|
Thalassocratic
A thalassocracy or thalattocracy, sometimes also maritime empire, is a state with primarily maritime realms, an empire at sea, or a seaborne empire. Traditional thalassocracies seldom dominate interiors, even in their home territories. Examples of this were the Phoenician states of Tyre, Sidon and Carthage; the Italian maritime republics of Venice and Genoa of the Mediterranean; the Omani Empire of Arabia; and the empires of Srivijaya and Majapahit in Maritime Southeast Asia. Thalassocracies can thus be distinguished from traditional empires, where a state's territories, though possibly linked principally or solely by the sea lanes, generally extend into mainland interiors in a tellurocracy ("land-based hegemony"). The term ''thalassocracy'' can also simply refer to naval supremacy, in either military or commercial senses. The ancient Greeks first used the word ''thalassocracy'' to describe the government of the Minoan civilization, whose power depended on its navy. Herodotus dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tellurocracy
Tellurocracy (from and ) is a concept proposed by Aleksandr Dugin to describe a type of civilization or state system that is defined by the development of land territories and consistent penetration into inland territories. Tellurocratic states possess a set state-territory in which the state-forming ethnic majority lives, around this territory further land expansion occurs. Tellurocracy is conceived of as an antonym to thalassocracy. Most states display an amalgam of tellurocratic and thalassocratic features. In political geography, geopolitics and geo-economics, the term is used to explain the power of a country through its control over land. For example, prior to their merger, the Sultanate of Muscat was thalassocratic, but the Imamate of Oman was landlocked and purely tellurocratic. It could be suggested that most or all landlocked states are tellurocracies. Defining tellurocracy Tellurocracies are generally not purely tellurocratic. In particular, most large tellurocrac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the Southeast Asian countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. The terms Island Southeast Asia and Insular Southeast Asia are sometimes given the same meaning as Maritime Southeast Asia. Other definitions restrict Island Southeast Asia to just the islands between mainland Southeast Asia and the continental shelf of Australia and New Guinea. There is some variability as to whether Taiwan is included in this. Peter Bellwood includes Taiwan in his definition, as did Robert Blust, whilst there are examples that do not. The 16th-century term " East Indies" and the later 19th-century term " Malay Archipelago" are also used to refer to Maritime Southeast Asia. In Indonesia, the Old Javanese term " Nusantara" is also used as a synonym for Maritime Southeast Asia. The term, however, is nationalistic and has shifting boundaries. It usually only encompasses Peninsular Malaysia, the Sunda Islands, Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Majapahit
Majapahit (; (eastern and central dialect) or (western dialect)), also known as Wilwatikta (; ), was a Javanese people, Javanese Hinduism, Hindu-Buddhism, Buddhist thalassocracy, thalassocratic empire in Southeast Asia based on the island of Java (in modern-day Indonesia). At its greatest extent, following significant military expansions, the territory of the empire and its tributary states covered almost the entire Nusantara (term), Nusantara archipelago, spanning both Asia and Oceania. After a Regreg war, civil war that weakened control over the vassal states, the empire slowly declined before collapsing in 1527 due to an Demak–Majapahit conflicts, invasion by the Demak Sultanate, Sultanate of Demak. The fall of Majapahit saw the rise of History of Indonesia#Islamic civilizations, Islamic kingdoms in Java. Established by Raden Wijaya in 1292, Majapahit rose to power after the Mongol invasion of Java and reached its peak during the era of the queen Tribhuwana Wijayatungga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
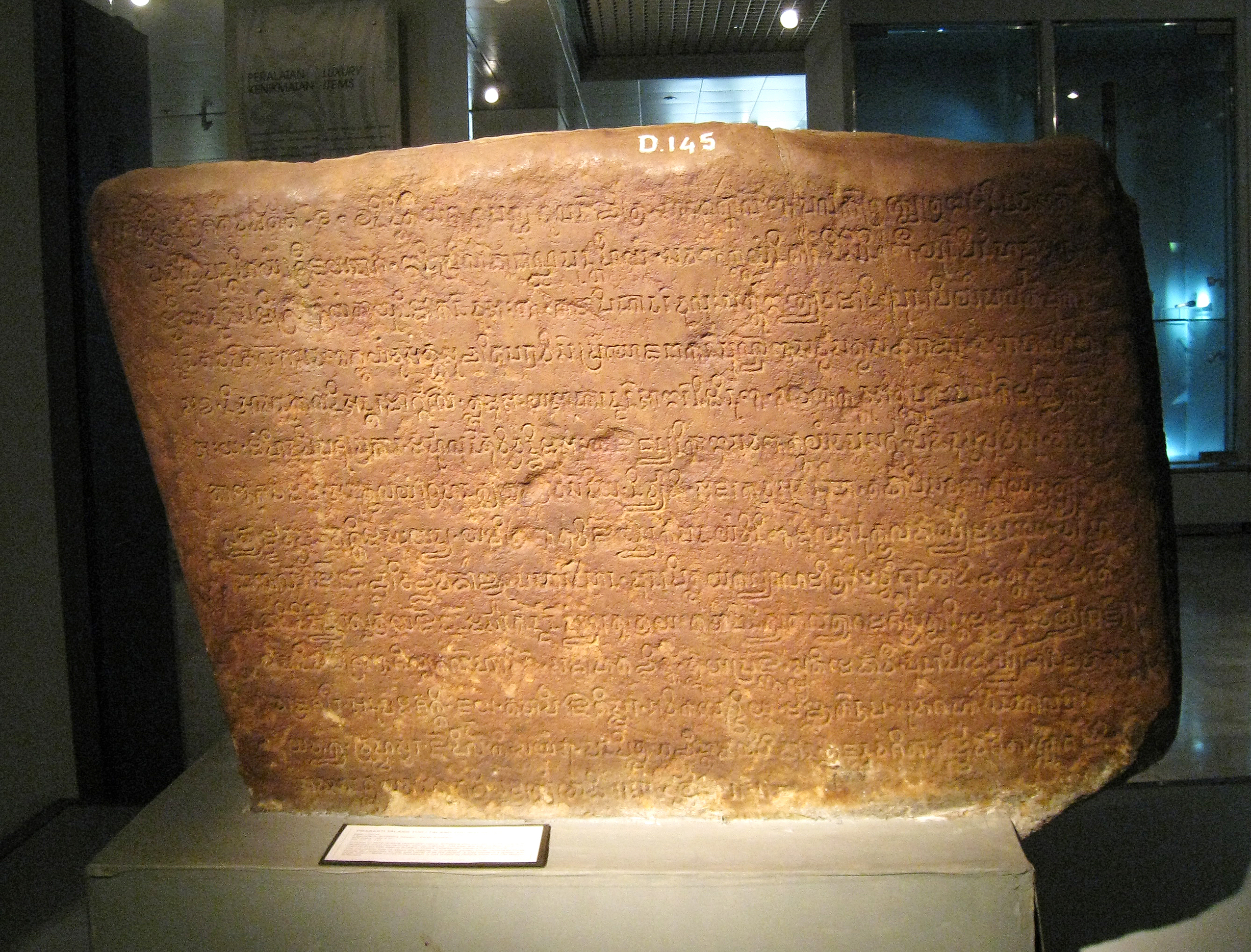
Srivijaya
Srivijaya (), also spelled Sri Vijaya, was a Hinduism, Hindu-Buddhism, Buddhist thalassocracy, thalassocratic empire based on the island of Sumatra (in modern-day Indonesia) that influenced much of Southeast Asia. Srivijaya was an important centre for the expansion of Buddhism from the 7th to 11th century AD. Srivijaya was the first polity to dominate much of western Maritime Southeast Asia. Due to its location, Srivijaya developed complex technology utilizing maritime resources. In addition, its economy became progressively reliant on Maritime Silk Road, the booming trade in the region, thus transforming it into a luxury good, prestige goods-based economy. The earliest reference to it dates from the 7th century. A Tang dynasty Chinese people, Chinese Bhikkhu, monk, Yijing (monk), Yijing, wrote that he visited Srivijaya in 671 for six months. The earliest known inscription in which the name Srivijaya appears also dates from the 7th century in the Kedukan Bukit inscription fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime Republics
The maritime republics (), also called merchant republics (), were Italian Thalassocracy , thalassocratic Port city, port cities which, starting from the Middle Ages, enjoyed political autonomy and economic prosperity brought about by their maritime activities. The term, coined during the 19th century, generally refers to four Italian cities, whose coats of arms have been shown since 1947 on the flags of the Italian Navy and the Italian Merchant Navy: Duchy of Amalfi, Amalfi, Republic of Genoa , Genoa, Republic of Pisa, Pisa, and Republic of Venice, Venice. In addition to the four best known cities, Republic of Ancona, Ancona,Peris Persi, in ''Conoscere l'Italia'', vol. Marche, Istituto Geografico De Agostini, Novara 1982 (p. 74); AA.VV. ''Meravigliosa Italia, Enciclopedia delle regioni'', edited by Valerio Lugoni, Aristea, Milano; Guido Piovene, in ''Tuttitalia'', Casa Editrice Sansoni, Firenze & Istituto Geografico De Agostini, Novara (p. 31); Pietro Zampetti, in ''Itinerari de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continentalism
Continentalism refers to the agreements or policies that favor the regionalization and/or cooperation between states within a continent. The term is used more often in the European and North American contexts, but the concept has been applied to other continents including Africa, Asia and South America. In North American history, continentalism became linked to manifest destiny and involved merging continental expansion with international growth. Continentalism in Europe Continentalism in North America United States Historically, the United States of America saw itself as a blossoming continental nation-state. Accordingly, the first governing body for the North American colonists was called the Continental Congress, which sought to receive delegates from across the British colonized areas of the continent, including the future Canadian provinces of Quebec and Nova Scotia. Continentalism in the United States was developed through the expeditions and experiences of front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
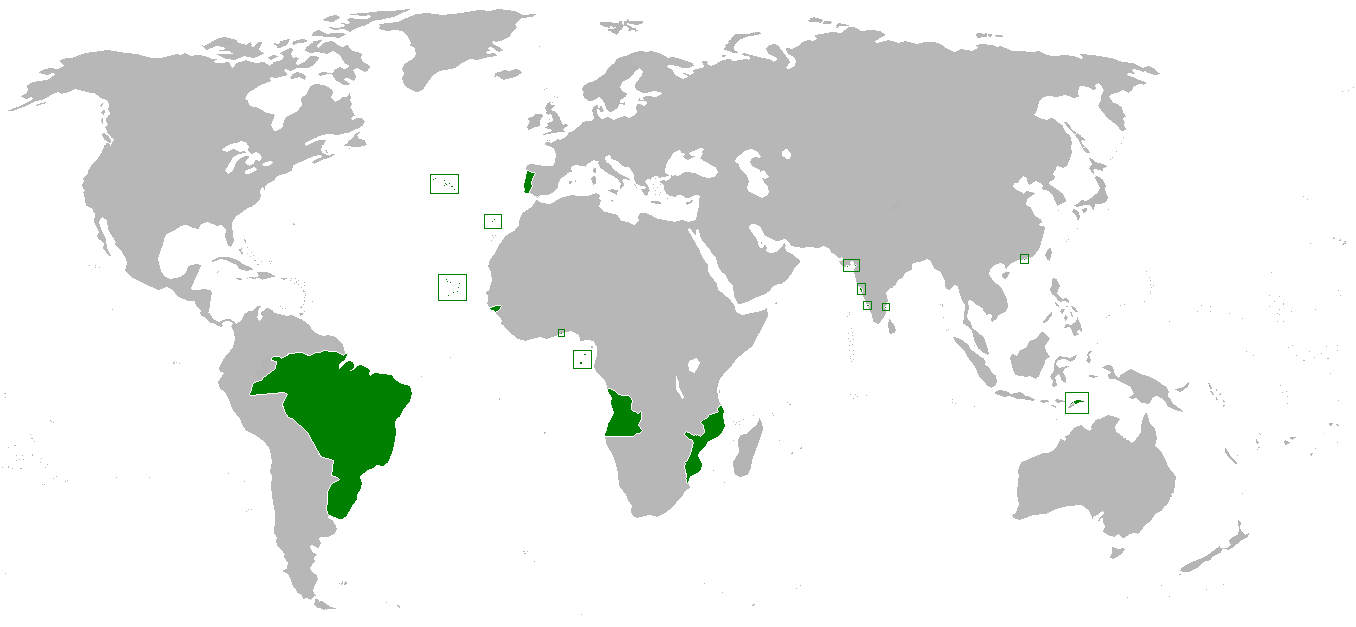
Pluricontinentalism
Pluricontinentalism () was a geopolitical concept, positing that Portugal was a transcontinental country and a unitary nation-state consisting of continental Portugal and its overseas provinces. With origins as early as the 14th century, pluricontinentalism gained official state sponsorship in the Estado Novo regime. It was the idea that Portugal was not a colonial empire (Portuguese Empire) but a singular nation-state spread across continents (hence the name). As such, overseas possessions were a part of Portuguese identity. The first time that Portugal was a pluricontinental country was during the reign of Maria I of Portugal, with the creation of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves, when the Portuguese court was living in Brazil and Rio de Janeiro served as the capital for the country. The idea of pluricontinentalism quickly collapsed following the Carnation Revolution in 1974. People associated with pluricontinentalism * António Vieira * Luís ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlanticism
Atlanticism, also known as Transatlanticism or North Atlanticism, is the ideology which advocates a close alliance between nations in Northern America (the United States and Canada) and in Europe on political, economic, and defense issues. The term derives from the North Atlantic Ocean, which is bordered by North America and Europe. The term can be used in a more specific way to refer to support for North Atlantic military alliances against the Soviet Union, or in a more expansive way to imply broader cooperation, perceived deeply shared values, a merging of diplomatic cultures, as well as a sense of community and some degree of integration between North America and Europe. In practice, the philosophy of Atlanticism encourages active North American, particularly American, engagement in Europe and close cooperation between states on both sides of the ocean. Atlanticism manifested itself most strongly during the Second World War and in its aftermath, the Cold War, through the estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Myres
Sir John Linton Myres (3 July 1869 – 6 March 1954) was a British archaeologist and academic, who conducted excavations in Cyprus during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Having been a fellow at Magdalen College, Oxford and then Christ Church, Oxford, he was briefly Gladstone Professor of Greek at the University of Liverpool (1907–1910). Having returned to the University of Oxford, he was the first Wykeham Professor of Ancient History from 1910 until 1939. During the First World War, he served with the Royal Naval Volunteer Reserve in the Eastern Mediterranean. Early life and education John Lynton Myres was the son of the Rev. William Miles Myres and his wife, Jane Linton, and was educated at Winchester College, then an all-boys independent boarding school. He studied '' Literae humaniores'' (i.e. classics) at New College, Oxford, achieving first class honours in both Mods and Greats, and graduated with a Bachelor of Arts (BA) degree in 1892. During the sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasianism
Eurasianism ( ) is a Political sociology, socio-political movement in Russia that emerged in the early 20th century under the Russian Empire, which states that Russia does not belong in the "European" or "Asian" categories but instead to the Geopolitics, geopolitical concept of Eurasia and the "Russian world", forming an ostensibly standalone Russian civilization. The first Eurasianists were mostly ''émigrés'', Pacifism, pacifists, and their vision of the future had features of romanticism and utopianism. The goal of the Eurasianists was the unification of the Nicene Christianity, main Christian churches under the leadership of the Russian Orthodox Church. A key feature of Eurasianism is the rejection of Russian ethnic nationalism, which seeks to build a Pan-Slavism, pan-Slavic state. The Eurasianists strongly opposed the territorial fragmentation of the Russian Empire that had occurred due to the October Revolution, Bolshevik Revolution and the following Russian Civil War, civi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minoan Civilization
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age culture which was centered on the island of Crete. Known for its monumental architecture and energetic art, it is often regarded as the first civilization in Europe. The ruins of the Minoan palaces at Knossos and Phaistos are popular tourist attractions. The Minoan civilization developed from the local Neolithic culture around 3100BC, with complex urban settlements beginning around 2000BC. After 1450BC, they came under the cultural and perhaps political domination of the mainland Mycenaean Greeks, forming a hybrid culture which lasted until around 1100BC. Minoan art included elaborately decorated pottery, seals, figurines, and colorful frescoes. Typical subjects include nature and ritual. Minoan art is often described as having a fantastical or ecstatic quality, with figures rendered in a manner suggesting motion. Little is known about the structure of Minoan society. Minoan art contains no unambiguous depiction of a monarch, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronicon (Eusebius)
The ''Chronicon'' or ''Chronicle'' (Ancient Greek, Greek: Παντοδαπὴ ἱστορία ''Pantodape historia'', "Universal history (genre), Universal history") was a work in two books by Eusebius, Eusebius of Caesarea. It seems to have been compiled in the early 4th century. It contained a world chronicle from Abraham until the vicennalia of Constantine I in A.D. 325. Book 1 contained sets of extracts from earlier writers; book 2 contained a technically innovative list of dates and events in tabular format. The original Koine Greek, Greek text is lost, although substantial quotations exist in later chronographers. Both books are mostly preserved in an Armenian language, Armenian translation. Book 2 is entirely preserved in the Latin translation by Jerome. Portions also exist in quotation in later Syriac writers such as the fragments by James of Edessa and, following him, Michael the Syrian. The ''Chronicle'' as preserved extends to the year 325, and was written befo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |