Andor Szentivanyi on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 During an asthma episode, inflamed airways react to environmental triggers such as smoke, dust, or pollen. The airways narrow and produce excess
During an asthma episode, inflamed airways react to environmental triggers such as smoke, dust, or pollen. The airways narrow and produce excess
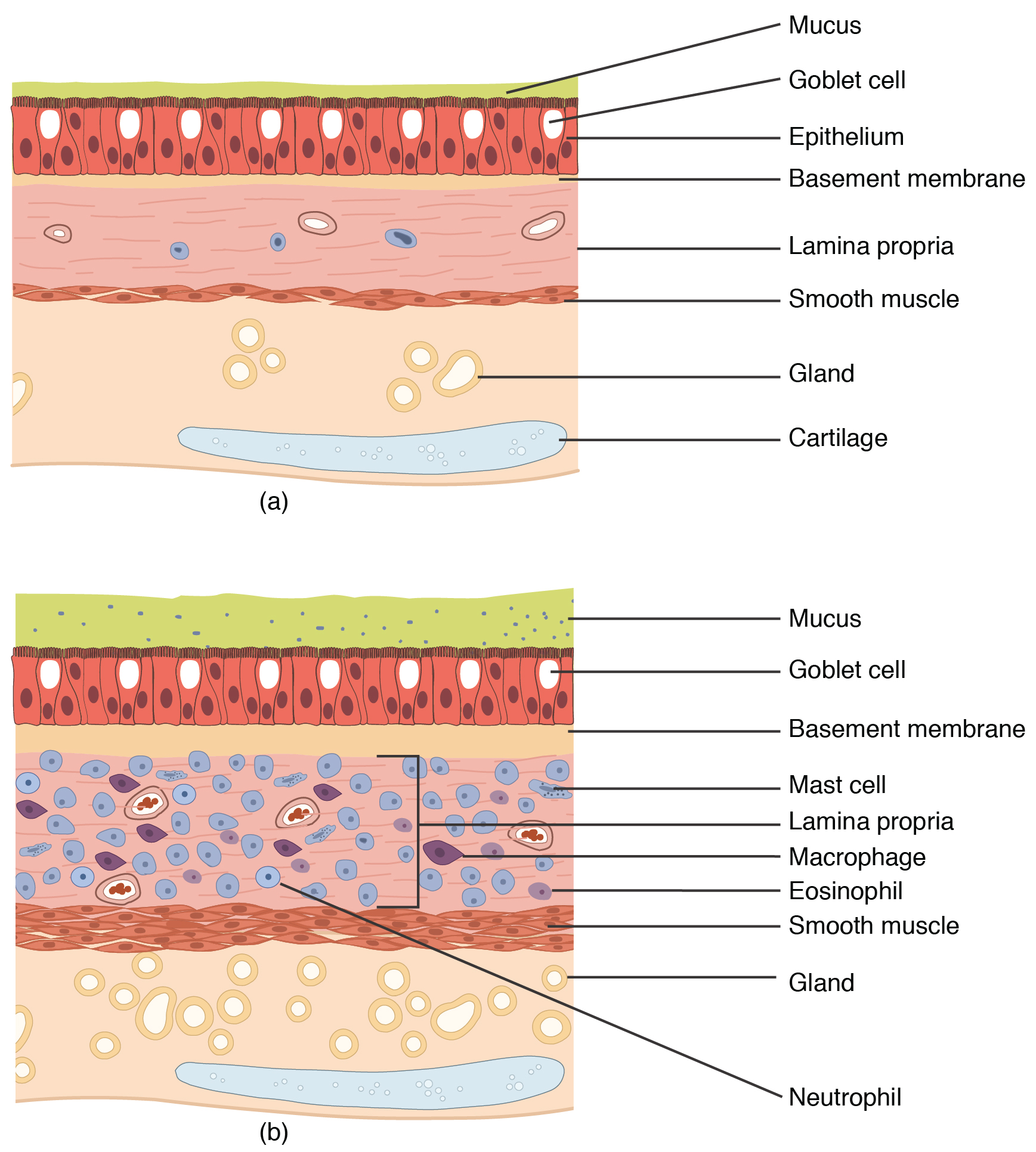 The mechanisms behind allergic asthma—i.e., asthma resulting from an
The mechanisms behind allergic asthma—i.e., asthma resulting from an
Asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
is a common pulmonary
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory syste ...
condition defined by chronic inflammation of respiratory tubes, tightening of respiratory smooth muscle, and episodes of bronchoconstriction. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimate that 1 in 11 children and 1 in 12 adults have asthma in the United States of America. According to the World Health Organization, asthma affects 235 million people worldwide. There are two major categories of asthma: allergic and non-allergic. The focus of this article will be allergic asthma. In both cases, bronchoconstriction is prominent.
Bronchoconstriction
mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
, making it difficult to breathe.
In essence, asthma is the result of an immune response
An immune response is a physiological reaction which occurs within an organism in the context of inflammation for the purpose of defending against exogenous factors. These include a wide variety of different toxins, viruses, intra- and extracellula ...
in the bronchial
A bronchus ( ; : bronchi, ) is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts Atmosphere of Earth, air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi to branch from the trachea at the Carina of trachea, carina are the right main b ...
airways.
The airways of asthma patients are "hypersensitive
''Hypersensitive'' is the second album by American rock band Ghost Machine. It was released on November 21, 2006, via Corporate Punishment Records.
The original track listing of the album, displayed on sites like Amazon and AllMusic
A ...
" to certain triggers, also known as ''stimuli'' (see below). (It is usually classified as type I hypersensitivity
Type I hypersensitivity (or immediate hypersensitivity), in the Hypersensitivity, Gell and Coombs classification of allergic reactions, is an allergic reaction provoked by re-exposure to a specific type of antigen referred to as an allergen. Type ...
.) In response to exposure to these triggers, the bronchi
A bronchus ( ; : bronchi, ) is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. Thes ...
(large airways) contract into spasm
A spasm is a sudden involuntary contraction of a muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ, such as the bladder.
A spasmodic muscle contraction may be caused by many medical conditions, including dystonia. Most commonly, it is a musc ...
(an "asthma attack"). Inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
soon follows, leading to a further narrowing of the airways and excessive mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
production, which leads to coughing and other breathing difficulties. Bronchospasm may resolve spontaneously in 1–2 hours, or in about 50% of subjects, may become part of a 'late' response, where this initial insult is followed 3–12 hours later with further bronchoconstriction and inflammation.Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine, 4th Ed. Robert J. Mason, John F. Murray, Jay A. Nadel, 2005, Elsevier
Elsevier ( ) is a Dutch academic publishing company specializing in scientific, technical, and medical content. Its products include journals such as ''The Lancet'', ''Cell (journal), Cell'', the ScienceDirect collection of electronic journals, ...
pp. 334
The normal caliber of the bronchus is maintained by a balanced functioning of the autonomic nervous system, which both operate reflexively. The parasympathetic
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system.
The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulat ...
reflex loop consists of afferent nerve endings which originate under the inner lining of the bronchus. Whenever these afferent nerve endings are stimulated (for example, by dust, cold air or fumes) impulses travel to the brain-stem vagal center, then down the vagal efferent pathway to again reach the bronchial small airways. Acetylcholine is released from the efferent nerve endings. This acetylcholine results in the excessive formation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) in bronchial smooth muscle cells which leads to muscle shortening and this initiates bronchoconstriction.
Bronchial inflammation
 The mechanisms behind allergic asthma—i.e., asthma resulting from an
The mechanisms behind allergic asthma—i.e., asthma resulting from an immune response
An immune response is a physiological reaction which occurs within an organism in the context of inflammation for the purpose of defending against exogenous factors. These include a wide variety of different toxins, viruses, intra- and extracellula ...
to inhaled allergen
An allergen is an otherwise harmless substance that triggers an allergic reaction in sensitive individuals by stimulating an immune response.
In technical terms, an allergen is an antigen that is capable of stimulating a type-I hypersensitivi ...
s—are the best understood of the causal factors. In both people with asthma and people who are free of the disease, inhaled allergens that find their way to the inner airways are ingested
Ingestion is the consumption of a substance by an organism. In animals, it normally is accomplished by taking in a substance through the mouth into the gastrointestinal tract, such as through eating or drinking. In single-celled organisms, inges ...
by a type of cell known as antigen-presenting cell
An antigen-presenting cell (APC) or accessory cell is a Cell (biology), cell that displays an antigen bound by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins on its surface; this process is known as antigen presentation. T cells may recognize the ...
s, or APCs. APCs then "present" pieces of the allergen to other immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
cells. In most people, these other immune cells ( TH0 cells) "check" and usually ignore the allergen molecules. In asthma patients, however, these cells transform into a different type of cell (TH2), for reasons that are not well understood. A possible reason could be the release of Interleukin-4 by Mast cells that induce differentiation of naive helper T cells (Th0 cells) to Th2 cells.
The resultant TH2 cells activate an important arm of the immune system, known as the humoral immune system. The humoral immune system produces antibodies
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that caus ...
against the inhaled allergen. Later, when a patient inhales the same allergen, these antibodies "recognize" it and activate a humoral response. Inflammation results: chemicals are produced that cause the wall of the airway to thicken, cells which produce scarring to proliferate and contribute to further 'airway remodeling', causes mucus producing cells to grow larger and produce more and thicker mucus, and the cell-mediated arm of the immune system is activated. Inflamed airways are more hyper-reactive, and will be more prone to bronchospasm.
The "hygiene hypothesis
In medicine, the hygiene hypothesis states that early childhood exposure to particular microorganisms (such as the gut flora and helminth parasites) protects against allergies by properly tuning the immune system. In particular, a lack of such e ...
" postulates that in early life, an imbalance in the regulation of these TH cell types leads to a long-term domination of the cells involved in allergic responses over those involved in fighting infection. The suggestion is that for a child being exposed to microbes early in life, taking fewer antibiotics, living in a large family, and growing up in the country stimulate the TH1 response and reduce the odds of developing asthma.
Asthma is associated with a procoagulant
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The process of coagulation ...
state in the bronchoalveolar space.
Stimuli
*Allergen
An allergen is an otherwise harmless substance that triggers an allergic reaction in sensitive individuals by stimulating an immune response.
In technical terms, an allergen is an antigen that is capable of stimulating a type-I hypersensitivi ...
s from nature, typically inhaled, which include waste from common household pests, the house dust mite
House dust mites (HDM, or simply dust mites) are various species of acariform mites belonging to the family Pyroglyphidae that are found in association with dust in dwellings. They are known for causing allergies.
Biology
Species
The curren ...
and cockroach
Cockroaches (or roaches) are insects belonging to the Order (biology), order Blattodea (Blattaria). About 30 cockroach species out of 4,600 are associated with human habitats. Some species are well-known Pest (organism), pests.
Modern cockro ...
, as well as grass pollen, mold
A mold () or mould () is one of the structures that certain fungus, fungi can form. The dust-like, colored appearance of molds is due to the formation of Spore#Fungi, spores containing Secondary metabolite#Fungal secondary metabolites, fungal ...
spores, and pet epithelial cells
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
;''Middleton's Allergy Principles & Practice'', N. F. Adkinson, B. S. Bochner, W. W. Busse, S. T. Holgate, R. F. Lemanske, F. E. R. Simons. Chapter 33: "Indoor Allergens." 2008. Elsevier.
*Indoor air pollution
Indoor air quality (IAQ) is the air quality within buildings and structures. Poor indoor air quality due to indoor air pollution is known to affect the health, comfort, and well-being of building occupants. It has also been linked to sick build ...
from volatile organic compound
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are organic compounds that have a high vapor pressure at room temperature. They are common and exist in a variety of settings and products, not limited to Indoor mold, house mold, Upholstery, upholstered furnitur ...
s, including perfumes and perfumed products. Examples include soap
Soap is a salt (chemistry), salt of a fatty acid (sometimes other carboxylic acids) used for cleaning and lubricating products as well as other applications. In a domestic setting, soaps, specifically "toilet soaps", are surfactants usually u ...
, dishwashing liquid
Dishwashing liquid (washing-up liquid or fairy liquid in British English), also known as dishwashing soap, dish detergent, or dish soap, is a detergent used in dishwashing. Dishwashing detergent for dishwashers comes in various forms such a ...
, laundry detergent
Laundry detergent is a type of detergent (cleaning agent) used for cleaning dirty laundry (clothes). Laundry detergent is manufactured in powder (washing powder) and liquid form.
While powdered and liquid detergents hold roughly equal share of ...
, fabric softener
A fabric softener (American English) or fabric conditioner (British English) is a conditioner applied to laundry after it has been washed in a washing machine. A similar, more dilute preparation meant to be applied to dry fabric is known as a wrin ...
, paper tissues, paper towel
A paper towel is an absorbent, disposable towel made from paper. In Commonwealth English, paper towels for kitchen use are also known as kitchen rolls, kitchen paper, or kitchen towels. For home use, paper towels are usually sold in a roll of p ...
s, toilet paper, shampoo
Shampoo () is a hair care product, typically in the form of a viscous liquid, that is formulated to be used for cleaning (scalp) hair. Less commonly, it is available in solid bar format. (" Dry shampoo" is a separate product.) Shampoo is use ...
, hair spray
Hair spray (also hair lacquer or spritz) is a common cosmetic hairstyling product that is sprayed onto hair to protect against humidity and wind and have it stay in a desired shape. Hair sprays typically consist of several components for the ...
, hair gel
Hair gel is a hairstyling product that is used to harden hair into a particular hairstyle.
History
Analysis of ancient Egyptian mummies has shown that they styled their hair using a fat-based gel. The researchers behind the analysis say that t ...
, cosmetics
Cosmetics are substances that are intended for application to the body for cleansing, beautifying, promoting attractiveness, or altering appearance. They are mixtures of chemical compounds derived from either Natural product, natural source ...
, facial cream, sun cream, deodorant
A deodorant is a substance applied to the body to prevent or mask body odor caused by bacterial breakdown of perspiration, for example in the armpits, groin, or feet. A subclass of deodorants, called antiperspirants, prevents sweating itself, t ...
, cologne, shaving cream
Shaving cream or shave cream is a category of cream cosmetics used for shaving preparation. The purpose of shaving cream is to soften the hair by providing lubrication.
Different types of shaving creams include aerosol shaving cream (also kn ...
, aftershave lotion, air freshener
Air fresheners are products designed to reduce unwanted odors in indoor spaces, to introduce pleasant fragrances, or both. They typically emit fragrance to mask odors but may use other methods of action such as absorbing, bonding to, or chemically ...
and candles, and products such as oil-based paint.
*Medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to medical diagnosis, diagnose, cure, treat, or preventive medicine, prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmaco ...
s, including aspirin
Aspirin () is the genericized trademark for acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is ...
, β-adrenergic antagonists (beta blockers), ibuprofen, and penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of beta-lactam antibiotic, β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' Mold (fungus), moulds, principally ''Penicillium chrysogenum, P. chrysogenum'' and ''Penicillium rubens, P. ru ...
.
*Food allergies
A food allergy is an abnormal immune response to food. The symptoms of the allergic reaction may range from mild to severe. They may include itchiness, swelling of the tongue, vomiting, diarrhea, hives, trouble breathing, or low blood pressu ...
such as milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of lactating mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfeeding, breastfed human infants) before they are able to digestion, digest solid food. ...
, peanut
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), goober pea, pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics by small and large ...
s, and eggs
An egg is an organic vessel in which an embryo begins to develop.
Egg, EGG or eggs may also refer to:
Biology
* Egg cell, the female reproductive cell (gamete) in oogamous organisms
Food
* Eggs as food
Places
* Egg, Austria
* Egg, Switzerland ...
. However, asthma is rarely the only symptom, and not all people with food or other allergies have asthma
* Sulfite sensitivity Asthma can occur in reaction to ingestion or inhalation of sulfites, which are added to foods and wine as preservatives.
* Salicylate sensitivity
Salicylate sensitivity is any adverse effect that occurs when a usual amount of salicylate is ingested. People with salicylate intolerance are unable to consume a normal amount of salicylate without adverse effects.
Salicylate sensitivity diff ...
Salicylates can trigger asthma in sensitive individuals. Salicylates occur naturally in many healthy foods. Aspirin is also a salicylate.
*Use of fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geolog ...
related allergen
An allergen is an otherwise harmless substance that triggers an allergic reaction in sensitive individuals by stimulating an immune response.
In technical terms, an allergen is an antigen that is capable of stimulating a type-I hypersensitivi ...
ic air pollution
Air pollution is the presence of substances in the Atmosphere of Earth, air that are harmful to humans, other living beings or the environment. Pollutants can be Gas, gases like Ground-level ozone, ozone or nitrogen oxides or small particles li ...
, such as ozone
Ozone () (or trioxygen) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , break ...
, smog
Smog, or smoke fog, is a type of intense air pollution. The word "smog" was coined in the early 20th century, and is a portmanteau of the words ''smoke'' and ''fog'' to refer to smoky fog due to its opacity, and odour. The word was then inte ...
, summer smog
Smog, or smoke fog, is a type of intense air pollution. The word "smog" was coined in the early 20th century, and is a portmanteau of the words ''smoke'' and ''fog'' to refer to smoky fog due to its opacity, and odour. The word was then inte ...
, nitrogen dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide is a chemical compound with the formula . One of several nitrogen oxides, nitrogen dioxide is a reddish-brown gas. It is a paramagnetic, bent molecule with C2v point group symmetry. Industrially, is an intermediate in the s ...
, and sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless gas with a pungent smell that is responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is r ...
, which is thought to be one of the major reasons for the high prevalence of asthma in urban
Urban means "related to a city". In that sense, the term may refer to:
* Urban area, geographical area distinct from rural areas
* Urban culture, the culture of towns and cities
Urban may also refer to:
General
* Urban (name), a list of people ...
areas.
*Various industrial compounds (e.g. toluene diisocyanate
Toluene diisocyanate (TDI) is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H3(NCO)2. Two of the six possible isomers are commercially important: 2,4-TDI (CAS: 584-84-9) and 2,6-TDI (CAS: 91-08-7). 2,4-TDI is produced in the pure state, but TDI is oft ...
) and other chemicals, notably sulfite
Sulfites or sulphites are compounds that contain the sulfite ion (systematic name: sulfate(IV) ion), . The sulfite ion is the conjugate base of bisulfite. Although its acid (sulfurous acid) is elusive, its salts are widely used.
Sulfites are ...
s; chlorinated
In chemistry, halogenation is a chemical reaction which introduces one or more halogens into a chemical compound. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transformation important, e.g. in the production of polymers, drugs. ...
swimming pools generate monochloramine
Monochloramine, often called chloramine, is the chemical compound with the formula NH2Cl. Together with dichloramine (NHCl2) and nitrogen trichloride (NCl3), it is one of the three chloramines of ammonia. It is a colorless liquid at its melting ...
(NH2Cl), dichloramine
Dichloramine (IUPAC name: ''Azonous dichloride'') is a reactive inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is one of the three chloramines of ammonia, the others being monochloramine () and nitrogen trichloride (). This yellow gas is unstab ...
(NHCl2) and trichloramine
Nitrogen trichloride, also known as trichloramine, is the chemical compound with the formula . This yellow, oily, and explosive liquid is most commonly encountered as a product of chemical reactions between ammonia-derivatives and chlorine (for ex ...
(NCl3)—in the air around them, which are known to induce asthma.
*Early childhood infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
s, especially viral
The word ''Viral'' means "relating to viruses" (small infectious agents).
It may also refer to:
Viral behavior, or virality
Memetic behavior likened that of a virus, for example:
* Viral marketing, the use of existing social networks to spre ...
upper respiratory tract infection
An upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) is an illness caused by an acute infection, which involves the upper respiratory tract, including the nose, sinuses, pharynx, larynx or trachea. This commonly includes nasal obstruction, sore throat ...
s. Children who suffer from frequent respiratory infections prior to the age of six are at higher risk of developing asthma, particularly if they have a parent with the condition. However, persons of any age can have asthma triggered by colds
The common cold, or the cold, is a virus, viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract that primarily affects the Respiratory epithelium, respiratory mucosa of the human nose, nose, throat, Paranasal sinuses, sinuses, and larynx. ...
and other respiratory infections even though their normal stimuli might be from another category (e.g. pollen) and absent at the time of infection. In many cases, significant asthma may not even occur until the respiratory infection is in its waning stage, and the person is seemingly improving. In children, the most common triggers are viral illnesses such as those that cause the common cold
The common cold, or the cold, is a virus, viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract that primarily affects the Respiratory epithelium, respiratory mucosa of the human nose, nose, throat, Paranasal sinuses, sinuses, and larynx. ...
.
*Exercise
Exercise or workout is physical activity that enhances or maintains fitness and overall health. It is performed for various reasons, including weight loss or maintenance, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardio ...
or intense use of respiratory system—the effects of which differ somewhat from those of the other triggers, since they are brief. They are thought to be primarily in response to the exposure of the airway epithelium to cold, dry air.
*Hormonal
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones a ...
changes in adolescent
Adolescence () is a transitional stage of human physical and psychological development that generally occurs during the period from puberty to adulthood (typically corresponding to the age of majority). Adolescence is usually associated w ...
girls and adult women associated with their menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that makes pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eg ...
can lead to a worsening of asthma. Some women also experience a worsening of their asthma during pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
whereas others find no significant changes, and in other women their asthma improves during their pregnancy.
*Psychological stress
In psychology, stress is a feeling of emotional strain and pressure. Stress is a form of psychological and mental discomfort. Small amounts of stress may be beneficial, as it can improve athletic performance, motivation and reaction to the envi ...
. There is growing evidence that psychological stress is a trigger. It can modulate the immune system, causing an increased inflammatory response to allergens and pollutants.
*Cold weather can make it harder for patients to breathe. Whether high altitude helps or worsens asthma is debatable and may vary from person to person.
* Obesity and the systemic inflammation of obesity has been shown to worsen lung function and increase the risk of developing asthma exacerbations.
Pathogenesis
The fundamental problem in asthma appears to beimmunological
Immunology is a branch of biology and medicine that covers the study of immune systems in all organisms.
Immunology charts, measures, and contextualizes the physiological functioning of the immune system in states of both health and disease ...
: young children in the early stages of asthma show signs of excessive inflammation in their airways. Epidemiological findings give clues as to the pathogenesis
In pathology, pathogenesis is the process by which a disease or disorder develops. It can include factors which contribute not only to the onset of the disease or disorder, but also to its progression and maintenance. The word comes .
Descript ...
: the incidence of asthma seems to be increasing worldwide, and asthma is now very much more common in affluent countries.
In 1968 Andor Szentivanyi first described ''The Beta Adrenergic Theory of Asthma''; in which blockage of the Beta-2 receptors of pulmonary smooth muscle cells causes asthma.
Szentivanyi's Beta Adrenergic Theory is a citation classicLockey, Richard, In lasting tribute: Andor Szentivanyi, MD. ''J. Allergy and Clinical Immunology'', January, 2006 using the Science Citation Index
The Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE) is a citation index owned by Clarivate and previously by Thomson Reuters.
It was created by the Eugene Garfield at the Institute for Scientific Information, launched in 1964 as Science Citation Index ( ...
and has been cited more times than any other article in the history of the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology
A journal, from the Old French ''journal'' (meaning "daily"), may refer to:
*Bullet journal, a method of personal organization
*Diary, a record of personal secretive thoughts and as open book to personal therapy or used to feel connected to onesel ...
.
In 1995 Szentivanyi and colleagues demonstrated that IgE blocks beta-2 receptors.
Since overproduction of IgE is central to all atopic diseases, this was a watershed moment in the world of allergies.
Asthma and sleep apnea
It is recognized with increasing frequency that patients who have bothobstructive sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common sleep-related breathing disorder and is characterized by recurrent episodes of complete or partial airway obstruction, obstruction of the respiratory tract#Upper respiratory tract, upper airway lea ...
and asthma often improve tremendously when the sleep apnea is diagnosed and treated. CPAP
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) is a form of positive airway pressure (PAP) ventilation in which a constant level of pressure greater than atmospheric pressure is continuously applied to the upper respiratory tract of a person. The a ...
is not effective in patients with nocturnal asthma only.
Asthma and gastro-esophageal reflux disease
If gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD) is present, the patient may have repetitive episodes of acid aspiration. GERD may be common in difficult-to-control asthma, but according to one study, treating it does not seem to affect the asthma. When there is a clinical suspicion for GERD as the cause of the asthma, anEsophageal pH Monitoring
In gastroenterology, esophageal pH monitoring is the current gold standard for diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It provides direct physiologic measurement of acid in the esophagus and is the most objective method to document ...
is required to confirm the diagnosis and establish the relationship between GERD and asthma.
Asthma and exposure to air pollution during pregnancy
Asthma affects four to eight out of a hundred pregnant women. This is due to the fact that during pregnancy, there is an immunological shift due to hormonal fluctuations. In some cases, there is an increase in Estrogen levels which in turn reduce the activity of natural killer cells, Th1 cell production of inflammatory cytokines, and production of anti-inflammatory cytokines. As we have seen, these play an important role in the pathophysiology of asthma. Researchers found a link between the preterm birth and exposure to air pollution in asthmatic pregnant women. Results suggested that women with asthma have a higher risk of preterm birth. Researchers suggested that asthmatic episodes in pregnant women were associated with ongoing exposure to nitrogen dioxide and carbon monoxide - types of air pollutants. Researchers also studied when women were most susceptible to develop asthma. Data indicated that women were at a higher risk of developing asthma when exposed to pollutants before conception and during pregnancy. In particular, "an increase of 30 parts per billion (ppb) in nitrogen oxide exposure in the three months prior to pregnancy increased preterm birth risk by nearly 30 percent for women with asthma, compared to 8 percent for women without asthma." In other studies, Scientists have found a link between asthma in children and prenatal exposure to air pollution. Results from a study that consisted of 65, 000 Canadian children suggested that children of mothers who lived near highways during pregnancy had a 25% increased risk of developing asthma before the age of five when compared with children of mothers who did not live near highways. Highways are a major source of traffic-related air pollution such that there is an accumulation of air pollutants such as nitrogen dioxide and carbon monoxide (emitted from vehicles) in the vicinity of highways. In another study, researchers collected data from 6,000 children attending public schools in California. The results suggested that a high exposure to prenatal air pollution was strongly correlated with increased susceptibility to asthma during childhood.References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pathophysiology Of Asthma Asthma