Acute Radiation Poisoning on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Acute radiation syndrome (ARS), also known as radiation sickness or radiation poisoning, is a collection of health effects that are caused by being exposed to high amounts of
 Classically, ARS is divided into three main presentations:
Classically, ARS is divided into three main presentations:


 ARS is caused by exposure to a large dose of ionizing radiation (> ~0.1 Gy) over a short period of time (> ~0.1 Gy/h). Alpha and beta radiation have low penetrating power and are unlikely to affect vital internal organs from outside the body. Any type of ionizing radiation can cause burns, but alpha and beta radiation can only do so if
ARS is caused by exposure to a large dose of ionizing radiation (> ~0.1 Gy) over a short period of time (> ~0.1 Gy/h). Alpha and beta radiation have low penetrating power and are unlikely to affect vital internal organs from outside the body. Any type of ionizing radiation can cause burns, but alpha and beta radiation can only do so if
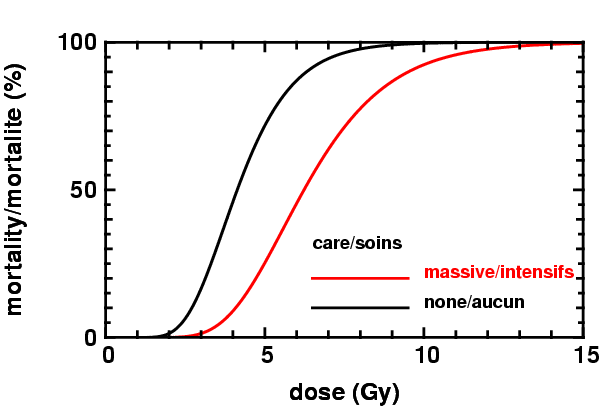 Treatment usually involves supportive care with possible symptomatic measures employed. The former involves the possible use of
Treatment usually involves supportive care with possible symptomatic measures employed. The former involves the possible use of
Health Physics Radiation Safety Journal
' article: , or in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the Nuclear Energy Agency (NEA)'s 2015 report
"Occupational Radiation Protection in Severe Accident Management"
{{DEFAULTSORT:Acute Radiation Syndrome Radioactive contamination Radiology Radiobiology Radiation health effects Medical emergencies Causes of death Effects of external causes Syndromes affecting blood Occupational hazards Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate
ionizing radiation
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including Radioactive decay, nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have enough energy per individual photon or particle to ionization, ionize atoms or molecules by detaching ...
in a short period of time. Symptoms can start within an hour of exposure, and can last for several months. Early symptoms are usually nausea, vomiting and loss of appetite. In the following hours or weeks, initial symptoms may appear to improve, before the development of additional symptoms, after which either recovery or death follows.
ARS involves a total dose of greater than 0.7 Gy (70 rad), that generally occurs from a source outside the body, delivered within a few minutes. Sources of such radiation can occur accidentally or intentionally. They may involve nuclear reactors
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction. They are used for commercial electricity, marine propulsion, weapons production and research. Fissile nuclei (primarily uranium-235 or plutonium-2 ...
, cyclotrons
A cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator invented by Ernest Lawrence in 1929–1930 at the University of California, Berkeley, and patented in 1932. Lawrence, Ernest O. ''Method and apparatus for the acceleration of ions'', filed: January ...
, certain devices used in cancer therapy
Cancer treatments are a wide range of treatments available for the many different types of cancer, with each cancer type needing its own specific treatment. Treatments can include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, targe ...
, nuclear weapons
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either nuclear fission, fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and nuclear fusion, fusion reactions (thermonuclear weap ...
, or radiological weapons
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
. It is generally divided into three types: bone marrow, gastrointestinal, and neurovascular syndrome, with bone marrow syndrome occurring at 0.7 to 10 Gy, and neurovascular syndrome occurring at doses that exceed 50 Gy. The cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
* Cellphone, a phone connected to a cellular network
* Clandestine cell, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization
* Electrochemical cell, a de ...
s that are most affected are generally those that are rapidly dividing. At high doses, this causes DNA damage that may be irreparable. Diagnosis is based on a history of exposure and symptoms. Repeated complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC) or full haemogram (FHG), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide cytometry, information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blo ...
s (CBCs) can indicate the severity of exposure.
Treatment of ARS is generally supportive care
Symptomatic treatment, supportive care, supportive therapy, or palliative treatment is any medical therapy of a disease that only affects its symptoms, not the underlying cause. It is usually aimed at reducing the signs and symptoms for the co ...
. This may include blood transfusions
Blood transfusion is the process of transferring blood products into a person's circulation intravenously. Transfusions are used for various medical conditions to replace lost components of the blood. Early transfusions used whole blood, but ...
, antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
, colony-stimulating factors
Colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) are secreted glycoproteins that bind to receptor proteins on the surfaces of committed progenitors in the bone marrow, thereby activating intracellular signaling pathways that can cause the cells to proliferate ...
, or stem cell transplant
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood, in order to replicate inside a patient and produce a ...
. Radioactive material remaining on the skin or in the stomach should be removed. If radioiodine
There are 40 known isotopes of iodine (53I) from 108I to 147I; all undergo radioactive decay except 127I, which is stable. Iodine is thus a monoisotopic element.
Its longest-lived radioactive isotope, 129I, has a half-life of 16.14 million ye ...
was inhaled or ingested, potassium iodide
Potassium iodide is a chemical compound, medication, and dietary supplement. It is a medication used for treating hyperthyroidism, in radiation emergencies, and for protecting the thyroid gland when certain types of radiopharmaceuticals are u ...
is recommended. Complications such as leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia; pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and produce high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or '' ...
and other cancers
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
among those who survive are managed as usual. Short-term outcomes depend on the dose exposure.
ARS is generally rare. A single event can affect a large number of people, as happened in the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
On 6 and 9 August 1945, the United States detonated two atomic bombs over the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, respectively, during World War II. The aerial bombings killed between 150,000 and 246,000 people, most of whom were civili ...
and the Chernobyl nuclear power plant disaster. ARS differs from chronic radiation syndrome
Chronic radiation syndrome (CRS), or chronic radiation enteritis, is a constellation of health effects of radiation that occur after months or years of chronic exposure to high amounts of radiation. Chronic radiation syndrome develops with a speed ...
, which occurs following prolonged exposures to relatively low doses of radiation.
Signs and symptoms
 Classically, ARS is divided into three main presentations:
Classically, ARS is divided into three main presentations: hematopoietic
Haematopoiesis (; ; also hematopoiesis in American English, sometimes h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells. In a healthy adult human, roughly ten ...
, gastrointestinal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. ...
, and neurovascular Vascular can refer to:
* blood vessels, the vascular system in animals
* vascular tissue
Vascular tissue is a complex transporting tissue, formed of more than one cell type, found in vascular plants. The primary components of vascular tissue ...
. These syndromes may be preceded by a prodrome
In medicine, a prodrome is an early sign or symptom (or set of signs and symptoms, referred to as prodromal symptoms) that often indicates the onset of a disease before more diagnostically specific signs and symptoms develop. More specifically, it ...
. The speed of symptom onset is related to radiation exposure, with greater doses resulting in a shorter delay in symptom onset. These presentations presume whole-body exposure, and many of them are markers that are invalid if the entire body has not been exposed. Each syndrome requires that the tissue showing the syndrome itself be exposed (e.g., gastrointestinal syndrome is not seen if the stomach and intestines are not exposed to radiation). Some areas affected are:
# Hematopoietic. This syndrome is marked by a drop in the number of blood cells
A blood cell (also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte) is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), ...
, called aplastic anemia
Aplastic anemia (AA) is a severe hematologic condition in which the body fails to make blood cells in sufficient numbers.
Normally, blood cells are produced in the bone marrow by stem cells that reside there, but patients with aplastic anemia ...
. This may result in infections, due to a low number of white blood cells
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are genera ...
, bleeding, due to a lack of platelets
Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cyto ...
, and anemia
Anemia (also spelt anaemia in British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin availabl ...
, due to too few red blood cells
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cel ...
in circulation. These changes can be detected by blood tests after receiving a whole-body acute dose as low as , though they might never be felt by the patient if the dose is below . Conventional trauma and burns resulting from a bomb blast are complicated by the poor wound healing caused by hematopoietic syndrome, increasing mortality.
# Gastrointestinal. This syndrome often follows absorbed doses of . The signs and symptoms of this form of radiation injury include nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. It can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat.
Over 30 d ...
, vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
, loss of appetite
Anorexia is a medical term for a loss of appetite. While the term outside of the scientific literature is often used interchangeably with anorexia nervosa, many possible causes exist for a loss of appetite, some of which may be harmless, while o ...
, and abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues. Since the abdomen contains most of the body's vital organs, it can be an indicator of a wide variety of diseases. Given th ...
. Vomiting in this time-frame is a marker for whole body exposures that are in the fatal range above . Without exotic treatment such as bone marrow transplant
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood, in order to replicate inside a patient and produce a ...
, death with this dose is common, due generally more to infection than gastrointestinal dysfunction.
# Neurovascular. This syndrome typically occurs at absorbed doses greater than , though it may occur at doses as low as . It presents with neurological symptoms such as dizziness
Dizziness is an imprecise term that can refer to a sense of disorientation in space, vertigo, or lightheadedness. It can also refer to Balance disorder, disequilibrium or a non-specific feeling, such as giddiness or foolishness.
Dizziness is a ...
, headache
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of Depression (mood), depression in those with severe ...
, or decreased level of consciousness
An altered level of consciousness is any measure of arousal other than normal. Level of consciousness (LOC) is a measurement of a person's arousability and responsiveness to stimuli from the environment.
A mildly depressed level of consciousn ...
, occurring within minutes to a few hours, with an absence of vomiting, and is almost always fatal, even with aggressive intensive care.
Early symptoms of ARS typically include nausea, vomiting, headaches, fatigue, fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
, and a short period of skin reddening. These symptoms may occur at radiation doses as low as . These symptoms are common to many illnesses, and may not, by themselves, indicate acute radiation sickness.
Dose effects
A similar table and description of symptoms (given in rems, where 100 rem = 1 Sv), derived from data from the effects on humans subjected to theatomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
On 6 and 9 August 1945, the United States detonated two atomic bombs over the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, respectively, during World War II. The aerial bombings killed between 150,000 and 246,000 people, most of whom were civili ...
, the indigenous peoples of the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands, officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands, is an island country west of the International Date Line and north of the equator in the Micronesia region of the Northwestern Pacific Ocean.
The territory consists of 29 c ...
subjected to the Castle Bravo
Castle Bravo was the first in a series of high-yield thermonuclear weapon design tests conducted by the United States at Bikini Atoll, Marshall Islands, as part of ''Operation Castle''. Detonated on 1 March 1954, the device remains the most powe ...
thermonuclear bomb, animal studies and lab experiment accidents, have been compiled by the U.S. Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and supervising the six U.S. armed services: the Army, Navy, Marines, Air Force, Space Force, t ...
.
A person who was less than from the atomic bomb ''Little Boy
Little Boy was a type of atomic bomb created by the Manhattan Project during World War II. The name is also often used to describe the specific bomb (L-11) used in the bombing of the Japanese city of Hiroshima by the Boeing B-29 Superfortress ...
'' hypocenter
A hypocenter or hypocentre (), also called ground zero or surface zero, is the point on the Earth's surface directly below a nuclear explosion, meteor air burst, or other mid-air explosion. In seismology, the hypocenter of an earthquake is its ...
at Hiroshima, Japan, was found to have absorbed about 9.46 grays (Gy) of ionizing radiation. The doses at the hypocenters of the Hiroshima and Nagasaki atomic bombings were 240 and 290 Gy, respectively.
Skin changes

Cutaneous radiation syndrome
Acute radiation syndrome (ARS), also known as radiation sickness or radiation poisoning, is a collection of health effects that are caused by being exposed to high amounts of ionizing radiation in a short period of time. Symptoms can start wit ...
(CRS) refers to the skin symptoms of radiation exposure. Within a few hours after irradiation, a transient and inconsistent redness (associated with itch
An itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes a strong desire or reflex to scratch. Itches have resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itches have many similarities to pain, and while both ...
ing) can occur. Then, a latent phase may occur and last from a few days up to several weeks, when intense reddening, blister
A blister is a small pocket of body fluid (lymph, serum, plasma, blood, or pus) within the upper layers of the skin, usually caused by forceful rubbing (friction), burning, freezing, chemical exposure or infection. Most blisters are filled ...
ing, and ulceration
An ulcer is a discontinuity or break in a bodily membrane that impedes normal function of the affected Organ (biology), organ. According to Robbins's pathology, "ulcer is the breach of the continuity of skin, epithelium or mucous membrane caus ...
of the irradiated site is visible. In most cases, healing occurs by regenerative means; however, very large skin doses can cause permanent hair loss, damaged sebaceous
A sebaceous gland or oil gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in t ...
and sweat gland
Sweat glands, also known as sudoriferous or sudoriparous glands, , are small tubular structures of the skin that produce sweat. Sweat glands are a type of exocrine gland, which are glands that produce and secrete substances onto an epithelial s ...
s, atrophy
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), malnutrition, poor nourishment, poor circulatory system, circulation, loss of hormone, ...
, fibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is the development of fibrous connective tissue in response to an injury. Fibrosis can be a normal connective tissue deposition or excessive tissue deposition caused by a disease.
Repeated injuries, ch ...
(mostly keloids
Keloid, also known as keloid disorder and keloidal scar, is the formation of a type of scar which, depending on its maturity, is composed mainly of either type III (early) or type I (late) collagen. It is a result of an overgrowth of granulation t ...
), decreased or increased skin pigmentation, and ulceration or necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. The term "necrosis" came about in the mid-19th century and is commonly attributed to German pathologist Rudolf Virchow, who i ...
of the exposed tissue.
As seen at Chernobyl
Chernobyl, officially called Chornobyl, is a partially abandoned city in Vyshhorod Raion, Kyiv Oblast, Ukraine. It is located within the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone, to the north of Kyiv and to the southwest of Gomel in neighbouring Belarus. ...
, when skin is irradiated with high energy beta particles
A beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation (symbol β), is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus, known as beta decay. There are two forms of beta decay, β− decay and � ...
, moist desquamation
Desquamation, or peeling skin, is the shedding of dead cells from the outermost layer of skin.
The term is .
Physiologic desquamation
Keratinocytes are the predominant cells of the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Living keratin ...
(peeling of skin) and similar early effects can heal, only to be followed by the collapse of the dermal vascular system after two months, resulting in the loss of the full thickness of the exposed skin. Another example of skin loss caused by high-level exposure of radiation is during the 1999 Tokaimura nuclear accident, where technician Hisashi Ouchi had lost a majority of his skin due to the high amounts of radiation he absorbed during the irradiation. This effect had been demonstrated previously with pig skin using high energy beta sources at the Churchill Hospital Research Institute, in Oxford
Oxford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and non-metropolitan district in Oxfordshire, England, of which it is the county town.
The city is home to the University of Oxford, the List of oldest universities in continuou ...
.
Cause

 ARS is caused by exposure to a large dose of ionizing radiation (> ~0.1 Gy) over a short period of time (> ~0.1 Gy/h). Alpha and beta radiation have low penetrating power and are unlikely to affect vital internal organs from outside the body. Any type of ionizing radiation can cause burns, but alpha and beta radiation can only do so if
ARS is caused by exposure to a large dose of ionizing radiation (> ~0.1 Gy) over a short period of time (> ~0.1 Gy/h). Alpha and beta radiation have low penetrating power and are unlikely to affect vital internal organs from outside the body. Any type of ionizing radiation can cause burns, but alpha and beta radiation can only do so if radioactive contamination
Radioactive contamination, also called radiological pollution, is the deposition of, or presence of Radioactive decay, radioactive substances on surfaces or within solids, liquids, or gases (including the human body), where their presence is uni ...
or nuclear fallout
Nuclear fallout is residual radioactive material that is created by the reactions producing a nuclear explosion. It is initially present in the mushroom cloud, radioactive cloud created by the explosion, and "falls out" of the cloud as it is ...
is deposited on the individual's skin or clothing.
Gamma and neutron radiation can travel much greater distances and penetrate the body easily, so whole-body irradiation generally causes ARS before skin effects are evident. Local gamma irradiation can cause skin effects without any sickness. In the early twentieth century, radiographers would commonly calibrate their machines by irradiating their own hands and measuring the time to onset of erythema
Erythema (, ) is redness of the skin or mucous membranes, caused by hyperemia (increased blood flow) in superficial capillaries. It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation. Examples of erythema not associated with pathology inc ...
.
Accidental
Accidental exposure may be the result of a criticality orradiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignant cells. It is normally delivered by a linear particle ...
accident. There have been numerous criticality accidents dating back to atomic testing
Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine the performance of nuclear weapons and the effects of their explosion. Nuclear testing is a sensitive political issue. Governments have often performed tests to signal strength. Bec ...
during World War II, while computer-controlled radiation therapy machines such as Therac-25
The Therac-25 is a computer-controlled radiation therapy machine produced by Atomic Energy of Canada Limited (AECL) in 1982 after the Therac-6 and Therac-20 units (the earlier units had been produced in partnership with of France).
The Therac-25 ...
played a major part in radiotherapy accidents. The latter of the two is caused by the failure of equipment software used to monitor the radiational dose given. Human error has played a large part in accidental exposure incidents, including some of the criticality accidents, and larger scale events such as the Chernobyl disaster
On 26 April 1986, the no. 4 reactor of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, located near Pripyat, Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian SSR, Soviet Union (now Ukraine), exploded. With dozens of direct casualties, it is one of only ...
. Other events have to do with orphan source An orphan source is a self-contained radioactive source that is no longer under regulatory control.
The United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission definition is:
...a sealed source of radioactive material contained in a small volume—but not ra ...
s, in which radioactive material is unknowingly kept, sold, or stolen. The Goiânia accident
The Goiânia accident was a radioactive contamination accident that occurred on September 13, 1987, in Goiânia, Goiás, Brazil, after an unsecured radiation therapy, radiotherapy source was stolen from an abandoned hospital site in the city. ...
is an example, where a forgotten radioactive source was taken from a hospital, resulting in the deaths of 4 people from ARS. Theft and attempted theft of radioactive material by clueless thieves has also led to lethal exposure in at least one incident.
Exposure may also come from routine spaceflight and solar flare
A solar flare is a relatively intense, localized emission of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and ot ...
s that result in radiation effects on earth in the form of solar storm
A solar storm is a disturbance on the Sun, which can emanate outward across the heliosphere, affecting the entire Solar System, including Earth and its magnetosphere, and is the cause of space weather in the short-term with long-term patterns compr ...
s. During spaceflight, astronauts are exposed to both galactic cosmic radiation
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Sola ...
(GCR) and solar particle event
In solar physics, a solar particle event (SPE), also known as a solar energetic particle event or solar radiation storm, is a solar phenomenon which occurs when particles emitted by the Sun, mostly protons, become accelerated either in the Sun's ...
(SPE) radiation. The exposure particularly occurs during flights beyond low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an geocentric orbit, orbit around Earth with a orbital period, period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an orbital eccentricity, eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial object ...
(LEO). Evidence indicates past SPE radiation levels that would have been lethal for unprotected astronauts. GCR levels that might lead to acute radiation poisoning are less well understood. The latter cause is rarer, with an event possibly occurring during the solar storm of 1859
The Carrington Event was the most intense geomagnetic storm in recorded history, peaking on 1–2 September 1859 during solar cycle 10. It created strong auroral displays that were reported globally and caused sparking and even fires in telegr ...
.
Intentional
Intentional exposure is controversial as it involves the use ofnuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear exp ...
s, human experiments
''Human Experiments'' (also known as ''Beyond the Gate'') is a 1979 American horror film directed and co-produced by Gregory Goodell. It stars Linda Haynes, Geoffrey Lewis, Ellen Travolta, Aldo Ray,
Jackie Coogan and Lurene Tuttle. This film e ...
, or is given to a victim in an act of murder. The intentional atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki resulted in tens of thousands of casualties; the survivors of these bombings are known today as . Nuclear weapons emit large amounts of thermal radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted by the thermal motion of particles in matter. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. The emission of energy arises from a combination of electro ...
as visible, infrared, and ultraviolet light, to which the atmosphere is largely transparent. This event is also known as "flash", where radiant heat and light are bombarded into any given victim's exposed skin, causing radiation burns. Death is highly likely, and radiation poisoning is almost certain if one is caught in the open with no terrain or building masking-effects within a radius of 0–3 km from a 1 megaton airburst. The 50% chance of death from the blast extends out to ~8 km from a 1 megaton atmospheric explosion.
Scientific testing on humans within the United States occurred extensively throughout the atomic age. Experiments took place on a range of subjects including, but not limited to; the disabled, children, soldiers, and incarcerated persons, with the level of understanding and consent given by subjects varying from complete to none. Since 1997 there have been requirements for patients to give informed consent, and to be notified if experiments were classified. The human experiments that fall under intentional ARS exclude those that involved long term exposure. Criminal activity has involved murder and attempted murder carried out through abrupt victim contact with a radioactive substance such as polonium
Polonium is a chemical element; it has symbol Po and atomic number 84. A rare and highly radioactive metal (although sometimes classified as a metalloid) with no stable isotopes, polonium is a chalcogen and chemically similar to selenium and tel ...
or plutonium
Plutonium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is a silvery-gray actinide metal that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four ...
.
Pathophysiology
The most commonly used predictor of ARS is the whole-bodyabsorbed dose
Absorbed dose is a dose quantity which represents the specific energy (energy per unit mass) deposited by ionizing radiation in living matter. Absorbed dose is used in the calculation of dose uptake in living tissue in both radiation protecti ...
. Several related quantities, such as the equivalent dose
Equivalent dose (symbol ''H'') is a dose quantity representing the stochastic health effects of low levels of ionizing radiation on the human body which represents the probability of radiation-induced cancer and genetic damage. It is derived fro ...
, effective dose, and committed dose
The committed dose in radiological protection is a measure of the stochastic health risk due to an intake of radioactive material into the human body. Stochastic in this context is defined as the ''probability'' of cancer induction and genetic dam ...
, are used to gauge long-term stochastic biological effects such as cancer incidence, but they are not designed to evaluate ARS. To help avoid confusion between these quantities, absorbed dose is measured in units of grays (in SI, unit symbol ''Gy'') or rad (in CGS), while the others are measured in sieverts (in SI, unit symbol ''Sv'') or rem (in CGS). 1 rad = 0.01 Gy and 1 rem = 0.01 Sv.
In most of the acute exposure scenarios that lead to radiation sickness, the bulk of the radiation is external whole-body gamma, in which case the absorbed, equivalent, and effective doses are all equal. There are exceptions, such as the Therac-25 accidents and the 1958 Cecil Kelley criticality accident
A criticality accident occurred on December 30, 1958, at Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) in Los Alamos, New Mexico, in the United States. It is one of 60 known criticality events that have occurred globally outside the controlled conditions ...
, where the absorbed doses in Gy or rad are the only useful quantities, because of the targeted nature of the exposure to the body.
Radiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignant cells. It is normally delivered by a linear particle ...
treatments are typically prescribed in terms of the local absorbed dose, which might be 60 Gy or higher. The dose is fractionated to about 2 Gy per day for ''curative'' treatment, which allows normal tissues to undergo repair
The technical meaning of maintenance involves functional checks, servicing, repairing or replacing of necessary devices, equipment, machinery, building infrastructure and supporting utilities in industrial, business, and residential installat ...
, allowing them to tolerate a higher dose than would otherwise be expected. The dose to the targeted tissue mass must be averaged over the entire body mass, most of which receives negligible radiation, to arrive at a whole-body absorbed dose that can be compared to the table above.
DNA damage
Exposure to high doses of radiation causesDNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
damage, later creating serious and even lethal chromosomal aberrations
A chromosomal abnormality, chromosomal anomaly, chromosomal aberration, chromosomal mutation, or chromosomal disorder is a missing, extra, or irregular portion of Chromosome, chromosomal DNA. These can occur in the form of numerical abnormalities ...
if left unrepaired. Ionizing radiation can produce reactive oxygen species
In chemistry and biology, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (), water, and hydrogen peroxide. Some prominent ROS are hydroperoxide (H2O2), superoxide (O2−), hydroxyl ...
, and does directly damage cells by causing localized ionization events. The former is very damaging to DNA, while the latter events create clusters of DNA damage. This damage includes loss of nucleobases
Nucleotide bases (also nucleobases, nitrogenous bases) are nitrogen-containing biological compounds that form nucleosides, which, in turn, are components of nucleotides, with all of these monomers constituting the basic building blocks of nuc ...
and breakage of the sugar-phosphate backbone that binds to the nucleobases. The DNA organization at the level of histones
In biology, histones are highly Base (chemistry), basic proteins abundant in lysine and arginine residues that are found in eukaryotic cell nuclei and in most Archaea, Archaeal Phylum, phyla. They act as spools around which DNA winds to create st ...
, nucleosomes, and chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important r ...
also affects its susceptibility to radiation damage
Radiation damage is the effect of ionizing radiation on physical objects including non-living structural materials. It can be either detrimental or beneficial for materials.
Radiobiology is the study of the action of ionizing radiation on living ...
. Clustered damage, defined as at least two lesions within a helical turn, is especially harmful. While DNA damage happens frequently and naturally in the cell from endogenous sources, clustered damage is a unique effect of radiation exposure. Clustered damage takes longer to repair than isolated breakages, and is less likely to be repaired at all. Larger radiation doses are more prone to cause tighter clustering of damage, and closely localized damage is increasingly less likely to be repaired.
Somatic mutations cannot be passed down from parent to offspring, but these mutations can propagate in cell lines within an organism. Radiation damage can also cause chromosome and chromatid
A chromatid (Greek ''khrōmat-'' 'color' + ''-id'') is one half of a duplicated chromosome. Before replication, one chromosome is composed of one DNA molecule. In replication, the DNA molecule is copied, and the two molecules are known as chrom ...
aberrations, and their effects depend on in which stage of the mitotic cycle the cell is when the irradiation occurs. If the cell is in interphase
Interphase is the active portion of the cell cycle that includes the G1, S, and G2 phases, where the cell grows, replicates its DNA, and prepares for mitosis, respectively. Interphase was formerly called the "resting phase," but the cell i ...
, while it is still a single strand of chromatin, the damage will be replicated during the S1 phase of the cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell (biology), cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA re ...
, and there will be a break on both chromosome arms; the damage then will be apparent in both daughter cells. If the irradiation occurs after replication, only one arm will bear the damage; this damage will be apparent in only one daughter cell. A damaged chromosome may cyclize, binding to another chromosome, or to itself.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is typically made based on a history of significant radiation exposure and suitable clinical findings. An absolute lymphocyte count can give a rough estimate of radiation exposure. Time from exposure to vomiting can also give estimates of exposure levels if they are less than 10 Gy (1000 rad).Prevention
A guiding principle of radiation safety is ''as low as reasonably achievable'' (ALARA). This means try to avoid exposure as much as possible and includes the three components of time, distance, and shielding.Time
The longer that humans are subjected to radiation the larger the dose will be. The advice in thenuclear war
Nuclear warfare, also known as atomic warfare, is a War, military conflict or prepared Policy, political strategy that deploys nuclear weaponry. Nuclear weapons are Weapon of mass destruction, weapons of mass destruction; in contrast to conven ...
manual entitled ''Nuclear War Survival Skills
''Nuclear War Survival Skills'' or NWSS, by Cresson Kearny, is a civil defense manual. It contains information gleaned from research performed at Oak Ridge National Laboratory during the Cold War, as well as from Kearny's extensive jungle livin ...
'' published by Cresson Kearny Cresson Henry Kearny (; – ) wrote several Survival skills, survival-related books based primarily on research performed at Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
Career
Kearny attended TMI — The Episcopal School of Texas, Texas Military Institute in t ...
in the U.S.
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous ...
was that if one needed to leave the shelter then this should be done as rapidly as possible to minimize exposure.
In chapter 12, he states that " ickly putting or dumping wastes outside is not hazardous once fallout is no longer being deposited. For example, assume the shelter is in an area of heavy fallout and the dose rate outside is 400 roentgen (R) per hour, enough to give a potentially fatal dose in about an hour to a person exposed in the open. If a person needs to be exposed for only 10 seconds to dump a bucket, in this 1/360 of an hour he will receive a dose of only about 1 R. Under war conditions, an additional 1-R dose is of little concern." In peacetime, radiation workers are taught to work as quickly as possible when performing a task that exposes them to radiation. For instance, the recovery of a radioactive source should be done as quickly as possible.
Shielding
Usually, matter attenuates radiation, so placing any mass (e.g., lead, dirt, sandbags, vehicles, water, even air) between humans and the source will reduce the radiation dose. This is not always the case, however; care should be taken when constructing shielding for a specific purpose. For example, although high atomic number materials are very effective in shieldingphoton
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can ...
s, using them to shield beta particle
A beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation (symbol β), is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus, known as beta decay. There are two forms of beta decay, β− decay and � ...
s may cause higher radiation exposure due to the production of bremsstrahlung
In particle physics, bremsstrahlung (; ; ) is electromagnetic radiation produced by the deceleration of a charged particle when deflected by another charged particle, typically an electron by an atomic nucleus. The moving particle loses kinetic ...
x-rays, and hence low atomic number materials are recommended. Also, using material with a high neutron activation
Neutron activation is the process in which neutron radiation induces radioactivity in materials, and occurs when atomic nuclei capture free neutrons, becoming heavier and entering excited states. The excited nucleus decays immediately by emi ...
cross section
Cross section may refer to:
* Cross section (geometry)
** Cross-sectional views in architecture and engineering 3D
*Cross section (geology)
* Cross section (electronics)
* Radar cross section, measure of detectability
* Cross section (physics)
**A ...
to shield neutrons will result in the shielding material itself becoming radioactive and hence more dangerous than if it were not present.
There are many types of shielding strategies that can be used to reduce the effects of radiation exposure. Internal contamination protective equipment such as respirators are used to prevent internal deposition as a result of inhalation and ingestion of radioactive material. Dermal protective equipment, which protects against external contamination, provides shielding to prevent radioactive material from being deposited on external structures. While these protective measures do provide a barrier from radioactive material deposition, they do not shield from externally penetrating gamma radiation. This leaves anyone exposed to penetrating gamma rays at high risk of ARS.
Naturally, shielding the entire body from high energy gamma radiation is optimal, but the required mass to provide adequate attenuation makes functional movement nearly impossible. In the event of a radiation catastrophe, medical and security personnel need mobile protection equipment in order to safely assist in containment, evacuation, and many other necessary public safety objectives.
Research has been done exploring the feasibility of partial body shielding, a radiation protection strategy that provides adequate attenuation to only the most radio-sensitive organs and tissues inside the body. Irreversible stem cell damage in the bone marrow is the first life-threatening effect of intense radiation exposure and therefore one of the most important bodily elements to protect. Due to the regenerative property of hematopoietic stem cell
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the stem cells that give rise to other blood cells. This process is called haematopoiesis. In vertebrates, the first definitive HSCs arise from the ventral endothelial wall of the embryonic aorta within the ...
s, it is only necessary to protect enough bone marrow to repopulate the exposed areas of the body with the shielded supply. This concept allows for the development of lightweight mobile radiation protection equipment, which provides adequate protection, deferring the onset of ARS to much higher exposure doses. One example of such equipment is the 360 gamma, a radiation protection belt that applies selective shielding to protect the bone marrow stored in the pelvic area as well as other radio sensitive organs in the abdominal region without hindering functional mobility.
Reduction of incorporation
Where radioactive contamination is present, anelastomeric respirator
Elastomeric respirators, also called reusable air-purifying respirators, seal to the face with elastomeric material, which may be a Natural rubber, natural or synthetic rubber. They are generally reusable.
Full-face versions of elastomeric respi ...
, dust mask
A dust mask is a flexible paper pad held over the nose and mouth made for protection against ''chronically'' toxic nuisance dusts, like from occupational exposure to plant dusts like hay. They are not intended to provide protection from most ai ...
, or good hygiene practices may offer protection, depending on the nature of the contaminant. Potassium iodide
Potassium iodide is a chemical compound, medication, and dietary supplement. It is a medication used for treating hyperthyroidism, in radiation emergencies, and for protecting the thyroid gland when certain types of radiopharmaceuticals are u ...
(KI) tablets can reduce the risk of cancer in some situations due to slower uptake of ambient radioiodine. Although this does not protect any organ other than the thyroid gland, their effectiveness is still highly dependent on the time of ingestion, which would protect the gland for the duration of a twenty-four-hour period. They do not prevent ARS as they provide no shielding from other environmental radionuclides.
Fractionation of dose
If an intentional dose is broken up into a number of smaller doses, with time allowed for recovery between irradiations, the same total dose causes lesscell death
Cell death is the event of a biological cell ceasing to carry out its functions. This may be the result of the natural process of old cells dying and being replaced by new ones, as in programmed cell death, or may result from factors such as di ...
. Even without interruptions, a reduction in dose rate below 0.1 Gy/h also tends to reduce cell death. This technique is routinely used in radiotherapy.
The human body contains many types of cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
* Cellphone, a phone connected to a cellular network
* Clandestine cell, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization
* Electrochemical cell, a de ...
s and a human can be killed by the loss of a single type of cells in a vital organ. For many short term radiation deaths (3–30 days), the loss of two important types of cells that are constantly being regenerated causes death. The loss of cells forming blood cells
A blood cell (also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte) is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), ...
(bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
) and the cells in the digestive system (microvilli
Microvilli (: microvillus) are microscopic cellular membrane protrusions that increase the surface area for diffusion and minimize any increase in volume, and are involved in a wide variety of functions, including absorption, secretion, cellula ...
, which form part of the wall of the intestines
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. ...
) is fatal.
Management
 Treatment usually involves supportive care with possible symptomatic measures employed. The former involves the possible use of
Treatment usually involves supportive care with possible symptomatic measures employed. The former involves the possible use of antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
, blood products
A blood product is any therapeutic substance prepared from blood, usually human blood; in some medicolegal contexts, the term refers specifically to human-blood-derived products. Blood products include whole blood, blood components, and blood pla ...
, colony stimulating factors, and stem cell transplant
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood, in order to replicate inside a patient and produce a ...
.
Antimicrobials
There is a direct relationship between the degree of theneutropenia
Neutropenia is an abnormally low concentration of neutrophils (a type of white blood cell) in the blood. Neutrophils make up the majority of circulating white blood cells and serve as the primary defense against infections by destroying bacteria ...
that emerges after exposure to radiation and the increased risk of developing infection. Since there are no controlled studies of therapeutic intervention in humans, most of the current recommendations are based on animal research.
The treatment of established or suspected infection following exposure to radiation (characterized by neutropenia and fever) is similar to the one used for other febrile neutropenic patients. However, important differences between the two conditions exist. Individuals that develop neutropenia after exposure to radiation are also susceptible to irradiation damage in other tissues, such as the gastrointestinal tract, lungs and central nervous system. These patients may require therapeutic interventions not needed in other types of neutropenic patients. The response of irradiated animals to antimicrobial therapy can be unpredictable, as was evident in experimental studies where metronidazole
Metronidazole, sold under the brand name Flagyl and Metrogyl among others, is an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication. It is used either alone or with other antibiotics to treat pelvic inflammatory disease, endocarditis, and bacterial vagino ...
and pefloxacin
Pefloxacin is a quinolone antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections. Pefloxacin has not been approved for use in the United States.
History
Pefloxacin was developed in 1979 and approved in France for human use in 1985.
Licensed uses
*Unc ...
therapies were detrimental.
Antimicrobials that reduce the number of the strict anaerobic
Anaerobic means "living, active, occurring, or existing in the absence of free oxygen", as opposed to aerobic which means "living, active, or occurring only in the presence of oxygen." Anaerobic may also refer to:
*Adhesive#Anaerobic, Anaerobic ad ...
component of the gut flora (i.e., metronidazole) generally should not be given because they may enhance systemic infection by aerobic or facultative bacteria, thus facilitating mortality after irradiation.
An empirical regimen of antimicrobials should be chosen based on the pattern of bacterial susceptibility and nosocomial infections
A hospital-acquired infection, also known as a nosocomial infection (from the Greek , meaning "hospital"), is an infection that is acquired in a hospital or other healthcare facility. To emphasize both hospital and nonhospital settings, it is s ...
in the affected area and medical center and the degree of neutropenia. Broad-spectrum empirical therapy (see below for choices) with high doses of one or more antibiotics should be initiated at the onset of fever. These antimicrobials should be directed at the eradication of Gram-negative aerobic bacilli (i.e., Enterobacteriaceae
Enterobacteriaceae is a large family (biology), family of Gram-negative bacteria. It includes over 30 genera and more than 100 species. Its classification above the level of Family (taxonomy), family is still a subject of debate, but one class ...
, ''Pseudomonas
''Pseudomonas'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria belonging to the family Pseudomonadaceae in the class Gammaproteobacteria. The 348 members of the genus demonstrate a great deal of metabolic diversity and consequently are able to colonize a ...
'') that account for more than three quarters of the isolates causing sepsis. Because aerobic and facultative Gram-positive bacteria (mostly alpha-hemolytic streptococci
''Streptococcus'' is a genus of gram-positive spherical bacteria that belongs to the family Streptococcaceae, within the order Lactobacillales (lactic acid bacteria), in the phylum Bacillota. Cell division in streptococci occurs along a single ...
) cause sepsis
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs.
This initial stage of sepsis is followed by suppression of the immune system. Common signs and s ...
in about a quarter of the victims, coverage for these organisms may also be needed.
A standardized management plan for people with neutropenia and fever should be devised. Empirical regimens contain antibiotics broadly active against Gram-negative aerobic bacteria (quinolones
Quinolone may refer to:
* 2-Quinolone
* 4-Quinolone
* Quinolone antibiotic
Quinolone antibiotics constitute a large group of broad-spectrum bacteriocidals that share a bicyclic core structure related to the substance 4-quinolone. They ar ...
: i.e., ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes bone and joint infections, intra-abdominal infections, certain types of infectious diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, skin ...
, levofloxacin
Levofloxacin, sold under the brand name Levaquin among others, is a broad-spectrum antibiotic of the fluoroquinolone drug class. It is the left-handed isomer of the medication ofloxacin. It is used to treat a number of bacterial infections ...
, a third- or fourth-generation cephalosporin with pseudomonal coverage: e.g., cefepime
Cefepime is a fourth-generation cephalosporin antibiotic. Cefepime has an extended spectrum of activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, with greater activity against both types of organism than third-generation agents. A 2007 ...
, ceftazidime
Ceftazidime, sold under the brand name Fortaz among others, is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. Specifically it is used for joint infections, meningitis, pneumonia, sepsi ...
, or an aminoglycoside: i.e. gentamicin
Gentamicin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic used to treat several types of bacterial infections. This may include bone infections, endocarditis, pelvic inflammatory disease, meningitis, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and sepsis amo ...
, amikacin
Amikacin is an antibiotic medication used for a number of bacterial infections. This includes joint infections, intra-abdominal infections, meningitis, pneumonia, sepsis, and urinary tract infections. It is also used for the treatment of ...
).
Prognosis
The prognosis for ARS is dependent on the exposure dose, with anything above 8 Gy being almost always lethal, even with medical care.Radiation burn
A radiation burn is a damage to the skin or other biological tissue and organs as an effect of radiation. The radiation types of greatest concern are thermal radiation, radio frequency energy, ultraviolet light and ionizing radiation.
The most ...
s from lower-level exposures usually manifest after 2 months, while reactions from the burns occur months to years after radiation treatment. Complications from ARS include an increased risk of developing radiation-induced cancer later in life. According to the controversial but commonly applied linear no-threshold model
The linear no-threshold model (LNT) is a dose-response model used in radiation protection to estimate stochastic health effects such as radiation-induced cancer, genetic mutations and teratogenic effects on the human body due to exposure to io ...
, any exposure to ionizing radiation, even at doses too low to produce any symptoms of radiation sickness, can induce cancer due to cellular and genetic damage. The probability of developing cancer is a linear function with respect to the effective radiation dose
Effective dose is a dose quantity in the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) system of radiological protection.ICRP publication, 103 para 103
It is the tissue-weighted sum of the equivalent doses in all specified tissues and ...
. Radiation cancer may occur after ionizing radiation exposure following a latent period averaging 20 to 40 years.
History
Acute effects of ionizing radiation were first observed whenWilhelm Röntgen
Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen (; 27 March 1845 – 10 February 1923), sometimes Transliteration, transliterated as Roentgen ( ), was a German physicist who produced and detected electromagnetic radiation in a wavelength range known as X-rays. As ...
intentionally subjected his fingers to X-rays in 1895. He published his observations concerning the burns that developed that eventually healed, and misattributed them to ozone. Röntgen believed the free radical
A daughter category of ''Ageing'', this category deals only with the biological aspects of ageing.
Ageing
Biogerontology
Biological processes
Causes of death
Cellular processes
Gerontology
Life extension
Metabolic disorders
Metabolism
...
produced in air by X-rays from the ozone was the cause, but other free radicals produced within the body are now understood to be more important. David Walsh first established the symptoms of radiation sickness in 1897.
Ingestion of radioactive materials caused many radiation-induced cancer
Exposure to ionizing radiation is known to increase the future incidence of cancer, particularly leukemia. The mechanism by which this occurs is well understood, but quantitative models predicting the level of risk remain controversial. The most wi ...
s in the 1930s, but no one was exposed to high enough doses at high enough rates to bring on ARS.
The atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
On 6 and 9 August 1945, the United States detonated two atomic bombs over the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, respectively, during World War II. The aerial bombings killed between 150,000 and 246,000 people, most of whom were civili ...
resulted in high acute doses of radiation to a large number of Japanese people, allowing for greater insight into its symptoms and dangers. Red Cross Hospital Surgeon Terufumi Sasaki led intensive research into the syndrome in the weeks and months following the Hiroshima and Nagasaki bombings. Sasaki and his team were able to monitor the effects of radiation in patients of varying proximities to the blast itself, leading to the establishment of three recorded stages of the syndrome. Within 25–30 days of the explosion, Sasaki noticed a sharp drop in white blood cell count and established this drop, along with symptoms of fever, as prognostic standards for ARS. Actress Midori Naka
Midori Naka (; 19 June 1909 – 24 August 1945) was a Japanese stage actress of the Shingeki style. She initially survived the atomic bombing of Hiroshima on 6 August 1945, but died 18 days later. She was the first person in the world whose de ...
, who was present during the atomic bombing of Hiroshima, was the first incident of radiation poisoning to be extensively studied. Her death on 24 August 1945 was the first death ever to be officially certified as a result of ARS (or "Atomic bomb disease").
There are two major databases that track radiation accidents: The American ORISE REAC/TS and the European IRSN ACCIRAD. REAC/TS shows 417 accidents occurring between 1944 and 2000, causing about 3000 cases of ARS, of which 127 were fatal. ACCIRAD lists 580 accidents with 180 ARS fatalities for an almost identical period. The two deliberate bombings are not included in either database, nor are any possible radiation-induced cancers from low doses. The detailed accounting is difficult because of confounding factors. ARS may be accompanied by conventional injuries such as steam burns, or may occur in someone with a pre-existing condition undergoing radiotherapy. There may be multiple causes for death, and the contribution from radiation may be unclear. Some documents may incorrectly refer to radiation-induced cancers as radiation poisoning, or may count all overexposed individuals as survivors without mentioning if they had any symptoms of ARS.
Notable cases
The following table includes only those known for their attempted survival with ARS. These cases exclude chronic radiation syndrome such as Albert Stevens, in which radiation is exposed to a given subject over a long duration. The table also necessarily excludes cases where the individual was exposed to so much radiation that death occurred before medical assistance or dose estimations could be made, such as an attempted cobalt-60 thief who reportedly died 30 minutes after exposure. The result column represents the time of exposure to the time of death attributed to the short and long term effects attributed to initial exposure. As ARS is measured by a whole-bodyabsorbed dose
Absorbed dose is a dose quantity which represents the specific energy (energy per unit mass) deposited by ionizing radiation in living matter. Absorbed dose is used in the calculation of dose uptake in living tissue in both radiation protecti ...
, the exposure column only includes units of gray (Gy).
Other animals
Thousands of scientific experiments have been performed to study ARS in animals. There is a simple guide for predicting survival and death in mammals, including humans, following the acute effects of inhaling radioactive particles.See also
* 5-Androstenediol *Biological effects of ionizing radiation
The Committee on the Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation (BEIR) is a committee of the American National Research Council. It publishes reports on the effects of ionizing radiation
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including Radioactive decay, ...
* Biological effects of radiation on the epigenome
Ionizing radiation can cause biological effects which are passed on to offspring through the epigenome. The radiobiology, effects of radiation on cells has been found to be dependent on the Radiation dose, dosage of the radiation, the location of t ...
* CBLB502
* Ex-Rad
* List of civilian nuclear accidents
This article lists notable civilian accidents involving fissile nuclear material or nuclear reactors. Military accidents are listed at List of military nuclear accidents. Civil radiation accidents not involving fissile material are listed at Li ...
* List of military nuclear accidents
This article lists notable military accidents involving nuclear material. Civilian accidents are listed at List of civilian nuclear accidents. For a general discussion of both civilian and military accidents, see nuclear and radiation accidents. F ...
* Nuclear terrorism
Nuclear terrorism is the use of a nuclear weapon or radiological weapon as an act of terrorism. There are many possible terror incidents, ranging in feasibility and scope. These include the sabotage of a nuclear facility, the intentional irrad ...
* Orders of magnitude (radiation)
Radiation Dosages
Recognized effects of higher acute radiation doses are described in more detail in the article on radiation poisoning. Although the International System of Units (SI) defines the sievert (Sv) as the unit of radiation dose eq ...
* Prehydrated electrons
* Rongelap Atoll
Rongelap Atoll ( ; , ) is an uninhabited coral atoll of 61 islands (or motus) in the Pacific Ocean, and forms a legislative district of the Ralik Chain of the Marshall Islands. Its total land area is . It encloses a lagoon with an area of . ...
References
:''This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the U.S.Armed Forces Radiobiology Research Institute
The Armed Forces Radiobiology Research Institute (AFRRI) is an American triservice research laboratory in Bethesda, Maryland chartered by Congress in 1960 and formally established in 1961. It conducts research in the field of radiobiology and r ...
and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
''
External links
* * * – A well documented account of the biological effects of a criticality accident. * * More information on bone marrow shielding can be found in theHealth Physics Radiation Safety Journal
' article: , or in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the Nuclear Energy Agency (NEA)'s 2015 report
"Occupational Radiation Protection in Severe Accident Management"
{{DEFAULTSORT:Acute Radiation Syndrome Radioactive contamination Radiology Radiobiology Radiation health effects Medical emergencies Causes of death Effects of external causes Syndromes affecting blood Occupational hazards Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate