’А’°’µ’°’љ’њ’°’ґ on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a
 Armenia lies in the highlands surrounding the mountains of Ararat. There is evidence of an early civilisation in Armenia in the
Armenia lies in the highlands surrounding the mountains of Ararat. There is evidence of an early civilisation in Armenia in the
–Ч–∞–Ї–∞–≤–Ї–∞–Ј—М–µ –Є —Б–Њ–њ—А–µ–і–µ–ї—М–љ—Л–µ —Б—В—А–∞–љ—Л –≤ –њ–µ—А–Є–Њ–і —Н–ї–ї–Є–љ–Є–Ј–Љ–∞
¬ї During the late 6th century BC, the first geographical entity that was called Armenia by neighbouring populations was established under the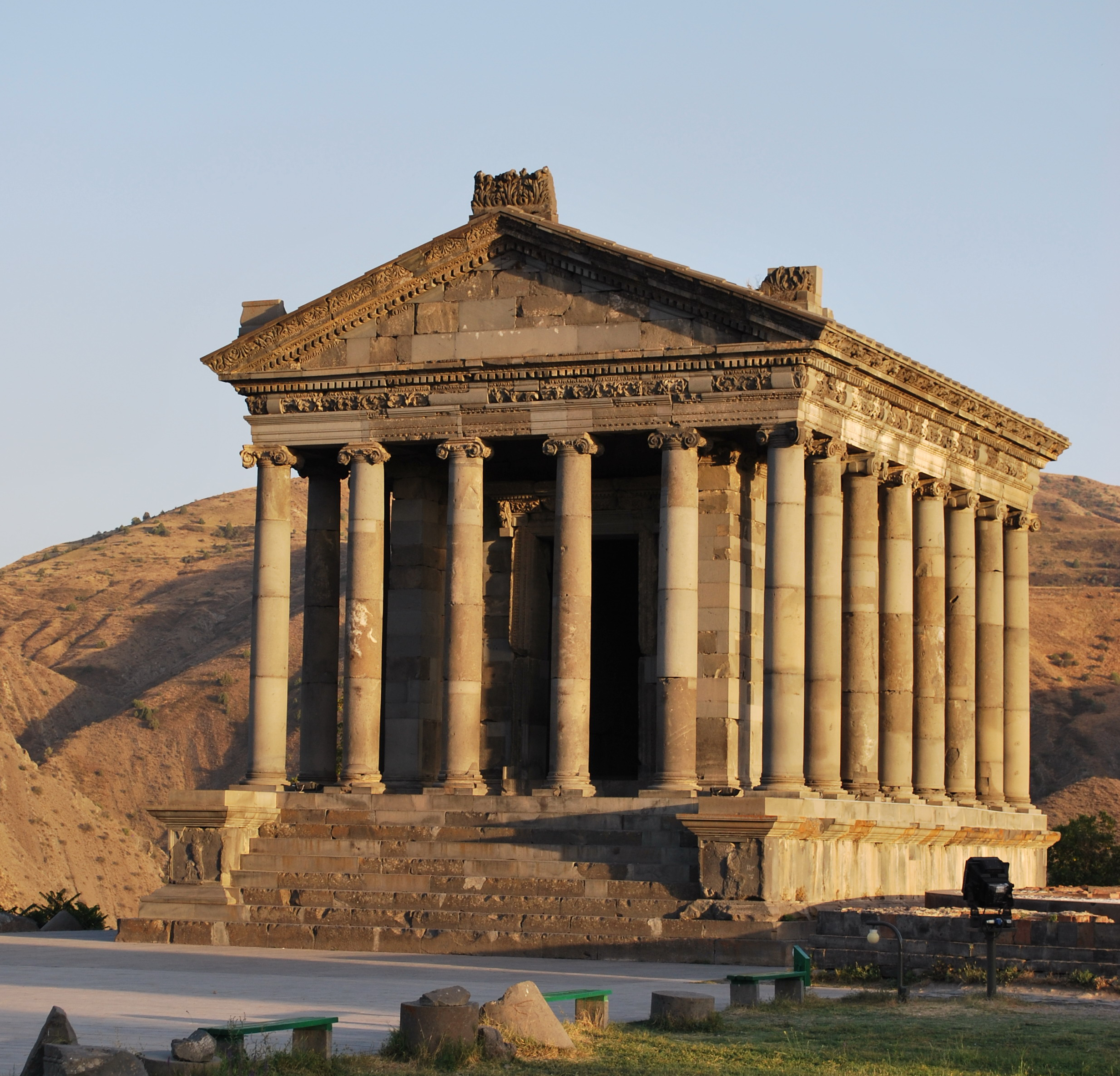 Religion in ancient Armenia was historically related to a set of beliefs that, in Persia, led to the emergence of
Religion in ancient Armenia was historically related to a set of beliefs that, in Persia, led to the emergence of
''Zoroastrians: Their Religious Beliefs and Practices''
Psychology Press, 2001 p. 84 becoming the first officially Christian state, ten years before the
 The Sassanid Empire was conquered by the
The Sassanid Empire was conquered by the
 During the 1230s, the Mongol Empire conquered Zakarid Armenia and then the remainder of Armenia. The Mongolian invasions were soon followed by those of other Central Asian tribes, such as the Kara Koyunlu, Timurid dynasty and AƒЯ Qoyunlu, which continued from the 13th century until the 15th century. After incessant invasions, each bringing destruction to the country, with time Armenia became weakened.
In the 16th century, the
During the 1230s, the Mongol Empire conquered Zakarid Armenia and then the remainder of Armenia. The Mongolian invasions were soon followed by those of other Central Asian tribes, such as the Kara Koyunlu, Timurid dynasty and AƒЯ Qoyunlu, which continued from the 13th century until the 15th century. After incessant invasions, each bringing destruction to the country, with time Armenia became weakened.
In the 16th century, the  In the 1813 Treaty of Gulistan and the 1828 Treaty of Turkmenchay, following the Russo-Persian War (1804вАУ13) and the Russo-Persian War (1826вАУ28), respectively, the Qajar dynasty of Iran was forced to irrevocably cede
In the 1813 Treaty of Gulistan and the 1828 Treaty of Turkmenchay, following the Russo-Persian War (1804вАУ13) and the Russo-Persian War (1826вАУ28), respectively, the Qajar dynasty of Iran was forced to irrevocably cede  During the 1890s, the Armenian Revolutionary Federation, commonly known as ''Dashnaktsutyun'', became active within the
During the 1890s, the Armenian Revolutionary Federation, commonly known as ''Dashnaktsutyun'', became active within the
 Although the Russian Caucasus Army (World War I), Russian Caucasus Army of Imperial forces commanded by Nikolai Yudenich and Armenians in volunteer units and Armenian militia led by Andranik Ozanian and Tovmas Nazarbekian succeeded in gaining most of
Although the Russian Caucasus Army (World War I), Russian Caucasus Army of Imperial forces commanded by Nikolai Yudenich and Armenians in volunteer units and Armenian militia led by Andranik Ozanian and Tovmas Nazarbekian succeeded in gaining most of  The First Republic's short-lived independence was fraught with war, territorial disputes, Muslim uprisings in Kars and SharurвАУNakhichevan, large-scale rebellions, and a mass influx of refugees from Western Armenia, bringing with them disease and starvation. The Allies of World War I, Entente Powers sought to help the newly founded Armenian state through relief funds and other forms of support.
At the end of the war, the victorious powers sought to divide up the Ottoman Empire. Signed between the Allies of World War I, Allied and Associated Powers and
The First Republic's short-lived independence was fraught with war, territorial disputes, Muslim uprisings in Kars and SharurвАУNakhichevan, large-scale rebellions, and a mass influx of refugees from Western Armenia, bringing with them disease and starvation. The Allies of World War I, Entente Powers sought to help the newly founded Armenian state through relief funds and other forms of support.
At the end of the war, the victorious powers sought to divide up the Ottoman Empire. Signed between the Allies of World War I, Allied and Associated Powers and

''–С–Њ–ї—М—И–∞—П —Б–Њ–≤–µ—В—Б–Ї–∞—П —Н–љ—Ж–Є–Ї–ї–Њ–њ–µ–і–Є—П'', 3-–µ –Є–Ј–і., –≥–ї. —А–µ–і. –Р. –Ь. –Я—А–Њ—Е–Њ—А–Њ–≤. –Ь–Њ—Б–Ї–≤–∞: –°–Њ–≤–µ—В—Б–Ї–∞—П —Н–љ—Ж–Є–Ї–ї–Њ–њ–µ–і–Є—П, 1972. –Ґ. 9 () With this annexation, the Treaty of Alexandropol was superseded by the Turkish-Soviet Treaty of Kars. In the agreement, Turkey allowed the Soviet Union to assume control over Adjara with the port city of Batumi in return for sovereignty over the cities of Kars, Ardahan, and IƒЯdƒ±r, all of which were part of Russian Armenia. The TSFSR existed from 1922 to 1936, when it was divided up into three separate entities (
 Armenia was not the scene of any battles in Eastern Front (World War II), World War II. An estimated 500,000 Armenians (nearly a third of the population) served in the Red Army during the war, and 175,000 died. A total of 117 citizens of Armenia including 10 non ethnic Armenians were awarded Hero of the Soviet Union. Six special military divisions were formed in Soviet Armenia in 1941вАУ42, partly because so many draftees from the republic could not understand Russian. Five of them, the Soviet 89th "Tamanyan" Division, 89th, 409th Rifle Division, 409th, 408th Rifle Division (Soviet Union), 408th, 390th Rifle Division, 390th, and 76th Rifle Division (Soviet Union), 76th Divisions, would have a distinguished war record, while the sixth was ordered to stay in Armenia to guard the republic's western borders against a possible incursion by neighboring Turkey.
The Soviet 89th "Tamanyan" Division, 89th Tamanyan Division, composed of ethnic Armenians, fought in the Battle of Berlin and entered Berlin.
It is claimed that the freedom index in the region had seen an improvement after the State funeral of Joseph Stalin, death of Joseph Stalin in 1953 and the emergence of Nikita Khrushchev as the new general secretary of the CPSU. Soon, life in Armenia's SSR began to see rapid improvement. The church, which was limited during the secretaryship of Stalin, was revived when Catholicos of All Armenians, Catholicos Vazgen I assumed the duties of his office in 1955. In 1967, a memorial to the victims of the Armenian genocide was built at the Tsitsernakaberd hill above the Hrazdan Canyon, gorge in
Armenia was not the scene of any battles in Eastern Front (World War II), World War II. An estimated 500,000 Armenians (nearly a third of the population) served in the Red Army during the war, and 175,000 died. A total of 117 citizens of Armenia including 10 non ethnic Armenians were awarded Hero of the Soviet Union. Six special military divisions were formed in Soviet Armenia in 1941вАУ42, partly because so many draftees from the republic could not understand Russian. Five of them, the Soviet 89th "Tamanyan" Division, 89th, 409th Rifle Division, 409th, 408th Rifle Division (Soviet Union), 408th, 390th Rifle Division, 390th, and 76th Rifle Division (Soviet Union), 76th Divisions, would have a distinguished war record, while the sixth was ordered to stay in Armenia to guard the republic's western borders against a possible incursion by neighboring Turkey.
The Soviet 89th "Tamanyan" Division, 89th Tamanyan Division, composed of ethnic Armenians, fought in the Battle of Berlin and entered Berlin.
It is claimed that the freedom index in the region had seen an improvement after the State funeral of Joseph Stalin, death of Joseph Stalin in 1953 and the emergence of Nikita Khrushchev as the new general secretary of the CPSU. Soon, life in Armenia's SSR began to see rapid improvement. The church, which was limited during the secretaryship of Stalin, was revived when Catholicos of All Armenians, Catholicos Vazgen I assumed the duties of his office in 1955. In 1967, a memorial to the victims of the Armenian genocide was built at the Tsitsernakaberd hill above the Hrazdan Canyon, gorge in
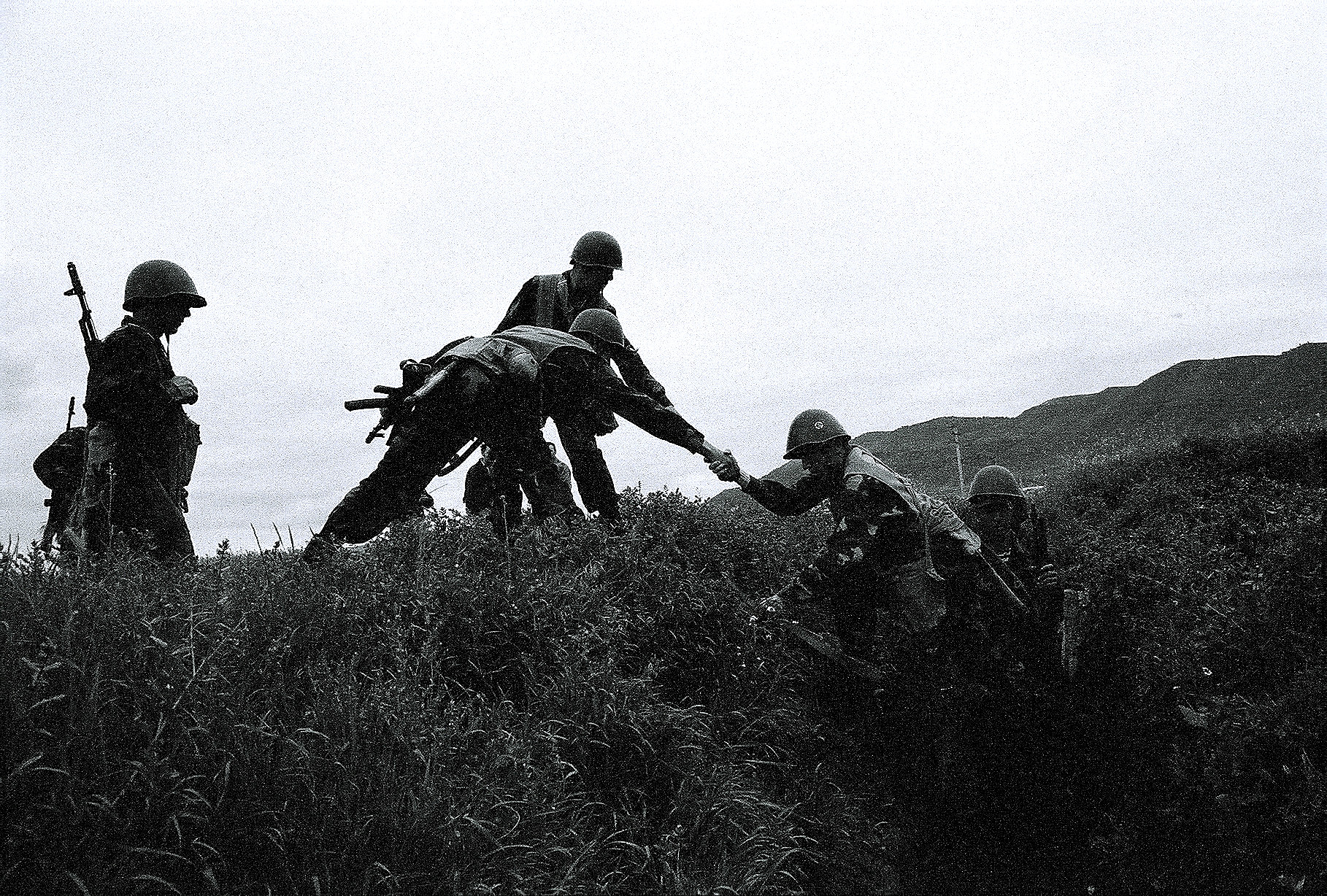 On 21 September 1991, Armenia officially declared its statehood after the 1991 Soviet coup d'état attempt, failed August coup in Moscow, Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, RSFSR. Levon Ter-Petrosyan was popularly elected the first President of the newly independent Republic of Armenia on 16 October 1991. He had risen to prominence by leading the Karabakh movement for the unification of the Armenian-populated Nagorno-Karabakh. On 26 December 1991, the Soviet Union ceased to exist and Armenia's independence was recognised.
Ter-Petrosyan led Armenia alongside defence minister Vazgen Sargsyan through the First Nagorno-Karabakh War with neighbouring Azerbaijan. The initial post-Soviet years were marred by economic difficulties, which had their roots early in the Karabakh conflict when the Azerbaijani Popular Front Party, Azerbaijani Popular Front managed to pressure the Azerbaijan SSR to instigate a railway and air blockade against Armenia. This move effectively debilitated Armenia's economy as 85% of its cargo and goods arrived through rail traffic. In 1993, Turkey joined the blockade against Armenia in support of Azerbaijan.
The Karabakh war ended after a Russian-brokered ceasefire was put in place in 1994. The war was a success for the Karabakh Armenian forces who managed to capture 16% of Azerbaijan's internationally recognised territory including almost all of the Nagorno-Karabakh itself. The Armenian backed forces remained in control of practically all of that territory until 2020. The economies of both Armenia and Azerbaijan have been hurt in the absence of a complete resolution and Armenia's borders with Turkey and Azerbaijan remain closed. By the time both Azerbaijan and Armenia had finally agreed to a ceasefire in 1994, an estimated 30,000 people had been killed and over a million had been displaced. Several thousand were killed in the later 2020 Karabakh war.
On 21 September 1991, Armenia officially declared its statehood after the 1991 Soviet coup d'état attempt, failed August coup in Moscow, Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, RSFSR. Levon Ter-Petrosyan was popularly elected the first President of the newly independent Republic of Armenia on 16 October 1991. He had risen to prominence by leading the Karabakh movement for the unification of the Armenian-populated Nagorno-Karabakh. On 26 December 1991, the Soviet Union ceased to exist and Armenia's independence was recognised.
Ter-Petrosyan led Armenia alongside defence minister Vazgen Sargsyan through the First Nagorno-Karabakh War with neighbouring Azerbaijan. The initial post-Soviet years were marred by economic difficulties, which had their roots early in the Karabakh conflict when the Azerbaijani Popular Front Party, Azerbaijani Popular Front managed to pressure the Azerbaijan SSR to instigate a railway and air blockade against Armenia. This move effectively debilitated Armenia's economy as 85% of its cargo and goods arrived through rail traffic. In 1993, Turkey joined the blockade against Armenia in support of Azerbaijan.
The Karabakh war ended after a Russian-brokered ceasefire was put in place in 1994. The war was a success for the Karabakh Armenian forces who managed to capture 16% of Azerbaijan's internationally recognised territory including almost all of the Nagorno-Karabakh itself. The Armenian backed forces remained in control of practically all of that territory until 2020. The economies of both Armenia and Azerbaijan have been hurt in the absence of a complete resolution and Armenia's borders with Turkey and Azerbaijan remain closed. By the time both Azerbaijan and Armenia had finally agreed to a ceasefire in 1994, an estimated 30,000 people had been killed and over a million had been displaced. Several thousand were killed in the later 2020 Karabakh war.
 Armenia is a
Armenia is a
 Armenia has a territorial area of . The terrain is mostly mountainous, with fast flowing rivers, and few forests. The land rises to Metres above sea level, above sea level at Mount Aragats, and no point is below Metres above sea level, above sea level. List of countries by average elevation, Average elevation of the country area is tenth highest in the world and it has 85.9% mountain area, more than Switzerland or Nepal.
Mount Ararat, which was historically part of Armenia, is the highest mountain in the region at 5,137 meters (16,854 feet). Now located in Turkey, but clearly visible from Armenia, it is regarded by the Armenians as a symbol of their land. Because of this, the mountain is present on the Coat of arms of Armenia, Armenian national emblem today.
Armenia has a territorial area of . The terrain is mostly mountainous, with fast flowing rivers, and few forests. The land rises to Metres above sea level, above sea level at Mount Aragats, and no point is below Metres above sea level, above sea level. List of countries by average elevation, Average elevation of the country area is tenth highest in the world and it has 85.9% mountain area, more than Switzerland or Nepal.
Mount Ararat, which was historically part of Armenia, is the highest mountain in the region at 5,137 meters (16,854 feet). Now located in Turkey, but clearly visible from Armenia, it is regarded by the Armenians as a symbol of their land. Because of this, the mountain is present on the Coat of arms of Armenia, Armenian national emblem today.
 The climate in Armenia is markedly highland Continental climate, continental. Summers are hot, dry and sunny, lasting from June to mid-September. The temperature fluctuates between . However, the low humidity level mitigates the effect of high temperatures. Evening breezes blowing down the mountains provide a welcome refreshing and cooling effect. Springs are short, while autumns are long. Autumns are known for their vibrant and colourful foliage.
Winters are quite cold with plenty of snow, with temperatures ranging between . Winter sports enthusiasts enjoy skiing down the hills of Tsaghkadzor, located thirty minutes outside Yerevan. Lake Sevan, nestled up in the Armenian highlands, is the second largest lake in the world relative to its altitude, at Metres above sea level, above sea level.
The climate in Armenia is markedly highland Continental climate, continental. Summers are hot, dry and sunny, lasting from June to mid-September. The temperature fluctuates between . However, the low humidity level mitigates the effect of high temperatures. Evening breezes blowing down the mountains provide a welcome refreshing and cooling effect. Springs are short, while autumns are long. Autumns are known for their vibrant and colourful foliage.
Winters are quite cold with plenty of snow, with temperatures ranging between . Winter sports enthusiasts enjoy skiing down the hills of Tsaghkadzor, located thirty minutes outside Yerevan. Lake Sevan, nestled up in the Armenian highlands, is the second largest lake in the world relative to its altitude, at Metres above sea level, above sea level.
 Because of the illicit border blockades by Azerbaijan and Turkey, Armenia continues to maintain solid relations with its southern neighbour Iran, especially in the economic sector. Economic projects are being developed between the two nations, including a gas pipeline going from Iran to Armenia.
Armenia is a member of the Council of Europe and maintains close relations with the European Union; especially with its Member state of the European Union, member states France and Greece. In January 2002, the European Parliament noted that Armenia may enter the EU in the future. A 2005 survey reported that 64% of Armenians favoured joining the EU, a move multiple Armenian officials have voiced support for.
Armenian SSR, A former republic of the
Because of the illicit border blockades by Azerbaijan and Turkey, Armenia continues to maintain solid relations with its southern neighbour Iran, especially in the economic sector. Economic projects are being developed between the two nations, including a gas pipeline going from Iran to Armenia.
Armenia is a member of the Council of Europe and maintains close relations with the European Union; especially with its Member state of the European Union, member states France and Greece. In January 2002, the European Parliament noted that Armenia may enter the EU in the future. A 2005 survey reported that 64% of Armenians favoured joining the EU, a move multiple Armenian officials have voiced support for.
Armenian SSR, A former republic of the
 Human rights in Armenia tend to be better than those in most Post-Soviet states, former Soviet republics and have drawn closer to acceptable standards, especially economically. Nonetheless, there are still several considerable problems.
Armenia scored 5.63 on The Economist Democracy Index, published in January 2023 (data for 2022). Although still classified as "hybrid regime", Armenia recorded the strongest improvement among European countries and reached its ever-best score since calculation began in 2006.
Armenia is classified as "partly free" in the 2019 report (with data from 2018) by Freedom House, which gives it a score of 51 out of 100, which is 6 points ahead of the previous estimate.
Armenia recorded unprecedented progress in the 2019 Press Freedom Index, World Press Freedom Index published by Reporters Without Borders, improving its position by 19 points and ranking 61st on the list. The publication also confirms the absence of cases of killed journalists, citizen journalists or media assistants.
Armenia ranks 26th in the 2022 report of The Human Freedom Index published by the American CATO Institute and Canada's Fraser Institute.
Armenia ranked 29th for economic freedom and 76th for personal freedom among 159 countries in the 2017 List of freedom indices, Human Freedom Index published by the Cato Institute.
In October 2023 Armenia ratified signing the Rome statute, whereby Armenia will become a full member of the International Criminal Court.
Human rights in Armenia tend to be better than those in most Post-Soviet states, former Soviet republics and have drawn closer to acceptable standards, especially economically. Nonetheless, there are still several considerable problems.
Armenia scored 5.63 on The Economist Democracy Index, published in January 2023 (data for 2022). Although still classified as "hybrid regime", Armenia recorded the strongest improvement among European countries and reached its ever-best score since calculation began in 2006.
Armenia is classified as "partly free" in the 2019 report (with data from 2018) by Freedom House, which gives it a score of 51 out of 100, which is 6 points ahead of the previous estimate.
Armenia recorded unprecedented progress in the 2019 Press Freedom Index, World Press Freedom Index published by Reporters Without Borders, improving its position by 19 points and ranking 61st on the list. The publication also confirms the absence of cases of killed journalists, citizen journalists or media assistants.
Armenia ranks 26th in the 2022 report of The Human Freedom Index published by the American CATO Institute and Canada's Fraser Institute.
Armenia ranked 29th for economic freedom and 76th for personal freedom among 159 countries in the 2017 List of freedom indices, Human Freedom Index published by the Cato Institute.
In October 2023 Armenia ratified signing the Rome statute, whereby Armenia will become a full member of the International Criminal Court.
, Armenia National Statistical Service, Yerevan Armenian mines produce copper, zinc, gold, and lead. The vast majority of energy is produced with fuel imported from Russia, including gas and nuclear fuel (for its one nuclear power plant); the main domestic energy source is hydroelectric. Small deposits of coal, gas, and petroleum exist but have not yet been developed.
Access to biocapacity in Armenia is lower than world average. In 2016, Armenia had 0.8 global hectares of biocapacity per person within its territory, much less than the world average of 1.6 global hectares per person. In 2016 Armenia used 1.9 global hectares of biocapacity per personвАФtheir ecological footprint of consumption. This means they use double as much biocapacity as Armenia contains. As a result, Armenia is running a biocapacity deficit.
Like other Post-Soviet states, newly independent states of the former Soviet Union, Armenia's economy suffers from the breakdown of former Soviet trading patterns. Soviet investment in and support of Armenian industry has virtually disappeared, so that few major enterprises are still able to function. In addition, the effects of the 1988 Armenian earthquake, 1988 Spitak earthquake, which killed more than 25,000 people and made 500,000 homeless, are still being felt. The conflict with Azerbaijan over Nagorno-Karabakh has not been resolved. Shutdown of the nuclear power plant in 1989 led to the Armenian energy crisis of 1990s. The GDP fell nearly 60% between 1989 and 1993, but then resumed robust growth after the power plant was reopened in 1995. The national currency, the dram, suffered hyperinflation for the first years after its introduction in 1993.
Nevertheless, the government was able to make wide-ranging economic reforms that paid off in dramatically lower inflation and steady growth. The 1994 ceasefire in the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict has also helped the economy. Armenia has had strong economic growth since 1995, building on the turnaround that began the previous year, and inflation has been negligible for the past several years. New sectors, such as precious-stone processing and jewelry making, information and communication technology and Tourism in Armenia, tourism are beginning to supplement more traditional sectors of the economy, such as agriculture.
This steady economic progress has earned Armenia increasing support from international institutions. The International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Bank,
Armenian mines produce copper, zinc, gold, and lead. The vast majority of energy is produced with fuel imported from Russia, including gas and nuclear fuel (for its one nuclear power plant); the main domestic energy source is hydroelectric. Small deposits of coal, gas, and petroleum exist but have not yet been developed.
Access to biocapacity in Armenia is lower than world average. In 2016, Armenia had 0.8 global hectares of biocapacity per person within its territory, much less than the world average of 1.6 global hectares per person. In 2016 Armenia used 1.9 global hectares of biocapacity per personвАФtheir ecological footprint of consumption. This means they use double as much biocapacity as Armenia contains. As a result, Armenia is running a biocapacity deficit.
Like other Post-Soviet states, newly independent states of the former Soviet Union, Armenia's economy suffers from the breakdown of former Soviet trading patterns. Soviet investment in and support of Armenian industry has virtually disappeared, so that few major enterprises are still able to function. In addition, the effects of the 1988 Armenian earthquake, 1988 Spitak earthquake, which killed more than 25,000 people and made 500,000 homeless, are still being felt. The conflict with Azerbaijan over Nagorno-Karabakh has not been resolved. Shutdown of the nuclear power plant in 1989 led to the Armenian energy crisis of 1990s. The GDP fell nearly 60% between 1989 and 1993, but then resumed robust growth after the power plant was reopened in 1995. The national currency, the dram, suffered hyperinflation for the first years after its introduction in 1993.
Nevertheless, the government was able to make wide-ranging economic reforms that paid off in dramatically lower inflation and steady growth. The 1994 ceasefire in the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict has also helped the economy. Armenia has had strong economic growth since 1995, building on the turnaround that began the previous year, and inflation has been negligible for the past several years. New sectors, such as precious-stone processing and jewelry making, information and communication technology and Tourism in Armenia, tourism are beginning to supplement more traditional sectors of the economy, such as agriculture.
This steady economic progress has earned Armenia increasing support from international institutions. The International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Bank,
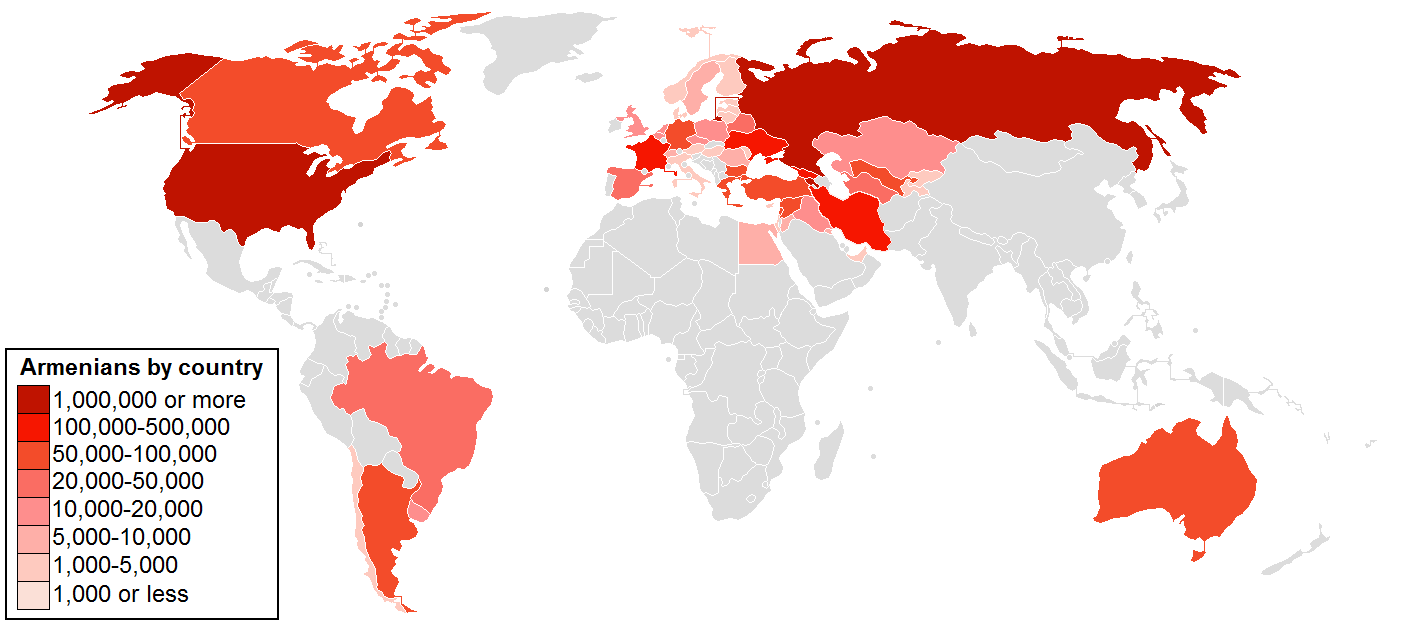 Armenia has Armenian diaspora, a relatively large external diaspora (8 million by some estimates, greatly exceeding the 3 million population of Armenia itself), with communities existing across the globe. The largest Armenian communities outside of Armenia can be found in Russia, France, Iran, the United States, Georgia, Syria, Lebanon, Australia, Canada, Greece, Cyprus, Israel, Poland, Ukraine and Brazil. 40,000 to 70,000 Armenians still live in Turkey (mostly in and around Istanbul).
About 1,000 Armenians reside in the Armenian Quarter in the Old City (Jerusalem), Old City of Jerusalem, a remnant of a once-larger community. Italy is home to the San Lazzaro degli Armeni, an island located in the Venetian Lagoon, which is completely occupied by a monastery run by the Mechitarists, an Armenian Catholic Church, Armenian Catholic congregation. Approximately 139,000 Armenians lived in the de facto independent country
Armenia has Armenian diaspora, a relatively large external diaspora (8 million by some estimates, greatly exceeding the 3 million population of Armenia itself), with communities existing across the globe. The largest Armenian communities outside of Armenia can be found in Russia, France, Iran, the United States, Georgia, Syria, Lebanon, Australia, Canada, Greece, Cyprus, Israel, Poland, Ukraine and Brazil. 40,000 to 70,000 Armenians still live in Turkey (mostly in and around Istanbul).
About 1,000 Armenians reside in the Armenian Quarter in the Old City (Jerusalem), Old City of Jerusalem, a remnant of a once-larger community. Italy is home to the San Lazzaro degli Armeni, an island located in the Venetian Lagoon, which is completely occupied by a monastery run by the Mechitarists, an Armenian Catholic Church, Armenian Catholic congregation. Approximately 139,000 Armenians lived in the de facto independent country
 Ethnic
Ethnic
. ''Demoscope.ru'' However, due to the conflict over Nagorno-Karabakh, virtually all of them emigrated from Armenia to Azerbaijan. Conversely, Armenia received a large influx of Armenian refugees from Azerbaijan, thus giving Armenia a more homogeneous character. According to Gallup research conducted in 2017 Armenia has one of the highest migrant acceptance (welcoming) rates in eastern Europe.
 In medieval times, the University of Gladzor and Tatev Monastery#Tatev University, University of Tatev took an important role for Armenian education.
A literacy rate of 100% was reported as early as 1960.Curtis, Glenn E. and Ronald G. Suny. "Education"
In medieval times, the University of Gladzor and Tatev Monastery#Tatev University, University of Tatev took an important role for Armenian education.
A literacy rate of 100% was reported as early as 1960.Curtis, Glenn E. and Ronald G. Suny. "Education"
Armenia: A Country Study
. Library of Congress Federal Research Division (March 1994). ''This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.'' Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic, In the communist era, Armenian education followed the standard Soviet model of complete state control (from Moscow) of curriculum, curricula and teaching methods and close integration of education activities with other aspects of society, such as politics, culture, and the economy. In the 1988вАУ89 school year, 301 students per 10,000 were in specialized secondary or higher education, a figure slightly lower than the Soviet average. In 1989, some 58% of Armenians over age fifteen had completed their secondary education, and 14% had a higher education. In the 1990вАУ91 school year, the estimated 1,307 primary and secondary schools were attended by 608,800 students. Another seventy specialised secondary institutions had 45,900 students, and 68,400 students were enrolled in a total of ten postsecondary institutions that included universities. In addition, 35% of eligible children attended preschool education, preschools. In 1992 Armenia's largest institution of higher learning, Yerevan State University, had eighteen departments, including ones for social sciences, sciences, and law. Its faculty numbered about 1,300 teachers and its student population about 10,000 students. The National Polytechnic University of Armenia is operating since 1933. In the early 1990s, Armenia made substantial changes to the centralised and regimented Soviet system. Because at least 98% of students in higher education were Armenian, curricula began to emphasise History of Armenia, Armenian history and culture.
 Armenian music is a mix of indigenous folk music, perhaps best-represented by Djivan Gasparyan's well-known duduk music, as well as light pop, and extensive Christian music.
Instruments like the duduk, dhol, zurna, and Kanun (instrument), kanun are commonly found in Armenian folk music. Artists such as Sayat Nova are famous due to their influence in the development of Armenian folk music. One of the oldest types of Armenian music is the Armenian chant which is the most common kind of religious music in Armenia. Many of these chants are ancient in origin, extending to pre-Christian times, while others are relatively modern, including several composed by Saint Mesrop Mashtots, the inventor of the Armenian alphabet. Whilst under Soviet Union, Soviet rule, the Armenian classical music composer Aram Khatchaturian became internationally well known for his music, for various ballets and the Sabre Dance from his composition for the ballet Gayane (ballet), Gayane.
The Armenian Genocide caused widespread emigration that led to the settlement of Armenians in various countries in the world. Armenians kept to their traditions and certain diasporans rose to fame with their music. In the post-genocide Armenian community of the United States, the so-called "kef" style Armenian dance music, using Armenian and Middle Eastern folk instruments (often electrified/amplified) and some western instruments, was popular. This style preserved the folk songs and dances of
Armenian music is a mix of indigenous folk music, perhaps best-represented by Djivan Gasparyan's well-known duduk music, as well as light pop, and extensive Christian music.
Instruments like the duduk, dhol, zurna, and Kanun (instrument), kanun are commonly found in Armenian folk music. Artists such as Sayat Nova are famous due to their influence in the development of Armenian folk music. One of the oldest types of Armenian music is the Armenian chant which is the most common kind of religious music in Armenia. Many of these chants are ancient in origin, extending to pre-Christian times, while others are relatively modern, including several composed by Saint Mesrop Mashtots, the inventor of the Armenian alphabet. Whilst under Soviet Union, Soviet rule, the Armenian classical music composer Aram Khatchaturian became internationally well known for his music, for various ballets and the Sabre Dance from his composition for the ballet Gayane (ballet), Gayane.
The Armenian Genocide caused widespread emigration that led to the settlement of Armenians in various countries in the world. Armenians kept to their traditions and certain diasporans rose to fame with their music. In the post-genocide Armenian community of the United States, the so-called "kef" style Armenian dance music, using Armenian and Middle Eastern folk instruments (often electrified/amplified) and some western instruments, was popular. This style preserved the folk songs and dances of  Richard Hagopian is perhaps the most famous artist of the traditional "kef" style and the Vosbikian Band was notable in the 1940s and 1950s for developing their own style of "kef music" heavily influenced by the popular American Big Band Jazz of the time. Later, stemming from the Middle Eastern Armenian diaspora and influenced by Continental European (especially French) pop music, the Armenian pop music genre grew to fame in the 1960s and 1970s with artists such as Adiss Harmandian and Harout Pamboukjian performing to the Armenian diaspora and Armenia; also with artists such as Sirusho, performing pop music combined with Armenian folk music in today's entertainment industry.
Other Armenian diasporans that rose to fame in classical or international music circles are world-renowned List of French-Armenians, French-Armenian singer and composer Charles Aznavour, pianist Sahan Arzruni, prominent opera sopranos such as Hasmik Papian and more recently Isabel Bayrakdarian and Anna Kasyan. Certain Armenians settled to sing non-Armenian tunes such as the heavy metal band System of a Down (which nonetheless often incorporates traditional Armenian instrumentals and styling into their songs) or pop star Cher. In the Armenian diaspora, Armenian Revolutionary Songs, Armenian revolutionary songs are popular with the youth. These songs encourage Armenian patriotism and are generally about Armenian history and national heroes.
Richard Hagopian is perhaps the most famous artist of the traditional "kef" style and the Vosbikian Band was notable in the 1940s and 1950s for developing their own style of "kef music" heavily influenced by the popular American Big Band Jazz of the time. Later, stemming from the Middle Eastern Armenian diaspora and influenced by Continental European (especially French) pop music, the Armenian pop music genre grew to fame in the 1960s and 1970s with artists such as Adiss Harmandian and Harout Pamboukjian performing to the Armenian diaspora and Armenia; also with artists such as Sirusho, performing pop music combined with Armenian folk music in today's entertainment industry.
Other Armenian diasporans that rose to fame in classical or international music circles are world-renowned List of French-Armenians, French-Armenian singer and composer Charles Aznavour, pianist Sahan Arzruni, prominent opera sopranos such as Hasmik Papian and more recently Isabel Bayrakdarian and Anna Kasyan. Certain Armenians settled to sing non-Armenian tunes such as the heavy metal band System of a Down (which nonetheless often incorporates traditional Armenian instrumentals and styling into their songs) or pop star Cher. In the Armenian diaspora, Armenian Revolutionary Songs, Armenian revolutionary songs are popular with the youth. These songs encourage Armenian patriotism and are generally about Armenian history and national heroes.
 Yerevan Vernissage (arts and crafts market), close to Republic Square, bustles with hundreds of vendors selling a variety of crafts on weekends and Wednesdays (though the selection is much reduced mid-week). The market offers woodcarving, antiques, fine lace, and the hand-knotted wool carpets and kilims that are a Caucasus speciality. Obsidian, which is found locally, is crafted into assortment of jewellery and ornamental objects. Armenian gold smithery enjoys a long tradition, populating one corner of the market with a selection of gold items. Soviet relics and souvenirs of recent Russian manufacture вАУ nesting dolls, watches, enamel boxes and so on вАУ are also available at the Vernisage.
Across from the Opera House, a popular art market fills another city park on the weekends. Armenia's long history as a crossroads of the ancient history, ancient world has resulted in a landscape with innumerable fascinating archaeological sites to explore. Middle Ages, Medieval, Iron Age,
Yerevan Vernissage (arts and crafts market), close to Republic Square, bustles with hundreds of vendors selling a variety of crafts on weekends and Wednesdays (though the selection is much reduced mid-week). The market offers woodcarving, antiques, fine lace, and the hand-knotted wool carpets and kilims that are a Caucasus speciality. Obsidian, which is found locally, is crafted into assortment of jewellery and ornamental objects. Armenian gold smithery enjoys a long tradition, populating one corner of the market with a selection of gold items. Soviet relics and souvenirs of recent Russian manufacture вАУ nesting dolls, watches, enamel boxes and so on вАУ are also available at the Vernisage.
Across from the Opera House, a popular art market fills another city park on the weekends. Armenia's long history as a crossroads of the ancient history, ancient world has resulted in a landscape with innumerable fascinating archaeological sites to explore. Middle Ages, Medieval, Iron Age,  The National Art Gallery in Yerevan has more than 16,000 works that date back to the
The National Art Gallery in Yerevan has more than 16,000 works that date back to the
 Armenian cuisine is closely related to eastern and Mediterranean cuisine; various spices, vegetables, fish, and fruits combine to present unique dishes. The main characteristics of Armenian cuisine are a reliance on the quality of the ingredients rather than heavily spicing food, the use of herbs, the use of wheat in a variety of forms, of legumes, nuts, and fruit (as a main ingredient as well as to sour food), and the stuffing of a wide variety of leaves.
The pomegranate, with its symbolic association with fertility, represents the nation. The apricot is the national fruit.
Armenian cuisine is closely related to eastern and Mediterranean cuisine; various spices, vegetables, fish, and fruits combine to present unique dishes. The main characteristics of Armenian cuisine are a reliance on the quality of the ingredients rather than heavily spicing food, the use of herbs, the use of wheat in a variety of forms, of legumes, nuts, and fruit (as a main ingredient as well as to sour food), and the stuffing of a wide variety of leaves.
The pomegranate, with its symbolic association with fertility, represents the nation. The apricot is the national fruit.
 A wide array of sports are played in Armenia, the most popular among them being wrestling, weightlifting, judo, association football, chess, and boxing. Armenia's mountainous terrain provides great opportunities for the practice of sports like skiing and climbing. Being a landlocked country, water sports can only be practised on lakes, notably Lake Sevan. Competitively, Armenia has been successful in chess, weightlifting and wrestling at the international level. Armenia is also an active member of the international sports community, with full membership in the Union of European Football Associations (UEFA) and International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF). It also hosts the Pan-Armenian Games.
Prior to 1992, Armenians would participate in the Olympics representing the USSR. As part of the Soviet Union, Armenia was very successful, winning plenty of medals and helping the USSR win the medal standings at the Olympics on numerous occasions. The first medal won by an Armenian in modern Olympic history was by Hrant Shahinyan (sometimes spelled as Grant Shaginyan), who won two golds and two silvers in gymnastics at the 1952 Summer Olympics in Helsinki. To highlight the level of success of Armenians in the Olympics, Shahinyan was quoted as saying:
"Armenian sportsmen had to outdo their opponents by several notches for the shot at being accepted into any Soviet team. But those difficulties notwithstanding, 90 percent of Armenian athletes on Soviet Olympic teams came back with medals."
Armenia first participated at the 1992 Summer Olympics in Barcelona under a unified CIS team, where it was very successful, winning three golds and one silver in weightlifting, wrestling and sharp shooting, despite only having five athletes. Since the 1994 Winter Olympics in Lillehammer, Armenia has participated as an independent nation.
Armenia participates in the Summer Olympic Games in boxing, wrestling, weightlifting, judo, gymnastics, track and field, diving, swimming and sharp shooting. It also participates in the Winter Olympic Games in alpine skiing, cross-country skiing and figure skating.
Football in Armenia, Football is also popular in Armenia. The most successful team was the FC Ararat Yerevan team of the 1970s who won the Soviet Cup in 1973 and 1975 and the Soviet Top League 1973, Soviet Top League in 1973. The latter achievement saw FC Ararat gain entry to the 1974вАУ75 European Cup, European Cup where вАУ despite a home victory in the second leg вАУ they lost on aggregate at the quarter-final stage to eventual winner FC Bayern Munich. Armenia competed internationally as part of the USSR national football team until the Armenian national football team was formed in 1992 after the split of the Soviet Union. Armenia have never qualified for a major tournament although recent improvements saw the team to achieve 44th position in the FIFA World Rankings in September 2011. The national team is controlled by the Football Federation of Armenia. The Armenian Premier League is the highest level football competition in Armenia, and has been dominated by FC Pyunik in recent seasons. The league currently consists of eight teams and relegates to the Armenian First League.
Armenia and the Armenian diaspora have produced many successful footballers, including Henrikh Mkhitaryan, Youri Djorkaeff, Alain Boghossian, Andranik Eskandarian, Andranik Teymourian, Edgar Manucharyan, Khoren Oganesian and Nikita Simonyan. Djokaeff and Boghossian won the 1998 FIFA World Cup with France national football team, France, Teymourian competed in the 2006 FIFA World Cup, 2006 World Cup for Iran national football team, Iran and Manucharyan played in the Dutch Eredivisie for AFC Ajax, Ajax. Mkhitaryan has been one of the most successful Armenian footballers in recent years, playing for international clubs such as Borussia Dortmund, Manchester United F.C., Manchester United, Arsenal F.C., Arsenal, A.S. Roma and currently for Inter Milan.
Wrestling has been a successful sport in the Olympics for Armenia. At the Armenia at the 1996 Summer Olympics, 1996 Summer Olympics in Atlanta, Armen Nazaryan won the gold in the Men's Greco-Roman wrestling, Greco-Roman Flyweight (52 kg) category and Armen Mkrtchyan won the silver in Men's Freestyle wrestling, Freestyle Paperweight (48 kg) category, securing Armenia's first two medals in its Olympic history.
Traditional Armenian wrestling is called Kokh and practised in traditional garb; it was one of the influences included in the Soviet combat sport of Sambo (martial art), Sambo, which is also very popular.
The Politics of Armenia, government of Armenia budgets about $2.8 million annually for sports and gives it to the National Committee of Physical Education and Sports, the body that determines which programmes should benefit from the funds.
Due to the lack of success lately on the international level, in recent years, Armenia has rebuilt 16 Soviet-era sports schools and furnished them with new equipment for a total cost of $1.9 million. The rebuilding of the regional schools was financed by the Armenian government. $9.3 million has been invested in the resort town of Tsaghkadzor to improve the winter sports infrastructure because of dismal performances at recent winter sports events. In 2005, a cycling centre was opened in
A wide array of sports are played in Armenia, the most popular among them being wrestling, weightlifting, judo, association football, chess, and boxing. Armenia's mountainous terrain provides great opportunities for the practice of sports like skiing and climbing. Being a landlocked country, water sports can only be practised on lakes, notably Lake Sevan. Competitively, Armenia has been successful in chess, weightlifting and wrestling at the international level. Armenia is also an active member of the international sports community, with full membership in the Union of European Football Associations (UEFA) and International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF). It also hosts the Pan-Armenian Games.
Prior to 1992, Armenians would participate in the Olympics representing the USSR. As part of the Soviet Union, Armenia was very successful, winning plenty of medals and helping the USSR win the medal standings at the Olympics on numerous occasions. The first medal won by an Armenian in modern Olympic history was by Hrant Shahinyan (sometimes spelled as Grant Shaginyan), who won two golds and two silvers in gymnastics at the 1952 Summer Olympics in Helsinki. To highlight the level of success of Armenians in the Olympics, Shahinyan was quoted as saying:
"Armenian sportsmen had to outdo their opponents by several notches for the shot at being accepted into any Soviet team. But those difficulties notwithstanding, 90 percent of Armenian athletes on Soviet Olympic teams came back with medals."
Armenia first participated at the 1992 Summer Olympics in Barcelona under a unified CIS team, where it was very successful, winning three golds and one silver in weightlifting, wrestling and sharp shooting, despite only having five athletes. Since the 1994 Winter Olympics in Lillehammer, Armenia has participated as an independent nation.
Armenia participates in the Summer Olympic Games in boxing, wrestling, weightlifting, judo, gymnastics, track and field, diving, swimming and sharp shooting. It also participates in the Winter Olympic Games in alpine skiing, cross-country skiing and figure skating.
Football in Armenia, Football is also popular in Armenia. The most successful team was the FC Ararat Yerevan team of the 1970s who won the Soviet Cup in 1973 and 1975 and the Soviet Top League 1973, Soviet Top League in 1973. The latter achievement saw FC Ararat gain entry to the 1974вАУ75 European Cup, European Cup where вАУ despite a home victory in the second leg вАУ they lost on aggregate at the quarter-final stage to eventual winner FC Bayern Munich. Armenia competed internationally as part of the USSR national football team until the Armenian national football team was formed in 1992 after the split of the Soviet Union. Armenia have never qualified for a major tournament although recent improvements saw the team to achieve 44th position in the FIFA World Rankings in September 2011. The national team is controlled by the Football Federation of Armenia. The Armenian Premier League is the highest level football competition in Armenia, and has been dominated by FC Pyunik in recent seasons. The league currently consists of eight teams and relegates to the Armenian First League.
Armenia and the Armenian diaspora have produced many successful footballers, including Henrikh Mkhitaryan, Youri Djorkaeff, Alain Boghossian, Andranik Eskandarian, Andranik Teymourian, Edgar Manucharyan, Khoren Oganesian and Nikita Simonyan. Djokaeff and Boghossian won the 1998 FIFA World Cup with France national football team, France, Teymourian competed in the 2006 FIFA World Cup, 2006 World Cup for Iran national football team, Iran and Manucharyan played in the Dutch Eredivisie for AFC Ajax, Ajax. Mkhitaryan has been one of the most successful Armenian footballers in recent years, playing for international clubs such as Borussia Dortmund, Manchester United F.C., Manchester United, Arsenal F.C., Arsenal, A.S. Roma and currently for Inter Milan.
Wrestling has been a successful sport in the Olympics for Armenia. At the Armenia at the 1996 Summer Olympics, 1996 Summer Olympics in Atlanta, Armen Nazaryan won the gold in the Men's Greco-Roman wrestling, Greco-Roman Flyweight (52 kg) category and Armen Mkrtchyan won the silver in Men's Freestyle wrestling, Freestyle Paperweight (48 kg) category, securing Armenia's first two medals in its Olympic history.
Traditional Armenian wrestling is called Kokh and practised in traditional garb; it was one of the influences included in the Soviet combat sport of Sambo (martial art), Sambo, which is also very popular.
The Politics of Armenia, government of Armenia budgets about $2.8 million annually for sports and gives it to the National Committee of Physical Education and Sports, the body that determines which programmes should benefit from the funds.
Due to the lack of success lately on the international level, in recent years, Armenia has rebuilt 16 Soviet-era sports schools and furnished them with new equipment for a total cost of $1.9 million. The rebuilding of the regional schools was financed by the Armenian government. $9.3 million has been invested in the resort town of Tsaghkadzor to improve the winter sports infrastructure because of dismal performances at recent winter sports events. In 2005, a cycling centre was opened in
Key Development Forecasts for Armenia
from International Futures {{Authority control Armenia, Armenian-speaking countries and territories Caucasus Christian states Countries in Asia Countries in Europe Member states of the United Nations Landlocked countries Member states of the Commonwealth of Independent States Member states of the Council of Europe Member states of the Eurasian Economic Union Member states of the Collective Security Treaty Organization Republics South Caucasus States and territories established in 1918 States and territories established in 1991 States and territories disestablished in 1920 West Asian countries States with limited recognition 1991 establishments in Europe
landlocked country
A landlocked country is a country that has no territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie solely on endorheic basins. Currently, there are 44 landlocked countries, two of them doubly landlocked (Liechtenstein and Uzbekistan), and t ...
in the Armenian Highlands
The Armenian highlands (; also known as the Armenian upland, Armenian plateau, or Armenian tableland)Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: ...
of West Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian ...
. It is a part of the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
region and is bordered by Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of T√Љrkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
to the west, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
to the north and Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
to the east, and Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
and the Azerbaijani exclave
An enclave is a territory that is entirely surrounded by the territory of only one other state or entity. An enclave can be an independent territory or part of a larger one. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is s ...
of Nakhchivan to the south. Yerevan
Yerevan ( , , ; ; sometimes spelled Erevan) is the capital and largest city of Armenia, as well as one of the world's List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerev ...
is the capital
Capital and its variations may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** Capital region, a metropolitan region containing the capital
** List of national capitals
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter
Econom ...
, largest city and financial center
A financial centre (financial center in American English) or financial hub is a location with a significant concentration of commerce in financial services.
The commercial activity that takes place in a financial centre may include banking, ...
.
The Armenian Highlands has been home to the Hayasa-Azzi
Hayasa-Azzi or Azzi-Hayasa (, ) was a Late Bronze Age confederation in the Armenian Highlands and/or Pontic region of Asia Minor. The Hayasa-Azzi confederation was in conflict with the Hittite Empire in the 14th century BC, leading up to the ...
, Shupria
Shubria or Shupria was a kingdom in the southern Armenian highlands, known from Assyrian sources in the first half of the 1st millennium BC. It was located north of the upper Tigris River and to the southwest of Lake Van, extending eastwards to t ...
and Nairi
Nairi (, also ''Na-'i-ru''; ) was the Akkadian name for a region inhabited by a particular group (possibly a confederation or league) of tribal principalities in the Armenian Highlands, approximately spanning the area between modern Diyarbakır ...
. By at least 600 BC, an archaic form of Proto-Armenian
Proto-Armenian is the earlier, unattested stage of the Armenian language which has been reconstructed by linguists. As Armenian is the only known language of its branch of the Indo-European languages, the comparative method cannot be used to re ...
, an Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
language, had diffused into the Armenian Highlands.Robert Drews (2017). ''Militarism and the Indo-Europeanizing of Europe''. Routledge. . p. 228: "The vernacular of the Great Kingdom of Biainili was quite certainly Armenian. The Armenian language was obviously the region's vernacular in the fifth century BC, when Persian commanders and Greek writers paired it with Phrygian. That it as brought into the region between the early sixth and the early fifth century BC, and that it immediately obliterated whatever else had been spoken there, can hardly be supposed; ..Because Proto-Armenian speakers seem to have lived not far from Hurrian speakers our conclusion must be that the Armenian language of Mesrop Mashtots was descended from an Indo-European language that had been spoken in southern Caucasia in the Bronze Age." The first Armenian state of Urartu
Urartu was an Iron Age kingdom centered around the Armenian highlands between Lake Van, Lake Urmia, and Lake Sevan. The territory of the ancient kingdom of Urartu extended over the modern frontiers of Turkey, Iran, Iraq, and Armenia.Kleiss, Wo ...
was established in 860 BC, and by the 6th century BC it was replaced by the Satrapy of Armenia
The Satrapy of Armenia ( Old Persian: рРО†рРОЉрРОЈрРО°рРОі or рРО†рРОЉрРОЈрРО°рРОірРОє ), a region controlled by the Orontid dynasty (570вАУ201 BC), was one of the satrapies of the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC that later became an ...
. The Kingdom of Armenia reached its height under Tigranes the Great
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great (''Tigran Mets'' in Armenian language, Armenian; 140вАУ55 BC), was a king of Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Armenia. A member of the Artaxiad dynasty, he ruled from 95 BC to 55 BC. Under hi ...
in the 1st century BC and in the year 301 became the first state in the world to adopt Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
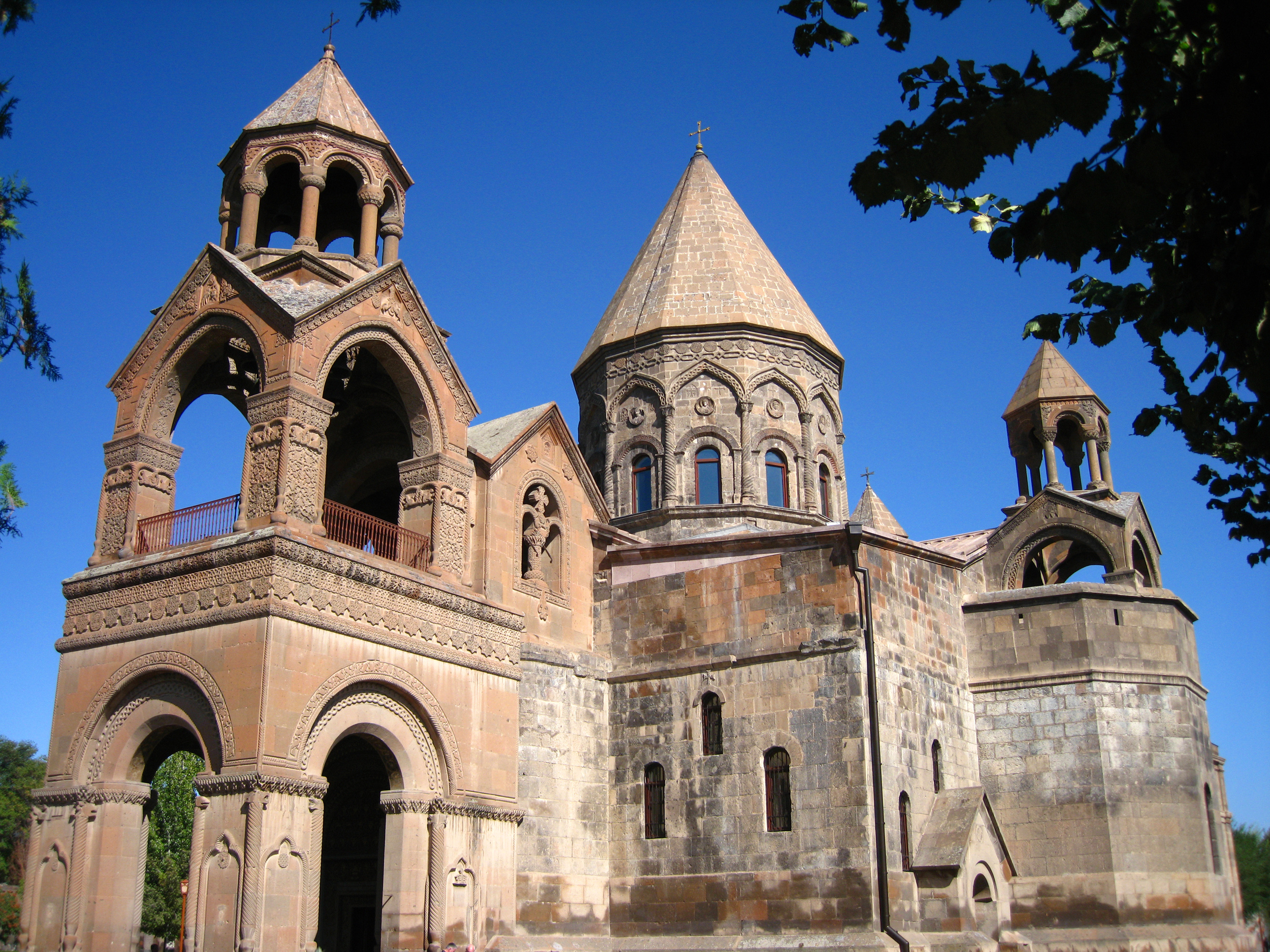
as its official religion. Armenia still recognises the Armenian Apostolic Church
The Armenian Apostolic Church () is the Autocephaly, autocephalous national church of Armenia. Part of Oriental Orthodoxy, it is one of the most ancient Christianity, Christian churches. The Armenian Apostolic Church, like the Armenian Catholic ...
, the world's oldest national church
A national church is a Christian church associated with a specific ethnic group or nation state. The idea was notably discussed during the 19th century, during the emergence of modern nationalism.
Samuel Taylor Coleridge, in a draft discussing ...
, as the country's primary religious establishment. The ancient Armenian kingdom was split between the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
and Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranian peoples, Iranians"), was an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, th ...
s around the early 5th century. Under the Bagratuni dynasty
The Bagratuni or Bagratid dynasty (, ) was an Armenian royal dynasty which ruled the medieval Kingdom of Armenia from until 1045. Originating as vassals of the Kingdom of Armenia of antiquity, they rose to become the most prominent Armenian n ...
, the Bagratid Kingdom of Armenia
Bagratid Armenia was an independent Armenian state established by Ashot I of the Bagratuni dynasty in the early 880s following nearly two centuries of foreign domination of Greater Armenia under Arab Umayyad and Abbasid rule. With each of t ...
was restored in the 9th century before falling in 1045. Cilician Armenia
The Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia, also known as Cilician Armenia, Lesser Armenia, Little Armenia or New Armenia, and formerly known as the Armenian Principality of Cilicia, was an Armenians, Armenian state formed during the High Middle Ages b ...
, an Armenian principality and later a kingdom, was located on the coast of the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
between the 11th and 14th centuries.
Between the 16th and 19th centuries, the traditional Armenian homeland composed of Eastern Armenia Eastern Armenia (Armenian: ‘±÷А÷З’•’ђ’µ’°’ґ ’А’°’µ’°’љ’њ’°’ґ, ''Arevelyan Hayastan'') refers to the eastern portion of the Armenian Highlands, historically inhabited by the Armenian people. Throughout history, Eastern Armenia has been contested and ...
and Western Armenia
Western Armenia (Western Armenian: ‘±÷А’•÷В’і’њ’•’°’ґ ’А’°’µ’°’љ’њ’°’ґ, ''Arevmdian Hayasdan'') is a term to refer to the western parts of the Armenian highlands located within Turkey (formerly the Ottoman Empire) that comprise the historic ...
came under the rule of the Ottoman and Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
empires, repeatedly ruled by either of the two over the centuries. By the 19th century, Eastern Armenia had been conquered by the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
, while most of the western parts of the traditional Armenian homeland remained under Ottoman rule. During World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 вАУ 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, up to 1.5 million Armenians living in their ancestral lands in the Ottoman Empire were systematically exterminated in the Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenians, Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was implemented primarily t ...
. In 1918, following the Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution, social change in Russian Empire, Russia, starting in 1917. This period saw Russia Dissolution of the Russian Empire, abolish its mona ...
, all non-Russian countries declared their independence after the Russian Empire ceased to exist, leading to the establishment of the First Republic of Armenia
The First Republic of Armenia, officially known at the time of its existence as the Republic of Armenia, was an independent History of Armenia, Armenian state that existed from May (28th ''de jure'', 30th ''de facto'') 1918 to 2 December 1920 in ...
. By 1920, the state was incorporated into the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
as the Armenian SSR
The Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic (ArSSR), also known as Soviet Armenia, or simply Armenia, was one of the constituent republics of the Soviet Union, located in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Soviet Armenia bordered the Soviet republics ...
. Today's Republic of Armenia became independent in 1991 during the dissolution of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was formally dissolved as a sovereign state and subject of international law on 26 December 1991 by Declaration No. 142-N of the Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union. Declaration No. 142-–Э of ...
.
Modern Armenia is a unitary
Unitary may refer to:
Mathematics
* Unitary divisor
* Unitary element
* Unitary group
* Unitary matrix
* Unitary morphism
* Unitary operator
* Unitary transformation
* Unitary representation
* Unitarity (physics)
* ''E''-unitary inverse semigr ...
, multi-party
In political science, a multi-party system is a political system where more than two meaningfully-distinct political parties regularly run for office and win elections. Multi-party systems tend to be more common in countries using proportional r ...
, democratic nation-state
A nation state, or nation-state, is a political entity in which the state (a centralized political organization ruling over a population within a territory) and the nation (a community based on a common identity) are (broadly or ideally) con ...
. Armenia is a developing country
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreeme ...
and ranks 69th on the Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistical composite index of life expectancy, Education Index, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income i ...
as of 2023. Its economy is primarily based on industrial output and mineral extraction. While Armenia is geographically located in the South Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and West Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Armenia, ...
, Armenia views itself as part of Europe and is generally considered geopolitically European. Since Armenia aligns itself in many respects geopolitically with Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, the country is a member of numerous European organisations including the Organization for Security and Co-Operation in Europe
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is a regional security-oriented intergovernmental organization comprising member states in Europe, North America, and Asia. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, the p ...
, the Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; , CdE) is an international organisation with the goal of upholding human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it is Europe's oldest intergovernmental organisation, represe ...
, the Eastern Partnership
The Eastern Partnership (EaP) is a joint initiative of the European Union, together with its member states, and six Eastern Europe, Eastern European countries. The EaP framework governs the EU's relationship with the post-Soviet states of Armen ...
, Eurocontrol
The European Organisation for the Safety of Air Navigation, commonly known as Eurocontrol (stylised ''EUROCONTROL''), is an international organisation working to achieve safe and seamless air traffic management across Europe. Founded in 1963, Eur ...
, the Assembly of European Regions
The Assembly of European Regions (AER) is the largest independent network of regions in wider Europe. Bringing together regions from 25 countries and 15 interregional organizations, AER is a forum for interregional cooperation.
Historical b ...
, and the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development
The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, shortened to EBRD ( French: ''Banque européenne pour la reconstruction et le développement'' or ''BERD''), is an international financial institution founded in 1991 in Paris. As a multilat ...
. Armenia is also a member of certain regional groups throughout Eurasia
Eurasia ( , ) is a continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. According to some geographers, Physical geography, physiographically, Eurasia is a single supercontinent. The concept of Europe and Asia as distinct continents d ...
, including the Asian Development Bank
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank to promote social and economic development in Asia. The bank is headquartered in Metro Manila, Philippines and maintains 31 field offices around the world.
The bank was establishe ...
, the Collective Security Treaty Organization
The Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO, ) is an Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental military alliance in Eurasia consisting of six post-Soviet states: Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Tajikistan. Th ...
, the Eurasian Economic Union
The Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU or EEU)EAEU is the acronym used on thorganisation's website However, many media outlets use the acronym EEU. is an economic union of five post-Soviet states located in Eurasia. The EAEU has an integrated single ...
, and the Eurasian Development Bank
The Eurasian Development Bank (EDB) is an international development finance institution investing in the development of the economies, trade and other economic ties, and integration in Eurasian countries. The EDB was founded in 2006 and is head ...
. Armenia supported the once ''de facto'' independent Republic of Artsakh
Artsakh ( ), officially the Republic of Artsakh or the Republic of Nagorno-Karabakh ( ), was a breakaway state in the South Caucasus whose territory was internationally recognised as part of Azerbaijan. Between 1991 and 2023, Artsakh cont ...
(Nagorno-Karabakh), which was proclaimed in 1991 on territory internationally recognized as part of Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
, until the republic's dissolution in September 2023.
Etymology
The original nativeArmenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian diaspora, Armenian communities around the ...
name for the country was ( ); however, it is currently rarely used. The contemporary name ('' Hayastan'') became popular in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
by addition of the Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
suffix ''-stan
-stan ( Persian: Ў≥Ў™ЎІўЖ )(Sanskrit: ''sthƒБn'' or ''sthƒБnam)'' is a Persian suffix that has the meaning of "a place abounding in" or "place where anything abounds" as a suffix. It is widely used by Iranian languages (mainly Persian) and ...
'' (place). However the origins of the name Hayastan trace back to much earlier dates and were first attested in in the works of Agathangelos
Agathangelos (in , in Greek "bearer of good news", 5th century AD) is the pseudonym of the author of a life of the first apostle of Armenia, Gregory the Illuminator, who died about 332. The history attributed to Agathangelos is the main sou ...
, Faustus of Byzantium
The name Faustus primarily refers to Faust, the protagonist of the German legend.
Faustus may also refer to:
* Faustus (praenomen), a Latin personal name
* Faustus of Alexandria (died 250), priest and martyr
* Faustus of Byzantium, 5th-centur ...
, Ghazar Parpetsi
Ghazar Parpetsi (; ) was a fifth-to-sixth-century Armenian historian. He had close ties with the powerful Mamikonian noble family and is most prominent for writing a history of Armenia in the last years of the fifth century or at the beginning of ...
, Koryun, and Sebeos
Sebeos () was the reputed author of a 7th-century Armenian history. As this authorship attribution is widely accepted to be false (pseudepigraphical), the author is frequently referred to as Pseudo-Sebeos. Though his name is not known, he was likel ...
.
The name has traditionally been derived from Hayk
Hayk (, ), also known as Hayk Nahapet (, , ), is the legendary patriarch and founder of the Armenian nation. His story is told in the ''History of Armenia'' attributed to the Armenian historian Movses Khorenatsi and in the ''Primary History'' ...
(), the legendary patriarch of the Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiq ...
and a great-great-grandson of Noah
Noah (; , also Noach) appears as the last of the Antediluvian Patriarchs (Bible), patriarchs in the traditions of Abrahamic religions. His story appears in the Hebrew Bible (Book of Genesis, chapters 5вАУ9), the Quran and Bah√° Љ√≠ literature, ...
, who, according to the 5th-century AD author Moses of Chorene (Movsis Khorenatsi), defeated the Babylonian king
The king of Babylon (Akkadian language, Akkadian: , later also ) was the ruler of the ancient Mesopotamian city of Babylon and its kingdom, Babylonia, which existed as an independent realm from the 19th century BC to its fall in the 6th century BC. ...
Bel in 2492 BC and established his nation in the Ararat region. The further origin of the name is uncertain. It is also further postulatedElisabeth Bauer. ''Armenia: Past and Present'' (1981), p. 49 that the name ''Hay'' comes from one of the two confederated, Hittite vassal statesthe бЄ™aya≈°a-Azzi (1600вАУ1200 BC).
The exonym
An endonym (also known as autonym ) is a common, name for a group of people, individual person, geographical place, language, or dialect, meaning that it is used inside a particular group or linguistic community to identify or designate them ...
''Armenia'' is attested in the Old Persian
Old Persian is one of two directly attested Old Iranian languages (the other being Avestan) and is the ancestor of Middle Persian (the language of the Sasanian Empire). Like other Old Iranian languages, it was known to its native speakers as (I ...
Behistun Inscription
The Behistun Inscription (also Bisotun, Bisitun or Bisutun; , Old Persian: Bagastana, meaning "the place of god") is a multilingual Achaemenid royal inscriptions, Achaemenid royal inscription and large rock relief on a cliff at Mount Behistun i ...
(515 BC) as '' Armina'' (). The Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
terms (''Armenía'') and (''Arménioi'', "Armenians") are first mentioned by Hecataeus of Miletus
Hecataeus of Miletus (; ; c. 550 вАУ c. 476 BC), son of Hegesander, was an early Greek historian and geographer.
Biography
Hailing from a very wealthy family, he lived in Miletus, then under Persian rule in the satrapy of Lydia ...
( вАУ ). Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; ; 355/354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian. At the age of 30, he was elected as one of the leaders of the retreating Ancient Greek mercenaries, Greek mercenaries, the Ten Thousand, who had been ...
, a Greek general serving in some of the Persian expeditions, describes many aspects of Armenian village life and hospitality in around 401 BC.
Some scholars have linked the name ''Armenia'' with the Early Bronze Age state of '' Armani (Armanum, Armi)'' or the Late Bronze Age state of '' Arme (Shupria)''. These connections are inconclusive as it is not known what languages were spoken in these kingdoms. Additionally, while it is agreed that Arme was located to the immediate west of Lake Van
Lake Van (; ; ) is the largest lake in Turkey. It lies in the Eastern Anatolia Region of Turkey in the provinces of Van Province, Van and Bitlis Province, Bitlis, in the Armenian highlands. It is a Salt lake, saline Soda lake, soda lake, receiv ...
(probably in the vicinity of Sason
Sason is a town in the Batman Province of Turkey. It is the seat of the Sason District.İl ...
, and therefore in the greater Armenia region), the location of the older site of Armani is a matter of debate. Some modern researchers have placed it near modern Samsat
Samsat (, Ottoman Turkish ЎµўЕЎµЎІЎѓ ''Semisat''), formerly Samosata () is a small town in the Adƒ±yaman Province of Turkey, situated on the upper Euphrates river. It is the seat of Samsat District.Mushki
The Mushki (sometimes transliterated as Mu≈°ki) were an Iron Age people of Anatolia who appear in sources from Assyria but not from the Hittites. Several authors have connected them with the Moschoi (ќЬѕМѕГѕЗќњќє) of Greek sources and the Geor ...
and the Kaskians
The Kaska (also Kaška, later Tabal (state), Tabalian Kasku and Gasga) were a loosely affiliated Bronze Age non-Indo-European tribal people, who spoke the unclassified Kaskian language and lived in mountainous East Pontus (region), Pontic Anatolia ...
. The Urumu apparently settled in the vicinity of Sason, lending their name to the regions of Arme and the nearby lands of Urme and Inner Urumu.
According to the histories of both Moses of Chorene and Michael Chamchian, ''Armenia'' derives from the name of Aram, a lineal descendant of Hayk.''History of Armenia'' by Father Michael Chamich from B.C. 2247 to the Year of Christ 1780, or 1229 of the Armenian era, Bishop's College Press, Calcutta, 1827, p. 19: "ram
Ram, ram, or RAM most commonly refers to:
* A male sheep
* Random-access memory, computer memory
* Ram Trucks, US, since 2009
** List of vehicles named Dodge Ram, trucks and vans
** Ram Pickup, produced by Ram Trucks
Ram, ram, or RAM may also ref ...
was the first to raise the Armenian name to any degree of renown; so that contemporary nations... called them the Aramians, or followers of Aram, a name which has been corrupted into Armenians; and the country they inhabited, by universal consent, took the name of Armenia." In the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
. '' Old Testament The Old Testament (OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew and occasionally Aramaic writings by the Isr ...
, the . '' Old Testament The Old Testament (OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew and occasionally Aramaic writings by the Isr ...
Table of Nations
The Generations of Noah, also called the Table of Nations or ''Origines Gentium'', is a genealogy of the sons of Noah, according to the Hebrew Bible (Book of Genesis, Genesis ), and their dispersion into many lands after Genesis flood narrative ...
lists Aram as the son of Shem
Shem (; ''≈†ƒУm''; ) is one of the sons of Noah in the Bible ( Genesis 5вАУ11 and 1 Chronicles 1:4).
The children of Shem are Elam, Ashur, Arphaxad, Lud and Aram, in addition to unnamed daughters. Abraham, the patriarch of Jews, Christ ...
, to whom the Book of Jubilees
The Book of Jubilees is an ancient Jewish apocryphal text of 50 chapters (1,341 verses), considered canonical by the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church, as well as by Haymanot Judaism, a denomination observed by members of Ethiopian Jewish ...
attests, Jubilees 8:21 also apportions the Mountains of Ararat to Shem
Shem (; ''≈†ƒУm''; ) is one of the sons of Noah in the Bible ( Genesis 5вАУ11 and 1 Chronicles 1:4).
The children of Shem are Elam, Ashur, Arphaxad, Lud and Aram, in addition to unnamed daughters. Abraham, the patriarch of Jews, Christ ...
, which Jubilees 9:5 expounds to be apportioned to Aram.
The historian Flavius Josephus also states in his Antiquities of the Jews
''Antiquities of the Jews'' (; , ''IoudaikƒУ archaiologia'') is a 20-volume historiographical work, written in Greek, by the Roman-Jewish historian Josephus in the 13th year of the reign of the Roman emperor Domitian, which was 94 CE. It cont ...
,
History
Prehistoric
The first human traces are supported by the presence of Acheulean tools, generally close to the obsidian outcrops more than 1 million years ago. The most recent and important excavation is at the Nor Geghi 1 Stone Age site in theHrazdan river
The Hrazdan (, ) is a major river and the second largest in Armenia. It originates at the northwest extremity of Lake Sevan and flows south through the Kotayk Province and Armenia's capital, Yerevan; the lake in turn is fed by several streams. In ...
valley. Thousands of 325,000 year-old artifacts may indicate that this stage of human technological innovation occurred intermittently throughout the Old World, rather than spreading from a single point of origin (usually hypothesized to be Africa), as was previously thought.
Many early Bronze Age settlements were built in Armenia (Valley of Ararat, Shengavit, Harich, Karaz, Amiranisgora, Margahovit, Garni, etc.). One of the important sites of the Early Bronze Age is Shengavit Settlement
The Shengavit Settlement (, ''Shengavit' h…Щnavayr'') is an archaeological site in present-day Yerevan, Armenia located on a hill south-east of Yerevan Lake. It was inhabited during a series of settlement phases from around 3000 BC cal to 2500 ...
. It was located on the site of today's capital of Armenia, Yerevan
Yerevan ( , , ; ; sometimes spelled Erevan) is the capital and largest city of Armenia, as well as one of the world's List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerev ...
.
Such things were discovered in Armenia, for example, the oldest shoe
A shoe is an item of footwear intended to protect and comfort the human foot. Though the human foot can adapt to varied terrains and climate conditions, it is vulnerable, and shoes provide protection. Form was originally tied to function, but ...
, oldest wagon
A wagon (or waggon) is a heavy four-wheeled vehicle pulled by Working animal#Draft animals, draft animals or on occasion by humans, used for transporting goods, commodities, agricultural materials, supplies and sometimes people.
Wagons are i ...
, oldest skirt
A skirt is the lower part of a dress or a separate outer garment that covers a person from the waist downwards.
At its simplest, a skirt can be a draped garment made out of a single piece of fabric (such as pareos). However, most skirts are ...
, and the oldest wine-making facility.
Antiquity
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
and earlier, dating to about 4000 BC. Archaeological surveys in 2010 and 2011 at the Areni-1 cave complex
The Areni-1 cave complex () is a multicomponent site, and late Chalcolithic/Early Bronze Age ritual site and settlement, located near the Areni village in southern Armenia along the Arpa River.
Findings
In 2008, Armenian PhD student and ar ...
have resulted in the discovery of the world's earliest known leather shoe, skirt, and wine-producing facility.
Several Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
cultures and states flourished in the area of Greater Armenia, including the Trialeti-Vanadzor culture, Hayasa-Azzi
Hayasa-Azzi or Azzi-Hayasa (, ) was a Late Bronze Age confederation in the Armenian Highlands and/or Pontic region of Asia Minor. The Hayasa-Azzi confederation was in conflict with the Hittite Empire in the 14th century BC, leading up to the ...
, and Mitanni
Mitanni (вАУ1260 BC), earlier called бЄ™abigalbat in old Babylonian texts, ; Hanigalbat or Hani-Rabbat in Assyrian records, or in Ancient Egypt, Egyptian texts, was a Hurrian language, Hurrian-speaking state in northern Syria (region), Syria an ...
(located in southwestern historical Armenia), all of which are believed to have had Indo-European populations. The Nairi
Nairi (, also ''Na-'i-ru''; ) was the Akkadian name for a region inhabited by a particular group (possibly a confederation or league) of tribal principalities in the Armenian Highlands, approximately spanning the area between modern Diyarbakır ...
confederation and its successor, Urartu
Urartu was an Iron Age kingdom centered around the Armenian highlands between Lake Van, Lake Urmia, and Lake Sevan. The territory of the ancient kingdom of Urartu extended over the modern frontiers of Turkey, Iran, Iraq, and Armenia.Kleiss, Wo ...
, successively established their sovereignty over the Armenian Highlands
The Armenian highlands (; also known as the Armenian upland, Armenian plateau, or Armenian tableland)Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: ...
. Each of the aforementioned nations and confederacies participated in the ethnogenesis of the Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiq ...
. A large cuneiform lapidary inscription found in Yerevan
Yerevan ( , , ; ; sometimes spelled Erevan) is the capital and largest city of Armenia, as well as one of the world's List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerev ...
established that the modern capital of Armenia was founded in the summer of 782 BC by King Argishti I
Argishti I, was the sixth known king of Urartu, reigning from 786 BC to 764 BC. He founded the citadel of Erebuni in 782 BC, which is the present capital of Armenia, Yerevan. Alternate transliterations of the name include ''Argishtis'', ''Argisti' ...
. Yerevan is one of the world's oldest continuously inhabited cities
This is a list of present-day cities by the time period over which they have been continuously inhabited as a city. The age claims listed are generally disputed. Differences in opinion can result from different definitions of "city" as well as "c ...
.
After the fall of the state of Urartu
Urartu was an Iron Age kingdom centered around the Armenian highlands between Lake Van, Lake Urmia, and Lake Sevan. The territory of the ancient kingdom of Urartu extended over the modern frontiers of Turkey, Iran, Iraq, and Armenia.Kleiss, Wo ...
at the beginning of the 6th century BC, the Armenian Highlands
The Armenian highlands (; also known as the Armenian upland, Armenian plateau, or Armenian tableland)Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: ...
were for some time under the hegemony of the Medes
The Medes were an Iron Age Iranian peoples, Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media (region), Media between western Iran, western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, they occupied the m ...
, and after that they were part of the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, i ...
. Armenia was part of the Achaemenid state from the second half of the 6th century BC until the second half of the 4th century BC divided into two satrapies - XIII (western part, with the capital in Melitene) and XVIII (northeastern part).–Ш—Б—В–Њ—А–Є—П –Т–Њ—Б—В–Њ–Ї–∞: –≤ —И–µ—Б—В–Є —В–Њ–Љ–∞—Е. –Ґ. 1. –Т–Њ—Б—В–Њ–Ї –≤ –і—А–µ–≤–љ–Њ—Б—В–Є / –Ю—В–≤. —А–µ–і. –Т. –Р. –ѓ–Ї–Њ–±—Б–µ–љ. вАФ –Ь.: –Т–Њ—Б—В. –ї–Є—В., 1997. вАФ 688 —Б. вАФ . –†–∞–Ј–і–µ–ї –Ч–∞–Ї–∞–≤–Ї–∞–Ј—М–µ –Є —Б–Њ–њ—А–µ–і–µ–ї—М–љ—Л–µ —Б—В—А–∞–љ—Л –≤ –њ–µ—А–Є–Њ–і —Н–ї–ї–Є–љ–Є–Ј–Љ–∞
¬ї During the late 6th century BC, the first geographical entity that was called Armenia by neighbouring populations was established under the
Orontid Dynasty
The Orontid dynasty, also known as the Eruandids or Eruandunis, ruled the Satrapy of Armenia until 330 BC and the Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Kingdom of Armenia from 321 BC to 200 BC. The Orontids ruled first as client kings or satraps of t ...
within the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, i ...
, as part of the latter's territories.
The kingdom became fully sovereign from the sphere of influence of the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire ( ) was a Greek state in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great ...
in 190 BC under King Artaxias I
Artaxias I (from ) was the founder of the Artaxiad dynasty of Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Armenia, ruling from 189 BC to 160 BC. Artaxias was a member of a branch of the Orontid dynasty, the earlier ruling dynasty of Armenia. He expanded his ...
and begun the rule of the Artaxiad dynasty
The Artaxiad dynasty (also Artashesian) ruled the Kingdom of Armenia from 189 BC until their overthrow by the Romans in 12 AD. It was founded by Artaxias I, who claimed kinship with the previous ruling dynasty of Armenia, the Orontids. Their ...
. Armenia reached its height between 95 and 66 BC under Tigranes the Great
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great (''Tigran Mets'' in Armenian language, Armenian; 140вАУ55 BC), was a king of Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Armenia. A member of the Artaxiad dynasty, he ruled from 95 BC to 55 BC. Under hi ...
, becoming the most powerful kingdom of its time east of the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
.
In the next centuries, Armenia was in the Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the larg ...
's sphere of influence during the reign of Tiridates I, the founder of the Arsacid dynasty of Armenia
The Arsacid dynasty, called the Arshakuni () in Armenian, ruled the Kingdom of Armenia (with some interruptions) from 12 to 428 AD. The dynasty was a branch of the Arsacid dynasty of Parthia. Arsacid kings reigned intermittently throughout the ...
, which itself was a branch of the Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power centered in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe ...
. Throughout its history, the kingdom of Armenia enjoyed both periods of independence and periods of autonomy subject to contemporary empires. Its strategic location between two continents has subjected it to invasions by many peoples, including Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''mƒБt A≈°≈°ur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
(under Ashurbanipal
Ashurbanipal (, meaning " Ashur is the creator of the heir")вАФor Osnappar ()вАФwas the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 669 BC to his death in 631. He is generally remembered as the last great king of Assyria. Ashurbanipal inherited the th ...
, at around 669вАУ627 BC, the boundaries of Assyria reached as far as Armenia and the Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains
*
* Azerbaijani: ,
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* is a mountain range at the intersection of Asia and Europe. Stretching between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, they are surrounded by the Caucasus region ...
), Medes
The Medes were an Iron Age Iranian peoples, Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media (region), Media between western Iran, western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, they occupied the m ...
, Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, i ...
, Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
, Parthians
Parthia ( ''ParќЄava''; ''ParќЄaw''; ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Medes during the 7th century BC, was incorporated into the subsequent Achaemen ...
, Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
, Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranian peoples, Iranians"), was an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, th ...
, Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
, Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of yea ...
, Seljuk Empire
The Seljuk Empire, or the Great Seljuk Empire, was a High Middle Ages, high medieval, culturally Turco-Persian tradition, Turco-Persian, Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim empire, established and ruled by the Qiniq (tribe), Q√ѓn√ѓq branch of Oghuz Turks. ...
, Mongols
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China ( Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family o ...
, Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
, the successive Safavid
The Guarded Domains of Iran, commonly called Safavid Iran, Safavid Persia or the Safavid Empire, was one of the largest and longest-lasting Iranian empires. It was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often considered the begi ...
, Afsharid, and Qajar
The Guarded Domains of Iran, alternatively the Sublime State of Iran and commonly called Qajar Iran, Qajar Persia or the Qajar Empire, was the Iranian state under the rule of the Qajar dynasty, which was of Turkic origin,Cyrus Ghani. ''Iran an ...
dynasties of Iran, and the Russians.
Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism ( ), also called MazdayasnƒБ () or Beh-dƒЂn (), is an Iranian religions, Iranian religion centred on the Avesta and the teachings of Zoroaster, Zarathushtra Spitama, who is more commonly referred to by the Greek translation, ...
. It particularly focused on the worship of Mithra
Mithra ( ; ) is an ancient Iranian deity ('' yazata'') of covenants, light, oaths, justice, the Sun, contracts, and friendship. In addition to being the divinity of contracts, Mithra is also a judicial figure, an all-seeing protector of Truth ( ...
and also included a pantheon of gods such as Aramazd
Aramazd was the chief and creator god in the Armenian version of Zoroastrianism.; ; ; ; ; The deity and his name were derived from the deity Ahura Mazda after the Median conquest of Armenia in the 6th century BC. Aramazd was regarded as a gene ...
, Vahagn
Vahagn or Vahakn (), also known as Vahagn Vishapakagh (), is a warrior god in Armenian mythology. Scholars consider him to be either the thunder, or sun and fire god of the pre-Christian Armenian pantheon, as well as the god of war, bravery and ...
, Anahit
Anahit () was the goddess of fertility and healing, wisdom and water in Armenian mythology. In early periods, she was the goddess of war. By the 5th century BCE, she was the main deity in Armenia along with Aramazd. The Armenian goddess Anahit ...
, and Astghik. The country used the solar Armenian calendar
The Armenian calendar is the calendar traditionally used in Armenia, primarily during the medieval ages. Since 1918, the civil calendar in Armenia is the Gregorian calendar.
The Armenian calendar was based on an invariant year length of 365 days. ...
, which consisted of 12 months.
Christianity spread into the country in the early 4th century AD. Tiridates III of Armenia
Tiridates III ( вАУ ), also known as Tiridates the Great or Tiridates IV, was the Armenian Arsacid king from to . In the early 4th century (the traditional date is 301), Tiridates proclaimed Christianity as the state religion of Armenia, maki ...
(238вАУ314) made Christianity the state religion in 301, partly, in defiance of the Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranian peoples, Iranians"), was an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, th ...
, it seems,Mary Boyce''Zoroastrians: Their Religious Beliefs and Practices''
Psychology Press, 2001 p. 84 becoming the first officially Christian state, ten years before the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
granted Christianity an official toleration under Galerius
Galerius Valerius Maximianus (; Greek: ќУќ±ќїќ≠ѕБќєќњѕВ; 258 вАУ May 311) was Roman emperor from 305 to 311. He participated in the system of government later known as the Tetrarchy, first acting as '' caesar'' under Emperor Diocletian. In th ...
, and 36 years before Constantine the Great
Constantine I (27 February 27222 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was a Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337 and the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity. He played a Constantine the Great and Christianity, pivotal ro ...
was baptised. Prior to this, during the latter part of the Parthian period, Armenia was a predominantly Zoroastrian country.
After the fall of the Kingdom of Armenia in 428, most of Armenia was incorporated as a ''marzpanate'' within the Sasanian Empire. Following the Battle of Avarayr
The Battle of Avarayr () was fought on 26 May 451 on the Avarayr Plain in Vaspurakan between a Christian Armenian army under Vardan Mamikonian and Sassanid Persia. It is considered one of the first battles in defense of the Christian faith. ...
in 451, Christian Armenians maintained their religion and Armenia gained autonomy.
Middle Ages
 The Sassanid Empire was conquered by the
The Sassanid Empire was conquered by the Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate () is a title given for the reigns of first caliphs (lit.вАЙ"successors") вАФ Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali collectively вАФ believed to Political aspects of Islam, represent the perfect Islam and governance who led the ...
in the mid 7th century, reuniting Armenian lands previously taken by the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
, and Armenia subsequently emerged as Arminiya, an autonomous principality under the Umayyad Caliphate. The principality was ruled by the Prince of Armenia, and recognised by the Caliphate, Caliph and the List of Byzantine emperors, Byzantine Emperor. It was part of the administrative division/emirate ''Arminiya'' created by the Arabs, which also included parts of Georgia and Caucasian Albania, and had its centre in the Armenian city, Dvin (ancient city), Dvin. Arminiya lasted until 884, when it regained its independence from the weakened Abbasid Caliphate under Ashot I of Armenia.
The reemergent Armenian kingdom was ruled by the Bagratuni dynasty
The Bagratuni or Bagratid dynasty (, ) was an Armenian royal dynasty which ruled the medieval Kingdom of Armenia from until 1045. Originating as vassals of the Kingdom of Armenia of antiquity, they rose to become the most prominent Armenian n ...
and lasted until 1045. In time, several areas of the Bagratid Armenia separated as independent kingdoms and principalities such as the Kingdom of Vaspurakan ruled by the House of Artsruni in the south, Kingdom of Syunik Province, Syunik in the east, or Kingdom of Artsakh on the territory of modern Nagorno-Karabakh, while still recognising the supremacy of the Bagratid kings.
In 1045, the Byzantine Empire conquered Bagratid Armenia. Soon, the other Armenian states fell under Byzantine control as well. The Byzantine rule was short-lived, as in 1071 the Seljuk Empire
The Seljuk Empire, or the Great Seljuk Empire, was a High Middle Ages, high medieval, culturally Turco-Persian tradition, Turco-Persian, Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim empire, established and ruled by the Qiniq (tribe), Q√ѓn√ѓq branch of Oghuz Turks. ...
defeated the Byzantines and conquered Armenia at the Battle of Manzikert, establishing the Seljuk Empire. To escape death or servitude at the hands of those who had assassinated his relative, Gagik II of Armenia, King of Ani, an Armenian named Ruben I, Prince of Armenia, went with some of his countrymen into the gorges of the Taurus Mountains and then into Tarsus, Mersin, Tarsus of Cilicia. The Byzantine governor of the palace gave them shelter where the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia was eventually established on 6 January 1198 under Leo I, King of Armenia, a descendant of Prince Ruben.
Cilicia was a strong ally of the Crusades, European Crusaders, and saw itself as a bastion of Christendom in the East. Cilicia's significance in Armenian history and statehood is also attested by the transfer of the seat of the Catholicos of the Armenian Apostolic Church, the spiritual leader of the Armenian people, to the region.
The Seljuk Empire soon started to collapse. In the early 12th century, Armenian princes of the Zakarid family drove out the Seljuk Turks and established a semi-independent principality in northern and eastern Armenia known as Zakarid Armenia, which lasted under the patronage of the History of Georgia (country), Georgian Kingdom. The Orbelian Dynasty shared control with the Zakarids in various parts of the country, especially in Syunik and Vayots Dzor Province, Vayots Dzor, while the House of Hasan-Jalalyan controlled provinces of Artsakh (historic province), Artsakh and Utik as the Kingdom of Artsakh.
Early Modern era
 During the 1230s, the Mongol Empire conquered Zakarid Armenia and then the remainder of Armenia. The Mongolian invasions were soon followed by those of other Central Asian tribes, such as the Kara Koyunlu, Timurid dynasty and AƒЯ Qoyunlu, which continued from the 13th century until the 15th century. After incessant invasions, each bringing destruction to the country, with time Armenia became weakened.
In the 16th century, the
During the 1230s, the Mongol Empire conquered Zakarid Armenia and then the remainder of Armenia. The Mongolian invasions were soon followed by those of other Central Asian tribes, such as the Kara Koyunlu, Timurid dynasty and AƒЯ Qoyunlu, which continued from the 13th century until the 15th century. After incessant invasions, each bringing destruction to the country, with time Armenia became weakened.
In the 16th century, the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
and the Safavid dynasty of Iran divided Armenia. From the early 16th century, both Western Armenia
Western Armenia (Western Armenian: ‘±÷А’•÷В’і’њ’•’°’ґ ’А’°’µ’°’љ’њ’°’ґ, ''Arevmdian Hayasdan'') is a term to refer to the western parts of the Armenian highlands located within Turkey (formerly the Ottoman Empire) that comprise the historic ...
and Eastern Armenia Eastern Armenia (Armenian: ‘±÷А÷З’•’ђ’µ’°’ґ ’А’°’µ’°’љ’њ’°’ґ, ''Arevelyan Hayastan'') refers to the eastern portion of the Armenian Highlands, historically inhabited by the Armenian people. Throughout history, Eastern Armenia has been contested and ...
fell to the Safavid Empire. Owing to the century long OttomanвАУSafavid relations, Turco-Iranian geopolitical rivalry that would last in West Asia, significant parts of the region were frequently fought over between the two rivalling empires during the OttomanвАУPersian Wars. From the mid 16th century with the Peace of Amasya, and decisively from the first half of the 17th century with the Treaty of Zuhab until the first half of the 19th century, Eastern Armenia was ruled by the successive Safavid, Afsharid and Qajar
The Guarded Domains of Iran, alternatively the Sublime State of Iran and commonly called Qajar Iran, Qajar Persia or the Qajar Empire, was the Iranian state under the rule of the Qajar dynasty, which was of Turkic origin,Cyrus Ghani. ''Iran an ...
empires, while Western Armenia remained under Ottoman Turkey, Ottoman rule.
From 1604, Abbas I of Persia, Abbas I of Iran implemented a "scorched earth" policy in the region to protect his north-western frontier against any OttomanвАУSafavid War (1603вАУ1618), invading Ottoman forces, a policy that involved a History of Armenia#Persian Armenia, forced resettlement of masses of Armenians outside of their homelands.
 In the 1813 Treaty of Gulistan and the 1828 Treaty of Turkmenchay, following the Russo-Persian War (1804вАУ13) and the Russo-Persian War (1826вАУ28), respectively, the Qajar dynasty of Iran was forced to irrevocably cede
In the 1813 Treaty of Gulistan and the 1828 Treaty of Turkmenchay, following the Russo-Persian War (1804вАУ13) and the Russo-Persian War (1826вАУ28), respectively, the Qajar dynasty of Iran was forced to irrevocably cede Eastern Armenia Eastern Armenia (Armenian: ‘±÷А÷З’•’ђ’µ’°’ґ ’А’°’µ’°’љ’њ’°’ґ, ''Arevelyan Hayastan'') refers to the eastern portion of the Armenian Highlands, historically inhabited by the Armenian people. Throughout history, Eastern Armenia has been contested and ...
, consisting of the Erivan Khanate, Erivan and Karabakh Khanates, to Imperial Russia. This period is known as Russian Armenia.
While Western Armenia still remained under Ottoman rule, the Armenians were granted considerable autonomy within their own enclaves and lived in relative harmony with other groups in the empire (including the ruling Turks). However, as Christians under a strict Muslim social structure, Armenians faced pervasive discrimination. In response to the 1894 Sasun rebellion, Sultan Abdul Hamid II organised state-sponsored massacres against the Armenians between 1894 and 1896, resulting in an estimated death toll of 80,000 to 300,000 people. The Hamidian massacres, as they came to be known, gave Hamid international infamy as the "Red Sultan" or "Bloody Sultan".
 During the 1890s, the Armenian Revolutionary Federation, commonly known as ''Dashnaktsutyun'', became active within the
During the 1890s, the Armenian Revolutionary Federation, commonly known as ''Dashnaktsutyun'', became active within the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
with the aim of unifying the various small groups in the empire that were advocating for reform and defending Armenian villages from massacres that were widespread in some of the Armenian-populated areas of the empire. Dashnaktsutyun members also formed Armenian fedayi groups that defended Armenian civilians through armed resistance. The Dashnaks also worked for the wider goal of creating a "free, independent and unified" Armenia, although they sometimes set aside this goal in favour of a more realistic approach, such as advocating autonomy.
The Ottoman Empire began to collapse, and in 1908, the Young Turk Revolution overthrew the government of Sultan Hamid. In April 1909, the Adana massacre occurred in the Adana Vilayet of the Ottoman Empire resulting in the deaths of as many as 20,000вАУ30,000 Armenians. The Armenians living in the empire hoped that the Committee of Union and Progress would change their second-class status. The Armenian reform package (1914) was presented as a solution by appointing an inspector general over Armenian issues.
World War I and the Armenian genocide
The outbreak of World War I led to confrontation between theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
and the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
in the Caucasus campaign, Caucasus and Persian campaign (World War I), Persian campaigns. The new government in Istanbul began to look on the Armenians with distrust and suspicion because the Imperial Russian Army contained a contingent of Armenian volunteer units, Armenian volunteers. On 24 April 1915, Deportation of Armenian intellectuals on 24 April 1915, Armenian intellectuals were arrested by Ottoman authorities and, with the Tehcir Law (29 May 1915), eventually a large proportion of Armenians living in Anatolia perished in what has become known as the Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenians, Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was implemented primarily t ...
.
The genocide was implemented in two phases: the wholesale killing of the able-bodied male population through massacre and subjection of army conscripts to forced labour, followed by the deportation of women, children, the elderly and infirm on death marches leading to the Syrian desert. Driven forward by military escorts, the deportees were deprived of food and water and subjected to periodic robbery, rape, and massacre. There was local Armenian resistance during the Armenian genocide, Armenian resistance in the region, developed against the activities of the Ottoman Empire. The events of 1915 to 1917 are regarded by Armenians and the vast majority of Western historians to have been state-sponsored mass killings, or genocide.
Turkish authorities deny the genocide took place to this day. The Armenian Genocide is acknowledged to have been one of the first modern genocides. According to the research conducted by Arnold J. Toynbee, an estimated 600,000 Armenians died during deportation from 1915 to 1916. This figure, however, accounts for solely the first year of the Genocide and does not take into account those who died or were killed after the report was compiled on 24 May 1916. The International Association of Genocide Scholars places the death toll at "more than a million". The total number of people killed has been most widely estimated at between 1 and 1.5 million.
Armenia and the Armenian diaspora have been campaigning for Recognition of the Armenian genocide, official recognition of the events as genocide for over 30 years. These events are traditionally commemorated yearly on 24 April, the Armenian Martyr Day, or the Day of the Armenian genocide.
First Republic of Armenia
 Although the Russian Caucasus Army (World War I), Russian Caucasus Army of Imperial forces commanded by Nikolai Yudenich and Armenians in volunteer units and Armenian militia led by Andranik Ozanian and Tovmas Nazarbekian succeeded in gaining most of
Although the Russian Caucasus Army (World War I), Russian Caucasus Army of Imperial forces commanded by Nikolai Yudenich and Armenians in volunteer units and Armenian militia led by Andranik Ozanian and Tovmas Nazarbekian succeeded in gaining most of Western Armenia
Western Armenia (Western Armenian: ‘±÷А’•÷В’і’њ’•’°’ґ ’А’°’µ’°’љ’њ’°’ґ, ''Arevmdian Hayasdan'') is a term to refer to the western parts of the Armenian highlands located within Turkey (formerly the Ottoman Empire) that comprise the historic ...
during World War I, their gains were lost with the October Revolution, Bolshevik Revolution of 1917. At the time, Russian-controlled Eastern Armenia Eastern Armenia (Armenian: ‘±÷А÷З’•’ђ’µ’°’ґ ’А’°’µ’°’љ’њ’°’ґ, ''Arevelyan Hayastan'') refers to the eastern portion of the Armenian Highlands, historically inhabited by the Armenian people. Throughout history, Eastern Armenia has been contested and ...
, Georgia, and Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
attempted to bond together in the Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic. This federation, however, lasted from only February to May 1918, when all three parties decided to dissolve it. As a result, the Dashnaktsutyun government of Eastern Armenia declared its independence on 28 May as the First Republic of Armenia
The First Republic of Armenia, officially known at the time of its existence as the Republic of Armenia, was an independent History of Armenia, Armenian state that existed from May (28th ''de jure'', 30th ''de facto'') 1918 to 2 December 1920 in ...
under the leadership of Aram Manukian.
 The First Republic's short-lived independence was fraught with war, territorial disputes, Muslim uprisings in Kars and SharurвАУNakhichevan, large-scale rebellions, and a mass influx of refugees from Western Armenia, bringing with them disease and starvation. The Allies of World War I, Entente Powers sought to help the newly founded Armenian state through relief funds and other forms of support.
At the end of the war, the victorious powers sought to divide up the Ottoman Empire. Signed between the Allies of World War I, Allied and Associated Powers and
The First Republic's short-lived independence was fraught with war, territorial disputes, Muslim uprisings in Kars and SharurвАУNakhichevan, large-scale rebellions, and a mass influx of refugees from Western Armenia, bringing with them disease and starvation. The Allies of World War I, Entente Powers sought to help the newly founded Armenian state through relief funds and other forms of support.
At the end of the war, the victorious powers sought to divide up the Ottoman Empire. Signed between the Allies of World War I, Allied and Associated Powers and Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
at Sèvres on 10 August 1920, the Treaty of Sèvres promised to maintain the existence of the Armenian republic and to attach the former territories of Western Armenia to it. Because the new borders of Armenia were to be drawn by United States President Woodrow Wilson, Western Armenia was also referred to as "Wilsonian Armenia". In addition, just days prior, on 5 August 1920, Mihran Damadian of the Armenian National Union, the de facto Armenian administration in Cilicia, declared the independence of Cilicia as an Armenian autonomous republic under French protectorate.
There was even consideration of making Armenia a mandate under the protection of the United States. The treaty, however, was rejected by the Turkish National Movement, and never came into effect. The movement used the treaty as the occasion to declare itself the rightful Politics of Turkey, government of Turkey, replacing the monarchy based in Istanbul with a republic based in Ankara.
In 1920, Turkish nationalist forces invaded the fledgling Armenian republic from the east. Turkish forces under the command of K√Ґzƒ±m Karabekir, Kazƒ±m Karabekir captured Armenian territories that Russia had annexed in the aftermath of the Russo-Turkish War (1877вАУ78), 1877вАУ1878 Russo-Turkish War and occupied the old city of Alexandropol (present-day Gyumri). The violent conflict finally concluded with the Treaty of Alexandropol on 2 December 1920. The treaty forced Armenia to disarm most of its Armed forces, military forces, cede all former Ottoman territory granted to it by the Treaty of S√®vres, and to give up all the "Wilsonian Armenia" granted to it at the S√®vres treaty. Simultaneously, the 11th Army (RSFSR), Soviet Eleventh Army, under the command of Grigoriy Ordzhonikidze, invaded Armenia at Karavansarai (present-day Ijevan) on 29 November. By 4 December, Ordzhonikidze's forces entered Yerevan and the short-lived Armenian republic collapsed.
After the fall of the republic, the February Uprising soon took place in 1921, and led to the establishment of the Republic of Mountainous Armenia by Armenian forces under command of Garegin Nzhdeh on 26 April, which fought off both Soviet and Turkish intrusions in the Zangezur region of southern Armenia. After Soviet agreements to include the Syunik Province in Armenia's borders, the rebellion ended and the Red Army took control of the region on 13 July.
Armenian SSR
1922 to World War II
Armenia was annexed by the Red Army and along with Democratic Republic of Georgia, Georgia and Azerbaijan Democratic Republic, Azerbaijan, was incorporated into the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics as part of the Transcaucasian SFSR (TSFSR) on 4 March 1922.–Ч–∞–Ї–∞–≤–Ї–∞–Ј—Б–Ї–∞—П —Д–µ–і–µ—А–∞—Ж–Є—П''–С–Њ–ї—М—И–∞—П —Б–Њ–≤–µ—В—Б–Ї–∞—П —Н–љ—Ж–Є–Ї–ї–Њ–њ–µ–і–Є—П'', 3-–µ –Є–Ј–і., –≥–ї. —А–µ–і. –Р. –Ь. –Я—А–Њ—Е–Њ—А–Њ–≤. –Ь–Њ—Б–Ї–≤–∞: –°–Њ–≤–µ—В—Б–Ї–∞—П —Н–љ—Ж–Є–Ї–ї–Њ–њ–µ–і–Є—П, 1972. –Ґ. 9 () With this annexation, the Treaty of Alexandropol was superseded by the Turkish-Soviet Treaty of Kars. In the agreement, Turkey allowed the Soviet Union to assume control over Adjara with the port city of Batumi in return for sovereignty over the cities of Kars, Ardahan, and IƒЯdƒ±r, all of which were part of Russian Armenia. The TSFSR existed from 1922 to 1936, when it was divided up into three separate entities (
Armenian SSR
The Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic (ArSSR), also known as Soviet Armenia, or simply Armenia, was one of the constituent republics of the Soviet Union, located in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Soviet Armenia bordered the Soviet republics ...
, Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic, Azerbaijan SSR, and Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic, Georgian SSR). Armenians enjoyed a period of relative stability within USSR in contrast to the turbulent final years of the Ottoman Empire. The situation was difficult for the church, which struggled with Religion in soviet union, secular policies of USSR. After the death of Vladimir Lenin, Joseph Stalin, the general secretary of the CPSU, Communist Party, gradually established himself as the dictator of the USSR. Stalin's reign was characterized by mass repressions, that cost millions of lives all over the USSR.
World War II and post-Stalinist period
 Armenia was not the scene of any battles in Eastern Front (World War II), World War II. An estimated 500,000 Armenians (nearly a third of the population) served in the Red Army during the war, and 175,000 died. A total of 117 citizens of Armenia including 10 non ethnic Armenians were awarded Hero of the Soviet Union. Six special military divisions were formed in Soviet Armenia in 1941вАУ42, partly because so many draftees from the republic could not understand Russian. Five of them, the Soviet 89th "Tamanyan" Division, 89th, 409th Rifle Division, 409th, 408th Rifle Division (Soviet Union), 408th, 390th Rifle Division, 390th, and 76th Rifle Division (Soviet Union), 76th Divisions, would have a distinguished war record, while the sixth was ordered to stay in Armenia to guard the republic's western borders against a possible incursion by neighboring Turkey.
The Soviet 89th "Tamanyan" Division, 89th Tamanyan Division, composed of ethnic Armenians, fought in the Battle of Berlin and entered Berlin.
It is claimed that the freedom index in the region had seen an improvement after the State funeral of Joseph Stalin, death of Joseph Stalin in 1953 and the emergence of Nikita Khrushchev as the new general secretary of the CPSU. Soon, life in Armenia's SSR began to see rapid improvement. The church, which was limited during the secretaryship of Stalin, was revived when Catholicos of All Armenians, Catholicos Vazgen I assumed the duties of his office in 1955. In 1967, a memorial to the victims of the Armenian genocide was built at the Tsitsernakaberd hill above the Hrazdan Canyon, gorge in
Armenia was not the scene of any battles in Eastern Front (World War II), World War II. An estimated 500,000 Armenians (nearly a third of the population) served in the Red Army during the war, and 175,000 died. A total of 117 citizens of Armenia including 10 non ethnic Armenians were awarded Hero of the Soviet Union. Six special military divisions were formed in Soviet Armenia in 1941вАУ42, partly because so many draftees from the republic could not understand Russian. Five of them, the Soviet 89th "Tamanyan" Division, 89th, 409th Rifle Division, 409th, 408th Rifle Division (Soviet Union), 408th, 390th Rifle Division, 390th, and 76th Rifle Division (Soviet Union), 76th Divisions, would have a distinguished war record, while the sixth was ordered to stay in Armenia to guard the republic's western borders against a possible incursion by neighboring Turkey.
The Soviet 89th "Tamanyan" Division, 89th Tamanyan Division, composed of ethnic Armenians, fought in the Battle of Berlin and entered Berlin.
It is claimed that the freedom index in the region had seen an improvement after the State funeral of Joseph Stalin, death of Joseph Stalin in 1953 and the emergence of Nikita Khrushchev as the new general secretary of the CPSU. Soon, life in Armenia's SSR began to see rapid improvement. The church, which was limited during the secretaryship of Stalin, was revived when Catholicos of All Armenians, Catholicos Vazgen I assumed the duties of his office in 1955. In 1967, a memorial to the victims of the Armenian genocide was built at the Tsitsernakaberd hill above the Hrazdan Canyon, gorge in Yerevan
Yerevan ( , , ; ; sometimes spelled Erevan) is the capital and largest city of Armenia, as well as one of the world's List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerev ...
. This occurred after 1965 Yerevan demonstrations, mass demonstrations took place on the tragic event's fiftieth anniversary in 1965.
Gorbachev era
During the Mikhail Gorbachev, Gorbachev era of the 1980s, with the reforms of Glasnost and Perestroika, Armenians began to demand better environmental care for their country, opposing the pollution that Soviet-built factories brought. Tensions also developed between Soviet Azerbaijan and its autonomous district of Nagorno-Karabakh, a majority-Armenian region. About 484,000 Armenians in Azerbaijan, Armenians lived in Azerbaijan in 1970. The Armenians of Karabakh demanded unification with Soviet Armenia. Peaceful protests in Armenia supporting the Karabakh Armenians were met with anti-Armenian pogroms in Azerbaijan, such as the one in Sumgait pogrom, Sumgait, which was followed by Gugark massacre, anti-Azerbaijani violence in Armenia. Compounding Armenia's problems was a 1988 Armenian earthquake, devastating earthquake in 1988 with a moment magnitude scale, moment magnitude of 7.2. Gorbachev's inability to alleviate any of Armenia's problems created disillusionment among the Armenians and fed a growing hunger for independence. In May 1990, the New Armenian Army (NAA) was established, serving as a defence force separate from the Soviet Red Army. Clashes soon broke out between the NAA and Russian Ministry of Internal Affairs, Soviet Internal Security Forces (MVD) troops based in Yerevan when Armenians decided to commemorate the establishment of the 1918 First Republic of Armenia. The violence resulted in the deaths of five Armenians killed in a shootout with the MVD at the railway station. Witnesses there claimed that the MVD used excessive force and that they had instigated the fighting. Further firefights between Armenian militiamen and Soviet troops occurred in Nubarashen, Sovetashen, near the capital and resulted in the deaths of over 26 people, mostly Armenians. The pogrom of Armenians in Baku in January 1990 forced almost all of the 200,000 Armenians in the Azerbaijani capital Baku to flee to Armenia. On 23 August 1990, Armenia declared its sovereignty on its territory. On 17 March 1991, Armenia, along with the Baltic states, Georgia and Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic, Moldova, boycotted a nationwide 1991 Soviet Union referendum, referendum in which 78% of all voters voted for the retention of the Soviet Union in a reformed form.Restoration of independence
21st century
In the 21st century, Armenia faces many hardships. It has made a full switch to a market economy. One study ranks it the 50th most "economically free" nation in the world, . Its relations with Europe, the Arab League, and the Commonwealth of Independent States have allowed Armenia to increase trade. Gas, oil, and other supplies come through two vital routes: Iran and Georgia. , Armenia maintained cordial relations with both countries. The 2018 Armenian revolution, 2018 Armenian Revolution was a series of anti-government protests in Armenia from April to May 2018 staged by various political and civil groups led by a member of the Armenian parliament вАФ Nikol Pashinyan (head of the Civil Contract (Armenia), Civil Contract party). Protests and marches took place initially in response to Serzh Sargsyan's third consecutive term as President of Armenia and later against the Republican Party of Armenia, Republican Party controlled government in general. Pashinyan declared the movement, which led to Sargsyan's resignation, a "velvet revolution". In March 2018, the Armenian parliament elected Armen Sarkissian as the new President of Armenia. The controversial constitutional reform to reduce presidential power was implemented, while the authority of the prime minister was strengthened. In May 2018, parliament elected opposition leader Nikol Pashinyan as the new prime minister. His predecessor Serzh Sargsyan resigned two weeks earlier following 2018 Armenian revolution, widespread anti-government demonstrations. On 27 September 2020, a full-scale war erupted due to the unresolved Nagorno-Karabakh conflict. Both the armed forces of Armenia and Azerbaijan reported military and civilian casualties. The 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh ceasefire agreement, Nagorno-Karabakh ceasefire agreement to end the six-week 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war, war between Armenia and Azerbaijan was seen by many as Armenia's defeat and capitulation. The year-long 2020вАУ2021 Armenian protests, March of Dignity protests forced early elections. On 20 June 2021, Pashinyan's Civil Contract party won an early parliamentary 2021 Armenian parliamentary election, election. Acting Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan was officially appointed to the post of prime minister by Armenia's President Armen Sarkissian. In January 2022, Armenian President Armen Sarkissian resigned from office, stating that the constitution no longer gives the president sufficient powers or influence. On 3 March 2022, Vahagn Khachaturyan was elected as the fifth president of Armenia in the second round of parliamentary vote. The next month 2022 Armenian protests, yet more protests broke out.2023 Azerbaijani offensive in Nagorno-Karabakh
Between 19 and 20 September 2023,Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
launched a large-scale military offensive against the Political status of Nagorno-Karabakh, self-declared breakaway state of Republic of Artsakh, Artsakh, a move seen by the European Parliament as a violation of the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh ceasefire agreement, 2020 ceasefire agreement. The offensive took place in the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh, which is internationally recognized as part of Azerbaijan, but populated by Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiq ...
. The attacks occurred in the midst of an escalating crisis caused by Azerbaijan Blockade of the Republic of Artsakh (2022вАУpresent), blockading Artsakh, which resulted in significant scarcities of essential supplies such as food, medicine, and other goods in the affected region.
One day after the offensive started, on 20 September, a 2023 Nagorno-Karabakh ceasefire agreement, ceasefire agreement was reached at the mediation of the Peacekeeping operations in Nagorno-Karabakh, Russian peacekeeping command in Nagorno-Karabakh. Azerbaijan held a meeting with representatives of the Nagorno-Karabakh Armenians on 21 September in Yevlakh, to be followed by another meeting in October. Ceasefire violations by Azerbaijan were nonetheless reported by both Artsakhi residents and officials.
Human rights organisations and experts in genocide prevention issued multiple alerts, stating that the region's Armenian population was at risk or actively Flight of Nagorno-Karabakh Armenians, being subjected to ethnic cleansing and genocide. Luis Moreno Ocampo, a former prosecutor of the International Criminal Court, warned that another Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenians, Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was implemented primarily t ...
could take place, and attributed the inaction of the international community to encouraging Azerbaijan that it would face no serious consequences.
Geography
 Armenia is a
Armenia is a landlocked country
A landlocked country is a country that has no territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie solely on endorheic basins. Currently, there are 44 landlocked countries, two of them doubly landlocked (Liechtenstein and Uzbekistan), and t ...
in the geopolitical Transcaucasus (South Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
) region, that is located in the Southern Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains
*
* Azerbaijani: ,
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* is a mountain range at the intersection of Asia and Europe. Stretching between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, they are surrounded by the Caucasus region ...
and their lowlands between the Black Sea and Caspian Sea, and northeast of the Armenian Highlands. Armenia is widely accepted as part of West Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian ...
geographically, although other definitions place it either fully in Europe or across Europe and Asia. Located on the Armenian Highlands
The Armenian highlands (; also known as the Armenian upland, Armenian plateau, or Armenian tableland)Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: ...
, it is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
to the north, the Lachin corridor which is a part of Lachin District that is under the control of a Russian peacekeeping force and Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
proper to the east, and Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
and Azerbaijan's exclave
An enclave is a territory that is entirely surrounded by the territory of only one other state or entity. An enclave can be an independent territory or part of a larger one. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is s ...
of Nakhchivan to the south. Armenia lies between latitudes 38th parallel north, 38° and 42nd parallel north, 42° N, and meridians 43rd meridian east, 43° and 47th meridian east, 47° E. It contains two terrestrial ecoregions: Caucasus mixed forests and Eastern Anatolian montane steppe.
Topography
 Armenia has a territorial area of . The terrain is mostly mountainous, with fast flowing rivers, and few forests. The land rises to Metres above sea level, above sea level at Mount Aragats, and no point is below Metres above sea level, above sea level. List of countries by average elevation, Average elevation of the country area is tenth highest in the world and it has 85.9% mountain area, more than Switzerland or Nepal.
Mount Ararat, which was historically part of Armenia, is the highest mountain in the region at 5,137 meters (16,854 feet). Now located in Turkey, but clearly visible from Armenia, it is regarded by the Armenians as a symbol of their land. Because of this, the mountain is present on the Coat of arms of Armenia, Armenian national emblem today.
Armenia has a territorial area of . The terrain is mostly mountainous, with fast flowing rivers, and few forests. The land rises to Metres above sea level, above sea level at Mount Aragats, and no point is below Metres above sea level, above sea level. List of countries by average elevation, Average elevation of the country area is tenth highest in the world and it has 85.9% mountain area, more than Switzerland or Nepal.
Mount Ararat, which was historically part of Armenia, is the highest mountain in the region at 5,137 meters (16,854 feet). Now located in Turkey, but clearly visible from Armenia, it is regarded by the Armenians as a symbol of their land. Because of this, the mountain is present on the Coat of arms of Armenia, Armenian national emblem today.
Climate
Environment
Armenia ranked 63rd out of 180 countries on Environmental Performance Index (EPI) in 2018. Its rank on subindex Environmental Health (which is weighted at 40% in EPI) is 109, while Armenia's rank on subindex of Ecosystem Vitality (weighted at 60% in EPI) is 27th best in the world. This suggests that main environmental issues in Armenia are with #Health care, population health, while environment vitality is of lesser concern. Out of sub-subindices contributing to Environmental Health subindex ranking on Air Quality to which population is exposed is particularly unsatisfying. In Armenia forest cover is around 12% of the total land area, equivalent to 328,470 hectares (ha) of forest in 2020, down from 334,730 hectares (ha) in 1990. In 2020, naturally regenerating forest covered 310,000 hectares (ha) and planted forest covered 18,470 hectares (ha). Of the naturally regenerating forest 5% was reported to be primary forest (consisting of native tree species with no clearly visible indications of human activity) and around 0% of the forest area was found within protected areas. For the year 2015, 100% of the forest area was reported to be under State ownership, public ownership. Waste management in Armenia is underdeveloped, as no waste sorting or recycling takes place at Armenia's 60 landfills. A waste processing plant is scheduled for construction near Hrazdan city, which will allow for closure of 10 waste dumps. Despite the availability of abundant renewable energy sources in Armenia (especially Hydroelectricity, hydroelectric and wind power) and calls from EU officials to shut down the Metsamor Nuclear Power Plant, nuclear power plant at Metsamor, the Armenian Government is exploring the possibilities of installing new small modular nuclear reactors. In 2018 existing nuclear plant is scheduled for modernisation to enhance its safety and increase power production by about 10%.Government and politics
Armenia is a Representative democracy, representative parliamentary democratic republic. The Armenian constitution adhered to the model of a Semi-Presidential Republic, semi-presidential republic until April 2018. According to the current Constitution of Armenia, the President of Armenia, President is the head of state holding largely representational functions, while the Prime Minister of Armenia, Prime Minister is the head of government and exercises Executive (government), executive power. Since 1995 Legislature, Legislative power is vested in the National Assembly of Armenia, Azgayin Zhoghov or ''National Assembly of Armenia, National Assembly'', which is a unicameral parliament consisting of 105 members. The Fragile States Index since its first report in 2006 until most recent in 2019, consistently ranked Armenia better than all its neighboring countries (with one exception in 2011). Armenia has universal suffrage above the age of eighteen.Foreign relations
Armenia became a member of the United Nations on 2 March 1992, and is a signatory to a number of its organisations and other international agreements. Armenia is also a member of international organisations such as theCouncil of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; , CdE) is an international organisation with the goal of upholding human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it is Europe's oldest intergovernmental organisation, represe ...
, the Asian Development Bank
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank to promote social and economic development in Asia. The bank is headquartered in Metro Manila, Philippines and maintains 31 field offices around the world.
The bank was establishe ...
, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development
The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, shortened to EBRD ( French: ''Banque européenne pour la reconstruction et le développement'' or ''BERD''), is an international financial institution founded in 1991 in Paris. As a multilat ...
, the European Political Community, the Commonwealth of Independent States, the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe, the International Monetary Fund, the World Trade Organization, the World Customs Organization, the Organization of the Black Sea Economic Cooperation and Organisation internationale de la Francophonie, La Francophonie. It is a member of the Collective Security Treaty Organisation, CSTO military alliance, and also participates in NATO's Partnership for Peace programme and the Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council. In 2004, its forces joined Kosovo Force, KFOR, a NATO-led international force in Kosovo. Armenia is also an observer member of the Arab League, the Organization of American States, the Pacific Alliance, the Non-Aligned Movement, and a dialogue partner in the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation. As a result of its historical ties to France, Armenia was selected to host the biennial Organisation internationale de la Francophonie, Francophonie summit in 2018.
Armenia has a difficult relation with neighbouring countries ArmeniaвАУAzerbaijan relations, Azerbaijan and ArmeniaвАУTurkey relations, Turkey. Tensions were running high between Armenians and Azerbaijanis during the final years of the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
. The Nagorno-Karabakh conflict dominated the region's politics throughout the 1990s. To this day, Armenia's borders with Turkey and Azerbaijan are under severe blockade. In addition, a permanent solution for the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict has not been reached despite the mediation provided by organisations such as the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, OSCE.
Turkey also has a long history of poor relations with Armenia over its refusal to acknowledge the Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenians, Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was implemented primarily t ...
, even though it was one of the first countries to recognize the Republic of Armenia (the third republic) after its independence from the USSR in 1991. Despite this, for most of the 20th century and early 21st century, relations remain tense and there are no formal diplomatic relations between the two countries due to Turkey's refusal to establish them for numerous reasons. During the first Nagorno-Karabakh War, and citing it as the reason, Turkey closed its border with Armenia in 1993. It has not lifted its blockade despite pressure from the powerful Turkish business lobby interested in Armenian markets.
On 10 October 2009, Armenia and Turkey Zurich Protocols, signed protocols on the normalisation of relations, which set a timetable for restoring diplomatic ties and reopening their joint border. The ratification of those had to be made in the national parliaments. In Armenia, before sending the protocols to the parliament, it was sent to the Constitutional Court to have their constitutionality to be approved. The Constitutional Court made references to the preamble of the protocols underlying three main issues. One of them stated that the implementation of the protocols did not imply Armenia's official recognition of the existing Turkish-Armenian border established by the Treaty of Kars. By doing so, the Constitutional Court rejected one of the main premises of the protocols, i.e. "the mutual recognition of the existing border between the two countries as defined by relevant treaties of international law". This was for the Turkish Government the reason to back down from the Protocols. The Armenian President had made multiple public announcements, both in Armenia and abroad, that, as the leader of the political majority of Armenia, he assured the parliamentary ratification of the protocols if Turkey also ratified them. Despite this, the process stopped, as Turkey continuously added more preconditions to its ratification and also "delayed it beyond any reasonable time-period".
Due to its position between two hostile neighbours, Armenia has close security ties with Russia. At the request of the Armenian government, Russia maintains a Russian 102nd Military Base, military base in the city of Gyumri located in Northwestern Armenia
as a deterrent against Turkey. Despite this, Armenia has also been looking toward European integration, Euro-Atlantic structures in recent years. Armenia maintains positive relations with the United States, which is home to the second largest Armenian diaspora community in the world. According to the United States Census, US Census Bureau, there are 427,822 Armenian Americans in the country.
 Because of the illicit border blockades by Azerbaijan and Turkey, Armenia continues to maintain solid relations with its southern neighbour Iran, especially in the economic sector. Economic projects are being developed between the two nations, including a gas pipeline going from Iran to Armenia.
Armenia is a member of the Council of Europe and maintains close relations with the European Union; especially with its Member state of the European Union, member states France and Greece. In January 2002, the European Parliament noted that Armenia may enter the EU in the future. A 2005 survey reported that 64% of Armenians favoured joining the EU, a move multiple Armenian officials have voiced support for.
Armenian SSR, A former republic of the
Because of the illicit border blockades by Azerbaijan and Turkey, Armenia continues to maintain solid relations with its southern neighbour Iran, especially in the economic sector. Economic projects are being developed between the two nations, including a gas pipeline going from Iran to Armenia.
Armenia is a member of the Council of Europe and maintains close relations with the European Union; especially with its Member state of the European Union, member states France and Greece. In January 2002, the European Parliament noted that Armenia may enter the EU in the future. A 2005 survey reported that 64% of Armenians favoured joining the EU, a move multiple Armenian officials have voiced support for.
Armenian SSR, A former republic of the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
and an emerging democracy, Armenia was negotiating to become an associate EU partner and had completed negotiations to sign an European Union Association Agreement, Association Agreement with a Deep and Comprehensive Free Trade Area with the EU in 2013. However, the government opted not to finalize EUвАУArmenia Partnership and Cooperation Agreement#Cancellation of Association Agreement, the agreement, and instead joined the Eurasian Economic Union
The Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU or EEU)EAEU is the acronym used on thorganisation's website However, many media outlets use the acronym EEU. is an economic union of five post-Soviet states located in Eurasia. The EAEU has an integrated single ...
. Despite this, Armenia and the EU finalized the Armenia-EU Comprehensive and Enhanced Partnership Agreement (CEPA) on 24 November 2017. The agreement enhances the relationship between Armenia and the EU to a new partnership level, further develops cooperation in economic, trade and political areas, aims to improve investment climate, and is designed to bring Law of Armenia, Armenian law gradually closer to the Acquis communautaire, EU acquis.
Legally speaking, Armenia has the right to be considered as a Potential enlargement of the European Union, prospective EU member provided it meets necessary standards and criteria, though officially such a plan does not exist in Brussels. Armenia is included in the EU's European Neighbourhood Policy (ENP) and participates in both the Eastern Partnership
The Eastern Partnership (EaP) is a joint initiative of the European Union, together with its member states, and six Eastern Europe, Eastern European countries. The EaP framework governs the EU's relationship with the post-Soviet states of Armen ...
and the Euronest Parliamentary Assembly, which aims at bringing the EU and its neighbours closer.
Following the 2023 Azerbaijani offensive in Nagorno-Karabakh, Armenia's relations with a long-term ally Russia started to deteriorate. In February 2024, Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan said that the CSTO "hasn't fulfilled its security obligations towards Armenia" and that "in practice we have basically frozen our participation in the CSTO". On 28 February 2024, during a speech made in the National Assembly (Armenia), National Assembly, Pashinyan further stated that the CSTO is "a threat to the national security of Armenia". In March 2024, Armenia officially expelled Russian border guards from the Zvartnots International Airport in Yerevan.
On 2 March 2024, Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan advised that Armenia would officially "apply to become a candidate for EU membership in the coming days, within a month at most". On 5 March, Pashinyan stated that Armenia would apply for EU candidacy by Autumn 2024 at the latest. On 8 March 2024, Armenian Foreign Minister Ararat Mirzoyan stated, "Armenia is seeking to get closer to the West amid worsening relations with Russia" and "New opportunities are largely being discussed in Armenia nowadays, that includes membership in the European Union".
On 12 February 2025, Armenia's parliament approved a bill officially endorsing Accession of Armenia to the European Union, Armenia's EU accession. The decision for the government to pass the bill was reported to be the first step of "the beginning of the accession process of Armenia to the European Union".
Military
The Armenian Army and Armenian Air Force, Air Force are the two branches of the Armed Forces of Armenia. The Armenian military was formed after the History of the Soviet Union (1985вАУ91), collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 and with the establishment of the Ministry of Defence in 1992. The Commander-in-chief, Commander-in-Chief of the military is the Prime Minister of Armenia, Nikol Pashinyan. The Ministry of Defence is in charge of political leadership, headed by David Tonoyan, Davit Tonoyan, while military command remains in the hands of the general staff, headed by the Chief of the General Staff (Armenia), Chief of Staff, who is Lieutenant-General Onik Gasparyan. Active forces now number about 81,000 soldiers, with an additional Military reserve force, reserve of 32,000 troops. Armenian border guards are in charge of patrolling the country's borders withGeorgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
and Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
, while Russian troops continue to monitor its borders with Iran and Turkey. In the case of an attack, Armenia is able to mobilize every able-bodied man between the age of 15 and 59, with military preparedness.
The Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe, which establishes comprehensive limits on key categories of military equipment, was ratified by the Armenian parliament in July 1992. In March 1993, Armenia signed the multilateral Chemical Weapons Convention, which calls for the eventual elimination of chemical weapons. Armenia acceded to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) as a non-nuclear weapons state in July 1993. Armenia is a member of the Collective Security Treaty Organisation (CSTO). Armenia also has an Individual Partnership Action Plan with NATO and it participates in NATO's Partnership for Peace (PiP) programme and the Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council (EAPC).
Human rights and freedom
 Human rights in Armenia tend to be better than those in most Post-Soviet states, former Soviet republics and have drawn closer to acceptable standards, especially economically. Nonetheless, there are still several considerable problems.
Armenia scored 5.63 on The Economist Democracy Index, published in January 2023 (data for 2022). Although still classified as "hybrid regime", Armenia recorded the strongest improvement among European countries and reached its ever-best score since calculation began in 2006.
Armenia is classified as "partly free" in the 2019 report (with data from 2018) by Freedom House, which gives it a score of 51 out of 100, which is 6 points ahead of the previous estimate.
Armenia recorded unprecedented progress in the 2019 Press Freedom Index, World Press Freedom Index published by Reporters Without Borders, improving its position by 19 points and ranking 61st on the list. The publication also confirms the absence of cases of killed journalists, citizen journalists or media assistants.
Armenia ranks 26th in the 2022 report of The Human Freedom Index published by the American CATO Institute and Canada's Fraser Institute.
Armenia ranked 29th for economic freedom and 76th for personal freedom among 159 countries in the 2017 List of freedom indices, Human Freedom Index published by the Cato Institute.
In October 2023 Armenia ratified signing the Rome statute, whereby Armenia will become a full member of the International Criminal Court.
Human rights in Armenia tend to be better than those in most Post-Soviet states, former Soviet republics and have drawn closer to acceptable standards, especially economically. Nonetheless, there are still several considerable problems.
Armenia scored 5.63 on The Economist Democracy Index, published in January 2023 (data for 2022). Although still classified as "hybrid regime", Armenia recorded the strongest improvement among European countries and reached its ever-best score since calculation began in 2006.
Armenia is classified as "partly free" in the 2019 report (with data from 2018) by Freedom House, which gives it a score of 51 out of 100, which is 6 points ahead of the previous estimate.
Armenia recorded unprecedented progress in the 2019 Press Freedom Index, World Press Freedom Index published by Reporters Without Borders, improving its position by 19 points and ranking 61st on the list. The publication also confirms the absence of cases of killed journalists, citizen journalists or media assistants.
Armenia ranks 26th in the 2022 report of The Human Freedom Index published by the American CATO Institute and Canada's Fraser Institute.
Armenia ranked 29th for economic freedom and 76th for personal freedom among 159 countries in the 2017 List of freedom indices, Human Freedom Index published by the Cato Institute.
In October 2023 Armenia ratified signing the Rome statute, whereby Armenia will become a full member of the International Criminal Court.
Administrative divisions
Armenia is divided into ten Administrative divisions of Armenia, provinces (''marzer'', singular ''marz''), with the city (''kaghak'') ofYerevan
Yerevan ( , , ; ; sometimes spelled Erevan) is the capital and largest city of Armenia, as well as one of the world's List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerev ...
() having special administrative status as the country's capital. The chief executive in each of the ten provinces is the ''marzpet'' (''marz'' governor), appointed by the government of Armenia. In Yerevan, the chief executive is the mayor, elected since 2009.
Within each province there are List of municipalities of Armenia, communities (''hamaynkner'', singular ''hamaynk''). Each community is self-governing and consists of one or more settlements (''bnakavayrer'', singular ''bnakavayr''). Settlements are classified as either towns (''kaghakner'', singular ''kaghak'') or villages (''gyugher'', singular ''gyugh''). , Armenia includes 915 communities, of which 49 are considered urban and 866 are considered rural. The capital, Yerevan, also has the status of a community. Additionally, Yerevan is divided into twelve semi-autonomous districts.
Economy
The economy relies heavily on investment and support from Armenians abroad. Before independence, Armenia's economy was largely industry-based вАУ chemical substance, chemicals, electronics, machinery, food processing, processed food, synthetic rubber, and textile вАУ and highly dependent on outside resources. The republic had developed a modern Secondary sector of the economy, industrial sector, supplying machine tools, textiles, and other Final goods, manufactured goods to sister republics in exchange for raw materials and energy. Agriculture accounted for less than 20% of both net material product and Full employment, total employment before the History of the Soviet Union (1985вАУ1991), dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. After independence, the importance of agriculture in the economy increased markedly, its share at the end of the 1990s rising to more than 30% of GDP and more than 40% of total employment.Z. Lerman and A. Mirzakhanian, ''Private Agriculture in Armenia'', Lexington Books, Lanham, MD, 2001. This increase in the importance of agriculture was attributable to food security needs of the population in the face of uncertainty during the first phases of transition economy, transition and the collapse of the non-agricultural sectors of the economy in the early 1990s. As the economic situation stabilised and growth resumed, the share of agriculture in GDP dropped to slightly over 20% (2006 data), although the share of agriculture in employment remained more than 40%.Statistical Yearbook 2007, Armenia National Statistical Service, Yerevan
 Armenian mines produce copper, zinc, gold, and lead. The vast majority of energy is produced with fuel imported from Russia, including gas and nuclear fuel (for its one nuclear power plant); the main domestic energy source is hydroelectric. Small deposits of coal, gas, and petroleum exist but have not yet been developed.
Access to biocapacity in Armenia is lower than world average. In 2016, Armenia had 0.8 global hectares of biocapacity per person within its territory, much less than the world average of 1.6 global hectares per person. In 2016 Armenia used 1.9 global hectares of biocapacity per personвАФtheir ecological footprint of consumption. This means they use double as much biocapacity as Armenia contains. As a result, Armenia is running a biocapacity deficit.
Like other Post-Soviet states, newly independent states of the former Soviet Union, Armenia's economy suffers from the breakdown of former Soviet trading patterns. Soviet investment in and support of Armenian industry has virtually disappeared, so that few major enterprises are still able to function. In addition, the effects of the 1988 Armenian earthquake, 1988 Spitak earthquake, which killed more than 25,000 people and made 500,000 homeless, are still being felt. The conflict with Azerbaijan over Nagorno-Karabakh has not been resolved. Shutdown of the nuclear power plant in 1989 led to the Armenian energy crisis of 1990s. The GDP fell nearly 60% between 1989 and 1993, but then resumed robust growth after the power plant was reopened in 1995. The national currency, the dram, suffered hyperinflation for the first years after its introduction in 1993.
Nevertheless, the government was able to make wide-ranging economic reforms that paid off in dramatically lower inflation and steady growth. The 1994 ceasefire in the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict has also helped the economy. Armenia has had strong economic growth since 1995, building on the turnaround that began the previous year, and inflation has been negligible for the past several years. New sectors, such as precious-stone processing and jewelry making, information and communication technology and Tourism in Armenia, tourism are beginning to supplement more traditional sectors of the economy, such as agriculture.
This steady economic progress has earned Armenia increasing support from international institutions. The International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Bank,
Armenian mines produce copper, zinc, gold, and lead. The vast majority of energy is produced with fuel imported from Russia, including gas and nuclear fuel (for its one nuclear power plant); the main domestic energy source is hydroelectric. Small deposits of coal, gas, and petroleum exist but have not yet been developed.
Access to biocapacity in Armenia is lower than world average. In 2016, Armenia had 0.8 global hectares of biocapacity per person within its territory, much less than the world average of 1.6 global hectares per person. In 2016 Armenia used 1.9 global hectares of biocapacity per personвАФtheir ecological footprint of consumption. This means they use double as much biocapacity as Armenia contains. As a result, Armenia is running a biocapacity deficit.
Like other Post-Soviet states, newly independent states of the former Soviet Union, Armenia's economy suffers from the breakdown of former Soviet trading patterns. Soviet investment in and support of Armenian industry has virtually disappeared, so that few major enterprises are still able to function. In addition, the effects of the 1988 Armenian earthquake, 1988 Spitak earthquake, which killed more than 25,000 people and made 500,000 homeless, are still being felt. The conflict with Azerbaijan over Nagorno-Karabakh has not been resolved. Shutdown of the nuclear power plant in 1989 led to the Armenian energy crisis of 1990s. The GDP fell nearly 60% between 1989 and 1993, but then resumed robust growth after the power plant was reopened in 1995. The national currency, the dram, suffered hyperinflation for the first years after its introduction in 1993.
Nevertheless, the government was able to make wide-ranging economic reforms that paid off in dramatically lower inflation and steady growth. The 1994 ceasefire in the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict has also helped the economy. Armenia has had strong economic growth since 1995, building on the turnaround that began the previous year, and inflation has been negligible for the past several years. New sectors, such as precious-stone processing and jewelry making, information and communication technology and Tourism in Armenia, tourism are beginning to supplement more traditional sectors of the economy, such as agriculture.
This steady economic progress has earned Armenia increasing support from international institutions. The International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Bank, European Bank for Reconstruction and Development
The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, shortened to EBRD ( French: ''Banque européenne pour la reconstruction et le développement'' or ''BERD''), is an international financial institution founded in 1991 in Paris. As a multilat ...
(EBRD), and other Global financial system, international financial institutions (IFIs) and foreign countries are extending considerable grants and loans. Loans to Armenia since 1993 exceed $1.1 billion. These loans are targeted at reducing the budget deficit and stabilising the currency; developing private businesses; energy; agriculture; food processing; transportation; the health and education sectors; and ongoing rehabilitation in the earthquake zone. The government joined the WTO on 5 February 2003. But one of the main sources of foreign direct investments remains the Armenian diaspora, which finances major parts of the reconstruction of infrastructure and other public projects. Being a growing democratic state, Armenia also hopes to get more financial aid from the Western World.
A liberal foreign investment law was approved in June 1994, and a law on privatisation was adopted in 1997, as well as a programme of state property privatisation. Continued progress will depend on the ability of the government to strengthen its macroeconomic management, including increasing revenue collection, improving the investment climate, and making strides against corruption. However, unemployment, which was 18.5% in 2015, still remains a major problem due to the influx of thousands of refugees from the Karabakh conflict.
In 2017, the economy grew by 7.5% due to rising copper prices.
In 2022, Armenia's GDP stood at $39.4 billion, and enjoyed an economic freedom index of 65.3, according to Heritage Organisation.
The Armenian economy is predicted to grow by 13% in 2022 due to a huge influx of Russian citizens. The IMF's preliminary forecast as of March 2022 predicted growth of 1.5% for the year.
Science and technology
Research spending is low in Armenia, averaging 0.25% of GDP over 2010вАУ2013. However, the statistical record of research expenditure is incomplete, as expenditure by privately owned business enterprises is not surveyed in Armenia. The world average for domestic expenditure on research was 1.7% of GDP in 2013. The country's ''Strategy for the Development of Science 2011вАУ2020'' envisions that 'by 2020, Armenia is a country with a knowledge-based economy and is competitive within the European Research Area with its level of basic and applied research.' It fixes the following targets: * Creation of a system capable of sustaining the development of science and technology; * Development of scientific potential, modernisation of scientific infrastructure; * Promotion of basic and applied research; * Creation of a synergistic system of education, science and innovation; and * Becoming a prime location for scientific specialisation in the European Research Area. Based on this strategy, the accompanying ''Action Plan'' was approved by the government in June 2011. It defines the following targets: * Improve the management system for science and technology and create the requisite conditions for sustainable development; * Involve more young, talented people in education and research, while upgrading research infrastructure; * Create the requisite conditions for the development of an integrated national innovation system; and * Enhance international co-operation in research and development. Although the ''Strategy'' clearly pursues a 'science push' approach, with public research institutes serving as the key policy target, it nevertheless mentions the goal of establishing an innovation system. However, the main driver of innovation, the business sector, is not mentioned. In between publishing the ''Strategy'' and ''Action Plan'', the government issued a resolution in May 2010 on ''Science and Technology Development Priorities for 2010вАУ2014''. These priorities are: * Armenian studies, humanities and social sciences; * Life sciences; * Renewable energy, new energy sources; * Advanced technologies, information technologies; * Space, Earth sciences, sustainable use of natural resources; and * Basic research promoting essential applied research. The Law on the National Academy of Sciences was adopted in May 2011. This law is expected to play a key role in shaping the Armenian innovation system. It allows the National Academy of Sciences to extend its business activities to the commercialisation of research results and the creation of spin-offs; it also makes provision for restructuring the National Academy of Sciences by combining institutes involved in closely related research areas into a single body. Three of these new centres are particularly relevant: the Centre for Biotechnology, the Centre for Zoology and Hydro-ecology and the Centre for Organic and Pharmaceutical Chemistry. The government is focusing its support on selected industrial sectors. More than 20 projects have been cofunded by the State Committee of Science in targeted branches: pharmaceuticals, medicine and biotechnology, agricultural mechanisation and machine building, electronics, engineering, chemistry and, in particular, the sphere of information technology. Over the past decade, the government has made an effort to encourage scienceвАУindustry linkages. The Armenian information technology sector has been particularly active: a number of publicвАУprivate partnerships have been established between companies and universities, in order to give students marketable skills and generate innovative ideas at the interface of science and business. Examples are Synopsys Inc. and the Enterprise Incubator Foundation. Armenia was ranked 63rd in the Global Innovation Index in 2024.Demographics
Armenia has a population of 3,081,100 as of 2025 and is the third most densely populated of the former Soviet republics. There has been a problem of population decline due to elevated levels of emigration after the break-up of the USSR. In the past years emigration levels have declined and some population growth is observed since 2012. Armenia has Armenian diaspora, a relatively large external diaspora (8 million by some estimates, greatly exceeding the 3 million population of Armenia itself), with communities existing across the globe. The largest Armenian communities outside of Armenia can be found in Russia, France, Iran, the United States, Georgia, Syria, Lebanon, Australia, Canada, Greece, Cyprus, Israel, Poland, Ukraine and Brazil. 40,000 to 70,000 Armenians still live in Turkey (mostly in and around Istanbul).
About 1,000 Armenians reside in the Armenian Quarter in the Old City (Jerusalem), Old City of Jerusalem, a remnant of a once-larger community. Italy is home to the San Lazzaro degli Armeni, an island located in the Venetian Lagoon, which is completely occupied by a monastery run by the Mechitarists, an Armenian Catholic Church, Armenian Catholic congregation. Approximately 139,000 Armenians lived in the de facto independent country
Armenia has Armenian diaspora, a relatively large external diaspora (8 million by some estimates, greatly exceeding the 3 million population of Armenia itself), with communities existing across the globe. The largest Armenian communities outside of Armenia can be found in Russia, France, Iran, the United States, Georgia, Syria, Lebanon, Australia, Canada, Greece, Cyprus, Israel, Poland, Ukraine and Brazil. 40,000 to 70,000 Armenians still live in Turkey (mostly in and around Istanbul).
About 1,000 Armenians reside in the Armenian Quarter in the Old City (Jerusalem), Old City of Jerusalem, a remnant of a once-larger community. Italy is home to the San Lazzaro degli Armeni, an island located in the Venetian Lagoon, which is completely occupied by a monastery run by the Mechitarists, an Armenian Catholic Church, Armenian Catholic congregation. Approximately 139,000 Armenians lived in the de facto independent country Republic of Artsakh
Artsakh ( ), officially the Republic of Artsakh or the Republic of Nagorno-Karabakh ( ), was a breakaway state in the South Caucasus whose territory was internationally recognised as part of Azerbaijan. Between 1991 and 2023, Artsakh cont ...
where they formed a majority before 1 October 2023, when almost the entire population of the region had fled to Armenia.
Cities
Ethnic groups
 Ethnic
Ethnic Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiq ...
make up 98.1% of the population. Yazidis make up 1.1%, and Russians 0.5%. Other minorities include Assyrian people, Assyrians, Ukrainians, Pontic Greeks, Greeks (usually called Caucasus Greeks), Kurdish people, Kurds, Georgians, Belarusians, and History of the Jews in Armenia, Jews. There are also smaller communities of Vlachs, Mordvins, Ossetians, Udi people, Udis, and Tat people (Caucasus), Tats. Minorities of Polish people, Poles and Caucasus Germans also exist though they are heavily Russification, Russified., part of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, OSCE As of 2022, there are 31,077 Yazidis in Armenia.
During the Soviet era, Azerbaijanis were historically the second largest population in the country, numbering 76,550 in 1922, and forming about 2.5% in 1989.The All-Union Population Census of 1989. ''Demoscope.ru'' However, due to the conflict over Nagorno-Karabakh, virtually all of them emigrated from Armenia to Azerbaijan. Conversely, Armenia received a large influx of Armenian refugees from Azerbaijan, thus giving Armenia a more homogeneous character. According to Gallup research conducted in 2017 Armenia has one of the highest migrant acceptance (welcoming) rates in eastern Europe.
Languages
Armenians have their own distinct Armenian alphabet, alphabet and Armenian language, language, which is the only official language. The alphabet was invented by Mesrop Mashtots and consists of thirty-nine letters, three of which were added during the Kingdom of Cilicia, Cilician period. The main foreign languages that Armenians know are Russian and English. Due to its Soviet past, most of the old population can speak Russian quite well. According to a 2013 survey, 95% of Armenians said they had some knowledge of Russian (24% advanced, 59% intermediate) compared to 40% who said they knew some English (4% advanced, 16% intermediate and 20% beginner). However, more adults (50%) think that English should be taught in public secondary schools than those who prefer Russian (44%).Religion
Armenia was the first nation to adoptChristianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
as a state religion, an event traditionally dated to AD 301.
The predominant religion in Armenia is Christianity. Its roots go back to the 1st century AD, when it was founded by two of Jesus' twelve Twelve Apostles, apostles вАУ Jude the Apostle, Thaddaeus and Bartholomew the Apostle, Bartholomew вАУ who preached Christianity in Armenia between AD 40вАУ60.
Over 93% of Christians in Armenia belong to the Armenian Apostolic Church
The Armenian Apostolic Church () is the Autocephaly, autocephalous national church of Armenia. Part of Oriental Orthodoxy, it is one of the most ancient Christianity, Christian churches. The Armenian Apostolic Church, like the Armenian Catholic ...
, which is in communion only with the churches comprising Oriental Orthodoxy#Oriental Orthodox Communion, Oriental OrthodoxyвАФof which it is itself a member.
The Catholic Church maintains jurisdictions of both the Latin Church and Armenian Catholic Church in Armenia. Of note are the Mechitarists (also spelled "Mekhitarists" ), a congregation of Order of Saint Benedict, Benedictine monks in the Armenian Catholic Church, founded in 1712 by Mekhitar of Sebaste. They are best known for their series of scholarly publications of ancient Armenians, Armenian versions of otherwise lost ancient Greek texts.
The Armenian Evangelical Church has several thousand members throughout the country.
Other Christian denominations in Armenia are the Pentecostal branches of Protestant community such as the Word of Life, the Armenian Brotherhood Church, the Baptists (which are known as one of the oldest existing denominations in Armenia, and were permitted by the authorities of the Soviet Union), and Presbyterians.
Armenia is also home to a Russians in Armenia, Russian community of Molokans which practice a form of Spiritual Christianity originated from the Russian Orthodox Church.
The Yazidis, who live in the western part of the country, practice Yazidism. The world's largest Yazidi temple, Quba M√™r√™ D√Ѓwan√™, was completed in 2019 in the village of Aknalich.
There is a History of the Jews in Armenia, Jewish community in Armenia of approximately 750 people since independence with most emigrants leaving for Israel. There are currently two synagogues in Armenia вАУ one in the capital, Yerevan, and the other in the city of Sevan (city), Sevan located near Lake Sevan.
Health care
Healthcare in Armenia has undergone significant changes since independence in 1991. Initially, the Soviet healthcare system was highly centralized and provided free medical assistance to all citizens. After independence, the healthcare system underwent reform and primary care services have been free of charge since 2006. Despite improvements in accessibility and the implementation of an Open Enrollment programme, out-of-pocket health expenditures remain high and corruption among healthcare professionals remains a concern. In 2019, healthcare became free for all citizens under the age of 18 and the number of people receiving free or subsidized care under the Basic Benefits Package was increased. After a significant decline in earlier decades, crude birth rates in Armenia slightly increased from 13.0 (per 1000 people) in the year 1998 to 14.2 in 2015; this timeframe also showed a similar trajectory in the crude death rate, which grew from 8.6 to 9.3. Life expectancy, Life expectancy at birth at 74.8 years was the 4th-highest among the Post-Soviet states in 2014.Education
 In medieval times, the University of Gladzor and Tatev Monastery#Tatev University, University of Tatev took an important role for Armenian education.
A literacy rate of 100% was reported as early as 1960.Curtis, Glenn E. and Ronald G. Suny. "Education"
In medieval times, the University of Gladzor and Tatev Monastery#Tatev University, University of Tatev took an important role for Armenian education.
A literacy rate of 100% was reported as early as 1960.Curtis, Glenn E. and Ronald G. Suny. "Education"Armenia: A Country Study
. Library of Congress Federal Research Division (March 1994). ''This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.'' Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic, In the communist era, Armenian education followed the standard Soviet model of complete state control (from Moscow) of curriculum, curricula and teaching methods and close integration of education activities with other aspects of society, such as politics, culture, and the economy. In the 1988вАУ89 school year, 301 students per 10,000 were in specialized secondary or higher education, a figure slightly lower than the Soviet average. In 1989, some 58% of Armenians over age fifteen had completed their secondary education, and 14% had a higher education. In the 1990вАУ91 school year, the estimated 1,307 primary and secondary schools were attended by 608,800 students. Another seventy specialised secondary institutions had 45,900 students, and 68,400 students were enrolled in a total of ten postsecondary institutions that included universities. In addition, 35% of eligible children attended preschool education, preschools. In 1992 Armenia's largest institution of higher learning, Yerevan State University, had eighteen departments, including ones for social sciences, sciences, and law. Its faculty numbered about 1,300 teachers and its student population about 10,000 students. The National Polytechnic University of Armenia is operating since 1933. In the early 1990s, Armenia made substantial changes to the centralised and regimented Soviet system. Because at least 98% of students in higher education were Armenian, curricula began to emphasise History of Armenia, Armenian history and culture.
Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian diaspora, Armenian communities around the ...
became the dominant language of instruction, and many schools that had taught in Russian closed by the end of 1991. Russian was still widely taught, however, as a second language.
In 2014, the National Programme for Educational Excellence embarked on creating an internationally competitive and academically rigorous alternative educational programme (the Araratian Baccalaureate) for Armenian schools and increasing the importance and status of the teacher's role in society.
The Ministry of Education and Science is responsible for regulation of the sector. Primary and secondary education in Armenia is free, and completion of secondary school is compulsory. Higher education in Armenia is harmonized with the Bologna Process, Bologna process and the European Higher Education Area. The Armenian National Academy of Sciences plays an important role in postgraduate education.
Schooling takes 12 years in Armenia and breaks down into primary (4 years), middle (5 years) and high school (3 years). Schools engage a 10-grade mark system. The government also supports List of Armenian schools#Schools outside Armenia, Armenian schools outside of Armenia.
Gross enrollment in tertiary education at 44% in 2015 surpassed peer countries of the South Caucasus but remained below the average for Europe and Central Asia. However, public spending per student in tertiary education in GDP-ratio terms is one of the lowest for post-USSR countries (for which data was available).
Culture
Architecture
Armenian architecture, as it originates in an earthquake-prone region, tends to be built with this hazard in mind. Armenian buildings tend to be rather low-slung and thick-walled in design. Armenia has abundant resources of stone, and relatively few forests, so stone was nearly always used throughout for large buildings. Small buildings and most residential buildings were normally constructed of lighter materials, and hardly any early examples survive, as at the abandoned medieval capital of Ani.Music and dance
Western Armenia
Western Armenia (Western Armenian: ‘±÷А’•÷В’і’њ’•’°’ґ ’А’°’µ’°’љ’њ’°’ґ, ''Arevmdian Hayasdan'') is a term to refer to the western parts of the Armenian highlands located within Turkey (formerly the Ottoman Empire) that comprise the historic ...
, and many artists also played the contemporary popular songs of Turkey and other Middle Eastern countries from which the Armenians emigrated.
 Richard Hagopian is perhaps the most famous artist of the traditional "kef" style and the Vosbikian Band was notable in the 1940s and 1950s for developing their own style of "kef music" heavily influenced by the popular American Big Band Jazz of the time. Later, stemming from the Middle Eastern Armenian diaspora and influenced by Continental European (especially French) pop music, the Armenian pop music genre grew to fame in the 1960s and 1970s with artists such as Adiss Harmandian and Harout Pamboukjian performing to the Armenian diaspora and Armenia; also with artists such as Sirusho, performing pop music combined with Armenian folk music in today's entertainment industry.
Other Armenian diasporans that rose to fame in classical or international music circles are world-renowned List of French-Armenians, French-Armenian singer and composer Charles Aznavour, pianist Sahan Arzruni, prominent opera sopranos such as Hasmik Papian and more recently Isabel Bayrakdarian and Anna Kasyan. Certain Armenians settled to sing non-Armenian tunes such as the heavy metal band System of a Down (which nonetheless often incorporates traditional Armenian instrumentals and styling into their songs) or pop star Cher. In the Armenian diaspora, Armenian Revolutionary Songs, Armenian revolutionary songs are popular with the youth. These songs encourage Armenian patriotism and are generally about Armenian history and national heroes.
Richard Hagopian is perhaps the most famous artist of the traditional "kef" style and the Vosbikian Band was notable in the 1940s and 1950s for developing their own style of "kef music" heavily influenced by the popular American Big Band Jazz of the time. Later, stemming from the Middle Eastern Armenian diaspora and influenced by Continental European (especially French) pop music, the Armenian pop music genre grew to fame in the 1960s and 1970s with artists such as Adiss Harmandian and Harout Pamboukjian performing to the Armenian diaspora and Armenia; also with artists such as Sirusho, performing pop music combined with Armenian folk music in today's entertainment industry.
Other Armenian diasporans that rose to fame in classical or international music circles are world-renowned List of French-Armenians, French-Armenian singer and composer Charles Aznavour, pianist Sahan Arzruni, prominent opera sopranos such as Hasmik Papian and more recently Isabel Bayrakdarian and Anna Kasyan. Certain Armenians settled to sing non-Armenian tunes such as the heavy metal band System of a Down (which nonetheless often incorporates traditional Armenian instrumentals and styling into their songs) or pop star Cher. In the Armenian diaspora, Armenian Revolutionary Songs, Armenian revolutionary songs are popular with the youth. These songs encourage Armenian patriotism and are generally about Armenian history and national heroes.
Art
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
and even Stone Age sites are all within a few hours drive from the city. All but the most spectacular remain virtually undiscovered, allowing visitors to view churches and fortresses in their original settings.
 The National Art Gallery in Yerevan has more than 16,000 works that date back to the
The National Art Gallery in Yerevan has more than 16,000 works that date back to the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, which indicate Armenia's rich tales and stories of the times. It houses paintings by many Ethnic groups in Europe, European masters as well. The Modern Art Museum, the Children's Picture Gallery, and the Martiros Saryan Museum are only a few of the other noteworthy collections of fine art on display in Yerevan. Moreover, many private galleries are in operation, with many more opening every year, featuring rotating exhibitions and sales.
On 13 April 2013, the Armenian government announced a change in law to allow freedom of panorama for 3D works of art.
Media
Television, magazines, and newspapers are all operated by both state-owned and for-profit corporations which depend on advertising, subscription, and other sales-related revenues. The Constitution of Armenia guarantees freedom of speech and Armenia ranks 61st in the 2020 Press Freedom Index report compiled by Reporters Without Borders, betweenGeorgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
and Poland. Armenia's press freedom rose considerably following the 2018 Velvet Revolution.
As of 2020, the biggest issue facing press freedom in Armenia is judicial harassment of journalists, specifically defamation suits and attacks on journalists' right to protect sources, as well as excessive responses to combat disinformation spread by social media users. Reporters Without Borders also cites continued concerns about lack of transparency regarding ownership of media outlets.
Cinema
Cinema of Armenia, Cinema in Armenia was officially established on 16 April 1923, with the founding of the Armenian State Committee of Cinema by a decree of the Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic, Soviet Armenian government. Prior to this, the first Armenian film, titled "Haykakan Sinema", was produced in 1912 in Cairo by Armenians in Egypt, Armenian-Egyptian publisher Vahan Zartarian and premiered on 13 March 1913. In March 1924, the first Armenian film studio, Armenfilm was established inYerevan
Yerevan ( , , ; ; sometimes spelled Erevan) is the capital and largest city of Armenia, as well as one of the world's List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerev ...
, beginning with the documentary film "Soviet Armenia".
"Namus (film), Namus" directed by Hamo Beknazarian in 1925, was the first Armenian silent Black-and-white, black-and-white film. Based on Alexander Shirvanzade's 1885 novel, it portrays the tragic fate of two lovers whose engagement is thwarted due to violations of "namus" (a tradition of honor), leading the girl's father to marry her to another man.
The first Armenian sound film, "Pepo (film), Pepo," was directed by Hamo Beknazarian in 1935.
Cuisine
 Armenian cuisine is closely related to eastern and Mediterranean cuisine; various spices, vegetables, fish, and fruits combine to present unique dishes. The main characteristics of Armenian cuisine are a reliance on the quality of the ingredients rather than heavily spicing food, the use of herbs, the use of wheat in a variety of forms, of legumes, nuts, and fruit (as a main ingredient as well as to sour food), and the stuffing of a wide variety of leaves.
The pomegranate, with its symbolic association with fertility, represents the nation. The apricot is the national fruit.
Armenian cuisine is closely related to eastern and Mediterranean cuisine; various spices, vegetables, fish, and fruits combine to present unique dishes. The main characteristics of Armenian cuisine are a reliance on the quality of the ingredients rather than heavily spicing food, the use of herbs, the use of wheat in a variety of forms, of legumes, nuts, and fruit (as a main ingredient as well as to sour food), and the stuffing of a wide variety of leaves.
The pomegranate, with its symbolic association with fertility, represents the nation. The apricot is the national fruit.
Sport
 A wide array of sports are played in Armenia, the most popular among them being wrestling, weightlifting, judo, association football, chess, and boxing. Armenia's mountainous terrain provides great opportunities for the practice of sports like skiing and climbing. Being a landlocked country, water sports can only be practised on lakes, notably Lake Sevan. Competitively, Armenia has been successful in chess, weightlifting and wrestling at the international level. Armenia is also an active member of the international sports community, with full membership in the Union of European Football Associations (UEFA) and International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF). It also hosts the Pan-Armenian Games.
Prior to 1992, Armenians would participate in the Olympics representing the USSR. As part of the Soviet Union, Armenia was very successful, winning plenty of medals and helping the USSR win the medal standings at the Olympics on numerous occasions. The first medal won by an Armenian in modern Olympic history was by Hrant Shahinyan (sometimes spelled as Grant Shaginyan), who won two golds and two silvers in gymnastics at the 1952 Summer Olympics in Helsinki. To highlight the level of success of Armenians in the Olympics, Shahinyan was quoted as saying:
"Armenian sportsmen had to outdo their opponents by several notches for the shot at being accepted into any Soviet team. But those difficulties notwithstanding, 90 percent of Armenian athletes on Soviet Olympic teams came back with medals."
Armenia first participated at the 1992 Summer Olympics in Barcelona under a unified CIS team, where it was very successful, winning three golds and one silver in weightlifting, wrestling and sharp shooting, despite only having five athletes. Since the 1994 Winter Olympics in Lillehammer, Armenia has participated as an independent nation.
Armenia participates in the Summer Olympic Games in boxing, wrestling, weightlifting, judo, gymnastics, track and field, diving, swimming and sharp shooting. It also participates in the Winter Olympic Games in alpine skiing, cross-country skiing and figure skating.
Football in Armenia, Football is also popular in Armenia. The most successful team was the FC Ararat Yerevan team of the 1970s who won the Soviet Cup in 1973 and 1975 and the Soviet Top League 1973, Soviet Top League in 1973. The latter achievement saw FC Ararat gain entry to the 1974вАУ75 European Cup, European Cup where вАУ despite a home victory in the second leg вАУ they lost on aggregate at the quarter-final stage to eventual winner FC Bayern Munich. Armenia competed internationally as part of the USSR national football team until the Armenian national football team was formed in 1992 after the split of the Soviet Union. Armenia have never qualified for a major tournament although recent improvements saw the team to achieve 44th position in the FIFA World Rankings in September 2011. The national team is controlled by the Football Federation of Armenia. The Armenian Premier League is the highest level football competition in Armenia, and has been dominated by FC Pyunik in recent seasons. The league currently consists of eight teams and relegates to the Armenian First League.
Armenia and the Armenian diaspora have produced many successful footballers, including Henrikh Mkhitaryan, Youri Djorkaeff, Alain Boghossian, Andranik Eskandarian, Andranik Teymourian, Edgar Manucharyan, Khoren Oganesian and Nikita Simonyan. Djokaeff and Boghossian won the 1998 FIFA World Cup with France national football team, France, Teymourian competed in the 2006 FIFA World Cup, 2006 World Cup for Iran national football team, Iran and Manucharyan played in the Dutch Eredivisie for AFC Ajax, Ajax. Mkhitaryan has been one of the most successful Armenian footballers in recent years, playing for international clubs such as Borussia Dortmund, Manchester United F.C., Manchester United, Arsenal F.C., Arsenal, A.S. Roma and currently for Inter Milan.
Wrestling has been a successful sport in the Olympics for Armenia. At the Armenia at the 1996 Summer Olympics, 1996 Summer Olympics in Atlanta, Armen Nazaryan won the gold in the Men's Greco-Roman wrestling, Greco-Roman Flyweight (52 kg) category and Armen Mkrtchyan won the silver in Men's Freestyle wrestling, Freestyle Paperweight (48 kg) category, securing Armenia's first two medals in its Olympic history.
Traditional Armenian wrestling is called Kokh and practised in traditional garb; it was one of the influences included in the Soviet combat sport of Sambo (martial art), Sambo, which is also very popular.
The Politics of Armenia, government of Armenia budgets about $2.8 million annually for sports and gives it to the National Committee of Physical Education and Sports, the body that determines which programmes should benefit from the funds.
Due to the lack of success lately on the international level, in recent years, Armenia has rebuilt 16 Soviet-era sports schools and furnished them with new equipment for a total cost of $1.9 million. The rebuilding of the regional schools was financed by the Armenian government. $9.3 million has been invested in the resort town of Tsaghkadzor to improve the winter sports infrastructure because of dismal performances at recent winter sports events. In 2005, a cycling centre was opened in
A wide array of sports are played in Armenia, the most popular among them being wrestling, weightlifting, judo, association football, chess, and boxing. Armenia's mountainous terrain provides great opportunities for the practice of sports like skiing and climbing. Being a landlocked country, water sports can only be practised on lakes, notably Lake Sevan. Competitively, Armenia has been successful in chess, weightlifting and wrestling at the international level. Armenia is also an active member of the international sports community, with full membership in the Union of European Football Associations (UEFA) and International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF). It also hosts the Pan-Armenian Games.
Prior to 1992, Armenians would participate in the Olympics representing the USSR. As part of the Soviet Union, Armenia was very successful, winning plenty of medals and helping the USSR win the medal standings at the Olympics on numerous occasions. The first medal won by an Armenian in modern Olympic history was by Hrant Shahinyan (sometimes spelled as Grant Shaginyan), who won two golds and two silvers in gymnastics at the 1952 Summer Olympics in Helsinki. To highlight the level of success of Armenians in the Olympics, Shahinyan was quoted as saying:
"Armenian sportsmen had to outdo their opponents by several notches for the shot at being accepted into any Soviet team. But those difficulties notwithstanding, 90 percent of Armenian athletes on Soviet Olympic teams came back with medals."
Armenia first participated at the 1992 Summer Olympics in Barcelona under a unified CIS team, where it was very successful, winning three golds and one silver in weightlifting, wrestling and sharp shooting, despite only having five athletes. Since the 1994 Winter Olympics in Lillehammer, Armenia has participated as an independent nation.
Armenia participates in the Summer Olympic Games in boxing, wrestling, weightlifting, judo, gymnastics, track and field, diving, swimming and sharp shooting. It also participates in the Winter Olympic Games in alpine skiing, cross-country skiing and figure skating.
Football in Armenia, Football is also popular in Armenia. The most successful team was the FC Ararat Yerevan team of the 1970s who won the Soviet Cup in 1973 and 1975 and the Soviet Top League 1973, Soviet Top League in 1973. The latter achievement saw FC Ararat gain entry to the 1974вАУ75 European Cup, European Cup where вАУ despite a home victory in the second leg вАУ they lost on aggregate at the quarter-final stage to eventual winner FC Bayern Munich. Armenia competed internationally as part of the USSR national football team until the Armenian national football team was formed in 1992 after the split of the Soviet Union. Armenia have never qualified for a major tournament although recent improvements saw the team to achieve 44th position in the FIFA World Rankings in September 2011. The national team is controlled by the Football Federation of Armenia. The Armenian Premier League is the highest level football competition in Armenia, and has been dominated by FC Pyunik in recent seasons. The league currently consists of eight teams and relegates to the Armenian First League.
Armenia and the Armenian diaspora have produced many successful footballers, including Henrikh Mkhitaryan, Youri Djorkaeff, Alain Boghossian, Andranik Eskandarian, Andranik Teymourian, Edgar Manucharyan, Khoren Oganesian and Nikita Simonyan. Djokaeff and Boghossian won the 1998 FIFA World Cup with France national football team, France, Teymourian competed in the 2006 FIFA World Cup, 2006 World Cup for Iran national football team, Iran and Manucharyan played in the Dutch Eredivisie for AFC Ajax, Ajax. Mkhitaryan has been one of the most successful Armenian footballers in recent years, playing for international clubs such as Borussia Dortmund, Manchester United F.C., Manchester United, Arsenal F.C., Arsenal, A.S. Roma and currently for Inter Milan.
Wrestling has been a successful sport in the Olympics for Armenia. At the Armenia at the 1996 Summer Olympics, 1996 Summer Olympics in Atlanta, Armen Nazaryan won the gold in the Men's Greco-Roman wrestling, Greco-Roman Flyweight (52 kg) category and Armen Mkrtchyan won the silver in Men's Freestyle wrestling, Freestyle Paperweight (48 kg) category, securing Armenia's first two medals in its Olympic history.
Traditional Armenian wrestling is called Kokh and practised in traditional garb; it was one of the influences included in the Soviet combat sport of Sambo (martial art), Sambo, which is also very popular.
The Politics of Armenia, government of Armenia budgets about $2.8 million annually for sports and gives it to the National Committee of Physical Education and Sports, the body that determines which programmes should benefit from the funds.
Due to the lack of success lately on the international level, in recent years, Armenia has rebuilt 16 Soviet-era sports schools and furnished them with new equipment for a total cost of $1.9 million. The rebuilding of the regional schools was financed by the Armenian government. $9.3 million has been invested in the resort town of Tsaghkadzor to improve the winter sports infrastructure because of dismal performances at recent winter sports events. In 2005, a cycling centre was opened in Yerevan
Yerevan ( , , ; ; sometimes spelled Erevan) is the capital and largest city of Armenia, as well as one of the world's List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerev ...
with the aim of helping produce world class Armenian cyclists. The government has also promised a cash reward of $700,000 to Armenians who win a gold medal at the Olympics.
Armenia has also been very successful in chess, winning the World Team Chess Championship, World Champion in 2011 and the Chess Olympiad, World Chess Olympiad on three occasions.
See also
*Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiq ...
* History of Armenia
* Index of Armenia-related articles
* Outline of Armenia
Explanatory notes
Source attribution
*Citations
Sources
*External links
* *Key Development Forecasts for Armenia
from International Futures {{Authority control Armenia, Armenian-speaking countries and territories Caucasus Christian states Countries in Asia Countries in Europe Member states of the United Nations Landlocked countries Member states of the Commonwealth of Independent States Member states of the Council of Europe Member states of the Eurasian Economic Union Member states of the Collective Security Treaty Organization Republics South Caucasus States and territories established in 1918 States and territories established in 1991 States and territories disestablished in 1920 West Asian countries States with limited recognition 1991 establishments in Europe