Anglo-Aquitanian on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Duchy of Aquitaine (, ; , ) was a historical

fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal alle ...
dom located in the western, central, and southern areas of present-day France, south of the river Loire
The Loire ( , , ; ; ; ; ) is the longest river in France and the 171st longest in the world. With a length of , it drains , more than a fifth of France's land, while its average discharge is only half that of the Rhône.
It rises in the so ...
. The full extent of the duchy
A duchy, also called a dukedom, is a country, territory, fiefdom, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess, a ruler hierarchically second to the king or Queen regnant, queen in Western European tradition.
There once existed an important differe ...
, as well as its name, fluctuated greatly over the centuries and at times comprised much of what is now southwestern (including Gascony
Gascony (; ) was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part of the combined Province of Guyenne and Gascon ...
) and central France.
The territory originated in 507 as a constituent kingdom of the Frankish kingdom after the Salian Franks conquered Aquitaine
Aquitaine (, ; ; ; ; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Aguiéne''), archaic Guyenne or Guienne (), is a historical region of southwestern France and a former Regions of France, administrative region. Since 1 January 2016 it has been part of the administ ...
following the Battle of Vouillé; its boundaries were ultimately a combination of the Roman provinces of . As a duchy, it broke up after the conquest of the independent Aquitanian duchy of Waiofar
Waiofar, also spelled Waifar, Waifer or Waiffre (died 2 June 768), was the last independent Duke of Aquitaine from 745 to 768. He peacefully succeeded his father, Hunald I, after the latter entered a monastery. He also inherited the conflict with ...
, going on to become a sub-kingdom within the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Franks, Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as List of Frankish kings, kings of the Franks since ...
. It was then absorbed by West Francia
In medieval historiography, West Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the West Franks () constitutes the initial stage of the Kingdom of France and extends from the year 843, from the Treaty of Verdun, to 987, the beginning of the Capet ...
after the partition of Verdun in 843 and soon reappeared as a duchy under West Francia. In 1153, an enlarged Aquitaine pledged loyalty to the Angevin kings of England. As a result, a rivalry
A rivalry is the state of two people or groups engaging in a lasting competitive relationship. Rivalry is the "against each other" spirit between two competing sides. The relationship itself may also be called "a rivalry", and each participant ...
emerged between the French monarchs
France was ruled by monarchs from the establishment of the kingdom of West Francia in 843 until the end of the Second French Empire in 1870, with several interruptions.
Classical French historiography usually regards Clovis I, king of the Fra ...
and the Angevins over control of the latter's territorial possessions in France. By the mid-13th century, only an enlarged Guyenne
Guyenne or Guienne ( , ; ) was an old French province which corresponded roughly to the Roman province of '' Aquitania Secunda'' and the Catholic archdiocese of Bordeaux.
Name
The name "Guyenne" comes from ''Aguyenne'', a popular transform ...
and Gascony
Gascony (; ) was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part of the combined Province of Guyenne and Gascon ...
remained in Angevin hands. The Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a conflict between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France and a civil war in France during the Late Middle Ages. It emerged from feudal disputes over the Duchy ...
finally saw the kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the Middle Ages, medieval and Early modern France, early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe from th ...
gain full control over Aquitaine in the 1450s, with much of its territory directly incorporated into the French royal domain itself.
states and territories disestablished in 1453
History
Early history

Gallia Aquitania
Gallia Aquitania (, ), also known as Aquitaine or Aquitaine Gaul, was a list of Roman provinces, province of the Roman Empire. It lies in present-day southwest France and the Comarques of Catalonia, comarca of Val d'Aran in northeast Spain, wher ...
fell under Visigothic
The Visigoths (; ) were a Germanic people united under the rule of a king and living within the Roman Empire during late antiquity. The Visigoths first appeared in the Balkans, as a Roman-allied barbarian military group united under the comman ...
rule in the 5th century. It was conquered by the Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty
The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which wa ...
under Clovis I
Clovis (; reconstructed Old Frankish, Frankish: ; – 27 November 511) was the first List of Frankish kings, king of the Franks to unite all of the Franks under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a ...
in 507, as a result of the Battle of Vouillé. During the 6th and early 7th century, it was under direct rule of Frankish kings, divided between the realms of Childebert II
Childebert II ( – 596) was the Merovingian king of Austrasia (which included Provence at the time) from 575 until his death in March 596, and the king of Burgundy from 592 to his death, as the adopted son of his uncle Guntram.
Childh ...
and Guntram in the Treaty of Andelot of 587. Under Chlothar II, Aquitaine was again an integral part of Francia, but after Chlothar's death in 629, his heir Dagobert I granted a subkingdom in southern Aquitaine to his younger brother Charibert II. This subkingdom, consisting of Gascony and the southern fringe of Aquitaine proper, is conventionally known as "Aquitaine" and forms the historical basis for the later duchy.
Charibert campaigned successfully against the Basques
The Basques ( or ; ; ; ) are a Southwestern European ethnic group, characterised by the Basque language, a Basque culture, common culture and shared genetic ancestry to the ancient Vascones and Aquitanians. Basques are indigenous peoples, ...
, but after his death in 632, they revolted again, in 635 subdued by an army sent by Dagobert (who was at the same time forced to deal with a rebellion in Brittany).
The duchy of Aquitaine established itself as a quasi-independent realm within the Frankish empire during the second half of the 7th century, certainly by 700 under Odo the Great. The first duke is on record under the name of Felix, and as having ruled from about 660. As his successor, Lupus held loose ties with the Frankish kings, ruling autonomously (''princeps'').Lewis, pp 400–401 and n127. Odo succeeded Lupus in 700 and signed a peace treaty with Charles Martel
Charles Martel (; – 22 October 741), ''Martel'' being a sobriquet in Old French for "The Hammer", was a Franks, Frankish political and military leader who, as Duke and Prince of the Franks and Mayor of the Palace, was the de facto ruler of ...
. He inflicted on the Moors
The term Moor is an Endonym and exonym, exonym used in European languages to designate the Muslims, Muslim populations of North Africa (the Maghreb) and the Iberian Peninsula (particularly al-Andalus) during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a s ...
a crushing defeat at the Battle of Toulouse in 721.
However, Charles Martel coveted the southern realm, crossed the Loire in 731 and looted much of Aquitaine. Odo engaged the Franks in battle, but lost and came out weakened. Soon after this battle, in 732, the Moors raided Vasconia and Aquitaine as far north as Poitiers
Poitiers is a city on the river Clain in west-central France. It is a commune in France, commune, the capital of the Vienne (department), Vienne department and the historical center of Poitou, Poitou Province. In 2021, it had a population of 9 ...
and defeated Odo twice near Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( ; ; Gascon language, Gascon ; ) is a city on the river Garonne in the Gironde Departments of France, department, southwestern France. A port city, it is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the Prefectures in F ...
. Odo saw no option but to invoke the aid of Charles Martel and pledge allegiance to the Frankish prince.
Odo was succeeded by his son Hunald, who reverted to former independence, so defying the Frankish Mayor of the Palace
Under the Merovingian dynasty, the mayor of the palace or majordomo,
( or ) was the manager of the household of the Frankish king. He was the head of the Merovingian administrative ladder and orchestrated the operation of the entire court. He ...
Charles Martel's authority. In 735 and 736 Martel attacked Hunald and his allies, the counts of key Aquitanian towns such as Bourges
Bourges ( ; ; ''Borges'' in Berrichon) is a commune in central France on the river Yèvre (Cher), Yèvre. It is the capital of the Departments of France, department of Cher (department), Cher, and also was the capital city of the former provin ...
and Limoges
Limoges ( , , ; , locally ) is a city and Communes of France, commune, and the prefecture of the Haute-Vienne Departments of France, department in west-central France. It was the administrative capital of the former Limousin region. Situated o ...
. Eventually Hunald retired to a monastery, leaving both the kingdom and the continuing conflict to Waifer, or Guaifer. Following the full occupation of Septimania in 759, Pepin turned now his attention to Aquitaine, initiating a cyclical military campaign that lasted for eight years, i.e. the War of Aquitaine. Waifer strenuously carried on an unequal struggle with the Carolingian Franks, but his assassination in 768 marked the demise of Aquitaine's relative independence. During these years Aquitaine underwent intensive destruction of urban, economic, military and intellectual centres. Pepin's forces destroyed up to 36 monasteries.
As a successor state to the Roman province of Gallia Aquitania and the Visigothic Kingdom
The Visigothic Kingdom, Visigothic Spain or Kingdom of the Goths () was a Barbarian kingdoms, barbarian kingdom that occupied what is now southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to the 8th centuries. One of the Germanic people ...
(418–721), Aquitania (Aquitaine) and Languedoc
The Province of Languedoc (, , ; ) is a former province of France.
Most of its territory is now contained in the modern-day region of Occitanie in Southern France. Its capital city was Toulouse. It had an area of approximately .
History
...
(Toulouse
Toulouse (, ; ; ) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Haute-Garonne department and of the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania region. The city is on the banks of the Garonne, River Garonne, from ...
) inherited the Visigothic Law and Roman Law
Roman law is the law, legal system of ancient Rome, including the legal developments spanning over a thousand years of jurisprudence, from the Twelve Tables (), to the (AD 529) ordered by Eastern Roman emperor Justinian I.
Roman law also den ...
which had combined to allow women more rights than their contemporaries in other parts of Europe. Particularly with the Liber Judiciorum, which was codified in 642 and 643 and expanded in the Code of Recceswinth in 653, women could inherit land and title and manage it independently from their husbands or male relations, dispose of their property in legal wills if they had no heirs, and women could represent themselves and bear witness in court by age 14 and arrange for their own marriages by age 20.Wemple, Suzanne Fonay; ''Women in the Fifth to the Tenth Century''. In: Klapisch-Zuber, Christine; ''A History of Women: Book II. Silences of the Middle Ages'', The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, London, England. 1992, 2000 (5th printing). Chapter 6, p 74. As a consequence, male-preference primogeniture
Primogeniture () is the right, by law or custom, of the firstborn Legitimacy (family law), legitimate child to inheritance, inherit all or most of their parent's estate (law), estate in preference to shared inheritance among all or some childre ...
was the practiced succession law for the nobility.
Carolingian kingdom of Aquitaine
The autonomous and troublesome duchy of Aquitaine was conquered by theFranks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty
The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which wa ...
in 769, after a series of revolts against their suzerainty. In order to avoid a new demonstration of Aquitain particularism, Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
decided to organize the land within his kingdom.
After the Carolingian conquest, the duchy ceased to exist as such, whose powers were taken over by the counts (dukes) of Toulouse, main seat of the Carolingian government in the Midi, represented by Chorso and, after being deposed, by Charlemagne's trustee William (of Gellone), a close relative of his. In 781, he made his third son Louis, then three years of age, king of Aquitaine. The Carolingian kingdom of Aquitaine subordinated to the Carolingian king or (later) emperor based in Francia
The Kingdom of the Franks (), also known as the Frankish Kingdom, or just Francia, was the largest History of the Roman Empire, post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks, Frankish Merovingian dynasty, Merovingi ...
(Austrasia, Neustria). It included not only Aquitaine proper, but also Gothia, Vasconia (Gascony) and the Carolingian possessions in Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
as well. In 806, Charlemagne planned to divide his empire between his sons. Louis received Provence
Provence is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which stretches from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the France–Italy border, Italian border to the east; it is bordered by the Mediterrane ...
and Burgundy
Burgundy ( ; ; Burgundian: ''Bregogne'') is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. ...
as additions to his kingdom.
When Louis succeeded Charlemagne as emperor in 814, he granted Aquitaine to his son Pepin I, after whose death in 838 the nobility of Aquitaine chose his son Pepin II of Aquitaine
Pepin II, called the Younger (823 – after 864 in Senlis, Oise, Senlis), was King of Aquitaine from 838 as the successor upon the death of his father, Pepin I of Aquitaine, Pepin I. Pepin II was eldest son of Pepin I and Ingeltrude, daughter ...
(d. 865) as their king. The emperor Louis I, however, opposed this arrangement and gave the kingdom to his youngest son Charles, afterwards the emperor Charles the Bald
Charles the Bald (; 13 June 823 – 6 October 877), also known as CharlesII, was a 9th-century king of West Francia (843–877), King of Italy (875–877) and emperor of the Carolingian Empire (875–877). After a series of civil wars during t ...
. Confusion and conflict resulted, eventually falling in favor of Charles; although from 845 to 852 Pepin II was in possession of the kingdom, at Eastertide 848 in Limoges
Limoges ( , , ; , locally ) is a city and Communes of France, commune, and the prefecture of the Haute-Vienne Departments of France, department in west-central France. It was the administrative capital of the former Limousin region. Situated o ...
, the magnates and prelates of Aquitaine formally elected Charles as their king. Later, at Orléans
Orléans (,"Orleans"
(US) and Wenilo, archbishop of Sens.Against this background of conflicted loyalties must be seen the career of Wenilo. In 852, Pepin II was imprisoned by Charles the Bald, who soon afterwards pronounced his own son Charles as the ruler of Aquitaine. On the death of the younger Charles in 866, his brother Louis the Stammerer succeeded to the kingdom, and when, in 877, Louis became king of the Franks, Aquitaine was fully absorbed into the Frankish crown. By a treaty made in 845 between Charles the Bald and Pepin II, the kingdom had been diminished by the loss of Poitou, Saintonge and Angoumois in the northwest of the region, which had been given to Rainulf I, count of Poitiers. The title of Duke of Aquitaine, already revived, was now borne by Rainulf, although it was also claimed by the counts of Toulouse. The new Duchy of Aquitaine, including the three districts already mentioned, remained in the hands of Ramulf's successors, despite disagreement with their Frankish overlords, until 893 when Count Rainulf II was poisoned by order of King Charles III, or Charles the Simple. Charles then bestowed the duchy upon William the Pious, count of Auvergne, the founder of the
 The Ramnulfids had become the dominant power in southwestern France by the end of the 11th century. By marriage rather than conquest, their possessions passed into the " Angevin Empire" under the English crown by 1153.
William IX, Duke of Aquitaine (d. 1127), who succeeded to the dukedom in 1087, gained fame as a crusader and a troubadour. His granddaughter, Eleanor of Aquitaine, succeeded to the duchy at the age of 15 as the eldest daughter and heir of William X (d. 1137), as his son did not live past childhood. She married Louis, heir to the French throne, three months after her father's death due to the quick thinking of Louis's father,
The Ramnulfids had become the dominant power in southwestern France by the end of the 11th century. By marriage rather than conquest, their possessions passed into the " Angevin Empire" under the English crown by 1153.
William IX, Duke of Aquitaine (d. 1127), who succeeded to the dukedom in 1087, gained fame as a crusader and a troubadour. His granddaughter, Eleanor of Aquitaine, succeeded to the duchy at the age of 15 as the eldest daughter and heir of William X (d. 1137), as his son did not live past childhood. She married Louis, heir to the French throne, three months after her father's death due to the quick thinking of Louis's father,
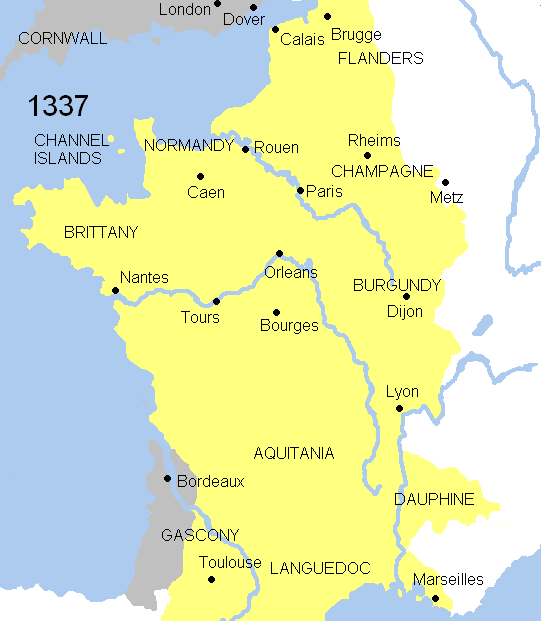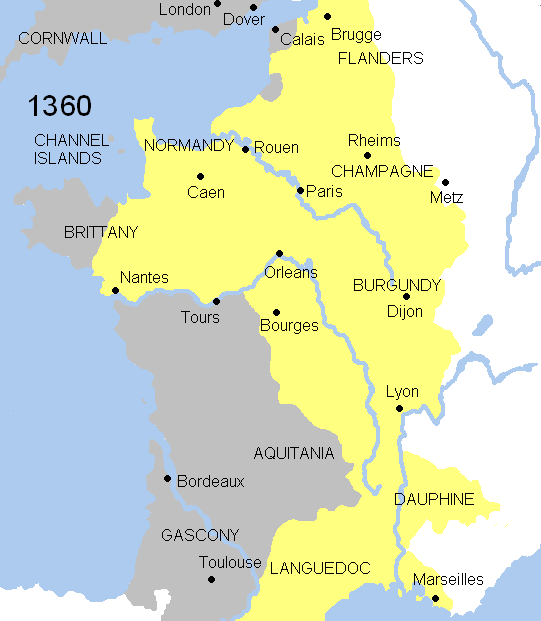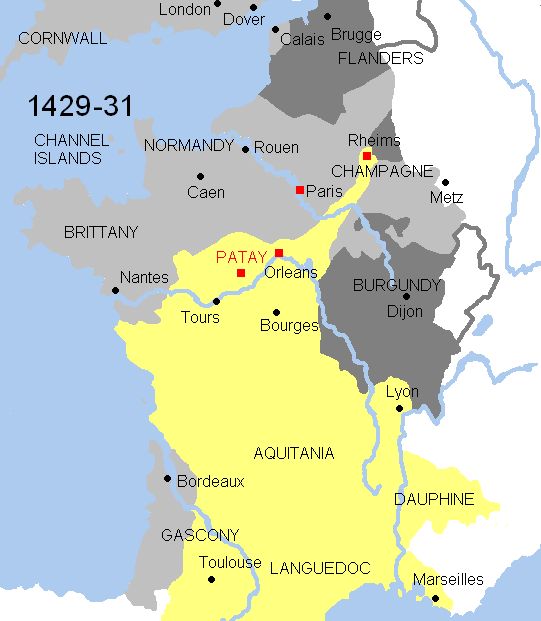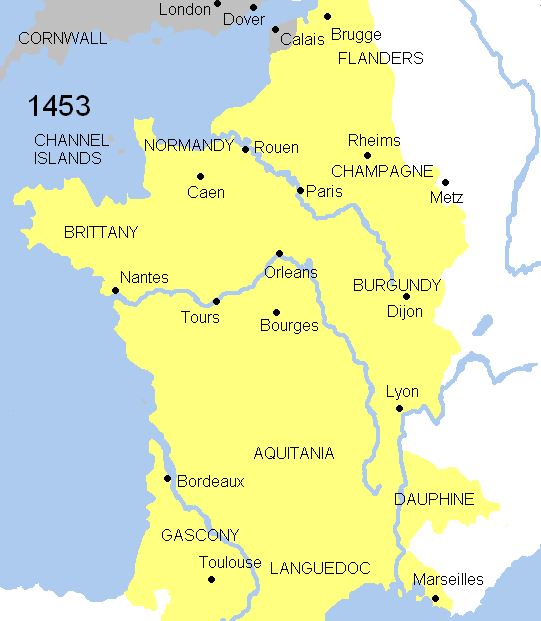 In 1337, King Philip VI of France reclaimed the fief of Aquitaine (essentially corresponding to Gascony) from Eleanor's descendant,
In 1337, King Philip VI of France reclaimed the fief of Aquitaine (essentially corresponding to Gascony) from Eleanor's descendant,
 Over the course of its existence, the duchy incorporated the Duchy of Gascony and, until 1271, the County of Toulouse, which now falls in the
Over the course of its existence, the duchy incorporated the Duchy of Gascony and, until 1271, the County of Toulouse, which now falls in the
The Dukes in the Regnum Francorum, A.D. 550-751.
''Speculum'', Vol. 51, No. 3. (July 1976), pp. 381–410. * Emile Mabille, (1870
''Le Royaume D'Aquitaine Et Ses Marches Sous Les Carlovingiens''
* Jean Penant, (2009) ''Occitanie, l'épopée des origines'' {{coord missing, France Former monarchies of Europe History of Aquitaine States and territories established in the 500s
(US) and Wenilo, archbishop of Sens.Against this background of conflicted loyalties must be seen the career of Wenilo. In 852, Pepin II was imprisoned by Charles the Bald, who soon afterwards pronounced his own son Charles as the ruler of Aquitaine. On the death of the younger Charles in 866, his brother Louis the Stammerer succeeded to the kingdom, and when, in 877, Louis became king of the Franks, Aquitaine was fully absorbed into the Frankish crown. By a treaty made in 845 between Charles the Bald and Pepin II, the kingdom had been diminished by the loss of Poitou, Saintonge and Angoumois in the northwest of the region, which had been given to Rainulf I, count of Poitiers. The title of Duke of Aquitaine, already revived, was now borne by Rainulf, although it was also claimed by the counts of Toulouse. The new Duchy of Aquitaine, including the three districts already mentioned, remained in the hands of Ramulf's successors, despite disagreement with their Frankish overlords, until 893 when Count Rainulf II was poisoned by order of King Charles III, or Charles the Simple. Charles then bestowed the duchy upon William the Pious, count of Auvergne, the founder of the
abbey of Cluny
Cluny Abbey (; , formerly also ''Cluni'' or ''Clugny''; ) is a former Benedictine monastery in Cluny, Saône-et-Loire, France. It was dedicated to Saints Peter and Paul.
The abbey was constructed in the Romanesque architectural style, with ...
, who was succeeded in 918 by his nephew, Count William II, who died in 926.
A succession of dukes followed, one of whom, William IV, fought against Hugh Capet
Hugh Capet (; ; 941 – 24 October 996) was the King of the Franks from 987 to 996. He is the founder of and first king from the House of Capet. The son of the powerful duke Hugh the Great and his wife Hedwige of Saxony, he was elected as t ...
, king of France, and another of whom, William V William V may refer to:
* William V, Duke of Aquitaine (969–1030)
* William V of Montpellier (1075–1121)
* William V, Marquess of Montferrat (1191)
* William V, Count of Nevers (before 11751181)
* William V, Duke of Jülich (1299–1361)
* Will ...
, called the Great, was able to strengthen and extend his authority considerably, although he yielded the proffered Lombard crown rather than fight Conrad II for it. William's duchy almost reached the limits of the old Roman Gallia Aquitania
Gallia Aquitania (, ), also known as Aquitaine or Aquitaine Gaul, was a list of Roman provinces, province of the Roman Empire. It lies in present-day southwest France and the Comarques of Catalonia, comarca of Val d'Aran in northeast Spain, wher ...
but did not stretch south of the Garonne, a district which was in the possession of the Gascons. William died in 1030. Odo or Eudes (d. 1039) joined Gascony to Aquitaine.
Angevin Empire
 The Ramnulfids had become the dominant power in southwestern France by the end of the 11th century. By marriage rather than conquest, their possessions passed into the " Angevin Empire" under the English crown by 1153.
William IX, Duke of Aquitaine (d. 1127), who succeeded to the dukedom in 1087, gained fame as a crusader and a troubadour. His granddaughter, Eleanor of Aquitaine, succeeded to the duchy at the age of 15 as the eldest daughter and heir of William X (d. 1137), as his son did not live past childhood. She married Louis, heir to the French throne, three months after her father's death due to the quick thinking of Louis's father,
The Ramnulfids had become the dominant power in southwestern France by the end of the 11th century. By marriage rather than conquest, their possessions passed into the " Angevin Empire" under the English crown by 1153.
William IX, Duke of Aquitaine (d. 1127), who succeeded to the dukedom in 1087, gained fame as a crusader and a troubadour. His granddaughter, Eleanor of Aquitaine, succeeded to the duchy at the age of 15 as the eldest daughter and heir of William X (d. 1137), as his son did not live past childhood. She married Louis, heir to the French throne, three months after her father's death due to the quick thinking of Louis's father, Louis VI of France
Louis VI (1 December 1081 – 1 August 1137), called the Fat () or the Fighter (), was List of French monarchs, King of the Franks from 1108 to 1137. Like his father Philip I of France, Philip I, Louis made a lasting contribution to centralizing ...
, who did not want to leave a territory such as Aquitaine governed by a child of fifteen. When Louis VI died, and Eleanor's new husband became King Louis VII, the duchy of Aquitaine officially came under the rule of the French Crown, and for fifteen years, Louis VII had territory that rivaled that of the English crown and the counts of Toulouse. The marriage was later annulled on the grounds of consanguinity by a bishop on 21 March 1152, and she kept her lands and title as Duchess of Aquitaine in her own right. On 18 May 1152, she married Henry, Duke of Normandy, the son of Empress Matilda
Empress Matilda (10 September 1167), also known as Empress Maud, was one of the claimants to the English throne during the civil war known as the Anarchy. The daughter and heir of Henry I, king of England and ruler of Normandy, she went to ...
, daughter of Henry I of England
Henry I ( – 1 December 1135), also known as Henry Beauclerc, was King of England from 1100 to his death in 1135. He was the fourth son of William the Conqueror and was educated in Latin and the liberal arts. On William's death in 1087, Henr ...
, and a claimant to the English throne. When he defeated his mother's cousin, King Stephen, in 1153 and became King of England as Henry II, Aquitaine merged with the English crown.
Having suppressed a revolt in his new possession, Henry gave it to his son Richard
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic language">Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'st ...
. When Richard died in 1199, it reverted to Eleanor, and on her death in 1204, it was inherited by her son John and absorbed into the English crown permanently. The duchy henceforward followed the fortunes of the other English possessions in France, such as Normandy
Normandy (; or ) is a geographical and cultural region in northwestern Europe, roughly coextensive with the historical Duchy of Normandy.
Normandy comprises Normandy (administrative region), mainland Normandy (a part of France) and insular N ...
and Anjou, ultimately leading to the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a conflict between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France and a civil war in France during the Late Middle Ages. It emerged from feudal disputes over the Duchy ...
between England and France.
Aquitaine as it came to the English kings stretched from the Loire to the Pyrenees, but its range was limited to the southeast by the extensive lands of the counts of Toulouse. The name Guienne, a corruption of Aquitaine, seems to have come into use about the 10th century, and the subsequent history of Aquitaine is merged in that of Gascony
Gascony (; ) was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part of the combined Province of Guyenne and Gascon ...
and Guienne.
Hundred Years' War
 In 1337, King Philip VI of France reclaimed the fief of Aquitaine (essentially corresponding to Gascony) from Eleanor's descendant,
In 1337, King Philip VI of France reclaimed the fief of Aquitaine (essentially corresponding to Gascony) from Eleanor's descendant, Edward III of England
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring royal authority after t ...
. Edward in turn claimed the entire Kingdom of France as the only grandson of King Philip IV of France
Philip IV (April–June 1268 – 29 November 1314), called Philip the Fair (), was King of France from 1285 to 1314. Jure uxoris, By virtue of his marriage with Joan I of Navarre, he was also King of Navarre and Count of Champagne as Philip&n ...
. This triggered the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a conflict between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France and a civil war in France during the Late Middle Ages. It emerged from feudal disputes over the Duchy ...
, in which both the Plantagenets and the House of Valois claimed supremacy over Aquitaine. In 1360, both sides signed the Treaty of Brétigny, in which Edward renounced his claim to the French crown but remained sovereign lord of Aquitaine (rather than merely duke). However, when the treaty was broken in 1369, both these English claims and the war resumed. In 1362, Edward III, as Lord of Aquitaine, made his eldest son Edward the Black Prince, Prince of Aquitaine. In 1390, King Richard II, son of Edward the Black Prince, appointed his uncle John of Gaunt as Duke of Aquitaine. That title passed on to John's descendants although they belonged to the crown because John of Gaunt's son, Henry IV, managed to successfully usurp the crown from Richard II, therefore 'inheriting' the title Lord of Aquitaine from his father, which was passed down to his descendants as they became Kings. His son, Henry V of England
Henry V (16 September 1386 – 31 August 1422), also called Henry of Monmouth, was King of England from 1413 until his death in 1422. Despite his relatively short reign, Henry's outstanding military successes in the Hundred Years' War against ...
, ruled over Aquitaine as King of England and Lord of Aquitaine from 1413 to 1422. He invaded France and emerged victorious at the Siege of Harfleur and the Battle of Agincourt
The Battle of Agincourt ( ; ) was an English victory in the Hundred Years' War. It took place on 25 October 1415 (Saint Crispin's Day) near Azincourt, in northern France. The unexpected victory of the vastly outnumbered English troops agains ...
in 1415. He succeeded in obtaining the French crown for his family by the Treaty of Troyes in 1420. Henry V died in 1422, and his son Henry VI inherited the French throne at the age of less than a year; his reign saw the gradual loss of English control of France.
The Valois kings of France, claiming supremacy over Aquitaine, granted the title of duke to their heirs, the Dauphins, during 1345 and 1415: John II (1345–50), Charles VII (1392?–1401), and Louis (1401–1415). French victory was complete with the Battle of Castillon
The Battle of Castillon was a battle between the forces of England and France which took place on 17 July 1453 in Gascony near the town of Castillon-sur-Dordogne (later Castillon-la-Bataille).
On the day of the battle, the English commande ...
of 1453. England and France nominally remained at war for another 20 years, but England was in no position to continue its campaign, due to its escalating internal conflicts. The Hundred Years' War was formally concluded with the Treaty of Picquigny of 1475. With the end of the Hundred Years' War, Aquitaine returned under direct rule of the king of France and remained in the possession of the king. Only occasionally was the title of "Duke of Aquitaine" granted to another member of the dynasty, and then as a purely nominal distinction.
Geography and subdivisions
region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ...
of Occitanie. Most of the rest of the post-1271 duchy now forms the region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine
Nouvelle-Aquitaine () is the largest Regions of France, administrative region in France by area, spanning the west and southwest of Metropolitan France. The region was created in 2014 by the merging of Aquitaine, Limousin, and Poitou-Charentes ...
, though parts fall into the three neighbouring regions of Pays de la Loire
Pays de la Loire (; but can also mean 'Lower Loire') is one of the eighteen administrative regions of France, located on the country's Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast. It was created in the 1950s to serve as a zone of influence for its capital an ...
, Centre-Val de Loire
Centre-Val de Loire (; ,In isolation, ''Centre'' is pronounced . ) or Centre Region (, ), as it was known until 2015, is one of the eighteen Regions of France, administrative regions of France. It straddles the middle Loire Valley in the interior ...
and Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes (; AURA) or ; or ; . is a Regions of France, region in southeast-central France created by the 2014 territorial reform of French regions; it resulted from the merger of Auvergne and Rhône-Alpes. The new region came into e ...
.
The county of Aquitaine as it stood in the High Middle Ages, then, was bordering the Pyrenees to the south (Navarre
Navarre ( ; ; ), officially the Chartered Community of Navarre, is a landlocked foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, bordering the Basque Autonomous Community, La Rioja, and Aragon in Spain and New Aquitaine in France. ...
, Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and ; ) is an autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces of Spain, ...
and Barcelona
Barcelona ( ; ; ) is a city on the northeastern coast of Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second-most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within c ...
, formerly the Marcha Hispanica) and the county of Toulouse and the kingdom of Burgundy
Kingdom of Burgundy was a name given to various successive Monarchy, kingdoms centered in the historical region of Burgundy during the Middle Ages. The heartland of historical Burgundy correlates with the border area between France and Switze ...
( Arelat to the east. To the north, it bordered on Bretagne, Anjou, Blois and Bourbonnais
The Bourbonnais (; Occitan language, Occitan: ''Borbonés'') was a Provinces of France, historic province in the centre of France that corresponds to the modern ''département in France, département'' of Allier, along with part of the ''dépar ...
, all of which had passed to the kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the Middle Ages, medieval and Early modern France, early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe from th ...
by the 13th century.
*Aquitaine proper
** County of Poitou
** County of La Marche
** County of Angoulême
**County of Périgord
The County of Périgord was a historical region of France. The name Périgord derived from the Gauls, Gaul Gallic tribes, tribe of the Petrocorii, who resisted the Roman Republic, Roman Roman conquest of Gaul, conquest. It was preserved in the ea ...
** County of Auvergne (passed to the royal domain in 1271)
***County of Velay
Velay () is a historical area of France situated in the east Haute-Loire ''Département in France, département'' and southeast of Massif central, Massif Central.
History
Julius Caesar mentioned the vellavi as the subordinate of the arverni. ...
** County of Saintonge
**Lordship of Déols
**Lordship of Issoudun
** Viscounty of Limousin
* Duchy of Gascony, personal union with Aquitaine from the 7th to the 9th century ( Felix of Aquitaine) and again from 1053.
**County of Agenais
* County of Toulouse (quasi-independent from 778, reverted to the royal domain in 1271)
**County of Quercy
Quercy (; , locally ) is a former province of France located in the country's southwest, bounded on the north by Limousin, on the west by Périgord and Agenais, on the south by Gascony and Languedoc, and on the east by Rouergue and Auverg ...
**County of Rouergue
*** County of Rodez
**County of Gevaudan
**Viscounty of Albi
** Marquisat of Gothia
See also
* Duke of Aquitaine * History of AquitaineReferences
Bibliography
*Lewis, Archibald R.The Dukes in the Regnum Francorum, A.D. 550-751.
''Speculum'', Vol. 51, No. 3. (July 1976), pp. 381–410. * Emile Mabille, (1870
''Le Royaume D'Aquitaine Et Ses Marches Sous Les Carlovingiens''
* Jean Penant, (2009) ''Occitanie, l'épopée des origines'' {{coord missing, France Former monarchies of Europe History of Aquitaine States and territories established in the 500s