2-10-0 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Under the
 The first boost in the number of Decapods occurred when
The first boost in the number of Decapods occurred when 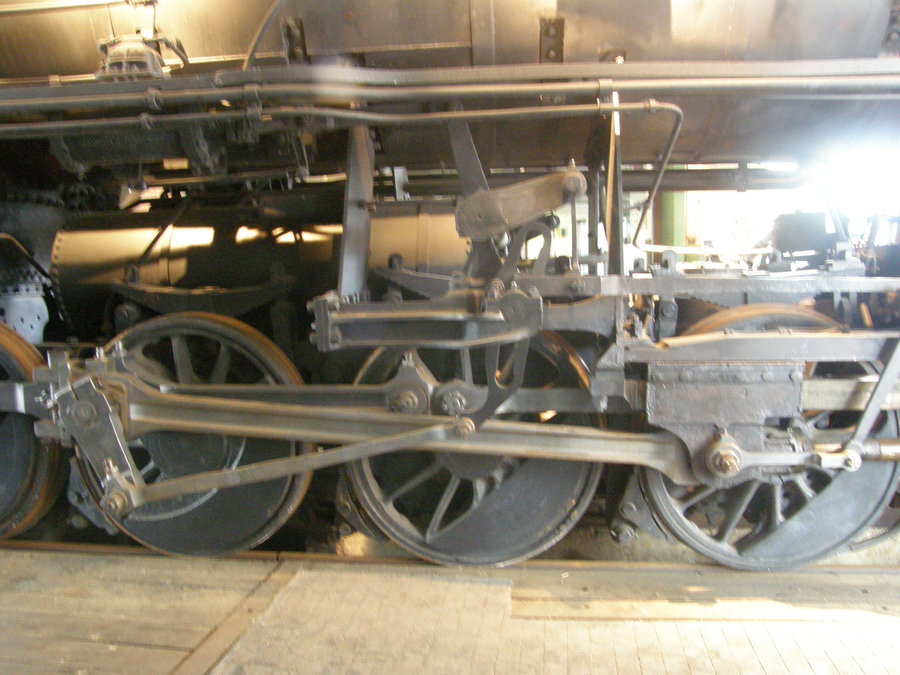 Swengel suggested the 2-10-0 arrangement was 'obsolete' by 1916, when the Pennsylvania Railroad commenced an experiment with a 2-10-0 locomotive at its Juniata plant. Most 10 coupled engines constructed for U.S. railroads during World War I were of the USRA 2-10-2 arrangement, but the PRR committed to 122 of the 2-10-0s. Swengel argued this commitment to the 2-10-0, nicknamed "Deks", was controversial even in 1916 and was more so in 1922 when the PRR placed additional orders. The PRR was soon the biggest user of Decapods in the United States. The type was ideally suited to the Pennsy's heavily graded
Swengel suggested the 2-10-0 arrangement was 'obsolete' by 1916, when the Pennsylvania Railroad commenced an experiment with a 2-10-0 locomotive at its Juniata plant. Most 10 coupled engines constructed for U.S. railroads during World War I were of the USRA 2-10-2 arrangement, but the PRR committed to 122 of the 2-10-0s. Swengel argued this commitment to the 2-10-0, nicknamed "Deks", was controversial even in 1916 and was more so in 1922 when the PRR placed additional orders. The PRR was soon the biggest user of Decapods in the United States. The type was ideally suited to the Pennsy's heavily graded
 The 2-10-0 arrangement was a very popular one in Germany. The first were built by the individual state railways from 1915 to 1918, and these later became the DRG BR58. The DRG then produced a number of standard classes of 2-10-0s: the heavy 3-cylinder BR44 (1753 built), the two-cylinder version BR43 (35 built), and the lightweight BR50 (3164 built). During wartime, the BR44 and BR50 designs were simplified as ÜK (''Übergangs Kriegslokomotiven'', or interim war locomotives). By 1941, it was clear that even these were too complicated, expensive, time-consuming to build, and used too much material in short supply, so new ''
The 2-10-0 arrangement was a very popular one in Germany. The first were built by the individual state railways from 1915 to 1918, and these later became the DRG BR58. The DRG then produced a number of standard classes of 2-10-0s: the heavy 3-cylinder BR44 (1753 built), the two-cylinder version BR43 (35 built), and the lightweight BR50 (3164 built). During wartime, the BR44 and BR50 designs were simplified as ÜK (''Übergangs Kriegslokomotiven'', or interim war locomotives). By 1941, it was clear that even these were too complicated, expensive, time-consuming to build, and used too much material in short supply, so new ''
 Locomotives with ten driving wheels were rare in British railway history. In 1913 an initial design for a four-cylinder 2-10-0 of
Locomotives with ten driving wheels were rare in British railway history. In 1913 an initial design for a four-cylinder 2-10-0 of

 Between early 1920s and 1958 Polish industry delivered to PKP some 1200 decapods of classes , , and . PKP also operated German decapods BR 52 ( Ty2) and BR 42 (Ty3), as well as American ones (, nicknamed "Trumman"). They were used to work the heaviest goods trains.
Between early 1920s and 1958 Polish industry delivered to PKP some 1200 decapods of classes , , and . PKP also operated German decapods BR 52 ( Ty2) and BR 42 (Ty3), as well as American ones (, nicknamed "Trumman"). They were used to work the heaviest goods trains.
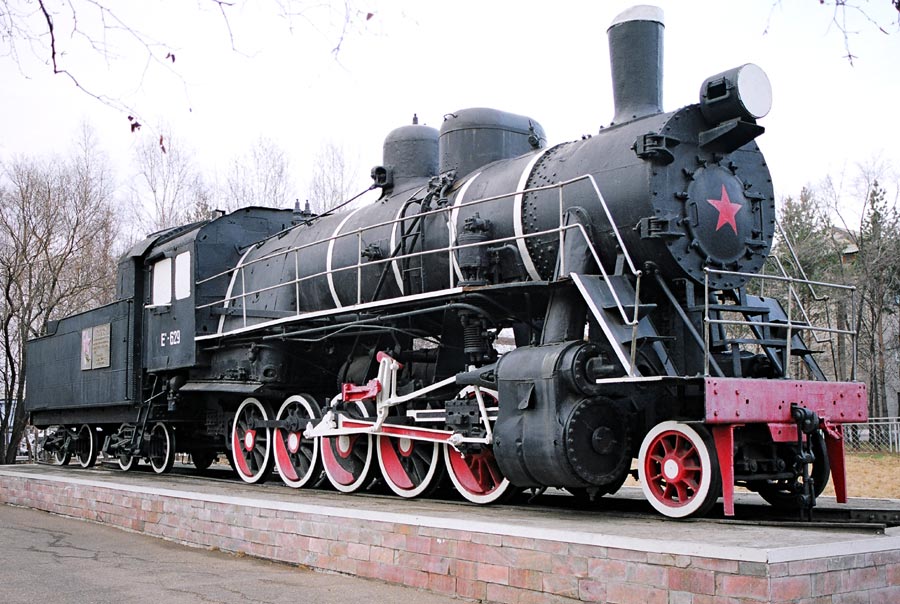 2-10-0 were fairly common freight locomotives in the former Soviet Union. They came from several sources: US imports ( class Ye (), built by ALCO and Baldwin, respectively), German war trophy DRB 52 class locomotives (what became the Soviet TE-series) and locally built. The locally built 2-10-0 locomotives were represented by some TE (built from captured German parts), SO (Sergo Ordjonikidze) and L (Lebedyanski)–series locomotives. The L-series locomotives were one of the more advanced steam locomotives built in the former Soviet Union. They used an automatic stoker to feed coal and had a relatively low axle load (18 tonnes or 40,000 lb) to be compatible with the war-torn railroads of the former Soviet Union. Several examples of these locomotives are still preserved in working order.
There is a 2-10-0 Lebedyanski series locomotive L 4657, marooned in a siding at Port Baikal.
2-10-0 were fairly common freight locomotives in the former Soviet Union. They came from several sources: US imports ( class Ye (), built by ALCO and Baldwin, respectively), German war trophy DRB 52 class locomotives (what became the Soviet TE-series) and locally built. The locally built 2-10-0 locomotives were represented by some TE (built from captured German parts), SO (Sergo Ordjonikidze) and L (Lebedyanski)–series locomotives. The L-series locomotives were one of the more advanced steam locomotives built in the former Soviet Union. They used an automatic stoker to feed coal and had a relatively low axle load (18 tonnes or 40,000 lb) to be compatible with the war-torn railroads of the former Soviet Union. Several examples of these locomotives are still preserved in working order.
There is a 2-10-0 Lebedyanski series locomotive L 4657, marooned in a siding at Port Baikal.
Illinois Railway Museum's roster page for SLSF 1630 (the operable 2-10-0)
{{Authority control 10,2-10-0 1867 in rail transport
Whyte notation
The Whyte notation is a classification method for steam locomotives, and some internal combustion locomotives and electric locomotives, by wheel arrangement. It was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte, and came into use in the early twenti ...
for the classification of steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, Fuel oil, oil or, rarely, Wood fuel, wood) to heat ...
s, 2-10-0 represents the wheel arrangement
In rail transport, a wheel arrangement or wheel configuration is a system of classifying the way in which wheels are distributed under a locomotive. Several notations exist to describe the wheel assemblies of a locomotive by type, position, and c ...
of two leading wheels on one axle, ten powered and coupled driving wheel
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons (or turbine, in the case of a steam turbine locomotive). On a conventional, non-articulated locomotive, the driving wheels are all coupled t ...
s on five axles, and no trailing wheel
On a steam locomotive, a trailing wheel or trailing axle is generally an unpowered wheel or axle (Wheelset (rail transport), wheelset) located behind the driving wheels. The axle of the trailing wheels is usually located in a trailing Bogie, t ...
s. This arrangement was often named Decapod, especially in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, although this name was sometimes applied to locomotives of 0-10-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, ten powered and coupled driving wheels on five axles and no trailing wheels. In the United Kingdom, this type is known ...
"Ten-Coupled" arrangement, particularly in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
. Notable German locomotives of this type include the war locomotives of Class 52.
These locomotives were popular in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, particularly in Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
and Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
; British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
use of the type was confined to the period during and after World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. In the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, the 2-10-0 was not widely popular but was a favorite of a small number of railroads which operated mostly in mountainous terrain. Among these was the Erie Railroad
The Erie Railroad was a railroad that operated in the Northeastern United States, originally connecting Pavonia Terminal in Jersey City, New Jersey, with Lake Erie at Dunkirk, New York. The railroad expanded west to Chicago following its 1865 ...
, a major Chicago to New York trunk line railroad, and the Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad ( reporting mark PRR), legal name as the Pennsylvania Railroad Company, also known as the "Pennsy," was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. At its ...
, whose heavily graded routes crossed the Allegheny Mountains.
The 2-10-0's main advantage was that five out of six of its axles were powered, meaning almost all the weight was available for traction rather than being distributed over pilot and trailing wheels. The long rigid wheelbase
In both road and rail vehicles, the wheelbase is the horizontal distance between the centers of the front and rear wheels. For road vehicles with more than two axles (e.g. some trucks), the wheelbase is the distance between the steering (front ...
caused problems on tightly curved track, so blind drivers were the norm, either on the central axle, and/or on the second and/or fourth axles. Often lateral motion devices were attached to the leading drive axle.
The wheel arrangement's disadvantages included the firebox size restriction caused by the lack of trailing wheel. This meant the firebox was fitted in between the wheels (common on earlier locomotives) and was long and narrow, or if mounted above the driving wheels, was wide and long but shallow. Many locomotives chose the latter option. A firebox mounted over the drivers also restricted the diameter of the driving wheels, which in turn limited speed. As with the Consolidation (2-8-0), "chopping" at speed ensured a rough ride for the crew due to instability caused by the wheel arrangement. In fact, backing any locomotive without a trailing axle was restricted to under twenty miles per hour or less. Most 2-10-0s were not operated at speeds greater than 50 mph (80 km/h).
The type operated as freight engine, although locomotives in Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
and the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
proved capable of hauling passenger train
A passenger train is a train used to transport people along a railroad line, as opposed to a freight train that carries goods. These trains may consist of unpowered passenger railroad cars (also known as coaches or carriages) push-pull train, ...
s.
United States
The first Decapods were built for theLehigh Valley Railroad
The Lehigh Valley Railroad was a railroad in the Northeastern United States built predominantly to haul anthracite, anthracite coal from the Coal Region in Northeastern Pennsylvania to major consumer markets in Philadelphia, New York City, and ...
in the late-1860s. They proved too rough on the track because of their long coupled wheelbase
In both road and rail vehicles, the wheelbase is the horizontal distance between the centers of the front and rear wheels. For road vehicles with more than two axles (e.g. some trucks), the wheelbase is the distance between the steering (front ...
. No more followed for 19 years, until the Northern Pacific Railway
The Northern Pacific Railway was an important American transcontinental railroad that operated across the northern tier of the Western United States, from Minnesota to the Pacific Northwest between 1864 and 1970. It was approved and chartered b ...
bought two for use on the switchbacks over Stampede Pass, while the tunnel was being built. In low-speed service where high tractive effort was critical, these Decapods were successful. Small numbers of other Decapods were built over the next twenty years, mostly for service in steeply graded mountainous areas where power at low speeds was the requirement. The type did not prove as popular as the successful Consolidation (2-8-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels. ...
) type. Among Decapod users was the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway
The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway , often referred to as the Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the largest Class 1 railroads in the United States between 1859 and 1996.
The Santa Fe was a pioneer in intermodal freight transport; at vario ...
. The engines were tandem compounds but their ongoing reversing limitations became the genesis of the 2-10-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels, ten powered and coupled driving wheels, and two trailing wheels. In the United States and elsewhere the is known as th ...
wheel arrangement.
 The first boost in the number of Decapods occurred when
The first boost in the number of Decapods occurred when Imperial Russia
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor/empress, or imperialism.
Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to:
Places
United States
* Imperial, California
* Imperial, Missouri
* Imperial, Nebraska
* Imperial, Pennsylvania
* ...
ordered approximately 1,200 Decapods
The Decapoda or decapods, from Ancient Greek δεκάς (''dekás''), meaning "ten", and πούς (''poús''), meaning "foot", is a large order (biology), order of crustaceans within the class Malacostraca, and includes crabs, lobsters, crayfis ...
from American builders during World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
. When the Bolshevik revolution
The October Revolution, also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution (in Soviet historiography), October coup, Bolshevik coup, or Bolshevik revolution, was the second of two revolutions in Russia in 1917. It was led by Vladimir L ...
occurred in 1917, 857 had already been delivered, but more than 200 were either awaiting shipment or were in the process of construction. These stranded locomotives were adopted by the United States Railroad Administration
The United States Railroad Administration (USRA) was the name of the nationalisation, nationalized railroad system of the United States between December 28, 1917, and March 1, 1920. It was the largest American experiment with nationalization, and ...
(USRA), the body created by the Government to oversee and control the railroads during the War, converted to American standards, and put to use on American railroads. Small and light-footed, these Russian decapods proved popular with smaller railroads, and many of them remained in service long after the USRA's control of the railroads ceased. Many indeed lasted until the end of steam on those railroads.
 Swengel suggested the 2-10-0 arrangement was 'obsolete' by 1916, when the Pennsylvania Railroad commenced an experiment with a 2-10-0 locomotive at its Juniata plant. Most 10 coupled engines constructed for U.S. railroads during World War I were of the USRA 2-10-2 arrangement, but the PRR committed to 122 of the 2-10-0s. Swengel argued this commitment to the 2-10-0, nicknamed "Deks", was controversial even in 1916 and was more so in 1922 when the PRR placed additional orders. The PRR was soon the biggest user of Decapods in the United States. The type was ideally suited to the Pennsy's heavily graded
Swengel suggested the 2-10-0 arrangement was 'obsolete' by 1916, when the Pennsylvania Railroad commenced an experiment with a 2-10-0 locomotive at its Juniata plant. Most 10 coupled engines constructed for U.S. railroads during World War I were of the USRA 2-10-2 arrangement, but the PRR committed to 122 of the 2-10-0s. Swengel argued this commitment to the 2-10-0, nicknamed "Deks", was controversial even in 1916 and was more so in 1922 when the PRR placed additional orders. The PRR was soon the biggest user of Decapods in the United States. The type was ideally suited to the Pennsy's heavily graded Allegheny Mountains
The Allegheny Mountain Range ( ) — also spelled Alleghany or Allegany, less formally the Alleghenies — is part of the vast Appalachian Mountain Range of the Eastern United States and Canada. Historically it represented a significant barr ...
routes, which required lugging ability according to tractive effort, not speed according to horse power.
The PRR bought 598 2-10-0s including 123 built at its own shops. In one of the largest locomotive orders ever, the rest came from the Baldwin Locomotive Works
The Baldwin Locomotive Works (BLW) was an American manufacturer of railway locomotives from 1825 to 1951. Originally located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, it moved to nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania, Eddystone in the early 20th century. The com ...
. The PRR 2-10-0s weighed and developed about of tractive effort with an axle loading of over . The engines steamed at and had a relatively large superheater. The grate area of about was on the small side, but a mechanical stoker partly compensated for this.
The PRR decapod, class I1s, was unlike the Russian decapod; it was huge, taking advantage of the PRR's heavy trackage and high axle loading, with a fat, free-steaming boiler that earned the type the nickname of 'Hippos' on the PRR. Two giant cylinders (30½ x 32 inch) gave the I1s power and their tenders permitted hard and long workings between stops. They were unpopular with the crews, for they were hard riding. The last operations on the PRR were 1957.
A small number of other Decapods were ordered by other railroads; the I-2 Decapods built for the Western Maryland Railway
The Western Maryland Railway was a small American Class I railroad (1852–1983) that operated in 3 Southern United States, Southern US States, Maryland (Western Maryland, Western Region), West Virginia (Potomac Highlands of West Virginia, Easte ...
were the largest ever built, at almost weight, and are a notable exception to the rule of thumb for the comfort of the ride on a 2-10-0 wheel arrangement, crews said the engines cruised smoothly up to 50 mph without becoming a rough ride. (After the running gear was redesigned by the WM) The WM's I-2 are also noted as the strongest Decapods ever built, at 96,315 lbs of tractive effort. (Not to be confused with the 10 Russian Decapods the WM held in their roster, which were standard Russian Decapods aside from heavier steel frames the WM used to replace the original cast iron frames, the new frames also made the WM Russian Decapods 2 inches longer than other Russian Decapods)
Baldwin developed two standard 2-10-0s for railroads with low axle-load requirements.King, E.W., Jr. in Drury p. 351
Thirteen Decapod locomotives survive in the US, including two Baldwin standards, six Russian Decapods and one PRR I1. Two, Great Western 90, a Baldwin Decapod at the Strasburg Rail Road, and Frisco 1630, a Russian Decapod at the Illinois Railway Museum, are operational. One Decapod survives as a static exhibit at the North Carolina Transportation Museum in Spencer, North Carolina ( Seaboard Air Line 2-10-0 #544).
Preserved Decapods in the United States
*1621 is on display at the National National Museum of Transportation - St. Louis, MO *1625 is on display at the Museum of the American Railroad - Frisco, TX * 1630 is operated by the Illinois Railway Museum - Union, IL. * 90 is operated by Strasburg Railroad - Strasburg, PA. * I1 class 4483 is atHamburg, New York
Hamburg ( ) is a Town (New York), town in Erie County, New York, Erie County, New York (state), New York, United States. As of the 2020 census, the town had a population of 60,085. It is named after the city of Hamburg, Germany. The town is on t ...
.
Proposed/Unbuilt (US)
L.D. Porta
Livio Dante Porta (21 March 1922 – 10 June 2003) was an Argentina, Argentine Locomotive#Steam, steam locomotive engineer. He is particularly remembered for his innovative modifications to existing locomotive systems in order to obtain better ...
proposed a 2-10-0, triple expansion Modern steam locomotive as a "second generation" fast-freight locomotive for the ACE 3000 project based on his previous works.
Germany
 The 2-10-0 arrangement was a very popular one in Germany. The first were built by the individual state railways from 1915 to 1918, and these later became the DRG BR58. The DRG then produced a number of standard classes of 2-10-0s: the heavy 3-cylinder BR44 (1753 built), the two-cylinder version BR43 (35 built), and the lightweight BR50 (3164 built). During wartime, the BR44 and BR50 designs were simplified as ÜK (''Übergangs Kriegslokomotiven'', or interim war locomotives). By 1941, it was clear that even these were too complicated, expensive, time-consuming to build, and used too much material in short supply, so new ''
The 2-10-0 arrangement was a very popular one in Germany. The first were built by the individual state railways from 1915 to 1918, and these later became the DRG BR58. The DRG then produced a number of standard classes of 2-10-0s: the heavy 3-cylinder BR44 (1753 built), the two-cylinder version BR43 (35 built), and the lightweight BR50 (3164 built). During wartime, the BR44 and BR50 designs were simplified as ÜK (''Übergangs Kriegslokomotiven'', or interim war locomotives). By 1941, it was clear that even these were too complicated, expensive, time-consuming to build, and used too much material in short supply, so new ''Kriegslokomotive
''Kriegslokomotiven'' (, singular: ''Kriegslokomotive'') or ''Kriegsloks'' were locomotives produced in large numbers during the Second World War under Nazi Germany.
Their construction was tailored to the economic circumstances of wartime Germa ...
'' (war locomotive) designs were developed: the lightweight BR52 (7794 built) and the intermediate weight BR42 (859 built).
Postwar locomotives of these types, particularly the BR 52, were spread all over Europe and were taken into service by the railways of many different countries:
* BR44 in France, SNCF 150X.
* BR50 in Belgium, NMBS/SNCB
The National Railway Company of Belgium (, NMBS; , SNCB; ) is the national railway company of Belgium. The company formally styles itself using the Dutch and French abbreviations NMBS/SNCB. The corporate logo designed in 1936 by Henry van de V ...
class 25; in Denmark, DSB class N.
* BR52 in Austria, ÖBB class 52; in Belgium, NMBS/SNCB class 26; in Norway, NSB Class 63.
United Kingdom
 Locomotives with ten driving wheels were rare in British railway history. In 1913 an initial design for a four-cylinder 2-10-0 of
Locomotives with ten driving wheels were rare in British railway history. In 1913 an initial design for a four-cylinder 2-10-0 of tractive effort
In railway engineering, the term tractive effort describes the pulling or pushing capability of a locomotive. The published tractive force value for any vehicle may be theoretical—that is, calculated from known or implied mechanical proper ...
was produced by the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway
The Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (L&YR) was a major History of rail transport in Great Britain, British railway company before the Railways Act 1921, 1923 Grouping. It was Incorporation (business)#Incorporation in the United Kingdom, incorpo ...
, but none were built. This had been inspired by Jean-Baptiste Flamme's 2-10-0s working in Belgium and used a similar tapered boiler, with the round-topped firebox almost filling the loading gauge. The first 2-10-0 was built during the Second World War, as a variant of the "Austerity" 2-8-0 for lightly built railways.
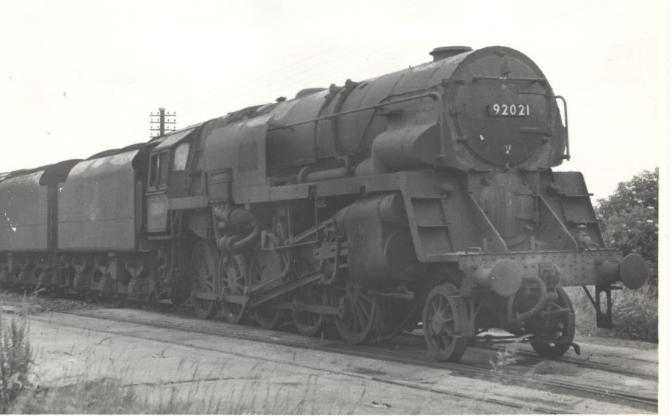
The only other 2-10-0 type was the 251-strong Standard class 9F introduced by British Railways
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Commis ...
in 1954. The class included 92220 ''Evening Star'', the last steam locomotive built for British Railways, in 1960; and 92203 (named ''Black Prince'' when preserved), which in 1983 set a record for the heaviest steam locomotive-hauled train in Britain when it started a 2,162-ton train at Foster Yeoman quarry in Somerset.
Finland
The State Railroads ofFinland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
purchased 20 American Decapods after WWII
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
- these were originally built for the Soviet Union, but never delivered to them. Of the 20 engines, 10 were made by Baldwin, 10 by Alco
The American Locomotive Company (often shortened to ALCO, ALCo or Alco) was an American manufacturer that operated from 1901 to 1969, initially specializing in the production of locomotives but later diversifying and fabricating at various time ...
. Since they were originally built for the USSR, they had the correct gauge for Finland, too ( exactly). One (Alco # 75214, 1947) is preserved at the Finnish Railway Museum in Hyvinkää
Hyvinkää (; , ) is a town in Finland, located in the southern interior of the country. Hyvinkää is situated in the northern part of the Uusimaa region. The population of Hyvinkää is approximately . It is the most populous municipality in ...
, Finland. The Finnish designation was Tr2.
The locomotive was nicknamed ''Truman'' in Finland. It was used for hauling heavy freight trains.
France
From 1910 to 1951, the French industry built more than 500 decapods for three railway companies (Paris-Orléans, Nord, Est) and for the national railways (SNCF
The Société nationale des chemins de fer français (, , SNCF ) is France's national State-owned enterprise, state-owned railway company. Founded in 1938, it operates the Rail transport in France, country's national rail traffic along with th ...
). Moreover, at the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, SNCF inherited more than 200 units of German decapods built in France, mostly BR 44. The last decapod, a SNCF 150P, was withdrawn in 1968. All 2-10-0s, of French or of German design, proved reliable and powerful in service. One can notice that some engines of the Paris-Orléans company were dedicated to passenger service on difficult mountain lines.
Poland

 Between early 1920s and 1958 Polish industry delivered to PKP some 1200 decapods of classes , , and . PKP also operated German decapods BR 52 ( Ty2) and BR 42 (Ty3), as well as American ones (, nicknamed "Trumman"). They were used to work the heaviest goods trains.
Between early 1920s and 1958 Polish industry delivered to PKP some 1200 decapods of classes , , and . PKP also operated German decapods BR 52 ( Ty2) and BR 42 (Ty3), as well as American ones (, nicknamed "Trumman"). They were used to work the heaviest goods trains.
Romania
After theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
built the 150.000 Class, after DRB Class 50. A total of 282 locomotives were built between 1946 and 1960, at Malaxa (later ''23 August Works'') in Bucharest
Bucharest ( , ; ) is the capital and largest city of Romania. The metropolis stands on the River Dâmbovița (river), Dâmbovița in south-eastern Romania. Its population is officially estimated at 1.76 million residents within a greater Buc ...
, and in Reşiţa.
Builder details:
* 150.001-150.050 Reşiţa
* 150.051-150.081 Malaxa
* 150.082-150.282 Reşiţa
Soviet Union
 2-10-0 were fairly common freight locomotives in the former Soviet Union. They came from several sources: US imports ( class Ye (), built by ALCO and Baldwin, respectively), German war trophy DRB 52 class locomotives (what became the Soviet TE-series) and locally built. The locally built 2-10-0 locomotives were represented by some TE (built from captured German parts), SO (Sergo Ordjonikidze) and L (Lebedyanski)–series locomotives. The L-series locomotives were one of the more advanced steam locomotives built in the former Soviet Union. They used an automatic stoker to feed coal and had a relatively low axle load (18 tonnes or 40,000 lb) to be compatible with the war-torn railroads of the former Soviet Union. Several examples of these locomotives are still preserved in working order.
There is a 2-10-0 Lebedyanski series locomotive L 4657, marooned in a siding at Port Baikal.
2-10-0 were fairly common freight locomotives in the former Soviet Union. They came from several sources: US imports ( class Ye (), built by ALCO and Baldwin, respectively), German war trophy DRB 52 class locomotives (what became the Soviet TE-series) and locally built. The locally built 2-10-0 locomotives were represented by some TE (built from captured German parts), SO (Sergo Ordjonikidze) and L (Lebedyanski)–series locomotives. The L-series locomotives were one of the more advanced steam locomotives built in the former Soviet Union. They used an automatic stoker to feed coal and had a relatively low axle load (18 tonnes or 40,000 lb) to be compatible with the war-torn railroads of the former Soviet Union. Several examples of these locomotives are still preserved in working order.
There is a 2-10-0 Lebedyanski series locomotive L 4657, marooned in a siding at Port Baikal.
Footnotes
References
* * * * * * * *External links
Illinois Railway Museum's roster page for SLSF 1630 (the operable 2-10-0)
{{Authority control 10,2-10-0 1867 in rail transport