2-10-2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Under the
 The mainstay of Chinese steam was their locomotives. This was the wheel arrangement of the Chinese QJ class locomotives that were based on the Soviet locomotive class LV and built by Datong Locomotive Works from 1959. They were produced until 1988 and were still in widespread service until the final steam runs in 2005.
After retirement, some of these QJ class locomotives found their way to the United States, where they are used in revenue freight and excursion service. In Train Festival 2011, Multipower International restored two Chinese locomotives to
The mainstay of Chinese steam was their locomotives. This was the wheel arrangement of the Chinese QJ class locomotives that were based on the Soviet locomotive class LV and built by Datong Locomotive Works from 1959. They were produced until 1988 and were still in widespread service until the final steam runs in 2005.
After retirement, some of these QJ class locomotives found their way to the United States, where they are used in revenue freight and excursion service. In Train Festival 2011, Multipower International restored two Chinese locomotives to
 While the wheel arrangement was not very common in Africa, the
While the wheel arrangement was not very common in Africa, the
 The Manila Railroad Company (now the Philippine National Railways) acquired ten 200-class locomotives in 1922 from the
The Manila Railroad Company (now the Philippine National Railways) acquired ten 200-class locomotives in 1922 from the
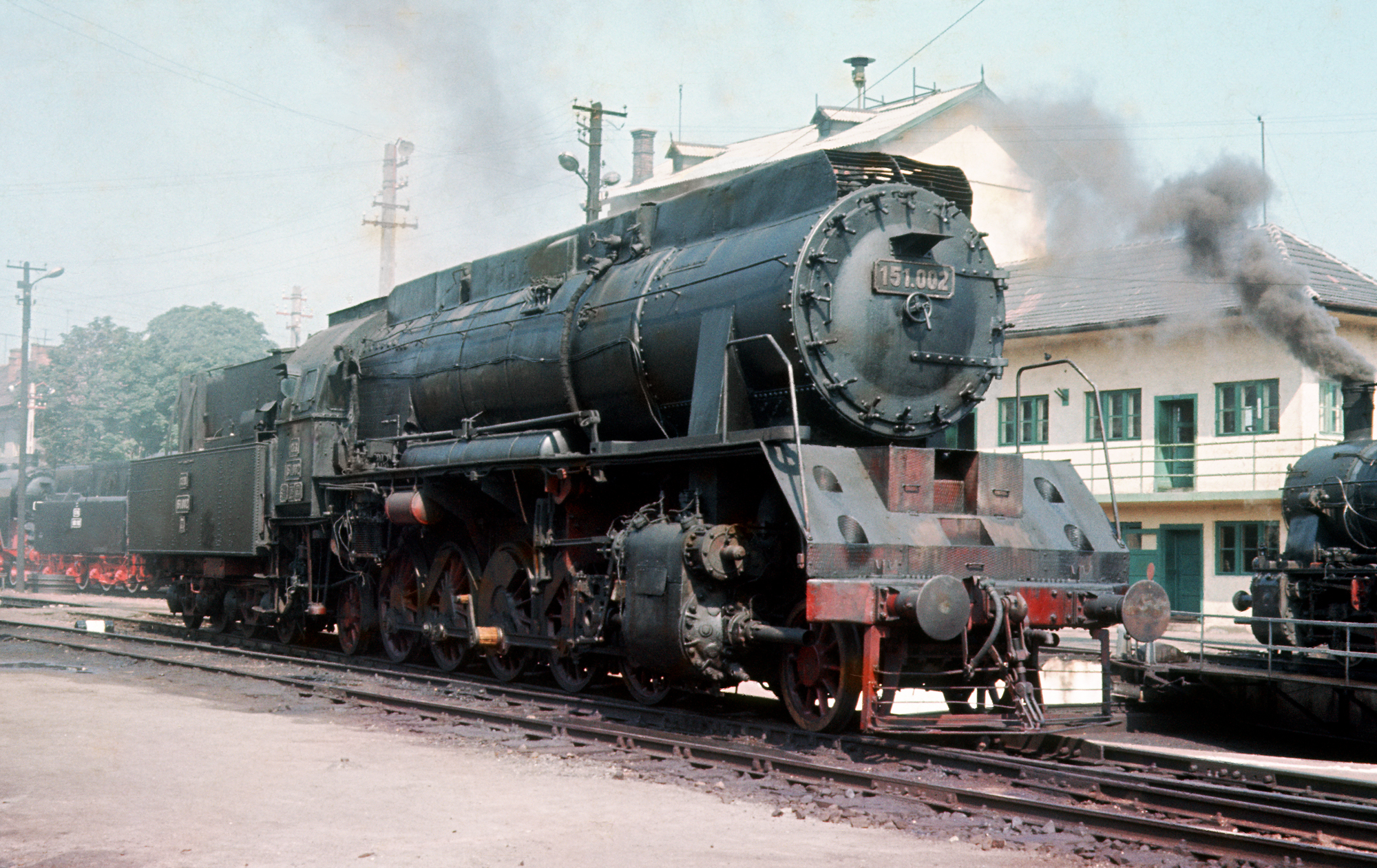
 In Spain, the wheel arrangement was represented by one series of 22 locomotives. They were initially ordered for the , but
In Spain, the wheel arrangement was represented by one series of 22 locomotives. They were initially ordered for the , but
 In the United States, the type was produced between 1903 and 1930. The first were the
In the United States, the type was produced between 1903 and 1930. The first were the 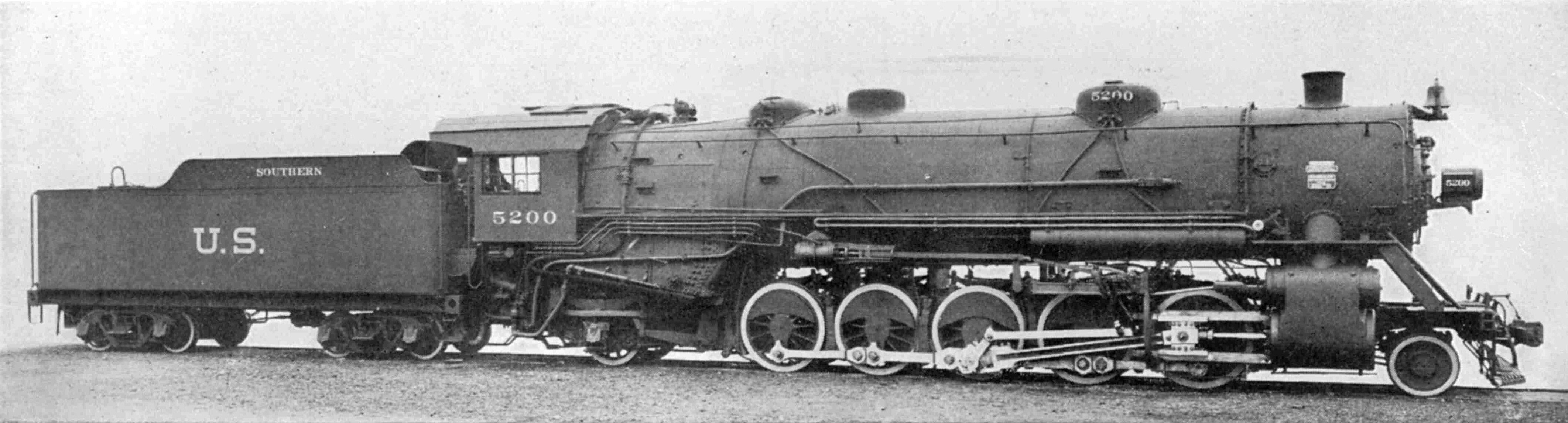 About 2,200 Santa Fe types were built, including about 500 of the two
About 2,200 Santa Fe types were built, including about 500 of the two  The heaviest were ten locomotives built by
The heaviest were ten locomotives built by
Whyte notation
The Whyte notation is a classification method for steam locomotives, and some internal combustion locomotives and electric locomotives, by wheel arrangement. It was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte, and came into use in the early twenti ...
for the classification of steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, Fuel oil, oil or, rarely, Wood fuel, wood) to heat ...
s, represents the wheel arrangement
In rail transport, a wheel arrangement or wheel configuration is a system of classifying the way in which wheels are distributed under a locomotive. Several notations exist to describe the wheel assemblies of a locomotive by type, position, and c ...
of two leading wheels, ten powered and coupled driving wheel
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons (or turbine, in the case of a steam turbine locomotive). On a conventional, non-articulated locomotive, the driving wheels are all coupled t ...
s, and two trailing wheel
On a steam locomotive, a trailing wheel or trailing axle is generally an unpowered wheel or axle (Wheelset (rail transport), wheelset) located behind the driving wheels. The axle of the trailing wheels is usually located in a trailing Bogie, t ...
s. In the United States and elsewhere the is known as the Santa Fe type, after the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway
The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway , often referred to as the Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the largest Class 1 railroads in the United States between 1859 and 1996.
The Santa Fe was a pioneer in intermodal freight transport; at vario ...
that first used the type in 1903.
Overview
The wheel arrangement evolved in the United States from the2-10-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-10-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, ten powered and coupled driving wheels on five axles, and no trailing wheels. This arrangement was of ...
Decapod of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway
The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway , often referred to as the Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the largest Class 1 railroads in the United States between 1859 and 1996.
The Santa Fe was a pioneer in intermodal freight transport; at vario ...
(ATSF). Their existing 2-10-0 tandem compound locomotives, used as pushers up Raton Pass
Ratón Pass is a 7,834 ft (2,388 m) elevation mountain pass on the Colorado–New Mexico border in the western United States. It is located on the eastern side of the Sangre de Cristo Mountains between Trinidad, Colorado and Raton, N ...
, encountered problems reversing back down the grade for their next assignments since they were unable to track around curves at speed in reverse and had to run very slowly to avoid derailing. Consequently, the ATSF added a trailing truck to the locomotives which allowed them to operate successfully in both directions. These first locomotives became the forerunners to the entire family.
The trailing truck allows a larger, deeper firebox than that of a . Like all ten-coupled designs, the long rigid wheelbase of the coupled wheels presented a problem on curves, requiring flangeless drivers, lateral motion devices and much sideplay on the outer axles. To limit this problem, the coupled wheels were generally small, up to in diameter, which in turn generated the problem of insufficient counterweights to balance the weight of the driving rods.pp.92, 138, 148-149, 172-173, 192-193
The 's inherent problem was the low speed restriction on the type, which was about . Further, the had other inherent restrictions. The massive cylinders that were required on locomotives in the United States for high tractive effort had the result that no reasonably sized valves could admit and exhaust steam at a sufficient rate to permit fast running. In addition the , like the , had its main rod connected to the middle coupled axle, very near to the centre of gravity, which created a violent nosing (waddling) action when operating at speed. The peak of the design limitations was reached in the United States in 1926 and was overcome with the advent of the superior 2-10-4 design.
Usage
Locomotives with a wheel arrangement were used in a number of countries around the world, including those in North America, Western Europe, China, the Soviet Union and Africa. Continental Europe saw a fair number of , although the type was always less popular than Mikados and 2-10-0 Decapods. A large number of European weretank locomotive
A tank locomotive is a steam locomotive which carries its water in one or more on-board water tanks, instead of a more traditional tender (rail), tender. Most tank engines also have Fuel bunker, bunkers (or fuel tanks) to hold fuel; in a #Tender ...
s, taking advantage of the symmetrical nature of the wheel arrangement.
Argentina
Themetre gauge
Metre-gauge railways ( US: meter-gauge railways) are narrow-gauge railways with track gauge of or 1 metre.
Metre gauge is used in around of tracks around the world. It was used by several European colonial powers including France, Britain and ...
General Manuel Belgrano Railway in Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
operated the E2 series of 2-10-2 locomotives. In 1956, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational engineering, electrical equipment and electronics corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. MHI is one of the core companies of the Mitsubishi Group and its automobile division is the prede ...
of Japan constructed a batch of ten 2-10-2s based on this design for the isolated Ramal Ferro Industrial Río Turbio (RFIRP) 750 mm gauge railway in the southern Patagonian Desert
The Patagonian Desert, also known as the Patagonian Steppe, is the largest desert in Argentina and is the list of deserts by area, eighth-largest desert in the world by area, occupying approx. 673,000 square kilometres (260,000 mi2). It is l ...
, to haul coal from Río Turbio for shipping from Río Gallegos, Santa Cruz. These required modification by Livio Dante Porta
Livio Dante Porta (21 March 1922 – 10 June 2003) was an Argentine steam locomotive engineer. He is particularly remembered for his innovative modifications to existing locomotive systems in order to obtain better performance and energy effi ...
to achieve their full potential. Ten more powerful examples were introduced into service in 1964.
Belgian Congo
Two classes of locomotives were used in theBelgian Congo
The Belgian Congo (, ; ) was a Belgian colonial empire, Belgian colony in Central Africa from 1908 until independence in 1960 and became the Republic of the Congo (Léopoldville). The former colony adopted its present name, the Democratic Repu ...
.
* Two locomotives were built by Forges, Usines et Fonderies de Haine-Saint-Pierre for the in 1937, numbered 60 and 61. They had cylinders and coupled wheels, with a working order mass of .
* One locomotive was built for the by Société Anonyme John Cockerill in 1947, numbered 901 and later renumbered 802. It had cylinders and coupled wheels, with a working order mass of , a grate area of and a tractive effort at 65% boiler pressure of .
Canada
In 1916, Canadian Government Railways (CGR) took delivery of ten built byALCO
The American Locomotive Company (often shortened to ALCO, ALCo or Alco) was an American manufacturer that operated from 1901 to 1969, initially specializing in the production of locomotives but later diversifying and fabricating at various time ...
. After CGR became part of Canadian National Railways
The Canadian National Railway Company () is a Canadian Class I freight railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec, which serves Canada and the Midwestern and Southern United States.
CN is Canada's largest railway, in terms of both revenue an ...
(CNR) in 1918, these locomotives were designated Class . Ten more were delivered from the Montreal Locomotive Works
Montreal Locomotive Works (MLW) was a Canadian railway locomotive manufacturer that existed under several names from 1883 to 1985, producing both Steam locomotive, steam and diesel locomotives. For many years it was a subsidiary of the American ...
in 1918, and another 25 slightly modified in 1920 that were lighter. Canadian Locomotive Company produced five in 1924. Ten ALCO's named were acquired from the Boston and Albany Railroad
The Boston and Albany Railroad was a railroad connecting Boston, Massachusetts to Albany, New York, later becoming part of the New York Central Railroad system, Conrail, and CSX Transportation. The mainline is currently used by CSX for freight a ...
in 1928. Canadian Locomotive Company produced the last series of for CNR, a batch of 15 in 1929, and 18 in 1930.
The began to be scrapped in the mid-1950s, with the last models being used until 1961. There are two surviving CNR locomotives. One is No. 4008, on display at the CNR Station in Rainy River, Ontario, and the other is No. 4100, on display at the Canadian Railway Museum
The Canadian Railway Museum () ''Musée ferroviaire canadien''), operating under the brand name Exporail in both official languages, is a rail transport museum in Saint-Constant, Quebec, Canada, on Montreal's south shore.
Collection
Establishe ...
in Delson, Quebec.
China
 The mainstay of Chinese steam was their locomotives. This was the wheel arrangement of the Chinese QJ class locomotives that were based on the Soviet locomotive class LV and built by Datong Locomotive Works from 1959. They were produced until 1988 and were still in widespread service until the final steam runs in 2005.
After retirement, some of these QJ class locomotives found their way to the United States, where they are used in revenue freight and excursion service. In Train Festival 2011, Multipower International restored two Chinese locomotives to
The mainstay of Chinese steam was their locomotives. This was the wheel arrangement of the Chinese QJ class locomotives that were based on the Soviet locomotive class LV and built by Datong Locomotive Works from 1959. They were produced until 1988 and were still in widespread service until the final steam runs in 2005.
After retirement, some of these QJ class locomotives found their way to the United States, where they are used in revenue freight and excursion service. In Train Festival 2011, Multipower International restored two Chinese locomotives to Federal Railroad Administration
The Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) is an agency in the United States Department of Transportation (DOT). The agency was created by the Department of Transportation Act of 1966. The purpose of the FRA is to promulgate and enforce railroa ...
(FRA) Part 230 specifications and delivered them to the Railroad Development Corporation.
Germany
Examples on the German railway systems included classes BR84 and BR85, both standard tank locomotive designs built in 1935 and 1937 respectively, and class BR95, a tank locomotive built in 1922 by the Prussian State Railways as the Prussian T 20. From 1936, the German railways built 28 three-cylinder tender freight locomotives of class BR45, which were the most powerfulsteam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, Fuel oil, oil or, rarely, Wood fuel, wood) to heat ...
s on the system.
Further examples, still in regular service, are the metre-gauge DR Class 99.23-24 on the Harz Narrow Gauge Railways
The Harz Narrow Gauge Railways (German: ''Harzer Schmalspurbahnen'' or HSB) is a railway company that operates a network in the Harz mountains, in central Germany (formerly East Germany – officially the German Democratic Republic). The compan ...
and the 750 mm-gauge DR Class 99.77-79 on the Rügen narrow-gauge railway.
Greece
SEK (, Hellenic State Railways) class Μα (or class Ma; Mu-alpha
Alpha (uppercase , lowercase ) is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of one. Alpha is derived from the Phoenician letter ''aleph'' , whose name comes from the West Semitic word for ' ...
) was a class of 2-10-2 steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, Fuel oil, oil or, rarely, Wood fuel, wood) to heat ...
s built by Ansaldo and Breda in 1953. They were numbered Μα 1001-1020.
The Μα locomotives were the last steam locomotives acquired by SEK before conversion to diesel traction. They were designed and built in Italy by Breda
Breda ( , , , ) is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the southern part of the Netherlands, located in the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of North Brabant. ...
(10 units) and Ansaldo (10 units) in 1953–1954, while some parts (including whole tender underframes) were made by Nuove Reggiane. The length of the locomotive with the tender was 24.93 m, the maximum height 4.51 m and service weight 136 t. The boiler operated at , and their rated power was . Maximum speed was 90 km/h.
Due to various technical problems, only two years after introduction they were modified by Henschel
Henschel & Son () was a German company, located in Kassel, best known during the 20th century as a maker of transportation equipment, including locomotives, trucks, buses and trolleybuses, and armoured fighting vehicles and weapons.
Georg C ...
(1957–1958). The boilers were converted to burn heavy fuel oil.
These locomotives were based at Aghios Ioannis Rentis and Thessaloniki depots and were used mainly for freight trains and for some express passenger trains on Piraeus–Thessaloniki and Thessaloniki–Idomeni mainlines until the early 1970s, when they were withdrawn by the Hellenic Railways Organisation
The Hellenic Railways Organisation or OSE ( or ) is the Greek national railway company which owns, maintains and operates all railway infrastructure in Greece with the exception of Athens Metro, Athens' rapid transit lines. Train services on t ...
(successor of SEK) due to complete conversion to diesel traction.
Only two examples survived the 1984-1985 steam locomotives scrappings. One of them, 1002 was set on display as part of the theatre , at Rouf station in Athens. The other one is at Thessaloniki old railway station, not preserved.
India
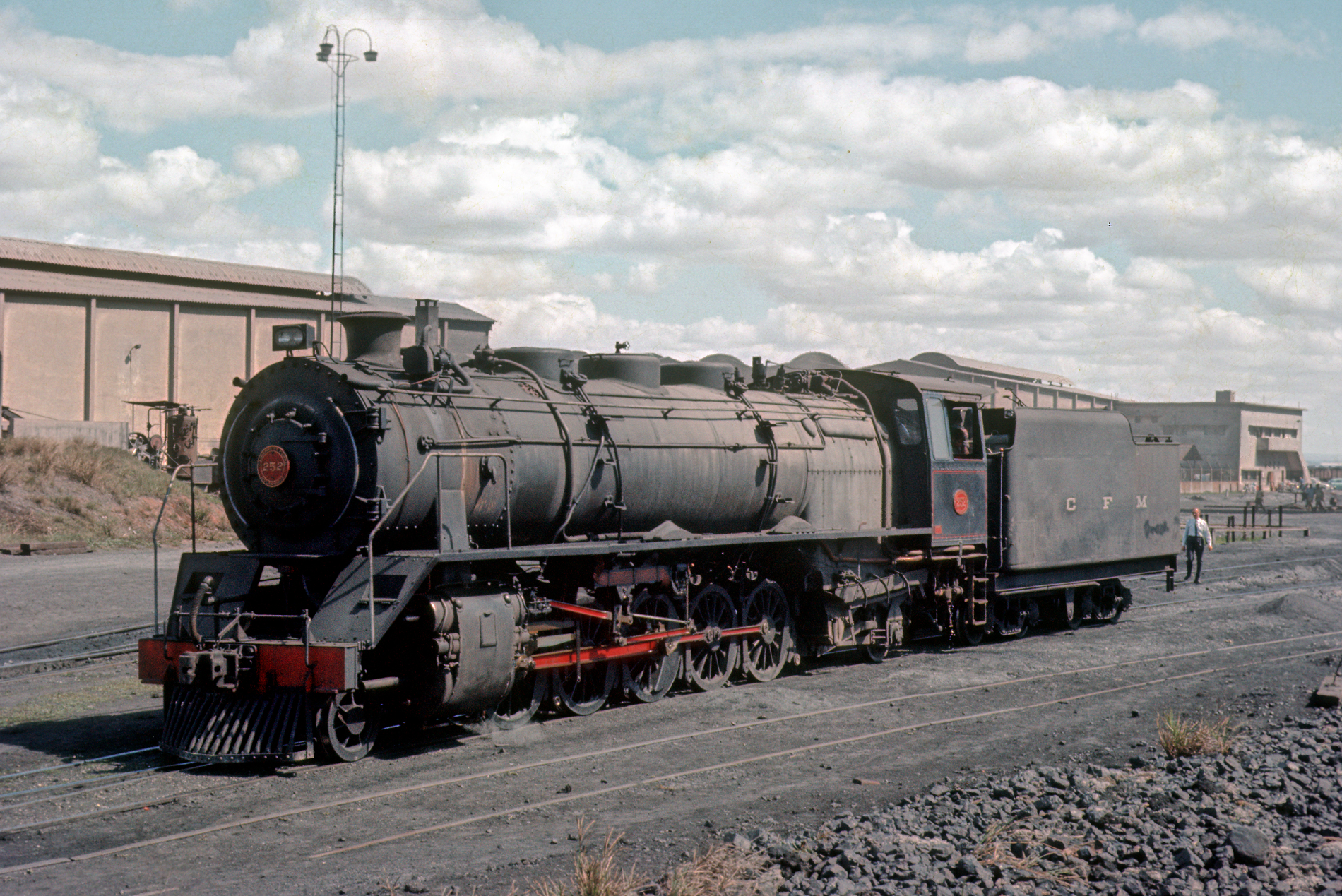
The Bombay Port Trust had a pair of 2-10-2 tank locomotives, numbered 25H and 26H, for hump shunting, weighing in at 105.5 tons. Built by Nasmyth, Wilson and Company in 1922, they had driving wheels, and cylinders. Both were withdrawn and scrapped in 1976.Mozambique
Lourenco Marques
Maputo () is the capital and largest city of Mozambique. Located near the southern end of the country, it is within of the borders with Eswatini and South Africa. The city has a population of 1,088,449 (as of 2017) distributed over a land are ...
system in Mozambique
Mozambique, officially the Republic of Mozambique, is a country located in Southeast Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi and Zambia to the northwest, Zimbabwe to the west, and Eswatini and South Afr ...
( or CFM) had altogether 37 locomotives of this type, in three classes.
* Nine locomotives of the Series 200, numbered 201 to 209, were built by Baldwin Locomotive Works
The Baldwin Locomotive Works (BLW) was an American manufacturer of railway locomotives from 1825 to 1951. Originally located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, it moved to nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania, Eddystone in the early 20th century. The com ...
between 1915 and 1919.Rolling Stock Diagrams,
* Six more Santa Fe type locomotives of the Series 214, numbered 214 to 219, were built by Henschel and Son in 1951.
* Twenty-two locomotives of the Series 250, numbered 251 to 272, were built by Henschel in 1955.
Philippines
 The Manila Railroad Company (now the Philippine National Railways) acquired ten 200-class locomotives in 1922 from the
The Manila Railroad Company (now the Philippine National Railways) acquired ten 200-class locomotives in 1922 from the American Locomotive Company
The American Locomotive Company (often shortened to ALCO, ALCo or Alco) was an American manufacturer that operated from 1901 to 1969, initially specializing in the production of locomotives but later diversifying and fabricating at various time ...
(Alco) and was purchased alongside the 4-8-2 170-class. Based on Henry Kirke Porter's acclaimed design of the 45 class, these were intended to replace the original Scottish-built tank locomotive
A tank locomotive is a steam locomotive which carries its water in one or more on-board water tanks, instead of a more traditional tender (rail), tender. Most tank engines also have Fuel bunker, bunkers (or fuel tanks) to hold fuel; in a #Tender ...
s as well as a small group of 4-4-2 tender locomotives that were acquired from the company's predecessors.
They were serviced to haul heavy freight trains on the South Main Line between Manila
Manila, officially the City of Manila, is the Capital of the Philippines, capital and second-most populous city of the Philippines after Quezon City, with a population of 1,846,513 people in 2020. Located on the eastern shore of Manila Bay on ...
and . This class also had one of the largest cylinders of any unarticulated Cape-gauge locomotive according to Alco, but it comparatively had small boilers and grills. Their arrival also called for larger turntables
A phonograph, later called a gramophone, and since the 1940s a record player, or more recently a turntable, is a device for the mechanical and analogue reproduction of sound. The sound vibration Waveform, waveforms are recorded as correspond ...
in both ends of the line, making them some of the largest and most powerful locomotives that entered Philippine service.
Out of ten locomotives, four managed to survive World War II, all of which were still in active service in 1952. However, these locomotives were retired after the MRR turned to upgrading its fleet to diesel locomotive
A diesel locomotive is a type of railway locomotive in which the prime mover (locomotive), power source is a diesel engine. Several types of diesel locomotives have been developed, differing mainly in the means by which mechanical power is con ...
s in 1956. Not a single unit was preserved.
Poland
Twenty-five OKz32 2-10-2 tank locomotives were built by H. Cegielski – Poznań and delivered to PKP between 1934 and 1936. They were used mainly to work passenger trains betweenKraków
, officially the Royal Capital City of Kraków, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 ...
and Zakopane
Zakopane (Gorals#Language, Podhale Goral: ''Zokopane'') is a town in the south of Poland, in the southern part of the Podhale region at the foot of the Tatra Mountains. From 1975 to 1998, it was part of Nowy Sącz Voivodeship; since 1999, it has ...
, a difficult railway line, steep in places, with many sharp curves, and requiring three direction changes. One has been preserved in working condition.
Romania
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
designed its 151.000 Class as freight locomotives to serve on the Căile Ferate Române
Căile Ferate Române (; abbreviated as the CFR) was the state railway carrier of Romania. The company was dissolved on 1 October 1998 by splitting into several successor companies. CFR as an entity existed from 1880, even though the first ra ...
(CFR). These locomotives used a straightforward two-cylinder engine with coupled wheels and a total weight in working order of . The heating surface of the boiler was , of which were superheated, while the grate area was . At a tractive effort
In railway engineering, the term tractive effort describes the pulling or pushing capability of a locomotive. The published tractive force value for any vehicle may be theoretical—that is, calculated from known or implied mechanical proper ...
of , they were the most powerful steam locomotives built in Romania.
Two of these locomotives were built by the Malaxa Works in 1939 and 1941, numbered 151.001 and 151.002. Number 151.002 was preserved.
South Africa
On , this wheel arrangement was first used by theSouth African Railways
Transnet Freight Rail is a Rail transport in South Africa, South African rail transport company, formerly known as Spoornet. It was part of the South African Railways and Harbours Administration, a state-controlled organisation that employed h ...
(SAR) in 1927. Two Class 18 steam locomotives, the most powerful non-articulated locomotives to see service on the SAR, were introduced on the line between Witbank
Witbank (), officially eMalahleni, is a city situated on the Highveld of Mpumalanga, South Africa, within the Emalahleni Local Municipality, Mpumalanga, Emalahleni Local Municipality. The name Witbank is Afrikaans for "white ridge", and is named ...
and Germiston
Germiston, also known as kwaDukathole, is a city in the East Rand region of Gauteng, South Africa, administratively forming part of the City of Ekurhuleni Metropolitan Municipality since the latter's establishment in 2000. It functions as the m ...
in an attempt to ease problems that were being experienced with increasingly heavy coal trains. It was designed by Colonel F.R. Collins DSO, Chief Mechanical Engineer of the SAR from 1922 to 1929, and built by Henschel and Son in Germany. They were three-cylinder locomotives, with the two outer cylinders using Walschaerts valve gear
The Walschaerts valve gear is a type of valve gear used to regulate the flow of steam to the pistons in steam locomotives, invented by Belgium, Belgian railway mechanical engineering, engineer Egide Walschaerts in 1844.
The gear is sometimes name ...
and the inner cylinder using Gresley conjugated valve gear
The Gresley conjugated valve gear is a valve gear for steam locomotives designed by Sir Nigel Gresley, chief mechanical engineer of the London and North Eastern Railway, LNER, assisted by Harold Holcroft. It enables a three-cylinder locomotive ...
, actuated by the motions of the outer cylinders. (Henschel & Son works list), compiled by Dietmar Stresow
One more locomotive, the Class 20, was designed for branch line work on light rail by A.G. Watson, Chief Mechanical Engineer from 1929 to 1936. Only one locomotive was built by the SAR at its Pretoria Mechanical Shops at Salvokop in 1935.
In 1950, this sole Class 20 locomotive was modified to an experimental condensing locomotive, equipped with a condensing tender that was ordered from Henschel in Germany in 1948. Beginning in 1951, tests with the condensing Class 20 were conducted in the Eastern Transvaal and the Karoo
The Karoo ( ; from the Afrikaans borrowing of the South Khoekhoe Khoemana (also known as !Orakobab or Korana) word is a semidesert natural region of South Africa. No exact definition of what constitutes the Karoo is available, so its extent is ...
. The positive results of the condensing trials proved the viability of condensing locomotives in South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
and led to the introduction of the Class 25 condensing locomotive fleet in 1953.
Soviet Union
In the Soviet Union, locomotives were used to haul heavy freight trains. Two series were relatively common, the FD (for Felix Dzerzhinsky) with more than three thousand built through the 1930s, and the LV (Lebedyansky, modified by the Voroshilovgrad plant). The FD class was developed from ALCO and Baldwin heavy freight locomotives that were imported to the Soviet Union, where they were designated as the Ta and Tb classes respectively. The first FD class locomotive was built at the Voroshilovgrad Locomotive Plant in 1931. In 1932, the Voroshilovgrad plant began with the mass production of FD20 locomotives. In the process of production, their construction was improved constantly. Production was interrupted at the outbreak of the Great Patriotic war in 1941 and was only resumed in 1942, when four locomotives were built in Ulan Ude. The total production was 2,927 locomotives of FD20, and 286 locomotives of FD21. The two subclasses only differed in respect of their types of superheater. In 1958, 1,054 FD class locomotives were sold to China, where they worked until the 1980s. A much lesser number were sold to North Korea at around the same time. The Soviet locomotive class LV was developed from the previous L class 2-10-0 locomotive by the Voroshilovgrad plant. It used afeedwater heater
A feedwater heater is a power plant component used to pre-heat water delivered to a steam generating boiler. Preheating the feedwater reduces the irreversibilities involved in steam generation and therefore improves the thermodynamic efficiency o ...
to increase thermal efficiency
In thermodynamics, the thermal efficiency (\eta_) is a dimensionless performance measure of a device that uses thermal energy, such as an internal combustion engine, steam turbine, steam engine, boiler, furnace, refrigerator, ACs etc.
For ...
and was the most efficient freight steam locomotive in the Soviet Union, with thermal efficiency of 9.3%. The first prototype was named OR18-01 (October Revolution plant, 18 ton axle load). A total of 522 LV class locomotives were built. Several were preserved, including the first, OR18-01, and the last, LV-0522.
Spain
 In Spain, the wheel arrangement was represented by one series of 22 locomotives. They were initially ordered for the , but
In Spain, the wheel arrangement was represented by one series of 22 locomotives. They were initially ordered for the , but RENFE
Renfe (, ), officially Renfe-Operadora, is Spain's national state-owned railway company.
It was created in 2005 upon the split of the former Spanish National Railway Network (RENFE) into the Administrador de Infraestructuras Ferroviarias ( ...
kept the entire series in reserve. Built between 1941 and 1944 in the factory in Barcelona
Barcelona ( ; ; ) is a city on the northeastern coast of Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second-most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within c ...
for hauling heavy coal trains, they were amongst the most powerful steam locomotives in Europe. They had three cylinders, but used simple expansion and were known as ''Santa Fe'' locomotives.
United States
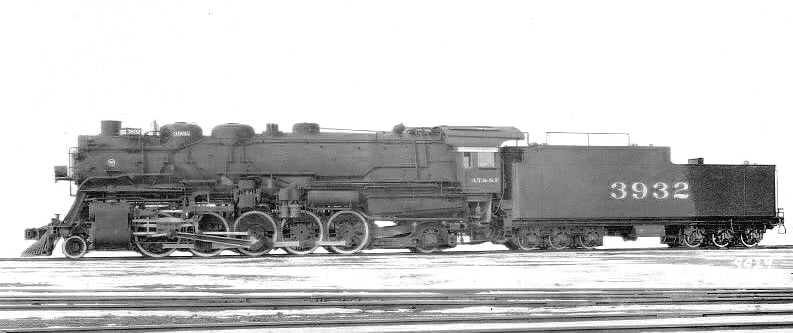
 In the United States, the type was produced between 1903 and 1930. The first were the
In the United States, the type was produced between 1903 and 1930. The first were the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway
The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway , often referred to as the Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the largest Class 1 railroads in the United States between 1859 and 1996.
The Santa Fe was a pioneer in intermodal freight transport; at vario ...
(AT&SF) engines of the 900 and 1600 series, which were an early type with few advantages over the Decapod, save their ability to operate in reverse without derailing. By 1919, the AT&SF was building the definitive type, with the trailing truck supporting a large firebox. These were of the AT&SF 3800 class. One of them, AT&SF engine No. 3829, was equipped with an experimental two-axle trailing truck to become the first Texas type.
 About 2,200 Santa Fe types were built, including about 500 of the two
About 2,200 Santa Fe types were built, including about 500 of the two United States Railroad Administration
The United States Railroad Administration (USRA) was the name of the nationalisation, nationalized railroad system of the United States between December 28, 1917, and March 1, 1920. It was the largest American experiment with nationalization, and ...
(USRA) First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
standard designs. There were two USRA standard , the heavy version with an engine weight of and the light version with an engine weight of . The Santa Fe had the most with 352 engines.
Of the built for the Santa Fe, only one has been preserved. AT&SF No. 940 is on static display outside the Santa Fe depot, now a Visitor Center, in Bartlesville, Oklahoma
Bartlesville is a city mostly in Washington County and Osage County, Oklahoma. The population was 37,290 at the 2020 census. Bartlesville is north of Tulsa and south of the Kansas border. It is the county seat of Washington County. The Cane ...
.
 The heaviest were ten locomotives built by
The heaviest were ten locomotives built by Baldwin Locomotive Works
The Baldwin Locomotive Works (BLW) was an American manufacturer of railway locomotives from 1825 to 1951. Originally located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, it moved to nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania, Eddystone in the early 20th century. The com ...
for the Reading Railway , weighing , engine only.
At , the Illinois Central Railroad
The Illinois Central Railroad , sometimes called the Main Line of Mid-America, is a railroad in the Central United States. Its primary routes connected Chicago, Illinois, with New Orleans, New Orleans, Louisiana, and Mobile, Alabama, and thus, ...
's 2800 class rebuilds probably had the highest calculated tractive effort of any two-cylinder steam locomotive, although the adhesive weight was only .Staufer, Alvin F. (ed.), ''B&O Power: Steam, Diesel and Electric Power of the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad 1829–1965'', Staufer, Medina, n.d. pp. 152–167
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was the oldest railroads in North America, oldest railroad in the United States and the first steam engine, steam-operated common carrier. Construction of the line began in 1828, and it operated as B&O from 1830 ...
ordered its first from Baldwin in 1914. From 1914 to 1956, their bore numbers commencing with ''6'', hence the nickname "Big Sixes". Designated the S class, there were several sub-classes. The first of the Big Sixes was retired in 1951 and were all scrapped by 1960.
The Southern Railway (SOU) ordered its first batches of fifty-five Ss class steam locomotives (Nos. 5000–5054) from Baldwin in 1917. The second batches of twenty-five (Nos. 6350–6374) were built by the American Locomotive Company
The American Locomotive Company (often shortened to ALCO, ALCo or Alco) was an American manufacturer that operated from 1901 to 1969, initially specializing in the production of locomotives but later diversifying and fabricating at various time ...
's (ALCO) Richmond Works in 1918 originally for SOU's Cincinnati, New Orleans and Texas Pacific (CNO&TP) division. The latter batches were later moved to the SOU's main division and renumbered to 5055–5079 when they were proved to be too bulky for the CNO&TP tunnel
A tunnel is an underground or undersea passageway. It is dug through surrounding soil, earth or rock, or laid under water, and is usually completely enclosed except for the two portals common at each end, though there may be access and ve ...
s' tight clearances. After receiving the last batches of Ss types, the SOU received fifty more (Nos. 5200–5249) from ALCO's Brook Works in a USRA Light Santa Fe design which were classified as Ss-1. Both classes were assigned to SOU's Asheville division, banking
A bank is a financial institution that accepts Deposit account, deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital m ...
and hauling heavy freight trains up the steep Saluda Grade and Old Fort Loops in the Blue Ridge Mountains
The Blue Ridge Mountains are a Physiographic regions of the United States, physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Highlands range. The mountain range is located in the Eastern United States and extends 550 miles southwest from southern ...
. Between the late 1930s and the early 1950s, all of the Ss and Ss-1 steam locomotives were retired and scrapped with none surviving into preservation.
The Union Pacific Railroad rostered 144 locomotives, under the designation of TTT (Two-Ten-Two). They were divided into classes TTT-1 through TTT-7, but all had the same cylinder dimensions, driving wheel diameter and boiler pressure. Of these, only one locomotive survives; Union Pacific 5511 was donated to the Railroading Heritage of Midwest America, who are restoring the locomotive to operation.
The Denver and Rio Grande Western rostered ten locomotives, under the class designation of F-81, rostered as Nos. 1400–1409, and purchased from Alco in 1916. None survived into preservation, all of them being scrapped between 1952 and 1955.
References
{{Whyte types 10,2-10-2