Afrovenator on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Afrovenator'' (; "African hunter") is a
 The remains of ''Afrovenator'' were discovered in 1993 in the Tiourarén Formation of the department of
The remains of ''Afrovenator'' were discovered in 1993 in the Tiourarén Formation of the department of
 Judging from the one skeleton known, this dinosaur was about long, from snout to tail tip, and had a weight of about 1 tonne according to
Judging from the one skeleton known, this dinosaur was about long, from snout to tail tip, and had a weight of about 1 tonne according to
 Most analyses place ''Afrovenator'' within the
Most analyses place ''Afrovenator'' within the
genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
of megalosaurid theropod
Theropoda (; from ancient Greek , (''therion'') "wild beast"; , (''pous, podos'') "foot"">wiktionary:ποδός"> (''pous, podos'') "foot" is one of the three major groups (clades) of dinosaurs, alongside Ornithischia and Sauropodom ...
dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutio ...
from the Middle or Late Jurassic
The Late Jurassic is the third Epoch (geology), epoch of the Jurassic Period, and it spans the geologic time scale, geologic time from 161.5 ± 1.0 to 143.1 ± 0.8 million years ago (Ma), which is preserved in Upper Jurassic stratum, strata.Owen ...
Period on the Tiourarén Formation and maybe the Irhazer II Formation of the Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
region in Western Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
. ''Afrovenator'' represents the only properly identified Gondwanan megalosaur, with proposed material of the group present in the Late Jurassic on Tacuarembó Formation of Uruguay
Uruguay, officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay, is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast, while bordering the Río de la Plata to the south and the A ...
and the Tendaguru Formation
The Tendaguru Formation, or Tendaguru Beds are a highly List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Tanzania, fossiliferous Lithostratigraphy, formation and Lagerstätte located in the Lindi Region of southeastern Tanzania. The formation represe ...
of Tanzania
Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to t ...
.
Discovery and naming
 The remains of ''Afrovenator'' were discovered in 1993 in the Tiourarén Formation of the department of
The remains of ''Afrovenator'' were discovered in 1993 in the Tiourarén Formation of the department of Agadez
Agadez ( Air Tamajeq: ⴰⴶⴰⴷⴰⵣ, ''Agadaz''), formerly spelled Agadès, is the fifth largest city in Niger, with a population of 110,497 based on the 2012 census. The capital of the eponymous Agadez Region, the city lies in the Sahara ...
in Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
. The Tiourarén was originally thought to represent the Hauterivian
The Hauterivian is, in the geologic timescale, an age in the Early Cretaceous Epoch or a stage in the Lower Cretaceous Series. It spans the time between 132.6 ± 2 Ma and 125.77 (million years ago). The Hauterivian is preceded by the Valangi ...
to Barremian
The Barremian is an age in the geologic timescale (or a chronostratigraphic stage) between 125.77 Ma (million years ago) and 121.4 ± 1.0 Ma (Historically, this stage was placed at 129.4 million to approximately 125 million years ago) It is a ...
stages of the early Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
Period, or approximately 132 to 125 million years ago (Sereno et al. 1994). However, re-interpretation of the sediments showed that they are probably Middle to Late Jurassic in age, dating ''Afrovenator'' to the Bathonian
In the geologic timescale the Bathonian is an age (geology), age and stage (stratigraphy), stage of the Middle Jurassic. It lasted from approximately 168.2 ±1.2 annum, Ma to around 165.3 ±1.1 Ma (million years ago). The Bathonian Age succeeds ...
to Oxfordian stages, between 167 and 161 mya. The sauropod
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their b ...
'' Jobaria'', whose remains were first mentioned in the same paper which named ''Afrovenator'', is also known from this formation.
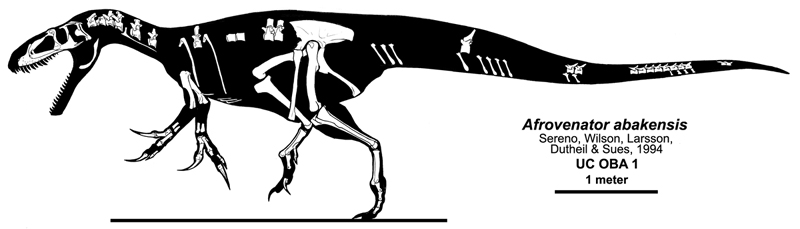
''Afrovenator'' is known from a single relatively complete skeleton, holotype
A holotype (Latin: ''holotypus'') is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of s ...
UC OBA 1, featuring most of the skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
minus its top (likewise the mandible
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla).
The jawbone i ...
, or lower jaws, are lacking apart from the prearticular bone), parts of the spinal column
The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmen ...
, partial forelimbs, a partial pelvis
The pelvis (: pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of an Anatomy, anatomical Trunk (anatomy), trunk, between the human abdomen, abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also c ...
, and most of the hind limbs. This skeleton is housed at the University of Chicago
The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, or UChi) is a Private university, private research university in Chicago, Illinois, United States. Its main campus is in the Hyde Park, Chicago, Hyde Park neighborhood on Chicago's South Side, Chic ...
.
The generic name comes from the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
''afer'', "African", and ''venator'', "hunter". There is one named species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
, ''Afrovenator abakensis''. The generic name refers to its predatory nature, and its provenance from Africa. The specific name refers to Abaka, the Tuareg
The Tuareg people (; also spelled Twareg or Touareg; endonym, depending on variety: ''Imuhaɣ'', ''Imušaɣ'', ''Imašeɣăn'' or ''Imajeɣăn'') are a large Berber ethnic group, traditionally nomadic pastoralists, who principally inhabit th ...
name for the region of Niger where the fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserve ...
was found. The original short description of both genus and species is found in a 1994 paper which appeared in the prestigious journal ''Science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
''. The primary author was well-known American paleontologist
Paleontology, also spelled as palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of the life of the past, mainly but not exclusively through the study of fossils. Paleontologists use fossils as a means to classify organisms, measure geolo ...
Paul Sereno
Paul Callistus Sereno (born October 11, 1957) is a professor of paleontology at the University of Chicago who has discovered several new dinosaur species on several continents, including at sites in Inner Mongolia, Argentina, Morocco and Niger. ...
, with Jeffrey Wilson, Hans Larsson, Didier Dutheil, and Hans-Dieter Sues
Hans-Dieter Sues (born 1956) is a German-born American palaeontologist who is a Senior Research Geologist and Curator of Vertebrate Paleontology at the National Museum of Natural History of the Smithsonian Institution in Washington, DC.
Career ...
as coauthors.
Recent discoveries in the region include referred teeth (MUPE HB-118, 125, 142) from the underliying Irhazer II Formation and TP4-12, a rostral part of left maxilla from the Tiourarén Formation at NE Tadibene. New semiarticulated specimens, including previously unknown sections of the skeleton, were also recovered from the locality of Tawachi.
Description
Gregory S. Paul
Gregory Scott Paul (born December 24, 1954) is an American freelance researcher, author and illustrator who works in paleontology. He is best known for his work and research on theropoda, theropod dinosaurs and his detailed illustrations, both l ...
. Thomas R. Holtz Jr. estimated it at in length and in weight. In 2016 it was given a lower estimation of in length, tall at the hips and in weight. Sereno stressed that the general build was gracile and that the forelimbs and the lower leg were relatively long: the humerus
The humerus (; : humeri) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius (bone), radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extrem ...
has length of forty centimetres and the tibia and fourth metatarsal measure 687 and 321 millimetres respectively, as compared to a thighbone length of seventy-six centimetres.
Several autapomorphies have been established, traits that distinguish ''Afrovenator'' from its nearest relatives. The depression in which the antorbital fenestra
An antorbital fenestra (plural: fenestrae) is an opening in the skull that is in front of the eye sockets. This skull character is largely associated with Archosauriformes, archosauriforms, first appearing during the Triassic Period. Among Extant ...
is located, has a front end in the form of a lobe. The third neck vertebra has a low rectangular spine. The crescent-shaped wrist bone is very flat. The first metacarpal has a broadly expanding contact surface with the second metacarpal. The foot of the pubic bone
In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone () forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing (ventral and anterior) of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones ar ...
is notched from behind.
In general the skull is rather flat, its height being less than three times its length, which cannot be exactly determined because the praemaxillae are lacking. The maxilla
In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxil ...
, which has a long front branch, bears fourteen teeth, as can be deduced from the tooth sockets: the teeth themselves have been lost. There is a small maxillary fenestra, which does not reach the edge of the antorbital depression and is located behind a promaxillary fenestra. The lacrimal bone
The lacrimal bones are two small and fragile bones of the facial skeleton; they are roughly the size of the little fingernail and situated at the front part of the medial wall of the orbit. They each have two surfaces and four borders. Several bon ...
has a distinctive rounded horn on top. The lower branch of the postorbital bone
The ''postorbital'' is one of the bones in vertebrate skulls which forms a portion of the dermal skull roof and, sometimes, a ring about the orbit. Generally, it is located behind the postfrontal and posteriorly to the orbital fenestra. In some ...
is transversely wide. The jugal bone
The jugal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians and birds. In mammals, the jugal is often called the malar or zygomatic bone, zygomatic. It is connected to the quadratojugal and maxilla, as well as other bones, which may vary by spe ...
is short, deep and pneumatised. The teeth wear distinctive proximodistally subrectangular distocentral denticles and a sigmoidal shape in distal view, seen also on ''Torvosaurus
''Torvosaurus'' () is a genus of large Megalosaurinae, megalosaurine Theropoda, theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 165 to 148 million years ago during the Callovian to Tithonian ages of the late Middle Jurassic, Middle and Late Jurassi ...
''. Afrovenator had a flexible, S-shaped neck and probably had well-developed neck muscles, allowing for stronger side-to-side and up-and-down movements, as well more power for feeding than ''Allosaurus
''Allosaurus'' ( ) is an extinct genus of theropod dinosaur that lived 155 to 145 million years ago during the Late Jurassic period ( Kimmeridgian to late Tithonian ages). The first fossil remains that could definitively be ascribed to th ...
'', but not as strong as ''Spinosaurus
''Spinosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of large spinosaurid theropod dinosaurs that lived in what now is North Africa during the Cenomanian faunal stage, stage of the Late Cretaceous Period (geology), period, about 100 to 94 annum, million year ...
'' & other Spinosaurids. New specimens uncovered recently have record an updated premaxillae that shows a nasal process with a less steep angle than previously thought, giving ''Afrovenator'' a slightly larger nostril.
Limb material from new specimens revelated hindlimbs shorter than the holotype, with a proportional larger tibia. Based on a new nearly complete foot, ''Afrovenator'' had better running adaptations than ''Allosaurus'' but not as good as '' Aucasaurus'', lacking some features for fast running seen in abelisaurids.
Classification
 Most analyses place ''Afrovenator'' within the
Most analyses place ''Afrovenator'' within the Megalosauridae
Megalosauridae is a monophyletic Family (taxonomy), family of Carnivore, carnivorous theropod dinosaurs within the group Megalosauroidea. Appearing in the Middle Jurassic, megalosaurids were among the first major radiation of large theropod dino ...
, which was formerly a "wastebasket family" which contained many large and hard-to-classify theropods, but has since been redefined in a meaningful way, as a sister taxon
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and ...
to the family Spinosauridae
Spinosauridae (or spinosaurids) is a clade or Family (taxonomy), family of tetanuran theropod dinosaurs comprising ten to seventeen known genera. Spinosaurid fossils have been recovered worldwide, including Africa, Europe, South America, and Asia. ...
within the Megalosauroidea.
A 2002 analysis, focused mainly on the noasaurids, found ''Afrovenator'' to be a basal megalosaurid. However, it did not include '' Dubreuillosaurus'' (formerly '' Poekilopleuron valesdunensis''), which could affect the results in that region of the cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not s ...
(Carrano ''et al''. 2002).
Other more recent and more complete cladistic analyses show ''Afrovenator'' in a group of Megalosauridae with '' Eustreptospondylus'' and ''Dubreuillosaurus''. This group is either called Megalosaurinae
Megalosauridae is a monophyletic family of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs within the group Megalosauroidea. Appearing in the Middle Jurassic, megalosaurids were among the first major radiation of large theropod dinosaurs. They were a relatively ...
(Allain 2002) or Eustreptospondylinae (Holtz ''et al''. 2004). The latter study also includes '' Piatnitzkysaurus'' in this taxon. A study by Matthew Carrano from 2012 placed ''Afrovenator'' in a megalosaurid Afrovenatorinae.
A few alternative hypotheses have been presented for ''Afrovenators relationships. In Sereno's original description, ''Afrovenator'' was found to be a basal spinosauroid (he at the time used the name " Torvosauroidea"), outside of Spinosauridae and Megalosauridae (which he called " Torvosauridae"). Finally, another recent study places ''Afrovenator'' outside of the Megalosauroidea completely, and instead finds it more closely related to ''Allosaurus
''Allosaurus'' ( ) is an extinct genus of theropod dinosaur that lived 155 to 145 million years ago during the Late Jurassic period ( Kimmeridgian to late Tithonian ages). The first fossil remains that could definitively be ascribed to th ...
'' (Rauhut 2003). This is the only study to draw this conclusion.
In a revision of Carnosauria led by the discovery of the basal Allosauroid ''Asfaltovenator
''Asfaltovenator'' (meaning "Cañadón Asfalto Formation hunter" after the fossil formation in which its fossils were found) is a genus of possibly allosauroid dinosaur from the Lower Jurassic (Middle Toarcian) Cañadón Asfalto Formation of Chubu ...
'' recovering a paraphyletic Megalosauroidea, but was later re-recovered as a monophyletic group, with ''Afrovenator'' alone, and taxa referred previously to Afrovenatorinae such as Dubreuillosaurus, Magnosaurus and Piveteausaurus clading with Eustreptospondylus.
References
Further reading
* * * Holtz, T.R., Molnar, R.E., Currie, P.J. (2004). "Basal Tetanurae". In: Weishampel, D.B., Dodson, P., & Osmolska, H. (eds.). ''The Dinosauria'' (2nd edition). Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 71–110. * Rauhut, O.W.M. (2003). ''The Interrelationships and Evolution of Basal Theropod Dinosaurs. Special Papers in Palaeontology'' 69. London: The Palaeontological Association. pp. 1–215. Megalosauridae Dinosaur genera Middle Jurassic dinosaurs Dinosaurs of Niger Fossil taxa described in 1994 Taxa named by Paul Sereno Taxa named by Hans-Dieter Sues {{interwiki extra, qid=Q131155