Adrenocortical Carcinoma on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC) is an aggressive
 Adrenal tumors are often not biopsied prior to surgery, so diagnosis is confirmed on examination of the surgical specimen by a
Adrenal tumors are often not biopsied prior to surgery, so diagnosis is confirmed on examination of the surgical specimen by a
 Differential diagnosis includes:
*
Differential diagnosis includes:
*
with an overall 5-year survival rate of about 50%. Five-year disease-free survival for a complete resection of a
cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
originating in the cortex
Cortex or cortical may refer to:
Biology
* Cortex (anatomy), the outermost layer of an organ
** Cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the vertebrate cerebrum, part of which is the ''forebrain''
*** Motor cortex, the regions of the cerebral cortex i ...
(steroid hormone
A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into two classes: corticosteroids (typically made in the adrenal cortex, hence ''cortico-'') and sex steroids (typically made in the gonads or placenta). Wit ...
-producing tissue) of the adrenal gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer adrenal corte ...
.
Adrenocortical carcinoma is remarkable for the many hormonal syndromes that can occur in patients with steroid hormone-producing ("functional") tumors, including Cushing's syndrome
Cushing's syndrome is a collection of signs and symptoms due to prolonged exposure to glucocorticoids such as cortisol. Signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure, abdominal obesity but with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, ...
, Conn syndrome
Primary aldosteronism (PA)'','' also known as primary hyperaldosteronism, refers to the excess production of the hormone aldosterone from the adrenal glands, resulting in low renin levels and high blood pressure. This abnormality is a paraneo ...
, virilization
Virilization or masculinization is the biological development of adult male characteristics in young males or females. Most of the changes of virilization are produced by androgens.
Virilization is a medical term commonly used in three medical a ...
, and feminization. Adrenocortical carcinoma has often invaded nearby tissues or metastasized to distant organs at the time of diagnosis, and the overall 5-year survival rate is about 50%.
Adrenocortical carcinoma is a rare tumor, with incidence of one to two per million population annually. It has a bimodal distribution by age, with cases clustering in children under 5 and in adults 30–40 years old. The widely used angiotensin-II-responsive steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes t ...
-producing cell line
An immortalised cell line is a population of cells from a multicellular organism that would normally not proliferate indefinitely but, due to mutation, have evaded normal cellular senescence and instead can keep undergoing division. The cells ...
H295R was originally isolated from a tumor diagnosed as adrenocortical carcinoma.
Signs and symptoms
Adrenocortical carcinoma may present differently in children and adults. Most tumors in children are functional, andvirilization
Virilization or masculinization is the biological development of adult male characteristics in young males or females. Most of the changes of virilization are produced by androgens.
Virilization is a medical term commonly used in three medical a ...
is by far the most common presenting symptom(s), followed by Cushing's syndrome
Cushing's syndrome is a collection of signs and symptoms due to prolonged exposure to glucocorticoids such as cortisol. Signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure, abdominal obesity but with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, ...
and precocious puberty
In medicine, precocious puberty is puberty occurring at an unusually early age. In most cases, the process is normal in every aspect except the unusually early age and simply represents a variation of normal development. There is early developm ...
. Among adults presenting with hormonal syndromes, Cushing's syndrome alone is most common, followed by mixed Cushing's and virilization (glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebra ...
and androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning ) is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes ...
overproduction). Feminization and Conn syndrome
Primary aldosteronism (PA)'','' also known as primary hyperaldosteronism, refers to the excess production of the hormone aldosterone from the adrenal glands, resulting in low renin levels and high blood pressure. This abnormality is a paraneo ...
(mineralocorticoid
Mineralocorticoids are a class of corticosteroids, which in turn are a class of steroid hormones. Mineralocorticoids are produced in the adrenal cortex and influence salt and water balances (electrolyte balance and fluid balance). The primary ...
excess) occur in less than 10% of cases. Rarely, pheochromocytoma
Pheochromocytoma is a rare tumor of the adrenal medulla composed of chromaffin cells and is part of the paraganglioma (PGL) family of tumors, being defined as an intra-adrenal PGL. These neuroendocrine tumors can be sympathetic, where they relea ...
-like hypersecretion of catecholamine
A catecholamine (; abbreviated CA), most typically a 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine, is a monoamine neurotransmitter, an organic compound that has a catechol (benzene with two hydroxyl side groups next to each other) and a side-chain amine.
Cate ...
s has been reported in adrenocortical cancers. Nonfunctional tumors (about 40%, authorities vary) usually present with abdominal or flank pain, varicocele, and renal vein thrombosis or they may be asymptomatic and detected incidentally.
All patients with suspected ACC should be carefully evaluated for signs and symptoms of hormonal syndromes. For Cushing's syndrome (glucocorticoid excess), these include weight gain
Weight gain is an increase in body weight. This can involve an increase in muscle mass, fat deposits, excess fluids such as water or other factors. Weight gain can be a symptom of a serious medical condition.
Description
Weight gain occurs ...
, muscle wasting, purple lines on the abdomen, a fatty " buffalo hump" on the neck, a "moon-like" face, and thinning, fragile skin. Virilism (androgen excess) is most obvious in women, and may produce excess facial and body hair, acne
Acne ( ), also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term Cutaneous condition, skin condition that occurs when Keratinocyte, dead skin cells and Sebum, oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include comedo, ...
, enlargement of the clitoris
In amniotes, the clitoris ( or ; : clitorises or clitorides) is a female sex organ. In humans, it is the vulva's most erogenous zone, erogenous area and generally the primary anatomical source of female Human sexuality, sexual pleasure. Th ...
, deepening of the voice, coarsening of facial features, cessation of menstruation. Conn syndrome (mineralcorticoid excess) is marked by high blood pressure
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms itself. It is, however, a major ri ...
, which can result in headache
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of Depression (mood), depression in those with severe ...
and hypokalemia
Hypokalemia is a low level of potassium (K+) in the blood serum. Mild low potassium does not typically cause symptoms. Symptoms may include feeling tired, leg cramps, weakness, and constipation. Low potassium also increases the risk of an a ...
(low serum potassium, which can in turn produce muscle weakness, confusion, and palpitations
Palpitations occur when a person becomes aware of their heartbeat. The heartbeat may feel hard, fast, or uneven in their chest.
Symptoms include a very fast or irregular heartbeat. Palpitations are a sensory symptom. They are often described as ...
), low plasma renin
Renin ( etymology and pronunciation), also known as an angiotensinogenase, is an aspartic protease protein and enzyme secreted by the kidneys that participates in the body's renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)—also known as the reni ...
activity, and high serum aldosterone
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays ...
. Feminization (estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
excess) is most readily noted in men, and includes breast enlargement, decreased libido
In psychology, libido (; ) is psychic drive or energy, usually conceived of as sexual in nature, but sometimes conceived of as including other forms of desire. The term ''libido'' was originally developed by Sigmund Freud, the pioneering origin ...
, and impotence
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also referred to as impotence, is a form of sexual dysfunction in males characterized by the persistent or recurring inability to achieve or maintain a Human penis, penile erection with sufficient rigidity and durat ...
.
Pathophysiology
The main etiologic factor of ACC is unknown, although families withLi–Fraumeni syndrome
Li–Fraumeni syndrome (LFS) is a rare, autosomal dominant, hereditary disorder that predisposes carriers to cancer development. It was named after two American physicians, Frederick Pei Li and Joseph F. Fraumeni Jr., who first recognized the ...
, caused by an inherited inactivation mutation in ''TP53
p53, also known as tumor protein p53, cellular tumor antigen p53 (UniProt name), or transformation-related protein 53 (TRP53) is a regulatory transcription factor protein that is often mutated in human cancers. The p53 proteins (originally thou ...
'', have increased risk. Several genes have been shown to be recurrently mutated, including ''TP53'', ''CTNNB1
Catenin beta-1, also known as β-catenin (''beta''-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
β-Catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcr ...
'', '' MEN1'', ''PRKAR1A
cAMP-dependent protein kinase type I-alpha regulatory subunit is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PRKAR1A'' gene.
Function
cAMP is a signaling molecule important for a variety of cellular functions. cAMP exerts its effects by act ...
'', '' RPL22'', and '' DAXX''. The telomerase
Telomerase, also called terminal transferase, is a ribonucleoprotein that adds a species-dependent telomere repeat sequence to the 3' end of telomeres. A telomere is a region of repetitive sequences at each end of the chromosomes of most euka ...
gene '' TERT'' is often amplified while '' ZNRF3'' and ''CDKN2A
''CDKN2A'', also known as cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A, is a gene which in humans is located at chromosome 9, band p21.3. It is ubiquitously expressed in many tissues and cell types. The gene codes for two proteins, including the INK4 f ...
'' are often homozygously deleted. The genes ''h19'', insulin-like growth factor II ( ''IGF-II''), and ''p57kip2'' are important for fetal growth and development. They are located on chromosome 11p. Expression of the ''h19'' gene is markedly reduced in both nonfunctioning and functioning adrenal cortical carcinomas, especially in tumors producing cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone in the glucocorticoid class of hormones and a stress hormone. When used as medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
Cortisol is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal corte ...
and aldosterone
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays ...
. Also, a loss occurs of activity of the ''p57kip2'' gene product in virilizing adenomas and adrenal cortical carcinomas. In contrast, ''IGF-II ''gene expression has been shown to be high in adrenal cortical carcinomas. Finally,'' c-myc ''gene expression is relatively high in neoplasms, and it is often linked to poor prognosis.
Bilateral adrenocortical tumors are less common than unilateral. The majority of bilateral tumours can be distinguished according to size and aspect of the nodules: primary pigmented nodular adrenocortical disease, which can be sporadic or part of Carney complex, and primary bilateral macro nodular adrenal hyperplasia.Metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, ...
is most commonly to the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
and lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
.
Diagnosis
Laboratory findings
Hormonal syndromes should be confirmed with laboratory testing. Laboratory findings in Cushing syndrome include increased serum glucose (blood sugar) and increased urinecortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone in the glucocorticoid class of hormones and a stress hormone. When used as medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
Cortisol is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal corte ...
. Adrenal virilism is confirmed by the finding of an excess of serum androstenedione
Androstenedione, or 4-androstenedione (abbreviated as A4 or Δ4-dione), also known as androst-4-ene-3,17-dione, is an endogenous weak androgen steroid hormone and intermediate in the biosynthesis of estrone and of testosterone from dehydroe ...
and dehydroepiandrosterone
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), also known as androstenolone, is an endogenous steroid hormone precursor. It is one of the most abundant circulating steroids in humans. DHEA is produced in the adrenal glands, the gonads, and the brain. It funct ...
. Findings in Conn syndrome include low serum potassium, low plasma renin activity, and high serum aldosterone. Feminization is confirmed with the finding of excess serum estrogen.
Imaging
Radiological studies of theabdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal ...
, such as CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
s and magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
are useful for identifying the site of the tumor, differentiating it from other diseases, such as adrenocortical adenoma
An adrenocortical adenoma or adrenal adenoma is commonly described as a benign neoplasm emerging from the cells that comprise the adrenal cortex. Like most adenomas, the adrenocortical adenoma is considered a benign tumor since the majority of th ...
, and determining the extent of invasion of the tumor into surrounding organs and tissues. On CT, it shows heterogeneous appearance due to necrosis, calcifications, and haemorrhage. After contrast injection, it shows peripheral enhancement. Invasion of adjacent structures such as kidney, vena cava, liver, and retroperitoneal lymph nodes are also common.
On MRI, it shows low intensity on T1-weighted images, and high T2 signal with strong heterogeneous contrast enhancement and slow washout. Haemorrhagic areas may show high T1-signal.
Pathology
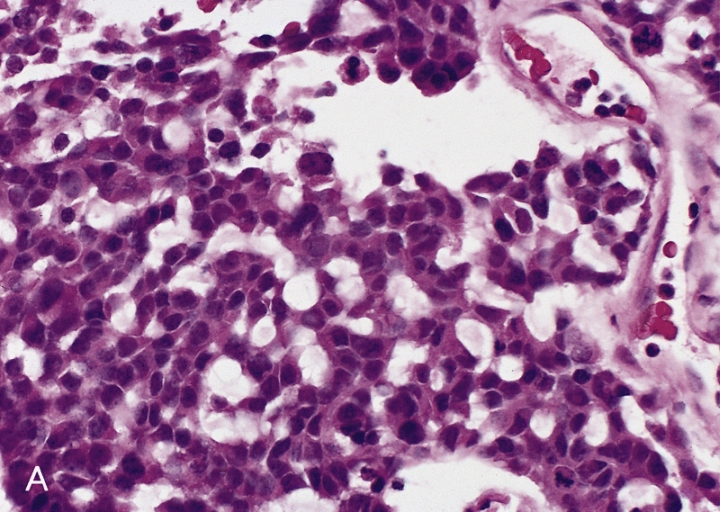
 Adrenal tumors are often not biopsied prior to surgery, so diagnosis is confirmed on examination of the surgical specimen by a
Adrenal tumors are often not biopsied prior to surgery, so diagnosis is confirmed on examination of the surgical specimen by a pathologist
Pathology is the study of disease. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatme ...
. Grossly, ACCs are often large, with a tan-yellow cut surface, and areas of hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, ...
and necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. The term "necrosis" came about in the mid-19th century and is commonly attributed to German pathologist Rudolf Virchow, who i ...
. On microscopic examination, the tumor usually displays sheets of atypical cells with some resemblance to the cells of the normal adrenal cortex
The adrenal cortex is the outer region and also the largest part of the adrenal gland. It is divided into three separate zones: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis. Each zone is responsible for producing specific hormones. I ...
. The presence of invasion
An invasion is a Offensive (military), military offensive of combatants of one geopolitics, geopolitical Legal entity, entity, usually in large numbers, entering territory (country subdivision), territory controlled by another similar entity, ...
and mitotic activity help differentiate small cancers from adrenocortical adenoma
An adrenocortical adenoma or adrenal adenoma is commonly described as a benign neoplasm emerging from the cells that comprise the adrenal cortex. Like most adenomas, the adrenocortical adenoma is considered a benign tumor since the majority of th ...
s.
Several relatively rare variants of ACC include:
* Oncocytic adrenal cortical carcinoma
* Myxoid adrenal cortical carcinoma
* Carcinosarcoma
* Adenosquamous adrenocortical carcinoma
* Clear cell adrenal cortical carcinoma
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis includes:
*
Differential diagnosis includes:
* Adrenocortical adenoma
An adrenocortical adenoma or adrenal adenoma is commonly described as a benign neoplasm emerging from the cells that comprise the adrenal cortex. Like most adenomas, the adrenocortical adenoma is considered a benign tumor since the majority of th ...
* Renal cell carcinoma
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a kidney cancer that originates in the lining of the Proximal tubule, proximal convoluted tubule, a part of the very small tubes in the kidney that transport primary urine. RCC is the most common type of kidney cance ...
* Pheochromocytoma
Pheochromocytoma is a rare tumor of the adrenal medulla composed of chromaffin cells and is part of the paraganglioma (PGL) family of tumors, being defined as an intra-adrenal PGL. These neuroendocrine tumors can be sympathetic, where they relea ...
* Hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
HCC most common ...
Adrenocortical carcinomas are most commonly distinguished from adrenocortical adenoma
An adrenocortical adenoma or adrenal adenoma is commonly described as a benign neoplasm emerging from the cells that comprise the adrenal cortex. Like most adenomas, the adrenocortical adenoma is considered a benign tumor since the majority of th ...
s (their benign counterparts) by the Weiss system, as follows:
Total score indicates:
* 0-2: Adrenocortical adenoma
* 3: Undetermined
* 4-9: Adrenocortical carcinoma
Treatment
The only curative treatment is complete surgical excision of the tumor, which can be performed even in the case of invasion into large blood vessels, such as therenal vein
The renal veins in the renal circulation, are large-calibre veins that drain blood filtered by the kidneys into the inferior vena cava. There is one renal vein draining each kidney. Each renal vein is formed by the convergence of the interlobar v ...
or inferior vena cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the ...
. The 5-year survival rate after successful surgery is 50–60%, but unfortunately, many patients are not surgical candidates. A 2018 systematic review suggests that laparoscopic retroperotenial adrenalectomy appears to reduce late morbidity, time to oral fluid or food intake and time to ambulation when compared to laparoscopic transperitoneal adrenalectomy, however there is uncertainty about these effects due to very low-quality evidence. For outcomes such as all-cause mortality, early morbidity, socioeconomic effects, and operative and postoperative parameter, the evidence is uncertain about the effects of either interventions over the other.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), ...
and radiofrequency ablation
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA), also called fulguration, is a medical procedure in which part of the electrical conduction system of the heart, tumor, sensory nerves or a dysfunctional tissue is ablated using the heat generated from medium fre ...
may be used for palliation in patients who are not surgical candidates. Minimally invasive surgical techniques remain controversial due to the absence of long-term data, with a particular concern for rates of recurrence and peritoneal carcinomatosis.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
regimens typically include the drug mitotane, an inhibitor of steroid synthesis, which is toxic to cells of the adrenal cortex
The adrenal cortex is the outer region and also the largest part of the adrenal gland. It is divided into three separate zones: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis. Each zone is responsible for producing specific hormones. I ...
, as well as standard cytotoxic drugs. A retrospective analysis showed a survival benefit for mitotane in addition to surgery when compared to surgery alone.
The two most common regimens are cisplatin
Cisplatin is a chemical compound with chemical formula, formula ''cis''-. It is a coordination complex of platinum that is used as a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of cancers. These include testicular cancer, ovarian cancer, c ...
, doxorubicin
Doxorubicin, sold under the brand name Adriamycin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. This includes breast cancer, bladder cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, lymphoma, and acute lymphocytic leukemia. It is often used toge ...
, etoposide
Etoposide, sold under the brand name Vepesid among others, is a chemotherapy medication used for the treatments of a number of types of cancer including testicular cancer, lung cancer, lymphoma, leukemia, neuroblastoma, and ovarian cancer. It is ...
(EDP) + mitotane, and streptozotocin
Streptozotocin or streptozocin ( INN, USP) (STZ) is a naturally occurring alkylating antineoplastic agent that is particularly toxic to the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas in mammals. It is used in medicine for treating certain can ...
+ mitotane. The FIRM-ACT trial demonstrated higher rates of response and longer progression-free survival with EDP + mitotane than with streptozotocin + mitotane.
Prognosis
ACC, generally, carries a poor prognosis,Free Full Textwith an overall 5-year survival rate of about 50%. Five-year disease-free survival for a complete resection of a
stage
Stage, stages, or staging may refer to:
Arts and media Acting
* Stage (theatre), a space for the performance of theatrical productions
* Theatre, a branch of the performing arts, often referred to as "the stage"
* ''The Stage'', a weekly Brit ...
I–III ACC is about 30%. The most important prognostic factors are age of the patient and stage of the tumor. Poor prognostic factors include mitotic activity, venous invasion, weight of 50 g or more, diameter of 6.5 cm or more, Ki-67/MIB1 labeling index of 4% or more, and p53 positive.
In its malignancy, adrenocortical carcinoma is unlike most tumours of the adrenal cortex, which are benign
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer.
A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malig ...
(adenoma
An adenoma is a benign tumor of epithelium, epithelial tissue with glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or both. Adenomas can grow from many glandular organ (anatomy), organs, including the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, thyroid, prosta ...
s) and only occasionally cause Cushing's syndrome
Cushing's syndrome is a collection of signs and symptoms due to prolonged exposure to glucocorticoids such as cortisol. Signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure, abdominal obesity but with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, ...
.
References
External links
{{Endocrine gland neoplasia Rare cancers Endocrine neoplasia Endocrine-related cutaneous conditions Adrenal gland disorders