‚ÄėAlawńę on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Alawites () are an
 When the French began to occupy Syria in 1920, an
When the French began to occupy Syria in 1920, an  In 1939, the
In 1939, the
Return of the Pink Panthers?
" ''Mideast Monitor''. Vol. 3, No. 2, August 2008. issued a
 After the Syrian civil war broke out in 2011, the
After the Syrian civil war broke out in 2011, the
Reuters (8 December 2024). In May 2013, pro-opposition
 Other beliefs and practices include: the
Other beliefs and practices include: the
 According to a disputed letter, in 1936, six Alawi notables petitioned the French colonialists not to merge their Alawi enclave with the rest of Syria, insisting that "the spirit of hatred and fanaticism embedded in the hearts of the Arab Muslims against everything that is non-Muslim has been perpetually nurtured by the Islamic religion." Worth, ''A Rage for Order'', 2016: p.85 However, according to associate professor Stefan Winter, this letter is a forgery. According to Worth, later ''
According to a disputed letter, in 1936, six Alawi notables petitioned the French colonialists not to merge their Alawi enclave with the rest of Syria, insisting that "the spirit of hatred and fanaticism embedded in the hearts of the Arab Muslims against everything that is non-Muslim has been perpetually nurtured by the Islamic religion." Worth, ''A Rage for Order'', 2016: p.85 However, according to associate professor Stefan Winter, this letter is a forgery. According to Worth, later ''
 Some sources have discussed the "Sunnification" of Alawites under the al-Assad regime.
Some sources have discussed the "Sunnification" of Alawites under the al-Assad regime.
8 October 2004 In a paper, "Islamic Education in Syria", Landis wrote that "no mention" is made in Syrian textbooks (controlled by the Al-Assad regime) of Alawites, Druze,
 To avoid confusion with the ethnic Turkish and Kurdish
To avoid confusion with the ethnic Turkish and Kurdish
 In 2011, there were an estimated 150,000 Alawites in Lebanon, where they have lived since at least the 16th century. They are one of the 18 official Lebanese sects; due to the efforts of their leader, Ali Eid, the
In 2011, there were an estimated 150,000 Alawites in Lebanon, where they have lived since at least the 16th century. They are one of the 18 official Lebanese sects; due to the efforts of their leader, Ali Eid, the
Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
ethnoreligious group who live primarily in the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
region in West Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian ...
and follow Alawism
Alawism (), also known as Nusayrism (), is an offshoot of early Shia Islam with influences from ancient Iranian, Christian, and Gnostic traditions. Its adherents, called the Alawites, are estimated to number around 4 million and are primarily conc ...
, a sect of Islam that splintered from early Shia
Shia Islam is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that Muhammad designated Ali ibn Abi Talib () as both his political successor (caliph) and as the spiritual leader of the Muslim community (imam). However, his right is understood ...
as a ''ghulat
The () were a branch of history of Shia Islam, early Shi'a Islam. The term mainly refers to a wide variety of List of extinct Shia sects, extinct Shi'i sects active in 8th- and 9th-century Kufa in Lower Mesopotamia, and who, despite their somet ...
'' branch during the ninth century. Alawites venerate Ali ibn Abi Talib
Ali ibn Abi Talib (; ) was the fourth Rashidun caliph who ruled from until Assassination of Ali, his assassination in 661, as well as the first imamate in Shia doctrine, Shia Imam. He was the cousin and son-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muha ...
, the " first Imam" in the Twelver
Twelver Shi'ism (), also known as Imamism () or Ithna Ashari, is the Islamic schools and branches, largest branch of Shia Islam, Shi'a Islam, comprising about 90% of all Shi'a Muslims. The term ''Twelver'' refers to its adherents' belief in twel ...
school, as a manifestation of the divine essence. It is the only ''ghulat'' sect still in existence today. The group was founded during the ninth century by Ibn Nusayr
Abu Shu'ayb Muhammad ibn Nusayr al-Numayri (died ), commonly known simply as Ibn Nusayr, was an Arab religious leader who is considered the founder of Alawism. He was a contemporary of Ali al-Hadi and Hasan al-Askari, the tenth and eleventh imam ...
, who was a disciple of the tenth Twelver Imam, Ali al-Hadi
Ali al-Hadi (; ‚Äď ) was a descendant of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and the tenth Imamate in Shia doctrine, Imam in Twelver Shi'ism, Twelver Shia, succeeding his father, Muhammad al-Jawad (). Born in Medina in 828, Ali is known with the ti ...
, and of the eleventh Twelver Imam, Hasan al-Askari
Hasan al-Askari (; ) was a descendant of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He is regarded as the eleventh of the Twelve Imams, succeeding his father, Ali al-Hadi. Hasan Al-Askari was born in Medina in 844 and brought with his father to the garris ...
. For this reason, Alawites are also called ''Nusayris''.
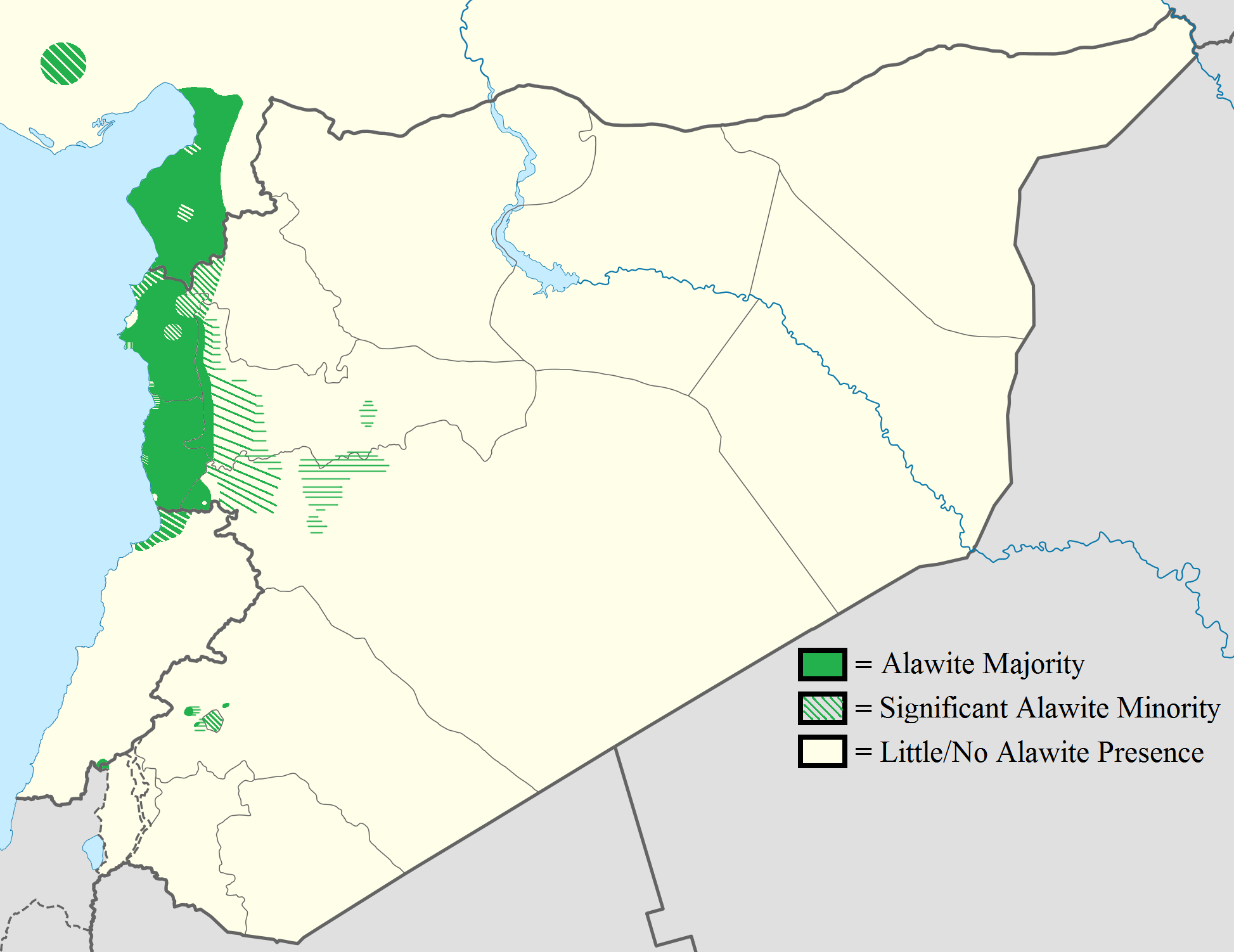
Surveys suggest Alawites represent an important portion of the Syrian population and are a significant minority in the Hatay Province
Hatay Province (, ) is the southernmost province and metropolitan municipality of Turkey. Its area is , and its population is 1,686,043 (2022). It is situated mostly outside Anatolia, along the eastern coast of the Levantine Sea. The province ...
of Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of T√ľrkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
and northern Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
. There is also a population living in the village of Ghajar
Ghajar (, or ), also Rhadjar, is an Alawite-Arab village on the Hasbani River, on the border between Lebanon and the Israeli-occupied portion of the Golan Heights. The name of the village means "gypsy" in Arabic. As of , it had a population ...
in the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights, or simply the Golan, is a basaltic plateau at the southwest corner of Syria. It is bordered by the Yarmouk River in the south, the Sea of Galilee and Hula Valley in the west, the Anti-Lebanon mountains with Mount Hermon in t ...
, where there had been two other Alawite villages ( Ayn Fit and Za'ura) before the Six-Day War
The Six-Day War, also known as the June War, 1967 Arab‚ÄďIsraeli War or Third Arab‚ÄďIsraeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states, primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan from 5 to 10June ...
. The Alawites form the dominant religious group on the Syrian coast and towns near the coast, which are also inhabited by Sunni
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Mu ...
s, Christians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
, and Ismailis
Ismailism () is a branch of Shia Islam. The Isma'ili () get their name from their acceptance of Imam Isma'il ibn Jafar as the appointed spiritual successor ( imńĀm) to Ja'far al-Sadiq, wherein they differ from the Twelver Shia, who accept M ...
. They are often confused with the Alevis
Alevism (; ; ) is a syncretic heterodox Islamic tradition, whose adherents follow the mystical Islamic teachings of Haji Bektash Veli, who taught the teachings of the Twelve Imams, whilst incorporating some traditions from shamanism. Differing ...
, a religious group in Turkey that shares certain similarities with the Alawites but has key differences.
The Quran
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a WaŠł•y, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, AllńĀh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which ...
is one of their holy books, but its interpretation differs significantly from Shia Muslim interpretations and aligns with early Batiniyya
Batiniyya () refers to groups that distinguish between an outer, exoteric ('' zńĀhir'') and an inner, esoteric ('' bńĀŠĻ≠in'') meaning in Islamic scriptures.
Ismaili Batiniya
The term has been used in particular for an allegoristic type of scr ...
and other ''ghulat'' sects. Alawite theology and rituals differ sharply from Shia Islam in several important ways. For instance, various Alawite rituals involve the drinking of wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink made from Fermentation in winemaking, fermented fruit. Yeast in winemaking, Yeast consumes the sugar in the fruit and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Wine is most often made f ...
and the sect does not prohibit the consumption of alcohol for its adherents. As a creed that teaches the symbolic/esoteric reading of Qur'anic verses, Alawite theology is based on the belief in reincarnation
Reincarnation, also known as rebirth or transmigration, is the Philosophy, philosophical or Religion, religious concept that the non-physical essence of a living being begins a new lifespan (disambiguation), lifespan in a different physical ...
and views Ali as a divine incarnation of God. Moreover, Alawite clergy
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the ter ...
and scholarships insist that their religion is theologically distinct from Shi'ism
Shia Islam is the second-largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam. It holds that Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad designated Ali ibn Abi Talib () as both his political Succession to Muhammad, successor (caliph) and as the spiritual le ...
. Alawites have historically kept their beliefs secret from outsiders and non-initiated Alawites, so rumours about them have arisen. Arabic accounts of their beliefs tend to be partisan (either positively or negatively). However, since the early 2000s, Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
scholarship on the Alawite religion has made significant advances. At the core of the Alawite creed is the belief in a divine Trinity, comprising three aspects of the one God. The aspects of the Trinity are ''Mana'' (meaning), ''Ism'' (Name) and ''Bab'' (Door). Alawite beliefs hold that these emanations underwent re-incarnation cyclically seven times in human form throughout history. According to Alawites, the seventh incarnation of the trinity consists of Ali ibn Abi Talib
Ali ibn Abi Talib (; ) was the fourth Rashidun caliph who ruled from until Assassination of Ali, his assassination in 661, as well as the first imamate in Shia doctrine, Shia Imam. He was the cousin and son-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muha ...
, Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
and Salman al-Farisi
Salman Farsi (; ) was a Persian religious scholar and one of the companions of Muhammad. As a practicing Zoroastrian, he dedicated much of his early life to studying to become a magus, after which he began travelling extensively throughout Wester ...
.
Alawites, considered disbelievers by classical Sunni and Shi'ite theologians, faced periods of subjugation or persecution under various Muslim empires such as the Ottomans, Abbasids, Mamluks, and others. The establishment of the French Mandate of Syria
The Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon (; , also referred to as the Levant States; 1923‚ąí1946) was a League of Nations mandate founded in the aftermath of the First World War and the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire, concerning the territories ...
in 1920 marked a turning point in Alawite history. Until then, the community had commonly self-identified as "Nusayris", emphasizing their connections to Ibn Nusayr
Abu Shu'ayb Muhammad ibn Nusayr al-Numayri (died ), commonly known simply as Ibn Nusayr, was an Arab religious leader who is considered the founder of Alawism. He was a contemporary of Ali al-Hadi and Hasan al-Askari, the tenth and eleventh imam ...
. The French administration prescribed the label "Alawite" to categorise the sect alongside Shiism in official documents. The French
French may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France
** French people, a nation and ethnic group
** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices
Arts and media
* The French (band), ...
recruited a large number of minorities into their armed forces and created exclusive areas for minorities, including the Alawite State
The Alawite State (, '; ), initially named the Territory of the Alawites ()‚ÄĒafter the locally-dominant Alawites‚ÄĒfrom its inception until its integration to the Syrian Federation in 1922, was a French mandate territory on the coast of pre ...
. The Alawite State was later dismantled, but the Alawites continued to play a significant role in the Syrian military
The Syrian Armed Forces () are the military forces of Syria.
Up until the fall of Bashar al-Assad's Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party ‚Äď Syria Region, Ba'ath Party Ba'athist Syria, regime in December 2024, the Syrian Arab Armed Forces were the sta ...
and later in the Ba'ath Party
The Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party ( ' ), also known simply as Bath Party (), was a political party founded in Syria by Michel Aflaq, Salah al-Din al-Bitar, and associates of Zaki al-Arsuzi. The party espoused Ba'athism, which is an ideology ...
. After Hafez al-Assad
Hafez al-Assad (6 October 193010 June 2000) was a Syrian politician and military officer who was the president of Syria from 1971 until Death and state funeral of Hafez al-Assad, his death in 2000. He was previously the Prime Minister of Syria ...
's seizure of power during the 1970 coup, the Ba'athist state enforced Assadist ideology amongst Alawites to supplant their traditional identity. During the Syrian revolution
The Syrian revolution, also known as the Syrian Revolution of Dignity, was a series of mass protests and civilian uprisings throughout Syria ‚Äď with a subsequent violent reaction by the Ba'athist regime ‚Äď lasting from 15 March 2011 to 8 De ...
, communal tensions were further exacerbated as the country destabilized into a full-scale sectarian civil war.
Etymology
In older sources, Alawis are often called "Ansaris". According toSamuel Lyde
Samuel Lyde (1825–1860) was an English writer and Church of England missionary who lived and worked in Syria in the 1850s and wrote a pioneering book on the Alawite sect. In 1856, he sparked months of anti-Christian rioting in Ottoman Pales ...
, who lived among the Alawites during the mid-19th century, this was a term they used among themselves. Other sources indicate that "Ansari" is simply a Western error in the transliteration of "Nusayri". Alawites historically self-identified as Nusayrites, after their religious founder Ibn Nusayr al-Numayri. However, the term "Nusayri" had fallen out of currency by the 1920s, as a movement led by intellectuals within the community during the French Mandate
Mandate most often refers to:
* League of Nations mandates, quasi-colonial territories established under Article 22 of the Covenant of the League of Nations, 28 June 1919
* Mandate (politics), the power granted by an electorate
Mandate may also r ...
sought to replace it with the modern term "Alawi". They characterised the older name (which implied "a separate ethnic and religious identity") as an "invention of the sect's enemies", ostensibly favouring an emphasis on "connection with mainstream Islam"‚ÄĒparticularly the Shia branch. The term "Nusayrites" is now used as a slur and was frequently used as by Sunni fundamentalists fighting against Bashar al-Assad
Bashar al-Assad (born 11September 1965) is a Syrian politician, military officer and former dictator
Sources characterising Assad as a dictator:
who served as the president of Syria from 2000 until fall of the Assad regime, his government ...
's government in the Syrian civil war, who use its emphasis on Ibn Nusayr to insinuate that Alawi beliefs are "man-made" and not divinely inspired.
Necati Alkan argued in an article that the "Alawi" appellation was used in an 11th-century Nusayri book and was not a 20th-century invention. The following quote from the same article illustrates his point: As to the change from "NuŠĻ£ayrńę" to " ŅAlawńę": most studies agree that the term " ŅAlawńę" was not used until after WWI and probably coined and circulated by MuŠł•ammad Amńęn GhńĀlib al-ŠĻ¨awńęl, an Ottoman official and writer of the famous ''Ta ĺrńękh al- ŅAlawiyyńęn'' (1924). However, the name 'Alawńę' appears in an 11th century NuŠĻ£ayrńę tract as one of the names of the believer (‚Ķ). Moreover, the term 'Alawńę' was already used at the beginning of the 20th century. In 1903 the Belgian-born Jesuit and OrientalistThe Alawites are distinct from the ''Henri Lammens Henri Lammens (1 July 1862 ‚Äď 23 April 1937) was a Belgian Orientalist historian and Jesuit, who wrote (in French) on the early history of Islam. Education and career as a Jesuit Born in Ghent, Belgium of Catholic Flemish stock, Henri Lammens ...(d. 1937) visited a certain Šł§aydarńę-NuŠĻ£ayrńę sheikh Abdullah in a village near Antakya and mentions that the latter preferred the name 'Alawńę' for his people. Lastly, it is interesting to note that in the above-mentioned petitions of 1892 and 1909 the NuŠĻ£ayrńęs called themselves the 'Arab Alawńę people' ( ŅArab ŅAlevńę ŠĻ≠ńĀ ĺifesi) 'our ŅAlawńę NuŠĻ£ayrńę people' (ŠĻ≠ńĀ ĺifatunńĀ al-NuŠĻ£ayriyya al- ŅAlawiyya) or 'signed with Alawńę people' ( ŅAlevńę ŠĻ≠ńĀ ĺifesi imŇľńĀsńĪyla). This early self-designation is, in my opinion, of triple importance. Firstly, it shows that the word 'Alawńę' was always used by these people, as ŅAlawńę authors emphasize; secondly, it hints at the reformation of the NuŠĻ£ayrńęs, launched by some of their sheikhs in the 19th century and their attempt to be accepted as part of Islam; and thirdly, it challenges the claims that the change of the identity and name from 'NuŠĻ£ayrńę' to ' ŅAlawńę' took place around 1920, in the beginning of the French mandate in Syria (1919‚Äď1938).
Alevi
Alevism (; ; ) is a syncretic heterodox Islamic tradition, whose adherents follow the mystical Islamic teachings of Haji Bektash Veli, who taught the teachings of the Twelve Imams, whilst incorporating some traditions from shamanism. Differing ...
'' religious sect in Turkey, although the terms share a common etymology and pronunciation.
Genealogical origin theories
The origin of the genetics of Alawites is disputed. Local folklore suggests that they are descendants of the followers of the eleventh Imam,Hasan al-Askari
Hasan al-Askari (; ) was a descendant of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He is regarded as the eleventh of the Twelve Imams, succeeding his father, Ali al-Hadi. Hasan Al-Askari was born in Medina in 844 and brought with his father to the garris ...
(d. 873), and his pupil, Ibn Nusayr (d. 868). During the 19th and 20th centuries some Western scholars believed that Alawites were descended from ancient Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
ern peoples such as the Arameans
The Arameans, or Aramaeans (; ; , ), were a tribal Semitic people in the ancient Near East, first documented in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. Their homeland, often referred to as the land of Aram, originally covered c ...
, Canaanites
{{Cat main, Canaan
See also:
* :Ancient Israel and Judah
Ancient Levant
Hebrew Bible nations
Ancient Lebanon
0050
Ancient Syria
Wikipedia categories named after regions
0050
0050
Phoenicia
Amarna Age civilizations ...
, Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian peoples, Anatolian Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European people who formed one of the first major civilizations of the Bronze Age in West Asia. Possibly originating from beyond the Black Sea, they settled in mo ...
, and Mardaites
The Mardaites () or al-Jarajima (; /ALA-LC: ''al-JarńĀjimah'') were early Christians following Chalcedonian Christianity in the Nur Mountains. Little is known about their ethnicity, but it has been speculated that they might have been Persians ( ...
. Many prominent Alawite tribes are also descended from 13th century settlers from Sinjar
Sinjar (; , ) is a town in the Sinjar District of the Nineveh Governorate in northern Iraq. It is located about five kilometers south of the Sinjar Mountains. Its population in 2013 was estimated at 88,023, and is predominantly Yazidi.
History ...
.
In his Natural History
Natural history is a domain of inquiry involving organisms, including animals, fungi, and plants, in their natural environment, leaning more towards observational than experimental methods of study. A person who studies natural history is cal ...
, Book V, Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
said:
The "Tetrarchy of the Nazerini" refers to the western region, between the Orontes and the sea, which consists of a small mountain range called Alawi Mountains
The Coastal Mountain Range (, ''Silsilat al-JibńĀl as-SńĀŠł•ilńęyah'') also called Jabal al-Ansariya, Jabal an-Nusayria or Jabal al-`Alawńęyin (Ansari, Nusayri or Alawi Mountains) is a mountain range in northwestern Syria running north‚Äďsouth, ...
bordered by a valley running from south-east to north-west known as Al-Ghab Plain; the region was populated by a portion of Syrians, who were called Nazerini. However scholars are reluctant to link Nazerini and Nazarenes. Yet the term "Nazerini" can be possibly connected to words which include the Arabic triliteral root
The roots of verbs and most nouns in the Semitic languages are characterized as a sequence of consonants or " radicals" (hence the term consonantal root). Such abstract consonantal roots are used in the formation of actual words by adding the vowel ...
'' n-ŠĻ£-r'' such as the subject ''naŠĻ£er'' in Eastern Aramaic
Eastern Aramaic refers to a group of dialects that evolved historically from the varieties of Aramaic spoken in the core territories of Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq, southeastern Turkey and parts of northeastern Syria) and further expanded into n ...
, which means "''keeper of wellness''".
History
Ibn Nusayr
Abu Shu'ayb Muhammad ibn Nusayr al-Numayri (died ), commonly known simply as Ibn Nusayr, was an Arab religious leader who is considered the founder of Alawism. He was a contemporary of Ali al-Hadi and Hasan al-Askari, the tenth and eleventh imam ...
and his followers are considered the founders of the religion. After the death of the Eleventh Imam, al-Askari, problems emerged in the Shia Community concerning his succession, and then Ibn Nusayr claimed to be the Bab and Ism of the deceased Imam and that he received his secret teachings. Ibn Nusayr and his followers' development seems to be one of many other early ghulat mystical Islamic sects, and were apparently excommunicated by the Shia representatives of the 12th Hidden Imam.
The Alawites were later organised during Hamdanid
The Hamdanid dynasty () was a Shia Muslim Arab dynasty that ruled modern day Northern Mesopotamia and Syria (890‚Äď1004). They descended from the ancient Banu Taghlib tribe of Mesopotamia and Arabia.
History Origin
The Hamdanids hailed ...
rule in northern Syria (947‚Äď1008) by a follower of Muhammad ibn Nusayr known as al-KhaŠĻ£ńębńę, who died in Aleppo
Aleppo is a city in Syria, which serves as the capital of the Aleppo Governorate, the most populous Governorates of Syria, governorate of Syria. With an estimated population of 2,098,000 residents it is Syria's largest city by urban area, and ...
about 969, after a rivalry with the Ishaqiyya sect, which claimed also to have the doctrine of Ibn Nusayr. The embrace of Alawism by the majority of the population in the Syrian coastal mountains was likely a protracted process occurring over several centuries. Modern research indicates that after its initial establishment in Aleppo, Alawism spread to Sarmin
Sarmin ( also spelled Sarmeen) is a town in northwestern Syria, administratively part of the Idlib Governorate, located 15 kilometers southeast of Idlib. It has an altitude of about 390 meters. Nearby localities include Binnish to the north, Tal ...
, Salamiyah
file:Hama qalat shmemis salamiyyah syria 1995.jpg, A full view of Shmemis (spring 1995)
Salamiyah (; also transliterated ''Salamiyya'', ''Salamieh'' or ''Salamya'') is a city in central Syria, administratively part of the Hama Governorate. It is ...
, Homs
Homs ( ; ), known in pre-Islamic times as Emesa ( ; ), is a city in western Syria and the capital of the Homs Governorate. It is Metres above sea level, above sea level and is located north of Damascus. Located on the Orontes River, Homs is ...
and Hama
Hama ( ', ) is a city on the banks of the Orontes River in west-central Syria. It is located north of Damascus and north of Homs. It is the provincial capital of the Hama Governorate. With a population of 996,000 (2023 census), Hama is one o ...
before becoming concentrated in low-lying villages west of Hama, including Baarin
Baarin (, ''Ba Ņrńęn'' or ''Bi Ņrńęn'') is a village in northern Syria, administratively part of the Hama Governorate, located in Homs Gap roughly southwest of Hama. Nearby localities include Taunah and Awj to the south, Aqrab and Houla to th ...
, Deir Shamil
Deir Shamil (, also spelled Deir el-Shemil) is a village in northwestern Syria, administratively part of the Hama Governorate, located west of Hama. Nearby localities include Nahr al-Bared to the north, Tell Salhab to the northeast, Jubb Ramlah ...
, and Deir Mama
Deir Mama () is a village in northwestern Syria, administratively part of the Hama Governorate. It is located west of Hama along the eastern foothills of the Syrian Coastal Mountain Range. The village may have been one of the earliest rural areas ...
, the Wadi al-Uyun
Wadi al-'Uyun (, also spelled Wadi al-Oyun, Wady Aloyon, or Wadi al-Ayun; transliteration: "Valley of the Springs") is a town in northwestern Syria, administratively part of the Hama Governorate, located west of Hama.
According to the Syria Cent ...
valley, and in the mountains around Tartus
Tartus ( / ALA-LC: ''ŠĻ¨arŠĻ≠Ňęs''; known in the County of Tripoli as Tortosa and also transliterated from French language, French Tartous) is a major port city on the Mediterranean coast of Syria. It is the second largest port city in Syria (af ...
and Safita
Safita ( '; , ''SŇćpŇęte'') is a city in the Tartus Governorate, western Syria, located to the southeast of Tartus and to the northwest of Krak des Chevaliers. It is situated on the tops of three hills and the valleys between them, in the Syrian ...
.
In 1032, al-KhaŠĻ£ńębńę's grandson and pupil, Abu Sa'id Maymun al-Tabarani (d. 1034), moved to Latakia
Latakia (; ; Syrian Arabic, Syrian pronunciation: ) is the principal port city of Syria and capital city of the Latakia Governorate located on the Mediterranean coast. Historically, it has also been known as Laodicea in Syria or Laodicea ad Mar ...
(then controlled by the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
). Al-Tabarani succeeded his mentor al-Jilli of Aleppo as head missionary in Syria and became "the last definitive scholar of Alawism", founding its calendar and giving Alawite teachings their final form, according to the historian Stefan Winter
Stefan Winter (born 16 March 1968''List of licenses ordered by country''
. Al-Tabarani influenced the Alawite faith through his writings and by converting the rural population of the Syrian Coastal Mountain Range.
Winter argues that while it is likely the Alawite presence in Latakia dates to Tabarani's lifetime, it is unclear if Alawite teachings spread to the city's mountainous hinterland, where the Muslim population generally leaned toward Shia Islam, in the eleventh century. In the early part of the century, the Jabal al-Rawadif (part of the Syrian Coastal Mountains around Latakia) were controlled by the local Arab chieftain Nasr ibn Mushraf al-Rudafi, who vacillated between alliance and conflict with Byzantium. There is nothing in the literary sources indicating al-Rudafi patronized the Alawites.
To the south of Jabal al-Rawadif, in the Jabal Bahra, a 13th-century Alawite treatise mentions the sect was sponsored by the Banu'l-Ahmar, Banu'l-Arid, and Banu Muhriz
The Banu Muhriz were an Arab princely family that controlled the fortresses of Marqab (Margat), Kahf and Qadmus in the late 11th and early 12th centuries.
The family is credited by a 13th-century Alawite treatise for patronizing the budding A ...
, three local families who controlled fortresses in the region in the 11th and 12th centuries. From this southern part of the Syrian coastal mountain range, a significant Alawite presence developed in the mountains east of Latakia and Jableh
Jableh (; ', also spelt ''Jebleh'', ''Jabala'', ''Jablah, Gabala'' or ''Gibellum'') is a Mediterranean coastal city in Syria, north of Baniyas and south of Latakia, with c. 80,000 inhabitants (2004 census). As Ancient ''Gabala'', it was a By ...
during the Mamluk
Mamluk or Mamaluk (; (singular), , ''mamńĀlńęk'' (plural); translated as "one who is owned", meaning "slave") were non-Arab, ethnically diverse (mostly Turkic, Caucasian, Eastern and Southeastern European) enslaved mercenaries, slave-so ...
period (1260s‚Äď1516).
According to Bar Hebraeus
Gregory Bar Hebraeus (, b. 1226 - d. 30 July 1286), known by his Syriac ancestral surname as Barebraya or Barebroyo, in Arabic sources by his kunya Abu'l-Faraj, and his Latinized name Abulpharagius in the Latin West, was a Maphrian (region ...
, many Alawites were killed when the Crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding ...
initially entered Syria in 1097; however, they tolerated them when they concluded they were not a truly Islamic sect. They even incorporated them within their ranks, along with the Maronites
Maronites (; ) are a Syriac Christian ethnoreligious group native to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant (particularly Lebanon) whose members belong to the Maronite Church. The largest concentration has traditionally resided near Mount ...
and Turcopoles
During the period of the Crusades, turcopoles (also "turcoples" or "turcopoli"; from the , literally "sons of Turks") were locally recruited mounted archers and light cavalry employed by the Byzantine Empire and the Crusader states. A leader of t ...
. Two prominent Alawite leaders in the following centuries, credited with uplifting the group, were Shaykhs al-Makzun (d. 1240) and al-Tubani (d. 1300), both originally from Mount Sinjar
The Sinjar Mountains (, , ), are a mountain range that runs east to west, rising above the surrounding alluvial steppe plains in northwestern Iraq to an elevation of . The highest segment of these mountains, about long, lies in the Nineveh Gover ...
in modern Iraq.
In the 14th century, the Alawites were forced by Mamluk Sultan Baibars
Al-Malik al-Zahir Rukn al-Din Baybars al-Bunduqdari (; 1223/1228 ‚Äď 1 July 1277), commonly known as Baibars or Baybars () and nicknamed Abu al-Futuh (, ), was the fourth Mamluk sultan of Egypt and Syria, of Turkic Kipchak origin, in the Ba ...
to build mosques in their settlements, to which they responded with token gestures described by the Muslim traveller Ibn Battuta
Ibn Battuta (; 24 February 13041368/1369), was a Maghrebi traveller, explorer and scholar. Over a period of 30 years from 1325 to 1354, he visited much of Africa, the Middle East, Asia and the Iberian Peninsula. Near the end of his life, Ibn ...
.
Ottoman Empire
During the reign of Sultan Selim I, of the Ottoman Empire, the Alawites would again experience significant persecution; especially inAleppo
Aleppo is a city in Syria, which serves as the capital of the Aleppo Governorate, the most populous Governorates of Syria, governorate of Syria. With an estimated population of 2,098,000 residents it is Syria's largest city by urban area, and ...
when a massacre occurred in the Great Mosque of Aleppo
The Great Mosque of Aleppo, also known as the Great Umayyad Mosque of Aleppo, is the largest and one of the oldest mosques in the city of Aleppo, Syria built by the Umayyad Caliphate. It is located in the al-Jalloum district of the Ancient City o ...
on 24 April 1517. The massacre was known as the "Massacre of the Telal" () in which the corpses of thousands of victims accumulated as a tell located west of the castle
A castle is a type of fortification, fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by Military order (monastic society), military orders. Scholars usually consider a ''castle'' to be the private ...
. The horrors of the massacre which caused the immigration of the survivors to the coastal region are documented at the National and University Library National and University Library or National University Library may refer to:
*Australian National University Library
*National and University Library "St. Kliment of Ohrid", North Macedonia
*National and University Library of Bosnia and Herzegovina ...
in Strasbourg
Strasbourg ( , ; ; ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est Regions of France, region of Geography of France, eastern France, in the historic region of Alsace. It is the prefecture of the Bas-Rhin Departmen ...
.
The Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
took aggressive actions against Alawites, due to their alleged "treacherous activities" as "they had a long history of betraying the Muslim governments due to their mistrust towards Sunnis." The Alawis rose up against the Ottomans on several occasions, and maintained their autonomy in their mountains.
In his book ''Seven Pillars of Wisdom
''Seven Pillars of Wisdom'' is the autobiographical account of the experiences of British Army Colonel T. E. Lawrence ("Lawrence of Arabia") while serving as a military advisor to Bedouin forces during the Arab Revolt against the Ottoman Empi ...
'' T. E. Lawrence
Thomas Edward Lawrence (16 August 1888 ‚Äď 19 May 1935) was a British Army officer, archaeologist, diplomat and writer known for his role during the Arab Revolt and Sinai and Palestine campaign against the Ottoman Empire in the First W ...
wrote:
During the 18th century, the Ottomans employed a number of Alawite leaders as tax collectors under the ''iltizam
An iltizam () was a form of tax farm that appeared in the 15th century in the Ottoman Empire. The system began under Mehmed the Conqueror and was abolished during the Tanzimat reforms in 1856.
Iltizams were sold off by the government to wealthy n ...
'' system. Between 1809 and 1813, Mustafa Agha Barbar
Mustafa Agha Barbar El Korek (1767 ‚Äď 28 April 1835) was an Ottoman Syrian statesman and military officer who was governor of the Ottoman province of Tripoli, ruling between 1800‚Äď08, 1810‚Äď20 and 1821-35.
Name
The middle word in his name, A ...
, the governor of Tripoli, attacked the Kalbiyya
The Kalbiyya (), or Kalbi or Kelbi tribe is one of four tribes, or tribal confederations, of the Alawite community in Syria. Appearing in historical sources from the 16th century, the Kalbiyya came to prominence when Hafez al-Assad, the son of ...
Alawites with "marked savagery." Some Alawites supported Ottoman involvement in the Egyptian-Ottoman Wars of 1831‚Äď1833 and 1839‚Äď1841, and had careers in the Ottoman army or as Ottoman governors. Moreover, they even initiated the Alawite revolt (1834‚Äď35)
Alawites () are an Arab ethnoreligious group who live primarily in the Levant region in West Asia and follow Alawism, a sect of Islam that splintered from early Shia as a ''ghulat'' branch during the ninth century. Alawites venerate Ali ibn ...
against the Egyptian rule of the region, which was later suppressed by the Governor of Homs.
By the mid-19th century, the Alawite people, customs and way of life were described by Samuel Lyde
Samuel Lyde (1825–1860) was an English writer and Church of England missionary who lived and worked in Syria in the 1850s and wrote a pioneering book on the Alawite sect. In 1856, he sparked months of anti-Christian rioting in Ottoman Pales ...
, an English missionary among them, as suffering from nothing except a gloomy plight.
Early in the 20th century, the mainly-Sunni Ottoman leaders were bankrupt and losing political power; the Alawites were poor peasant
A peasant is a pre-industrial agricultural laborer or a farmer with limited land-ownership, especially one living in the Middle Ages under feudalism and paying rent, tax, fees, or services to a landlord. In Europe, three classes of peasan ...
s.
French Mandate period
After the end of World War I and the fall of the Ottoman Empire, Syria and Lebanon were placed by theLeague of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919‚Äď1920), Paris Peace ...
under the French Mandate for Syria and Lebanon
The Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon (; , also referred to as the Levant States; 1923‚ąí1946) was a League of Nations mandate founded in the aftermath of the First World War and the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire, concerning the territori ...
. On 15 December 1918, Alawite leader Saleh al-Ali
Salih al-Ali (1883 ‚Äď 13 April 1950) was a Syrian Alawite military commander who led the Alawite revolt of 1919‚Äď1921 against the French mandate of Syria.
Background
Salih al-Ali was born in 1883 to a family of Alawite notables from al-Shayk ...
called for a meeting of Alawite leaders in the town of Al-Shaykh Badr
Al-Shaykh Badr (, also transliterated ''Sheikh Bader'') is a city in western Syria, administratively part of the Tartus Governorate. Al-Shaykh Badr has an altitude of . According to the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS), al-Shaykh Badr, w ...
, urging them to revolt and expel the French from Syria.
When French authorities heard about the meeting, they sent a force to arrest Saleh al-Ali. He and his men ambushed and defeated the French forces at Al-Shaykh Badr, inflicting more than 35 casualties. After this victory, al-Ali began organizing his Alawite rebels into a disciplined force, with its general command and military ranks.
The Al-Shaykh Badr skirmish began the Syrian Revolt of 1919. Al-Ali responded to French attacks by laying siege to (and occupying) al-Qadmus
Al-Qadmus (, also spelled al-Qadmous or Cadmus) is a town in northwestern Syria, administratively part of the Tartus Governorate, located northeast of Tartus and southeast of Baniyas. Nearby localities include Kaff al-Jaa and Masyaf to the east, ...
, from which the French had conducted their military operations against him. In November, General Henri Gouraud
Henri Gouraud (17 November 1867 - 16 September 1946) was a French army general. He played a central role in the colonization of French Africa and the Levant. During World War I, he fought in major battles such as those of the Argonne, the Dard ...
mounted a campaign against Saleh al-Ali's forces in the Alawi Mountains. His forces entered al-Ali's village of Al-Shaykh Badr, arresting many Alawi leaders; however, al-Ali fled to the north. When a large French force overran his position, he went underground.
Despite these instances of opposition, the Alawites mostly favored French rule and sought its continuation beyond the mandate period.
Alawite State
Alawite State
The Alawite State (, '; ), initially named the Territory of the Alawites ()‚ÄĒafter the locally-dominant Alawites‚ÄĒfrom its inception until its integration to the Syrian Federation in 1922, was a French mandate territory on the coast of pre ...
was created in the coastal and mountain country comprising most Alawite villages. The division was intended to protect the Alawite people from more powerful majorities, such as the Sunnis.
The French also created microstate
A microstate or ministate is a sovereign state having a very small population or land area, usually both. However, the meanings of "state" and "very small" are not well-defined in international law. Some recent attempts to define microstates ...
s, such as Greater Lebanon
The State of Greater Lebanon (; ), informally known as French Lebanon, was a state declared on 1 September 1920, which became the Lebanese Republic (; ) in May 1926, and is the predecessor of modern Lebanon.
The state was declared on 1 Septembe ...
for the Maronite Christians
Maronites (; ) are a Syriac Christian ethnoreligious group native to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant (particularly Lebanon) whose members belong to the Maronite Church. The largest concentration has traditionally resided near Mount ...
and Jabal al-Druze
Jabal al-Druze (), is an elevated volcanic region in the Suwayda Governorate of southern Syria. Most of the inhabitants of this region are Druze, and there are also significant Christian communities. Safaitic inscriptions were first found in ...
for the Druze
The Druze ( ; , ' or ', , '), who Endonym and exonym, call themselves al-MuwaŠł•Šł•idŇęn (), are an Arabs, Arab Eastern esotericism, esoteric Religious denomination, religious group from West Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic ...
. Aleppo and Damascus were also separate states.Longrigg, Stephen Hemsley. ''Syria and Lebanon Under French Mandate''. London: Oxford University Press, 1958. Under the Mandate, many Alawite chieftains supported a separate Alawite nation, and tried to convert their autonomy into independence.
The French Mandate Administration encouraged Alawites to join their military forces, in part to provide a counterweight to the Sunni majority, which was more hostile to their rule. According to a 1935 letter by the French minister of war, the French considered the Alawites and the Druze
The Druze ( ; , ' or ', , '), who Endonym and exonym, call themselves al-MuwaŠł•Šł•idŇęn (), are an Arabs, Arab Eastern esotericism, esoteric Religious denomination, religious group from West Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic ...
the only " warlike races" in the Mandate territories. Between 1926 and 1939, the Alawites and other minority groups provided the majority of the locally recruited component of the Army of the Levant
The Army of the Levant () identifies the armed forces of France and then Vichy France which occupied, and were in part recruited from, the Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon, French Mandated territories in the Levant during the interwar period and ...
‚ÄĒthe designation given to the French military forces garrisoning Syria and the Lebanon.
The region was home to a mostly-rural, heterogeneous population. The landowning families and 80 percent of the population of the port city of Latakia
Latakia (; ; Syrian Arabic, Syrian pronunciation: ) is the principal port city of Syria and capital city of the Latakia Governorate located on the Mediterranean coast. Historically, it has also been known as Laodicea in Syria or Laodicea ad Mar ...
were Sunni Muslims; however, in rural areas 62 percent of the population were Alawite. According to some researchers, there was considerable Alawite separatist sentiment in the region, their evidence is a 1936 letter signed by 80 Alawi leaders addressed to the French Prime Minister which said that the "Alawite people rejected attachment to Syria and wished to stay under French protection." Among the signatories was Sulayman Ali al-Assad, father of Hafez al-Assad
Hafez al-Assad (6 October 193010 June 2000) was a Syrian politician and military officer who was the president of Syria from 1971 until Death and state funeral of Hafez al-Assad, his death in 2000. He was previously the Prime Minister of Syria ...
.Khoury, Philip S. ''Syria and the French Mandate: The Politics of Arab Nationalism, 1920‚Äď1945''. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1987. However, according to Associate Professor Stefan Winter
Stefan Winter (born 16 March 1968''List of licenses ordered by country''
, this letter is a forgery. Even during this time of increased Alawite rights, the situation was still so bad for the group that many women had to leave their homes to work for urban Sunnis.
In May 1930, the Alawite State was renamed the Government of Latakia in one of the few concessions by the French to Arab nationalists before 1936. Nevertheless, on 3 December 1936, the Alawite State was re-incorporated into Syria as a concession by the French to the National Bloc (the party in power in the semi-autonomous Syrian government). The law went into effect in 1937.Shambrook, Peter A. ''French Imperialism in Syria, 1927‚Äď1936''. Reading: Ithaca Press, 1998.
 In 1939, the
In 1939, the Sanjak of Alexandretta
The Sanjak of Alexandretta (; ; ) was a sanjak of the Mandate of Syria composed of two qadaas of the former Aleppo Vilayet ( Alexandretta and Antioch, now ńįskenderun and Antakya). It became autonomous under Article 7 of the 1921 Treaty of An ...
(now Hatay
Hatay Province (, ) is the southernmost Provinces of Turkey, province and Metropolitan municipalities in Turkey, metropolitan municipality of Turkey. Its area is , and its population is 1,686,043 (2022). It is situated mostly outside Anatolia, ...
) contained a large number of Alawites. The Hatayan land was given to Turkey by the French after a League of Nations plebiscite
A referendum, plebiscite, or ballot measure is a direct vote by the electorate (rather than their representatives) on a proposal, law, or political issue. A referendum may be either binding (resulting in the adoption of a new policy) or adv ...
in the province. This development greatly angered most Syrians; to add to Alawi contempt, in 1938, the Turkish military went into ńįskenderun
ńįskenderun (), historically known as Alexandretta (, ) and Scanderoon, is a municipality and Districts of Turkey, district of Hatay Province, Turkey. Its area is 247 km2, and its population is 251,682 (2022). It is on the Mediterranean coas ...
and expelled most of the Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
and Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian diaspora, Armenian communities around the ...
population. Before this, the Alawite Arabs and Armenians comprised most of the province's population. Zaki al-Arsuzi
Zaki al-Arsuzi (; June 18992 July 1968) was a Syrian philosopher, philologist, sociologist, historian, and Arab nationalist. His ideas played a significant role in the development of Ba'athism and its political movement. He published several b ...
, a young Alawite leader from Iskandarun province in the Sanjak of Alexandretta who led the resistance to the province's annexation by the Turks, later became a co-founder of the Ba'ath Party
The Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party ( ' ), also known simply as Bath Party (), was a political party founded in Syria by Michel Aflaq, Salah al-Din al-Bitar, and associates of Zaki al-Arsuzi. The party espoused Ba'athism, which is an ideology ...
with Eastern Orthodox Christian
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
schoolteacher Michel Aflaq
Michel Aflaq (, ; 9 January 1910 ‚Äď 23 June 1989) was a Syrian philosopher, sociology, sociologist and Arab nationalism, Arab nationalist. His ideas played a significant role in the development of Ba'athism and its political movement; he ...
and Sunni politician Salah ad-Din al-Bitar.
After World War II, Sulayman al-Murshid
Salman al-Murshid (1907 ‚Äď 16 December 1946) was a Syrian Alawite religious figure who reunited the Ghassanid clan, that later was called al-Murshidiyeen of the Alawites. Early beginnings
Salman al-Murshid was born to an Alawite family in the vil ...
played a major role in uniting the Alawite province with Syria. He was executed by the Syrian government in Damascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Kno ...
on 12 December 1946, only three days after a political trial.
After Syrian independence
Syria became independent on 17 April 1946. In 1949, after the1948 Arab‚ÄďIsraeli War
The 1948 Arab‚ÄďIsraeli War, also known as the First Arab‚ÄďIsraeli War, followed the 1947‚Äď1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine, civil war in Mandatory Palestine as the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. The civil war becam ...
, Syria experienced a number of military coups and the rise of the Ba'ath Party.
In 1958, Syria and Egypt were united by a political agreement into the United Arab Republic
The United Arab Republic (UAR; ) was a sovereign state in the Middle East from 1958 to 1971. It was initially a short-lived political union between Republic of Egypt (1953‚Äď1958), Egypt (including Occupation of the Gaza Strip by the United Ara ...
. The UAR lasted for three years, breaking apart in 1961, when a group of army officers seized power and declared Syria independent.
A succession of coups ensued until, in 1963, a secretive military committee (including Alawite officers Hafez al-Assad
Hafez al-Assad (6 October 193010 June 2000) was a Syrian politician and military officer who was the president of Syria from 1971 until Death and state funeral of Hafez al-Assad, his death in 2000. He was previously the Prime Minister of Syria ...
and Salah Jadid
Salah Jadid (; 1926 ‚Äď 19 August 1993) was a Syrian military officer and politician who was the leader of the far-left bloc of the Syrian Regional Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party, and the ''de facto'' leader of Ba'athist Syria from 1966 until 1970 ...
) helped the Ba'ath Party seize power. In 1966, Alawite-affiliated military officers successfully rebelled and expelled the Ba’ath Party old guard followers of Greek Orthodox
Greek Orthodox Church (, , ) is a term that can refer to any one of three classes of Christian Churches, each associated in some way with Greek Christianity, Levantine Arabic-speaking Christians or more broadly the rite used in the Eastern Rom ...
Christian Michel Aflaq
Michel Aflaq (, ; 9 January 1910 ‚Äď 23 June 1989) was a Syrian philosopher, sociology, sociologist and Arab nationalism, Arab nationalist. His ideas played a significant role in the development of Ba'athism and its political movement; he ...
and Sunni Muslim Salah ad-Din al-Bitar, calling Zaki al-Arsuzi
Zaki al-Arsuzi (; June 18992 July 1968) was a Syrian philosopher, philologist, sociologist, historian, and Arab nationalist. His ideas played a significant role in the development of Ba'athism and its political movement. He published several b ...
the "Socrates
Socrates (; ; ‚Äď 399 BC) was a Ancient Greek philosophy, Greek philosopher from Classical Athens, Athens who is credited as the founder of Western philosophy and as among the first moral philosophers of the Ethics, ethical tradition ...
" of the reconstituted Ba'ath Party.
In 1970, Air Force
An air force in the broadest sense is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an army aviati ...
General Hafez al-Assad, an Alawite, took power and instigated a "Corrective Movement" in the Ba'ath Party, overthrowing Salah Jadid
Salah Jadid (; 1926 ‚Äď 19 August 1993) was a Syrian military officer and politician who was the leader of the far-left bloc of the Syrian Regional Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party, and the ''de facto'' leader of Ba'athist Syria from 1966 until 1970 ...
(another Alawite). The coup ended the political instability which had existed since independence. Alawites were among Syria's poorest and most marginalized groups until Hafez al-Assad's seizure of power. Robert D. Kaplan compared his rise to "an untouchable becoming maharaja
Maharaja (also spelled Maharajah or Maharaj; ; feminine: Maharani) is a royal title in Indian subcontinent, Indian subcontinent of Sanskrit origin. In modern India and Medieval India, medieval northern India, the title was equivalent to a pri ...
h in India or a Jew becoming tsar
Tsar (; also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar''; ; ; sr-Cyrl-Latn, —Ü–į—Ä, car) is a title historically used by Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word '' caesar'', which was intended to mean ''emperor'' in the Euro ...
in Russia‚ÄĒan unprecedented development shocking to the Sunni majority population which had monopolized power for so many centuries."
Under Hafez al-Assad and his son Bashar al-Assad
Bashar al-Assad (born 11September 1965) is a Syrian politician, military officer and former dictator
Sources characterising Assad as a dictator:
who served as the president of Syria from 2000 until fall of the Assad regime, his government ...
, who succeeded his father upon his death in June 2000, Alawites made up the majority of Syria's military and political elites, including in the intelligence services and the ''shabiha
''Shabiha'' (North Levantine Arabic, Levantine Arabic: ', ; also romanized ''Shabeeha'' or ''Shabbiha''; ) is a colloquial and generally derogatory term for various loosely-organised Syrian militias loyal to the Ba'athist Syria, Ba'athist govern ...
'' (loyalist paramilitaries). The economic and social situation of Alawites improved, but the community remained relatively poor compared to other Syrians, and the Sunni-Alawite divisions persisted.
In 1971, al-Assad declared himself president of Syria, a position the constitution at the time permitted only for Sunni Muslims. In 1973, a new constitution was adopted, replacing Islam as the state religion with a mandate that the president's religion be Islam, and protests erupted. In 1974, to satisfy this constitutional requirement, Musa as-Sadr
Musa Sadr al-Din al-Sadr (; ; 4 June 1928 ‚Äď disappeared 31 August 1978) was a Lebanese-Iranian Shia Muslim cleric, politician and revolutionary In Lebanon. He founded and revived many Lebanese Shia organizations, including schools, charities ...
(a leader of the Twelvers of Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
and founder of the Amal Movement
The Amal Movement () is a Lebanese political party and militia affiliated mainly with the Shia community of Lebanon. It was founded by Musa al-Sadr and Hussein el-Husseini in 1974 as the "Movement of the Deprived." The party has been led by ...
, who had unsuccessfully sought to unite Lebanese Alawites and Shiites under the Supreme Islamic Shiite Council)Riad Yazbeck.Return of the Pink Panthers?
" ''Mideast Monitor''. Vol. 3, No. 2, August 2008. issued a
fatwa
A fatwa (; ; ; ) is a legal ruling on a point of Islamic law (sharia) given by a qualified Islamic jurist ('' faqih'') in response to a question posed by a private individual, judge or government. A jurist issuing fatwas is called a ''mufti'', ...
that Alawites were a community of Twelver Shiite Muslims.''The New Encyclopedia of Islam'' by Cyril Glasse, Altamira, 2001, p.36‚Äď7
A significant majority of Sunni Syrians accepted Hafez al-Assad's rule, but the Muslim Brotherhood in Syria
The Muslim Brotherhood in Syria () is the Syrian branch of the Sunni Islamist Muslim Brotherhood organization. Its objective is the transformation of Syria into an Islamic state governed by Sharia law through a gradual legal and political proce ...
, an Islamist group, did not. In the 1970s and 1980s, the Muslim Brotherhood
The Society of the Muslim Brothers ('' ''), better known as the Muslim Brotherhood ( ', is a transnational Sunni Islamist organization founded in Egypt by Islamic scholar, Imam and schoolteacher Hassan al-Banna in 1928. Al-Banna's teachings s ...
pushed anti-Alawite propaganda and a violent anti-Ba'athist campaign in Syria. Thirty-two cadets, mostly Alawites, were killed in the June 1979 Aleppo Artillery School massacre. In response to the Brothehood's attempted assassination of Hafez al-Assad in 1980, the regime ordered a violent crackdown; Hafez's brother Rifaat al-Assad
Rifaat Ali al-Assad (; born 22 August 1937) is a Syrian former military officer and politician. He is the younger brother of the late President of Syria, Hafez al-Assad, and Jamil al-Assad, and the uncle of the former President Bashar al-Assad. ...
ordered the slaughter of hundreds of Brotherhood members at the Tadmor Prison
Tadmor prison () was located in Palmyra (''Tadmor'' in Arabic) in the deserts of eastern Syria approximately 200 kilometers northeast of Damascus. It was also referred to as the ''Desert Prison''.
Tadmor prison was known for harsh conditions, e ...
in Palmyra
Palmyra ( ; Palmyrene dialect, Palmyrene: (), romanized: ''Tadmor''; ) is an ancient city in central Syria. It is located in the eastern part of the Levant, and archaeological finds date back to the Neolithic period, and documents first menti ...
.
The Brotherhood responded with increased violence, culminating in an attempt to seize control of the city of Hama
Hama ( ', ) is a city on the banks of the Orontes River in west-central Syria. It is located north of Damascus and north of Homs. It is the provincial capital of the Hama Governorate. With a population of 996,000 (2023 census), Hama is one o ...
in February 1982. The regime deployed between 6,000 and 8,000 troops to suppress the insurgency, and in the Hama massacre Hama massacre may refer to:
* 1925 Hama uprising during the Great Syrian Revolt
The Great Syrian Revolt (), also known as the Revolt of 1925, was a general uprising across the State of Syria (1925‚Äď1930), State of Syria and Greater Lebanon duri ...
, up to 25,000 people were killed over 27 days. Seeking to ensure that troops would not turn against the government, the Assad regime was careful to ensure the dominance of Alawites in the units deployed to Hama: Rifaat al-Assad's Defense Companies
The Companies for the Defense of the Revolution (; ), commonly referred to as Defense Companies, Defense Corps or Defense Brigades (; ), were a Syrian all-Alawite paramilitary force commanded by Rifaat al-Assad. Their task was to safeguard and d ...
were reported to be 90% Alawite, and in other units, up to 70% of officers corps were Alawites. After 1982, Syria remained relatively stable until the outbreak of the Syrian civil war in 2011, but the events in Hama left enduring Sunni-Alawite sectarian resentments.
Syrian civil war
 After the Syrian civil war broke out in 2011, the
After the Syrian civil war broke out in 2011, the Ba'athist
Ba'athism, also spelled Baathism, is an Arab nationalist ideology which advocates the establishment of a unified Arab state through the rule of a Ba'athist vanguard party operating under a revolutionary socialist framework. The ideology ...
state conscripted able-bodied men, mostly youth, into the regime's military. Fearing mass defections in military ranks, the Assad regime preferred to send Alawite recruits for active combat on the frontlines, and conscriptions disproportionately targeted Alawite regions. This has resulted in a large number of 'Alawite casualties and immense suffering to Alawite villages along the Syrian coast. Many younger Alawites were greatly angered by the Assad government, held the government responsible for the crisis, and increasingly called for an end the conflict via reconciliation with the Syrian opposition
Syrians () are the majority inhabitants of Syria, indigenous to the Levant, most of whom have Arabic, especially its Levantine and Mesopotamian dialects, as a mother tongue. The cultural and linguistic heritage of the Syrian people is a blend ...
and preventing their community from being perceived as being associated with the Assad government.
In the early days of the Syrian civil war, many Alawites felt compelled to back Assad, fearing that a rebel victory would lead to a slaughter of the Alawite community, especially as the conflict took on an increasingly sectarian
Sectarianism is a debated concept. Some scholars and journalists define it as pre-existing fixed communal categories in society, and use it to explain political, cultural, or religious conflicts between groups. Others conceive of sectarianism a ...
cast.Assad loyalists shaken by his fall, some relieved by lack of violenceReuters (8 December 2024). In May 2013, pro-opposition
SOHR
The Syrian Observatory for Human Rights (also known as SOHR; ), founded in May 2006, is a United Kingdom-based information office whose stated aim is to document human rights abuses in Syria; since 2011 it has focused on the Syrian Civil War. ...
stated that out of 94,000 Syrian regime soldiers killed during the war, at least 41,000 were Alawites. Reports estimate that up to a third of 250,000 young Alawite men of fighting age has been killed in the war by 2015, due to being disproportionately sent to fight in the frontlines by the Assad government. In April 2017, a pro-opposition source claimed 150,000 young Alawites had died. Another report estimates that around 100,000 Alawite youths were killed in combat by 2020.
Many Alawites feared significant danger during the Syrian civil war, particularly from Islamic groups who were a part of the opposition, though denied by secular opposition factions. Alawites have also been wary of the increased Iranian influence in Syria since the Syrian civil war, viewing it as a threat to their long-term survival due to Khomeinist
Khomeinism, also transliterated Khumaynism, refers to the religious and political ideas and practices connected with the leader of the 1979 Iranian Islamic RevolutionRuhollah Khomeini. While primarily referring to the ideas and practices of Kho ...
conversion campaigns focused in Alawite coastal regions. Many Alawites, including Assad loyalists, criticize such activities as a plot to absorb their ethno-religious identity into Iran's Twelver Shia umbrella and spread religious extremism
Religious fanaticism or religious extremism is a pejorative designation used to indicate uncritical zeal or obsessive enthusiasm that is related to one's own, or one's group's, devotion to a religion ‚Äď a form of human fanaticism that co ...
in Syria.
Alawite villages and neighborhoods were targeted by Islamist rebel attacks during the war. These include the Aqrab
Aqrab (, also spelled Akrab) is a village in central Syria, administratively part of the Hama Governorate, located southwest of Hama. Nearby localities include Nisaf and Baarin to the west, Awj to the southwest, Qarmas to the south, Taldou an ...
, Maan and Adra massacres, the 2013 Latakia offensive
The 2013 Latakia offensive (called The Descendants of Aisha, Mother of the Believers by Salafist jihadists, and the Operation Liberation of the Coast by the Free Syrian Army and its supporters) was a campaign during the Syrian Civil War laun ...
, the Homs school bombing, the Zara'a attack, and the February 2016 Homs bombings.
While many Alawites were Assad loyalists throughout the civil war, the Baathist regime faced increasing discontent in the war's later years from Alawite-dominated areas. By 2023, some Alawites had criticized the regime for its corruption, economic mismanagement, and disregard for civil liberties. During a rapid offense in November and December 2024 by opposition forces fighting the Assad regime, thousands of Alawites fled the city of Homs
Homs ( ; ), known in pre-Islamic times as Emesa ( ; ), is a city in western Syria and the capital of the Homs Governorate. It is Metres above sea level, above sea level and is located north of Damascus. Located on the Orontes River, Homs is ...
ahead of the capture of the city; those who left headed to coastal Tartus Governorate
Tartus Governorate, also transliterated as Tartous Governorate ( / ALA-LC: ''MuŠł•ńĀfaŠļďat ŠĻ¨arŠĻ≠Ňęs''), is one of the 14 governorates of Syria. It is situated in western Syria, bordering Latakia Governorate to the north, Homs and Hama Governo ...
. Upon the fall of Damascus and collapse of the Assad regime
On 8 December 2024, the Assad regime collapsed during a major offensive by opposition forces. The offensive was spearheaded by Hay'at Tahrir al-Sham (HTS) and supported mainly by the Turkish-backed Syrian National Army as part of the ongoi ...
days later, Alawite communities continued to express uncertainty about their future, although fears receded somewhat because the opposition forces did not target Alawites after capturing Homs.
Alleged attempt to establish an Alawite state
According to the UK-based war monitor Syrian Observatory for Human Rights (SOHR), former Syrian President Bashar al-Assad sought to establish an Alawite state on the Syrian coast as a fallback plan. This proposed coastal statelet was reportedly intended to serve as a stronghold for his regime in the event of losing control over the rest of the country. Russia, a key ally of Assad, allegedly rejected this plan, viewing it as an attempt to divide Syria. The SOHR claimed that Assad subsequently fled to Russia on his plane after facing opposition to the proposal and refused to deliver a speech about stepping down from power. There were also reports claiming that Assad had been relying heavily on Iran's support to maintain his position.Post-Assad Syria
On 25 December 2024, thousands of people protested across Syria in various regions including Latakia, Tartus, Jableh and Homs after a video surfaced showing an attack on the Alawite shrine ofAl-Khasibi
Abu Abd Allah al-Husayn ibn Hamdan al-Junbalani al-Khasibi (died 957 or 968), commonly known simply as al-Khasibi, was an Alawite religious leader and missionary. He originally from a village called ''JonbalńĀ'', between Kufa and Wasit in Iraq, wh ...
in Aleppo's Maysaloon district following the rebel offensive and the fall of the regime of Bashar al-Assad
Bashar al-Assad (born 11September 1965) is a Syrian politician, military officer and former dictator
Sources characterising Assad as a dictator:
who served as the president of Syria from 2000 until fall of the Assad regime, his government ...
. During the shrine attack at least five people were killed and the shrine was set ablaze. The UK-based SOHR
The Syrian Observatory for Human Rights (also known as SOHR; ), founded in May 2006, is a United Kingdom-based information office whose stated aim is to document human rights abuses in Syria; since 2011 it has focused on the Syrian Civil War. ...
reported significant demonstrations, including in Qardaha
Qardaha ( / ALA-LC: ''QardńĀŠł•ah'') is a town in northwestern Syria, in the mountains overlooking the coastal town of Latakia. Nearby localities include Kilmakho to the west, Bustan al-Basha to the southwest, Harf al-Musaytirah to the south ...
, President Assad's hometown.
The transitional authorities, appointed by Hay'at Tahrir al-Sham
Hay'at Tahrir al-Sham (HTS) was a Sunni Islamist political organisation and paramilitary group involved in the Syrian civil war. It was formed on 28January 2017 as a merger between several armed groups: Jaysh al-Ahrar (an Ahrar al-Sham facti ...
(HTS) which led the offensive that toppled Assad, said in a statement that the shrine attack was from earlier December, attributing its resurfacing to "unknown groups" aiming to incite unrest. This incident followed protests in Damascus against the burning of a Christmas tree
A Christmas tree is a decorated tree, usually an evergreen pinophyta, conifer, such as a spruce, pine or fir, associated with the celebration of Christmas. It may also consist of an artificial tree of similar appearance.
The custom was deve ...
, highlighting ongoing sectarian tensions in Syria. Demonstrators chanting slogans including ‚ÄúAlawite, Sunni, we want peace‚ÄĚ and placards with "No to burning holy places and religious discrimination, no to sectarianism, yes to a free Syria".
There have also been hundreds of reports across Syria of civilians belonging to the Alawite sect and other religious minorities being murdered and persecuted by HTS forces following the collapse of the Assad regime. Most notably, a massacre of Alawites was reported in the village of Fahil near Homs by HTS-affiliated gunmen. The UK-based formerly pro-opposition monitor SOHR
The Syrian Observatory for Human Rights (also known as SOHR; ), founded in May 2006, is a United Kingdom-based information office whose stated aim is to document human rights abuses in Syria; since 2011 it has focused on the Syrian Civil War. ...
confirmed the deaths of at least 16 people.
In March 2025, the UK-based SOHR
The Syrian Observatory for Human Rights (also known as SOHR; ), founded in May 2006, is a United Kingdom-based information office whose stated aim is to document human rights abuses in Syria; since 2011 it has focused on the Syrian Civil War. ...
reported that Syrian security forces and pro-government fighters had committed a massacre
A massacre is an event of killing people who are not engaged in hostilities or are defenseless. It is generally used to describe a targeted killing of civilians Glossary of French words and expressions in English#En masse, en masse by an armed ...
of more than 1,500 Alawite civilians during clashes in western Syria. There were reports that Alawites who had opposed the Assad regime in the past were murdered in sectarian attacks. Belteleradio
The National State TV and Radio Company of the Republic of Belarus (; ), known as Belteleradiocompany (; ) or simply Belteleradio, is the state television and radio broadcasting service in Belarus.
From 1993 until 2021, it was a full active memb ...
described the violence as ethnic cleansing. Syrian President Ahmed al-Sharaa
Ahmed Hussein al-Sharaa (born 29 October 1982) also known by his ''nom de guerre'' Abu Mohammad al-Julani, is a Syrian politician and former rebel commander serving as the president of Syria since January 2025. He previously served as the coun ...
said that the Alawite sect had made an "unforgivable mistake" and urged them to lay down their weapons and surrender before it was too late. Later that month, nearly 13,000 Alawites crossed the Nahr al-Kabir
The Nahr al-Kabir, also known in Syria as al-Nahr al-Kabir al-Janoubi (, in contrast with the Nahr al-Kabir al-Shamali) or in Lebanon simply as the Kebir, is a river in Syria and Lebanon flowing into the Mediterranean Sea at Arida. The river ...
into Lebanon to escape sectarian violence.
Beliefs
Alawites and their beliefs have been described as "secretive". Yaron Friedman, for example, in his scholarly work on the sect, has written that the Alawi religious material quoted in his book came only from "public libraries and printed books" since the "sacred writings" of the Alawi "are kept secret". Some tenets of the faith are kept secret from most Alawi and known only to a select few. They have, therefore, been described as amystical
Mysticism is popularly known as becoming one with God or the Absolute, but may refer to any kind of ecstasy or altered state of consciousness which is given a religious or spiritual meaning. It may also refer to the attainment of insight ...
sect.
Alawite doctrines originated from the teachings of Iraqi priest Muhammad ibn Nusayr who claimed prophethood, declared himself as the "'' BńĀb'' (Door) of the Imams
Imam (; , '; : , ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a prayer leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Islamic prayers, serve as community leaders, and provide relig ...
", and attributed divinity to Hasan al-Askari
Hasan al-Askari (; ) was a descendant of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He is regarded as the eleventh of the Twelve Imams, succeeding his father, Ali al-Hadi. Hasan Al-Askari was born in Medina in 844 and brought with his father to the garris ...
. Al-Askari denounced Ibn Nusayr, and Islamic authorities expelled his disciples‚ÄĒmost of whom emigrated to the Syrian Coastal Mountain Range
The Coastal Mountain Range (, ''Silsilat al-JibńĀl as-SńĀŠł•ilńęyah'') also called Jabal al-Ansariya, Jabal an-Nusayria or Jabal al-`Alawńęyin (Ansari, Nusayri or Alawi Mountains) is a mountain range in northwestern Syria running north‚Äďsouth, ...
, wherein they established a distinct community. Nusayri theology treats Ali
Ali ibn Abi Talib (; ) was the fourth Rashidun caliph who ruled from until his assassination in 661, as well as the first Shia Imam. He was the cousin and son-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Born to Abu Talib ibn Abd al-Muttalib an ...
, the cousin of the Prophet Muhammad, as a manifestation of "the supreme eternal God" and consists of various gnostic
Gnosticism (from Ancient Greek: , romanized: ''gnŇćstik√≥s'', Koine Greek: £nostiňąkos 'having knowledge') is a collection of religious ideas and systems that coalesced in the late 1st century AD among early Christian sects. These diverse g ...
beliefs. Alawite doctrine regards the souls of Alawites as re-incarnations of "lights that rebelled against God."
Alawites' beliefs have never been confirmed by their modern religious authorities.'Abd al‚ÄĎLatif al‚ÄĎYunis, Mudhakkirat al‚ÄĎDuktur 'Abd al‚ÄĎLatif al‚ÄĎYunis, Damascus: Dar al‚ÄĎ'Ilm, 1992, p. 63. As a highly secretive and esoteric sect, Nusayri priests tend to conceal their core doctrines, which are introduced only to a chosen minority of the sect's adherents. Alawites have also adopted the practice of ''taqiya
In Islam, ''taqiyya'' ()R. STROTHMANN, MOKTAR DJEBLI. Encyclopedia of Islam, 2nd ed, Brill. "TAKIYYA", vol. 10, p. 134. Quote: "TAKIYYA "prudence, fear" ... denotes dispensing with the ordinances of religion in cases of constraint of preaching ...
'' to avoid victimization.
Theology and practices
Alawite doctrine incorporates elements ofPhoenician mythology
Sanchuniathon (; Ancient Greek: ; probably from , "Sakkun has given"), variant ''Ň°knytn'' also known as Sanchoniatho the Berytian, was a Phoenician author. His three works, originally written in the Phoenician language, survive only in partial ...
, Gnostic
Gnosticism (from Ancient Greek: , romanized: ''gnŇćstik√≥s'', Koine Greek: £nostiňąkos 'having knowledge') is a collection of religious ideas and systems that coalesced in the late 1st century AD among early Christian sects. These diverse g ...
ism, neo-Platonism
Neoplatonism is a version of Platonic philosophy that emerged in the 3rd century AD against the background of Hellenistic philosophy and religion. The term does not encapsulate a set of ideas as much as a series of thinkers. Among the common i ...
, Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
Trinitarianism
The Trinity (, from 'threefold') is the Christian doctrine concerning the nature of God, which defines one God existing in three, , consubstantial divine persons: God the Father, God the Son (Jesus Christ) and God the Holy Spirit, three ...
(for example, they celebrate Mass
Mass is an Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsic property of a physical body, body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the physical quantity, quantity of matter in a body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physi ...
including the consecration of bread and wine); blending them with Muslim symbolism and has, therefore, been described as syncretic
Syncretism () is the practice of combining different beliefs and various schools of thought. Syncretism involves the merging or assimilation of several originally discrete traditions, especially in the theology and mythology of religion, thus ...
.
Alawite Trinity envisions God as being composed of three distinct manifestations, ''Ma'na'' (meaning), ''Ism'' (Name), and ''Bab'' (Door), which together constitute an "indivisible Trinity". ''Ma'na'' symbolises the "source and meaning of all things" in Alawite mythology. According to Alawite doctrines, ''Ma'na'' generated the ''Ism'', which in turn built the ''Bab''. These beliefs are closely tied to the Nusayri doctrine of re-incarnations of the Trinity.
''The Oxford Encyclopedia of the Modern Islamic World'' classifies Alawites as part of extremist Shia sects referred to as the ''ghulat
The () were a branch of history of Shia Islam, early Shi'a Islam. The term mainly refers to a wide variety of List of extinct Shia sects, extinct Shi'i sects active in 8th- and 9th-century Kufa in Lower Mesopotamia, and who, despite their somet ...
'' which are unrelated to Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam is the largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any Succession to Muhammad, successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr ...
; owing to the secretive nature of the Alawite religious system and hierarchy. Due to their esoteric doctrines of strict secrecy, conversions into the community were also forbidden.
Alawites do not believe in daily Muslim prayers (''salah
''Salah'' (, also spelled ''salat'') is the practice of formal worship in Islam, consisting of a series of ritual prayers performed at prescribed times daily. These prayers, which consist of units known as ''rak'ah'', include a specific s ...
''). The central tenet of the Alawite is their belief of Ali ibn Abi Talib
Ali ibn Abi Talib (; ) was the fourth Rashidun caliph who ruled from until Assassination of Ali, his assassination in 661, as well as the first imamate in Shia doctrine, Shia Imam. He was the cousin and son-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muha ...
being an incarnation of God. The Alawite testimony of faith is translated as "There is no God but Ali."
Reincarnation
Alawites hold that they were originally stars or divine lights that were cast out of heaven through disobedience and must undergo repeatedreincarnation
Reincarnation, also known as rebirth or transmigration, is the Philosophy, philosophical or Religion, religious concept that the non-physical essence of a living being begins a new lifespan (disambiguation), lifespan in a different physical ...
(or metempsychosis
In philosophy and theology, metempsychosis () is the transmigration of the soul, especially its reincarnation after death. The term is derived from ancient Greek philosophy, and has been recontextualized by modern philosophers such as Arthur Sc ...
) before returning to heaven. According to Alawite beliefs, females are excluded from re-incarnation.
Alawite theologians divided history into seven eras, associating each era with one of the seven re-incarnations of the Alawite Trinity (''Ma'na'', ''Ism'', ''Bab''). The seven re-incarnations of the Trinity in the Alawite faith can be summarized in the following table.
The last triad of reincarnations in the Nusayri Trinity consists of Ali (''Ma'na''), Muhammad (''Ism''), and Salman al-Farsi (''Bab''). Alawites depict them as the sky, the sun, and the moon, respectively. They deify Ali as the "last and supreme manifestation of God" who built the universe, attributing him with divine superiority and believing that Ali created Muhammad, bestowing upon him the mission to spread Qur'anic teachings on earth.
The Israeli institution of Begin‚ÄďSadat Center for Strategic Studies
The Begin‚ÄďSadat Center for Strategic Studies (BESA Center) is an Israeli think tank affiliated with Bar-Ilan University and supported by the NATO ''Mediterranean Initiative'', conducting policy-relevant research on Middle Eastern and global st ...
describes the Alawite faith as Judeophilic and " anti-Sunni" since they believe that God's incarnations consist of Israelite
Israelites were a Hebrew language, Hebrew-speaking ethnoreligious group, consisting of tribes that lived in Canaan during the Iron Age.
Modern scholarship describes the Israelites as emerging from indigenous Canaanites, Canaanite populations ...
Prophet Joshua
Joshua ( ), also known as Yehoshua ( ''Y…ôhŇćŇ°ua Ņ'', Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: ''YŇŹhŇćŇ°ua Ņ,'' Literal translation, lit. 'Yahweh is salvation'), Jehoshua, or Josue, functioned as Moses' assistant in the books of Book of Exodus, Exodus and ...
who conquered Canaan
CanaanThe current scholarly edition of the Septuagint, Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus Testamentum graece iuxta LXX interprets. 2. ed. / recogn. et emendavit Robert Hanhart. Stuttgart : D ...
, in addition to the fourth Caliph, Ali
Ali ibn Abi Talib (; ) was the fourth Rashidun caliph who ruled from until his assassination in 661, as well as the first Shia Imam. He was the cousin and son-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Born to Abu Talib ibn Abd al-Muttalib an ...
. This institution also denies the Arab ethnicity of Alawites even though Alawites themselves self-identify ethnically as Arabs and assert that Alawites claim to be Arabs because of "political expediency."
Other beliefs
 Other beliefs and practices include: the
Other beliefs and practices include: the consecration
Sacred describes something that is dedicated or set apart for the service or worship of a deity; is considered worthy of spiritual respect or devotion; or inspires awe or reverence among believers. The property is often ascribed to objects ( ...
of wine in a secret form of Mass
Mass is an Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsic property of a physical body, body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the physical quantity, quantity of matter in a body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physi ...
performed only by males; frequently being given Christian name
A Christian name, sometimes referred to as a baptismal name, is a religious personal name given on the occasion of a Christian baptism, though now most often given by parents at birth. In English-speaking cultures, a person's Christian name ...
s; entombing the dead in sarcophagi
A sarcophagus (: sarcophagi or sarcophaguses) is a coffin, most commonly carved in stone, and usually displayed above ground, though it may also be buried. The word ''sarcophagus'' comes from the Greek ŌÉő¨ŌĀőĺ ' meaning "flesh", and ŌÜő ...
above ground; observing Epiphany
Epiphany may refer to:
Psychology
* Epiphany (feeling), an experience of sudden and striking insight
Religion
* Epiphany (holiday), a Christian holiday celebrating the revelation of God the Son as a human being in Jesus Christ
** Epiphany seaso ...
, Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating Nativity of Jesus, the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a Religion, religious and Culture, cultural celebration among billions of people Observance of Christmas by coun ...
and the feast days of John Chrysostom
John Chrysostom (; ; ‚Äď 14 September 407) was an important Church Father who served as archbishop of Constantinople. He is known for his preaching and public speaking, his denunciation of abuse of authority by both ecclesiastical and p ...
and Mary Magdalene
Mary Magdalene (sometimes called Mary of Magdala, or simply the Magdalene or the Madeleine) was a woman who, according to the four canonical gospels, traveled with Jesus as one of his followers and was a witness to crucifixion of Jesus, his cr ...
; the only religious structures they have are the shrines of tombs; the book '' Kitab al-Majmu'', which is allegedly a central source of Alawite doctrine, where they have their own trinity, comprising Mohammed, Ali, and Salman the Persian
Salman Farsi (; ) was a Persian religious scholar and one of the companions of Muhammad. As a practicing Zoroastrian, he dedicated much of his early life to studying to become a magus, after which he began travelling extensively throughout Weste ...
.
In addition, they celebrate different holidays such as Old New Year
The Old New Year, the Orthodox New Year, also known as ''Ra's as-Sanah'' or ''Ras el-Seni'' in the Middle East, is an informal traditional holiday, celebrated as the start of the New Year by the Julian calendar. In the 20th and 21st centuries, the ...
, Akitu
Akitu or Akitum
()
()
is a spring festival and New Year's celebration, held on the first day of the Assyrian and Babylonian Nisan in ancient Mesopotamia and in Assyrian communities around the world, to celebrate the sowing of barley. Akit ...
, Eid al-Ghadir
Eid al-Ghadir () is a commemorative holiday, and is considered to be among the most significant holidays of Shi'ite Muslims and Alawites. The Eid is held on 18 Dhul-Hijjah at the time when the Islamic prophet Muhammad‚ÄĒaccording to interpreta ...
, Mid-Sha'ban
Mid-Sha'ban ( or ''laylat niŠĻ£f min Ň°a ŅbńĀn'' "night on the half of Sha'ban") is a Muslim holiday observed by Shia and Sunni Muslim communities on the eve of 15th of Sha'ban (i.e., the night following the sunset on the 14th day) ‚ÄĒ the s ...
and Eid il-Burbara. They believe in intercession
Intercession or intercessory prayer is the act of prayer, praying on behalf of others, or Intercession of saints, asking a saint in heaven to pray on behalf of oneself or for others.
The Apostle Paul's exhortation to Saint Timothy, Timothy speci ...
of certain legendary saints such as Khidr
Al-Khidr (, ; also Romanized as ''al-Khadir, Khader, Khidr, Hidr, Khizr, Kezr, Kathir, Khazer, Khadr, Khedher, Khizir, Khizar, Khilr'') is a folk figure of Islam. He is described in Surah Al-Kahf, as a righteous servant of God possessing great w ...
(Saint George
Saint George (;Ge Ĺez: ŠĆäŠčģŠą≠ŠĆ䊹Ķ, , ka, ŠÉíŠÉėŠÉ̊ɆŠÉíŠÉė, , , died 23 April 303), also George of Lydda, was an early Christian martyr who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to holy tradition, he was a soldier in the ...
) and Simeon Stylites
Simeon Stylites or Symeon the Stylite ', Koine Greek ', ' (Greek language, Greek: ő£ŌÖőľőĶŌéőĹ ŌĆ ő£ŌĄŌÖőĽőĮŌĄő∑Ōā; ; 2 September 459) was a Syrian Asceticism#Christianity, Christian ascetic, who achieved notability by living 36 years on a s ...
.
Development
Yaron Friedman and many researchers of Alawi doctrine write that the founder of the religion, Ibn Nusayr, did not necessarily believe he was representative of a splinter, rebel group of the Shias, but believed he held the true doctrine of the Shias and most of the aspects that are similar toChristianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
are considered more a coincidence and not a direct influence from it, as well as other external doctrines that were popular among Shia esoteric groups in Basra in the 8th century. According to Friedman and other scholars, the Alawi movement started as many other mystical ghulat sects with an explicit concentration on an allegorical and esoteric meaning of the Quran
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a WaŠł•y, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, AllńĀh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which ...
and other mystical practices, and not as a pure syncretic sect, though later, they embraced some other practices, as they believed all religions had the same ''Batin'' core.
Journalist Robert F. Worth argues the idea that the Alawi religion as a branch of Islam is a rewriting of history made necessary by the French colonialists' abandonment of the Alawi and departure from Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria‚ÄďTurkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq‚ÄďSyria border, t ...
. Worth describes the "first ... authentic source for outsiders about the religion", written by Soleyman of Adana ‚Äď a 19th-century Alawi convert to Christianity who broke his oath of secrecy on the religion, explaining that the Alawi, according to Soleyman, deified Ali
Ali ibn Abi Talib (; ) was the fourth Rashidun caliph who ruled from until his assassination in 661, as well as the first Shia Imam. He was the cousin and son-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Born to Abu Talib ibn Abd al-Muttalib an ...
, venerated Christ
Jesus ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Christianity, central figure of Christianity, the M ...
, Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
, Plato
Plato ( ; Greek language, Greek: , ; born BC, died 348/347 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical Greece, Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the writte ...
, Socrates
Socrates (; ; ‚Äď 399 BC) was a Ancient Greek philosophy, Greek philosopher from Classical Athens, Athens who is credited as the founder of Western philosophy and as among the first moral philosophers of the Ethics, ethical tradition ...
, and Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384‚Äď322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
, and held themselves apart from Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
and Christians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
, whom they considered heretics
Heresy is any belief or theory that is strongly at variance with established beliefs or customs, particularly the accepted beliefs or religious law of a religious organization. A heretic is a proponent of heresy.
Heresy in Christianity, Judai ...
. Worth, ''A Rage for Order'', 2016: p.82 According to Tom Heneghan:
 According to a disputed letter, in 1936, six Alawi notables petitioned the French colonialists not to merge their Alawi enclave with the rest of Syria, insisting that "the spirit of hatred and fanaticism embedded in the hearts of the Arab Muslims against everything that is non-Muslim has been perpetually nurtured by the Islamic religion." Worth, ''A Rage for Order'', 2016: p.85 However, according to associate professor Stefan Winter, this letter is a forgery. According to Worth, later ''
According to a disputed letter, in 1936, six Alawi notables petitioned the French colonialists not to merge their Alawi enclave with the rest of Syria, insisting that "the spirit of hatred and fanaticism embedded in the hearts of the Arab Muslims against everything that is non-Muslim has been perpetually nurtured by the Islamic religion." Worth, ''A Rage for Order'', 2016: p.85 However, according to associate professor Stefan Winter, this letter is a forgery. According to Worth, later ''fatwa
A fatwa (; ; ; ) is a legal ruling on a point of Islamic law (sharia) given by a qualified Islamic jurist ('' faqih'') in response to a question posed by a private individual, judge or government. A jurist issuing fatwas is called a ''mufti'', ...
s'' declaring Alawi to be part of the Shia community were by Shia clerics "eager for Syrian patronage" from Syria's Alawi president Hafez al-Assad
Hafez al-Assad (6 October 193010 June 2000) was a Syrian politician and military officer who was the president of Syria from 1971 until Death and state funeral of Hafez al-Assad, his death in 2000. He was previously the Prime Minister of Syria ...
, who was eager for Islamic legitimacy in the face of the hostility of Syria's Muslim majority.
Yaron Friedman does not suggest that Alawi did not consider themselves Muslims but does state that:
According to Peter Theo Curtis
Theo Padnos (also known as Peter Theo Curtis; born 1968) is an American journalist who was released by the al-Nusra Front in August 2014, after being held hostage for almost two years. He was the cellmate of American war photographer Matt Schrie ...
, the Alawi religion underwent a process of "Sunnification" during the years under Hafez al-Assad's rule so that Alawites became not Shia but effectively Sunni. Public manifestations or "even mentioning of any Alawite religious activities" were banned, as were any Alawite religious organizations, and "any formation of a unified religious council" or a higher Alawite religious authority. "Sunni-style" mosques were built in every Alawite village, and Alawis were encouraged to perform Hajj
Hajj (; ; also spelled Hadj, Haj or Haji) is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for capable Muslims that must be carried out at least once in their lifetim ...
. It's also worth noting that the grand mosque in Qardaha
Qardaha ( / ALA-LC: ''QardńĀŠł•ah'') is a town in northwestern Syria, in the mountains overlooking the coastal town of Latakia. Nearby localities include Kilmakho to the west, Bustan al-Basha to the southwest, Harf al-Musaytirah to the south ...
, the hometown of the Assad family, being dedicated to Abu Bakr Al-Siddiq who is venerated by Sunnis but not Shi'ites.
Opinions on position within Islam
The SunniGrand Mufti of Jerusalem
The Grand Mufti of Jerusalem is the Sunni Muslim cleric in charge of Jerusalem's Islamic holy places, including Al-Aqsa. The position was created by the British military government led by Ronald Storrs in 1918.See Islamic Leadership in Jerusa ...
, Haj Amin al-Husseini
Mohammed Amin al-Husseini (; 4 July 1974) was a Palestinian Arab nationalist and Muslim leader in Mandatory Palestine. was the scion of the family of Jerusalemite Arab nobles, who trace their origins to the Islamic prophet Muhammad.
Hussein ...
, issued a ''fatwa'' recognizing them as part of the Muslim community
' (; ) is an Arabic word meaning Muslim identity, nation, religious community, or the concept of a Commonwealth of the Muslim Believers ( '). It is a synonym for ' (, lit. 'the Islamic nation'); it is commonly used to mean the collective comm ...
in the interest of Arab nationalism
Arab nationalism () is a political ideology asserting that Arabs constitute a single nation. As a traditional nationalist ideology, it promotes Arab culture and civilization, celebrates Arab history, the Arabic language and Arabic literatur ...
. However, classical Sunni scholars such as the Syrian historian Ibn Kathir
Abu al-Fida Isma'il ibn Umar ibn Kathir al-Dimashqi (; ), known simply as Ibn Kathir, was an Arab Islamic Exegesis, exegete, historian and scholar. An expert on (Quranic exegesis), (history) and (Islamic jurisprudence), he is considered a lea ...
categorized Alawites as non-Muslim and mushrikeen
The Mushrikites ( or , singular ) were the Arab polytheists who committed shirk and opposed the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his followers, the Muslims, in the early 7th century. Their leaders were mostly from the Quraysh, but others also belong ...
(polytheist
Polytheism is the belief in or worship of more than one god. According to Oxford Reference, it is not easy to count gods, and so not always obvious whether an apparently polytheistic religion, such as Chinese folk religions, is really so, or whet ...
s), in their writings.Abd-Allah, Umar F., ''Islamic Struggle in Syria'', Berkeley : Mizan Press, c1983, pp. 43‚Äď48 Ibn Taymiyya
Ibn Taymiyya (; 22 January 1263 ‚Äď 26 September 1328)Ibn Taymiyya, Taqi al-Din Ahmad, The Oxford Dictionary of Islam. http://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/acref/9780195125580.001.0001/acref-9780195125580-e-959 was a Sunni Muslim schola ...
, Ibn Kathir's mentor and arguably the most polemical anti-Alawite Sunni theologian, categorised Alawite as non-Muslims and listed them amongst the worst sects of polytheists.
Through many of his ''fatawa
A fatwa (; ; ; ) is a legal ruling on a point of Islamic law (sharia) given by a qualified Islamic jurist ('' faqih'') in response to a question posed by a private individual, judge or government. A jurist issuing fatwas is called a ''mufti'', ...
'', Ibn Taymiyya described Alawites as "the worst enemies of the Muslims" who were far more dangerous than Crusaders and Mongols. Ibn Taymiyya also accused Alawites of aiding the Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding t ...
and Mongol invasions
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire, the Mongol Empire (1206‚Äď1368), which by 1260 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastati ...
against the Muslim World
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
. Other Sunni scholars, such as Al-Ghazali
Al-Ghazali ( ‚Äď 19 December 1111), archaically Latinized as Algazelus, was a Shafi'i Sunni Muslim scholar and polymath. He is known as one of the most prominent and influential jurisconsults, legal theoreticians, muftis, philosophers, the ...
, likewise considered them as non-Muslims. Benjamin Disraeli
Benjamin Disraeli, 1st Earl of Beaconsfield (21 December 1804 ‚Äď 19 April 1881) was a British statesman, Conservative Party (UK), Conservative politician and writer who twice served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom. He played a ...
, in his novel '' Tancred'', also expressed the view that Alawites are not Shia Muslims.
Historically, Twelver Shia scholars (such as Shaykh Tusi
Shaykh Tusi (), full name ''Abu Ja'far Muhammad ibn al-Hasan al-Tusi'' (), known as Shaykh al-Ta'ifah () was a Persian scholar of the Twelver school of Shia Islam. He is the author of two of the Four Books of hadith; namely, '' Tahdhib al-Ahka ...
) did not consider Alawites as Shia Muslims while condemning their heretical beliefs.
In 2016, according to several international media reports, an unspecified number of Alawite community leaders released a "Declaration of an Alawite Identity Reform" (of the Alawite community). The manifesto presents Alawism as a current "within Islam" and rejects attempts to incorporate the Alawite community into Twelver Shiism. The document was interpreted as an attempt by representatives of the Alawite community to overcome the sectarian polarisation and to distance themselves from the growing Sunni‚ÄďShia divide in the Middle East.
According to Matti Moosa,
The Christian elements in the Nusayri religion are unmistakable. They include the concept of trinity; the celebration of Christmas, the consecration of theQurbana The Holy Qurbana (, ''QurbńĀnńĀ QaddiŇ°ńĀ'' in Eastern Syriac or ''QurbńĀnńĀ QandiŇ°ńĀ'' in the Indian variant of Eastern Syriac, the "Holy Offering" or "Holy Sacrifice" in English), refers to the Eucharistic liturgy as celebrated in Syriac Chr ..., that is, thesacrament A sacrament is a Christian rite which is recognized as being particularly important and significant. There are various views on the existence, number and meaning of such rites. Many Christians consider the sacraments to be a visible symbol ...of the flesh and blood which Christ offered to his disciples, and, most importantly, the celebration of the Quddas (a lengthy prayer proclaiming the divine attributes of Ali and the personification of all the biblical patriarchs fromAdam Adam is the name given in Genesis 1‚Äď5 to the first human. Adam is the first human-being aware of God, and features as such in various belief systems (including Judaism, Christianity, Gnosticism and Islam). According to Christianity, Adam ...toSimon Peter Saint Peter (born Shimon Bar Yonah; 1 BC ‚Äď AD 64/68), also known as Peter the Apostle, Simon Peter, Simeon, Simon, or Cephas, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus and one of the first leaders of the early Christian Church. He appears repe ..., founder of the Church, who is seen, paradoxically, as the embodiment of true Islam).
Barry Rubin
Barry M. Rubin (Hebrew: ◊Ď◊ź◊®◊ô ◊®◊ē◊Ď◊ô◊ü) (28 January 1950 ‚Äď February 3, 2014) was an American-born Israeli writer and academic on terrorism and Middle Eastern affairs.
Career
Rubin was the director of the Global Research in International Af ...
has suggested that Syrian leader Hafez al-Assad and his son and successor Bashar al-Assad
Bashar al-Assad (born 11September 1965) is a Syrian politician, military officer and former dictator
Sources characterising Assad as a dictator:
who served as the president of Syria from 2000 until fall of the Assad regime, his government ...
pressed their fellow Alawites "to behave like 'regular Muslims', shedding (or at least concealing) their distinctive aspects". During the early 1970s, a booklet, ''al-'Alawiyyun Shi'atu Ahl al-Bait'' ("The Alawites are Followers of the Household of the Prophet") was published, which was "signed by numerous 'Alawi' men of religion", described the doctrines of the Imami
Twelver Shi'ism (), also known as Imamism () or Ithna Ashari, is the largest branch of Shi'a Islam, comprising about 90% of all Shi'a Muslims. The term ''Twelver'' refers to its adherents' belief in twelve divinely ordained leaders, known as th ...
Shia as Alawite.
The relationship between Alawite-ruled Ba'athist Syria
Ba'athist Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic (SAR), was the Syrian state between 1963 and 2024 under the One-party state, one-party rule of the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party ‚Äď Syria Region, Syrian regional branch of the Ba'ath Party (Syri ...
and Khomeinist Iran has been described as a "marriage of convenience" due to the former being ruled by the ultra-secularist Arab Socialist Ba'ath party
The Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party ( ' ), also known simply as Bath Party (), was a political party founded in Syria by Michel Aflaq, Salah al-Din al-Bitar, and associates of Zaki al-Arsuzi. The party espoused Ba'athism, which is an ideology mixi ...
and the latter by the anti-secular Twelver Shi'ite clergy. The alliance was established during the Iran-Iraq war in the 1980s, when Hafez al-Assad
Hafez al-Assad (6 October 193010 June 2000) was a Syrian politician and military officer who was the president of Syria from 1971 until Death and state funeral of Hafez al-Assad, his death in 2000. He was previously the Prime Minister of Syria ...
backed Iran against his Iraqi Ba'athist rivals, departing from the consensus of the rest of the Arab world
The Arab world ( '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, comprises a large group of countries, mainly located in West Asia and North Africa. While the majority of people in ...
. Iranian-backed militant groups like Hezbollah
Hezbollah ( ; , , ) is a Lebanese Shia Islamist political party and paramilitary group. Hezbollah's paramilitary wing is the Jihad Council, and its political wing is the Loyalty to the Resistance Bloc party in the Lebanese Parliament. I ...
, Fatemeyoun, Zainabyoun, etc., have been acting as proxy forces for the Assad regime
Ba'athist Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic (SAR), was the Syrian state between 1963 and 2024 under the one-party rule of the Syrian regional branch of the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party. From 1971 until its collapse in 2024, it was rule ...
in various conflicts in the region, such as the Lebanese Civil War
The Lebanese Civil War ( ) was a multifaceted armed conflict that took place from 1975 to 1990. It resulted in an estimated 150,000 fatalities and led to the exodus of almost one million people from Lebanon.
The religious diversity of the ...
, the 2006 Lebanon War
The 2006 Lebanon War was a 34-day armed conflict in Lebanon, fought between Hezbollah and Israel. The war started on 12 July 2006, and continued until a United Nations-brokered ceasefire went into effect in the morning on 14 August 2006, thoug ...
and the Syrian civil war.
 Some sources have discussed the "Sunnification" of Alawites under the al-Assad regime.
Some sources have discussed the "Sunnification" of Alawites under the al-Assad regime. Joshua Landis
Joshua M. Landis (born May 14, 1957) is an American academic who specializes in the Middle East and is an expert on Syria. He is the head of the Center for Middle East Studies at the University of Oklahoma, and since 2004, he has published the blog ...
, director of the Center for Middle East Studies, writes that Hafiz al-Assad "tried to turn Alawites into 'good' (read Sunnified) Muslims in exchange for preserving a modicum of secularism and tolerance in society". On the other hand, Al-Assad "declared the Alawites to be nothing but Twelver Shiites".Syrian comment. Asad's Alawi dilemma8 October 2004 In a paper, "Islamic Education in Syria", Landis wrote that "no mention" is made in Syrian textbooks (controlled by the Al-Assad regime) of Alawites, Druze,
Ismailis
Ismailism () is a branch of Shia Islam. The Isma'ili () get their name from their acceptance of Imam Isma'il ibn Jafar as the appointed spiritual successor ( imńĀm) to Ja'far al-Sadiq, wherein they differ from the Twelver Shia, who accept M ...
or Shia Islam; Islam was presented as a monolithic religion.
Ali Sulayman al-Ahmad, chief judge of the Baathist Syrian state, has said:
Population

Syria
Alawites have traditionally lived in the Coastal Mountain Range, along the Mediterranean coast of western Syria.Latakia
Latakia (; ; Syrian Arabic, Syrian pronunciation: ) is the principal port city of Syria and capital city of the Latakia Governorate located on the Mediterranean coast. Historically, it has also been known as Laodicea in Syria or Laodicea ad Mar ...
and Tartus
Tartus ( / ALA-LC: ''ŠĻ¨arŠĻ≠Ňęs''; known in the County of Tripoli as Tortosa and also transliterated from French language, French Tartous) is a major port city on the Mediterranean coast of Syria. It is the second largest port city in Syria (af ...
are the region's principal cities. They are also concentrated in the plains around Hama
Hama ( ', ) is a city on the banks of the Orontes River in west-central Syria. It is located north of Damascus and north of Homs. It is the provincial capital of the Hama Governorate. With a population of 996,000 (2023 census), Hama is one o ...
and Homs
Homs ( ; ), known in pre-Islamic times as Emesa ( ; ), is a city in western Syria and the capital of the Homs Governorate. It is Metres above sea level, above sea level and is located north of Damascus. Located on the Orontes River, Homs is ...
. Alawites also live in Syria's major cities. They make up about 11% of the country's population.
There are four Alawite confederations‚ÄĒKalbiyya
The Kalbiyya (), or Kalbi or Kelbi tribe is one of four tribes, or tribal confederations, of the Alawite community in Syria. Appearing in historical sources from the 16th century, the Kalbiyya came to prominence when Hafez al-Assad, the son of ...
, Khaiyatin, Haddadin, and Matawirah‚ÄĒeach divided into tribes based on their geographical origins or their main religious leader, such as Šł§aidarńęya of Alńę Šł§aidar, and KalńĀziyya of Sheikh MuŠł•ammad ibn YŇęnus from the village KalńĀzŇę near Antakya
Antakya (), Turkish form of Antioch, is a municipality and the capital Districts of Turkey, district of Hatay Province, Turkey. Its area is . Prior to the devastating 2023 Turkey‚ÄďSyria earthquakes, 2023 earthquakes, its population was recorded ...
. Those Alawites are concentrated in the Latakia region of Syria, extending north to Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; , ) "Antioch on Daphne"; or "Antioch the Great"; ; ; ; ; ; ; . was a Hellenistic Greek city founded by Seleucus I Nicator in 300 BC. One of the most important Greek cities of the Hellenistic period, it served as ...
(Antakya
Antakya (), Turkish form of Antioch, is a municipality and the capital Districts of Turkey, district of Hatay Province, Turkey. Its area is . Prior to the devastating 2023 Turkey‚ÄďSyria earthquakes, 2023 earthquakes, its population was recorded ...
), Turkey, and in and around Homs and Hama.
Before 1953, Alawites held specifically reserved seats in the Syrian Parliament, in common with all other religious communities. After that (including the 1960 census), there were only general Muslim and Christian categories, without mention of subgroups, to reduce sectarianism
Sectarianism is a debated concept. Some scholars and journalists define it as pre-existing fixed communal categories in society, and use it to explain political, cultural, or Religious violence, religious conflicts between groups. Others conceiv ...
(''taifiyya'').
Golan Heights
Before the 1967 war, Alawites in the Golan Heights lived mainly in three northern villages,'Ayn Fit
'Ayn Fit (), was a Syrian Alawite village situated in the northwestern Golan Heights.
, Za'ura and Ghajar. There are about 3,900 Alawites living in the village of Ghajar
Ghajar (, or ), also Rhadjar, is an Alawite-Arab village on the Hasbani River, on the border between Lebanon and the Israeli-occupied portion of the Golan Heights. The name of the village means "gypsy" in Arabic. As of , it had a population ...
, which is located on the border between Lebanon and the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights
The Golan Heights, or simply the Golan, is a basaltic plateau at the southwest corner of Syria. It is bordered by the Yarmouk River in the south, the Sea of Galilee and Hula Valley in the west, the Anti-Lebanon mountains with Mount Hermon in t ...
. In 1932, the residents of Ghajar were given the option of choosing their nationality, and overwhelmingly chose to be a part of Syria, which has a sizable Alawite minority. Before the 1967 Arab-Israeli War
The Six-Day War, also known as the June War, 1967 Arab‚ÄďIsraeli War or Third Arab‚ÄďIsraeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states, primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan from 5 to 10June ...
, the residents of Ghajar were counted in the 1960 Syrian census. According to Joshua Project
The Joshua Project is an Evangelicalism, evangelical Christian organization based in Colorado Springs, Colorado, Colorado Springs, United States, which seeks to coordinate the work of Christian_mission#Contemporary_concepts_of_mission, missionary ...
, after Israel captured the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights, or simply the Golan, is a basaltic plateau at the southwest corner of Syria. It is bordered by the Yarmouk River in the south, the Sea of Galilee and Hula Valley in the west, the Anti-Lebanon mountains with Mount Hermon in t ...
from Syria, and after implementing Israeli civil law in 1981, the Alawite community chose to become Israeli citizens. However, according to Al-Marsad
Al-Marsad ‚Äď Arab Human Rights Centre in Golan Heights is an independent, not-for-profit international human rights organization with no religious or political affiliation that operates in the Golan Heights.Humphries, IsabelleIn the Ghost Towns ...
, Alawites were forced to undergo a process of naturalisation.
Turkey
 To avoid confusion with the ethnic Turkish and Kurdish
To avoid confusion with the ethnic Turkish and Kurdish Alevis
Alevism (; ; ) is a syncretic heterodox Islamic tradition, whose adherents follow the mystical Islamic teachings of Haji Bektash Veli, who taught the teachings of the Twelve Imams, whilst incorporating some traditions from shamanism. Differing ...
, the Alawites call themselves ''Arap Alevileri'' ("Arab Alevis") in Turkish. The term ''Nusayrńę'', previously used in theological texts, has been revived in recent studies. A quasi-official name used during the 1930s by Turkish authorities was ''Eti T√ľrkleri'' ("Hittite Turks"), to conceal their Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
origins. Although this term is obsolete, it is still used by some older people as a euphemism
A euphemism ( ) is when an expression that could offend or imply something unpleasant is replaced with one that is agreeable or inoffensive. Some euphemisms are intended to amuse, while others use bland, inoffensive terms for concepts that the u ...
.
In 1939, the Alawites accounted for some 40 percent of the population of the province of Iskenderun. According to French geographer Fabrice Balanche
Fabrice Balanche (born November 3, 1969, in Belfort, France) is a French geographer and specialist in the political geography and geopolitics of Syria, Lebanon, Iraq and the wider Middle East.
He was described by the Carnegie Endowment for Inter ...
, relations between the Alawites of Turkey and the Alawites of Syria are limited. Community ties were broken by the Turkification
Turkification, Turkization, or Turkicization () describes a shift whereby populations or places receive or adopt Turkic attributes such as culture, language, history, or ethnicity. However, often this term is more narrowly applied to mean specif ...
policy and the decades-long closure of the Syria-Turkey border.
The exact number of Alawites in Turkey is unknown; there were 185,000 in 1970. As Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
s, they are not recorded separately from Sunnis. In the 1965 census (the last Turkish census where informants were asked about their mother tongue
A first language (L1), native language, native tongue, or mother tongue is the first language a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother tongue'' refers ...
), 185,000 people in the three provinces declared their mother tongue as Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
; however, Arabic-speaking Sunnis and Christians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
were also included in this figure. Turkish Alawites traditionally speak the same dialect of Levantine Arabic
Levantine Arabic, also called Shami (Endonym and exonym, autonym: or ), is an Varieties of Arabic, Arabic variety spoken in the Levant, namely in Syria, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, Israel and southern Turkey (historically only in Adana Prov ...
as Syrian Alawites. Arabic is preserved in rural communities and in Samandańü
Samandańü, formerly known as S√ľveydiye (), is a municipality and district of Hatay Province, Turkey. Its area is 384 km2, and its population is 123,447 (2022). It lies at the mouth of the Asi River on the Mediterranean coast, near Turkey's ...
. Younger people in the cities of √áukurova and ńįskenderun
ńįskenderun (), historically known as Alexandretta (, ) and Scanderoon, is a municipality and Districts of Turkey, district of Hatay Province, Turkey. Its area is 247 km2, and its population is 251,682 (2022). It is on the Mediterranean coas ...
tend to speak Turkish. The Turkish spoken by Alawites is distinguished by its accents and vocabulary
A vocabulary (also known as a lexicon) is a set of words, typically the set in a language or the set known to an individual. The word ''vocabulary'' originated from the Latin , meaning "a word, name". It forms an essential component of languag ...
. Knowledge of the Arabic alphabet
The Arabic alphabet, or the Arabic abjad, is the Arabic script as specifically codified for writing the Arabic language. It is a unicase, unicameral script written from right-to-left in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters, of which most ...
is confined to religious leaders and men who have worked or studied in Arab countries
The Arab world ( '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, comprises a large group of countries, mainly located in West Asia and North Africa. While the majority of people in ...
.
Alawites demonstrate considerable social mobility
Social mobility is the movement of individuals, families, households or other categories of people within or between social strata in a society. It is a change in social status relative to one's current social location within a given socie ...
. Until the 1960s, they were bound to Sunni ''aghas'' (landholders) around Antakya and were poor. Alawites are prominent in the sectors of transportation and commerce and a large, professional middle class has emerged. Male exogamy
Exogamy is the social norm of mating or marrying outside one's social group. The group defines the scope and extent of exogamy, and the rules and enforcement mechanisms that ensure its continuity. One form of exogamy is dual exogamy, in which tw ...
has increased, particularly among those who attend universities or live in other parts of Turkey. These marriages are tolerated; however, female exogamy (as in other patrilineal
Patrilineality, also known as the male line, the spear side or agnatic kinship, is a common kinship system in which an individual's family membership derives from and is recorded through their father's lineage. It generally involves the inheritanc ...
groups) is discouraged.
Alawites, like Alevis, have strong leftist
Left-wing politics describes the range of political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy either as a whole or of certain social hierarchies. Left-wing politi ...
political beliefs. However, some people in rural areas (usually members of notable Alawite families) may support secular, conservative parties such as the Democrat Party. Most Alawites feel oppressed by the policies of the Presidency of Religious Affairs
A presidency is an Administration (government), administration or the Executive (government), executive, the collective administrative and governmental entity that exists around an office of President (government title), president of a state or na ...
in Turkey (''Diyanet ńįŇüleri BaŇükanlńĪńüńĪ'').
There are religious festivals celebrated by Alawites in Turkey that have origins in the pre-Islamic periods, such as the Evvel Temmuz Festival.
Lebanon
 In 2011, there were an estimated 150,000 Alawites in Lebanon, where they have lived since at least the 16th century. They are one of the 18 official Lebanese sects; due to the efforts of their leader, Ali Eid, the
In 2011, there were an estimated 150,000 Alawites in Lebanon, where they have lived since at least the 16th century. They are one of the 18 official Lebanese sects; due to the efforts of their leader, Ali Eid, the Taif Agreement
The 1989 Taif Agreement (, ), officially known as the ('')'', was reached to provide "the basis for the ending of the civil war and the return to political normalcy in Lebanon". Negotiated in Taif, Saudi Arabia, it was designed to end the 15 y ...
of 1989 gave them two reserved seats in Parliament. Lebanese Alawites live primarily in the Jabal Mohsen neighbourhood of Tripoli
Tripoli or Tripolis (from , meaning "three cities") may refer to:
Places Greece
*Tripolis (region of Arcadia), a district in ancient Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (Larisaia), an ancient Greek city in the Pelasgiotis district, Thessaly, near Larissa ...
and in 10 villages in the Akkar District
Akkar District () is the only district in Akkar Governorate, Lebanon. It is coextensive with the governorate and covers an area of . The UNHCR estimated the population of the district to be 389,899 in 2015, including 106,935 registered refugees of ...
, and are represented by the Arab Democratic Party. Their Mufti is Sheikh Assad Assi. The Bab al-Tabbaneh‚ÄďJabal Mohsen conflict between pro-Syrian Alawites and anti-Syrian Sunnis has affected Tripoli for decades.
Language
Alawites in Syria speak a special dialect (part ofLevantine Arabic
Levantine Arabic, also called Shami (Endonym and exonym, autonym: or ), is an Varieties of Arabic, Arabic variety spoken in the Levant, namely in Syria, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, Israel and southern Turkey (historically only in Adana Prov ...
) famous for the usage of letter (qńĀf), but this feature is shared with neighboring non-Alawite villages, such as Idlib. Due to foreign occupation of Syria, the same dialect is characterized by multiple borrowings, mainly from Turkish and then French, especially terms used for imported inventions such as television, radio, elevator (ascenseur), etc.
See also
* List of AlawitesNotes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * Kazimi, Nibras. ''Syria Through Jihadist Eyes: A Perfect Enemy'', Hoover Institution Press, 2010. . * RFWRfO2016External links
{{Authority control Alawites, Arab ethnic groups Islam in Syria Ethnic groups in Syria Islamic mysticism Ghulat sects Shia Islamic branches Arab Muslims Ethnoreligious groups in Asia Muslim ethnoreligious groups