|
Urachus
The urachus forms from the distal end of the allantois in the embryo, and develops into a closed cord between the base of the bladder, and the navel. It drains the bladder of the fetus that joins and runs within the umbilical cord. The fibrous remnant lies in the space of Retzius, between the transverse fascia anteriorly and the peritoneum posteriorly. At birth, the urachus develops into the median umbilical ligament. Development The part of the urogenital sinus related to the bladder and urethra absorbs the ends of the Wolffian ducts and the associated ends of the renal diverticula. This gives rise to the trigone of the bladder and part of the prostatic urethra. The remainder of this part of the urogenital sinus forms the body of the bladder and part of the prostatic urethra. The apex of the bladder stretches and is connected to the umbilicus as a narrow canal. This canal is initially open, but later closes as the urachus goes on to definitively form the median umbilical li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Umbilical Ligament
In human anatomy, the median umbilical ligament is an unpaired midline ligamentous structure upon the lower inner surface of the anterior abdominal wall. It is covered by the median umbilical fold. The median umbilical ligament represents the remnant of the fetal urachus. It extends from the apex of the bladder to the umbilicus, on the deep surface of the anterior abdominal wall. The median umbilical ligament represents one of the five ligaments of the internal anterior abdominal wall inferior to the umbilicus; laterally on either side of it are one medial umbilical ligament and finally one lateral umbilical ligament. Development The median umbilical ligament begins as the allantois in the embryonic period. It then becomes the urachus in the fetus. This later develops into the median umbilical ligament at birth. It is also formed from the cloaca in utero. Function The median umbilical ligament has no known function. Clinical significance The median umbilical ligame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allantois
The allantois ( ; : allantoides or allantoises) is one of the extraembryonic membranes arising from the yolk sac. It is a hollow sac-like structure filled with clear fluid that forms part of the developing conceptus in an amniote that helps the embryo exchange gases and handle liquid waste. The other extraembryonoic membranes are the yolk sac, the amnion, and the chorion. In mammals these membranes are known as fetal membranes. The allantois, along with the amnion, chorion, and yolk sac (other extraembryonic membranes), identify humans and other mammals, birds, and reptiles as amniotes. These extraembryonic membranes that form the embryo have aided amniotes in the transition from aquatic to terrestrial environments. Fish and amphibians are '' anamniotes'', lacking the allantois. Function This sac-like structure, whose name is Greek for sausage (from ἀλλαντοειδής ''allantoeidḗs'', in reference to its shape when first formed) is primarily involved in nutrition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urachal Fistula
A urachal fistula is a congenital disorder caused by the persistence of the allantois (later, urachus), the structure that connects an embryo's bladder to the yolk sac. Normally, the urachus closes off to become the median umbilical ligament; however, if it remains open, urine Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and many other animals. In placental mammals, urine flows from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and exits the urethra through the penile meatus (mal ... can drain from the bladder to an opening by the umbilicus. This condition is a rare defect, mostly found in children, and is also known as an open or patent urachus. References Congenital disorders of urinary system {{Genitourinary-disease-stub} ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urachal Cyst
A urachal cyst is a sinus remaining from the allantois during embryogenesis. It is a cyst which occurs in the remnants between the umbilicus and bladder. This is a type of cyst occurring in a persistent portion of the urachus, presenting as an extraperitoneal mass in the umbilical region. It is characterized by abdominal pain, and fever if infected. It may rupture, leading to peritonitis, or it may drain through the umbilicus. Urachal cysts are usually silent clinically until infection, calculi or adenocarcinoma develop. Symptoms and signs * Lower abdominal pain * Pain on urination * Persistent umbilical discharge * Fever * Urinary tract infection * Lump * Hematuria Diagnosis Urachal cysts are rare defects found mostly in young children and hence medical ultrasound of the abdomen, bladder and pelvis is the most used diagnostic tool combined with MRI scan and CT scan in older patients who can remain still during a scan. See also * urachus * cyst A cyst is a closed sac, ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urachal Diverticulum
A urachal diverticulum (also ''vesicourachal diverticulum'') is a congenital disorder caused by the partial persistence of the allantois. The allantois, which later becomes the urachus, connects an embryo's bladder to the yolk sac. Normally, the urachus closes off to become the median umbilical ligament; however, if it does not seal close to the bladder, a blind pouch connected to the bladder remains. This is usually asymptomatic but can lead to recurrent urinary tract infections. If the urachus is wholly patent, urine can drain from the bladder to an opening by the umbilicus, a condition known as urachal fistula A urachal fistula is a congenital disorder caused by the persistence of the allantois (later, urachus), the structure that connects an embryo's bladder to the yolk sac. Normally, the urachus closes off to become the median umbilical ligament; howev .... References Congenital disorders of urinary system {{Genitourinary-disease-stub} ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urachal Cancer
Urachal cancer is a very rare type of cancer arising from the urachus or its remnants. The disease might arise from metaplastic glandular epithelium or embryonic epithelial remnants originating from the cloaca region. It occurs in roughly about one person per 1 million people per year varying on the geographical region. Men are affected slightly more often than women mostly in the 5th decade of life but the disease can occur in also in other age groups. It can involve the urinary bladder, but is not bladder cancer in the usual sense. Urachal cancer can occur at any site along the urachal tract. Urachal cancer was mentioned by Hue and Jacquin in 1863 followed by an elaborate work by T. Cullen in 1916 about diseases of the umbilicus, while C. Begg further characterized urachal cancer in the 1930s. Detailed diagnostic and staging schemes were proposed by Sheldon et al. in 1984, which remain widely used today. Classification Urachal cancer usually is an adenocarcinoma (about 90%) m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navel
The navel (clinically known as the umbilicus; : umbilici or umbilicuses; also known as the belly button or tummy button) is a protruding, flat, or hollowed area on the abdomen at the attachment site of the umbilical cord. Structure The umbilicus is used to visually separate the abdomen into quadrants. The umbilicus is a prominent Scar#Umbilical, scar on the abdomen, with its position being relatively consistent among humans. The skin around the waist at the level of the umbilicus is supplied by the tenth thoracic spinal nerve (T10 dermatome (anatomy), dermatome). The umbilicus itself typically lies at a vertical level corresponding to the junction between the L3 and L4 vertebrae, with a normal variation among people between the L3 and L5 vertebrae. Parts of the adult navel include the "umbilical cord remnant" or "umbilical tip", which is the often protruding scar left by the detachment of the umbilical cord. This is located in the center of the navel, sometimes described ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbilical Cord
In Placentalia, placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or ''funiculus umbilicalis'') is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologically and genetically part of the fetus and (in humans) normally contains two arteries (the umbilical arteries) and one vein (the umbilical vein), buried within Wharton's jelly. The umbilical vein supplies the fetus with oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood from the placenta. Conversely, the fetal heart pumps low-oxygen, nutrient-depleted blood through the umbilical arteries back to the placenta. Structure and development The umbilical cord develops from and contains remnants of the yolk sac and allantois. It forms by the fifth week of human embryogenesis, development, replacing the yolk sac as the source of nutrients for the embryo. The cord is not directly connected to the mother's circulatory system, but instead joins the pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
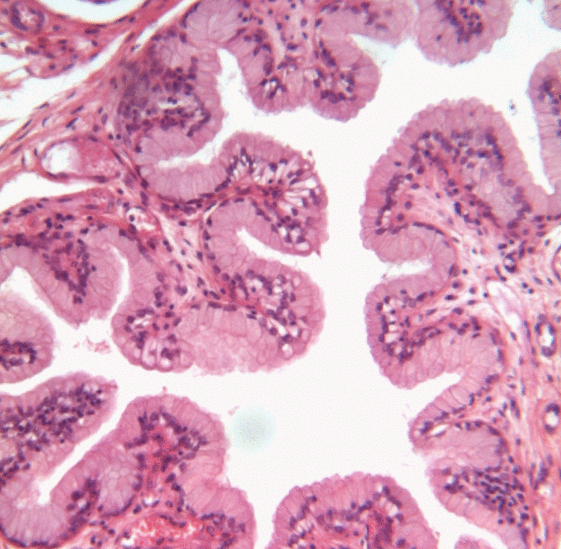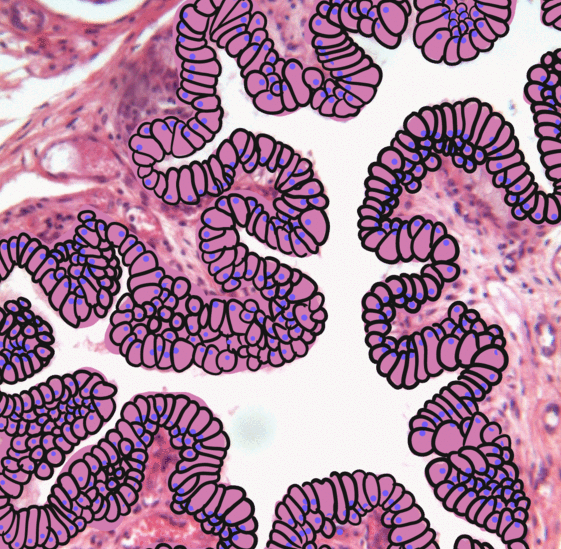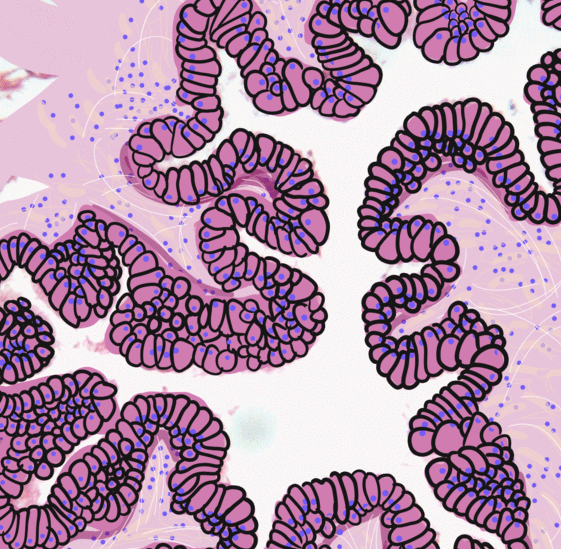
Uroepithelium
Transitional epithelium is a type of stratified epithelium. Transitional epithelium is a type of tissue that changes shape in response to stretching (stretchable epithelium). The transitional epithelium usually appears cuboidal when relaxed and squamous when stretched. This tissue consists of multiple layers of epithelial cells which can contract and expand in order to adapt to the degree of distension needed. Transitional epithelium lines the organs of the urinary system and is known here as urothelium (: urothelia). The bladder, for example, has a need for great distension. Structure The appearance of transitional epithelium differs according to its cell layer. Cells of the basal layer are cuboidal (cube-shaped), or columnar (column-shaped), while the cells of the superficial layer vary in appearance depending on the degree of distension. These cells appear to be cuboidal with a domed apex when the organ or the tube in which they reside is not stretched. When the organ or tube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |