Umbilical Cord on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In

 The umbilical cord develops from and contains remnants of the
The umbilical cord develops from and contains remnants of the
 A number of abnormalities can affect the umbilical cord, which can cause problems that affect both mother and child:
* Umbilical cord compression can result from, for example, entanglement of the cord, a knot in the cord, or a nuchal cord,P02.5 Fetus and newborn affected by other compression of umbilical cord
A number of abnormalities can affect the umbilical cord, which can cause problems that affect both mother and child:
* Umbilical cord compression can result from, for example, entanglement of the cord, a knot in the cord, or a nuchal cord,P02.5 Fetus and newborn affected by other compression of umbilical cord
in
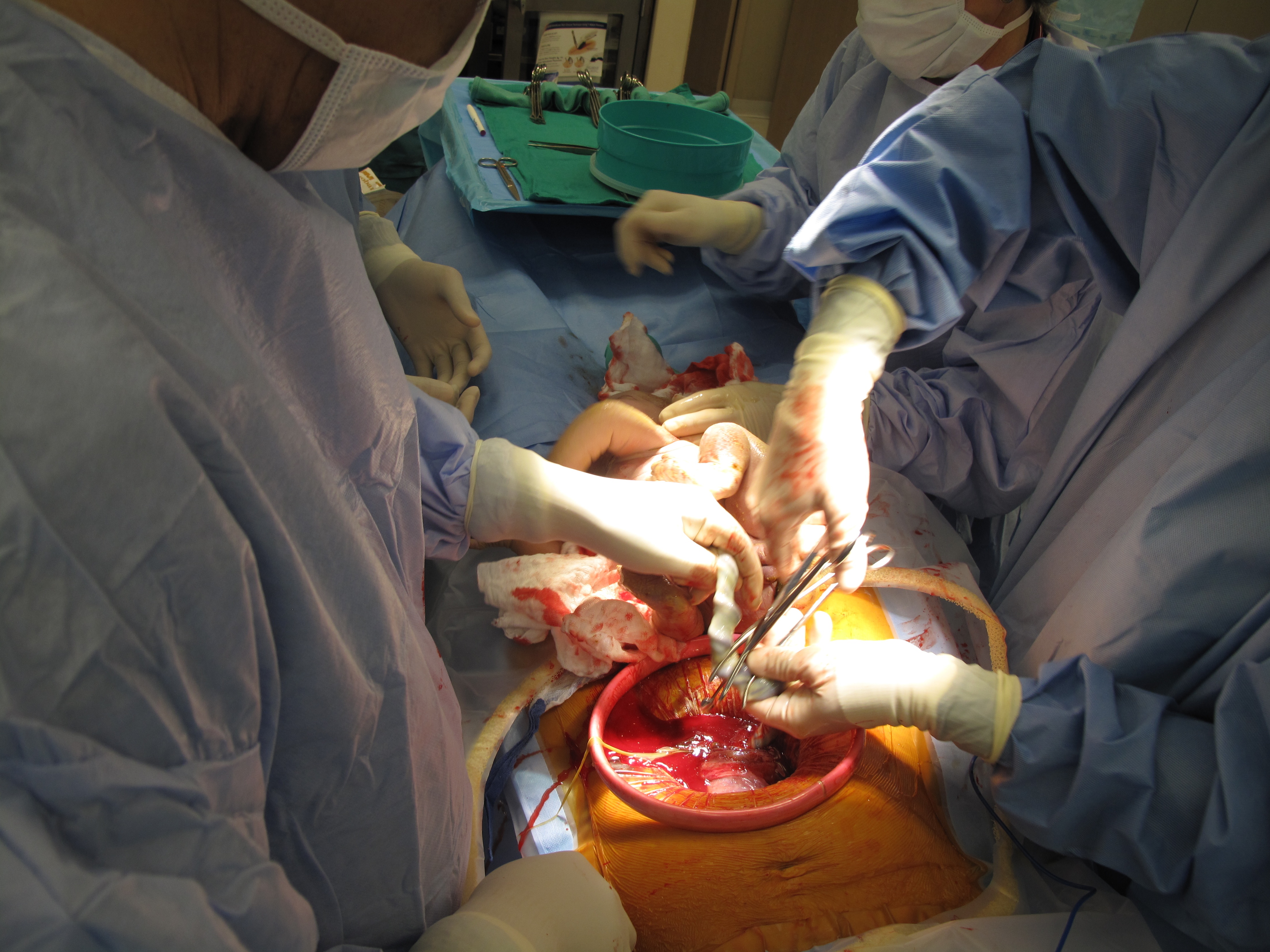


 The cord can be clamped at different times; however, delaying the clamping of the umbilical cord until at least one minute after birth improves outcomes as long as there is the ability to treat the small risk of
The cord can be clamped at different times; however, delaying the clamping of the umbilical cord until at least one minute after birth improves outcomes as long as there is the ability to treat the small risk of
Institute of Medicine (IoM) report
which recommended that expectant parents be given a balanced perspective on their options for cord blood banking. In response to their constituents, state legislators across the country are introducing legislation intended to help inform physicians and expectant parents on the options for donating, discarding or banking lifesaving newborn stem cells. Currently 17 states, representing two-thirds of U.S. births, have enacted legislation recommended by the IoM guidelines. The use of cord blood stem cells in treating conditions such as brain injury and Type 1 Diabetes is already being studied in humans, and earlier stage research is being conducted for treatments of stroke, and hearing loss. Cord blood stored with private banks is typically reserved for use of the donor child only. In contrast, cord blood stored in public banks is accessible to anyone with a closely matching tissue type and demonstrated need. The use of cord blood from public banks is increasing. Currently it is used in place of a bone marrow transplant in the treatment of blood disorders such as leukemia, with donations released for transplant through one registry, Netcord.org, passing 1,000,000 as of January 2013. Cord blood is used when the patient cannot find a matching bone marrow donor; this "extension" of the donor pool has driven the expansion of public banks.
File:Gray34.png, Sectional plan of the gravid uterus in the third and fourth month.
File:Gray38.png, Fetus in utero, between fifth and sixth months.
File:Newborn umbilical suction.jpg, A newborn at 45 seconds, with umbilical cord clamped.
File:Slide2BLA.JPG, Umbilic. Deep dissection. Serial cross section.
File:Umbcord.jpg, dried umbilical cord stump.
placental
Placental mammals (infraclass Placentalia ) are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupialia. Placentalia contains the vast majority of extant mammals, which are partly distinguished ...
mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or ''funiculus umbilicalis'') is a conduit between the developing embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
or fetus
A fetus or foetus (; : fetuses, foetuses, rarely feti or foeti) is the unborn offspring of a viviparous animal that develops from an embryo. Following the embryonic development, embryonic stage, the fetal stage of development takes place. Pren ...
and the placenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between ...
. During prenatal development
Prenatal development () involves the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal de ...
, the umbilical cord is physiologically and genetically part of the fetus and (in humans) normally contains two arteries
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
(the umbilical arteries
The umbilical artery is a paired artery (with one for each half of the body) that is found in the abdominal and pelvic regions. In the fetus, it extends into the umbilical cord.
Structure Development
The umbilical arteries supply systemic arte ...
) and one vein
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and feta ...
(the umbilical vein
The umbilical vein is a vein present during fetal development that carries oxygenated blood from the placenta into the growing fetus. The umbilical vein provides convenient access to the central circulation of a neonate for restoration of blood vo ...
), buried within Wharton's jelly. The umbilical vein supplies the fetus with oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
ated, nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
-rich blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
from the placenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between ...
. Conversely, the fetal heart pumps low-oxygen, nutrient-depleted blood through the umbilical arteries back to the placenta.
Structure and development

 The umbilical cord develops from and contains remnants of the
The umbilical cord develops from and contains remnants of the yolk sac
The yolk sac is a membranous wikt:sac, sac attached to an embryo, formed by cells of the hypoblast layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc. This is alternatively called the umbilical vesicle by the Terminologia Embryologica (TE), though ''yolk sac' ...
and allantois
The allantois ( ; : allantoides or allantoises) is one of the extraembryonic membranes arising from the yolk sac. It is a hollow sac-like structure filled with clear fluid that forms part of the developing conceptus in an amniote that helps the ...
. It forms by the fifth week of development
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development (music), the process by which thematic material is reshaped
* Photographic development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
* Development hell, when a proje ...
, replacing the yolk sac as the source of nutrients for the embryo. The cord is not directly connected to the mother's circulatory system, but instead joins the placenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between ...
, which transfers materials to and from the maternal blood without allowing direct mixing. The length of the umbilical cord is approximately equal to the crown-rump length of the fetus throughout pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
. The umbilical cord in a full term neonate
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to Juvenile (orga ...
is usually about long and about in diameter. This diameter decreases rapidly within the placenta. The fully patent umbilical artery has two main layers: an outer layer consisting of circularly arranged smooth muscle cells and an inner layer which shows rather irregularly and loosely arranged cells embedded in abundant ground substance
Ground substance is an amorphous gel-like substance in the extracellular space of animals that contains all components of the extracellular matrix (ECM) except for fibrous materials such as collagen and elastin. Ground substance is active in the d ...
staining metachromatic. The smooth muscle cells of the layer are rather poorly differentiated, contain only a few tiny myofilament
Myofilaments are the three protein filaments of myofibrils in muscle cells. The main proteins involved are myosin, actin, and titin. Myosin and actin are the ''contractile proteins'' and titin is an elastic protein. The myofilaments act togeth ...
s and are thereby unlikely to contribute actively to the process of post-natal closure.
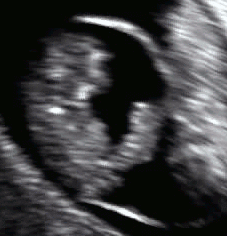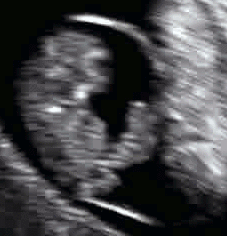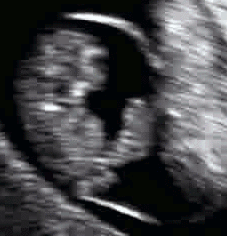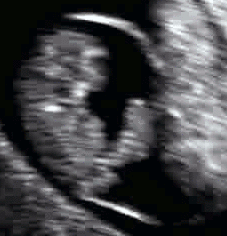
The umbilical cord can be detected by ultrasound by six weeks of gestation and well-visualized by eight to nine weeks of gestation.
The umbilical cord lining is a good source of mesenchymal and epithelial stem cells. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), also known as mesenchymal stromal cells or medicinal signaling cells, are multipotent stromal cells that can Cellular differentiation, differentiate into a variety of cell types, including osteoblasts (bone cells), ...
s (UC-MSC) have been used clinically to treat osteoarthritis, autoimmune diseases, and multiple other conditions. Their advantages include a better harvesting, and multiplication, and immunosuppressive properties that define their potential for use in transplantations. Their use would also overcome the ethical objections raised by the use of embryonic stem cell
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are Cell potency#Pluripotency, pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage pre-Implantation (human embryo), implantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4� ...
s.
The umbilical cord contains Wharton's jelly, a gelatinous substance made largely from mucopolysaccharides that protects the blood vessels inside. It contains one vein, which carries oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood to the fetus, and two arteries that carry deoxygenated, nutrient-depleted blood away. Occasionally, only two vessels (one vein and one artery) are present in the umbilical cord. This is sometimes related to fetal abnormalities, but it may also occur without accompanying problems.
It is unusual for a vein to carry oxygenated blood and for arteries to carry deoxygenated blood (the only other examples being the pulmonary veins
The pulmonary veins are the veins that transfer oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. The largest pulmonary veins are the four ''main pulmonary veins'', two from each lung that drain into the left atrium of the heart. The pulmonary ve ...
and arteries
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
, connecting the lungs to the heart). However, this naming convention reflects the fact that the umbilical vein carries blood towards the fetus' heart, while the umbilical arteries carry blood away.
The blood flow through the umbilical cord is approximately 35 ml / min at 20 weeks, and 240 ml / min at 40 weeks of gestation. Adapted to the weight of the fetus, this corresponds to 115 ml / min / kg at 20 weeks and 64 ml / min / kg at 40 weeks.
For terms of location, the ''proximal'' part of an umbilical cord refers to the segment closest to the embryo or fetus in embryology and fetal medicine, and closest to the placenta in placental pathology, and opposite for the ''distal'' part, respectively.
Function
Connection to fetal circulatory system
The umbilical cord enters the fetus via theabdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal ...
, at the point which (after separation) will become the umbilicus (belly button or navel). Within the fetus, the umbilical vein continues towards the transverse fissure of the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
, where it splits into two. One of these branches joins with the hepatic portal vein
The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Appro ...
(connecting to its left branch), which carries blood into the liver. The second branch (known as the ductus venosus) bypasses the liver and flows into the inferior vena cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the ...
, which carries blood towards the heart. The two umbilical arteries branch from the internal iliac arteries
The internal iliac artery (formerly known as the hypogastric artery) is the main artery of the pelvis.
Structure
The internal iliac artery supplies the walls and viscera of the pelvis, the buttock, the reproductive organs, and the medial compart ...
and pass on either side of the urinary bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the ...
into the umbilical cord, completing the circuit back to the placenta.
Changes after birth
After birth, the umbilical cord stump will dry up and drop away by the time the baby is three weeks old. If the stump still has not separated after three weeks, it might be a sign of an underlying problem, such as an infection or immune system disorder. In absence of external interventions, the umbilical cord occludes physiologically shortly after birth, explained both by a swelling and collapse of Wharton's jelly in response to a reduction in temperature and byvasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of the blood vessels resulting from contraction of the muscular wall of the vessels, in particular the large arteries and small arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasodilation, the widening of blood vesse ...
of the blood vessels by smooth muscle contraction. In effect, a natural clamp is created, halting the flow of blood. In air at 18 °C, this physiological clamping will take three minutes or less. In water birth, where the water temperature is close to body temperature, normal pulsation can be five minutes and longer.
Closure of the umbilical artery by vasoconstriction consists of multiple constrictions which increase in number and degree with time. There are segments of dilations with trapped uncoagulated blood between the constrictions before complete occlusion. Both the partial constrictions and the ultimate closure are mainly produced by muscle cells of the outer circular layer. In contrast, the inner layer seems to serve mainly as a plastic tissue which can easily be shifted in an axial direction and then folded into the narrowing lumen to complete the closure. The vasoconstrictive occlusion appears to be mainly mediated by serotonin
Serotonin (), also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a monoamine neurotransmitter with a wide range of functions in both the central nervous system (CNS) and also peripheral tissues. It is involved in mood, cognition, reward, learning, ...
and thromboxane A2. The artery in cords of preterm infants contracts more to angiotensin II
Angiotensin is a peptide hormone that causes vasoconstriction and an increase in blood pressure. It is part of the renin–angiotensin system, which regulates blood pressure. Angiotensin also stimulates the release of aldosterone from the ...
and arachidonic acid
Arachidonic acid (AA, sometimes ARA) is a polyunsaturated omega−6 fatty acid 20:4(ω−6), or 20:4(5,8,11,14). It is a precursor in the formation of leukotrienes, prostaglandins, and thromboxanes.
Together with omega−3 fatty acids an ...
and is more sensitive to oxytocin
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone and neuropeptide normally produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary. Present in animals since early stages of evolution, in humans it plays roles in behavior that include Human bonding, ...
than in term ones. In contrast to the contribution of Wharton's jelly, cooling causes only temporary vasoconstriction.
Within the child, the umbilical vein and ductus venosus close up, and degenerate into fibrous remnants known as the round ligament of the liver and the ligamentum venosum
The ligamentum venosum, also known as Arantius' ligament, is the fibrous remnant of the ductus venosus of the fetal circulation. Usually, it is attached to the left branch of the portal vein within the porta hepatis. It may be continuous with the ...
respectively. Part of each umbilical artery closes up (degenerating into what are known as the medial umbilical ligaments), while the remaining sections are retained as part of the circulatory system.
Clinical significance
Problems and abnormalities
 A number of abnormalities can affect the umbilical cord, which can cause problems that affect both mother and child:
* Umbilical cord compression can result from, for example, entanglement of the cord, a knot in the cord, or a nuchal cord,P02.5 Fetus and newborn affected by other compression of umbilical cord
A number of abnormalities can affect the umbilical cord, which can cause problems that affect both mother and child:
* Umbilical cord compression can result from, for example, entanglement of the cord, a knot in the cord, or a nuchal cord,P02.5 Fetus and newborn affected by other compression of umbilical cordin
ICD-10
ICD-10 is the 10th revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), a medical classification list by the World Health Organization (WHO). It contains codes for diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social cir ...
, the International Statistical Classification of Diseases (which is the wrapping of the umbilical cord around the fetal neck) but these conditions do not always cause obstruction of fetal circulation.
* Velamentous cord insertion
* Single umbilical artery
* Umbilical cord prolapse
Umbilical cord prolapse is when the umbilical cord comes out of the uterus with or before the presenting part of the baby. The concern with cord prolapse is that pressure on the cord from the baby will compromise blood flow to the baby. It usuall ...
* Vasa praevia
Clamping and cutting



 The cord can be clamped at different times; however, delaying the clamping of the umbilical cord until at least one minute after birth improves outcomes as long as there is the ability to treat the small risk of
The cord can be clamped at different times; however, delaying the clamping of the umbilical cord until at least one minute after birth improves outcomes as long as there is the ability to treat the small risk of jaundice
Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a yellowish or, less frequently, greenish pigmentation of the skin and sclera due to high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving ...
if it occurs. Clamping is followed by cutting of the cord, which is painless due to the absence of nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons). Nerves have historically been considered the basic units of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the Electrochemistry, electrochemical nerv ...
s. The cord is extremely tough, like thick sinew
A tendon or sinew is a tough band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It sends the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system, while withstanding tension.
Tendons, like ligaments, are made of ...
, and so cutting it requires a suitably sharp instrument. While umbilical severance may be delayed until after the cord has stopped pulsing (one to three minutes after birth), there is ordinarily no significant loss of either venous or arterial blood while cutting the cord. Current evidence neither supports, nor refutes, delayed cutting of the cord, according to the American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) guidelines.
There are umbilical cord clamps which incorporate a knife. These clamps are safer and faster, allowing one to first apply the cord clamp and then cut the umbilical cord. After the cord is clamped and cut, the newborn wears a plastic clip on the navel area until the compressed region of the cord has dried and sealed sufficiently.
The length of umbilical left attached to the newborn varies by practice; in most hospital settings the length of cord left attached after clamping and cutting is minimal. In the United States, however, where the birth occurred outside of the hospital and an emergency medical technician
An emergency medical technician (often, more simply, EMT) is a medical professional that provides emergency medical services. EMTs are most commonly found serving on ambulances and in fire departments in the US and Canada, as full-time and som ...
(EMT) clamps and cuts the cord, a longer segment up to in length is left attached to the newborn.
The remaining umbilical stub remains for up to ten days as it dries and then falls off.
Early versus delayed clamping
ACochrane review
Cochrane is a British international charitable organisation formed to synthesize medical research findings to facilitate evidence-based choices about health interventions involving health professionals, patients and policy makers. It includes ...
in 2013 came to the conclusion that delayed cord clamping (between one and three minutes after birth) is "likely to be beneficial as long as access to treatment for jaundice requiring phototherapy is available". In this review delayed clamping, as contrasted to early, resulted in no difference in risk of severe maternal postpartum hemorrhage
Postpartum bleeding or postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is often defined as the loss of more than 500 ml or 1,000 ml of blood following childbirth. Some have added the requirement that there also be signs or symptoms of low blood volume fo ...
or neonatal mortality, and a low Apgar score
The Apgar score is a quick way for health professionals to evaluate the health of all newborns at 1 and 5 minutes after birth and in response to resuscitation. It was originally developed in 1952 by an anesthesiologist at Columbia University, ...
. On the other hand, delayed clamping resulted in an increased birth weight of on average about 100 g, and an increased hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin ...
concentration of on average 1.5 g/dL with half the risk of being iron deficient at three and six months, but an increased risk of jaundice requiring phototherapy
Light therapy, also called phototherapy or bright light therapy is the exposure to direct sunlight or artificial light at controlled wavelengths in order to treat a variety of medical disorders, including seasonal affective disorder (SAD), circ ...
.
In 2012, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists officially endorsed delaying clamping of the umbilical cord for 30–60 seconds with the newborn held below the level of the placenta in all cases of preterm delivery based largely on evidence that it reduces the risk of intraventricular hemorrhage in these children by 50%. In the same committee statement, ACOG also recognize several other likely benefits for preterm infants, including "improved transitional circulation, better establishment of red blood cell volume, and decreased need for blood transfusion". In January 2017, a revised Committee Opinion extended the recommendation to term infants, citing data that term infants benefit from increased hemoglobin levels in the newborn period and improved iron stores in the first months of life, which may result in improved developmental outcomes. ACOG recognized a small increase in the incidence of jaundice in term infants with delayed cord clamping, and recommended policies be in place to monitor for and treat neonatal jaundice. ACOG also noted that delayed cord clamping is not associated with increased risk of postpartum hemorrhage.
Several studies have shown benefits of delayed cord clamping: A meta-analysis showed that delaying clamping of the umbilical cord in full-term neonates for a minimum of two minutes following birth is beneficial to the newborn in giving improved hematocrit
The hematocrit () (Ht or HCT), also known by several other names, is the volume percentage (vol%) of red blood cells (RBCs) in blood, measured as part of a blood test. The measurement depends on the number and size of red blood cells. It is nor ...
, iron status as measured by ferritin
Ferritin is a universal intracellular and extracellular protein that stores iron and releases it in a controlled fashion. The protein is produced by almost all living organisms, including archaea, bacteria, algae, higher plants, and animals. ...
concentration and stored iron, as well as a reduction in the risk of anemia (relative risk
The relative risk (RR) or risk ratio is the ratio of the probability of an outcome in an exposed group to the probability of an outcome in an unexposed group. Together with risk difference and odds ratio, relative risk measures the association bet ...
, 0.53; 95% CI, 0.40–0.70). A decrease was also found in a study from 2008.Examination of the Newborn & Neonatal Health: A Multidimensional Approach, p. 116-117 Although there is higher hemoglobin level at 2 months, this effect did not persist beyond 6 months of age."Effect of timing of umbilical cord clamping of term infants on maternal and neonatal outcomes." ''Cochrane Database Syst Rev''. 2008; (2):CD004074 Not clamping the cord for three minutes following the birth of a baby improved outcomes at four years of age. A delay of three minutes or more in umbilical cord clamping after birth reduce the prevalence of anemia in infants.
Negative effects of delayed cord clamping include an increased risk of polycythemia
Polycythemia (also known as polycythaemia) is a laboratory finding in which the hematocrit (the volume percentage of red blood cells in the blood) and/or hemoglobin concentration are increased in the blood. Polycythemia is sometimes called erythr ...
. Still, this condition appeared to be benign in studies. Infants whose cord clamping occurred later than 60 seconds after birth had a higher rate of neonatal jaundice
Neonatal jaundice is a yellowish discoloration of the white part of the eyes and skin in a newborn baby due to high bilirubin levels. Other symptoms may include excess sleepiness or poor feeding. Complications may include seizures, cerebral ...
requiring phototherapy
Light therapy, also called phototherapy or bright light therapy is the exposure to direct sunlight or artificial light at controlled wavelengths in order to treat a variety of medical disorders, including seasonal affective disorder (SAD), circ ...
.
Delayed clamping is not recommended as a response to cases where the newborn is not breathing well and needs resuscitation. Rather, the recommendation is instead to immediately clamp and cut the cord and perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure used during Cardiac arrest, cardiac or Respiratory arrest, respiratory arrest that involves chest compressions, often combined with artificial ventilation, to preserve brain function ...
. The umbilical cord pulsating is not a guarantee that the baby is receiving enough oxygen.
Umbilical nonseverance
Some parents choose to omit cord severance entirely, a practice called " lotus birth" or umbilical nonseverance. The entire intact umbilical cord is allowed to dry and separates on its own (typically on the 3rd day after birth), falling off and leaving a healed umbilicus. TheRoyal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists
The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) is a professional association based in London, United Kingdom. Its members, including people with and without medical degrees, work in the field of obstetrics and gynaecology, that is ...
has warned about the risks of infection as the decomposing placenta tissue becomes a nest for infectious bacteria such as Staphylococcus
''Staphylococcus'', from Ancient Greek σταφυλή (''staphulḗ''), meaning "bunch of grapes", and (''kókkos''), meaning "kernel" or " Kermes", is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillale ...
. In one such case, a 20-hour old baby whose parents chose UCNS was brought to the hospital in an agonal state, was diagnosed with sepsis
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs.
This initial stage of sepsis is followed by suppression of the immune system. Common signs and s ...
and required an antibiotic treatment for six weeks.
Umbilical cord catheterization
As the umbilical vein is directly connected to the central circulation, it can be used as a route for placement of a venous catheter for infusion and medication. The umbilical vein catheter is a reliable alternative to percutaneous peripheral or central venous catheters or intraosseous canulas and may be employed in resuscitation or intensive care of the newborn.Blood sampling
From 24 to 34 weeks of gestation, when the fetus is typically viable, blood can be taken from the cord in order to test for abnormalities (particularly for hereditary conditions). This diagnosticgenetic test
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, or ...
procedure is known as percutaneous umbilical cord blood sampling.
Storage of cord blood
The blood within the umbilical cord, known as cord blood, is a rich and readily available source of primitive, undifferentiatedstem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can change into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell ...
s (of type CD34
CD34 is a transmembrane phosphoglycoprotein protein encoded by the CD34 gene in humans, mice, rats and other species.
CD34 derives its name from the cluster of differentiation protocol that identifies cell surface antigens. CD34 was first desc ...
-positive and CD38
CD38 (cluster of differentiation 38), also known as cyclic ADP ribose hydrolase, is a glycoprotein found on the surface of many immune cells (white blood cells), including CD4+, CD8+, B lymphocytes and natural killer cells. CD38 also functions in ...
-negative). These cord blood cells can be used for bone marrow transplant
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood, in order to replicate inside a patient and produce a ...
.
Some parents choose to have this blood diverted from the baby's umbilical blood transfer through early cord clamping and cutting, to freeze for long-term storage at a cord blood bank should the child ever require the cord blood stem cells (for example, to replace bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
destroyed when treating leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia; pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and produce high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or '' ...
). This practice is controversial, with critics asserting that early cord blood withdrawal at the time of birth actually increases the likelihood of childhood disease, due to the high volume of blood taken (an average of 108ml) in relation to the baby's total supply (typically 300ml). The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists
The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) is a professional association based in London, United Kingdom. Its members, including people with and without medical degrees, work in the field of obstetrics and gynaecology, that is ...
stated in 2006 that "there is still insufficient evidence to recommend directed commercial cord blood collection and stem-cell storage in low-risk families".
The American Academy of Pediatrics
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) is the largest professional association of pediatricians in the United States. It is headquartered in Itasca, Illinois, and maintains an office in Washington, D.C. The AAP has published hundreds of poli ...
has stated that cord blood banking for self-use should be discouraged (as most conditions requiring the use of stem cells will already exist in the cord blood), while banking for general use should be encouraged. In the future, cord blood-derived embryonic-like stem cells (CBEs) may be banked and matched with other patients, much like blood and transplanted tissues. The use of CBEs could potentially eliminate the ethical difficulties associated with embryonic stem cells
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are Cell potency#Pluripotency, pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage pre-Implantation (human embryo), implantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4� ...
(ESCs).
While the American Academy of Pediatrics discourages private banking except in the case of existing medical need, it also says that information about the potential benefits and limitations of cord blood banking and transplantation should be provided so that parents can make an informed decision.
In the United States, cord blood education has been supported by legislators at the federal and state levels. In 2005, the National Academy of Sciences published aInstitute of Medicine (IoM) report
which recommended that expectant parents be given a balanced perspective on their options for cord blood banking. In response to their constituents, state legislators across the country are introducing legislation intended to help inform physicians and expectant parents on the options for donating, discarding or banking lifesaving newborn stem cells. Currently 17 states, representing two-thirds of U.S. births, have enacted legislation recommended by the IoM guidelines. The use of cord blood stem cells in treating conditions such as brain injury and Type 1 Diabetes is already being studied in humans, and earlier stage research is being conducted for treatments of stroke, and hearing loss. Cord blood stored with private banks is typically reserved for use of the donor child only. In contrast, cord blood stored in public banks is accessible to anyone with a closely matching tissue type and demonstrated need. The use of cord blood from public banks is increasing. Currently it is used in place of a bone marrow transplant in the treatment of blood disorders such as leukemia, with donations released for transplant through one registry, Netcord.org, passing 1,000,000 as of January 2013. Cord blood is used when the patient cannot find a matching bone marrow donor; this "extension" of the donor pool has driven the expansion of public banks.
In other animals
The umbilical cord in some mammals, including cattle and sheep, contains two distinct umbilical veins. There is only one umbilical vein in the human umbilical cord.''Meat Hygiene''. J. F. Gracey, D. S. Collins, Robert J. Huey. p. 32. In some animals, the mother will gnaw through the cord, thus separating the placenta from the offspring. The cord along with the placenta is often eaten by the mother, to provide nourishment and to dispose of tissues that would otherwise attract scavengers or predators. Inchimpanzee
The chimpanzee (; ''Pan troglodytes''), also simply known as the chimp, is a species of Hominidae, great ape native to the forests and savannahs of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed one. When its close rel ...
s, the mother leaves the cord in place and nurses her young with the cord and placenta attached until the cord dries out and separates naturally, within a day of birth, at which time the cord is discarded. (This was first documented by zoologists in the wild in 1974.)
Some species of shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ribless endoskeleton, dermal denticles, five to seven gill slits on each side, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the ...
— hammerheads, requiems
A Requiem (Latin: ''rest'') or Requiem Mass, also known as Mass for the dead () or Mass of the dead (), is a Mass (liturgy), Mass of the Catholic Church offered for the repose of the Soul (spirit), souls of the deceased, using a particular fo ...
and smooth-hounds—are viviparous and have an umbilical cord attached to their placenta.
Other uses for the term "umbilical cord"
The term "umbilical cord" or just "umbilical" has also come to be used for other cords with similar functions, such as the hose connecting surface-supplied divers to their surface supply of air and/or heating, or space-suitedastronaut
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a List of human spaceflight programs, human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member of a spa ...
s to their spacecraft. Engineers sometimes use the term to describe a complex or critical cable connecting a component, especially when composed of bundles of conductors of different colors, thickness and types, terminating in a single multi-contact disconnect.
Cancer-causing toxicants in human umbilical cords
In multiple American and international studies, cancer-causing chemicals have been found in the blood of umbilical cords. These originate from certain plastics, computer circuit boards, fumes and synthetic fragrances among others. Over 300chemical
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combin ...
toxicants have been found, including bisphenol A
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a chemical compound primarily used in the manufacturing of various plastics. It is a colourless solid which is Solubility, soluble in most common organic solvents, but has very poor solubility in water. BPA is produced on a ...
(BPA), tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA), Teflon
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene, and has numerous applications because it is chemically inert. The commonly known brand name of PTFE-based composition is Teflon by Chemours, a spin-off from ...
-related perfluorooctanoic acid
Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA; conjugate acid, conjugate base perfluorooctanoate; also known colloquially as C8, from its chemical formula C8HF15O2) is a perfluorinated carboxylic acid produced and used worldwide as an industrial surfactant in ch ...
, galaxolide and synthetic musks among others. The studies in America showed higher levels in African Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa ...
, Hispanic Americans
Hispanic and Latino Americans are Americans who have a Spaniards, Spanish or Latin Americans, Latin American background, culture, or family origin. This demographic group includes all Americans who identify as Hispanic or Latino (demonym), ...
and Asian Americans
Asian Americans are Americans with Asian diaspora, ancestry from the continent of Asia (including naturalized Americans who are Immigration to the United States, immigrants from specific regions in Asia and descendants of those immigrants).
A ...
due, it is thought, to living in areas of higher pollution.
Additional images
See also
*Navel
The navel (clinically known as the umbilicus; : umbilici or umbilicuses; also known as the belly button or tummy button) is a protruding, flat, or hollowed area on the abdomen at the attachment site of the umbilical cord.
Structure
The u ...
* Umbilical line
References
*External links
* {{Authority control Childbirth Cloning Embryology Stem cells Vertebrate developmental biology Navel