylum—the lifecycle involves both sexual and asexual stages. The asexual stages reproduce by schizogony. The male gametocyte produces a large number of gametes and the zygote gives rise to an oocyst, which is the infective stage. The majority are monoxenous (infect one host only), but a few are heteroxenous
Heteroxeny, or heteroxenous development, characterizes a parasite whose development involves several host species. Heteroxeny has been used as the basis for splitting genera.
When there are two or three hosts, the development cycle is named d ...
(lifecycle involves two or more hosts).
The number of families in this later suborder is debated, with the number of families being between one and 20 depending on the authority and the number of genera being between 19 and 25.
Taxonomy
History
The first Apicomplexa protozoan was seen byAntonie van Leeuwenhoek
Antonie Philips van Leeuwenhoek ( ; ; 24 October 1632 – 26 August 1723) was a Dutch microbiologist and microscopist in the Golden Age of Dutch art, science and technology. A largely self-taught man in science, he is commonly known as " ...
, who in 1674 saw probably oocysts of '' Eimeria stiedae'' in the gall bladder of a rabbit
Rabbits are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also includes the hares), which is in the order Lagomorpha (which also includes pikas). They are familiar throughout the world as a small herbivore, a prey animal, a domesticated ...
. The first species of the phylum
In biology, a phylum (; : phyla) is a level of classification, or taxonomic rank, that is below Kingdom (biology), kingdom and above Class (biology), class. Traditionally, in botany the term division (taxonomy), division has been used instead ...
to be described, '' Gregarina ovata'', in earwig
Earwigs make up the insect order (biology), order Dermaptera. With about 2,000 species in 12 families, they are one of the smaller insect orders. Earwigs have characteristic cercus, cerci, a pair of forceps-like pincer (biology), pincers on ...
s' intestines, was named by Dufour in 1828. He thought that they were a peculiar group related to the trematode
Trematoda is a Class (biology), class of flatworms known as trematodes, and commonly as flukes. They are obligate parasite, obligate Endoparasites, internal parasites with a complex biological life cycle, life cycle requiring at least two Host ( ...
s, at that time included in Vermes. Since then, many more have been identified and named. During 1826–1850, 41 species and six genera of Apicomplexa were named. In 1951–1975, 1873 new species and 83 new genera were added.
The older taxon Sporozoa, included in Protozoa
Protozoa (: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a polyphyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic debris. Historically ...
, was created by Leuckart in 1879 and adopted by Bütschli in 1880. Through history, it grouped with the current Apicomplexa many unrelated groups. For example, Kudo (1954) included in the Sporozoa species of the Ascetosporea (Rhizaria
The Rhizaria are a diverse and species-rich clade of mostly unicellular eukaryotes. Except for the Chlorarachniophytes and three species in the genus '' Paulinella'' in the phylum Cercozoa, they are all non-photosynthetic, but many Foraminifera ...
), Microsporidia
Microsporidia are a group of spore-forming unicellular parasites. These spores contain an extrusion apparatus that has a coiled polar tube ending in an anchoring disc at the apical part of the spore.Franzen, C. (2005). How do Microsporidia inva ...
(Fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
), Myxozoa
Myxozoa (etymology: Greek: μύξα ''myxa'' "slime" or "mucus" + thematic vowel o + ζῷον ''zoon'' "animal") is a subphylum of aquatic cnidarian animals – all obligate parasites. It contains the smallest animals ever known to have lived. ...
(Animalia
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
), and '' Helicosporidium'' (Chlorophyta
Chlorophyta is a division of green algae informally called chlorophytes.
Description
Chlorophytes are eukaryotic organisms composed of cells with a variety of coverings or walls, and usually a single green chloroplast in each cell. They are ...
), while Zierdt (1978) included the genus '' Blastocystis'' (Stramenopiles
The stramenopiles, also called heterokonts, are Protist, protists distinguished by the presence of stiff tripartite external hairs. In most species, the hairs are attached to flagella, in some they are attached to other areas of the cellular sur ...
). '' Dermocystidium'' was also thought to be sporozoan. Not all of these groups had spores, but all were parasitic. However, other parasitic or symbiotic unicellular organisms were included too in protozoan groups outside Sporozoa ( Flagellata, Ciliophora
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different ...
and Sarcodina), if they had flagella (e.g., many Kinetoplastida, Retortamonadida, Diplomonadida, Trichomonadida, Hypermastigida), cilia (e.g., '' Balantidium'') or pseudopods (e.g., '' Entamoeba, Acanthamoeba, Naegleria''). If they had cell walls, they also could be included in plant kingdom between bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
or yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom (biology), kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are est ...
s.
Sporozoa is no longer regarded as biologically valid and its use is discouraged, although some authors still use it as a synonym for the Apicomplexa. More recently, other groups were excluded from Apicomplexa, e.g., ''Perkinsus
''Perkinsus'' is a genus of alveolates in the phylum Perkinsozoa. The genus was erected in 1978 to better treat its type species, '' Perkinsus marinus'', known formerly as ''Dermocystidium marinum''. These are parasitic protozoans that infect ...
'' and '' Colpodella'' (now in Protalveolata).
The field of classifying Apicomplexa is in flux and classification has changed throughout the years since it was formally named in 1970.
By 1987, a comprehensive survey of the phylum was completed: in all, 4516 species and 339 genera had been named. They consisted of:
* Class Conoidasida
Conoidasida is a class of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. The class was defined in 1988 by Levine and contains two subclasses – the coccidia and the gregarines. All members of this class have a complete, hollow, truncated ...
** Subclass Gregarinasina
The gregarines are a group of Apicomplexan alveolates, classified as the Gregarinasina or Gregarinia. The large (roughly half a millimeter) parasites inhabit the intestines of many invertebrates. They are not found in any vertebrates. Gregarines ...
'' p.p.''
*** Order Eugregarinorida, with 1624 named species and 231 named genera
** Subclass Coccidiasina
Coccidia (Coccidiasina) are a subclass of microscopic, spore-forming, single-celled obligate intracellular parasites belonging to the apicomplexan class Conoidasida.
As obligate intracellular parasites, they must live and reproduce within an ...
''p.p''
*** Order Eucoccidiorida ''p.p''
**** Suborder Adeleorina
''Adeleorina'' is a suborder of parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa.
History
Léger proposed this taxon in 1911. The first species identified was '' Dactylosoma ranarum'' by Lankester (1871) in a frog in Europe. It was initially called ''Unduli ...
''p.p''
***** Group Hemogregarines, with 399 species and four genera
**** Suborder Eimeriorina, with 1771 species and 43 genera
* Class Aconoidasida
The Aconoidasida are a Class (biology), class of apicomplexan parasites coined by Mehlhorn ''et al'' in 1980.
Description
Organisms in this class bear a tip at one end of their outer membrane. This apical complex includes vesicles called rhoptr ...
** Order Haemospororida, with 444 species and nine genera
** Order Piroplasmorida, with 173 species and 20 genera
* Other minor groups omitted above, with 105 species and 32 genera
Although considerable revision of this phylum has been done (the order Haemosporidia now has 17 genera rather than 9), these numbers are probably still approximately correct.
Jacques Euzéby (1988)
Jacques Euzéby in 1988 created a new class Haemosporidiasina by merging subclass Piroplasmasina and suborder Haemospororina. * SubclassGregarinasina
The gregarines are a group of Apicomplexan alveolates, classified as the Gregarinasina or Gregarinia. The large (roughly half a millimeter) parasites inhabit the intestines of many invertebrates. They are not found in any vertebrates. Gregarines ...
(the gregarines)
* Subclass Coccidiasina
Coccidia (Coccidiasina) are a subclass of microscopic, spore-forming, single-celled obligate intracellular parasites belonging to the apicomplexan class Conoidasida.
As obligate intracellular parasites, they must live and reproduce within an ...
** Suborder Adeleorina
''Adeleorina'' is a suborder of parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa.
History
Léger proposed this taxon in 1911. The first species identified was '' Dactylosoma ranarum'' by Lankester (1871) in a frog in Europe. It was initially called ''Unduli ...
(the adeleorins)
** Suborder Eimeriorina (the eimeriorins)
* Subclass Haemosporidiasina
** Order Achromatorida
** Order Chromatorida
The division into Achromatorida and Chromatorida, although proposed on morphological grounds, may have a biological basis, as the ability to store haemozoin appears to have evolved only once.
Roberts and Janovy (1996)
Roberts and Janovy in 1996 divided the phylum into the following subclasses and suborders (omitting classes and orders): * SubclassGregarinasina
The gregarines are a group of Apicomplexan alveolates, classified as the Gregarinasina or Gregarinia. The large (roughly half a millimeter) parasites inhabit the intestines of many invertebrates. They are not found in any vertebrates. Gregarines ...
(the gregarines)
* Subclass Coccidiasina
Coccidia (Coccidiasina) are a subclass of microscopic, spore-forming, single-celled obligate intracellular parasites belonging to the apicomplexan class Conoidasida.
As obligate intracellular parasites, they must live and reproduce within an ...
** Suborder Adeleorina
''Adeleorina'' is a suborder of parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa.
History
Léger proposed this taxon in 1911. The first species identified was '' Dactylosoma ranarum'' by Lankester (1871) in a frog in Europe. It was initially called ''Unduli ...
(the adeleorins)
** Suborder Eimeriorina (the eimeriorins)
** Suborder Haemospororina (the haemospororins)
* Subclass Piroplasmasina (the piroplasms)
These form the following five taxonomic groups:
# The gregarines are, in general, one-host parasites of invertebrates.
# The adeleorins are one-host parasites of invertebrates or vertebrates, or two-host parasites that alternately infect haematophagous (blood-feeding) invertebrates and the blood of vertebrates.
# The eimeriorins are a diverse group that includes one host species of invertebrates, two-host species of invertebrates, one-host species of vertebrates and two-host species of vertebrates. The eimeriorins are frequently called the coccidia. This term is often used to include the adeleorins.
# Haemospororins, often known as the malaria parasites, are two-host Apicomplexa that parasitize blood-feeding dipteran flies and the blood of various tetrapod vertebrates.
# Piroplasms where all the species included are two-host parasites infecting ticks and vertebrates.
Perkins (2000)
 Perkins et al. proposed the following scheme. It is outdated as the Perkinsidae have since been recognised as a sister group to the dinoflagellates rather that the Apicomplexia:
* Class
Perkins et al. proposed the following scheme. It is outdated as the Perkinsidae have since been recognised as a sister group to the dinoflagellates rather that the Apicomplexia:
* Class Aconoidasida
The Aconoidasida are a Class (biology), class of apicomplexan parasites coined by Mehlhorn ''et al'' in 1980.
Description
Organisms in this class bear a tip at one end of their outer membrane. This apical complex includes vesicles called rhoptr ...
*: ''Conoid present only in the ookinete of some species''
::*Order Haemospororida
:::''Macrogamete and microgamete develop separately. Syzygy does not occur. Ookinete has a conoid. Sporozoites have three walls. Heteroxenous: alternates between vertebrate host (in which merogony occurs) and invertebrate host (in which sporogony occurs). Usually blood parasites, transmitted by blood-sucking insects.''
::*Order Piroplasmorida
* Class Conoidasida
Conoidasida is a class of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. The class was defined in 1988 by Levine and contains two subclasses – the coccidia and the gregarines. All members of this class have a complete, hollow, truncated ...
** Subclass Gregarinasina
The gregarines are a group of Apicomplexan alveolates, classified as the Gregarinasina or Gregarinia. The large (roughly half a millimeter) parasites inhabit the intestines of many invertebrates. They are not found in any vertebrates. Gregarines ...
*** Order Archigregarinorida
*** Order Eugregarinorida
**** Suborder Adeleorina
''Adeleorina'' is a suborder of parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa.
History
Léger proposed this taxon in 1911. The first species identified was '' Dactylosoma ranarum'' by Lankester (1871) in a frog in Europe. It was initially called ''Unduli ...
**** Suborder Eimeriorina
*** Order Neogregarinorida
** Subclass Coccidiasina
Coccidia (Coccidiasina) are a subclass of microscopic, spore-forming, single-celled obligate intracellular parasites belonging to the apicomplexan class Conoidasida.
As obligate intracellular parasites, they must live and reproduce within an ...
*** Order Agamococcidiorida
*** Order Eucoccidiorida
*** Order Ixorheorida
*** Order Protococcidiorida
* Class Perkinsasida
::*Order Perkinsorida
:::*Family Perkinsidae
The name Protospiromonadida has been proposed for the common ancestor of the Gregarinomorpha and Coccidiomorpha.
Another group of organisms that belong in this taxon are the corallicolids. These are found in coral reef gastric cavities. Their relationship to the others in this phylum has yet to be established.
Another genus has been identified - ''Nephromyces
''Nephromyces'' is a genus of apicomplexans that are symbionts of the ascidian genus '' Molgula'' (sea grapes).
Systematics
''Nephromyces'' was first described in 1888 by Alfred Mathieu Giard as a chytrid fungus, because of its filamentous ...
'' - which appears to be a sister taxon to the Hematozoa.Muñoz-Gómez SA, Durnin K, Eme L, Paight C, Lane CE, Saffo MB, Slamovits CH (2019) ''Nephromyces'' represents a diverse and novel lineage of the Apicomplexa that has retained apicoplasts. Genome Biol Evol This genus is found in the renal sac of molgulid ascidian tunicate
Tunicates are marine invertebrates belonging to the subphylum Tunicata ( ). This grouping is part of the Chordata, a phylum which includes all animals with dorsal nerve cords and notochords (including vertebrates). The subphylum was at one time ...
s.
Evolution
Members of this phylum, except for thephotosynthetic
Photosynthesis ( ) is a Biological system, system of biological processes by which Photoautotrophism, photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical ener ...
chromerids, are parasitic and evolved from a free-living ancestor. This lifestyle is presumed to have evolved at the time of the divergence of dinoflagellates and apicomplexans. Further evolution of this phylum has been estimated to have occurred about . The oldest extant clade is thought to be the archigregarines.
These phylogenetic relations have rarely been studied at the subclass level. The Haemosporidia are related to the gregarines, and the piroplasms and coccidians are sister groups. The Haemosporidia and the Piroplasma appear to be sister clades, and are more closely related to the coccidians than to the gregarines. Marosporida is a sister group to Coccidiomorphea.
Janouškovec et al. 2015 presents a somewhat different phylogeny, supporting the work of others showing multiple events of plastid
A plastid is a membrane-bound organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. Plastids are considered to be intracellular endosymbiotic cyanobacteria.
Examples of plastids include chloroplasts ...
s losing photosynthesis. More importantly this work provides the first phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ...
evidence that there have also been multiple events of plastids becoming genome-free.
See also
* CentroconeReferences
External links
* * {{Portal bar, Biology Alveolata phyla Endoparasites