|
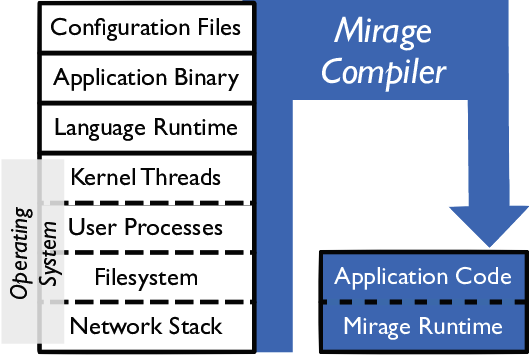
Unikernel
A unikernel is a type of computer program that is static linking, statically linked with the operating system code on which it depends. Unikernels are built with a specialized compiler that identifies the operating system services that a program uses and links it with one or more Operating_system#Library, library operating systems that provide them. Such a program requires no separate operating system and can run instead as the guest of a hypervisor. The unikernel architecture builds on concepts developed by Exokernel and Nemesis (operating system), Nemesis in the late 1990s. Design In a library operating system, protection boundaries are pushed to the lowest hardware layers, resulting in: # a set of libraries that implement mechanisms such as those needed to drive hardware or talk network protocols; # a set of policies that enforce access control and isolation in the application layer. The library OS architecture has several advantages and disadvantages compared with convent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unikernel Mirage Example
A unikernel is a type of computer program that is statically linked with the operating system code on which it depends. Unikernels are built with a specialized compiler that identifies the operating system services that a program uses and links it with one or more library operating systems that provide them. Such a program requires no separate operating system and can run instead as the guest of a hypervisor. The unikernel architecture builds on concepts developed by Exokernel and Nemesis in the late 1990s. Design In a library operating system, protection boundaries are pushed to the lowest hardware layers, resulting in: # a set of libraries that implement mechanisms such as those needed to drive hardware or talk network protocols; # a set of policies that enforce access control and isolation in the application layer. The library OS architecture has several advantages and disadvantages compared with conventional OS designs. One of the advantages is that since there is only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IncludeOS
IncludeOS is a minimal, open source, unikernel operating system for cloud services and IoT, developed by Alf Walla and Andreas Åkesson. IncludeOS allows users to run C++ applications in the cloud without any operating system. IncludeOS runs on virtual machines like Linux KVM, and VMWare ESXi/Fusion. IncludeOS applications boot in about 300 ms. On Solo5/uKVM from IBM Research, boot times as low as 10 milliseconds are possible. Architecture The minimalist architecture of IncludeOS means that it does not have any virtual memory space. In turn, therefore, there is no concept of either system calls or user space A modern computer operating system usually uses virtual memory to provide separate address spaces or regions of a single address space, called user space and kernel space. This separation primarily provides memory protection and hardware prote .... References {{reflist , refs= {{cite web , author= Stig Øyvann , date= November 12, 2018 , df= ymd , url= https:// ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating System
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of Scheduling (computing), processor time, mass storage, peripherals, and other resources. For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware, although the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on many devices that contain a computerfrom cellular phones and video game consoles to web servers and supercomputers. , Android (operating system), Android is the most popular operating system with a 46% market share, followed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compiler
In computing, a compiler is a computer program that Translator (computing), translates computer code written in one programming language (the ''source'' language) into another language (the ''target'' language). The name "compiler" is primarily used for programs that translate source code from a high-level programming language to a lower level language, low-level programming language (e.g. assembly language, object code, or machine code) to create an executable program.Compilers: Principles, Techniques, and Tools by Alfred V. Aho, Ravi Sethi, Jeffrey D. Ullman - Second Edition, 2007 There are many different types of compilers which produce output in different useful forms. A ''cross-compiler'' produces code for a different Central processing unit, CPU or operating system than the one on which the cross-compiler itself runs. A ''bootstrap compiler'' is often a temporary compiler, used for compiling a more permanent or better optimised compiler for a language. Related software ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypervisor
A hypervisor, also known as a virtual machine monitor (VMM) or virtualizer, is a type of computer software, firmware or hardware that creates and runs virtual machines. A computer on which a hypervisor runs one or more virtual machines is called a ''host machine'', and each virtual machine is called a ''guest machine''. The hypervisor presents the guest operating systems with a virtual operating platform and manages the execution of the guest operating systems. Unlike an emulator, the guest executes most instructions on the native hardware. Multiple instances of a variety of operating systems may share the virtualized hardware resources: for example, Linux, Windows, and macOS instances can all run on a single physical x86 machine. This contrasts with operating-system–level virtualization, where all instances (usually called ''containers'') must share a single kernel, though the guest operating systems can differ in user space, such as different Linux distributions with the sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exokernel
Exokernel is an operating system kernel developed by the MIT Parallel and Distributed Operating Systems group, and also a class of similar operating systems. Operating systems generally present hardware resources to applications through high-level abstractions such as (virtual) file systems. The idea behind exokernels is to force as few abstractions as possible on application developers, enabling them to make as many decisions as possible about hardware abstractions. Exokernels are tiny, since functionality is limited to ensuring protection and multiplexing In telecommunications and computer networking, multiplexing (sometimes contracted to muxing) is a method by which multiple analog or digital signals are combined into one signal over a shared medium. The aim is to share a scarce resource� ... of resources, which is considerably simpler than conventional microkernels' implementation of message passing and monolithic kernels' implementation of high-level abstractions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nemesis (operating System)
Nemesis was an operating system that was designed by the University of Cambridge, the University of Glasgow, the Swedish Institute of Computer Science and Citrix Systems. Nemesis was conceived with multimedia uses in mind. It was designed with a small lightweight kernel, using shared libraries to perform functions that most operating systems perform in the kernel. This reduces the processing that is performed in the kernel on behalf of application processes, transferring the activity to the processes themselves and facilitating accounting for resource usage. The ISAs that Nemesis supports include x86 ( Intel i486, Pentium, Pentium Pro, and Pentium II), Alpha and ARM (StrongARM The StrongARM is a family of computer microprocessors developed by Digital Equipment Corporation and manufactured in the late 1990s which implemented the ARM v4 instruction set architecture. It was later acquired by Intel in 1997 from DEC's o ... SA–110). Nemesis also runs on evaluation boards ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Context Switch
In computing, a context switch is the process of storing the state of a process or thread, so that it can be restored and resume execution at a later point, and then restoring a different, previously saved, state. This allows multiple processes to share a single central processing unit (CPU), and is an essential feature of a multiprogramming or multitasking operating system. In a traditional CPU, each process – a program in execution – uses the various CPU registers to store data and hold the current state of the running process. However, in a multitasking operating system, the operating system switches between processes or threads to allow the execution of multiple processes simultaneously. For every switch, the operating system must save the state of the currently running process, followed by loading the next process state, which will run on the CPU. This sequence of operations that stores the state of the running process and loads the following running process is called a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Linking
A static library or statically linked library contains functions and data that can be included in a consuming computer program at build-time such that the library does not need to be accessible in a separate file at run-time. If all libraries are statically linked, then the resulting executable will be stand-alone, a.k.a. a static build. A static library is either merged with other static libraries and object files at build-time to form a single executable or loaded at run-time into the address space of their corresponding executable at a static memory offset determined at compile-time/link-time. Comparison to dynamic linking Historically, all library linking was static, but today dynamic linking is an alternative and entails inherent trade-offs. An advantage of static over dynamic is that the application is guaranteed to have the library routines it requires available at run-time, as the code to those routines is embedded in the executable file. With dynamic linking, no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtualization
In computing, virtualization (abbreviated v12n) is a series of technologies that allows dividing of physical computing resources into a series of virtual machines, operating systems, processes or containers. Virtualization began in the 1960s with IBM CP/CMS. The control program CP provided each user with a simulated stand-alone System/360 computer. In hardware virtualization, the '' host machine'' is the machine that is used by the virtualization and the ''guest machine'' is the virtual machine. The words ''host'' and ''guest'' are used to distinguish the software that runs on the physical machine from the software that runs on the virtual machine. The software or firmware that creates a virtual machine on the host hardware is called a '' hypervisor'' or ''virtual machine monitor''. Hardware virtualization is not the same as hardware emulation. Hardware-assisted virtualization facilitates building a virtual machine monitor and allows guest OSes to be run in isolation. Deskt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attack Surface
The attack surface of a software environment is the sum of the different points (for " attack vectors") where an unauthorized user (the "attacker") can try to enter data to, extract data, control a device or critical software in an environment. Keeping the attack surface as small as possible is a basic security measure. Elements of an attack surface Worldwide digital change has accelerated the size, scope, and composition of an organization's attack surface. The size of an attack surface may fluctuate over time, adding and subtracting assets and digital systems (e.g. websites, hosts, cloud and mobile apps, etc.). Attack surface sizes can change rapidly as well. Digital assets eschew the physical requirements of traditional network devices, servers, data centers, and on-premise networks. This leads to attack surfaces changing rapidly, based on the organization's needs and the availability of digital services to accomplish it. Attack surface scope also varies from organization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |