Ancient UNIX on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ancient history is a
fro
K. Klein Goldewijk, A. Beusen and P. Janssen, "HYDE 3.1: Long-term dynamic modeling of global population and built-up area in a spatially explicit way", from table on p. 2, Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency (MNP), Bilthoven, The Netherlands.
 Mesopotamia is the site of some of the earliest known civilisations in the world. Agricultural communities emerged in the area with the
Mesopotamia is the site of some of the earliest known civilisations in the world. Agricultural communities emerged in the area with the
 The
The
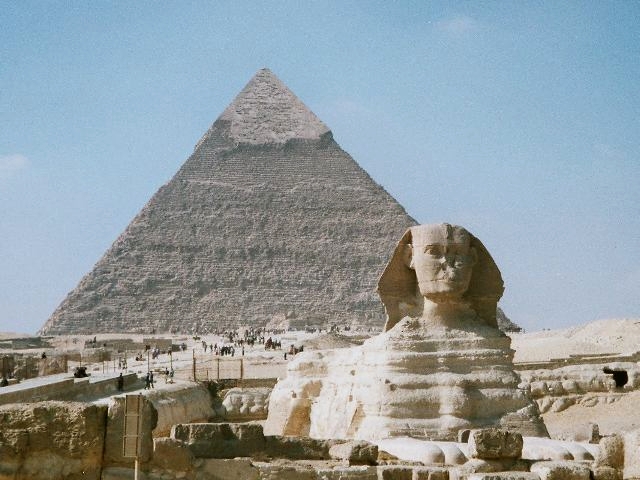
 Ancient Egypt was a long-lived civilisation geographically located in north-eastern Africa. It was concentrated along the middle to lower reaches of the Nile River, reaching its greatest extent during the 2nd millennium BC, which is referred to as the New Kingdom period. It reached broadly from the
Ancient Egypt was a long-lived civilisation geographically located in north-eastern Africa. It was concentrated along the middle to lower reaches of the Nile River, reaching its greatest extent during the 2nd millennium BC, which is referred to as the New Kingdom period. It reached broadly from the
 The Nok culture appeared in
The Nok culture appeared in
 Paleolithic tools have been discovered in India dating to 200,000 years ago, and Neolithic sites are known from near the
Paleolithic tools have been discovered in India dating to 200,000 years ago, and Neolithic sites are known from near the
 The earliest known evidence of copper and bronze production in Southeast Asia was found at Ban Chiang in north-east Thailand and among the Phùng Nguyên culture of northern Vietnam around 2000 BCE.
The Đông Sơn culture established a tradition of bronze production and the manufacture of evermore refined bronze and iron objects, such as plows, axes and sickles with shaft holes, socketed arrows and spearheads and small ornamented items. By about 500 BCE, large and delicately decorated bronze drums of remarkable quality, weighing more than , were produced in the laborious lost-wax casting process. This industry of highly sophisticated metal processing was developed independent of Chinese or Indian influence. Historians relate these achievements to the presence of organised, centralised and hierarchical communities and a large population.
Between 1000 BCE and 100 CE, the Sa Huỳnh culture flourished along the south-central coast of
The earliest known evidence of copper and bronze production in Southeast Asia was found at Ban Chiang in north-east Thailand and among the Phùng Nguyên culture of northern Vietnam around 2000 BCE.
The Đông Sơn culture established a tradition of bronze production and the manufacture of evermore refined bronze and iron objects, such as plows, axes and sickles with shaft holes, socketed arrows and spearheads and small ornamented items. By about 500 BCE, large and delicately decorated bronze drums of remarkable quality, weighing more than , were produced in the laborious lost-wax casting process. This industry of highly sophisticated metal processing was developed independent of Chinese or Indian influence. Historians relate these achievements to the presence of organised, centralised and hierarchical communities and a large population.
Between 1000 BCE and 100 CE, the Sa Huỳnh culture flourished along the south-central coast of
 Around 3000 to 1500 BCE, a large-scale migration of
Around 3000 to 1500 BCE, a large-scale migration of 
 Austronesians established prehistoric maritime trade networks in Island Southeast Asia, including the Maritime Jade Road, a jade trade network, in Southeast Asia which existed in
Austronesians established prehistoric maritime trade networks in Island Southeast Asia, including the Maritime Jade Road, a jade trade network, in Southeast Asia which existed in
 The Chinese civilisation that emerged within the
The Chinese civilisation that emerged within the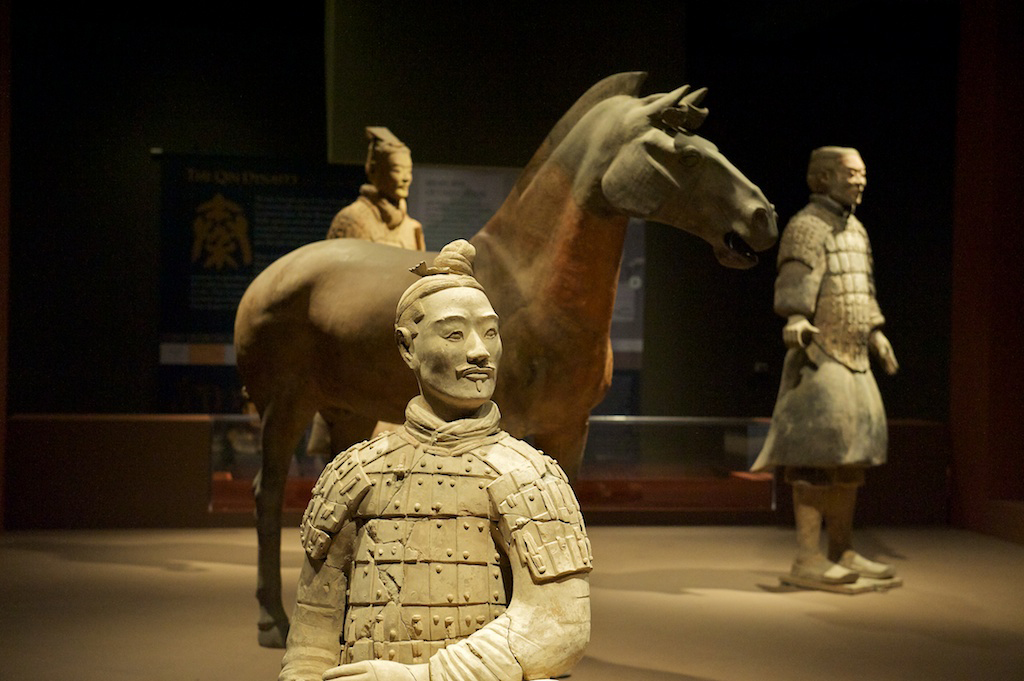  In the 8th century BC, power became decentralized during the Spring and Autumn period, named after the influential ''Spring and Autumn Annals''. In this period, local military leaders used by the Zhou began to assert their power and vie for hegemony. The situation was aggravated by the invasion of other peoples, forcing the Zhou to move their capital east to Luoyang. In each of the hundreds of states that eventually arose, local strongmen held most of the political power and continued their subservience to the Zhou kings in name only. The Hundred Schools of Thought of Chinese philosophy blossomed during this period, and such influential intellectual movements as Confucianism, Taoism, Legalism (Chinese philosophy), Legalism and Mohism were founded, partly in response to the changing political world.
After further political consolidation, seven prominent states remained by the end of the 5th century BC, and the years in which these few states battled each other is known as the Warring States period. Though there remained a nominal Zhou king until 256 BC, he was largely a figurehead and held little power. As neighboring territories of these warring states, including areas of modern Sichuan and Liaoning, were annexed by the growing power of the rulers of Qin (state), Qin, they were governed under the new local administrative system of Commandery (China), commandery. The final expansion in this period began during the reign of Ying Zheng, the king of Qin. His unification of the other six powers, and further annexations to the south and southeast by 213 BC enabled him to proclaim himself the Qin Shi Huang, First Emperor (Qin Shi Huangdi).
In the 8th century BC, power became decentralized during the Spring and Autumn period, named after the influential ''Spring and Autumn Annals''. In this period, local military leaders used by the Zhou began to assert their power and vie for hegemony. The situation was aggravated by the invasion of other peoples, forcing the Zhou to move their capital east to Luoyang. In each of the hundreds of states that eventually arose, local strongmen held most of the political power and continued their subservience to the Zhou kings in name only. The Hundred Schools of Thought of Chinese philosophy blossomed during this period, and such influential intellectual movements as Confucianism, Taoism, Legalism (Chinese philosophy), Legalism and Mohism were founded, partly in response to the changing political world.
After further political consolidation, seven prominent states remained by the end of the 5th century BC, and the years in which these few states battled each other is known as the Warring States period. Though there remained a nominal Zhou king until 256 BC, he was largely a figurehead and held little power. As neighboring territories of these warring states, including areas of modern Sichuan and Liaoning, were annexed by the growing power of the rulers of Qin (state), Qin, they were governed under the new local administrative system of Commandery (China), commandery. The final expansion in this period began during the reign of Ying Zheng, the king of Qin. His unification of the other six powers, and further annexations to the south and southeast by 213 BC enabled him to proclaim himself the Qin Shi Huang, First Emperor (Qin Shi Huangdi).
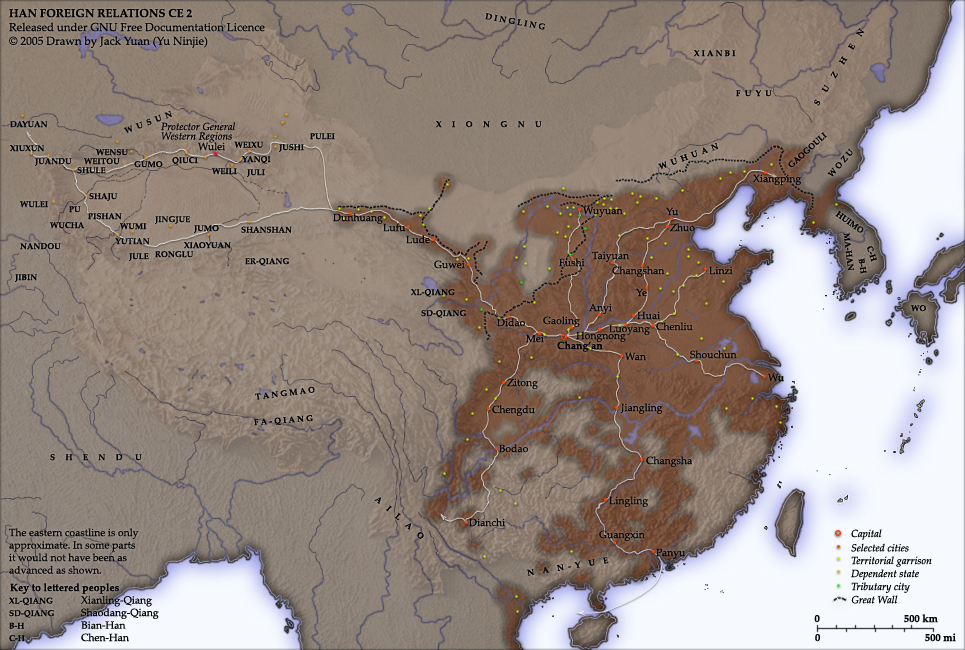 Qin Shi Huangdi ruled the unified China directly with absolute power. In contrast to the decentralised and feudal rule of earlier dynasties the Qin ruled directly. Nationwide the philosophy of Legalism (Chinese philosophy), legalism was enforced and publications promoting rival ideas such as Confucianism were prohibited. In his reign unified China created the first continuous Great Wall with the use of forced labour. Qin's campaign against the Yue tribes, Invasions were launched southward to annex Vietnam. The Qin period also saw the standardisation of the Chinese writing system and the government unified the legal systems as well as setting standardised units of measurement throughout the empire. After the emperor's death rebellions began and the Han dynasty took power and ruled China for over four centuries with a brief interruption from AD 9 to 23. The Han dynasty promoted the spread of iron agricultural tools, which helped create a food surplus that led to a large growth of population during the Han period. Silk production also increased and the manufacture of paper was invented. Though the Han enjoyed great military and economic success, it was strained by the rise of aristocrats who disobeyed the central government. Public frustration provoked the Yellow Turban Rebellion; though a failure it nonetheless accelerated the empire's downfall. After AD 208, the Han dynasty broke up into Three Kingdoms period, rival kingdoms. China would remain divided for almost the next 400 years.
Qin Shi Huangdi ruled the unified China directly with absolute power. In contrast to the decentralised and feudal rule of earlier dynasties the Qin ruled directly. Nationwide the philosophy of Legalism (Chinese philosophy), legalism was enforced and publications promoting rival ideas such as Confucianism were prohibited. In his reign unified China created the first continuous Great Wall with the use of forced labour. Qin's campaign against the Yue tribes, Invasions were launched southward to annex Vietnam. The Qin period also saw the standardisation of the Chinese writing system and the government unified the legal systems as well as setting standardised units of measurement throughout the empire. After the emperor's death rebellions began and the Han dynasty took power and ruled China for over four centuries with a brief interruption from AD 9 to 23. The Han dynasty promoted the spread of iron agricultural tools, which helped create a food surplus that led to a large growth of population during the Han period. Silk production also increased and the manufacture of paper was invented. Though the Han enjoyed great military and economic success, it was strained by the rise of aristocrats who disobeyed the central government. Public frustration provoked the Yellow Turban Rebellion; though a failure it nonetheless accelerated the empire's downfall. After AD 208, the Han dynasty broke up into Three Kingdoms period, rival kingdoms. China would remain divided for almost the next 400 years.
 The East Asian nations adjacent to China were all profoundly influenced by their interactions with East Asian cultural sphere, Chinese civilisation. Korea and
The East Asian nations adjacent to China were all profoundly influenced by their interactions with East Asian cultural sphere, Chinese civilisation. Korea and
 The Classical Greek world was dominated throughout the 5th century BC by the major powers of Ancient Athens, Athens and Sparta. Through the Delian League, Athens was able to convert pan-hellenist sentiment and fear of the Persian threat into a powerful empire, and this, along with the conflict between Sparta and Athens culminating in the Peloponnesian War, was the major political development of the first part of the Classical period. The period in Greek history from the death of Alexander the Great until the rise of the Roman empire and its conquest of Egypt in 30 BC is known as the Hellenistic period. After Alexander's death, a series of wars between his successors eventually led to three large states being formed from parts of Alexander's conquests, each ruled by a dynasty founded by one of the successors. These were the Antigonids, the Selucids, and the Ptolemies. These three kingdoms, along with smaller kingdoms, spread Greek culture and lifestyles into Asia and Egypt. These varying states eventually were conquered by Rome or the
The Classical Greek world was dominated throughout the 5th century BC by the major powers of Ancient Athens, Athens and Sparta. Through the Delian League, Athens was able to convert pan-hellenist sentiment and fear of the Persian threat into a powerful empire, and this, along with the conflict between Sparta and Athens culminating in the Peloponnesian War, was the major political development of the first part of the Classical period. The period in Greek history from the death of Alexander the Great until the rise of the Roman empire and its conquest of Egypt in 30 BC is known as the Hellenistic period. After Alexander's death, a series of wars between his successors eventually led to three large states being formed from parts of Alexander's conquests, each ruled by a dynasty founded by one of the successors. These were the Antigonids, the Selucids, and the Ptolemies. These three kingdoms, along with smaller kingdoms, spread Greek culture and lifestyles into Asia and Egypt. These varying states eventually were conquered by Rome or the
 Ancient Rome was a civilisation that grew out of the city-state of Rome, originating as a small agricultural community founded on the Italian peninsula in the 8th century BC, with influences from Greece and other Italian civilisations, such as the Etruscans. Traditionally Rome was founded as a Roman monarchy, monarchy that then became a Roman Republic, republic. Rome expanded through the Italian peninsula through a series of wars in the fifth through the third centuries BC. This expansion brought the Roman republic into conflict with
Ancient Rome was a civilisation that grew out of the city-state of Rome, originating as a small agricultural community founded on the Italian peninsula in the 8th century BC, with influences from Greece and other Italian civilisations, such as the Etruscans. Traditionally Rome was founded as a Roman monarchy, monarchy that then became a Roman Republic, republic. Rome expanded through the Italian peninsula through a series of wars in the fifth through the third centuries BC. This expansion brought the Roman republic into conflict with
 The Roman Empire underwent considerable social, cultural and organisational change starting with reign of Diocletian, who began the custom of splitting the empire into eastern and Western Roman Empire, western halves ruled by multiple emperors. Constantine the Great initiated the process of Christianization, Christianisation of the empire and established a new capital at Constantinople. Migration Period, Migrations of Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes disrupted Roman rule from the late 4th century onwards, culminating in the eventual Decline of the Roman Empire, collapse of the empire in the West in 476, replaced by the so-called Germanic monarchy, barbarian kingdoms. The resultant cultural fusion of Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman, Germanic and Christian traditions formed the cultural foundations of Europe. There has been attempt by scholars to connect European late antiquity to other areas in Eurasia.
The Roman Empire underwent considerable social, cultural and organisational change starting with reign of Diocletian, who began the custom of splitting the empire into eastern and Western Roman Empire, western halves ruled by multiple emperors. Constantine the Great initiated the process of Christianization, Christianisation of the empire and established a new capital at Constantinople. Migration Period, Migrations of Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes disrupted Roman rule from the late 4th century onwards, culminating in the eventual Decline of the Roman Empire, collapse of the empire in the West in 476, replaced by the so-called Germanic monarchy, barbarian kingdoms. The resultant cultural fusion of Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman, Germanic and Christian traditions formed the cultural foundations of Europe. There has been attempt by scholars to connect European late antiquity to other areas in Eurasia.
 The rise of civilisation corresponded with the institutional sponsorship of belief in gods, supernatural forces and the afterlife. During the Bronze Age, many civilisations adopted their own form of polytheism. Usually, polytheistic Gods manifested human personalities, strengths and failings. Early religion was often based on location, with cities or entire countries selecting a deity, that would grant them preferences and advantages over their competitors. Worship involved the construction of representation of deities, and the granting of sacrifices. Sacrifices could be material goods, food, or in extreme cases human sacrifice to please a deity. New philosophies and religions arose in both east and west, particularly about the 6th century BC. Over time, a great variety of religions developed around the world, with some of the earliest major ones being Hinduism (around 2000 BC),
The rise of civilisation corresponded with the institutional sponsorship of belief in gods, supernatural forces and the afterlife. During the Bronze Age, many civilisations adopted their own form of polytheism. Usually, polytheistic Gods manifested human personalities, strengths and failings. Early religion was often based on location, with cities or entire countries selecting a deity, that would grant them preferences and advantages over their competitors. Worship involved the construction of representation of deities, and the granting of sacrifices. Sacrifices could be material goods, food, or in extreme cases human sacrifice to please a deity. New philosophies and religions arose in both east and west, particularly about the 6th century BC. Over time, a great variety of religions developed around the world, with some of the earliest major ones being Hinduism (around 2000 BC),
World History Encyclopedia
nbsp;– British Museum's website on various topics of ancient civilisation
Ancient history sourcebook
The Perseus digital library
Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman world
– Academic Info: directory of online resources for the study of ancient history.
: Ancient history research links for high school and college students. {{Authority control Ancient history Historical eras Articles which contain graphical timelines
time period
The categorization of the past into discrete, quantified named blocks of time is called periodization.Adam Rabinowitz. And king It’s about time: historical periodization and Linked Ancient World Data''. Study of the Ancient universe Papers, 2 ...
from the beginning of writing and recorded human history
Human history or world history is the record of humankind from prehistory to the present. Early modern human, Modern humans evolved in Africa around 300,000 years ago and initially lived as hunter-gatherers. They Early expansions of hominin ...
through late antiquity
Late antiquity marks the period that comes after the end of classical antiquity and stretches into the onset of the Early Middle Ages. Late antiquity as a period was popularized by Peter Brown (historian), Peter Brown in 1971, and this periodiza ...
. The span of recorded history
Recorded history or written history describes the historical events that have been recorded in a written form or other documented communication which are subsequently evaluated by historians using the historical method. For broader world h ...
is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the development of Sumerian cuneiform
Cuneiform is a Logogram, logo-Syllabary, syllabic writing system that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Near East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. Cuneiform script ...
script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500, ending with the expansion of Islam in late antiquity. The three-age system
The three-age system is the periodization of human prehistory (with some overlap into the history, historical periods in a few regions) into three time-periods: the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, although the concept may also re ...
periodises ancient history into the Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistory, prehistoric period during which Rock (geology), stone was widely used to make stone tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years and ended b ...
, the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
, and the Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages vary between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others.
During the time period of ancient history, the world population
In demographics of the world, world demographics, the world population is the total number of humans currently alive. It was estimated by the United Nations to have exceeded eight billion in mid-November 2022. It took around 300,000 years of h ...
was exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, also known as the First Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period in Afro-Eurasia from a lifestyle of hunter-gatherer, hunting and gathering to one of a ...
, which was in full progress. In 10,000 BC, the world population stood at 2 million, it rose to 45 million by 3000 BC. By the Iron Age in 1000 BC, the population had risen to 72 million. By the end of the ancient period in AD 500, the world population is thought to have stood at 209 million. In 10,500 years, the world population increased by 100 times.Datafro
K. Klein Goldewijk, A. Beusen and P. Janssen, "HYDE 3.1: Long-term dynamic modeling of global population and built-up area in a spatially explicit way", from table on p. 2, Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency (MNP), Bilthoven, The Netherlands.
Prehistory
Prehistory
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use ...
is the period before written history. Most of our knowledge of that period comes from the work of archaeologists.
The early human migrations in the Lower Paleolithic saw ''Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' ( ) is an extinction, extinct species of Homo, archaic human from the Pleistocene, spanning nearly 2 million years. It is the first human species to evolve a humanlike body plan and human gait, gait, to early expansions of h ...
'' spread across Eurasia
Eurasia ( , ) is a continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. According to some geographers, Physical geography, physiographically, Eurasia is a single supercontinent. The concept of Europe and Asia as distinct continents d ...
1.8 million years ago. Evidence for the use of fire has been dated as early as 1.8 million years ago, a date which is contested, with generally accepted evidence for the controlled use of fire dating to 780,000 years ago. Actual use of hearths first appears 400,000 years ago. Dates for the emergence of ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
'' (modern humans) range from 250,000 to 160,000 years ago, with the varying dates being based on DNA studies and fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserve ...
s respectively. Some 50,000 years ago, ''Homo sapiens'' migrated out of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
. They reached Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
about 45,000 years ago, southwestern Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
about the same time, southeastern Europe and Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
around 40,000 years ago, and Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
about 30,000 years ago. Humans migrated to the Americas about 15,000 years ago.
Evidence for agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
emerges in about 9000 BC in what is now eastern Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
and spread through the Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent () is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, and Syria, together with northern Kuwait, south-eastern Turkey, and western Iran. Some authors also include ...
. Settlement at Göbekli Tepe began around 9500 BC and may have the world's oldest temple. The Nile River Valley has evidence of sorghum
''Sorghum bicolor'', commonly called sorghum () and also known as great millet, broomcorn, guinea corn, durra, imphee, jowar, or milo, is a species in the Poaceae, grass genus ''Sorghum (genus), Sorghum'' cultivated for its grain. The grain i ...
and millet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most millets belong to the tribe Paniceae.
Millets are important crops in the Semi-arid climate, ...
cultivation starting around 8000 BC and agricultural use of yams in Western Africa perhaps dates to the same time period. Cultivation of millet, rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much l ...
, and legume
Legumes are plants in the pea family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seeds of such plants. When used as a dry grain for human consumption, the seeds are also called pulses. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consum ...
s began around 7000 BC in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
. Taro
Taro (; ''Colocasia esculenta'') is a root vegetable. It is the most widely cultivated species of several plants in the family Araceae that are used as vegetables for their corms, leaves, stems and Petiole (botany), petioles. Taro corms are a ...
cultivation in New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is ...
dates to about 7000 BC also with squash cultivation in Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to the Pacific coast of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central and southern Mexico, all of Belize, Guatemala, El S ...
perhaps sharing that date. Animal domestication began with the domestication of dogs, which dates to at least 15,000 years ago, and perhaps even earlier. Sheep
Sheep (: sheep) or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are a domesticated, ruminant mammal typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to d ...
and goats
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a species of goat-antelope that is mostly kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the famil ...
were domesticated around 9000 BC in the Fertile Crescent, alongside the first evidence for agriculture. Other animals, such as pigs
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), also called swine (: swine) or hog, is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is named the domestic pig when distinguishing it from other members of the genus '' Sus''. Some authorities cons ...
and poultry
Poultry () are domesticated birds kept by humans for the purpose of harvesting animal products such as meat, Eggs as food, eggs or feathers. The practice of animal husbandry, raising poultry is known as poultry farming. These birds are most typ ...
, were later domesticated and used as food sources. Cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are calle ...
and water buffalo
The water buffalo (''Bubalus bubalis''), also called domestic water buffalo, Asian water buffalo and Asiatic water buffalo, is a large bovid originating in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. Today, it is also kept in Italy, the Balkans ...
were domesticated around 7000 BC and horses
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 milli ...
, donkey
The donkey or ass is a domesticated equine. It derives from the African wild ass, ''Equus africanus'', and may be classified either as a subspecies thereof, ''Equus africanus asinus'', or as a separate species, ''Equus asinus''. It was domes ...
s, and camel
A camel (from and () from Ancient Semitic: ''gāmāl'') is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. Camels have long been domesticated and, as livestock, they provid ...
s were domesticated by about 4000 BC. All of these animals were used not only for food, but to carry and pull people and loads, greatly increasing human ability to do work. The invention of the simple plough
A plough or ( US) plow (both pronounced ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses but modern ploughs are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden ...
by 6000 BC further increased agricultural efficiency.
Metal use in the form of hammered copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
items predates the discovery of smelting
Smelting is a process of applying heat and a chemical reducing agent to an ore to extract a desired base metal product. It is a form of extractive metallurgy that is used to obtain many metals such as iron-making, iron, copper extraction, copper ...
of copper ores, which happened around 6000 BC in western Asia and independently in eastern Asia before 2000 BC. Gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
and silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
use dates to between 6000 and 5000 BC. Alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
metallurgy began with bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
in about 3500 BC in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
and was developed independently in China by 2000 BC. Pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other raw materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is al ...
developed independently throughout the world, with fired pots appearing first among the Jomon of Japan and in West Africa at Mali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ...
. Sometime between 5000 and 4000 BC the potter's wheel
In pottery, a potter's wheel is a machine used in the shaping (known as throwing) of clay into round ceramic ware. The wheel may also be used during the process of trimming excess clay from leather-hard dried ware that is stiff but malleable, ...
was invented. By 3000 BC, the pottery wheel was adapted into wheeled vehicles which could be used to carry loads further and easier than with human or animal power alone.
Writing
Writing is the act of creating a persistent representation of language. A writing system includes a particular set of symbols called a ''script'', as well as the rules by which they encode a particular spoken language. Every written language ...
developed separately in five different locations in human history: Mesopotamia, Egypt, India, China, and Mesoamerica. By 3400 BC, "proto-literate" cuneiform
Cuneiform is a Logogram, logo-Syllabary, syllabic writing system that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Near East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. Cuneiform script ...
spread in the Middle East. Egypt developed its own system of hieroglyph
Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs ( ) were the formal writing system used in Ancient Egypt for writing the Egyptian language. Hieroglyphs combined ideographic, logographic, syllabic and alphabetic elements, with more than 1,000 distinct characters. ...
s by about 3200 BC. By 2800 BC the Indus Valley Civilisation
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the Northwestern South Asia, northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 Common Era, BCE to 1300 BCE, and in i ...
had developed its Indus script, which remains undeciphered. Chinese Characters
Chinese characters are logographs used Written Chinese, to write the Chinese languages and others from regions historically influenced by Chinese culture. Of the four independently invented writing systems accepted by scholars, they represe ...
were independently developed in China during the Shang dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty that ruled in the Yellow River valley during the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and followed by the Western Zhou d ...
in the form of the Oracle Bone Script
Oracle bone script is the oldest attested form of written Chinese, dating to the late 2nd millennium BC. Inscriptions were made by carving characters into oracle bones, usually either the shoulder bones of oxen or the plastrons of turtl ...
dating to the period 1600 to 1100 BC. Writing in Mesoamerica dates to 600 BC with the Zapotec civilization
The Zapotec civilization ( "The People"; 700 BC–1521 AD) is an Indigenous peoples, indigenous Pre-Columbian era, pre-Columbian civilization that flourished in the Valley of Oaxaca in Mesoamerica. Archaeological evidence shows that their cultu ...
.
History by region
West Asia
The ancient Near East is considered the cradle of civilisation. It was the first to practice intensive year-round agriculture; created one of the first coherent writing systems, invented thepotter's wheel
In pottery, a potter's wheel is a machine used in the shaping (known as throwing) of clay into round ceramic ware. The wheel may also be used during the process of trimming excess clay from leather-hard dried ware that is stiff but malleable, ...
and then the vehicular wheel
A wheel is a rotating component (typically circular in shape) that is intended to turn on an axle Bearing (mechanical), bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the Simple machine, six simple machin ...
, created the first centralised governments, law codes and empires, as well as displaying social stratification
Social stratification refers to a society's categorization of its people into groups based on socioeconomic factors like wealth, income, race, education, ethnicity, gender, occupation, social status, or derived power (social and political ...
, slavery, and organized warfare. It began the study of the stars and the sciences of astronomy and mathematics.
Mesopotamia
 Mesopotamia is the site of some of the earliest known civilisations in the world. Agricultural communities emerged in the area with the
Mesopotamia is the site of some of the earliest known civilisations in the world. Agricultural communities emerged in the area with the Halaf culture
The Halaf culture is a prehistoric period which lasted between about 6100 BC and 5100 BC. The period is a continuous development out of the earlier Pottery Neolithic and is located primarily in the fertile valley of the Khabur (Euphrates), Khabu ...
around 8000 BC and continued to expand through the Ubaid period around 6000 BC. Cities began in the Uruk period
The Uruk period (; also known as Protoliterate period) existed from the protohistory, protohistoric Chalcolithic to Early Bronze Age period in the history of Mesopotamia, after the Ubaid period and before the Jemdet Nasr period. Named after the S ...
(4000–3100 BC) and expanded during the Jemdet Nasr
Jemdet Nasr () (also Jamdat Nasr and Jemdat Nasr) is a Tell (archaeology), tell or settlement mound in Babil Governorate, Iraq that is best known as the eponymous type site for the Jemdet Nasr period (c. 3100–2900 BC), under an alternate period ...
(3100–2900 BC) and Early Dynastic (2900–2350 BC) periods. The surplus of storable foodstuffs created by this economy allowed the population to settle in one place instead of migrating after crops and herds. It also allowed for a much greater population density, and in turn required an extensive labour force and division of labour. This organisation led to the necessity of record keeping and the development of writing.
Babylonia
Babylonia (; , ) was an Ancient history, ancient Akkadian language, Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as a ...
was an Amorite
The Amorites () were an ancient Northwest Semitic-speaking Bronze Age people from the Levant. Initially appearing in Sumerian records c. 2500 BC, they expanded and ruled most of the Levant, Mesopotamia and parts of Egypt from the 21st century BC ...
state in lower Mesopotamia (modern southern Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
), with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged when Hammurabi
Hammurabi (; ; ), also spelled Hammurapi, was the sixth Amorite king of the Old Babylonian Empire, reigning from to BC. He was preceded by his father, Sin-Muballit, who abdicated due to failing health. During his reign, he conquered the ci ...
created an empire out of the territories of the former kingdoms of Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
and Akkad.
The Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to ancient Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the King of Babylon in 626 BC a ...
, or Chaldea
Chaldea () refers to a region probably located in the marshy land of southern Mesopotamia. It is mentioned, with varying meaning, in Neo-Assyrian cuneiform, the Hebrew Bible, and in classical Greek texts. The Hebrew Bible uses the term (''Ka� ...
, was Babylonia from the 7th and 6th centuries BC. Under the reign of Nebuchadnezzar II
Nebuchadnezzar II, also Nebuchadrezzar II, meaning "Nabu, watch over my heir", was the second king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling from the death of his father Nabopolassar in 605 BC to his own death in 562 BC. Often titled Nebuchadnezzar ...
, it conquered Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
. This empire also created the Hanging Gardens of Babylon and the still-surviving Ishtar Gate
The Ishtar Gate was the eighth gate to the inner city of Babylon (in the area of present-day Hillah, Babil Governorate, Iraq). It was constructed by order of King Nebuchadnezzar II on the north side of the city. It was part of a grand walled proce ...
as architectural embellishments of its capital at Babylon.
Akkad was a city and its surrounding region near Babylon. Akkad also became the capital of the Akkadian Empire. Despite an extensive search, the precise site has never been found. Akkad reached the height of its power between about 2330 and 2150 BC, following the conquests of King Sargon of Akkad. Through the spread of Sargon's empire, the language of Akkad, known as Akkadian from the city, spread and replaced the Sumerian language in Mesopotamia and eventually by 1450 BC was the main language of diplomacy in the Near East.
Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
was originally a region on the Upper Tigris
The Tigris ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the eastern of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian Desert, Syrian and Arabia ...
, where a small state was created in the 19th century BC. The capital was at Assur, which gave the state its name. Later, as a nation and empire that came to control all of the Fertile Crescent, Egypt and much of Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, the term "Assyria proper" referred to roughly the northern half of Mesopotamia (the southern half being Babylonia), with Nineveh
Nineveh ( ; , ''URUNI.NU.A, Ninua''; , ''Nīnəwē''; , ''Nīnawā''; , ''Nīnwē''), was an ancient Assyrian city of Upper Mesopotamia, located in the modern-day city of Mosul (itself built out of the Assyrian town of Mepsila) in northern ...
as its capital. The Assyrian kings controlled a large kingdom at three different times in history. These are called the ''Old'' (20th to 18th centuries BC), ''Middle'' (14th to 11th centuries BC), and '' Neo-Assyrian'' (9th to 7th centuries BC) kingdoms, or periods.
Mitanni
Mitanni (–1260 BC), earlier called Ḫabigalbat in old Babylonian texts, ; Hanigalbat or Hani-Rabbat in Assyrian records, or in Ancient Egypt, Egyptian texts, was a Hurrian language, Hurrian-speaking state in northern Syria (region), Syria an ...
was a Hurrian empire in northern Mesopotamia founded around 1500 BC. The Mitanians conquered and controlled Assyria until the 14th century BC while contending with Egypt for control of parts of modern Syria. Its capital was Washukanni, whose precise location has not been determined by archaeologists.
Iranian peoples
TheMedes
The Medes were an Iron Age Iranian peoples, Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media (region), Media between western Iran, western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, they occupied the m ...
and Persians
Persians ( ), or the Persian people (), are an Iranian ethnic group from West Asia that came from an earlier group called the Proto-Iranians, which likely split from the Indo-Iranians in 1800 BCE from either Afghanistan or Central Asia. They ...
were peoples who had appeared in the Iranian plateau around 1500 BC. Both peoples spoke Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
and were mostly pastoralists with a tradition of horse archery. The Medes established their own Median Empire by the 6th century BC, having defeated the Neo-Assyrian Empire with the Chaldea
Chaldea () refers to a region probably located in the marshy land of southern Mesopotamia. It is mentioned, with varying meaning, in Neo-Assyrian cuneiform, the Hebrew Bible, and in classical Greek texts. The Hebrew Bible uses the term (''Ka� ...
ns in 614 BC.
 The
The Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, i ...
was founded by Cyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia ( ; 530 BC), commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire. Achaemenid dynasty (i. The clan and dynasty) Hailing from Persis, he brought the Achaemenid dynasty to power by defeating the Media ...
, who first became king of the Persians, then conquered the Medes, Lydia
Lydia (; ) was an Iron Age Monarchy, kingdom situated in western Anatolia, in modern-day Turkey. Later, it became an important province of the Achaemenid Empire and then the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sardis.
At some point before 800 BC, ...
, and Babylon by 539 BC. The empire built on earlier Mesopotamian systems of government to govern their large empire. By building roads, they improved both the ability to send governmental instructions throughout their lands as well as improving the ability of their military forces to be deployed rapidly. Increased trade and upgraded farming techniques increased wealth, but also exacerbated inequalities between social classes. The empire's location at the centre of trading networks spread its intellectual and philosophical ideas throughout a wide area, and its religion, while not itself spreading far, had an impact on later religions such as Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
, Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
, and Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
. Cyrus' son Cambyses II
Cambyses II () was the second King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning 530 to 522 BCE. He was the son of and successor to Cyrus the Great (); his mother was Cassandane. His relatively brief reign was marked by his conquests in North Afric ...
conquered Egypt, while a later emperor, Darius the Great
Darius I ( ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his death in 486 BCE. He ruled the empire at its territorial peak, when it included much of West A ...
, expanded the empire to the Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayas, Himalayan river of South Asia, South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northw ...
, creating the largest empire in the world to that date. But Darius and his son Xerxes I
Xerxes I ( – August 465 BC), commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was a List of monarchs of Persia, Persian ruler who served as the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 486 BC until his assassination in 465 BC. He was ...
failed to expand into Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
, with expeditions in 490 and 480 BC eventually failing. The Achaemenid dynasty and empire fell to Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
by 330 BC, and after Alexander's death, much of the area previously ruled by the Cyrus and his successors was ruled by the Seleucid dynasty.
Parthia
Parthia ( ''Parθava''; ''Parθaw''; ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Medes during the 7th century BC, was incorporated into the subsequent Achaemeni ...
was an Iranian civilisation situated in the northeastern part of modern Iran. Their power was based on a combination of military power based on heavy cavalry with a decentralised governing structure based on a federated system. The Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power centered in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe ...
was led by the Arsacid dynasty, which by around 155 BC under Mithradates I had mostly conquered the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire ( ) was a Greek state in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great ...
. Parthia had many wars with the Romans, but it was rebellions within the empire that ended it in the 3rd century AD.
The Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranian peoples, Iranians"), was an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, th ...
began when the Parthian Empire ended in AD 224. Their rulers claimed the Achaemenids as ancestors and set up their capital at Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon ( ; , ''Tyspwn'' or ''Tysfwn''; ; , ; Thomas A. Carlson et al., “Ctesiphon — ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢ ” in The Syriac Gazetteer last modified July 28, 2014, http://syriaca.org/place/58.) was an ancient city in modern Iraq, on the eastern ba ...
in Mesopotamia. Their period of greatest military expansion occurred under Shapur I
Shapur I (also spelled Shabuhr I; ) was the second Sasanian Empire, Sasanian King of Kings of Iran. The precise dating of his reign is disputed, but it is generally agreed that he ruled from 240 to 270, with his father Ardashir I as co-regent u ...
, who by the time of his death in AD 272 had defeated Roman imperial armies and set up buffer states between the Sasanians and Roman Empires. After Shapur, the Sasanians were under more pressure from the Kushans to their east as well as the Roman then Byzantine Empire to its west. However, the Sasanians rebuilt and founded numerous cities and their merchants travelled widely and introduced crops such as sugar, rice, and cotton into the Iranian plateau. But in AD 651, the last Sassanid emperor was killed by the expanding Islamic Arabs.
Hittites
TheHittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian peoples, Anatolian Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European people who formed one of the first major civilizations of the Bronze Age in West Asia. Possibly originating from beyond the Black Sea, they settled in mo ...
first came to Anatolia about 1900 BC and during the period 1600-1500 they expanded into Mesopotamia where they adopted the cuneiform script to their Indo-European language. By 1200 their empire stretched to Phoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian ...
and eastern Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
. They improved two earlier technologies from Mesopotamia and spread these new techniques widely – improved iron working and light chariot
A chariot is a type of vehicle similar to a cart, driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid Propulsion, motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk O ...
s with spoked wheels in warfare. The Hittites introduced the casting of iron with molds and then hammering it which enabled weapons and tools to be made stronger and also cheaper. Although chariots had been used previously, the use of spoked wheels allowed the chariots to be much lighter and more maneuverable. In 1274 BC the Hittites clashed with the Egyptians at the Battle of Kadesh
The Battle of Kadesh took place in the 13th century BC between the New Kingdom of Egypt, Egyptian Empire led by pharaoh Ramesses II and the Hittites, Hittite Empire led by king Muwatalli II. Their armies engaged each other at the Orontes River, ...
, where both sides claimed victory. In 1207 the Hittite capital of Hattusa
Hattusa, also Hattuşa, Ḫattuša, Hattusas, or Hattusha, was the capital of the Hittites, Hittite Empire in the late Bronze Age during two distinct periods. Its ruins lie near modern Boğazkale, Turkey (originally Boğazköy) within the great ...
was sacked, ending the Hittite Empire
The Hittites () were an Anatolian peoples, Anatolian Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European people who formed one of the first major civilizations of the Bronze Age in West Asia. Possibly originating from beyond the Black Sea, they settled in mo ...
.
Israel
Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
and Judah were related Iron Age kingdoms of the ancient Levant and had existed during the Iron Ages and the Neo-Babylonian, Persian and Hellenistic periods. The name Israel first appears in the stele
A stele ( ) or stela ( )The plural in English is sometimes stelai ( ) based on direct transliteration of the Greek, sometimes stelae or stelæ ( ) based on the inflection of Greek nouns in Latin, and sometimes anglicized to steles ( ) or stela ...
of the Egyptian pharaoh Merneptah
Merneptah () or Merenptah (reigned July or August 1213–2 May 1203 BCE) was the fourth pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Nineteenth Dynasty of Ancient Egypt. According to contemporary historical records, he ruled Egypt for almost ten y ...
around 1209 BC. This "Israel" was a cultural and probably political entity of the central highlands, well enough established to be perceived by the Egyptians as a possible challenge to their hegemony
Hegemony (, , ) is the political, economic, and military predominance of one State (polity), state over other states, either regional or global.
In Ancient Greece (ca. 8th BC – AD 6th c.), hegemony denoted the politico-military dominance of ...
, but an ethnic group rather than an organised state.
Israel had emerged by the middle of the 9th century BC, when the Assyrian King Shalmaneser III
Shalmaneser III (''Šulmānu-ašarēdu'', "the god Shulmanu is pre-eminent") was king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 859 BC to 824 BC.
His long reign was a constant series of campaigns against the eastern tribes, the Babylonians, the nations o ...
named " Ahab the Israelite" among his enemies at the battle of Qarqar
The Battle of Qarqar (or Ḳarḳar) was fought in 853 BC when the army of the Neo-Assyrian Empire led by Emperor Shalmaneser III encountered an allied army of eleven kings at Qarqar led by Hadadezer, called in Assyrian ''Adad-idir'' and possib ...
(853). Judah emerged somewhat later than Israel, probably during the 9th century BC, but the subject is one of considerable controversy. Israel came into conflict with the Assyrians, who conquered Israel in 722 BC. The Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to ancient Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the King of Babylon in 626 BC a ...
did the same to Judah in 586. After both conquests, the conquering forces deported many of the inhabitants to other regions of their respective empires.
Following the fall of Babylon to the Persian Empire, Cyrus the Great allowed the rebuilding of the temple at Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
, and some of the exiles from Judah returned to Judea, where they remained under Persian rule until the Maccabean revolt
The Maccabean Revolt () was a Jewish rebellion led by the Maccabees against the Seleucid Empire and against Hellenistic influence on Jewish life. The main phase of the revolt lasted from 167 to 160 BCE and ended with the Seleucids in control of ...
led to independence during Hellenistic period until Roman conquest.
Phoenicia
Phoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian ...
was an ancient civilisation centred in the north of ancient Canaan
CanaanThe current scholarly edition of the Septuagint, Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus Testamentum graece iuxta LXX interprets. 2. ed. / recogn. et emendavit Robert Hanhart. Stuttgart : D ...
, with its heartland along the coastal regions of modern-day Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
, Syria and Israel. Phoenician civilisation was an enterprising maritime trading culture that spread across the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
between the period of 1550 to 300 BC. One Phoenician colony, Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
, ruled an empire in the Western Mediterranean until being defeated by Rome in the Punic Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of wars fought between the Roman Republic and the Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian Empire during the period 264 to 146BC. Three such wars took place, involving a total of forty-three years of warfare on both land and ...
. The Phoenicians invented the Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet is an abjad (consonantal alphabet) used across the Mediterranean civilization of Phoenicia for most of the 1st millennium BC. It was one of the first alphabets, attested in Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions fo ...
, the forerunner of the modern alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letter (alphabet), letters written to represent particular sounds in a spoken language. Specifically, letters largely correspond to phonemes as the smallest sound segments that can distinguish one word from a ...
still in use today.
Arabia
The history of Pre-Islamic Arabia before the rise ofIslam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
in the AD 630s is not known in great detail. Archaeological exploration in the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
has been sparse; indigenous written sources are limited to the many inscriptions and coins from southern Arabia. Existing material consists primarily of written sources from other traditions (such as Egyptians, Greeks, Persians, Romans, etc.) and oral tradition
Oral tradition, or oral lore, is a form of human communication in which knowledge, art, ideas and culture are received, preserved, and transmitted orally from one generation to another.Jan Vansina, Vansina, Jan: ''Oral Tradition as History'' (19 ...
s later recorded by Islamic scholars. A number of small kingdoms existed in Arabia from around AD 100 to perhaps about AD 400.
Africa
Afro-Asiatic Africa
=Carthage
= Carthage was founded around 814 BC byPhoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian ...
n settlers. Ancient Carthage
Ancient Carthage ( ; , ) was an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic civilisation based in North Africa. Initially a settlement in present-day Tunisia, it later became a city-state, and then an empire. Founded by the Phoenicians ...
was a city-state that ruled an empire through alliances and trade influence that stretched throughout North Africa and modern Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
. At the height of the city's influence, its empire included most of the western Mediterranean. The empire was in a constant state of struggle with the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
, which led to a series of conflicts known as the Punic Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of wars fought between the Roman Republic and the Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian Empire during the period 264 to 146BC. Three such wars took place, involving a total of forty-three years of warfare on both land and ...
. After the third and final Punic War, Carthage was destroyed and then occupied by Roman forces. Nearly all of the territory held by Carthage fell into Roman hands.
=Egypt
= Ancient Egypt was a long-lived civilisation geographically located in north-eastern Africa. It was concentrated along the middle to lower reaches of the Nile River, reaching its greatest extent during the 2nd millennium BC, which is referred to as the New Kingdom period. It reached broadly from the
Ancient Egypt was a long-lived civilisation geographically located in north-eastern Africa. It was concentrated along the middle to lower reaches of the Nile River, reaching its greatest extent during the 2nd millennium BC, which is referred to as the New Kingdom period. It reached broadly from the Nile Delta
The Nile Delta (, or simply , ) is the River delta, delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's larger deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the eas ...
in the north, as far south as Jebel Barkal
Jebel Barkal or Gebel Barkal () is a mesa or large rock outcrop located 400 km north of Khartoum, next to Karima in Northern State in Sudan, on the Nile River, in the region that is sometimes called Nubia. The jebel is 104 m tall, has a f ...
at the Fourth Cataract of the Nile. Extensions to the geographical range of ancient Egyptian civilisation included, at different times, areas of the southern Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
, the Eastern Desert and the Red Sea coastline, the Sinai Peninsula
The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai ( ; ; ; ), is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a land bridge between Asia and Afri ...
, and the Western Desert (focused on the several oases).
Ancient Egypt developed over at least three and a half millennia. It began with the incipient unification of Nile Valley polities around 3100 BC, traditionally under Menes. The civilisation of ancient Egypt was characterised primarily by intensive agricultural use of the fertile Nile Valley; the use of the Nile itself for transportation; the development of writing systems – first hieroglyphs and then later hieratic
Hieratic (; ) is the name given to a cursive writing system used for Ancient Egyptian and the principal script used to write that language from its development in the third millennium BCE until the rise of Demotic in the mid-first millennium BCE ...
and other derived scripts – and literature
Literature is any collection of Writing, written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially novels, Play (theatre), plays, and poetry, poems. It includes both print and Electroni ...
; the organisation of collective projects such as the pyramids
A pyramid () is a Nonbuilding structure, structure whose visible surfaces are triangular in broad outline and converge toward the top, making the appearance roughly a Pyramid (geometry), pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid ca ...
; trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
Traders generally negotiate through a medium of cr ...
with surrounding regions; and a polytheistic
Polytheism is the belief in or worship of more than one Deity, god. According to Oxford Reference, it is not easy to count gods, and so not always obvious whether an apparently polytheistic religion, such as Chinese folk religions, is really so, ...
religious tradition that included elaborate funeral customs including mummification. Overseeing these activities were a socio-political and economic elite
In political and sociological theory, the elite (, from , to select or to sort out) are a small group of powerful or wealthy people who hold a disproportionate amount of wealth, privilege, political power, or skill in a group. Defined by the ...
under the figure of a (semi)-divine ruler from a succession of ruling dynasties
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family, usually in the context of a monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A dynasty may also be referred to as a "house", "family" or "clan", among others.
Historians ...
.
Ancient Egyptian history is divided across various periods, beginning with the Old Kingdom
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning –2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth Dynast ...
, which saw pyramid building on a large scale. After 2100 BC, the Old Kingdom dissolved into smaller states during the First Intermediate Period
The First Intermediate Period, described as a 'dark period' in ancient Egyptian history, spanned approximately 125 years, c. 2181–2055 BC, after the end of the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom. It comprises the seventh Dynasty, Seventh (altho ...
, which lasted about 100 years. The Middle Kingdom began around 2000 BC with the reunification of Egypt under pharoes ruling from Thebes. The Middle Kingdom ended with the conquest of northern Egypt by the Hyksos
The Hyksos (; Egyptian language, Egyptian ''wikt:ḥqꜣ, ḥqꜣ(w)-wikt:ḫꜣst, ḫꜣswt'', Egyptological pronunciation: ''heqau khasut'', "ruler(s) of foreign lands"), in modern Egyptology, are the kings of the Fifteenth Dynasty of Egypt ( ...
around 1650 BC. The Hyksos were expelled from Egypt and the land was reunited in the New Kingdom around 1550 BC. This period lasted until about 1000 BC, and saw Egypt expand its borders into Palestine and Syria. The Third Intermediate Period was marked by the rule of priests as well as the conquest of Egypt by Nubia
Nubia (, Nobiin language, Nobiin: , ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the confluence of the Blue Nile, Blue and White Nile, White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), and the Cataracts of the Nile, first cataract ...
n kings and then later Assyria, Persia, and Macedonians.
=Nubia
= The Ta-Seti kingdom inNubia
Nubia (, Nobiin language, Nobiin: , ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the confluence of the Blue Nile, Blue and White Nile, White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), and the Cataracts of the Nile, first cataract ...
to the south of Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
was conquered by Egyptian rulers around 3100 BC, but by 2500 BC the Nubians had created a new kingdom further south, known as the Kingdom of Kush
The Kingdom of Kush (; Egyptian language, Egyptian: 𓎡𓄿𓈙𓈉 ''kꜣš'', Akkadian language, Assyrian: ''Kûsi'', in LXX Χους or Αἰθιοπία; ''Ecōš''; ''Kūš''), also known as the Kushite Empire, or simply Kush, was an an ...
, centred on the upper Nile with a capital at Kerma
Kerma was the capital city of the Kerma culture, which was founded in present-day Sudan before 3500 BC. Kerma is one of the largest archaeological sites in ancient Nubia. It has produced decades of extensive excavations and research, including t ...
. In the Egyptian New Kingdom period, Kush once more was conquered by Egypt. However, by 1100 BC a new kingdom of Kush had formed, with a capital at Napata
Napata
(2020). (Old Egyptian ''Npt'', ''Npy''; Meroitic language, Meroitic ''Napa''; and Ναπάται) was a city of ...
. Nubian rulers conquered Egypt around 760 BC and retained control for about a century.
(2020). (Old Egyptian ''Npt'', ''Npy''; Meroitic language, Meroitic ''Napa''; and Ναπάται) was a city of ...
=Aksum and ancient Ethiopia
= TheKingdom of Aksum
The Kingdom of Aksum, or the Aksumite Empire, was a kingdom in East Africa and South Arabia from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, based in what is now northern Ethiopia and Eritrea, and spanning present-day Djibouti and Sudan. Emerging ...
was an important trading nation in northeastern Africa centred in present-day Eritrea
Eritrea, officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa, with its capital and largest city being Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia in the Eritrea–Ethiopia border, south, Sudan in the west, and Dj ...
and northern Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
, it existed from approximately AD 100 to 940, growing from the Iron Age proto-Aksumite period around the 4th century BC to achieve prominence by the 1st century AD. The Kingdom of Aksum at its height by the early 6th-century AD extended through much of modern Ethiopia and across the Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and th ...
to Arabia. The capital city of the empire was Aksum, now in northern Ethiopia.
Niger-Congo Africa
=Nok culture
= The Nok culture appeared in
The Nok culture appeared in Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
around 1000 BC and mysteriously vanished around AD 200. The civilisation's social system
In sociology, a social system is the patterned network of relationships constituting a coherent whole that exist between individuals, groups, and institutions. It is the formal Social structure, structure of role and status that can form in a smal ...
is thought to have been highly advanced. The Nok civilisation was considered to be the earliest sub-Saharan producer of life-sized Terracotta which have been discovered by archaeologists. The Nok also used iron smelting
Smelting is a process of applying heat and a chemical reducing agent to an ore to extract a desired base metal product. It is a form of extractive metallurgy that is used to obtain many metals such as iron, copper, silver, tin, lead and zinc ...
that may have been independently developed.
Sahel
=Djenné-Djenno
= The civilisation of Djenné-Djenno was located in the Niger River Valley in the country ofMali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ...
and is considered to be among the oldest urbanised centres and the best-known archaeology site in sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the list of sovereign states and ...
. This archaeological site is located about away from the modern town and is believed to have been involved in long-distance trade and possibly the domestication of African rice. The site is believed to exceed ; however, this is yet to be confirmed with extensive survey work. With the help of archaeological excavations mainly by Susan and Roderick McIntosh, the site is known to have been occupied from 250 BC to AD 900. The city is believed to have been abandoned and moved where the current city is located due to the spread of Islam and the building of the Great Mosque of Djenné
The Great Mosque of Djenné in the Sudano-Sahelian architecture, Sudano-Sahelian architectural style is the largest adobe brick building in the world. The mosque is located in the city of Djenné, Mali, on the flood plain of the Bani River. The ...
. Previously, it was assumed that advanced trade networks and complex societies
A society () is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. ...
did not exist in the region until the arrival of traders from Southwest Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenia ...
. However, sites such as Djenné-Djenno disprove this, as these traditions in West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
flourished long before. Towns similar to that at Djenne-Jeno also developed at the site of Dia, also in Mali along the Niger River
The Niger River ( ; ) is the main river of West Africa, extending about . Its drainage basin is in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through Mali, Nige ...
, from around 900 BC.
=Dhar Tichitt and Oualata
= Dhar Tichitt and Oualata were prominent among the early urban centres, dated to 2000 BC, in present-day Mauritania. About 500 stone settlements littered the region in the former savannah of the Sahara. Its inhabitants fished and grew millet. It has been found that the Soninke of the Mandé peoples were responsible for constructing such settlements. Around 300 BC, the region became more desiccated and the settlements began to decline, most likely relocating to Koumbi Saleh. From the type of architecture and pottery, it is believed that Tichit was related to the subsequent Ghana Empire. Old Jenne (Djenne) began to be settled around 300 BC, producing iron and with sizeable population, evidenced in crowded cemeteries. The inhabitants and creators of these settlements during these periods are thought to have been ancestors of the Soninke people.=Bantu expansion
= Peoples speaking precursors to the modern-dayBantu languages
The Bantu languages (English: , Proto-Bantu language, Proto-Bantu: *bantʊ̀), or Ntu languages are a language family of about 600 languages of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern, East Africa, Eastern and Southeast Africa, South ...
began to spread throughout southern Africa, and by 2000 BC they were expanding past the Congo River
The Congo River, formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second-longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the third-largest river in the world list of rivers by discharge, by discharge volume, following the Amazon Ri ...
and into the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
area. By AD 1000 these groups had spread throughout all of southern Africa south of the equator. Iron metallurgy and agriculture spread along with these peoples, with the cultivation of millet, oil palms, sorghum, and yams as well as the use of domesticated cattle, pigs, and sheep. These technologies helped increase population, and settled communities became common in sub-Saharan Africa except in deserts or heavy forests.
South Asia
 Paleolithic tools have been discovered in India dating to 200,000 years ago, and Neolithic sites are known from near the
Paleolithic tools have been discovered in India dating to 200,000 years ago, and Neolithic sites are known from near the Indus Valley
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans- Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northwest through the disp ...
dating to around 8000 BC. Agriculture began in the Indus Valley around 7000 BC, and reached the Ganges Valley by 3000 BC. Barley
Barley (), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikele ...
, cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
, and wheat were grown and the population had domesticated cattle, goats, and sheep.
The Indus Valley Civilisation
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the Northwestern South Asia, northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 Common Era, BCE to 1300 BCE, and in i ...
developed around 3000 BC in the Indus and Ghaggar-Hakra river valleys of north-east Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
, Pakistan, and western India. Another name for this civilisation is Harappan, after the first of its cities to be excavated, Harappa
Harappa () is an archaeological site in Punjab, Pakistan, about west of Sahiwal, that takes its name from a modern village near the former course of the Ravi River, which now runs to the north. Harappa is the type site of the Bronze Age Indus ...
(now in the Pakistani province of Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
). Harappan civilisation grew out of the earlier agricultural communities as they evolved into cities. These communities created and traded jewelry, figurines, and seals that appear widely scattered throughout Mesopotamia, Afghanistan, and Iran. Chicken
The chicken (''Gallus gallus domesticus'') is a domesticated subspecies of the red junglefowl (''Gallus gallus''), originally native to Southeast Asia. It was first domesticated around 8,000 years ago and is now one of the most common and w ...
s were domesticated in addition to the earlier crops and animals. They developed their own writing system, the Indus Valley script, which is still mostly undeciphered. The exact structure of society and the way the cities were governed is not known. By about 1600 BC, the Indus Valley culture had abandoned many of their cities, including Mohenjo-Daro
Mohenjo-daro (; , ; ) is an archaeological site in Larkana District, Sindh, Pakistan. Built 2500 BCE, it was one of the largest settlements of the ancient Indus Valley Civilisation, and one of the world's earliest major city, cities, contemp ...
. The exact reason for this decline is not known.
Indo-European speaking peoples began to spread into India about 1500 BC. The ''Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' (, , from wikt:ऋच्, ऋच्, "praise" and wikt:वेद, वेद, "knowledge") is an ancient Indian Miscellany, collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canoni ...
'', in Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
, dates to this period and begins a period often known as the Vedic period
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, between the e ...
. Between 1500 and 500 BC these peoples spread throughout most of India and had begun to found small cities. Vedic society was characterised by the '' varna'' system which divided society into four broad castes, which were later elaborated. By the end of the Vedic period, this way of organising society had become central to Indian society. Religion in the late Vedic period was evolving into Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
, which spread throughout Southeast Asia. Siddhartha Gautama
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha (),*
*
*
was a śramaṇa, wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist lege ...
, born around 560 BC in northern India, went on to found a new religion based on his ascetic life – Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
. This faith also spread throughout Eastern and Southeastern Asia after his death. This period also saw the composition of the epics ''Ramayana
The ''Ramayana'' (; ), also known as ''Valmiki Ramayana'', as traditionally attributed to Valmiki, is a smriti text (also described as a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic) from ancient India, one of the two important epics ...
'' and ''Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; , , ) is one of the two major Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India revered as Smriti texts in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the events and aftermath of the Kuru ...
''.
The kingdom of Magadha rose to prominence under a number of dynasties that peaked in power under the reign of Ashoka
Ashoka, also known as Asoka or Aśoka ( ; , ; – 232 BCE), and popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was List of Mauryan emperors, Emperor of Magadha from until #Death, his death in 232 BCE, and the third ruler from the Mauryan dynast ...
Maurya, one of India's most legendary and famous emperors. During the reign of Ashoka, the four dynasties of Chola, Chera, and Pandya were ruling in the South, while Devanampiya Tissa (250–210 BC) controlled Anuradhapura
Anuradhapura (, ; , ) is a major city located in the north central plain of Sri Lanka. It is the capital city of North Central Province, Sri Lanka, North Central Province and the capital of Anuradhapura District. The city lies north of the cur ...
(now Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
). These kingdoms, while not part of Ashoka's empire, were in friendly terms with the Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary source ...
. An alliance existed between Devanampiya Tissa and Ashoka of India, who sent Buddhist missionaries to Sri Lanka.
Most of North India
North India is a geographical region, loosely defined as a cultural region comprising the northern part of India (or historically, the Indian subcontinent) wherein Indo-Aryans (speaking Indo-Aryan languages) form the prominent majority populati ...
was reunited under the Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an Indian empire during the classical period of the Indian subcontinent which existed from the mid 3rd century to mid 6th century CE. At its zenith, the dynasty ruled over an empire that spanned much of the northern Indian ...
beginning under Chandragupta I around AD 320. Under his successors the empire spread to include much of India except for the Deccan Plateau and the very south of the peninsula. This was a period of relative peace, and the Gupta rulers generally left administration in local rulers. The Gupta Empire was weakened and ultimately ruined by the raids of Hunas (a branch of the Hephthalite
The Hephthalites (), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit and Prakrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during the 5th to 8th centuries CE, ...
s emanating from Central Asia), and the empire broke up into smaller regional kingdoms by the end of the fifth century AD. India would remain fragmented into smaller states until the rise of the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to ...
in the 1500s.
Southeast Asia and Oceania
TheNeolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
period of Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
was characterised by several migrations into Mainland and Island Southeast Asia from southern China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
by Austronesian, Austroasiatic, Kra-Dai and Hmong-Mien-speakers.
Territorial principalities in both Insular and Mainland Southeast Asia, characterised as "agrarian kingdoms", developed an economy by around 500 BCE based on surplus crop cultivation and moderate coastal trade of domestic natural products. Several states of the Malayan-Indonesian " thalassian" zone shared these characteristics with Indochinese polities like the Pyu city-states
The Pyu city-states ( ) were a group of city-states that existed from about the 2nd century BCE to the mid-11th century in present-day Upper Myanmar. The city-states were founded as part of the southward migration by the Tibeto-Burman languages, ...
in the Irrawaddy River
The Irrawaddy River (, , Ayeyarwady) is the principal river of Myanmar, running through the centre of the country. Myanmar’s most important commercial waterway, it is about 1,350 miles (2,170 km) long. Originating from the confluence of the ...
valley, the Văn Lang kingdom in the Red River Delta and Funan
Funan (; , ; , Chữ Hán: ; ) was the name given by Chinese cartographers, geographers and writers to an ancient Khmer-Mon Indianized state—or, rather a loose network of states ''( Mandala)''—located in Mainland Southeast Asia covering ...
around the lower Mekong
The Mekong or Mekong River ( , ) is a transboundary river in East Asia and Southeast Asia. It is the world's twelfth-longest river and the third-longest in Asia with an estimated length of and a drainage area of , discharging of wat ...
. Văn Lang, founded in the 7th century BCE, endured until 258 BCE under the Hồng Bàng dynasty, as part of the Đông Sơn culture that sustained a dense and organised population that produced an elaborate Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
industry.
Intensive wet-rice cultivation in an ideal climate enabled the farming communities to produce a regular crop surplus that was used by the ruling elite to raise, command and pay work forces for public construction and maintenance projects such as canals and fortifications.
Mainland Southeast Asia
 The earliest known evidence of copper and bronze production in Southeast Asia was found at Ban Chiang in north-east Thailand and among the Phùng Nguyên culture of northern Vietnam around 2000 BCE.
The Đông Sơn culture established a tradition of bronze production and the manufacture of evermore refined bronze and iron objects, such as plows, axes and sickles with shaft holes, socketed arrows and spearheads and small ornamented items. By about 500 BCE, large and delicately decorated bronze drums of remarkable quality, weighing more than , were produced in the laborious lost-wax casting process. This industry of highly sophisticated metal processing was developed independent of Chinese or Indian influence. Historians relate these achievements to the presence of organised, centralised and hierarchical communities and a large population.
Between 1000 BCE and 100 CE, the Sa Huỳnh culture flourished along the south-central coast of
The earliest known evidence of copper and bronze production in Southeast Asia was found at Ban Chiang in north-east Thailand and among the Phùng Nguyên culture of northern Vietnam around 2000 BCE.
The Đông Sơn culture established a tradition of bronze production and the manufacture of evermore refined bronze and iron objects, such as plows, axes and sickles with shaft holes, socketed arrows and spearheads and small ornamented items. By about 500 BCE, large and delicately decorated bronze drums of remarkable quality, weighing more than , were produced in the laborious lost-wax casting process. This industry of highly sophisticated metal processing was developed independent of Chinese or Indian influence. Historians relate these achievements to the presence of organised, centralised and hierarchical communities and a large population.
Between 1000 BCE and 100 CE, the Sa Huỳnh culture flourished along the south-central coast of Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
. Ceramic jar burial sites that included grave goods have been discovered at various sites along the entire territory. Among large, thin-walled terracotta jars, ornamented and colorized cooking pots, glass items, jade
Jade is an umbrella term for two different types of decorative rocks used for jewelry or Ornament (art), ornaments. Jade is often referred to by either of two different silicate mineral names: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in t ...
earrings and metal objects were deposited near the rivers and along the coast.
Austronesia
Austronesians
The Austronesian people, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples who have settled in Taiwan, maritime Southeast Asia, parts of mainland Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesi ...
, known as the Austronesian expansion
The Austronesian people, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples who have settled in Taiwan, maritime Southeast Asia, parts of mainland Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesi ...
began from Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
. Population growth
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. The World population, global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to 8.2 billion in 2025. Actual global human population growth amounts to aroun ...
primarily fueled this migration. These first settlers settled in northern Luzon
Luzon ( , ) is the largest and most populous List of islands in the Philippines, island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the List of islands of the Philippines, Philippine archipelago, it is the economic and political ce ...
, in the archipelago of the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, intermingling with the earlier Australo-Melanesian population who had inhabited the islands since about 23,000 years earlier. Over the next thousand years, Austronesian peoples migrated southeast to the rest of the Philippines, and into the islands of the Celebes Sea and Borneo. From southwestern Borneo, Austronesians spread further west in a single migration event to both Sumatra
Sumatra () is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the list of islands by area, sixth-largest island in the world at 482,286.55 km2 (182,812 mi. ...
and the coastal regions of southern Vietnam, becoming the ancestors of the speakers of the Malayic and Chamic branches of the Austronesian language family.
Soon after reaching the Philippines, Austronesians colonized the Northern Mariana Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI), is an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territory and Commonwealth (U.S. insular area), commonwealth of the United States consistin ...
by 1500 BCE or even earlier, becoming the first humans to reach Remote Oceania. The Chamorro migration was also unique in that it was the only Austronesian migration to the Pacific Islands to successfully retain rice cultivation. Palau
Palau, officially the Republic of Palau, is an island country in the Micronesia subregion of Oceania in the western Pacific Ocean. The Republic of Palau consists of approximately 340 islands and is the western part of the Caroline Islands ...
and Yap were settled by separate voyages by 1000 BCE.
Another important migration branch was by the Lapita culture
The Lapita culture is the name given to a Neolithic Austronesian peoples, Austronesian people and their distinct material culture, who settled Island Melanesia via a seaborne migration at around 1600 to 500 BCE. The Lapita people are believed t ...
, which rapidly spread into the islands off the coast of northern New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is ...
and into the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands, also known simply as the Solomons,John Prados, ''Islands of Destiny'', Dutton Caliber, 2012, p,20 and passim is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 1000 smaller islands in Melanesia, part of Oceania, t ...
and other parts of coastal New Guinea and Island Melanesia
Island Melanesia is a subregion of Melanesia in Oceania.
It is located east of New Guinea island, from the Bismarck Archipelago to New Caledonia.Steadman, 2006. ''Extinction & biogeography of tropical Pacific birds''
See also Archaeology a ...
by 1200 BCE. They reached the islands of Fiji
Fiji, officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists of an archipelago of more than 330 islands—of which about ...
, Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa and known until 1997 as Western Samoa, is an island country in Polynesia, part of Oceania, in the South Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main islands (Savai'i and Upolu), two smaller, inhabited ...
, and Tonga
Tonga, officially the Kingdom of Tonga, is an island country in Polynesia, part of Oceania. The country has 171 islands, of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in the southern Pacific Ocean. accordin ...
by around 900 to 800 BCE. This remained the furthest extent of the Austronesian expansion into Polynesia until around 700 CE, when there was another surge of island colonisation. It reached the Cook Islands
The Cook Islands is an island country in Polynesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It consists of 15 islands whose total land area is approximately . The Cook Islands' Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) covers of ocean. Avarua is its ...
, Tahiti
Tahiti (; Tahitian language, Tahitian , ; ) is the largest island of the Windward Islands (Society Islands), Windward group of the Society Islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France. It is located in the central part of t ...
, and the Marquesas
The Marquesas Islands ( ; or ' or ' ; Marquesan: ' ( North Marquesan) and ' ( South Marquesan), both meaning "the land of men") are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in the southern Pacific ...
by 700 CE; Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
by 900 CE; Rapa Nui
Easter Island (, ; , ) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is renowned for its nearly 1,000 extant monumental statues, ...
by 1000 CE; and New Zealand by 1200 CE. For a few centuries, the Polynesian islands were connected by bidirectional long-distance sailing, with the exception of Rapa Nui, which had limited further contact due to its isolated geographical location. Island groups like the Pitcairns, the Kermadec Islands, and the Norfolk Islands were also formerly settled by Austronesians but later abandoned. There is also putative evidence, based in the spread of the sweet potato
The sweet potato or sweetpotato (''Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant in the morning glory family, Convolvulaceae. Its sizeable, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a root vegetable, which is a staple food in parts of ...
, that Austronesians may have reached South America from Polynesia, where they might have traded with the Indigenous peoples of the Americas
In the Americas, Indigenous peoples comprise the two continents' pre-Columbian inhabitants, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with them in the 15th century, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with the pre-Columbian population of ...
.Van Tilburg, Jo Anne. 1994. ''Easter Island: Archaeology, Ecology and Culture.'' Washington D.C.: Smithsonian Institution PressLangdon, Robert. The Bamboo Raft as a Key to the Introduction of the Sweet Potato in Prehistoric Polynesia, ''The Journal of Pacific History'', Vol. 36, No. 1, 2001

Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
and the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
for 3,000 years from 2000 BCE to 1000 CE. The trade was established by links between the indigenous peoples of Taiwan and the Philippines, and later included parts of Vietnam, Malaysia, Indonesia, Thailand, and other areas in Southeast Asia (known as the Sa Huynh- Kalanay Interaction Sphere). Lingling-o artifacts are one of the notable archeological finds originating from the Maritime Jade Road. During the operation of the Maritime Jade Road, the Austronesian spice trade
The spice trade involved historical civilizations in Asia, Northeast Africa and Europe. Spices, such as cinnamon, cassia, cardamom, ginger, pepper, nutmeg, star anise, clove, and turmeric, were known and used in antiquity and traded in t ...
networks were also established by Islander Southeast Asians with Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
and Southern India
South India, also known as Southern India or Peninsular India, is the southern part of the Deccan Peninsula in India encompassing the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Telangana as well as the union territories of ...
by around 1000 to 600 BCE.
They also established early long-distance contacts with Africa, possibly as early as before 500 BCE, based on archaeological evidence like banana phytolith
Phytoliths (from Greek language, Greek, "plant stone") are rigid, microscopic mineral deposits found in some plant tissues, often persisting after the decay of the plant. Although some use "phytolith" to refer to all mineral secretions by plants, ...
s in Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the R ...
and Uganda
Uganda, officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the ...
and remains of Neolithic chicken bones in Zanzibar
Zanzibar is a Tanzanian archipelago off the coast of East Africa. It is located in the Indian Ocean, and consists of many small Island, islands and two large ones: Unguja (the main island, referred to informally as Zanzibar) and Pemba Island. ...
. An Austronesian group, originally from the Makassar Strait region around Kalimantan
Kalimantan (; ) is the Indonesian portion of the island of Borneo. It constitutes 73% of the island's area, and consists of the provinces of Central Kalimantan, East Kalimantan, North Kalimantan, South Kalimantan, and West Kalimantan. The non-Ind ...
and Sulawesi
Sulawesi ( ), also known as Celebes ( ), is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the List of islands by area, world's 11th-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Min ...
, eventually settled Madagascar, either directly from Southeast Asia or from preexisting mixed Austronesian- Bantu populations from East Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the regi ...
. Estimates for when this occurred vary from the 1st century CE, to as late as the 6th to 7th centuries CE. It is likely that the Austronesians that settled Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
followed a coastal route through South Asia and East Africa, rather than directly across the Indian Ocean. Genetic evidence suggests that some individuals of Austronesian descent reached Africa and the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
.
By around the 2nd century BCE, the Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
Austronesian jade and spice trade networks in Southeast Asia connected with the maritime trade routes of South Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's populatio ...
, the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
, eastern Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
, and the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
, becoming what is now known as the Maritime Silk Road
The Maritime Silk Road or Maritime Silk Route is the maritime section of the historic Silk Road that connected Southeast Asia, East Asia, the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian Peninsula, eastern Africa, and Europe. It began by the 2nd century BCE ...
. Prior to the 10th century, the eastern part of the route was primarily used by Southeast Asian Austronesian traders using distinctive lashed-lug ships, although Tamil and Persian traders also sailed the western parts of the routes. It allowed the exchange of goods from East
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that ea ...
and Southeast Asia on one end, all the way to Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
and eastern Africa on the other.
Srivijaya
Srivijaya (), also spelled Sri Vijaya, was a Hinduism, Hindu-Buddhism, Buddhist thalassocracy, thalassocratic empire based on the island of Sumatra (in modern-day Indonesia) that influenced much of Southeast Asia. Srivijaya was an important ...
, an Austronesian polity founded at Palembang in 682 CE, rose to dominate the trade in the region around the straits of Malacca
Malacca (), officially the Historic State of Malacca (), is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state in Malaysia located in the Peninsular Malaysia#Other features, southern region of the Malay Peninsula, facing the Strait of Malacca ...
and Sunda and the South China Sea emporium by controlling the trade in luxury aromatics and Buddhist artifacts from West Asia to a thriving Tang market. It emerged through the conquest and subjugation of neighboring thalassocracies. These included Melayu, Kedah
Kedah (), also known by its honorific Darul Aman (Islam), Aman (دار الأمان; Arabic for 'The Safe Abode') and historically as Queda, is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state of Malaysia, located in the northwestern part of ...
, Tarumanagara
Tarumanagara or Taruma Kingdom or just Taruma was an early Sundanese Indianised kingdom, located in western Java, whose 5th-century ruler, Purnawarman, produced the earliest known inscriptions in Java, which are estimated to date from aro ...
, and Mataram, among others. These polities controlled the sea lanes in Southeast Asia and exploited the spice trade of the Spice Islands, as well as maritime trade-routes between India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
.
East Asia
China
 The Chinese civilisation that emerged within the
The Chinese civilisation that emerged within the Yellow River
The Yellow River, also known as Huanghe, is the second-longest river in China and the List of rivers by length, sixth-longest river system on Earth, with an estimated length of and a Drainage basin, watershed of . Beginning in the Bayan H ...
valley is one of earliest civilisations in the world. Prior to the formation of civilisation, neolithic cultures such as the Longshan and Yangshao dating to 5000 BC produced sophisticated pottery, cultivated millet, and likely produced clothes woven from hemp
Hemp, or industrial hemp, is a plant in the botanical class of ''Cannabis sativa'' cultivars grown specifically for industrial and consumable use. It can be used to make a wide range of products. Along with bamboo, hemp is among the fastest ...
and silk
Silk is a natural fiber, natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be weaving, woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is most commonly produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoon (silk), c ...
. Rice was also farmed and pigs and water buffalo
The water buffalo (''Bubalus bubalis''), also called domestic water buffalo, Asian water buffalo and Asiatic water buffalo, is a large bovid originating in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. Today, it is also kept in Italy, the Balkans ...
were kept for food. Longshan potters may have used the pottery wheel to produce their wares. Ancient Chinese traditions described three Dynasties in Chinese history, ancient dynasties that predated the unification under the Qin dynasty, Qin and Han dynasty, Han dynasties. These were the Xia dynasty, Xia, the Shang dynasty, Shang, and the Western Zhou, Zhou. It was not until the later 20th century that many historians considered the Shang or Xia to be anything other than legendary. Little is yet known about the Xia, which appears to have begun around 2200 BC, and may have controlled parts of the Yangtze River valley.
The Shang dynasty traditionally is dated to 1766 to 1122 BC. Bronze was central to Shang culture and technology, with chariots and bronze weapons helping to expand Shang control over northern China. The cities at Ao and Yinxu, near Anyang, have been excavated and city walls, royal palaces, and archives as well as tombs and workshops were found. A system of writing developed, beginning with oracle bones, of which over 100,000 are still extant.
Towards the end of the 2nd millennium BC, the Shang were overrun by the Zhou dynasty from the Wei River valley to the west. The Zhou rulers at this time invoked the concept of the Mandate of Heaven to legitimize their rule, a concept that would be influential for almost every successive dynasty. The Zhou initially established their capital in the west near modern Xi'an, near the Yellow River, but they would preside over a series of expansions into the Yangtze River valley. Zhou administration was decentralised, with local elites responsible for collecting tribute and providing military support to the Zhou rulers.
 In the 8th century BC, power became decentralized during the Spring and Autumn period, named after the influential ''Spring and Autumn Annals''. In this period, local military leaders used by the Zhou began to assert their power and vie for hegemony. The situation was aggravated by the invasion of other peoples, forcing the Zhou to move their capital east to Luoyang. In each of the hundreds of states that eventually arose, local strongmen held most of the political power and continued their subservience to the Zhou kings in name only. The Hundred Schools of Thought of Chinese philosophy blossomed during this period, and such influential intellectual movements as Confucianism, Taoism, Legalism (Chinese philosophy), Legalism and Mohism were founded, partly in response to the changing political world.
After further political consolidation, seven prominent states remained by the end of the 5th century BC, and the years in which these few states battled each other is known as the Warring States period. Though there remained a nominal Zhou king until 256 BC, he was largely a figurehead and held little power. As neighboring territories of these warring states, including areas of modern Sichuan and Liaoning, were annexed by the growing power of the rulers of Qin (state), Qin, they were governed under the new local administrative system of Commandery (China), commandery. The final expansion in this period began during the reign of Ying Zheng, the king of Qin. His unification of the other six powers, and further annexations to the south and southeast by 213 BC enabled him to proclaim himself the Qin Shi Huang, First Emperor (Qin Shi Huangdi).
In the 8th century BC, power became decentralized during the Spring and Autumn period, named after the influential ''Spring and Autumn Annals''. In this period, local military leaders used by the Zhou began to assert their power and vie for hegemony. The situation was aggravated by the invasion of other peoples, forcing the Zhou to move their capital east to Luoyang. In each of the hundreds of states that eventually arose, local strongmen held most of the political power and continued their subservience to the Zhou kings in name only. The Hundred Schools of Thought of Chinese philosophy blossomed during this period, and such influential intellectual movements as Confucianism, Taoism, Legalism (Chinese philosophy), Legalism and Mohism were founded, partly in response to the changing political world.
After further political consolidation, seven prominent states remained by the end of the 5th century BC, and the years in which these few states battled each other is known as the Warring States period. Though there remained a nominal Zhou king until 256 BC, he was largely a figurehead and held little power. As neighboring territories of these warring states, including areas of modern Sichuan and Liaoning, were annexed by the growing power of the rulers of Qin (state), Qin, they were governed under the new local administrative system of Commandery (China), commandery. The final expansion in this period began during the reign of Ying Zheng, the king of Qin. His unification of the other six powers, and further annexations to the south and southeast by 213 BC enabled him to proclaim himself the Qin Shi Huang, First Emperor (Qin Shi Huangdi).
 Qin Shi Huangdi ruled the unified China directly with absolute power. In contrast to the decentralised and feudal rule of earlier dynasties the Qin ruled directly. Nationwide the philosophy of Legalism (Chinese philosophy), legalism was enforced and publications promoting rival ideas such as Confucianism were prohibited. In his reign unified China created the first continuous Great Wall with the use of forced labour. Qin's campaign against the Yue tribes, Invasions were launched southward to annex Vietnam. The Qin period also saw the standardisation of the Chinese writing system and the government unified the legal systems as well as setting standardised units of measurement throughout the empire. After the emperor's death rebellions began and the Han dynasty took power and ruled China for over four centuries with a brief interruption from AD 9 to 23. The Han dynasty promoted the spread of iron agricultural tools, which helped create a food surplus that led to a large growth of population during the Han period. Silk production also increased and the manufacture of paper was invented. Though the Han enjoyed great military and economic success, it was strained by the rise of aristocrats who disobeyed the central government. Public frustration provoked the Yellow Turban Rebellion; though a failure it nonetheless accelerated the empire's downfall. After AD 208, the Han dynasty broke up into Three Kingdoms period, rival kingdoms. China would remain divided for almost the next 400 years.
Qin Shi Huangdi ruled the unified China directly with absolute power. In contrast to the decentralised and feudal rule of earlier dynasties the Qin ruled directly. Nationwide the philosophy of Legalism (Chinese philosophy), legalism was enforced and publications promoting rival ideas such as Confucianism were prohibited. In his reign unified China created the first continuous Great Wall with the use of forced labour. Qin's campaign against the Yue tribes, Invasions were launched southward to annex Vietnam. The Qin period also saw the standardisation of the Chinese writing system and the government unified the legal systems as well as setting standardised units of measurement throughout the empire. After the emperor's death rebellions began and the Han dynasty took power and ruled China for over four centuries with a brief interruption from AD 9 to 23. The Han dynasty promoted the spread of iron agricultural tools, which helped create a food surplus that led to a large growth of population during the Han period. Silk production also increased and the manufacture of paper was invented. Though the Han enjoyed great military and economic success, it was strained by the rise of aristocrats who disobeyed the central government. Public frustration provoked the Yellow Turban Rebellion; though a failure it nonetheless accelerated the empire's downfall. After AD 208, the Han dynasty broke up into Three Kingdoms period, rival kingdoms. China would remain divided for almost the next 400 years.
Neighbours of China
 The East Asian nations adjacent to China were all profoundly influenced by their interactions with East Asian cultural sphere, Chinese civilisation. Korea and
The East Asian nations adjacent to China were all profoundly influenced by their interactions with East Asian cultural sphere, Chinese civilisation. Korea and Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
were brought under Han rule by Han Wudi in the second century BC, and this rule led to cultural influences on both areas for many centuries to come. Wudi also faced a threat from the Xiongnu, a nomadic people from the Central Asian steppes. Wudi's invasions ended the Xiongnu state.
In 108 BC, the Han dynasty of China conquered much of Korea but when Han China began its decline, Three Kingdoms of Korea, three kingdoms in Korea – those of Baekje, Goguryeo and Silla – emerged and expelled the Chinese. Goguryeo and Baekje were eventually destroyed by a Tang dynasty and Silla alliance. Silla then drove out the Tang dynasty in 676 to control most of the Korean peninsula undisputed.
Jomon culture formed in Japan before 500 BC and under Chinese influence became the Yayoi culture which built large tombs by AD 200. In the 300s, a kingdom formed in the Yamato plain, perhaps influenced by Korean refugees.
Americas
In pre-Columbian times, several large, centralised ancient civilisations developed in the Western Hemisphere, both inMesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to the Pacific coast of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central and southern Mexico, all of Belize, Guatemala, El S ...
and western South America. Beyond these areas, the use of agriculture expanded East of the Andes Mountains in South America particularly with the Marajoara culture, and in the continental United States.
Andean civilisations
Ancient Andean civilisation began with the rise of organised fishing communities from 3500 BC onwards. Along with a sophisticated maritime society came the construction of large monuments, which likely existed as community centres. The peoples of this area grew beans, cotton, peanuts, and sweet potatoes, fished in the ocean, and by about 2000 BC had added the potato to their crops. The Chavin culture, based around the Chavin cult, emerged around 1000 BC and led to large temples and artworks as well as sophisticated textiles. Gold, silver, and copper were worked for jewelry and occasionally for small copper tools. After the decline of Chavin culture, a number of cities formed after about 200 BC. The cities at Huari (archaeological site), Huari, Pucara, and Tiahuanaco were all likely over 10,000 residents. From about AD 300, the Mochica culture arose along the Moche River. These people left painted pottery depicting their society and culture with a wide range of varied subjects. Besides the Mochica, there were a number of other large states in the Andes after about AD 100. Included amongst these are the Nazca culture, who were mainly village-dwelling but left behind a large ceremonial centre at Cahuachi as well as the Nazca lines, a large number of huge designs set into the desert floor.Mesoamerica
Agricultural cultivation began around 8000 BC inMesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to the Pacific coast of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central and southern Mexico, all of Belize, Guatemala, El S ...
, where avocados, beans, chili peppers, gourds, and squashes were grown from about 7000 BC. Around 4000 BC maize began to be grown, and soon after this tomatoes. Settlements appeared around 3000 BC and by 2000 BC most of Mesoamerica was practicing agriculture. Although some animals were domesticated — notably turkey (bird), turkeys and dogs — the lack of suitable large animals precluded the development of animals used for transportation or labour.
Around 1200 BC the first Olmec culture, Olmec centre of San Lorenzo Tenochtitlán, San Lorenzo was founded, which remained the centre of Olmec civilisation until around 800 BC when La Venta took over before losing primacy to Tres Zapotes around 400 BC. These and other Olmec centres were groups of tombs, temples, and other ceremonial sites built of stone. Their construction testifies to the complexity of Olmec society, although the exact nature of how they were governed is not known. They also erected large stone sculptures of human heads and other subjects. Jade jewelry and other Olmec objects are found throughout Mesoamerica, likely having travelled via trade networks. The Olmec hieroglyphs, Olmec writing system was mainly used for recording their Mesoamerican calendar, calendar, both of which influenced later Mesoamerican cultures.
After the decline of the Olmecs, other civilisations in Mesoamerica either arose or emerged from the Olmec shadow - the Maya civilization, Mayans, the Zapotec civilization, Zapotecs, and Teotihuacan. The Zapotecs began around 500 BC in the Oaxaca Valley at the site of Monte Alban. Monte Alban grew to around 25,000 residents in the period around AD 200, with the city having large stone temples and an expansive stone plaza. Like the Olmecs, they had a writing system and calendar. But by AD 900 Monte Alban was deserted for unknown reasons. Teotihuacan developed around AD 200 and centred on the city of Teotihuacan, which grew to perhaps as many as 200,000 inhabitants at its height. Teotihuacan lasted until around AD 700, when it was burned and vandalised.
Maya civilization, Maya culture began to emerge around AD 300 in the Yucatan Peninsula and modern-day Guatemala. During the 600 years of the Maya civilization#Classic period (c. 250–900 AD), Classical Maya period, more than 80 Mayan sites were built, with temples, pyramids, and palaces the focal point of each centre. The most influential was Tikal, but Mayan civilisation was based on city-states which often were at war with each other. This seems not to have restricted trade, which went on between the cities. A priestly elite kept astronomical and calendrical knowledge, recording it with a Mayan glyphs, writing system based on the Olmec system of glyphs. History, poetry, and other records were recorded in books, most of which did not survive the Spanish colonization of the Americas, Spanish conquest of Mesoamerica. Mathematics was also studied, and they used the concept of zero in their calculations. The Mayan civilisation began to decline about AD 800, and most of its cities were deserted soon afterwards.
Northern America
Organized societies, in the ancient United States or Canada, were often mound builder civilisations. One of the most significant of these was the Poverty Point culture that existed in the U.S. state of Louisiana, and was responsible for the creation of over 100 mound sites. The Mississippi River was a core area in the development of long-distance trade and culture. Following Poverty Point, successive complex cultures such as the Hopewell emerged in the Southeastern United States in the Woodland period, Early Woodland period. Before AD 500 many mound builder societies retained a hunter gatherer form of subsistence.Europe
Greece
Greece is home to the first advanced civilizations in Europe beginning with the Cycladic culture on the islands of the Aegean Sea around 3200 BC, and the Minoan civilization, Minoan civilisation in Crete (2700–1500 BC). The Minoans built large palaces decorated with frescoes and wrote in the Undeciphered writing systems, undeciphered script known as Linear A. The Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean civilization, the first distinctively Greek civilisation later emerged on the mainland (1600–1100 BC), consisting of a network of palace-centred states and writing the earliest Attested language, attested form of Greek language, Greek with the Linear B script. The Mycenaeans gradually absorbed the Minoans, but collapsed violently around 1200 BC, along with several other civilizations in the eastern Mediterranean, during the regional event known as the Late Bronze Age collapse. This ushered in a period known as the Greek Dark Ages, from which written records are absent. The Archaic Greece, Archaic Period in Greece is generally considered to have lasted from around the 8th century BC to the invasion by Xerxes in 480 BC. This period saw the expansion of the Greek world around the Mediterranean, with the founding of Greek city-states as far afield as Sicily in the west and the Black Sea in the east. Politically, the Archaic period in Greece saw the collapse of the power of the old aristocracies, with democratic reforms in Athens and the development of Spartan Constitution, Sparta's unique constitution. The end of the Archaic period also saw the rise of Athens, which would come to be a dominant power in the Classical Greece, Classical Period, after the reforms of Solon and the tyranny of Pisistratus. The Classical Greek world was dominated throughout the 5th century BC by the major powers of Ancient Athens, Athens and Sparta. Through the Delian League, Athens was able to convert pan-hellenist sentiment and fear of the Persian threat into a powerful empire, and this, along with the conflict between Sparta and Athens culminating in the Peloponnesian War, was the major political development of the first part of the Classical period. The period in Greek history from the death of Alexander the Great until the rise of the Roman empire and its conquest of Egypt in 30 BC is known as the Hellenistic period. After Alexander's death, a series of wars between his successors eventually led to three large states being formed from parts of Alexander's conquests, each ruled by a dynasty founded by one of the successors. These were the Antigonids, the Selucids, and the Ptolemies. These three kingdoms, along with smaller kingdoms, spread Greek culture and lifestyles into Asia and Egypt. These varying states eventually were conquered by Rome or the
The Classical Greek world was dominated throughout the 5th century BC by the major powers of Ancient Athens, Athens and Sparta. Through the Delian League, Athens was able to convert pan-hellenist sentiment and fear of the Persian threat into a powerful empire, and this, along with the conflict between Sparta and Athens culminating in the Peloponnesian War, was the major political development of the first part of the Classical period. The period in Greek history from the death of Alexander the Great until the rise of the Roman empire and its conquest of Egypt in 30 BC is known as the Hellenistic period. After Alexander's death, a series of wars between his successors eventually led to three large states being formed from parts of Alexander's conquests, each ruled by a dynasty founded by one of the successors. These were the Antigonids, the Selucids, and the Ptolemies. These three kingdoms, along with smaller kingdoms, spread Greek culture and lifestyles into Asia and Egypt. These varying states eventually were conquered by Rome or the Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power centered in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe ...
.
Rome
Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
, leading to a series of Punic Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of wars fought between the Roman Republic and the Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian Empire during the period 264 to 146BC. Three such wars took place, involving a total of forty-three years of warfare on both land and ...
, that ended with the destruction of Carthage in 146 BC. Rome then expanded into Greece and the eastern Mediterranean, while a series of internal conflicts led to the republic becoming an empire ruled by an Roman emperor, emperor by the first century AD. Throughout the first and second centuries AD, the Empire grew slightly while spreading Roman culture throughout its boundaries.
A number of factors led to the eventual decline of the Roman Empire. The western half of the empire, including Hispania, Gaul, and Italy, eventually broke into independent kingdoms in the 5th century AD; the Eastern Roman Empire, governed from Constantinople, is referred to as the Byzantine Empire after AD 476, the traditional date for the "fall of Rome" and subsequent onset of the Middle Ages.
Late antiquity
 The Roman Empire underwent considerable social, cultural and organisational change starting with reign of Diocletian, who began the custom of splitting the empire into eastern and Western Roman Empire, western halves ruled by multiple emperors. Constantine the Great initiated the process of Christianization, Christianisation of the empire and established a new capital at Constantinople. Migration Period, Migrations of Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes disrupted Roman rule from the late 4th century onwards, culminating in the eventual Decline of the Roman Empire, collapse of the empire in the West in 476, replaced by the so-called Germanic monarchy, barbarian kingdoms. The resultant cultural fusion of Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman, Germanic and Christian traditions formed the cultural foundations of Europe. There has been attempt by scholars to connect European late antiquity to other areas in Eurasia.
The Roman Empire underwent considerable social, cultural and organisational change starting with reign of Diocletian, who began the custom of splitting the empire into eastern and Western Roman Empire, western halves ruled by multiple emperors. Constantine the Great initiated the process of Christianization, Christianisation of the empire and established a new capital at Constantinople. Migration Period, Migrations of Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes disrupted Roman rule from the late 4th century onwards, culminating in the eventual Decline of the Roman Empire, collapse of the empire in the West in 476, replaced by the so-called Germanic monarchy, barbarian kingdoms. The resultant cultural fusion of Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman, Germanic and Christian traditions formed the cultural foundations of Europe. There has been attempt by scholars to connect European late antiquity to other areas in Eurasia.
Nomads and Iron Age peoples
The Celts were a diverse group of tribal societies in Iron Age Europe. Proto-Celtic culture formed in the Early Iron Age in Central Europe (Hallstatt culture, Hallstatt period, named for the site in present-day Austria). By the later Iron Age (La Tène culture, La Tène period), Celts had expanded over wide range of lands: as far west as Ireland and the Iberian Peninsula, as far east as Galatia (centralAnatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
), and as far north as Scotland. By the early centuries AD, following the expansion of the Roman Empire and the Great Migrations of Germanic peoples, Celtic culture had become restricted to the British Isles.
The Huns were a nomadic people who formed a large state in Eastern Europe by about AD 400, and under their leader Attila, they fought against both sections of the Roman Empire. However, after Attila's death, the state fell apart and the Huns' influence in history disappeared. The Huns, Hun-Xiongnu connection is controversial at best and is often disputed but is also not completely discredited.
Migration of Germanic peoples to Britain from what is now northern Germany and southern Scandinavia is attested from the 5th century. Groups of Goths migrated into western Europe, with the Ostrogoths eventually settling in Italy before being conquered by the Lombards. A related people, the Visigoths, settled in Spain, founding a kingdom that lasted until it was conquered by Islamic rulers in the AD 700s.
Several Indo-european speaking peoples inhabited the Balkans, Balkan peninsula including the Thracians and Illyrians, that were divided into many tribes. The first Illyrian tribe to create its own kingdom was the Enchelei, which formed its own state around the 8th-7th century BC and reached the height of their power under king Bardylis. The Ardiani were infamous for their piracy and Illyro-Roman Wars, wars against the Roman Empire, for the Illyro-Roman Wars#First Illyrian War, first time between 229 BC-228 BC, then for a Illyro-Roman Wars#Second Illyrian War, second time during 220 BC-219 BC and for a Illyro-Roman Wars#Third Illyrian War, third time during 168 BC.Battles of the Greek and Roman Worlds: A Chronological Compendium of 667 Battles to 31Bc, from the Historians of the Ancient World (Greenhill Historic Series) by John Drogo Montagu, , 2000, page 47
Developments
Religion and philosophy
Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
(5th century BC), and Jainism (6th century BC) in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, and Zoroastrianism in Achaemenid Empire, Persia. The Abrahamic religions trace their origin to Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
, around 1700 BC.
In the east, three schools of thought were to dominate Chinese thinking until the modern day. These were Taoism, Legalism (Chinese philosophy), Legalism and Confucianism. The Confucian tradition, which would attain dominance, looked for political morality not to the force of law but to the power and example of tradition. Confucianism would later spread into the Korean peninsula and Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
.
In the west, the Greek philosophical tradition, represented by Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle, was diffused throughout Europe and the Middle East in the 4th century BC by the conquests of Alexander the Great. After the Bronze and Iron Age religions formed, Christianity spread through the Roman world.
Science and technology
Ancient technological progress began before the recording of history, with tools, use of fire, domestication of animals, and agriculture all predating recorded history. The use of metals and the ability to make metal alloys was foundational for later technologies to develop. Medical knowledge, including the use of herbs to treat illnesses and wounds as well as some surgical techniques, advanced during antiquity. An early very important development that allowed for further advancement was writing, which allowed humans to record information for later use. The characteristics of ancient Egyptian technology are indicated by a set of artifacts and customs that lasted for thousands of years. The Egyptians invented and used many basic machines, such as the ramp and the lever, to aid construction processes. The Egyptians also played an important role in developing Mediterranean maritime technology, including ships. The Babylonians and Egyptians were early astronomers who recorded their observations of the night sky. Water managing Qanats which likely emerged on the Iranian plateau and possibly also in the Arabian peninsula sometime in the early 1st millennium BC spread from there slowly west- and eastward. The Hindu–Arabic numeral system with the concept of zero was developed in India, while modern forms of paper were invented in China in the first century AD.See also
* Outline of ancient historyReferences
Notes
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * Web edition is constantly updated. * *External links
Websites
World History Encyclopedia
nbsp;– British Museum's website on various topics of ancient civilisation
Ancient history sourcebook
The Perseus digital library
Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman world
Directories
– Academic Info: directory of online resources for the study of ancient history.
: Ancient history research links for high school and college students. {{Authority control Ancient history Historical eras Articles which contain graphical timelines