|
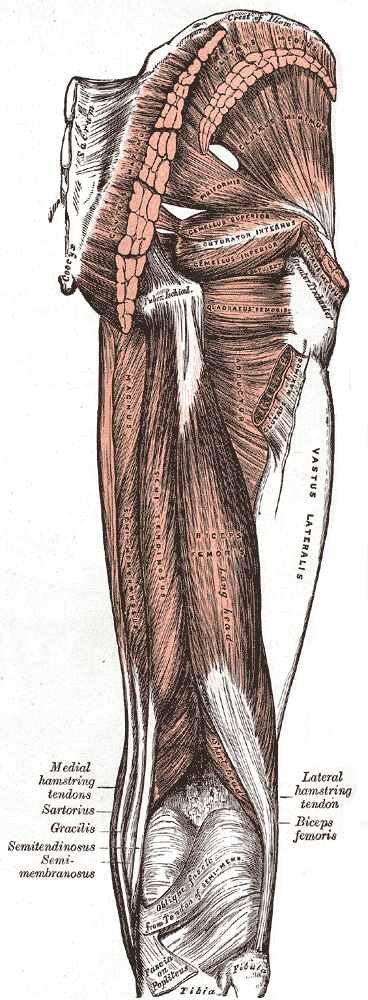
Vastus Muscle
The vastus muscles are three of the four muscles that make up the quadriceps femoris muscle of the thigh. The three muscles are the vastus intermedius, the vastus lateralis, and the vastus medialis located in the middle, on the outside, and inside of the thigh, respectively. The fourth muscle is the rectus femoris muscle a large fleshy muscle which covers the front and sides of the femur. Vastus intermedius The vastus intermedius arises from the front and lateral surfaces of the body of the femur in its upper two-thirds, sitting under the rectus femoris muscle and from the lower part of the lateral intermuscular septum. Its fibers end in a superficial aponeurosis, which forms the deep part of the quadriceps tendon. The vastus medialis and vastus intermedius appear to be inseparably united, but when the rectus femoris has been reflected a narrow interval will be observed extending upward from the medial border of the patella between the two muscles, and the separation may be con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectus Femoris Muscle
The rectus femoris muscle is one of the four quadriceps muscles of the human body. The others are the vastus medialis, the vastus intermedius (deep to the rectus femoris), and the vastus lateralis. All four parts of the quadriceps muscle attach to the patella (knee cap) by the quadriceps tendon. The rectus femoris is situated in the middle of the front of the thigh; it is fusiform in shape, and its superficial fibers are arranged in a bipenniform manner, the deep fibers running straight () down to the deep aponeurosis. Its functions are to flex the thigh at the hip joint and to extend the leg at the knee joint. Structure It arises by two tendons: one, the anterior or straight, from the anterior inferior iliac spine; the other, the posterior or reflected, from a groove above the rim of the acetabulum. The two unite at an acute angle and spread into an aponeurosis that is prolonged downward on the anterior surface of the muscle, and from this the muscular fibers arise. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Intermuscular Septum Of Thigh
The lateral intermuscular septum of thigh is a fold of deep fascia Deep fascia (or investing fascia) is a fascia, a layer of dense connective tissue that can surround individual muscles and groups of muscles to separate into fascial compartments. This fibrous connective tissue interpenetrates and surrounds the m ... in the thigh. It is between the vastus lateralis and biceps femoris. It separates the anterior compartment of the thigh from the posterior compartment of the thigh. See also * Medial intermuscular septum of thigh * Anterior compartment of thigh * Posterior compartment of thigh References External links Topographical Anatomy of the Lower Limb - Listed Alphabeticallyfrom UAMS Department of Neurobiology and Developmental Sciences from anatomy.med.umich.edu Lower limb anatomy {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadriceps Femoris Tendon
In human anatomy, the quadriceps tendon works with the quadriceps muscle to extend the leg. All four parts of the quadriceps muscle attach to the shin via the patella (knee cap), where the quadriceps tendon becomes the patellar ligament. It attaches the quadriceps to the top of the patella, which in turn is connected to the shin from its bottom by the patellar ligament. A tendon connects muscle to bone, while a ligament connects bone to bone.Saladin, Kenneth S. Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function. 6th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2012. Print. Injuries are common to this tendon, with tears, either partial or complete, being the most common. If the quadriceps tendon is completely torn, surgery will be required to regain function of the knee."Patellar Tendon Tear." OrthoInfo - AAOS. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, Aug. 2009. Web. 07 Dec. 2014. Without the quadriceps tendon, the knee cannot extend. Often, when the tendon is completely torn, part of the kne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biceps Femoris
The biceps femoris () is a muscle of the thigh located to the posterior, or back. As its name implies, it consists of two heads; the long head is considered part of the hamstring muscle group, while the short head is sometimes excluded from this characterization, as it only causes knee flexion (but not hip extension) and is activated by a separate nerve (the peroneal, as opposed to the tibial branch of the sciatic nerve). Structure It has two heads of origin: *the ''long head'' arises from the lower and inner impression on the posterior part of the tuberosity of the ischium. This is a common tendon origin with the semitendinosus muscle, and from the lower part of the sacrotuberous ligament. *the ''short head'', arises from the lateral lip of the linea aspera, between the adductor magnus and vastus lateralis extending up almost as high as the insertion of the gluteus maximus, from the lateral prolongation of the linea aspera to within 5 cm. of the lateral condyle; and from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Intermuscular Septum Of Thigh
The lateral intermuscular septum of thigh is a fold of deep fascia Deep fascia (or investing fascia) is a fascia, a layer of dense connective tissue that can surround individual muscles and groups of muscles to separate into fascial compartments. This fibrous connective tissue interpenetrates and surrounds the m ... in the thigh. It is between the vastus lateralis and biceps femoris. It separates the anterior compartment of the thigh from the posterior compartment of the thigh. See also * Medial intermuscular septum of thigh * Anterior compartment of thigh * Posterior compartment of thigh References External links Topographical Anatomy of the Lower Limb - Listed Alphabeticallyfrom UAMS Department of Neurobiology and Developmental Sciences from anatomy.med.umich.edu Lower limb anatomy {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gluteus Maximus
The gluteus maximus is the main extensor muscle of the hip in humans. It is the largest and outermost of the three gluteal muscles and makes up a large part of the shape and appearance of each side of the hips. It is the single largest muscle in the human body. Its thick fleshy mass, in a quadrilateral shape, forms the prominence of the buttocks. The other gluteal muscles are the medius and minimus, and sometimes informally these are collectively referred to as the glutes. Its large size is one of the most characteristic features of the muscular system in humans,Norman Eizenberg et al., ''General Anatomy: Principles and Applications'' (2008), p. 17. connected as it is with the power of maintaining the trunk in the erect posture. Other primates have much flatter hips and cannot sustain standing erectly. The muscle is made up of muscle fascicles lying parallel with one another, and are collected together into larger bundles separated by fibrous septa. Structure The gluteus maxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linea Aspera
The linea aspera () is a ridge of roughened surface on the posterior surface of the shaft of the femur. It is the site of attachments of muscles and the intermuscular septum. Its margins diverge above and below. The linea aspera is a prominent longitudinal ridge or crest, on the middle third of the bone, presenting a medial and a lateral lip, and a narrow rough, intermediate line. It is an important insertion point for the adductors and the lateral and medial intermuscular septa that divides the thigh into three compartments. The tension generated by muscle attached to the bones is responsible for the formation of the ridges. Structure Above Above, the linea aspera is prolonged by three ridges. * The lateral ridge is very rough, and runs almost vertically upward to the base of the greater trochanter. It is termed the gluteal tuberosity, and gives attachment to part of the gluteus maximus: its upper part is often elongated into a roughened crest, on which a more or less wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gluteal Tuberosity
The gluteal tuberosity is the lateral one of the three upward prolongations of the linea aspera of the femur, extending to the base of the greater trochanter. It serves as the principal insertion site for the gluteus maximus muscle. Structure The gluteal tuberosity is the lateral prolongation of three prolongations of the linea aspera that extending superior-ward from the superior extremity of the linea aspera on the posterior surface of the femur The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg. The Femo .... The gluteal tuberosity takes the form of either an elongated depression or a rough ridge. It extends from the linea aspera nearly vertically superior-ward to the base of the greater trochanter. Its superior part is often elongated to form a roughened crest, upon which a more or less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Trochanter
The greater trochanter of the femur is a large, irregular, quadrilateral eminence and a part of the skeletal system. It is directed lateral and medially and slightly posterior. In the adult it is about 2–4 cm lower than the femoral head.Standring, Susan, editor. ''Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice''. Forty-First edition, Elsevier Limited, 2016, p. 1327. Because the pelvic outlet in the female is larger than in the male, there is a greater distance between the greater trochanters in the female. It has two surfaces and four borders. It is a traction epiphysis. Surfaces The ''lateral surface'', quadrilateral in form, is broad, rough, convex, and marked by a diagonal impression, which extends from the postero-superior to the antero-inferior angle, and serves for the insertion of the tendon of the gluteus medius. Above the impression is a triangular surface, sometimes rough for part of the tendon of the same muscle, sometimes smooth for the interp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior (anatomy)
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. For example, '' Terminologia A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intertrochanteric Line
The intertrochanteric line is a line upon the anterior aspect of the proximal end of the femur, extending between the lesser trochanter and the greater trochanter. It is a rough, variable ridge. Structure The intertrochanteric line marks the boundary between the femoral neck and shaft anteriorly (whereas the intertrochanteric crest marks the same boundary posteriorly).Platzer (2004), p 192 Attachments The iliofemoral ligament — the largest ligament of the human body — attaches above the line.White (2005), p 256 The distal capsular attachment on the femur follows the shape of the irregular rim between the head and the neck. As a consequence, the capsule of hip joint, capsule of the hip joint attaches in the region of the intertrochanteric line on the anterior side, but a finger away from the intertrochanteric crest on the posterior side of the head.Platzer (2004), pp 192, 198 The fibers of the ischiocapsular ligament attach both into the joint capsule and onto the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patella
The patella (: patellae or patellas), also known as the kneecap, is a flat, rounded triangular bone which articulates with the femur (thigh bone) and covers and protects the anterior articular surface of the knee joint. The patella is found in many tetrapods, such as mice, cats, birds, and dogs, but not in whales, or most reptiles. In humans, the patella is the largest sesamoid bone (i.e., embedded within a tendon or a muscle) in the body. Babies are born with a patella of soft cartilage which begins to ossify into bone at about four years of age. Structure The patella is a sesamoid bone roughly triangular in shape, with the apex of the patella facing downwards. The apex is the most inferior (lowest) part of the patella. It is pointed in shape, and gives attachment to the patellar ligament. The front and back surfaces are joined by a thin margin and towards centre by a thicker margin. The tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle attaches to the base of the patella., with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |