Acetogenin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Acetogenins are a class of polyketide
Acetogenins are a class of polyketide
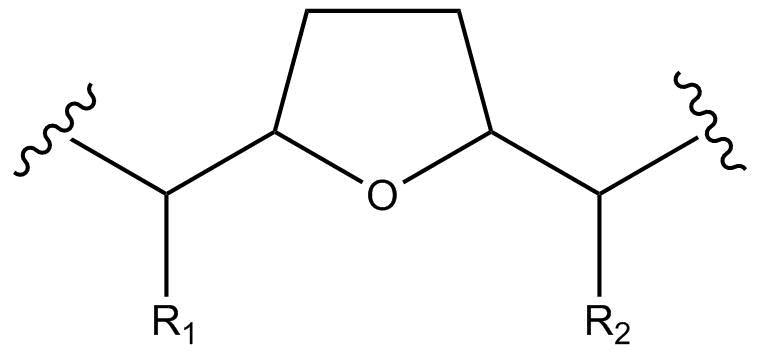
 Structurally, acetogenins are a series of C-35/C-37 compounds usually characterized by a long aliphatic chain bearing a terminal methyl-substituted α,β-unsaturated γ-lactone ring, as well as one to three tetrahydrofuran ( THF) rings. These THF rings are located along the
Structurally, acetogenins are a series of C-35/C-37 compounds usually characterized by a long aliphatic chain bearing a terminal methyl-substituted α,β-unsaturated γ-lactone ring, as well as one to three tetrahydrofuran ( THF) rings. These THF rings are located along the
natural product
A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical s ...
s found in plants of the family Annonaceae
The Annonaceae are a Family (biology), family of flowering plants consisting of trees, shrubs, or rarely lianas commonly known as the custard apple family or soursop family. With 108 accepted genera and about 2400 known species, it is the largest ...
. They are characterized by linear 32- or 34-carbon chains containing oxygenated functional groups including hydroxyls, ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure , where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group (a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone ( ...
s, epoxides, tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water- miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is ...
s and tetrahydropyrans. They are often terminated with a lactone or butenolide. Over 400 members of this family of compounds have been isolated from 51 different species of plants. Many acetogenins are characterized by neurotoxicity.
Examples include:
* Annonacin
* Annonins
* Bullatacin
* Uvaricin
Structure

 Structurally, acetogenins are a series of C-35/C-37 compounds usually characterized by a long aliphatic chain bearing a terminal methyl-substituted α,β-unsaturated γ-lactone ring, as well as one to three tetrahydrofuran ( THF) rings. These THF rings are located along the
Structurally, acetogenins are a series of C-35/C-37 compounds usually characterized by a long aliphatic chain bearing a terminal methyl-substituted α,β-unsaturated γ-lactone ring, as well as one to three tetrahydrofuran ( THF) rings. These THF rings are located along the hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and Hydrophobe, hydrophobic; their odor is usually fain ...
chain, along with a number of oxygenated moieties (hydroxyls, acetoxyls, ketones, epoxides) and/or double bonds.
Research
Acetogenins have been investigated for their biological properties, but are a concern due to neurotoxicity. Purified acetogenins and crudeextract
An extract (essence) is a substance made by extracting a part of a raw material, often by using a solvent such as ethanol, oil or water. Extracts may be sold as tinctures or absolutes or dried and powdered.
The aromatic principles of ma ...
s of the common North American pawpaw ('' Asimina triloba'') or the soursop (''Annona muricata
Soursop (also called graviola, guyabano, and in Latin America ) is the fruit of ''Annona muricata'', a broadleaf, flowering, evergreen tree. It is native to the tropical regions of the Americas and the Caribbean and is widely propagated. It ...
'') remain under laboratory studies.
Mechanism of action
Acetogenins inhibitNADH dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase is an enzyme that converts nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) from its reduced form (NADH) to its oxidized form (NAD+). Members of the NADH dehydrogenase family and analogues are commonly systematically named using the f ...
, a key enzyme in energy metabolism.
References
External links
* {{commons category-inline Fatty alcohols Polyketides NADH dehydrogenase inhibitors Plant toxins