|
Samandağ
Samandağ, formerly known as Süveydiye (), is a municipality and district of Hatay Province, Turkey. Its area is 384 km2, and its population is 123,447 (2022). It lies at the mouth of the Asi River on the Mediterranean coast, near Turkey's border with Syria, from the city of Antakya. In February 2023, the town was heavily damaged by powerful earthquakes. Etymology Samandağ was formerly known as ''Süveydiye'', ''Yukarı Alevışık'' and ''Levşiye''. It was officially named Samandağ (Seman Dağ, Turkish for Jabal Sem'an: St. Simeon Mountain) in 1948. In Armenian, it was known as ''Svetia'' (). History Samandağ lies near the site of the ancient Seleucia Pieria, founded in 300 BC after the Persian Empire was ousted from the region by Seleucus Nicator, a general of Alexander the Great, in the Seleucid era that followed Alexander's demise. Seleucia Pieria quickly became a major Mediterranean port of the Hellenistic and Roman eras, the port of Antioch. However, it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emrah Karaçay
Emrah Karaçay (born 1987, Samandağ) is a Turkish dentist and politician, and the mayor of Samandağ since the 2024 Turkish local elections. Biography Karaçay was born in 1987 in an Arab Alawite family in Samandağ, Hatay Hatay Province (, ) is the southernmost Provinces of Turkey, province and Metropolitan municipalities in Turkey, metropolitan municipality of Turkey. Its area is , and its population is 1,686,043 (2022). It is situated mostly outside Anatolia, .... There, he completed his primary, secondary, and high school education. He graduated from the Faculty of Dentistry at Samsun Ondokuz Mayıs University and later opened his own private practice in Samandağ, where he works as a dentist. Karaçay is married and has three children. Career Since 2019, he has been a member of the Workers' Party of Turkey (TİP). In the 2024 local elections, Emrah Karaçay was elected as the mayor of Samandağ and was the only candidate from the Workers' Party of Turkey to win ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatay Province
Hatay Province (, ) is the southernmost province and metropolitan municipality of Turkey. Its area is , and its population is 1,686,043 (2022). It is situated mostly outside Anatolia, along the eastern coast of the Levantine Sea. The province borders Syria to its south and east, the Turkish province of Adana to the northwest, Osmaniye to the north, and Gaziantep to the northeast. It is partially situated on the Cilician Plain, a large fertile plain along the Cilicia region. Its administrative capital is Antakya (ancient Antioch), making it one of the three Turkish provinces not named after its administrative capital or any settlement. The second-largest city is İskenderun (formerly Alexandretta). Sovereignty over most of the province was disputed with neighbouring Syria, which claimed that the province had a demographic Arab majority, and has separated from its territory in violation of the terms of the French Mandate for Syria that was established on the heels of World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asi River
The Orontes (; from Ancient Greek , ) or Nahr al-ʿĀṣī, or simply Asi (, ; ) is a long river in Western Asia that begins in Lebanon, flowing northwards through Syria before entering the Mediterranean Sea near Samandağ in Hatay Province, Turkey. As the chief river of the northern Levant, the Orontes has been the site of many major battles including the Battle of Kadesh (13th century BCE), and water distribution remains a controversial issue between the countries in the region. Among the most important cities on the river are Homs, Hama, Jisr al-Shughur, and Antakya (the ancient Antioch, which was also known as "Antioch on the Orontes"). Names In the 9th century BCE, the ancient Assyrians referred to the river as Arantu, and the nearby Egyptians called it Araunti. The etymology of the name is unknown, yet some sources indicate that it might be derived from ''Arnt'' which means "lioness" in Syriac languages; others called it ''Alimas'', a "water goddess" in Aramaic. ''Arantu' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antakya
Antakya (), Turkish form of Antioch, is a municipality and the capital Districts of Turkey, district of Hatay Province, Turkey. Its area is . Prior to the devastating 2023 Turkey–Syria earthquakes, 2023 earthquakes, its population was recorded at 399,045 (2022). It is in the Hatay Province, which is the southernmost region of Turkey. The city is located in a well-watered and fertile valley on the Orontes River, about from the Levantine Sea. Today's city stands partly on the site of the ancient Antiochia (also known as "Antioch on the Orontes"), which was founded in the fourth century BC by the Seleucid Empire. Antioch later became one of the Roman Empire's largest cities and was made the capital of the provinces of Roman Syria, Syria and Coele-Syria (Roman province), Coele-Syria. It was also an influential early center of Christianity; the New Testament asserts that the name "Christian" first emerged in Antioch. The city gained much ecclesiastical importance during the times o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
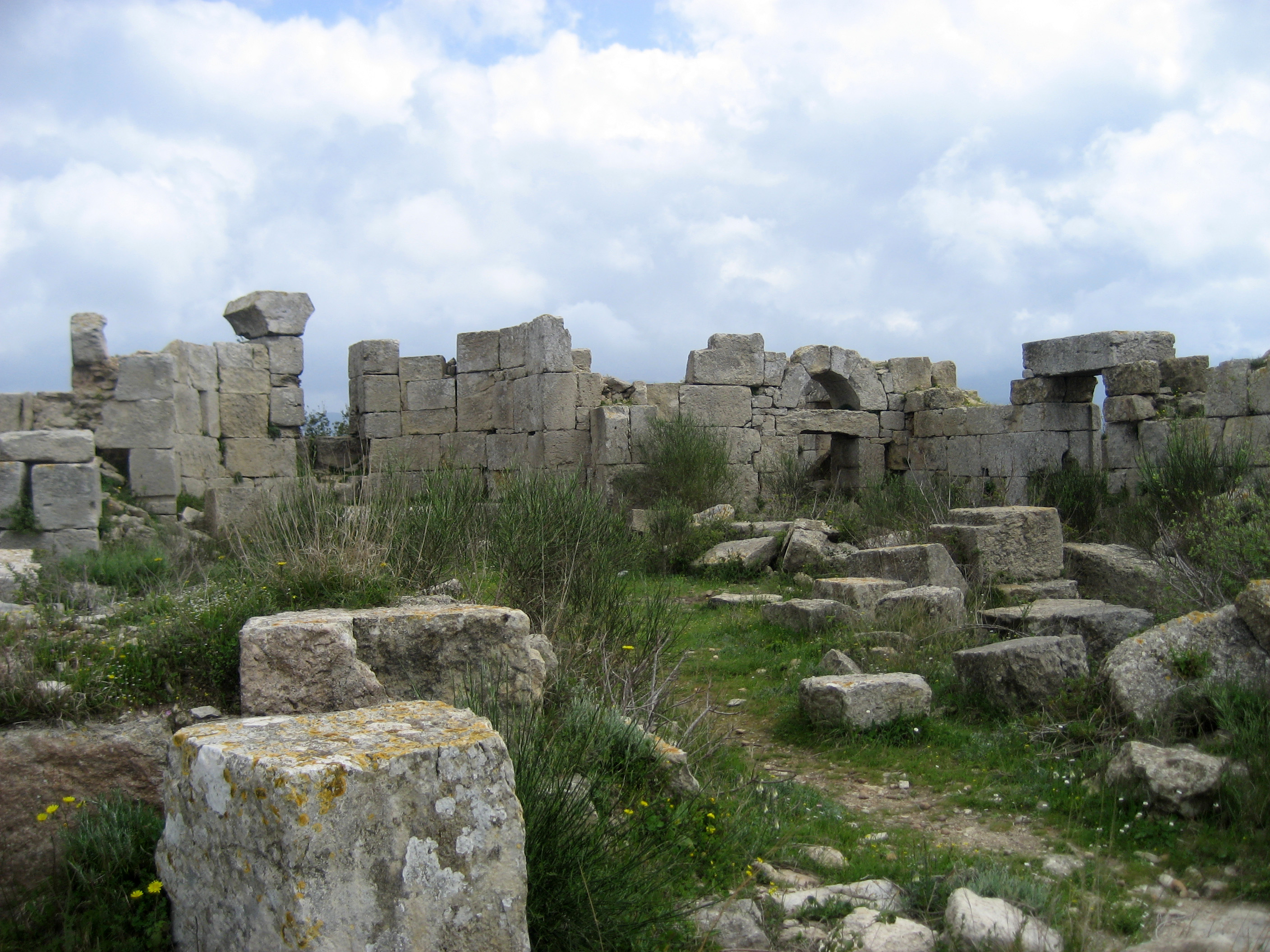
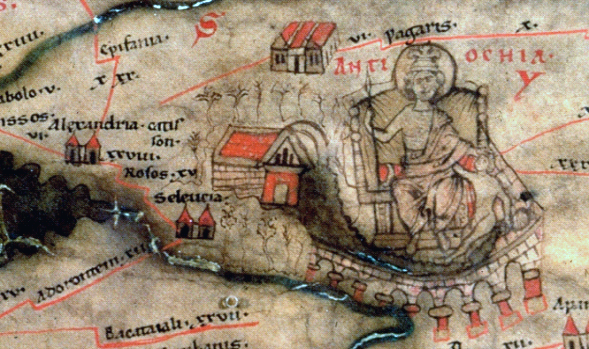
Seleucia Pieria
Seleucia in Pieria (Greek Σελεύκεια ἐν Πιερίᾳ), also known in English as Seleucia by the Sea, and later named Suedia, was a Hellenistic town, the seaport of Antioch ad Orontes ( Syria Prima), the Seleucid capital, modern Antakya (Turkey). The city was built slightly to the north of the estuary of the river Orontes, between small rivers on the western slopes of the Coryphaeus, one of the southern summits of the Amanus Mountains. According to Pausanias and Malalas, there was a previous city here named Palaeopolis ("Old City"). At present, it is located at the seaside village of Çevlik near the town of Samandağ in the Hatay Province of Turkey. Seleucia, Apamea, Laodicea, and Antioch formed the Syrian tetrapolis. History Seleucid period Seleucia Pieria was founded in ca. 300 BC by Seleucus I Nicator, one of the successors of the Macedonian conqueror Alexander the Great and the founder of the Seleucid Empire. The Macedonians called the landscape Pieri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simeon Stylites The Younger
Simeon Stylites the Younger, also known as Simeon of the Admirable Mountain (, Arabic: مار سمعان العمودي الأصغر ''mār semʻān l-ʻamūdī l-asghar''; 521 – 596/597), is a saint in the Catholic Church and Eastern Orthodox Church. Life Stylites were solitaries who, taking up their abode upon the tops of a pillar (stylos), chose to spend their days amid the restraints thus entailed and in the exercise of other forms of asceticism.Thurston, Herbert; "Stylites (Pillar Saints)", The Catholic Encyclopedia Vol. 14, New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1912, 9 December 2021 Simeon was born at Antioch in 521. His father, John, was a native of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Workers' Party Of Turkey (2017)
The Workers' Party of Turkey (, TİP) is a socialist political party in Turkey. The party was founded out of a split in the Communist Party of Turkey (TKP). As a result of the internal strife between two rival factions, the group led by former chairman Erkan Baş initially established People's Communist Party of Turkey (HTKP) in 2014, and after three years, it was rebranded as the Workers' Party of Turkey in 2017. Adopting Marxism-Leninism as its guide and reconciling it with left-wing populism, the TİP is against capitalism, imperialism, and all forms of exploitation, oppression and discrimination. The party embraces progressive values such as laicism and public ownership, and struggles for the preservation and improvement of democratic and civil rights, freedom of organization, assembly, speech and press. It also strongly advocates for the rights of the Kurdish people, women and LGBT groups in Turkey. In the most recent general election held in 2023, the TİP, as a pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Saint Symeon
St Symeon or Port StSymeon ( or ') was the medieval port for the Frankish Principality of Antioch, located on the mouth of the Orontes River. It may be named after Saint Simeon Stylites the Younger, who dwelt on a mountain only six miles from St Symeon, or the original Saint Simeon Stylites, who was buried in Antioch. History Seleucia Pieria had been the Roman port of Antioch, but silting and an earthquake had rendered it unusable. The harbour of St Symeon, some fourteen kilometres to the west of Antioch, was the main harbour of Antioch. Its possession was essential for the armies of the First Crusade during the siege of Antioch and it seems that the crusaders maintained a force there for this time. In November 1097, the Crusaders besieging Antioch were heartened by the appearance of reinforcements in a Genoese squadron at St Symeon, which they were then able to capture. The besiegers were very short of food, and supplies from Cyprus to St Symeon were subject to frequent atta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; , ) "Antioch on Daphne"; or "Antioch the Great"; ; ; ; ; ; ; . was a Hellenistic Greek city founded by Seleucus I Nicator in 300 BC. One of the most important Greek cities of the Hellenistic period, it served as the capital of the Seleucid Empire and later as regional capital to both the Roman and Byzantine Empire. During the Crusades, Antioch served as the capital of the Principality of Antioch, one of four Crusader states that were founded in the Levant. Its inhabitants were known as ''Antiochenes''. The remains of the ancient city of Antioch are mostly buried beneath alluvial deposits from the Orontes River. The modern city of Antakya, in Hatay Province of Turkey, lies in its place. Antioch was founded near the end of the fourth century BC by Seleucus I Nicator, one of Alexander the Great's generals, as one of the tetrapoleis of Seleucis of Syria. Seleucus encouraged Greeks from all over the Mediterranean to settle in the city. The ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of Turkey
The Provinces of Turkey, 81 provinces of Turkey are divided into 973 districts (''ilçeler''; sing. ''ilçe''). In the Ottoman Empire and in the early Turkish Republic, the corresponding unit was the ''qadaa, kaza''. Most provinces bear the same name as their respective provincial capital (political), capital districts. However, many urban provinces, designated as greater municipalities, have a center consisting of multiple districts, such as the provincial capital of Ankara Province, Ankara province, Ankara, The City of Ankara, comprising nine separate districts. Additionally three provinces, Kocaeli, Sakarya, and Hatay have their capital district named differently from their province, as İzmit, Adapazarı, and Antakya respectively. A district may cover both rural and urban areas. In many provinces, one district of a province is designated the central district (''merkez ilçe'') from which the district is administered. The central district is administered by an appointed pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros II Phokas
Nikephoros II Phokas (; – 11 December 969), Latinized Nicephorus II Phocas, was Byzantine emperor from 963 to 969. His career, not uniformly successful in matters of statecraft or of war, nonetheless greatly contributed to the resurgence of the Byzantine Empire during the 10th century. In the east, Nikephoros completed the conquest of Cilicia and retook the islands of Crete and Cyprus, opening the path for subsequent Byzantine incursions reaching as far as Upper Mesopotamia and the Levant; these campaigns earned him the sobriquet "pale death of the Saracens". Early life and career Nikephoros Phokas was born around 912. From his paternal side, he belonged to the Phokas family which had produced several distinguished generals, including Nikephoros' father Bardas Phokas, brother Leo Phokas, and grandfather Nikephoros Phokas the Elder, who had all served as commanders of the field army ('' domestikos tōn scholōn''). From his maternal side he belonged to the Maleinoi, a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; , ''Saljuqian'',) alternatively spelled as Saljuqids or Seljuk Turks, was an Oghuz Turks, Oghuz Turkic, Sunni Muslim dynasty that gradually became Persianate society, Persianate and contributed to Turco-Persian tradition, Turco-Persian culture. The founder of the Seljuk dynasty, Seljuk Beg, was a descendant of a royal Khazar chief Tuqaq who served as advisor to the King of the Khazars. in West Asia and Central Asia. The Seljuks established the Seljuk Empire (1037–1194), the Kerman Seljuk Sultanate, Sultanate of Kermân (1041–1186) and the Sultanate of Rum (1074–1308), which stretched from Iran to Anatolia and were the prime targets of the First Crusade. Early history The Seljuks originated from the Kınık (tribe), Kinik branch of the Oghuz Turks, who in the 8th century lived on the periphery of the Muslim world; north of the Caspian Sea and Aral Sea in their Oghuz Yabgu State in the Kazakh Steppe of Turkestan. During the 10th century, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |