2012 Slovenian Presidential Election on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Presidential elections were held in

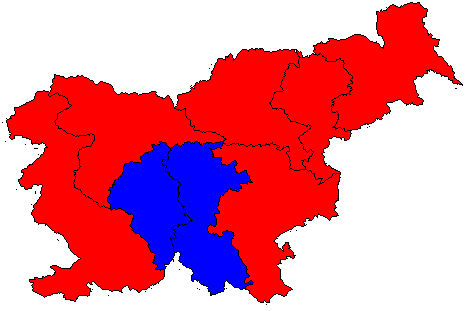 The first round took place on 11 November. Contrary to predictions, the exit polls indicated that the first round was won by Pahor (41.9%), followed by Türk (37.2%) and Zver (20.8%). After 99.91% of votes counted, Pahor got 40%, followed by Türk with 35.8% and Zver with 24.2%. The voter turnout was record-low at less than 48%. For comparison, the first round of the 2007 election saw 58% of the electorate casting their votes and the 1992 election even more than 85%.
In his first response, Pahor expressed a surprise by the amount of support in the first round and stated that he will aim to continue to be a candidate that is not limited to one side of the political spectrum. Türk mentioned that the low
The first round took place on 11 November. Contrary to predictions, the exit polls indicated that the first round was won by Pahor (41.9%), followed by Türk (37.2%) and Zver (20.8%). After 99.91% of votes counted, Pahor got 40%, followed by Türk with 35.8% and Zver with 24.2%. The voter turnout was record-low at less than 48%. For comparison, the first round of the 2007 election saw 58% of the electorate casting their votes and the 1992 election even more than 85%.
In his first response, Pahor expressed a surprise by the amount of support in the first round and stated that he will aim to continue to be a candidate that is not limited to one side of the political spectrum. Türk mentioned that the low
Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
on 11 November 2012, with a run-off held on 2 December. Slovenia's 1.7 million registered voters chose between the incumbent president Danilo Türk
Danilo Türk (; born 19 February 1952) is a Slovenian diplomat, professor of international law, human rights expert, and political figure who served as President of Slovenia from 2007 to 2012. He was the first Slovene ambassador to the United Nat ...
, the SDS/ NSi party candidate Milan Zver and Borut Pahor
Borut Pahor (; born 2 November 1963) is a Slovenian politician who served as President of Slovenia from 2012 to 2022. He previously served as Prime Minister of Slovenia from 2008 to 2012.
A longtime member and former president of the Social D ...
of the Social Democrats
Social democracy is a social, economic, and political philosophy within socialism that supports political and economic democracy and a gradualist, reformist, and democratic approach toward achieving social equality. In modern practice, s ...
who was also supported by the Civic List. The first round was won, contrary to the opinion poll predictions, by Pahor, with Türk placing second. In the run-off election, Pahor won with roughly two-thirds of the vote.
Electoral system
Under Slovenia's election law, candidates forpresident
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
require support of either:
*10 members of the National Assembly
In politics, a national assembly is either a unicameral legislature, the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or both houses of a bicameral legislature together. In the English language it generally means "an assembly composed of the repr ...
,
*one or more political parties and either 3 members of the National Assembly
In politics, a national assembly is either a unicameral legislature, the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or both houses of a bicameral legislature together. In the English language it generally means "an assembly composed of the repr ...
or 3,000 voters,
*or 5,000 voters.
Each political party can support only one candidate. In the election, the president is elected with a majority of the vote. If no candidate receives more than half of votes, the top two candidates meet in the second round of election.
Candidates
Danilo Türk
Danilo Türk
Danilo Türk (; born 19 February 1952) is a Slovenian diplomat, professor of international law, human rights expert, and political figure who served as President of Slovenia from 2007 to 2012. He was the first Slovene ambassador to the United Nat ...
, the incumbent president, announced that he would seek re-election for a second term as an independent candidate and submitted over 13,000 signatures of support to the election commission. Türk, a former United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
diplomat and professor at the Faculty of Law of the University of Ljubljana
The University of Ljubljana (, , ), abbreviated UL, is the oldest and largest university in Slovenia. It has approximately 38,000 enrolled students. The university has 23 faculties and three art academies with approximately 4,000 teaching and re ...
, entered the 2007 election as an independent candidate with the support of five political parties. Narrowly placing second in the first round, Türk won the second round in a landslide, defeating Lojze Peterle.
Türk was supported by two parliamentary parties, Positive Slovenia and Democratic Party of Pensioners of Slovenia, and four non-parliamentary parties, Liberal Democracy of Slovenia
Liberal Democracy of Slovenia (, LDS) is a social-liberal political party in Slovenia. Between 1992 and 2004, it (and its main predecessor, the Liberal Democratic Party) was the largest (and ruling) party in the country. In the 2011 Slovenian pa ...
, Democratic Labour Party, Party for Sustainable Development, and Zares.
Borut Pahor
Borut Pahor
Borut Pahor (; born 2 November 1963) is a Slovenian politician who served as President of Slovenia from 2012 to 2022. He previously served as Prime Minister of Slovenia from 2008 to 2012.
A longtime member and former president of the Social D ...
of the Social Democrats
Social democracy is a social, economic, and political philosophy within socialism that supports political and economic democracy and a gradualist, reformist, and democratic approach toward achieving social equality. In modern practice, s ...
had already considered running for the office in the 2007 election. However, he instead decided to concentrate on the then upcoming parliamentary election where his party won and he was elected Prime Minister. In September 2011, Pahor's government lost a confidence vote amidst an economic crisis and political tensions. In the following election, Pahor was elected to the National Assembly while his party lost the plurality of the votes. In June 2012, Pahor unsuccessfully ran for re-election as president of the Social Democrats. He was defeated by Igor Lukšič by a narrow margin. At the same party congress, Pahor announced he would run for President of Slovenia. He received support from the Social Democrats and also from the Civic List, a Conservative Liberal party in the Slovenian center-right government coalition. Pahor also submitted over 4.400 signatures of support. He also received open support by the right-wing leader Janez Janša
Ivan Janša (; born 17 September 1958), better known as Janez Janša (), is a Slovenian politician who served three times as a prime minister of Slovenia, a position he had held from 2004 to 2008, from 2012 to 2013, and from 2020 to 2022. Since ...
, which according to the newspaper ''Delo'' was the turning point in the campaign, because Pahor won due to the support of right-wing voters.
Milan Zver
Milan Zver entered the election as a candidate of two coalition parties,Slovenian Democratic Party
The Slovenian Democratic Party (, SDS), formerly the Social Democratic Party of Slovenia (, SDSS), is a conservative parliamentary party; it is also one of the largest parties in Slovenia, with approximately 30,000 reported members in 2013.
It ...
and Nova Slovenija. Zver, a sociologist and political scientist, served as the Minister for Education and Sports in the centre-right government led by Janez Janša
Ivan Janša (; born 17 September 1958), better known as Janez Janša (), is a Slovenian politician who served three times as a prime minister of Slovenia, a position he had held from 2004 to 2008, from 2012 to 2013, and from 2020 to 2022. Since ...
in 2004–2008. In 2009, Zver was elected member of the European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the two legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it ...
as a candidate of the Slovenian Democratic Party.
Failed or withdrawn
Zmago Jelinčič Plemeniti of the Slovenian National Party, who had run for office several times before, also suggested he would run, however, he later changed his decision. Monika Malešič, independent politician, also announced her candidacy. She later withdrew her candidacy due to lack of public support. Marko Kožar, independent politician, who attempted to run in 2002 and 2007 but failed to gather sufficient public support both times, announced his intention to run this year as well but later changed his mind. Other people who announced the intention to run include Miro Žitko, Ladislav Troha, Dušan Egidij Kubot - Totislo, Artur Štern, Martina Valenčič, Fani Eršte, and Milan Robič.Campaign
All three campaigns stated that their activities would be financially austere in accordance with the situation in the country. Each however, was marked by its own specific style. Pahor carried out a variety of voluntary jobs, and took part in a number of work actions organised by his campaign. Zver participated in numerous political and civil group rallies and similar events across the country. Türk organised a large political meeting in Križanke to inaugurate the campaign, but mostly appeared at presidential events rather than ones that were explicitly campaign oriented. An important part of the three campaigns were the live radio and television debates.First Round Debates
The very first debate between the three candidates occurred on the afternoon of 23 October 2012 on Radio Slovenia. The first television debate took place in the evening of the same day on TV Slovenia. Samo Uhan, a politologist at the Faculty of Social Sciences of the University of Ljubljana, stated that the first TV debate would not case a shift in support. He described Türks' performance as presidential, Zvers' as an advocacy of the current governing coalition, and Pahor as being burdened by his negative experiences in the previous parliamentary term. Božidar Novak stated that none of the candidates were outstanding in regard to substance, but that Pahor was slightly better than the other two in terms of style. He described Türk as calm, Zver as condescending, and Pahor as likeable. The second TV debate was organised and broadcast by POP TV on the evening of 25 October 2012. The broadcast featured a number of interactive elements including a live analysis of web based reactions to the three candidates. According to this method, Pahor performed the best, followed closely by Zver, with Türk shown as the least successful among the three. The third televised live appearance of all three candidates was aired on POP TV on the evening of 2 November 2012. This broadcast had a different format. The candidates were interrogated by a journalist for 25 minutes each and only interacted with each other at the beginning of the show and between the interviews. The above-mentioned method of reaction analysis showed that both Pahor and Zver performed better than Türk. The fourth TV debate aired on the newly opened Planet TV on the evening of 5 November 2012. During the live broadcast, Episcenter conducted a study of how convincing each of the candidates had been. The results showed that Pahor was successful at convincing 45% of the viewers, followed by Türk with 37% and Zver with 18%. The fifth one was again hosted by TV Slovenia on the evening of 6 November. The final POP TV debate was broadcast live on the evening of 8 November 2012. Aside from the usual confrontation between the candidates for president it also featured a segment where the women who would become the first lady were questioned by the moderator. An analysis of web based responses indicated that Pahor made the best impression, followed by Türk and revealed Zver as the least convincing. The final TV Slovenia debate was broadcast live on the evening of 9 November 2012. This event also featured a segment which included the companions of the three candidates.Election silence
Election blackout or election silence is the practice of banning political campaigning or media coverage of a general election, before or during that election. Often, the publication of opinion polls is illegal during this time.
Operation
In som ...
came into effect at midnight on the night of 9 November 2012 and lasted until 19:00 CET on the evening of 11 November when the polling stations closed.
Opinion polls
Tracking polls
During the last two weeks of the campaign, magazine Mladina, in association with Ninamedia agency, was running a tracking poll to monitor the trends of changes in support for all three candidates. The poll included n=100 daily with n=200 on the last day of the poll. The final prediction of the poll on Friday, 9 November, indicated 43.8% for Türk, 33.6% for Pahor, and 22.6% for Zver, what would result in a second round being necessary. Support for Zver was more or less stable during the two weeks, slightly above 20%. Long-term trend indicated a slight fall of support for Türk with the support beginning to rise again in the last days before the election. While the poll first allowed the possibility of Türk being elected in the first round already, the final prediction stated that Türk and Pahor will face the second round. Journal Delo ran a tracking poll during the last week of the campaign. Similarly, the final prediction indicated 44% for Türk, 33% for Pahor and 23% for Zver. In the last two days, the poll indicated that some of supporters of Türk migrated to Pahor.Results
First round
 The first round took place on 11 November. Contrary to predictions, the exit polls indicated that the first round was won by Pahor (41.9%), followed by Türk (37.2%) and Zver (20.8%). After 99.91% of votes counted, Pahor got 40%, followed by Türk with 35.8% and Zver with 24.2%. The voter turnout was record-low at less than 48%. For comparison, the first round of the 2007 election saw 58% of the electorate casting their votes and the 1992 election even more than 85%.
In his first response, Pahor expressed a surprise by the amount of support in the first round and stated that he will aim to continue to be a candidate that is not limited to one side of the political spectrum. Türk mentioned that the low
The first round took place on 11 November. Contrary to predictions, the exit polls indicated that the first round was won by Pahor (41.9%), followed by Türk (37.2%) and Zver (20.8%). After 99.91% of votes counted, Pahor got 40%, followed by Türk with 35.8% and Zver with 24.2%. The voter turnout was record-low at less than 48%. For comparison, the first round of the 2007 election saw 58% of the electorate casting their votes and the 1992 election even more than 85%.
In his first response, Pahor expressed a surprise by the amount of support in the first round and stated that he will aim to continue to be a candidate that is not limited to one side of the political spectrum. Türk mentioned that the low voter turnout
In political science, voter turnout is the participation rate (often defined as those who cast a ballot) of a given election. This is typically either the percentage of Voter registration, registered voters, Suffrage, eligible voters, or all Voti ...
indicated the disappointment of people regarding the political situation and that the voters should decide what country they want to live in. Zver thanked his supporters and stated he was "sad" but did not decide which of the remaining two candidates he would endorse in the second round.
In the following days, analysts expressed opinion that Pahor now has better chances in the runoff. Pahor appeared to attract votes from both sides of the political spectrum, even one third of the voters of the SDS party. On the other hand, Türk got most of his votes from supporters of Positive Slovenia and from one third of supporters of Pahor's SD. Increasing support of Pahor during the campaign was also attributed to better performance of his in televised debates.
Discrepancies between the opinion polls and the results in the first round were attributed to low voter turnout, especially as a part of Türk's supporters presumably stayed at home. Low turnout was also interpreted as people being "fed up" with the political situation in Slovenia.
Second round
Borut Pahor won the second round and the election with 67.3% of the vote. The results were first announced in an exit poll by the Mediana Institute. The result was later confirmed at 67.4% for Pahor to 32.6% for Danilo Türk by the Electoral Commission of Slovenia, with 99.7% of the votes counted. The voter turnout was 41.95%, the lowest in the history of presidential elections in Slovenia (until being surpassed by the 2017 election at 41.84%). After the results were announced, Pahor reiterated that this "only the beginning, the beginning of something new, a new hope, a new period." Pahor stressed that people need trust, respect, and tolerance. He stated he will keep the promises he made during the campaign and will keep working to help solving the problems the nation faces. Türk congratulated his opponent and stated he will keep an active role in the politics of the country.References
External links
* {{Slovenian elections Presidential elections in SloveniaSlovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
Presidential election
Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...