1920 Antwerp Olympics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The 1920 Summer Olympics (; ; ), officially known as the Games of the VII Olympiad (; ; ) and commonly known as Antwerp 1920 (;
Dutch
Dutch or Nederlands commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
** Dutch people as an ethnic group ()
** Dutch nationality law, history and regulations of Dutch citizenship ()
** Dutch language ()
* In specific terms, i ...
and German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
: ''Antwerpen 1920''), were an international multi-sport event
A multi-sport event is an organized sporting event, often held over multiple days, featuring competition in many different sports among organized teams of athletes from (mostly) nation-states. The first major, modern, multi-sport event of intern ...
held in 1920 in Antwerp
Antwerp (; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of Antwerp Province, and the third-largest city in Belgium by area at , after ...
, Belgium.
In March 1912, during the 13th session of the IOC, Belgium's bid to host the 1920 Summer Olympics was made by Baron Édouard de Laveleye, president of the Belgian Olympic Committee and of the Royal Belgian Football Association
The Royal Belgian Football Association (RBFA; ; ; ) is the governing body of football in Belgium. It was a founding member of FIFA in 1904 and UEFA in 1954 and was based in Brussels, not far from the King Baudouin Stadium. Since October 2021, th ...
. No fixed host city was proposed at the time.
The 1916 Summer Olympics
The 1916 Summer Olympics (), officially known as the Games of the VI Olympiad ( German: ''Spiele der VI. Olympiade''), were scheduled to be held in Berlin, Germany. However, they were cancelled due to the outbreak of World War I, the first tim ...
, to have been held in Berlin, capital of the German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
, were cancelled due to World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
. When the Olympic Games resumed after the war, Antwerp was awarded hosting the 1920 Summer Games as a tribute to the Belgian people. The aftermath of the war and the Paris Peace Conference, 1919
Paris () is the capital and largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the fourth-most populous city in the European Union and the 30th most densely pop ...
affected the Olympic Games not only due to new states being created, but also by sanctions against the nations that lost the war and were blamed for starting it. Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
, and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
were banned from competing in the Games. Soviet Russia
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
had just emerged from the Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
and chose not to attend the Games. Germany did not return to Olympic competition until 1928
Events January
* January – British bacteriologist Frederick Griffith reports the results of Griffith's experiment, indirectly demonstrating that DNA is the genetic material.
* January 1 – Eastern Bloc emigration and defection: Boris B ...
and instead hosted a series of games called Deutsche Kampfspiele
The German Combat Games () were a national multi-sport event established in 1922 by the Deutscher Reichsausschuss fĂĽr LeibesĂĽbungen under Carl Diem.
Deutsche Kampfspiele
The events lasted from 1922 to 1934. According to Diem the games shoul ...
, starting with the Winter edition of 1922 (which predated the first Winter Olympics).
The United States won the most gold and overall medals at the 1920 Summer Games.
Host city selection
In March 1912, during the 13th session of the IOC, the bid on behalf of Belgium to host the 1920 Summer Olympics was made by Baron Édouard de Laveleye, president of theBelgian Olympic Committee
Belgian may refer to:
* Something of, or related to, Belgium
* Belgians, people from Belgium or of Belgian descent
* Languages of Belgium, languages spoken in Belgium, such as Dutch, French, and German
*Ancient Belgian language, an extinct language ...
and of the Royal Belgian Football Association
The Royal Belgian Football Association (RBFA; ; ; ) is the governing body of football in Belgium. It was a founding member of FIFA in 1904 and UEFA in 1954 and was based in Brussels, not far from the King Baudouin Stadium. Since October 2021, th ...
. No fixed host city was proposed at the time.
The organizing committee was created on 9 August 1913. It had four presidents:
*Édouard de Laveleye, president of the Belgian Olympic Committee
*Henri de Baillet-Latour
Henri de Baillet-Latour, Count of Baillet-Latour (1 March 1876 – 6 January 1942) was a Belgian aristocrat and the third president of the International Olympic Committee (IOC).
Early life
Henri de Baillet-Latour was born in Brussels, Belgium, ...
, member of the IOC
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; , CIO) is the international, non-governmental, sports governing body of the modern Olympic Games. Founded in 1894 by Pierre de Coubertin and Demetrios Vikelas, it is based in L ...
*Robert Osterrieth
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''HrĹŤĂľiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' () "fame, glory, honour, praise, reno ...
, president of the Royal Yacht Club of Belgium
* Charles Cnoops, vice-president of the Belgian Fencing Association
Among the 22 vice-presidents of the committee were people with a military or industrial background, and further people from sports organizations like Paul Havenith, president of the football and athletics club K. Beerschot V.A.C.
Koninklijke Beerschot Voetbal en Atletiek Club, now K Beerschot VA was a Belgian football club from Antwerp. The club was founded in 1899 when most players of Antwerp left the club. It played in the 1920 Olympic Games Stadium named the "Kiel".
...
and Nicolaas Jan Cupérus, president of the Belgian Gymnastics Federation.
The first action of the committee was to send an official letter to the IOC in Paris, confirming Antwerp as the city for the Belgian Olympic bid. With Antwerp confirmed as the Olympic Games host, Belgium began reconstructing the Beerschot Stadium into the . Construction on the new Olympic stadium began in July 1919 and finished in May 1920.
In 1914, a 109-page brochure was created to promote the idea of Antwerp as a host city for the Olympics: ''Aurons-nous la VIIème Olympiade à Anvers?'' (''Will we have the 7th Olympiad at Antwerp?''). It was sent to all IOC members and was used during the 6th Olympic Congress in Paris in 1914, where the candidacies of Amsterdam (which would eventually host the 1928 Summer Olympics
The 1928 Summer Olympics (), officially the Games of the IX Olympiad (), was an international multi-sport event that was celebrated from 28 July to 12 August 1928 in Amsterdam, Netherlands. The city of Amsterdam had previously bid for ...
), Antwerp, Budapest, and Rome (which would eventually host the 1960 Summer Olympics
The 1960 Summer Olympics (), officially known as the Games of the XVII Olympiad () and commonly known as Rome 1960 (), were an international multi-sport event held from 25 August to 11 September 1960 in Rome, Italy. Rome had previously been awar ...
) were discussed. Despite a slight preference at the time for Budapest, no final choice was made, and the outbreak of World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
soon afterwards prevented any further progress.
In 1915, Lyon
Lyon (Franco-Provençal: ''Liyon'') is a city in France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of the French Alps, southeast of Paris, north of Marseille, southwest of Geneva, Switzerland, north ...
made a bid for the 1920 Games, but after some discussion, they agreed to support Antwerp and postpone their bid until 1924 if Antwerp was liberated in time to organize the Games. The support for Belgium by cousin country France, then the leading country of the IOC, also meant that Amsterdam and Budapest (in an enemy state) had no chance for the 1920 games against Antwerp.
New candidacies from American cities did not have that disadvantage, and bids were received from Cleveland
Cleveland is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located along the southern shore of Lake Erie, it is situated across the Canada–U.S. maritime border and approximately west of the Ohio-Pennsylvania st ...
, Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
, and Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Georgia (U.S. state), most populous city in the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. It is the county seat, seat of Fulton County, Georg ...
(which would eventually host the 1996 Summer Olympics
The 1996 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XXVI Olympiad, also known as Atlanta 1996 and commonly referred to as the Centennial Olympic Games) were an international multi-sport event held from July 19 to August 4, 1996, in Atlanta, ...
), while Cuba also submitted a bid for Havana
Havana (; ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center.Jan De Vos, mayor of Antwerp, and inaugurated less than a year later on 23 May 1920 with a
 There were 162 events in 28 disciplines that were part of the Olympic program in 1920. The number of events in each discipline is noted in parentheses.
There were 162 events in 28 disciplines that were part of the Olympic program in 1920. The number of events in each discipline is noted in parentheses.
Women's water polo was a demonstration sport.

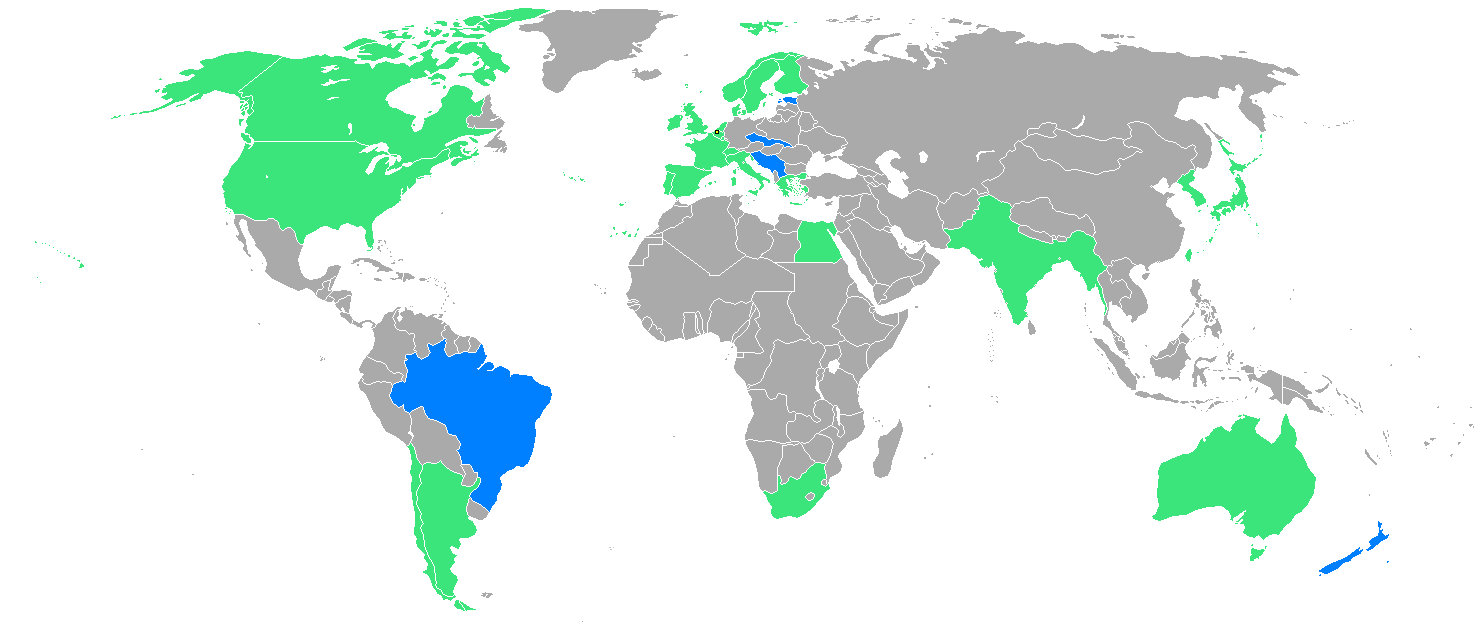
 A total of 29 nations participated in the Antwerp Games, only one more than in 1912, as
A total of 29 nations participated in the Antwerp Games, only one more than in 1912, as
Openingsceremonie
– An article about the opening ceremonies of the 1920 Antwerp Olympiade in Flemish (archived) {{Authority control Summer Olympics by year
gymnastics
Gymnastics is a group of sport that includes physical exercises requiring Balance (ability), balance, Strength training, strength, Flexibility (anatomy), flexibility, agility, Motor coordination, coordination, artistry and endurance. The movem ...
demonstration.
When the Olympic Games began, the stadium was still unfinished with some events being built over fortifications and others using existing locations. The athletes quarters were crowded and athletes slept on folding cots.
The nautical stadium or Stade Nautique d'Antwerp
Stade Nautique d'Antwerp (Dutch:''Zwemstadion van Antwerpen'') was an aquatics venue located in Antwerp, Belgium. For the 1920 Summer Olympics, it hosted the diving, swimming, and water polo.
This was the first structure devoted to the aquatics ev ...
was built at the end of the Jan Van Rijswijcklaan, using the city ramparts there as a spectator's stand. Other events, like shooting, boxing, and equestrian sports, were held at pre-existing locations in and around Antwerp and as far away as Ostend
Ostend ( ; ; ; ) is a coastal city and municipality in the province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It comprises the boroughs of Mariakerke, Raversijde, Stene and Zandvoorde, and the city of Ostend proper – the la ...
.
The number of spectators was low throughout Antwerp's Summer Olympics, since not many people could afford tickets. In the closing days of the Olympic Games, students were allowed to attend the event for free. After the conclusion of the Olympic Games, Belgium recorded a loss of more than 600 million francs.
Highlights
* The Olympic Games being a symbol of peace and global solidarity shone at Antwerp. These Olympics were the first in which theOlympic Oath
The Olympic Oath (distinct from the Olympic creed) is a solemn promise made by one athlete, judge or official, and one coach at the Opening Ceremony of each Olympic Games. Each oath taker is from the host nation and takes the oath on behalf of a ...
was voiced, the first in which doves were released to symbolize peace, and the first in which the Olympic Flag
The International Olympic Committee (IOC) uses icons, flags, and symbols to represent and enhance the Olympic Games. These symbols include those commonly used during Olympic competitions such as the flame, fanfare, and theme as well as those u ...
was flown to display the unity of the world's continents through its 5 rings.
* The United States won 41 gold, 27 silver, and 27 bronze medals. Sweden, Great Britain, Finland, and Belgium rounded out the five most successful medal-winning nations, with France and Belgium being the nations that fielded the most athletes, with the United States being only the third by that statistic.
* The Games also featured a week of winter sports, with figure skating
Figure skating is a sport in which individuals, pairs, or groups perform on figure skates on ice. It was the first winter sport to be included in the Olympic Games, with its introduction occurring at the Figure skating at the 1908 Summer Olympi ...
appearing for the first time since the 1908 Olympics
The 1908 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the IV Olympiad and also known as London 1908) were an international multi-sport event held in London, England, from 27 April to 31 October 1908. The 1908 Games were originally schedu ...
, and ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey in North America) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an Ice rink, ice skating rink with Ice hockey rink, lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. Tw ...
making its Olympic debut.
* Nedo Nadi
Nedo Nadi (9 June 1894 – 29 January 1940) was one of the best Italian fencers of all time. He is the only fencer to win a gold medal in each of the three weapons at a single Olympic Games and won the most fencing gold medals ever at a singl ...
won 5 gold medals in the fencing events.
* At the age of 72, Sweden's 100 metre running deer double-shot event champion Oscar Swahn
Oscar Gomer Swahn (20 October 1847 – 1 May 1927) was a Sweden, Swedish Shooting sports, shooter who competed at three Olympic games and won six medals, including three gold. Swahn holds records as the oldest Olympian at the time of competi ...
, who had participated in the 1908 and 1912 Games, came in second in the team event to become the oldest Olympic medal winner ever.
* 23-year-old Paavo Nurmi
Paavo Johannes Nurmi (; 13 June 1897 – 2 October 1973) was a Finland, Finnish middle-distance running, middle-distance and long-distance running, long-distance runner. He was called the "Flying Finn" because he dominated distance running in th ...
won the 10,000 m and 8000 m cross country races, took another gold in team cross country, and a silver in the 5000 m run. His contributions for Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
broke a record in track and field with 9 medals.
* Duke Kahanamoku
Duke Paoa Kahinu Mokoe Hulikohola Kahanamoku (August 24, 1890 – January 22, 1968) was a Hawaiian competition swimmer, lifeguard, and popularizer of the sport of surfing. A Native Hawaiian, he was born three years before the overthrow of the ...
retained the 100 m swimming title he won before the war.
* The sailing
Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the ''water'' (sailing ship, sailboat, raft, Windsurfing, windsurfer, or Kitesurfing, kitesurfer), on ''ice'' (iceboat) or on ''land'' (Land sa ...
events were among some of strangest moments in Olympic history:
**there were originally 16 events scheduled but there were no entrants for the 9 metre, 1907 rating class nor the 8.5 metre 1919 rating class
**the 12-foot dinghy event took place in two different countries. The final two races in the event were independently held in the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
, on its own accord, supposedly because the only two competitors in the event were Dutch.
*Sport shooter
Shooting sports is a group of competitive and recreational sporting activities involving proficiency tests of accuracy, precision and speed in shooting — the art of using ranged weapons, mainly small arms (firearms and airguns, in forms such ...
Guilherme Paraense won Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
's very first gold medal at the Olympic Games.
*The United States sent a women's swimming team for the first time, and the Americans won seven out of seven available swimming medals.
Sports/Events
 There were 162 events in 28 disciplines that were part of the Olympic program in 1920. The number of events in each discipline is noted in parentheses.
There were 162 events in 28 disciplines that were part of the Olympic program in 1920. The number of events in each discipline is noted in parentheses.
Korfball
Korfball ( ) is a ball sport, with similarities to netball, basketball, and ringball. The objective is to throw a ball into a netless basket that is mounted on a pole. Each team is composed of four female players and four male players. The s ...
was a demonstration sport.
Women's water polo was a demonstration sport.
Venues
Seventeen sports venues were used in the 1920 Summer Olympics. This marked the first time that the football tournament was spread throughout the country, which has mostly been the case since.
Participating nations

 A total of 29 nations participated in the Antwerp Games, only one more than in 1912, as
A total of 29 nations participated in the Antwerp Games, only one more than in 1912, as Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
, Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
and Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of TĂĽrkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
were not invited, having lost World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
and sanctioned for starting it. From the newly created European states, only Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
took part, as Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia ( ; Czech language, Czech and , ''ÄŚesko-Slovensko'') was a landlocked country in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland beca ...
succeeded Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was a country in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 to 1929, it was officially called the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, but the term "Yugoslavia" () has been its colloq ...
succeeded Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
, with both nations had sent athletes prior to World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
(in the case of Bohemia as part of the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
). Soviet Russia
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
was busy with the Polish-Soviet War and therefore was unable to form an Olympic team (Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
in turn, had never participated in the games before, only doing so in later editions). Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
and Monaco
Monaco, officially the Principality of Monaco, is a Sovereign state, sovereign city-state and European microstates, microstate on the French Riviera a few kilometres west of the Regions of Italy, Italian region of Liguria, in Western Europe, ...
competed as nations at the Olympic Games for the first time. New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
, which had competed as part of a combined team with Australia in 1908 and 1912, competed on its own for the first time. The games marked the return of Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
and India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
to the competitions.
At the time, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
, New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
and South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
were all part of the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
. Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
was a British protectorate (a state not part of the British Empire but nonetheless administered by the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
).
* The had one competitor, Eric Robertson. But as the dominion had no official Olympic committee, his nationality could not be confirmed and he represented Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
.
As the local Olympic Organizing Committee went bankrupt during the Antwerp 1920 Games, no official report of the Games was ever produced. The documents of the Games were archived at the Belgium Olympic Committee headquarters in Brussels.
Number of athletes by National Olympic Committees
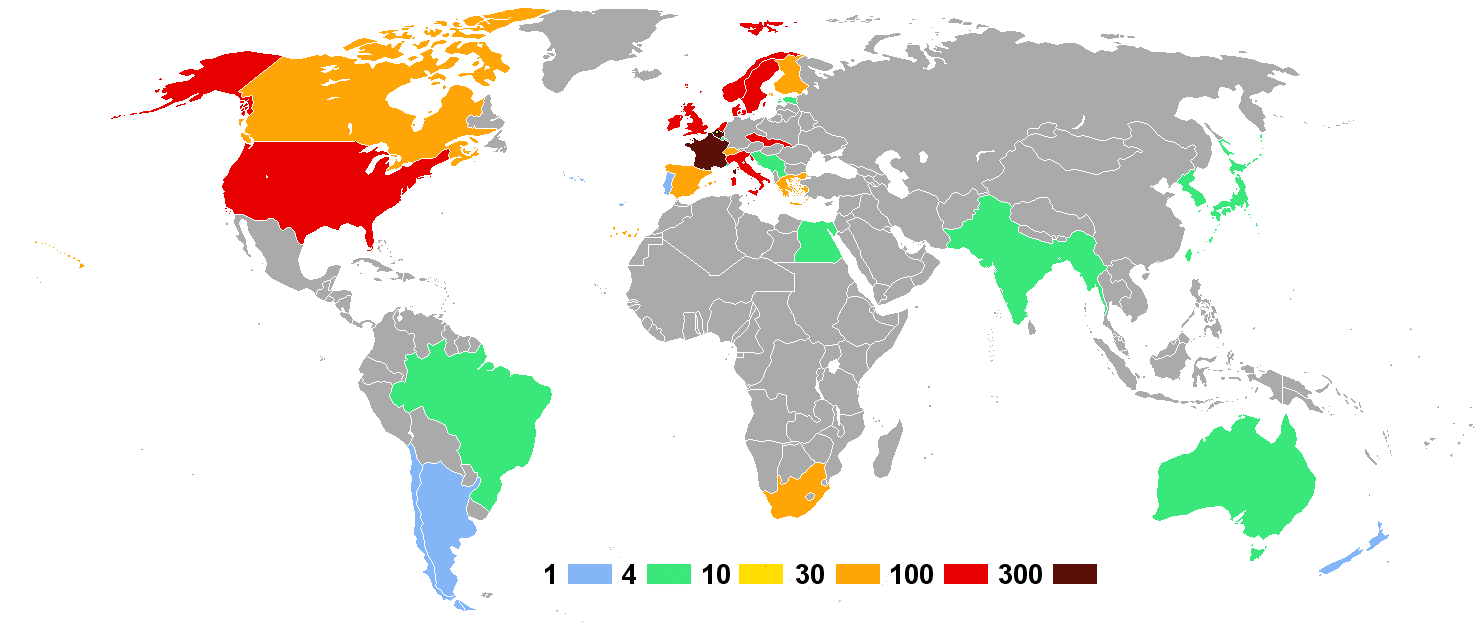
Medal count
These are the top ten nations that won medals at the 1920 Games. These were the first Olympics where the host nation did not win the most medals overall.See also
Notes
External links
*Openingsceremonie
– An article about the opening ceremonies of the 1920 Antwerp Olympiade in Flemish (archived) {{Authority control Summer Olympics by year
Summer Olympics
The Summer Olympic Games, also known as the Summer Olympics or the Games of the Olympiad, is a major international multi-sport event normally held once every four years. The inaugural Games took place in 1896 in Athens, then part of the King ...
Summer Olympics
The Summer Olympic Games, also known as the Summer Olympics or the Games of the Olympiad, is a major international multi-sport event normally held once every four years. The inaugural Games took place in 1896 in Athens, then part of the King ...
Olympic Games in Belgium
1920s in Antwerp
Sports competitions in Antwerp
August 1920 sports events in Europe
September 1920 sports events in Europe