|
Polyketide
In organic chemistry, polyketides are a class of natural products derived from a Precursor (chemistry), precursor molecule consisting of a Polymer backbone, chain of alternating ketone (, or Carbonyl reduction, its reduced forms) and Methylene group, methylene () groups: . First studied in the early 20th century, discovery, biosynthesis, and application of polyketides has evolved. It is a large and diverse group of secondary metabolites caused by its complex biosynthesis which resembles that of fatty acid synthesis. Because of this diversity, polyketides can have various medicinal, agricultural, and industrial applications. Many polyketides are medicinal or exhibit acute toxicity. Biotechnology has enabled discovery of more naturally-occurring polyketides and evolution of new polyketides with novel or improved bioactivity. History Naturally produced polyketides by various plants and organisms have been used by humans since before studies on them began in the 19th and 20th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyketide Synthase
Polyketide synthases (PKSs) are a family of multi- domain enzymes or enzyme complexes that produce polyketides, a large class of secondary metabolites, in bacteria, fungi, plants, and a few animal lineages. The biosyntheses of polyketides share striking similarities with fatty acid biosynthesis. The PKS genes for a certain polyketide are usually organized in one operon or in gene clusters. Type I and type II PKSs form either large modular protein complexes or dissociable molecular assemblies; type III PKSs exist as smaller homodimeric proteins. Classification PKSs can be classified into three types: * Type I PKSs are large, complex protein structures with multiple modules which in turn consist of several domains that are usually covalently connected to each other and fulfill different catalytic steps. The minimal composition of a type I PKS module consists of an acyltransferase (AT) domain, which is responsible for choosing the building block to be used, a keto synthase (KS) do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
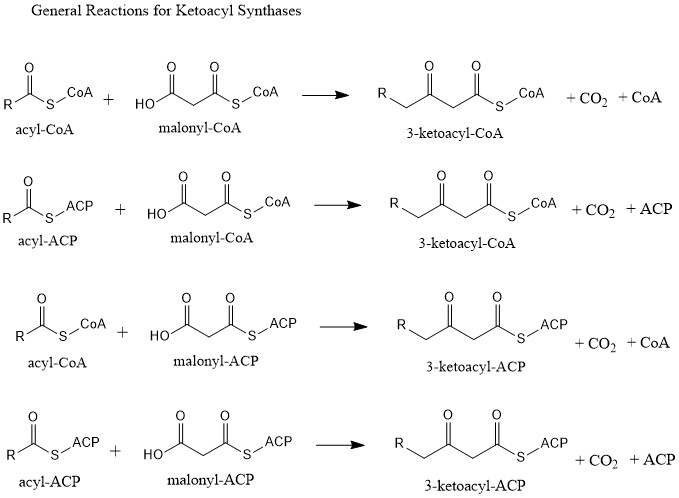
Ketosynthase
Ketoacyl synthases (KSs) catalyze the condensation reaction of acyl-CoA or acyl-acyl ACP with malonyl-CoA to form 3-ketoacyl-CoA or with malonyl-ACP to form 3-ketoacyl-ACP. This reaction is a key step in the fatty acid synthesis cycle, as the resulting acyl chain is two carbon atoms longer than before. KSs exist as individual enzymes, as they do in type II fatty acid synthesis and type II polyketide synthesis, or as domains in large multidomain enzymes, such as type I fatty acid synthases (FASs) and polyketide synthases (PKSs). KSs are divided into five families: KS1, KS2, KS3, KS4, and KS5. Multidomain enzyme systems Fatty acid synthase Fatty acid synthase (FAS) is the enzyme system involved in de novo fatty acid synthesis. FAS is an iterative multienzyme consisting of several component enzymes, one of which is ketoacyl synthase. There are two types of FASs: type I and type II. Type I FASs are highly integrated multidomain enzymes. They contain discrete functional domains resp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Product
A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical synthesis (both semisynthesis and total synthesis and have played a central role in the development of the field of organic chemistry by providing challenging synthetic targets). The term ''natural product'' has also been extended for commercial purposes to refer to cosmetics, dietary supplements, and foods produced from natural sources without added artificial ingredients. Within the field of organic chemistry, the definition of natural products is usually restricted to organic compounds isolated from natural sources that are produced by the pathways of primary or secondary metabolism. Within the field of medicinal chemistry, the definition is often further restricted to secondary metabolites. Secondary metabolites (or specialized meta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propionyl-CoA
Propionyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of propionic acid. It is composed of a 24 total carbon chain (without the coenzyme, it is a 3 carbon structure) and its production and metabolic fate depend on which organism it is present in. Several different pathways can lead to its production, such as through the catabolism of specific amino acids or the oxidation of odd-chain fatty acids. It later can be broken down by propionyl-CoA carboxylase or through the methylcitrate cycle. In different organisms, however, propionyl-CoA can be sequestered into controlled regions, to alleviate its potential toxicity through accumulation. Genetic deficiencies regarding the production and breakdown of propionyl-CoA also have great clinical and human significance. Production There are several different pathways through which propionyl-CoA can be produced: * Propionyl-CoA, a three-carbon structure, is considered to be a minor species of propionic acid. Therefore, odd-number chains of fatty acids a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malonyl-CoA
Malonyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of malonic acid. Biosynthesis Malonyl-CoA cannot cross membranes and there is no known malonyl-CoA import mechanism. The biosynthesis therefore takes place locally: * cytosol: Malonyl-CoA is formed by carboxylating acetyl-CoA using the highly regulated enzyme acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 (ACC1). One molecule of acetyl-CoA joins with a molecule of bicarbonate, requiring energy rendered from ATP. * Mitochondrial outer membrane: Malonyl-CoA is formed by carboxylating acetyl-CoA using the highly regulated enzyme acetyl-CoA carboxylase 2 (ACC2). The reaction is the same as with ACC1. * mitochondrial matrix: Malonyl-CoA is formed in coordinated fashion by mtACC1, a mitochondrial isoform of ACC1, and acyl-CoA synthetase family member 3 (ACSF3), a mitochondrial malonyl-CoA synthetase. MtACC1, like cytosolic ACC1 catalyses the carboxylation of acetyl-CoA, while ACSF3 catalyses the thioesterification of malonate to coenzyme A. The latter serves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6-Methylsalicylic Acid
6-Methylsalicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H3(CO2H)(OH). It is a white solid that is soluble in basic water and in polar organic solvents. At neutral pH, the acid exists as 6-methylsalicylate. Its functional groups include a carboxylic acid and a phenol Phenol (also known as carbolic acid, phenolic acid, or benzenol) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile and can catch fire. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () ... group. It is one of four isomers of methylsalicylic acid. It occurs naturally, being a biosynthetic precursor to ''m''-cresol. Its decarboxylation is catalyzed by 6-methylsalicylate decarboxylase: :6-methylsalicylate ⇌ ''m''-cresol + CO2 See also * 4-Methylsalicylic acid * 3-Methylsalicylic acid References Salicylic acids {{phenol-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orcinol
Orcinol is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H3(OH)2. It occurs in many species of lichens including ''Roccella tinctoria'' and ''Lecanora''. Orcinol has been detected in the "toxic glue" of the ant species ''Camponotus saundersi''. It is a colorless solid. It is related to resorcinol, 1,3-C6H4(OH)2. Synthesis and reactions Orcinol was first prepared by dehydroacetic acid, a conversion that involved ring-opening of the pyrone to a triketone. This early experiment helped establish the rich condensation chemistry of polyketides. It can be obtained by fusing extract of aloes with potash, followed by acidification. It undergoes ''O''-methylation with dimethylsulfate. It is used in the production of the dye orcein and as a reagent in some chemical tests for pentoses, such as Bial's Test. It may be synthesized from toluene; more interesting is its production when acetone dicarboxylic ester is condensed with the aid of sodium. It crystallizes in colorless prisms with one m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Metabolites
Secondary metabolites, also called ''specialised metabolites'', ''secondary products'', or ''natural products'', are organic compounds produced by any lifeform, e.g. bacteria, archaea, fungi, animals, or plants, which are not directly involved in the normal growth, development, or reproduction of the organism. Instead, they generally mediate ecological interactions, which may produce a selective advantage for the organism by increasing its survivability or fecundity. Specific secondary metabolites are often restricted to a narrow set of species within a phylogenetic group. Secondary metabolites often play an important role in plant defense against herbivory and other interspecies defenses. Humans use secondary metabolites as medicines, flavourings, pigments, and recreational drugs. The term secondary metabolite was first coined by Albrecht Kossel, the 1910 Nobel Prize laureate for medicine and physiology. 30 years later a Polish botanist Friedrich Czapek described secondary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure , where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group (a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone (where R and R' are methyl), with the formula . Many ketones are of great importance in biology and industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, ''e.g.'', testosterone, and the solvent acetone. Nomenclature and etymology The word ''ketone'' is derived from ''Aketon'', an old German word for ''acetone''. According to the rules of IUPAC nomenclature, ketone names are derived by changing the suffix ''-ane'' of the parent alkane to ''-anone''. Typically, the position of the carbonyl group is denoted by a number, but traditional nonsystematic names are still generally used for the most important ketones, for example acetone and benzophenone. These nonsystematic names are considered retained IUPAC names, although some introdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclohexanecarboxylate
Cyclohexanecarboxylic acid is the organic compound with the formula C6H11CO2H. It is the carboxylic acid of cyclohexane. It is a colorless oil that crystallizes near room temperature.. Preparation and reactions It is prepared by hydrogenation of benzoic acid. Cyclohexanecarboxylic acid is a precursor to the nylon-6 precursor caprolactam via its reaction with nitrosylsulfuric acid. It can also be oxidized to cyclohexene. Cyclohexanecarboxylic acid exhibits the reactions typical of carboxylic acids, including its conversion to the acid chloride cyclohexanecarbonyl chloride. Related compounds Derivatives related to cyclohexanecarboxylic acid include: * abscisic acid * buciclic acid * chlorogenic acid * chorismic acid * dicyclomine * quinic acid * shikimic acid * tranexamic acid Quinic acid flat.svg, Quinic acid Shikimi.svg, Shikimic acid Chorisminsäure.svg, Chorismic acid Chorismic acid, more commonly known as its ion, anionic form chorismate, is an important biochemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenzyme A
Coenzyme A (CoA, SHCoA, CoASH) is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the Fatty acid metabolism#Synthesis, synthesis and Fatty acid metabolism#.CE.B2-Oxidation, oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvic acid, pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. All genomes sequenced to date encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a Substrate (chemistry), substrate, and around 4% of cellular enzymes use it (or a thioester) as a substrate. In humans, CoA biosynthesis requires cysteine, pantothenic acid, pantothenate (vitamin B5), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In acetyl-CoA, its acetyl form, coenzyme A is a highly versatile molecule, serving metabolic functions in both the Anabolism, anabolic and Catabolism, catabolic pathways. Acetyl-CoA is utilised in the post-translational regulation and allosteric regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase and carboxylase to maintain and support the partition of Pyruvic acid, pyruvate synthesis and degradation. Discovery of structure Coenzyme A was ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |