|
Tris(2-aminoethyl)amine
Tris(2-aminoethyl)amine is the organic compound with the chemical formula, formula N(CH2CH2NH2)3. This colourless liquid is soluble in water and is highly basic, consisting of a tertiary amine center and three pendant primary amine groups. Tris(2-aminoethyl)amine is commonly abbreviated as tren or TREN. It is used a crosslinking agent in the synthesis of polyimine networks and a tripodal ligand in coordination chemistry. Supramolecular and polymer derivatives Tris(2-aminoethyl)amine has been used to prepare molecular capsules and related supramolecular structures. Metal complexes Tren is a C3-symmetric, tetradentate chelating ligand that forms stable complexes with transition metals, especially those in the 2+ and 3+ oxidation states. Tren complexes exist with relatively few isomers, reflecting the constrained connectivity of this tetramine. Thus, only a single achiral stereoisomer exists for [Co(tren)X2]+, where X is halide or pseudohalide. In contrast, for [Co(trien)X2]+ five di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diethylenetriamine
Diethylenetriamine (abbreviated and also known as 2,2’-Iminodi(ethylamine)) is an organic compound with the formula HN(CH2CH2NH2)2. This colourless hygroscopic liquid is soluble in water and polar organic solvents, but not simple hydrocarbons. Diethylenetriamine is structural analogue of diethylene glycol. Its chemical properties resemble those for ethylene diamine, and it has similar uses. It is a weak base and its aqueous solution is alkaline. DETA is a byproduct of the production of ethylenediamine from ethylene dichloride. Reactions and uses Diethylenetriamine is a common curing agent for epoxy resins in epoxy adhesives and other thermosets. It is N-alkylated upon reaction with epoxide groups forming crosslinks. In coordination chemistry, it serves as a tridentate ligand forming complexes such as Co(dien)(NO2)3. Like some related amines, it is used in oil industry for the extraction of acid gas. Like ethylenediamine, DETA can also be used to sensitize nitromethane, mak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
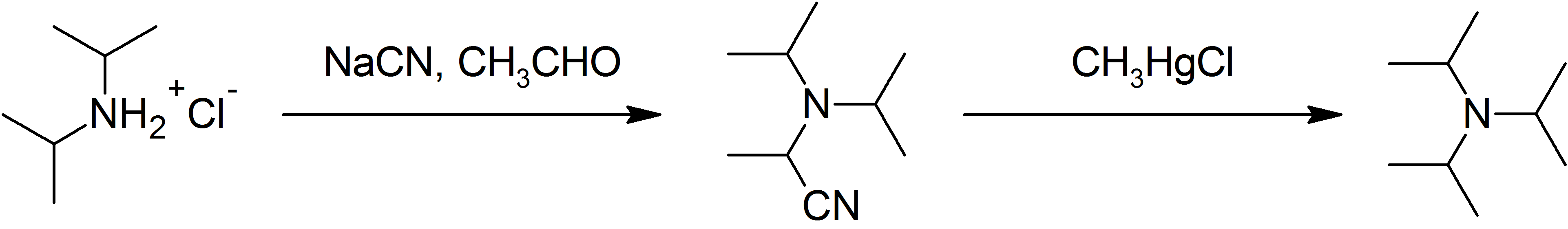
Triisopropylamine
Triisopropylamine is an organic chemical compound consisting of three isopropyl groups bound to a central nitrogen atom. As a hindered tertiary amine, it can be used as a non-nucleophilic base and as a stabilizer for polymers; however, its applications are limited by its relatively high cost and difficult synthesis. Structure In the early 1990s, theoretical studies and electron diffraction analysis of the 3D structure of the molecule, in the gas phase or in non-polar solvents, indicated that the bonds between the nitrogen atom and the three carbon atoms were nearly coplanar in the ground state, instead of forming a trigonal pyramid as in simpler amines. The average C-N-C angle was claimed to be 119.2°, much closer to the 120° of the flat configuration than to the 111.8° of trimethylamine. This peculiarity was attributed to steric hindrance by the bulky isopropyl radicals. However, in 1998 X-ray diffraction analysis of the crystallized solid showed that the C3N core is ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethylamine
Trimethylamine (TMA) is an organic compound with the formula N(CH3)3. It is a trimethylated derivative of ammonia. TMA is widely used in industry. At higher concentrations it has an ammonia-like odor, and can cause necrosis of mucous membranes on contact. At lower concentrations, it has a "fishy" odor, the odor associated with rotting fish. Physical and chemical properties TMA is a colorless, hygroscopic, and flammable tertiary amine. It is a gas at room temperature but is usually sold as a 40% solution in water. It is also sold in pressurized gas cylinders. TMA protonates to give the trimethylammonium cation. Trimethylamine is a good nucleophile, and this reactivity underpins most of its applications. Trimethylamine is a Lewis base that forms adducts with a variety of Lewis acids. Production Industry and laboratory Trimethylamine is prepared by the reaction of ammonia and methanol employing a catalyst: :3 CH3OH + NH3 → (CH3)3N + 3 H2O This reaction coproduces the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis acids and bases, Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent bond, covalent to ionic bond, ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acids and bases, Lewis acidic "ligands". Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in almost all circumstances, although gaseous "naked" metal ions can be generated in a high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity (chemistry), reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection requires critical consideration in many practical are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triethylamine
Triethylamine is the chemical compound with the formula N(CH2CH3)3, commonly abbreviated Et3N. Like triethanolamine and the tetraethylammonium ion, it is often abbreviated TEA. It is a colourless volatile liquid with a strong fishy odor reminiscent of ammonia. Like diisopropylethylamine (Hünig's base), triethylamine is commonly employed in organic synthesis, usually as a base. Synthesis and properties Triethylamine is prepared by the alkylation of ammonia with ethanol: :NH3 + 3 C2H5OH → N(C2H5)3 + 3 H2O The pKa of protonated triethylamine is 10.75,David Evans Research Group and it can be used to prepare buffer solutions at that pH. The hydrochloride |
HN3 (nitrogen Mustard)
2-Chloro-''N'',''N''-bis(2-chloroethyl)ethanamine, also known as trichlormethine, tris(2-chloroethyl)amine is the organic compound with the formula N(CH2CH2Cl)3. Often abbreviated HN3 or HN-3, it is a powerful blister agent and a nitrogen mustard used for chemical warfare. HN3 was the last of the nitrogen mustard agents developed. It was designed as a military agent and is the only one of the nitrogen mustards that is still used for military purposes. It is the principal representative of the nitrogen mustards because its vesicant properties are almost equal to those of HD and thus the analogy between the two types of mustard is the strongest.NITROGEN MUSTARD HN-3 Emergency Response Safety and Health Database. |
Dimethylaminopropylamine
Dimethylaminopropylamine (DMAPA) is a diamine used in the preparation of some surfactants, such as cocamidopropyl betaine which is an ingredient in many personal care products including soaps, shampoos, and cosmetics. BASF, a major producer, claims that DMAPA-derivatives do not sting the eyes and makes a fine-bubble foam, making it appropriate in shampoos. Preparation and reactions DMAPA is commonly produced commercially via the reaction between dimethylamine and acrylonitrile (a Michael reaction) to produce dimethylaminopropionitrile. A subsequent hydrogenation Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to redox, reduce or Saturated ... step yields DMAPA: : DMAPA is readily converted to the mustard dimethylaminopropyl-3-chloride, a powerful alkylating agent. Health effects Dimethylaminopropylamine is a kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HN1 (nitrogen Mustard)
Bis(2-chloroethyl)ethylamine is the organic compound with the formula C2H5N(CH2CH2Cl)2. Often abbreviated HN1, it is a powerful vesicant and a nitrogen mustard gas. HN1 was developed in the 1920s and 1930s to remove warts and later as a military agent. Because of the latter use, it is a Schedule 1 chemical within the Chemical Weapons Convention and therefore use and production is strongly restricted. It has never been used in warfare.The Emergency Response Safety and Health Database: NITROGEN MUSTARD HN-1 National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Accessed March 19, 2009. It is an oily liquid with a colorless to pale yellow appearance and a faint fishy or musty odor. HN1 is also an |
Mechlorethamine
Chlormethine ( INN, BAN), also known as mechlorethamine ( USAN, USP), mustine, HN2, and (in post-Soviet states) embikhin (эмбихин), is a nitrogen mustard sold under the brand name Mustargen among others. It is the prototype of alkylating agents, a group of anticancer chemotherapeutic drugs. It works by binding to DNA, crosslinking two strands and preventing cell duplication. It binds to the N7 nitrogen on the DNA base guanine. As the chemical is a blister agent, its use is strongly restricted within the Chemical Weapons Convention where it is classified as a Schedule 1 substance. Mechlorethamine belongs to the group of nitrogen mustard alkylating agents. Uses It has been derivatized into the estrogen analogue estramustine phosphate, used to treat prostate cancer. It can also be used in chemical warfare where it has the code-name HN2. This chemical is a form of nitrogen mustard gas and a powerful vesicant. Historically, some uses of mechlorethamine have included lymp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Chemistry
A coordination complex is a chemical compound consisting of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of chemical bond, bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing chemical compound, compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the periodic table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A Ligand#Polydentate and polyhapto ligand motifs and nomenclature, polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
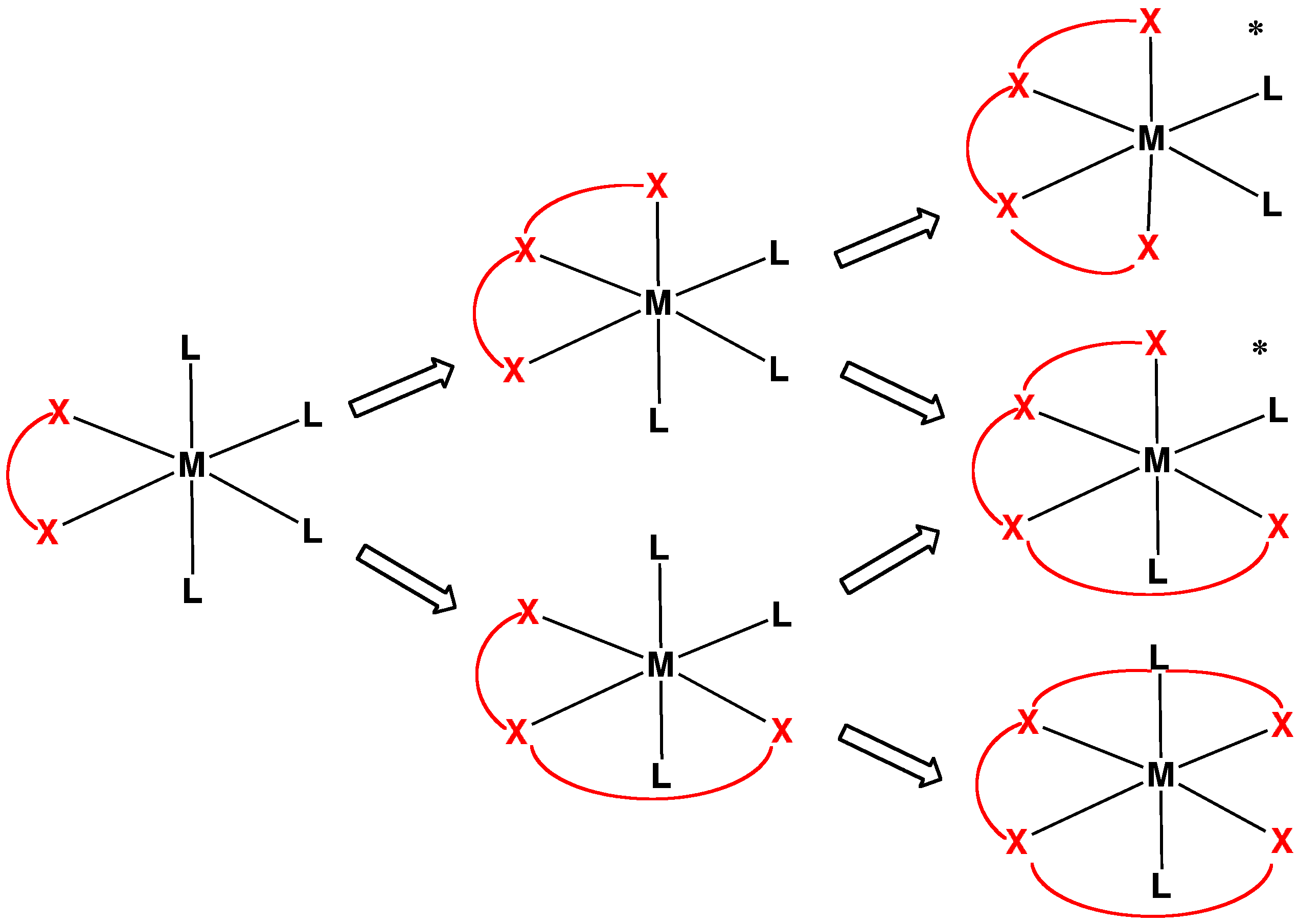
Tetradentate
In chemistry, tetradentate ligands are ligands that bind four donor atoms to a central atom to form a coordination complex. This number of donor atoms that bind is called denticity and is a method of classifying ligands. Tetradentate ligands are common in nature in the form of chlorophyll, which has a core ligand called chlorin, and heme, which has a core ligand called porphyrin. They are responsible for the colour observed in plants and humans. Phthalocyanine is an artificial macrocyclic tetradentate ligand that is used to make blue and green pigments. Shape Tetradentate ligands can be classified by the topology of the connections between donor atoms. Common forms are linear (also called sequential), ring or tripodal. A tetrapodal ligand that is also tetradentate has four legs with donor atoms and a bridgehead that is not a donor. Upon binding with a central atom, there are several arrangements possible (known as geometric isomers). Linear ligands A linear tetradentate ligand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloride
In chemistry, a hydrochloride is an acid salt resulting, or regarded as resulting, from the reaction of hydrochloric acid with an organic base (e.g. an amine). An alternative name is chlorhydrate, which comes from French. An archaic alternative name is muriate, derived from hydrochloric acid's ancient name: muriatic acid. Uses Converting amines into their hydrochlorides is a common way to improve their water solubility, which can be desirable for substances used in medications. The European Pharmacopoeia lists more than 200 hydrochlorides as active ingredients in medications. These hydrochlorides, compared to free bases, may more readily dissolve in the gastrointestinal tract and be absorbed into the bloodstream more quickly. Additionally, many hydrochlorides of amines have a longer shelf-life than their respective free bases. Amine hydrochlorides represent latent forms of a more reactive free base. In this regard, formation of an amine hydrochloride confers protection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |