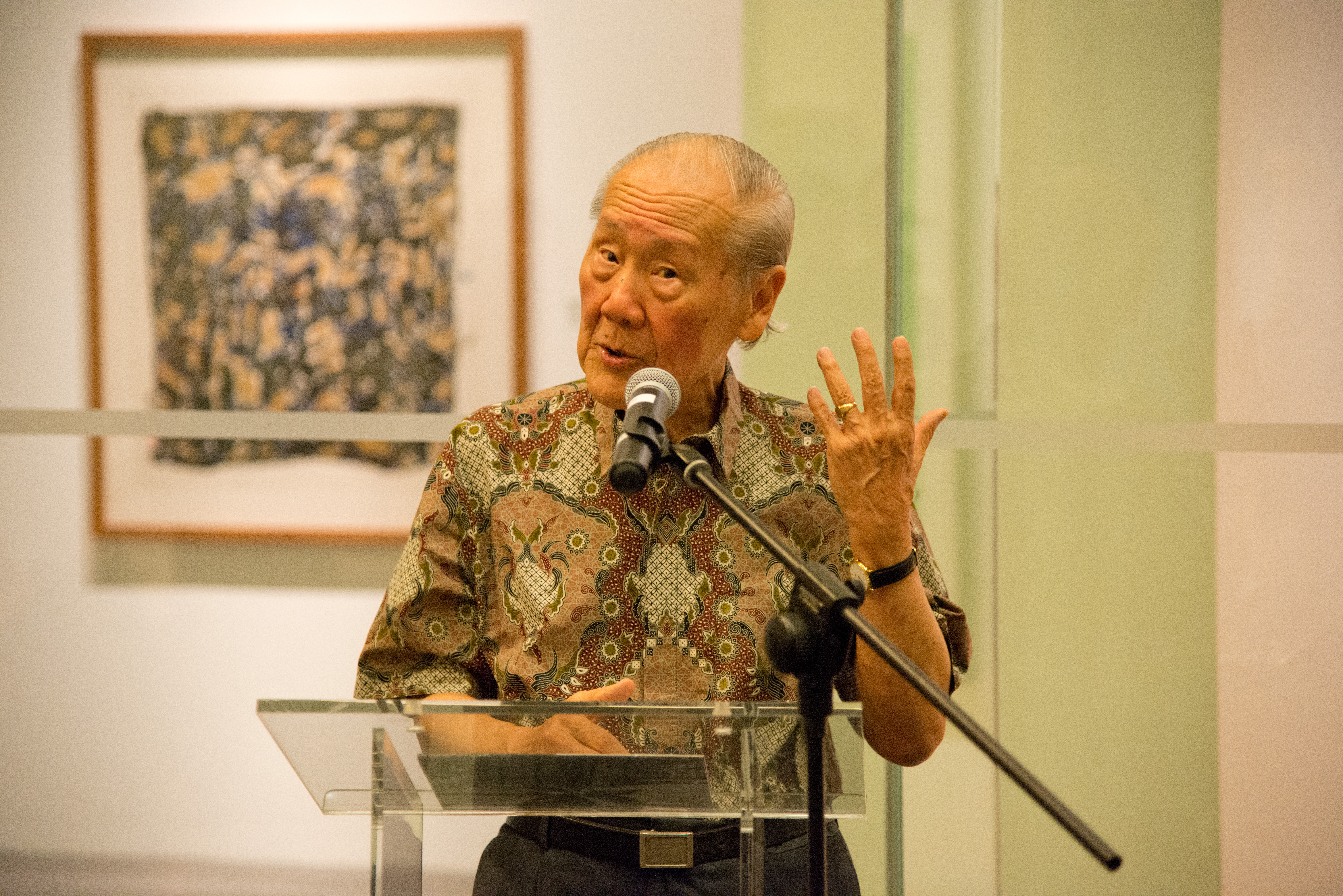|
Tianxia
''Tianxia'' (), literally meaning "(all) under Heaven", is a Chinese term for a historical Chinese cultural concept that denoted either the entire geographical world or the metaphysical realm of mortals, and later became associated with political sovereignty. In ancient China and imperial China, ''tianxia'' denoted the lands, space, and area divinely appointed to the Chinese sovereign by universal and well-defined principles of order. The center of this land was directly apportioned to the Chinese court, forming the center of a world view that centered on the Chinese court and went concentrically outward to major and minor officials and then the common subjects, tributary states, and finally ending with fringe "barbarians". The center of this world view was not exclusionary in nature, and outer groups, such as ethnic minorities and foreign people, who accepted the mandate of the Chinese Emperor were themselves received and included into the Chinese ''tianxia''. In classic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Tianxia
American Tianxia is a term coined by the historian Wang Gungwu in 2013 to refer to the contemporary global order centered on the United States. It was further developed by sociologist Salvatore Babones to analyze today's millennial world-system through the lens of the Chinese concept of ''tianxia'', meaning "all under heaven." While the United States is often called an "empire," this is a historically loaded term that is associated with perceptions of American imperialism. The concept of ''tianxia'' has a different set of meanings attached to it that Wang suggests and Babones argues are closer to what the United States actually displays in its contemporary approach to foreign affairs. Background The original Chinese term ''tianxia'' describes a world-system that, according to Wang, described "an enlightened realm that Confucian thinkers and mandarins raised to one of universal values that determined who was civilized and who was not." The term first became widely used during t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Son Of Heaven
Son of Heaven, or ''Tianzi'' (), was the sacred monarchical title of the Chinese sovereign. It originated with the Zhou dynasty and was founded on the political and spiritual doctrine of the Mandate of Heaven. Since the Qin dynasty, the secular imperial title of the Son of Heaven was "Huangdi". The title, "Son of Heaven", was subsequently adopted by other Sinospheric monarchs to justify their rule. The Son of Heaven was the supreme universal monarch, who ruled '' tianxia'' (means "all under heaven"). His status is rendered in English as "ruler of the whole world." The title, "Son of Heaven", was interpreted literally only in China and Japan, whose monarchs were referred to as demigods, deities, or " living gods", chosen by the gods and goddesses of heaven. History and adoption The title "Son of Heaven" (; Middle Chinese: ; Old Chinese ( B-S): ) stems from the concept of the Mandate of Heaven, created by the Zhou dynasty monarchs to justify their having deposed the Sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wang Gungwu
Wang Gungwu, (; born 9 October 1930) is a Chinese-Singaporean historian, sinologist, and writer. He is a historian of China and Southeast Asia. He has studied and written about the Chinese diaspora, but he has objected to the use of the word ''diaspora'' to describe the migration of Chinese from China because both it mistakenly implies that all overseas Chinese are the same and has been used to perpetuate fears of a " Chinese threat", under the control of the Chinese government. An expert on the Chinese tianxia ("all under heaven") concept, he was the first to suggest its application to the contemporary world as an American Tianxia. Background Wang was born in Surabaya, Indonesia to ethnic Chinese parents from Taizhou, Jiangsu and grew up in Ipoh, Malaysia. He completed his secondary education in Anderson School, an English medium school in Ipoh. Wang studied history in the University of Malaya, where he received his bachelor's and master's degrees. He was a founding member of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandate Of Heaven
The Mandate of Heaven () is a Chinese political philosophy that was used in ancient and imperial China to legitimize the rule of the King or Emperor of China. According to this doctrine, heaven (天, '' Tian'') – which embodies the natural order and will of the universe – bestows the mandate on a just ruler of China, the " Son of Heaven". If a ruler was overthrown, this was interpreted as an indication that the ruler was unworthy and had lost the mandate. It was also a common belief that natural disasters such as famine and flood were divine retributions bearing signs of Heaven's displeasure with the ruler, so there would often be revolts following major disasters as the people saw these calamities as signs that the Mandate of Heaven had been withdrawn. The Mandate of Heaven does not require a legitimate ruler to be of noble birth, depending instead on how well that person can rule. Chinese dynasties such as the Han and Ming were founded by men of common origins, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Sovereign
The Chinese sovereign was the ruler of a particular monarchical regime in the historical periods of ancient China and imperial China. Sovereigns ruling the same regime, and descended from the same paternal line, constituted a dynasty. Several titles and naming schemes have been used throughout Chinese history. Sovereign titles Emperor The characters ''Huang'' (皇 huáng "august (ruler)") and ''Di'' (帝 dì "divine ruler") had been used separately and never consecutively (see Three August Ones and Five Emperors). The character was reserved for mythological rulers until the first emperor of Qin ( Qin Shi Huang), who created a new title ''Huangdi'' (皇帝 in pinyin: huáng dì) for himself in 221 BCE, which is commonly translated as '' Emperor'' in English. This title continued in use until the fall of the Qing dynasty in 1912. From the Han Dynasty, the title ''Huangdi'' could also be abbreviated to ''huang'' or ''di''. The former nobility titles ''Qing'' (卿), ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbarian A barbarian (or savage) is someone who is perceived to be either uncivilized or primitive. The designation is usually applied as a generalization based on a popular stereotype; barbarians can be members of any nation judged by some to be less civilized or orderly (such as a tribal society) but may also be part of a certain "primitive" cultura |