|
Velopharyngeal Port
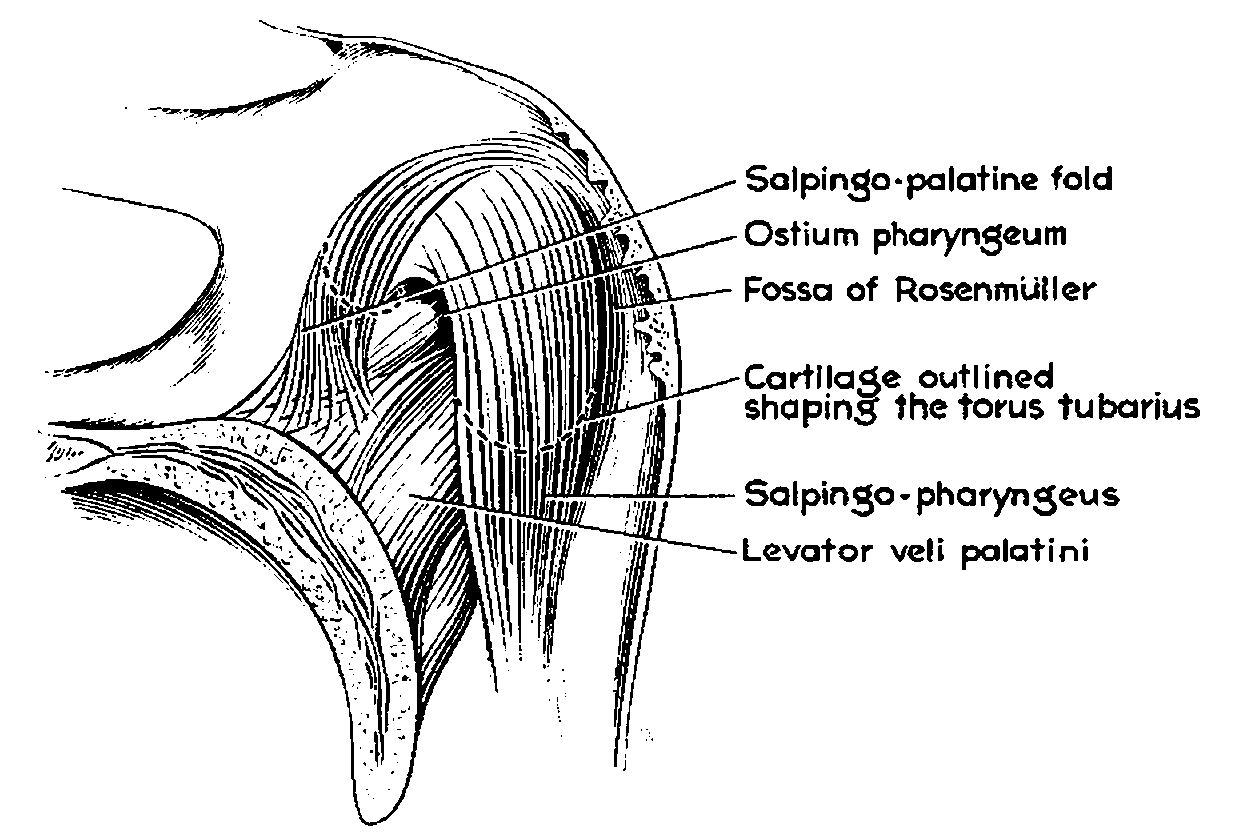
The velopharyngeal port or velopharyngeal sphincter is the passage between the nasopharynx and the oropharynx. It is closed off by the soft palate and uvula against the rear pharyngeal wall during swallowing to prevent food and water from entering the nasal passages. During speech, it is open for nasal sounds and closed for oral sounds. It is affected by cleft palate, resulting in velopharyngeal consonant The velopharyngeal fricatives, also known as the posterior nasal fricatives, are a family of sounds produced by some children with speech disorders, including some with a cleft palate, as a substitute for sibilants (in English, ), which canno ...s. Pharynx Human throat Human voice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food to the esophagus and air to the larynx. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx. In humans, the pharynx is part of the Digestion, digestive system and the conducting zone of the respiratory system. (The conducting zone—which also includes the nostrils of the Human nose, nose, the larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchi, and bronchioles—filters, warms, and moistens air and conducts it into the lungs). The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx (hypopharynx). In humans, two sets of pharyngeal muscles form the pharynx and determine the shape of its lumen (anatomy), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory System
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies greatly, depending on the size of the organism, the environment in which it lives and its evolutionary history. In terrestrial animal, land animals, the respiratory surface is internalized as linings of the lungs. Gas exchange in the lungs occurs in millions of small air sacs; in mammals and reptiles, these are called pulmonary alveolus, alveoli, and in birds, they are known as Bird anatomy#Respiratory system, atria. These microscopic air sacs have a very rich blood supply, thus bringing the air into close contact with the blood. These air sacs communicate with the external environment via a system of airways, or hollow tubes, of which the largest is the trachea, which branches in the middle of the chest into the two main bronchus, bronchi. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
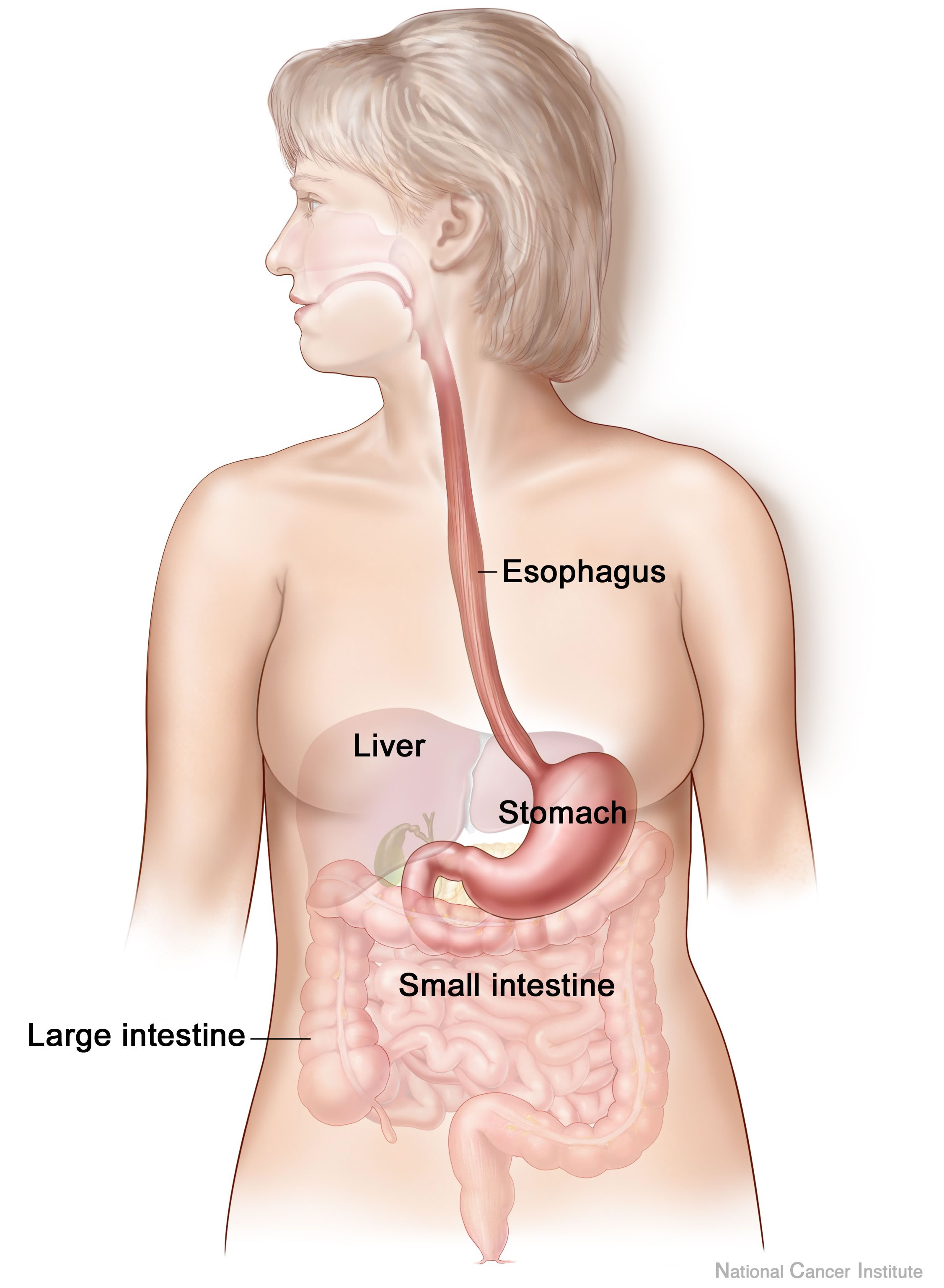
Digestive System
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has three stages: the cephalic phase, the gastric phase, and the intestinal phase. The first stage, the cephalic phase of digestion, begins with secretions from gastric glands in response to the sight and smell of food, and continues in the human mouth, mouth with the mechanical breakdown of food by chewing, and the chemical breakdown by digestive enzymes in the saliva. Saliva contains amylase, and lingual lipase, secreted by the salivary glands, and serous glands on the tongue. Chewing mixes the food with saliva to produce a Bolus (digestion), bolus to be Swallowing, swallowed down the esophagus to enter the stomach. The second stage, the gastric phase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasopharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food to the esophagus and air to the larynx. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx. In humans, the pharynx is part of the digestive system and the conducting zone of the respiratory system. (The conducting zone—which also includes the nostrils of the nose, the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles—filters, warms, and moistens air and conducts it into the lungs). The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx (hypopharynx). In humans, two sets of pharyngeal muscles form the pharynx and determine the shape of its lumen. They are arranged as an inner layer of longitudina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soft Palate
The soft palate (also known as the velum, palatal velum, or muscular palate) is, in mammals, the soft biological tissue, tissue constituting the back of the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is part of the palate of the mouth; the other part is the hard palate. The soft palate is distinguished from the hard palate at the front of the mouth in that it does not contain bone. Structure Muscles The five muscles of the soft palate play important roles in swallowing and breathing. The muscles are: # Tensor veli palatini, which is involved in swallowing # Palatoglossus, involved in swallowing # Palatopharyngeus, involved in breathing # Levator veli palatini, involved in swallowing # Musculus uvulae, which moves the palatine uvula, uvula These muscles are innervated by the pharyngeal plexus of vagus nerve, pharyngeal plexus via the vagus nerve, with the exception of the tensor veli palatini. The tensor veli palatini is innervated by the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uvula
The uvula (: uvulas or uvulae), also known as the palatine uvula or staphyle, is a conic projection from the back edge of the middle of the soft palate, composed of connective tissue containing a number of racemose glands, and some muscular fibers. It also contains many serous glands, which produce thin saliva. It is only found in humans. Structure Muscle The muscular part of the uvula () shortens and broadens the uvula. This changes the contour of the posterior part of the soft palate. This change in contour allows the soft palate to adapt closely to the posterior pharyngeal wall to help close the nasopharynx during swallowing. Its muscles are controlled by the pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve. Variation A bifid or bifurcated uvula is a split or cleft uvula. Newborns with cleft palate often also have a split uvula. The bifid uvula results from incomplete fusion of the palatine shelves but it is considered only a slight form of clefting. Bifid uvulas have les ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Sound
In phonetics, nasalization (or nasalisation in British English) is the production of a sound while the velum is lowered, so that some air escapes through the nose during the production of the sound by the mouth. An archetypal nasal sound is . In the International Phonetic Alphabet, nasalization is indicated by printing a tilde diacritic above the symbol for the sound to be nasalized: is the nasalized equivalent of , and is the nasalized equivalent of . A subscript diacritic , called an or , is sometimes seen, especially when the vowel bears tone marks that would interfere with the superscript tilde. For example, are more legible in most fonts than . Nasal vowels Many languages have nasal vowels to different degrees, but only a minority of world languages around the world have nasal vowels as contrasting phonemes. That is the case, among others, of French, Portuguese, Hindustani, Nepali, Breton, Gheg Albanian, Hmong, Hokkien, Yoruba, and Cherokee. Those nasal vowels co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleft Palate
A cleft lip contains an opening in the upper lip that may extend into the nose. The opening may be on one side, both sides, or in the middle. A cleft palate occurs when the palate (the roof of the mouth) contains an opening into the nose. The term orofacial cleft refers to either condition or to both occurring together. These disorders can result in feeding problems, speech problems, hearing problems, and frequent ear infections. Less than half the time the condition is associated with other disorders. Cleft lip and palate are the result of tissues of the face not joining properly during development. As such, they are a type of birth defect. The cause is unknown in most cases. Risk factors include smoking during pregnancy, diabetes, obesity, an older mother, and certain medications (such as some used to treat seizures). Cleft lip and cleft palate can often be diagnosed during pregnancy with an ultrasound exam. A cleft lip or palate can be successfully treated with surge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velopharyngeal Consonant
The velopharyngeal fricatives, also known as the posterior nasal fricatives, are a family of sounds produced by some children with speech disorders, including some with a cleft palate, as a substitute for sibilants (in English, ), which cannot be produced with a cleft palate. It results from "the approximation but inadequate closure of the upper border of the velum and the posterior pharyngeal wall."Martin Duckworth, George Allen, William Hardcastle & Martin Ball (1990) 'Extensions to the International Phonetic Alphabet for the transcription of atypical speech'. Clinical Linguistics & Phonetics 4: 4, p. 276. To produce a velopharyngeal fricative, the soft palate approaches the pharyngeal wall and narrows the velopharyngeal port, such that the restricted port creates fricative turbulence in air forced through it into the nasal cavity. The articulation may be aided by a posterior positioning of the tongue and may involve velar flutter (a snorting sound). The term 'velopharyng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Throat
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are great apes characterized by their hairlessness, bipedalism, and high intelligence. Humans have large brains, enabling more advanced cognitive skills that facilitate successful adaptation to varied environments, development of sophisticated tools, and formation of complex social structures and civilizations. Humans are highly social, with individual humans tending to belong to a multi-layered network of distinct social groups — from families and peer groups to corporations and political states. As such, social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, languages, and traditions (collectively termed institutions), each of which bolsters human society. Humans are also highly curious: the desire to understand and influence phenomena has motivated humanity's development of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |