Agaricus Xanthodermulus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Agaricus'' is a
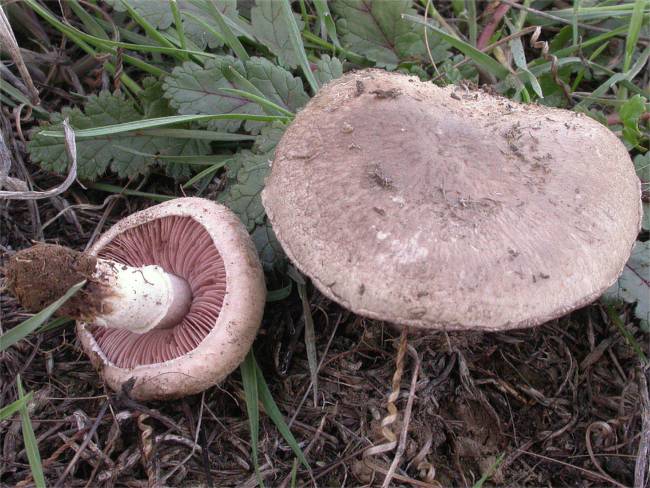 Subgenus ''
Subgenus '' Subgenus '' Flavoagaricus''
* Section ''Arvense'' Konrad & Maubl. (sometimes named ''Arvensis'')
:Traditionally contained about 20 rather large species similar to the horse mushroom '' A. arvensis'' in six subgroups. Today, several additional species are recognized – in particular in the ''A. arvensis''
Subgenus '' Flavoagaricus''
* Section ''Arvense'' Konrad & Maubl. (sometimes named ''Arvensis'')
:Traditionally contained about 20 rather large species similar to the horse mushroom '' A. arvensis'' in six subgroups. Today, several additional species are recognized – in particular in the ''A. arvensis''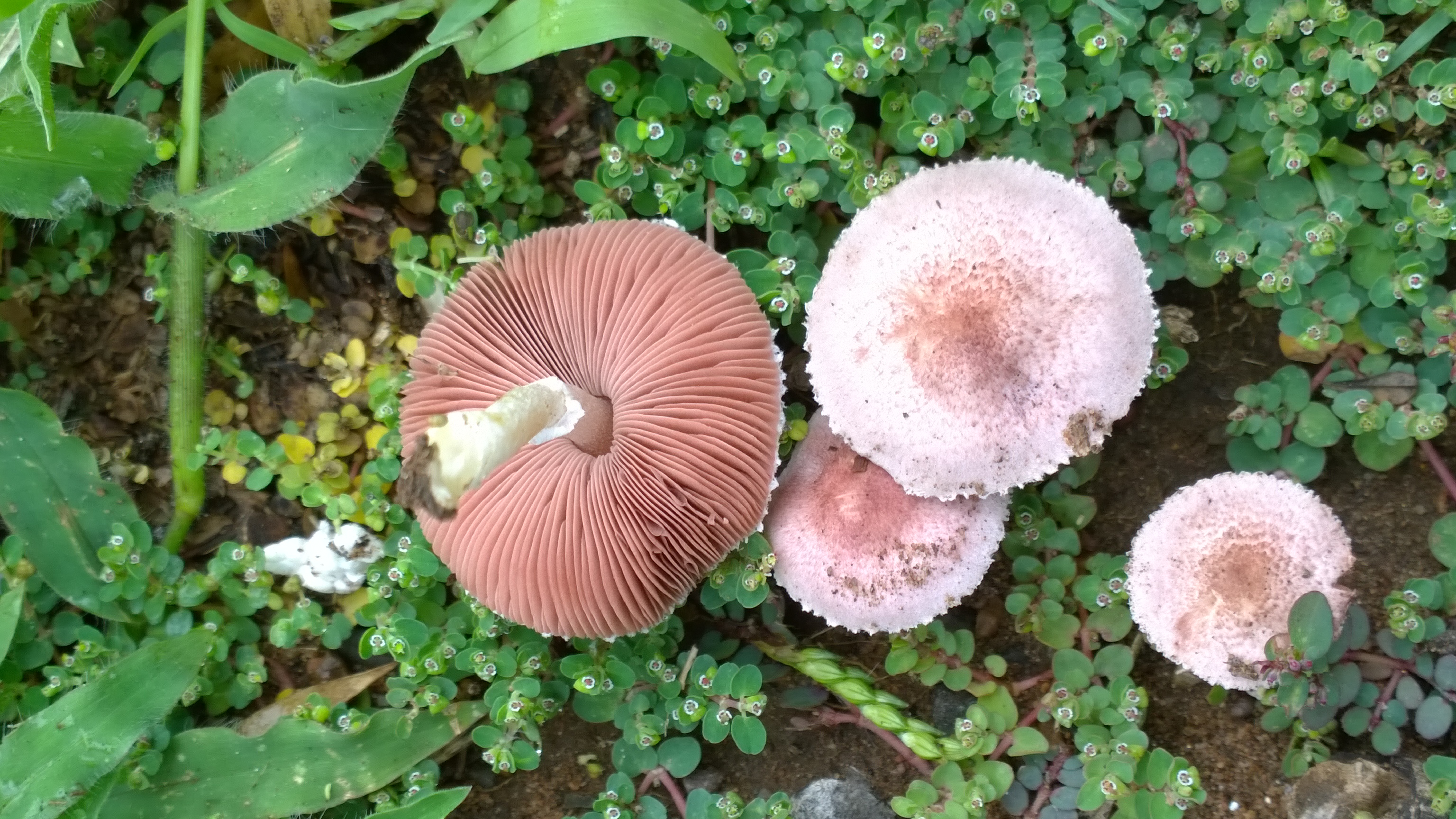 
 Subgenus '' Minores''
:A group of buff-white to reddish-brown species. Often delicate and slender, the typical members of this subgenus do not resemble the larger ''Agaricus'' species at a casual glance, but have the same telltale chocolate-brown gills at spore maturity. Their flesh has a barely noticeable to pronounced sweetish smell, typically
Subgenus '' Minores''
:A group of buff-white to reddish-brown species. Often delicate and slender, the typical members of this subgenus do not resemble the larger ''Agaricus'' species at a casual glance, but have the same telltale chocolate-brown gills at spore maturity. Their flesh has a barely noticeable to pronounced sweetish smell, typically 

 Subgenus '' Pseudochitonia''
:This highly diverse clade of mid-sized to largish species makes up much the bulk of the genus' extant diversity, and this subgenus contains numerous as of yet undescribed species. It includes both the most prized edible as well as the most notoriously poisonous ''Agaricus'', and some of its sections are in overall appearance more similar to the more distantly related ''Agaricus'' proper and ''Flavoagaricus'' than to their own closest relatives. Some species in this subgenus, such as '' A. goossensiae'' and '' A. rodmanii'', are not yet robustly assigned to one of the sections.
* Section '' Bohusia''
:Includes '' A. bohusii'' which resembles one of the dark-capped ''Flavoagaricus'' or ''Xanthodermatei'' but does not stain yellow with the standard (10%) KOH testing solution. It is a woodland species, edible when young, but when mature and easily distinguished from similar species it may be slightly poisonous. Other members of this section include '' A. crassisquamosus'', '' A. haematinus'', and '' A. pseudolangei''.
* Section '' Brunneopicti''
:A section notable for containing a considerable number of undescribed species in addition to '' A. bingensis'', '' A. brunneopictus'', '' A. brunneosquamulosus'', '' A. chiangmaiensis'', '' A. duplocingulatus'', '' A. megacystidiatus'', '' A. niveogranulatus'', '' A. sordidocarpus'', '' A. subsaharianus'', and '' A. toluenolens''.
* Section '' Chitonioides''
:Contains species such as '' A. bernardii'' and the doubtfully distinct '' A. bernardiiformis'', '' A. gennadii'', '' A. nevoi'', '' A. pequinii'', '' A. pilosporus'' and '' A. rollanii'', which strongly resemble the members of section ''Duploannulatae'' and are as widely distributed. However, their flesh tends to discolor more strongly red when bruised or cut, with the discoloration slowly getting stronger. Their smell is usually also more pronounced
Subgenus '' Pseudochitonia''
:This highly diverse clade of mid-sized to largish species makes up much the bulk of the genus' extant diversity, and this subgenus contains numerous as of yet undescribed species. It includes both the most prized edible as well as the most notoriously poisonous ''Agaricus'', and some of its sections are in overall appearance more similar to the more distantly related ''Agaricus'' proper and ''Flavoagaricus'' than to their own closest relatives. Some species in this subgenus, such as '' A. goossensiae'' and '' A. rodmanii'', are not yet robustly assigned to one of the sections.
* Section '' Bohusia''
:Includes '' A. bohusii'' which resembles one of the dark-capped ''Flavoagaricus'' or ''Xanthodermatei'' but does not stain yellow with the standard (10%) KOH testing solution. It is a woodland species, edible when young, but when mature and easily distinguished from similar species it may be slightly poisonous. Other members of this section include '' A. crassisquamosus'', '' A. haematinus'', and '' A. pseudolangei''.
* Section '' Brunneopicti''
:A section notable for containing a considerable number of undescribed species in addition to '' A. bingensis'', '' A. brunneopictus'', '' A. brunneosquamulosus'', '' A. chiangmaiensis'', '' A. duplocingulatus'', '' A. megacystidiatus'', '' A. niveogranulatus'', '' A. sordidocarpus'', '' A. subsaharianus'', and '' A. toluenolens''.
* Section '' Chitonioides''
:Contains species such as '' A. bernardii'' and the doubtfully distinct '' A. bernardiiformis'', '' A. gennadii'', '' A. nevoi'', '' A. pequinii'', '' A. pilosporus'' and '' A. rollanii'', which strongly resemble the members of section ''Duploannulatae'' and are as widely distributed. However, their flesh tends to discolor more strongly red when bruised or cut, with the discoloration slowly getting stronger. Their smell is usually also more pronounced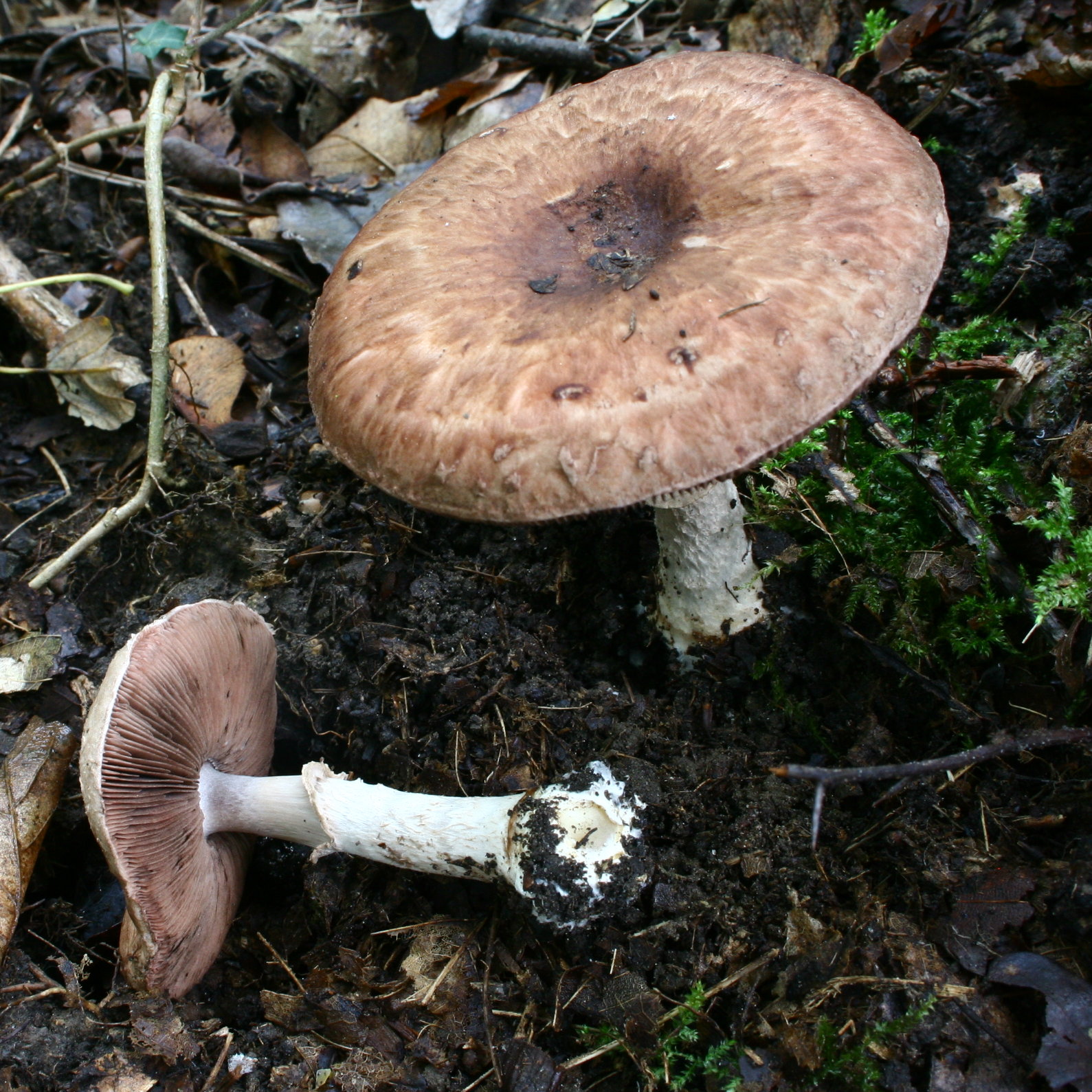  Subgenus ''Spissicaules (subgenus), Spissicaules''
:The flesh of members of this subgenus tends to turn more or less pronouncedly yellowish in the lower stalk, where the skin is often rough and scaly, and reddish in the cap. They typically resemble the darker members of subgenus ''Flavoagaricus'', with a sweet smell and mild taste; like that subgenus, ''Spissicaules'' belongs to the smaller of the two main groups of the genus, but they form entirely different branch therein. While some species are held to be edible, others are considered unappetizing or even slightly poisonous. Also includes ''Agaricus lanipes, A. lanipes'' and ''Agaricus maskae, A. maskae'', which probably belong to section ''Rarolentes'' or ''Spissicaules'', and possibly also '' A. bresadolanus'' and its doubtfully distinct relatives ''Agaricus radicatus, A. radicatus''/'' romagnesii''.
* Section ''Amoeni''
:Includes ''Agaricus amoenus, A. amoenus'' and ''Agaricus gratolens, A. gratolens''.
* Section ''Rarolentes''
:Includes ''Agaricus albosquamosus, A. albosquamosus'' and ''Agaricus leucolepidotus, A. leucolepidotus''.
* Section ''Spissicaules (section), Spissicaules'' (Hainem.) Richard W. Kerrigan, Kerrigan
:Includes species such as ''Agaricus leucotrichus, A. leucotrichus''/''Agaricus litoralis, litoralis'' (of which ''A. spissicaulis'' is a synonym, but see also Geml ''et al.'' 2004) and ''Agaricus litoraloides, A. litoraloides''. Most significantly, some species have a persistent and unpleasant rotting-wood smell entirely unlike the sweet aroma of ''Flavoagaricus'', and while not known to be poisonous, are certainly unpalatable.
* Section ''Subrutilescentes''
:Includes ''Agaricus brunneopilatus, A. brunneopilatus'', ''Agaricus linzhinensis, A. linzhinensis'' and ''Agaricus subrutilescens, A. subrutilescens''. Somewhat similar to section ''Sanguinolenti'' or the dark-capped species of section ''Xanthodermatei'', but the flesh does not show a pronounced red or yellow color change when cut or bruised. Edibility is disputed.
Subgenus ''Spissicaules (subgenus), Spissicaules''
:The flesh of members of this subgenus tends to turn more or less pronouncedly yellowish in the lower stalk, where the skin is often rough and scaly, and reddish in the cap. They typically resemble the darker members of subgenus ''Flavoagaricus'', with a sweet smell and mild taste; like that subgenus, ''Spissicaules'' belongs to the smaller of the two main groups of the genus, but they form entirely different branch therein. While some species are held to be edible, others are considered unappetizing or even slightly poisonous. Also includes ''Agaricus lanipes, A. lanipes'' and ''Agaricus maskae, A. maskae'', which probably belong to section ''Rarolentes'' or ''Spissicaules'', and possibly also '' A. bresadolanus'' and its doubtfully distinct relatives ''Agaricus radicatus, A. radicatus''/'' romagnesii''.
* Section ''Amoeni''
:Includes ''Agaricus amoenus, A. amoenus'' and ''Agaricus gratolens, A. gratolens''.
* Section ''Rarolentes''
:Includes ''Agaricus albosquamosus, A. albosquamosus'' and ''Agaricus leucolepidotus, A. leucolepidotus''.
* Section ''Spissicaules (section), Spissicaules'' (Hainem.) Richard W. Kerrigan, Kerrigan
:Includes species such as ''Agaricus leucotrichus, A. leucotrichus''/''Agaricus litoralis, litoralis'' (of which ''A. spissicaulis'' is a synonym, but see also Geml ''et al.'' 2004) and ''Agaricus litoraloides, A. litoraloides''. Most significantly, some species have a persistent and unpleasant rotting-wood smell entirely unlike the sweet aroma of ''Flavoagaricus'', and while not known to be poisonous, are certainly unpalatable.
* Section ''Subrutilescentes''
:Includes ''Agaricus brunneopilatus, A. brunneopilatus'', ''Agaricus linzhinensis, A. linzhinensis'' and ''Agaricus subrutilescens, A. subrutilescens''. Somewhat similar to section ''Sanguinolenti'' or the dark-capped species of section ''Xanthodermatei'', but the flesh does not show a pronounced red or yellow color change when cut or bruised. Edibility is disputed.
 As late as 2008, ''Agaricus'' was believed to contain about 200 species worldwide but since then, molecular phylogenetic studies have revalidated several disputed species, as well as resolved some
As late as 2008, ''Agaricus'' was believed to contain about 200 species worldwide but since then, molecular phylogenetic studies have revalidated several disputed species, as well as resolved some  ''Agaricus abruptibulbus'' – abruptly-bulbous agaricus, flat-bulb mushroom (disputed)
*
''Agaricus abruptibulbus'' – abruptly-bulbous agaricus, flat-bulb mushroom (disputed)
*  ''Agaricus aestivalis''
* ''Agaricus agrinferus'' (disputed)
* ''Agaricus alabamensis''
*
''Agaricus aestivalis''
* ''Agaricus agrinferus'' (disputed)
* ''Agaricus alabamensis''
*  ''Agaricus albolutescens'' (disputed)
* ''Agaricus alligator''
*
''Agaricus albolutescens'' (disputed)
* ''Agaricus alligator''
*  ''Agaricus amicosus''
* ''Agaricus angusticystidiatus''
* ''Agaricus annae''
* ''Agaricus arorae''
*
''Agaricus amicosus''
* ''Agaricus angusticystidiatus''
* ''Agaricus annae''
* ''Agaricus arorae''
*  ''Agaricus arvensis'' – horse mushroom
*
''Agaricus arvensis'' – horse mushroom
*  ''Agaricus augustus'' – the prince
*
''Agaricus augustus'' – the prince
*  ''Agaricus aurantioviolaceus''
* ''Agaricus benesii''
*
''Agaricus aurantioviolaceus''
* ''Agaricus benesii''
*  ''Agaricus bernardii'' – salt-loving mushroom
*
''Agaricus bernardii'' – salt-loving mushroom
*  ''Agaricus bisporus'' – cultivated/button/portobello mushroom (includes ''A.brunnescens'')
*
''Agaricus bisporus'' – cultivated/button/portobello mushroom (includes ''A.brunnescens'')
*  ''Agaricus bitorquis'' – pavement mushroom, banded agaric
* ''Agaricus braendlei''
* ''Agaricus bresadolanus''
*
''Agaricus bitorquis'' – pavement mushroom, banded agaric
* ''Agaricus braendlei''
* ''Agaricus bresadolanus''
*  ''Agaricus brunneofibrillosus'' (formerly in ''A.fuscofibrillosus'')
*
''Agaricus brunneofibrillosus'' (formerly in ''A.fuscofibrillosus'')
*  ''Agaricus californicus'' – California agaricus
*
''Agaricus californicus'' – California agaricus
*  ''
'' ''Agaricus cupreobrunneus'' – brown field mushroom
*
''Agaricus cupreobrunneus'' – brown field mushroom
*  ''Agaricus deserticola'' G.Moreno, Esqueda & Lizárraga (2010) – gasteroid agaricus (formerly in ''Longula'')
*
''Agaricus deserticola'' G.Moreno, Esqueda & Lizárraga (2010) – gasteroid agaricus (formerly in ''Longula'')
*  ''Agaricus dulcidulus'' – rosy wood mushroom (sometimes in ''A.semotus'')
*
''Agaricus dulcidulus'' – rosy wood mushroom (sometimes in ''A.semotus'')
*  ''Agaricus excellens'' (disputed)
* ''Agaricus freirei''
*
''Agaricus excellens'' (disputed)
* ''Agaricus freirei''
*  ''Agaricus hondensis'' – felt-ringed agaricus
*
''Agaricus hondensis'' – felt-ringed agaricus
*  ''Agaricus impudicus'' – tufted wood mushroom
* ''Agaricus inapertus'' (formerly in ''Endoptychum'')
* ''Agaricus julius''
* ''Agaricus lanatoniger''
* ''Agaricus langei'' (= ''A.fuscofibrillosus'')
*
''Agaricus impudicus'' – tufted wood mushroom
* ''Agaricus inapertus'' (formerly in ''Endoptychum'')
* ''Agaricus julius''
* ''Agaricus lanatoniger''
* ''Agaricus langei'' (= ''A.fuscofibrillosus'')
*  ''Agaricus lilaceps'' – giant cypress agaricus
* ''Agaricus litoralis'' – coastal mushroom (includes ''A.spissicaulis'')
*
''Agaricus lilaceps'' – giant cypress agaricus
* ''Agaricus litoralis'' – coastal mushroom (includes ''A.spissicaulis'')
*  ''Agaricus macrosporus'' (disputed)
*
''Agaricus macrosporus'' (disputed)
*  ''Agaricus moelleri'' – inky/dark-scaled mushroom (formerly in ''A.placomyces'', includes ''A.meleagris'')
* ''Agaricus nebularum''
*
''Agaricus moelleri'' – inky/dark-scaled mushroom (formerly in ''A.placomyces'', includes ''A.meleagris'')
* ''Agaricus nebularum''
*  ''Agaricus pattersoniae''
*
''Agaricus pattersoniae''
*  ''Agaricus perobscurus'' – American princess
*
''Agaricus perobscurus'' – American princess
*  ''Agaricus phaeolepidotus''
*
''Agaricus phaeolepidotus''
*  ''Agaricus pilatianus''
*
''Agaricus pilatianus''
*  ''Agaricus placomyces'' (includes ''A.praeclaresquamosus'')
*
''Agaricus placomyces'' (includes ''A.praeclaresquamosus'')
*  ''Agaricus pocillator''
*
''Agaricus pocillator''
*  ''Agaricus santacatalinensis''
*
''Agaricus santacatalinensis''
*  ''Agaricus semotus''
*
''Agaricus semotus''
*  ''Agaricus silvaticus'' – scaly/blushing wood mushroom, pinewood mushroom (= ''A.sylvaticus'', includes ''A.haemorrhoidarius'')
*
''Agaricus silvaticus'' – scaly/blushing wood mushroom, pinewood mushroom (= ''A.sylvaticus'', includes ''A.haemorrhoidarius'')
*  ''Agaricus silvicola'' – wood mushroom (= ''A.sylvicola'')
*
''Agaricus silvicola'' – wood mushroom (= ''A.sylvicola'')
*  ''Agaricus subrufescens'' (includes ''A.rufotegulis'', often confused with ''A.blazei'' and ''A.brasiliensis'') – almond mushroom, royal sun agaricus, and various fanciful names
*
''Agaricus subrufescens'' (includes ''A.rufotegulis'', often confused with ''A.blazei'' and ''A.brasiliensis'') – almond mushroom, royal sun agaricus, and various fanciful names
*  ''Agaricus subrutilescens'' – wine-colored agaricus
* ''Agaricus taeniatus''
*
''Agaricus subrutilescens'' – wine-colored agaricus
* ''Agaricus taeniatus''
*  ''Agaricus urinascens''
*
''Agaricus urinascens''
*  ''Agaricus xanthodermus'' – yellow-staining mushroom
''Agaricus xanthodermus'' – yellow-staining mushroom
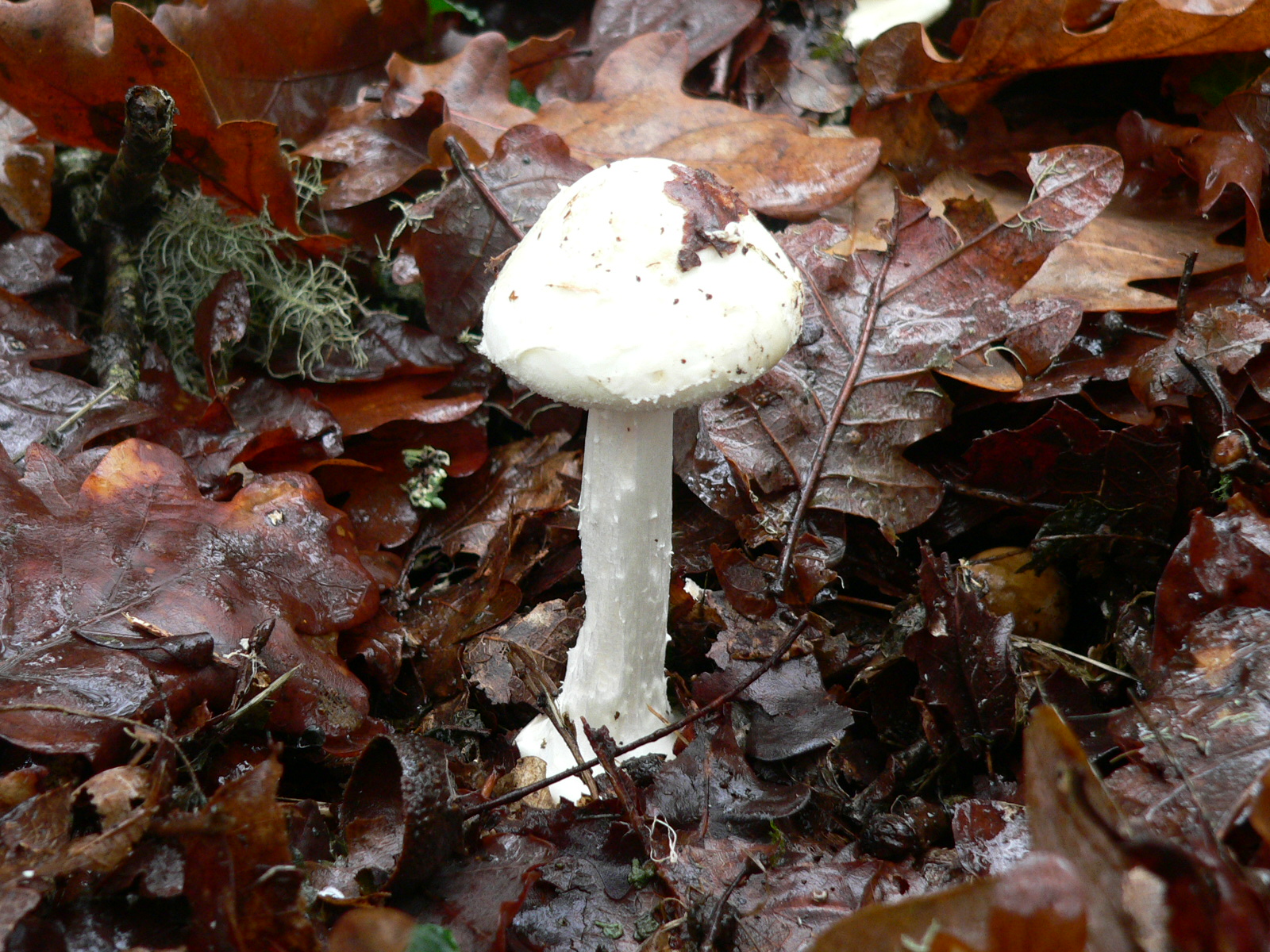 A notable group of poisonous ''Agaricus'' is the clade around the yellow-staining mushroom, ''Agaricus xanthodermus, A. xanthodermus''.
One species reported from Africa, ''Agaricus aurantioviolaceus, A. aurantioviolaceus'', is reportedly deadly poisonous.
Far more dangerous is the fact that ''Agaricus'', when still young and most valuable for eating, are easily confused with several deadly species of ''Amanita'' (in particular the species collectively called "destroying angels", as well as the white form of the appropriately-named "death cap" ''Amanita phalloides''), as well as some other highly poisonous fungi. An easy way to recognize ''Amanita'' is the gills, which remain whitish at all times in that genus. In ''Agaricus'', by contrast, the gills are only initially white, turning dull pink as they mature, and eventually the typical chocolate-brown as the spores are released.
Even so, ''Agaricus'' should generally be avoided by inexperienced collectors, since other harmful species are not as easily recognized, and clearly recognizable mature ''Agaricus'' are often too soft and maggot-infested for eating. When collecting ''Agaricus'' for food, it is important to identify every individual specimen with certainty, since one ''Amanita'' fungus of the most poisonous species is sufficient to kill an adult human – even the shed spores of a discarded specimen are suspected to cause life-threatening poisoning. Confusing poisonous ''Amanita'' with an edible ''Agaricus'' is the most frequent cause of fatal mushroom poisonings world-wide.
Reacting to some distributors marketing dried agaricus or agaricus extract to cancer patients, it has been identified by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a List of unproven and disproven cancer treatments, "fake cancer 'cure. The species most often sold as such quack cures is ''A. subrufescens'', which is often referred to by the erroneous name "Agaricus Blazei" and advertised by fanciful trade names such as "God's mushroom" or "mushroom of life", but can cause allergic reactions and even liver damage if consumed in excessive amounts.
A notable group of poisonous ''Agaricus'' is the clade around the yellow-staining mushroom, ''Agaricus xanthodermus, A. xanthodermus''.
One species reported from Africa, ''Agaricus aurantioviolaceus, A. aurantioviolaceus'', is reportedly deadly poisonous.
Far more dangerous is the fact that ''Agaricus'', when still young and most valuable for eating, are easily confused with several deadly species of ''Amanita'' (in particular the species collectively called "destroying angels", as well as the white form of the appropriately-named "death cap" ''Amanita phalloides''), as well as some other highly poisonous fungi. An easy way to recognize ''Amanita'' is the gills, which remain whitish at all times in that genus. In ''Agaricus'', by contrast, the gills are only initially white, turning dull pink as they mature, and eventually the typical chocolate-brown as the spores are released.
Even so, ''Agaricus'' should generally be avoided by inexperienced collectors, since other harmful species are not as easily recognized, and clearly recognizable mature ''Agaricus'' are often too soft and maggot-infested for eating. When collecting ''Agaricus'' for food, it is important to identify every individual specimen with certainty, since one ''Amanita'' fungus of the most poisonous species is sufficient to kill an adult human – even the shed spores of a discarded specimen are suspected to cause life-threatening poisoning. Confusing poisonous ''Amanita'' with an edible ''Agaricus'' is the most frequent cause of fatal mushroom poisonings world-wide.
Reacting to some distributors marketing dried agaricus or agaricus extract to cancer patients, it has been identified by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a List of unproven and disproven cancer treatments, "fake cancer 'cure. The species most often sold as such quack cures is ''A. subrufescens'', which is often referred to by the erroneous name "Agaricus Blazei" and advertised by fanciful trade names such as "God's mushroom" or "mushroom of life", but can cause allergic reactions and even liver damage if consumed in excessive amounts.
Mushroom Expert - The Genus Agaricus
{{Authority control Agaricus, Agaricales genera Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Taxa described in 1753
genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
of mushroom
A mushroom or toadstool is the fleshy, spore-bearing Sporocarp (fungi), fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground on soil or another food source. ''Toadstool'' generally refers to a poisonous mushroom.
The standard for the n ...
-forming fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
containing both edible
An edible item is any item that is safe for humans to eat. "Edible" is differentiated from " eatable" because it does not indicate how an item tastes, only whether it is fit to be eaten. Nonpoisonous items found in nature – such as some mushroo ...
and poisonous
A poison is any chemical substance that is harmful or lethal to living organisms. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figurati ...
species, with over 400 members worldwide and possibly again as many disputed or newly discovered species. The genus includes the common ("button") mushroom ('' A. bisporus'') and the field mushroom ('' A. campestris''), the dominant cultivated mushroom
Fungiculture is the cultivation of fungi such as mushrooms. Cultivating fungi can yield foods (which include mostly mushrooms), medicine, construction materials and other products. A ''mushroom farm'' is involved in the business of growing fun ...
s of the West.
Taxonomy
Several origins of genus name ''Agaricus'' have been proposed. It possibly originates from ancient Sarmatia Europaea, where people Agari, promontory Agarum and a river Agarus were known (all located on the northern shore ofSea of Azov
The Sea of Azov is an inland Continental shelf#Shelf seas, shelf sea in Eastern Europe connected to the Black Sea by the narrow (about ) Strait of Kerch, and sometimes regarded as a northern extension of the Black Sea. The sea is bounded by Ru ...
, probably, near modern Berdiansk
Berdiansk or Berdyansk (, ; , ) is a port city in Zaporizhzhia Oblast, south-eastern Ukraine. It is on the northern coast of the Sea of Azov, which is connected to the Black Sea. It serves as the administrative center of Berdiansk Raion. The c ...
in Ukraine).
Note also Greek , agarikón, "a sort of tree fungus" (There has been an ''Agaricon'' Adans. genus, treated by Donk in ''Persoonia'' 1:180.)
For many years, members of the genus ''Agaricus'' were given the generic name ''Psalliota'', and this can still be seen in older books on mushrooms. All proposals to conserve ''Agaricus'' against ''Psalliota'' or vice versa have so far been considered superfluous.
Dok reports Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming o ...
' name is devalidated (so the proper author citation apparently is "L. ''per'' Fr., 1821") because ''Agaricus'' was not linked to Tournefort's name. Linnaeus places both ''Agaricus'' Dill. and ''Amanita'' Dill. in synonymy, but truly a replacement for ''Amanita'' Dill., which would require ''A. quercinus'', not ''A. campestris'' be the type. This question is compounded because Elias Magnus Fries
Elias Magnus Fries (15 August 1794 – 8 February 1878) was a Swedish mycologist and botanist. He is sometimes called the Mycology, "Linnaeus of Mycology". In his works he described and assigned botanical names to hundreds of fungus and li ...
himself used ''Agaricus'' roughly in Linnaeus' sense (which leads to issues with ''Amanita''), and ''A. campestris'' was eventually excluded from ''Agaricus'' by Karsten and was apparently in ''Lepiota'' at the time Donk wrote this, commenting that a type conservation might become necessary.
The alternate name for the genus, ''Psalliota'', derived from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
''psalion''/ψάλιον, "ring", was first published by Fries (1821) as trib. ''Psalliota''. The type is ''Agaricus campestris
''Agaricus campestris'' is a widely eaten gilled mushroom closely related to the cultivated '' A. bisporus'' (button mushroom). ''A. campestris'' is commonly known as the field mushroom or, in North America, meadow mushroom.
It is ...
'' (widely accepted, except by Earle, who proposed ''A. cretaceus''). Paul Kummer
Paul Kummer (22 August 1834 – 6 December 1912) was a Minister (Christianity), minister, teacher, and scientist in Zerbst, Germany, known chiefly for his contribution to mycological botanical nomenclature, nomenclature. Earlier Taxonomy (biology), ...
(not Quélet, who merely excluded Stropharia) was the first to elevate the tribe to a genus. ''Psalliota'' was the tribe containing the type of ''Agaricus'', so when separated, it should have caused the rest of the genus to be renamed, but this is not what happened.
Phylogeny
The use ofphylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ...
analysis to determine evolutionary relationships amongst ''Agaricus'' species has increased the understanding of this taxonomically difficult genus, although much work remains to be done to fully delineate infrageneric relationships. Prior to these analyses, the genus ''Agaricus'', as circumscribed by Rolf Singer
Rolf Singer (June 23, 1906 – January 18, 1994) was a German mycologist and Taxonomy (biology), taxonomist of gilled mushrooms (agarics).
He wrote the book "The Agaricales in Modern Taxonomy (biology), Taxonomy". He fled to various countries d ...
, was divided into 42 species grouped into five sections based on reactions of mushroom tissue to air or various chemical reagents, as well as subtle differences in mushroom morphology. Restriction fragment length polymorphism
In molecular biology, restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) is a technique that exploits variations in homologous DNA sequences, known as polymorphisms, populations, or species or to pinpoint the locations of genes within a sequence. T ...
analysis demonstrated this classification scheme needed revision.
Subdivisions
As of 2018, this genus is divided into 6subgenera
In biology, a subgenus ( subgenera) is a taxonomic rank directly below genus.
In the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, a subgeneric name can be used independently or included in a species name, in parentheses, placed between the ge ...
and more than 20 sections
Section, Sectioning, or Sectioned may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* Section (music), a complete, but not independent, musical idea
* Section (typography), a subdivision, especially of a chapter, in books and documents
** Section sig ...
: Bon, Marcel (1987) ''The Mushrooms and Toadstools of Britain and North Western Europe''. Hodder and Stoughton, (paperback) (hardback)
 Subgenus ''
Subgenus ''Agaricus
''Agaricus'' is a genus of mushroom-forming fungi containing both edible and poisonous species, with over 400 members worldwide and possibly again as many disputed or newly discovered species. The genus includes the common ("button") mushroom ...
''
* Section ''Agaricus''
:This is the group around the type species
In International_Code_of_Zoological_Nomenclature, zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the spe ...
of the genus, the popular edible '' A. campestris'' which is common across the Holarctic
The Holarctic realm is a biogeographic realm that comprises the majority of habitats found throughout the continents in the Northern Hemisphere. It corresponds to the floristic Boreal Kingdom. It includes both the Nearctic zoogeographical reg ...
temperate zone
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (approximately 23.5° to 66.5° N/S of the Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ra ...
, and has been introduced to some other regions. One of the more ancient lineages of the genus, it contains species typically found in open grassland such as '' A. cupreobrunneus'', and it also includes at least one undescribed species. Their cap surface is whitish to pale reddish-brown and smooth to slightly fibrous, the flesh usually without characteristic smell, fairly soft, whitish, and remaining so after injury, application of KOH, or Schäffer's test (aniline
Aniline (From , meaning ' indigo shrub', and ''-ine'' indicating a derived substance) is an organic compound with the formula . Consisting of a phenyl group () attached to an amino group (), aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an in ...
and HNO3). '' A. annae'' may also belong here, as might '' A. porphyrocephalus'', but the flesh of the latter blushes red when bruised or cut, and it has an unpleasant smell of rotten fish when old; these traits are generally associated with subgenus ''Pseudochitonia'', in particular section ''Chitonioides''. The '' A. bresadolanus/ radicatus/ romagnesii'' group which may be one or several species is sometimes placed here, but may be quite distinct and belong to subgenus ''Spissicaules''.
 Subgenus '' Flavoagaricus''
* Section ''Arvense'' Konrad & Maubl. (sometimes named ''Arvensis'')
:Traditionally contained about 20 rather large species similar to the horse mushroom '' A. arvensis'' in six subgroups. Today, several additional species are recognized – in particular in the ''A. arvensis''
Subgenus '' Flavoagaricus''
* Section ''Arvense'' Konrad & Maubl. (sometimes named ''Arvensis'')
:Traditionally contained about 20 rather large species similar to the horse mushroom '' A. arvensis'' in six subgroups. Today, several additional species are recognized – in particular in the ''A. arvensis'' species complex
In biology, a species complex is a group of closely related organisms that are so similar in appearance and other features that the boundaries between them are often unclear. The taxa in the complex may be able to hybridize readily with each oth ...
and placed here, such as '' A. aestivalis'', '' A. augustus'', '' A. caroli'', '' A. chionodermus'', '' A. deserticola'' (formerly ''Longula texensis''), '' A. fissuratus'', '' A. inapertus'' (formerly ''Endoptychum
''Endoptychum'' is a genus of secotioid fungi in the family Agaricaceae. Like the majority of secotioid taxa, the individual species of ''Endoptychum'' are thought to be recent mutations from agaricoid species, hence, ''Endoptychum'' is likely ...
depressum''), '' A. macrocarpus'', '' A. nivescens'', '' A. osecanus'', '' A. silvicola'' and the doubtfully distinct '' A. essettei'', '' A. urinascens'', and the disputed taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
'' A. abruptibulbus'', '' A. albertii'', '' A. altipes'', '' A. albolutescens'', '' A. brunneolus'', '' A. excellens'' and '' A. macrosporus''. It also includes '' A. subrufescens'' which started to be widely grown and traded under various obsolete and newly-invented names in the early 21st century, as well as the Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
n '' A. blazei'' with which the Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
ian ''A. subrufescens'' was often confused in the past. They have versatile heterothallic
Heterothallic species have sexes that reside in different individuals. The term is applied particularly to distinguish heterothallic fungi, which require two compatible partners to produce sexual spores, from homothallic ones, which are capable ...
life cycles, are found in a variety of often rather arid
Aridity is the condition of geographical regions which make up approximately 43% of total global available land area, characterized by low annual precipitation, increased temperatures, and limited water availability.Perez-Aguilar, L. Y., Plata ...
habitats, and typically have a smooth white to scaly light brown cap. The flesh, when bruised, usually turns distinctly yellow to pinkish in particular on the cap, while the end of the stalk may remain white; a marked yellow stain is caused by applying KOH. Their sweetish smell of almond extract or marzipan
Marzipan is a confectionery, confection consisting primarily of sugar and almond meal (ground almonds), sometimes augmented with almond oil or extract.
It is often made into Confectionery, sweets; common uses are chocolate-covered marzipan and ...
due to benzaldehyde
Benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO) is an organic compound consisting of a benzene ring with a formyl substituent. It is among the simplest aromatic aldehydes and one of the most industrially useful.
It is a colorless liquid with a characteristic almond-li ...
and derived compounds distinguishes them from the section ''Xanthodermatei'', as does a bright dark-orange to brownish-red coloration in Schäffer's test. Many members of this subgenus are highly regarded as food, and even medically beneficial, but at least some are known to accumulate cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12 element, group 12, zinc and mercury (element), mercury. Like z ...
and other highly toxic chemicals from the environment, and may not always be safe to eat.

 Subgenus '' Minores''
:A group of buff-white to reddish-brown species. Often delicate and slender, the typical members of this subgenus do not resemble the larger ''Agaricus'' species at a casual glance, but have the same telltale chocolate-brown gills at spore maturity. Their flesh has a barely noticeable to pronounced sweetish smell, typically
Subgenus '' Minores''
:A group of buff-white to reddish-brown species. Often delicate and slender, the typical members of this subgenus do not resemble the larger ''Agaricus'' species at a casual glance, but have the same telltale chocolate-brown gills at spore maturity. Their flesh has a barely noticeable to pronounced sweetish smell, typically almond
The almond (''Prunus amygdalus'', Synonym (taxonomy)#Botany, syn. ''Prunus dulcis'') is a species of tree from the genus ''Prunus''. Along with the peach, it is classified in the subgenus ''Amygdalus'', distinguished from the other subgenera ...
-like, turns yellowish to brownish-red when cut or bruised at least in the lower stalk, yellow to orange with KOH, and orange to red in Schäffer's test. Species such as '' A. aridicola'' (formerly known as '' Gyrophragmium dunalii''), '' A. colpeteii'', '' A. columellatus'' (formerly ''Araneosa columellata''), '' A. diminutivus'', '' A. dulcidulus'', '' A. lamelliperditus'', '' A. luteomaculatus'', '' A. porphyrizon'', '' A. semotus'' and '' A. xantholepis'' are included here, but delimitation to and indeed distinctness from subgenus ''Flavoagaricus'' is a long-standing controversy. Unlike these however, subgenus ''Minores'' contains no choice edible species, and may even include some slightly poisonous ones; most are simply too small to make collecting them for food worthwhile, and their edibility is unknown.
* Section '' Leucocarpi''
:Includes '' A. leucocarpus''.
* Section '' Minores''
:Includes '' A. comtulus'' and '' A. huijsmanii''.
* Section '' Pantropicales''
:Includes '' A. candidolutescens'' and an undescribed relative.
Subgenus '' Minoriopsis''
:Somewhat reminiscent of subgenus ''Minores'' and like it closely related to subgenus ''Flavoagaricus'', it contains species such as '' A. martinicensis'' and '' A. rufoaurantiacus''.


 Subgenus '' Pseudochitonia''
:This highly diverse clade of mid-sized to largish species makes up much the bulk of the genus' extant diversity, and this subgenus contains numerous as of yet undescribed species. It includes both the most prized edible as well as the most notoriously poisonous ''Agaricus'', and some of its sections are in overall appearance more similar to the more distantly related ''Agaricus'' proper and ''Flavoagaricus'' than to their own closest relatives. Some species in this subgenus, such as '' A. goossensiae'' and '' A. rodmanii'', are not yet robustly assigned to one of the sections.
* Section '' Bohusia''
:Includes '' A. bohusii'' which resembles one of the dark-capped ''Flavoagaricus'' or ''Xanthodermatei'' but does not stain yellow with the standard (10%) KOH testing solution. It is a woodland species, edible when young, but when mature and easily distinguished from similar species it may be slightly poisonous. Other members of this section include '' A. crassisquamosus'', '' A. haematinus'', and '' A. pseudolangei''.
* Section '' Brunneopicti''
:A section notable for containing a considerable number of undescribed species in addition to '' A. bingensis'', '' A. brunneopictus'', '' A. brunneosquamulosus'', '' A. chiangmaiensis'', '' A. duplocingulatus'', '' A. megacystidiatus'', '' A. niveogranulatus'', '' A. sordidocarpus'', '' A. subsaharianus'', and '' A. toluenolens''.
* Section '' Chitonioides''
:Contains species such as '' A. bernardii'' and the doubtfully distinct '' A. bernardiiformis'', '' A. gennadii'', '' A. nevoi'', '' A. pequinii'', '' A. pilosporus'' and '' A. rollanii'', which strongly resemble the members of section ''Duploannulatae'' and are as widely distributed. However, their flesh tends to discolor more strongly red when bruised or cut, with the discoloration slowly getting stronger. Their smell is usually also more pronounced
Subgenus '' Pseudochitonia''
:This highly diverse clade of mid-sized to largish species makes up much the bulk of the genus' extant diversity, and this subgenus contains numerous as of yet undescribed species. It includes both the most prized edible as well as the most notoriously poisonous ''Agaricus'', and some of its sections are in overall appearance more similar to the more distantly related ''Agaricus'' proper and ''Flavoagaricus'' than to their own closest relatives. Some species in this subgenus, such as '' A. goossensiae'' and '' A. rodmanii'', are not yet robustly assigned to one of the sections.
* Section '' Bohusia''
:Includes '' A. bohusii'' which resembles one of the dark-capped ''Flavoagaricus'' or ''Xanthodermatei'' but does not stain yellow with the standard (10%) KOH testing solution. It is a woodland species, edible when young, but when mature and easily distinguished from similar species it may be slightly poisonous. Other members of this section include '' A. crassisquamosus'', '' A. haematinus'', and '' A. pseudolangei''.
* Section '' Brunneopicti''
:A section notable for containing a considerable number of undescribed species in addition to '' A. bingensis'', '' A. brunneopictus'', '' A. brunneosquamulosus'', '' A. chiangmaiensis'', '' A. duplocingulatus'', '' A. megacystidiatus'', '' A. niveogranulatus'', '' A. sordidocarpus'', '' A. subsaharianus'', and '' A. toluenolens''.
* Section '' Chitonioides''
:Contains species such as '' A. bernardii'' and the doubtfully distinct '' A. bernardiiformis'', '' A. gennadii'', '' A. nevoi'', '' A. pequinii'', '' A. pilosporus'' and '' A. rollanii'', which strongly resemble the members of section ''Duploannulatae'' and are as widely distributed. However, their flesh tends to discolor more strongly red when bruised or cut, with the discoloration slowly getting stronger. Their smell is usually also more pronounced umami
Umami ( from ), or savoriness, is one of the five basic tastes. It is characteristic of broths and cooked meats.
People taste umami through taste receptors that typically respond to glutamates and nucleotides, which are widely present in me ...
-like, in some even intensely so. Some are edible and indeed considered especially well-tasting, while the unusual '' A. maleolens'' which may also belong here has an overpowering aroma which renders it inedible except perhaps in small amounts as a vegan fish sauce
Fish sauce is a liquid condiment made from fish or krill that have been coated in salt and fermented for up to two years. It is used as a staple seasoning in East Asian cuisine and Southeast Asian cuisine, particularly Myanmar, Cambodia, L ...
substitute.
* Section '' Crassispori''
:Related to section ''Xanthodermatei'' as traditionally circumscribed, it includes such species as '' A. campestroides'', '' A. lamellidistans'', and '' A. variicystis''.
* Section '' Cymbiformes'' He, Chuankid, Hyde, Cheewangkoon & Zhao
:A section proposed in 2018, it is closely related to the traditional section ''Xanthodermatei''. The type species '' A. angusticystidiatus'' from Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
is a smallish beige ''Agaricus'' with characteristic boat-shaped basidiospore
A basidiospore is a reproductive spore produced by basidiomycete fungi, a grouping that includes mushrooms, shelf fungi, rusts, and smuts. Basidiospores typically each contain one haploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromos ...
s. It has a strong unpleasant smell like members of section ''Xanthodermatei'', but unlike these, its flesh does not change color when bruised, but turns dark reddish-brown when cut, and neither application of KOH nor Schäffer's test elicit a change in color.
* Section '' Duploannulatae'' (also known as section '' Bivelares'' or '' Hortenses'')
:Traditionally often included in section ''Agaricus'' as subsection ''Bitorques'', it seems to belong to a much younger radiation. It unites robust species, usually with a thick, almost fleshy ring, which inhabit diverse but often nutrient-rich locations. Some are well-known edibles; as they are frequently found along roads and in similar polluted places, they may not be safe to eat if collected from the wild. Their flesh is rather firm, white, with no characteristic smell, in some species turning markedly reddish when bruised or cut (though this may soon fade again), and generally changing color barely if at all after application of KOH or Schäffer's test. Based on DNA analysis of ITS1, ITS2, and 5.8S sequences, the studied species of this section could be divided into six distinct clades, four of which correspond to well-known species from the temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (approximately 23.5° to 66.5° N/S of the Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ran ...
Northern Hemisphere: '' A. bisporus'', '' A. bitorquis'' (and the doubtfully distinct '' A. edulis''), '' A. cupressicola'' and '' A. vaporarius''. The other two clades comprise the '' A. devoniensis'' (including '' A. subperonatus'') and '' A. subfloccosus'' (including '' A. agrinferus'') species complex
In biology, a species complex is a group of closely related organisms that are so similar in appearance and other features that the boundaries between them are often unclear. The taxa in the complex may be able to hybridize readily with each oth ...
es. Additional members of this section not included in that study are '' A. cappellianus'', '' A. cupressophilus'', '' A. subsubensis'', '' A. taeniatus'', '' A. tlaxcalensis'', and at least one undescribed species. The cultivated mushrooms traded as '' A. sinodeliciosus'' also belong here, though their relationship to the ''A. devoniensis'' complex and ''A. vaporarius'' is unclear.
* Section '' Flocculenti''
:Includes '' A. erectosquamosus'' and '' A. pallidobrunneus''; a more distant undescribed relative of these two may also belong in this section.
* Section '' Hondenses'' (disputed)
:Traditionally included in section ''Xanthodermatei'' ''sensu lato'', this clade may be included therein as the most basal (evolution), basal branch, or considered a section in its own right. It includes such species as ''Agaricus biannulatus, A. biannulatus'', ''Agaricus freirei, A. freirei'' and its North American relatives ''Agaricus grandiomyces, A. grandiomyces'', ''Agaricus hondensis, A. hondensis'', and probably also ''Agaricus phaeolepidotus, A. phaeolepidotus''. They are very similar to section ''Xanthodermatei'' ''sensu stricto'' in all aspects, except for a weaker discoloration tending towards reddish rather than chrome yellow when bruised.
* Section ''Nigrobrunnescentes''
:Includes ''Agaricus biberi, A. biberi'', ''Agaricus caballeroi, A. caballeroi'', ''Agaricus desjardinii, A. desjardinii'', ''Agaricus erythrosarx, A. erythrosarx'', ''Agaricus fuscovelatus, A. fuscovelatus'', ''Agaricus nigrobrunnescens, A. nigrobrunnescens'', ''Agaricus padanus, A. padanus'', ''Agaricus pattersoniae, A. pattersoniae'', and probably also ''Agaricus boisseletii, A. boisseletii''.
* Section ''Rubricosi''
:Includes ''Agaricus dolichopus, A. dolichopus'', ''Agaricus kunmingensis, A. kunmingensis'', ''Agaricus magnivelaris, A. magnivelaris'', ''Agaricus variabilicolor, A. variabilicolor'', and at least two undescribed species.
* Section ''Sanguinolenti''
:Usually found in woodland. Brownish cap with a fibrous surface, typically felt-like but sometimes scaly. The fairly soft flesh turns pink, blood-red or orange when cut or scraped, in particular the outer layer of the stalk, but does not change color after application of KOH or Schäffer's test. Some North American species traditionally placed here, such as ''Agaricus amicosus, A. amicosus'' and ''Agaricus brunneofibrillosus, A. brunneofibrillosus'', do not seem to be closely related to the section's type species ''Agaricus silvaticus, A. silvaticus'' (including ''A. haemorrhoidarius'' which is sometimes considered a distinct species), and represent at least a distinct subsection. Other species often placed in this section are ''Agaricus benesii, A. benesii'', ''Agaricus dilutibrunneus, A. dilutibrunneus'', ''Agaricus impudicus, A. impudicus'', ''Agaricus koelerionensis, A. koelerionensis'', ''Agaricus langei, A. langei'' and ''Agaricus variegans, A. variegans''; not all of these may actually belong here. They are generally (though not invariably) regarded as edible and tasty.
* Section ''Trisulphurati'' (disputed)
:Includes the ''Agaricus trisulphuratus, A. trisulphuratus'' species complex which is often placed in genus ''Cystoagaricus'', but seems to be a true ''Agaricus'' closely related to the traditional section ''Xanthodermatei''. Their stalk is typically bright yellow-orange, quite unlike that of other ''Agaricus'', as is the scaly cap. ''A. trisulphuratus'' was the type species of the obsolete polyphyletic subgenus ''Lanagaricus'', whose former species are now placed in various other sections.
* Section ''Xanthodermatei''
:As outlined by Singer in 1948, this section includes species with various characteristics similar to the type species ''Agaricus xanthodermus, A. xanthodermus''. The section forms a single clade based on analysis of ITS1+2. They are either bright white all over, or have a cap densely flecked with brownish scales or tufts of fibers. The ring is usually large but thin and veil-like. Most inhabit woodland, and in general they have a more or less pronounced unpleasant smell of phenolic compounds such as hydroquinone. As food, they should all be avoided, because even though they are occasionally reported to be eaten without ill effect, the chemicals they contain give them a acrid, metallic taste, especially when cooked, and are liable to cause severe gastrointestinal upset. Their flesh at least in the lower stalk turns pale yellow to intensely reddish-ochre when bruised or cut; more characteristic however is the a bright yellow reaction with KOH while Schäffer's test is negative. Apart from ''A. xanthodermus'', the core group of this section contains species such as ''Agaricus atrodiscus, A. atrodiscus'', ''Agaricus californicus, A. californicus'', ''Agaricus endoxanthus, A. endoxanthus'' and the doubtfully distinct ''Agaricus rotalis, A. rotalis'', ''Agaricus fuscopunctatus, A. fuscopunctatus'', ''Agaricus iodosmus, A. iodosmus'', ''Agaricus laskibarii, A. laskibarii'', ''Agaricus microvolvatulus, A. microvolvatulus'', ''Agaricus menieri, A. menieri'', ''Agaricus moelleri, A. moelleri'', ''Agaricus murinocephalus, A. murinocephalus'', ''Agaricus parvitigrinus, A. parvitigrinus'', ''Agaricus placomyces, A. placomyces'', ''Agaricus pocillator, A. pocillator'', ''Agaricus pseudopratensis, A. pseudopratensis'', ''Agaricus tibetensis, A. tibetensis'', ''Agaricus tollocanensis, A. tollocanensis'', ''Agaricus tytthocarpus, A. tytthocarpus'', ''Agaricus xanthodermulus, A. xanthodermulus'', ''Agaricus xanthosarcus, A. xanthosarcus'', as well as at least 4 undescribed species, and possibly ''Agaricus cervinifolius, A. cervinifolius'' and the doubtfully distinct ''Agaricus infidus, A. infidus''. Whether such species as ''Agaricus bisporiticus, A. bisporiticus'', ''Agaricus nigrogracilis, A. nigrogracilis'' and ''Agaricus pilatianus, A. pilatianus'' are more closely related to the mostly Eurasian core group, or to the more basal lineage here separated as section ''Hondenses'', requires clarification.
Selected species
 As late as 2008, ''Agaricus'' was believed to contain about 200 species worldwide but since then, molecular phylogenetic studies have revalidated several disputed species, as well as resolved some
As late as 2008, ''Agaricus'' was believed to contain about 200 species worldwide but since then, molecular phylogenetic studies have revalidated several disputed species, as well as resolved some species complex
In biology, a species complex is a group of closely related organisms that are so similar in appearance and other features that the boundaries between them are often unclear. The taxa in the complex may be able to hybridize readily with each oth ...
es, and aided in discovery and description of a wide range of mostly tropical species that were formerly unknown to science. As of 2020, the genus is believed to contain no fewer than 400 species, and possibly many more.
The medicinal mushroom known in Japan as Echigoshirayukidake was initially also thought to be an ''Agaricus'', either a subspecies of ''Agaricus "blazei"'' (i.e. Agaricus subrufescens, ''A. subrufescens''), or a new species. It was eventually identified as sclerotium of the crust-forming bark fungus ''Ceraceomyces tessulatus'', which is not particularly closely related to ''Agaricus''.
Several secotioid (puffball-like) fungi have in recent times be recognized as highly aberrant members of ''Agaricus'', and are now included here. These typically inhabit deserts where few fungiand even fewer of the familiar cap-and-stalk mushroom shapegrow. Another desert species, ''A. zelleri'', was erroneously placed in the present genus and is now known as ''Gyrophragmium californicum''. In addition, the scientific names ''Agaricus'' and – even more so – ''Psalliota'' were historically often used as a "wastebasket taxon" for any and all similar mushrooms, regardless of their actual relationships.
Species either confirmed or suspected to belong into this genus include:
* ''Agaricus abramsii''
*  ''Agaricus abruptibulbus'' – abruptly-bulbous agaricus, flat-bulb mushroom (disputed)
*
''Agaricus abruptibulbus'' – abruptly-bulbous agaricus, flat-bulb mushroom (disputed)
*  ''Agaricus aestivalis''
* ''Agaricus agrinferus'' (disputed)
* ''Agaricus alabamensis''
*
''Agaricus aestivalis''
* ''Agaricus agrinferus'' (disputed)
* ''Agaricus alabamensis''
*  ''Agaricus albolutescens'' (disputed)
* ''Agaricus alligator''
*
''Agaricus albolutescens'' (disputed)
* ''Agaricus alligator''
*  ''Agaricus amicosus''
* ''Agaricus angusticystidiatus''
* ''Agaricus annae''
* ''Agaricus arorae''
*
''Agaricus amicosus''
* ''Agaricus angusticystidiatus''
* ''Agaricus annae''
* ''Agaricus arorae''
*  ''Agaricus arvensis'' – horse mushroom
*
''Agaricus arvensis'' – horse mushroom
*  ''Agaricus augustus'' – the prince
*
''Agaricus augustus'' – the prince
*  ''Agaricus aurantioviolaceus''
* ''Agaricus benesii''
*
''Agaricus aurantioviolaceus''
* ''Agaricus benesii''
*  ''Agaricus bernardii'' – salt-loving mushroom
*
''Agaricus bernardii'' – salt-loving mushroom
*  ''Agaricus bisporus'' – cultivated/button/portobello mushroom (includes ''A.brunnescens'')
*
''Agaricus bisporus'' – cultivated/button/portobello mushroom (includes ''A.brunnescens'')
*  ''Agaricus bitorquis'' – pavement mushroom, banded agaric
* ''Agaricus braendlei''
* ''Agaricus bresadolanus''
*
''Agaricus bitorquis'' – pavement mushroom, banded agaric
* ''Agaricus braendlei''
* ''Agaricus bresadolanus''
*  ''Agaricus brunneofibrillosus'' (formerly in ''A.fuscofibrillosus'')
*
''Agaricus brunneofibrillosus'' (formerly in ''A.fuscofibrillosus'')
*  ''Agaricus californicus'' – California agaricus
*
''Agaricus californicus'' – California agaricus
*  ''
''Agaricus campestris
''Agaricus campestris'' is a widely eaten gilled mushroom closely related to the cultivated '' A. bisporus'' (button mushroom). ''A. campestris'' is commonly known as the field mushroom or, in North America, meadow mushroom.
It is ...
'' – field/meadow mushroom
* ''Agaricus columellatus'' (formerly in ''Araneosa'')
*  ''Agaricus cupreobrunneus'' – brown field mushroom
*
''Agaricus cupreobrunneus'' – brown field mushroom
*  ''Agaricus deserticola'' G.Moreno, Esqueda & Lizárraga (2010) – gasteroid agaricus (formerly in ''Longula'')
*
''Agaricus deserticola'' G.Moreno, Esqueda & Lizárraga (2010) – gasteroid agaricus (formerly in ''Longula'')
*  ''Agaricus dulcidulus'' – rosy wood mushroom (sometimes in ''A.semotus'')
*
''Agaricus dulcidulus'' – rosy wood mushroom (sometimes in ''A.semotus'')
*  ''Agaricus excellens'' (disputed)
* ''Agaricus freirei''
*
''Agaricus excellens'' (disputed)
* ''Agaricus freirei''
*  ''Agaricus hondensis'' – felt-ringed agaricus
*
''Agaricus hondensis'' – felt-ringed agaricus
*  ''Agaricus impudicus'' – tufted wood mushroom
* ''Agaricus inapertus'' (formerly in ''Endoptychum'')
* ''Agaricus julius''
* ''Agaricus lanatoniger''
* ''Agaricus langei'' (= ''A.fuscofibrillosus'')
*
''Agaricus impudicus'' – tufted wood mushroom
* ''Agaricus inapertus'' (formerly in ''Endoptychum'')
* ''Agaricus julius''
* ''Agaricus lanatoniger''
* ''Agaricus langei'' (= ''A.fuscofibrillosus'')
*  ''Agaricus lilaceps'' – giant cypress agaricus
* ''Agaricus litoralis'' – coastal mushroom (includes ''A.spissicaulis'')
*
''Agaricus lilaceps'' – giant cypress agaricus
* ''Agaricus litoralis'' – coastal mushroom (includes ''A.spissicaulis'')
*  ''Agaricus macrosporus'' (disputed)
*
''Agaricus macrosporus'' (disputed)
*  ''Agaricus moelleri'' – inky/dark-scaled mushroom (formerly in ''A.placomyces'', includes ''A.meleagris'')
* ''Agaricus nebularum''
*
''Agaricus moelleri'' – inky/dark-scaled mushroom (formerly in ''A.placomyces'', includes ''A.meleagris'')
* ''Agaricus nebularum''
*  ''Agaricus pattersoniae''
*
''Agaricus pattersoniae''
*  ''Agaricus perobscurus'' – American princess
*
''Agaricus perobscurus'' – American princess
*  ''Agaricus phaeolepidotus''
*
''Agaricus phaeolepidotus''
*  ''Agaricus pilatianus''
*
''Agaricus pilatianus''
*  ''Agaricus placomyces'' (includes ''A.praeclaresquamosus'')
*
''Agaricus placomyces'' (includes ''A.praeclaresquamosus'')
*  ''Agaricus pocillator''
*
''Agaricus pocillator''
*  ''Agaricus santacatalinensis''
*
''Agaricus santacatalinensis''
*  ''Agaricus semotus''
*
''Agaricus semotus''
*  ''Agaricus silvaticus'' – scaly/blushing wood mushroom, pinewood mushroom (= ''A.sylvaticus'', includes ''A.haemorrhoidarius'')
*
''Agaricus silvaticus'' – scaly/blushing wood mushroom, pinewood mushroom (= ''A.sylvaticus'', includes ''A.haemorrhoidarius'')
*  ''Agaricus silvicola'' – wood mushroom (= ''A.sylvicola'')
*
''Agaricus silvicola'' – wood mushroom (= ''A.sylvicola'')
*  ''Agaricus subrufescens'' (includes ''A.rufotegulis'', often confused with ''A.blazei'' and ''A.brasiliensis'') – almond mushroom, royal sun agaricus, and various fanciful names
*
''Agaricus subrufescens'' (includes ''A.rufotegulis'', often confused with ''A.blazei'' and ''A.brasiliensis'') – almond mushroom, royal sun agaricus, and various fanciful names
*  ''Agaricus subrutilescens'' – wine-colored agaricus
* ''Agaricus taeniatus''
*
''Agaricus subrutilescens'' – wine-colored agaricus
* ''Agaricus taeniatus''
*  ''Agaricus urinascens''
*
''Agaricus urinascens''
*  ''Agaricus xanthodermus'' – yellow-staining mushroom
''Agaricus xanthodermus'' – yellow-staining mushroom
Description
Members of ''Agaricus'' are characterized by having a fleshy cap or pileus (mycology), pileus, from the underside of which grow a number of radiating plates or gill (mushroom), gills, on which are produced the naked basidiospore, spores. They are distinguished from other members of their family, Agaricaceae, by their chocolate-brown spores. Members of ''Agaricus'' also have a stem or stipe, which elevates it above the object on which the mushroom grows, or substrate (biology), substrate, and a partial veil, which protects the developing gills and later forms a ring or annulus (mushroom), annulus on the stalk.Toxicity
 A notable group of poisonous ''Agaricus'' is the clade around the yellow-staining mushroom, ''Agaricus xanthodermus, A. xanthodermus''.
One species reported from Africa, ''Agaricus aurantioviolaceus, A. aurantioviolaceus'', is reportedly deadly poisonous.
Far more dangerous is the fact that ''Agaricus'', when still young and most valuable for eating, are easily confused with several deadly species of ''Amanita'' (in particular the species collectively called "destroying angels", as well as the white form of the appropriately-named "death cap" ''Amanita phalloides''), as well as some other highly poisonous fungi. An easy way to recognize ''Amanita'' is the gills, which remain whitish at all times in that genus. In ''Agaricus'', by contrast, the gills are only initially white, turning dull pink as they mature, and eventually the typical chocolate-brown as the spores are released.
Even so, ''Agaricus'' should generally be avoided by inexperienced collectors, since other harmful species are not as easily recognized, and clearly recognizable mature ''Agaricus'' are often too soft and maggot-infested for eating. When collecting ''Agaricus'' for food, it is important to identify every individual specimen with certainty, since one ''Amanita'' fungus of the most poisonous species is sufficient to kill an adult human – even the shed spores of a discarded specimen are suspected to cause life-threatening poisoning. Confusing poisonous ''Amanita'' with an edible ''Agaricus'' is the most frequent cause of fatal mushroom poisonings world-wide.
Reacting to some distributors marketing dried agaricus or agaricus extract to cancer patients, it has been identified by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a List of unproven and disproven cancer treatments, "fake cancer 'cure. The species most often sold as such quack cures is ''A. subrufescens'', which is often referred to by the erroneous name "Agaricus Blazei" and advertised by fanciful trade names such as "God's mushroom" or "mushroom of life", but can cause allergic reactions and even liver damage if consumed in excessive amounts.
A notable group of poisonous ''Agaricus'' is the clade around the yellow-staining mushroom, ''Agaricus xanthodermus, A. xanthodermus''.
One species reported from Africa, ''Agaricus aurantioviolaceus, A. aurantioviolaceus'', is reportedly deadly poisonous.
Far more dangerous is the fact that ''Agaricus'', when still young and most valuable for eating, are easily confused with several deadly species of ''Amanita'' (in particular the species collectively called "destroying angels", as well as the white form of the appropriately-named "death cap" ''Amanita phalloides''), as well as some other highly poisonous fungi. An easy way to recognize ''Amanita'' is the gills, which remain whitish at all times in that genus. In ''Agaricus'', by contrast, the gills are only initially white, turning dull pink as they mature, and eventually the typical chocolate-brown as the spores are released.
Even so, ''Agaricus'' should generally be avoided by inexperienced collectors, since other harmful species are not as easily recognized, and clearly recognizable mature ''Agaricus'' are often too soft and maggot-infested for eating. When collecting ''Agaricus'' for food, it is important to identify every individual specimen with certainty, since one ''Amanita'' fungus of the most poisonous species is sufficient to kill an adult human – even the shed spores of a discarded specimen are suspected to cause life-threatening poisoning. Confusing poisonous ''Amanita'' with an edible ''Agaricus'' is the most frequent cause of fatal mushroom poisonings world-wide.
Reacting to some distributors marketing dried agaricus or agaricus extract to cancer patients, it has been identified by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a List of unproven and disproven cancer treatments, "fake cancer 'cure. The species most often sold as such quack cures is ''A. subrufescens'', which is often referred to by the erroneous name "Agaricus Blazei" and advertised by fanciful trade names such as "God's mushroom" or "mushroom of life", but can cause allergic reactions and even liver damage if consumed in excessive amounts.
Uses
The genus contains the most widely consumed and best-known mushroom today, '' A. bisporus''. Other well-known and highly regarded species include ''Agaricus arvensis, A. arvensis'', '' A. augustus'', and '' A. campestris''. ''Agaricus porphyrocephalus'' is a choice edible when young, while '' A. subrufescens'' may be edible in some cases. Many other species are of culinary value, especially within sections ''Agaricus'', ''Arvense'', ''Duploannulatae'' and ''Sanguinolenti''.References
Sources
* *External links
Mushroom Expert - The Genus Agaricus
{{Authority control Agaricus, Agaricales genera Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Taxa described in 1753