|
Tetrahedral Angle
In geometry, a tetrahedron (: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertices. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ordinary convex polyhedra. The tetrahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a Euclidean simplex, and may thus also be called a 3-simplex. The tetrahedron is one kind of pyramid, which is a polyhedron with a flat polygon base and triangular faces connecting the base to a common point. In the case of a tetrahedron, the base is a triangle (any of the four faces can be considered the base), so a tetrahedron is also known as a "triangular pyramid". Like all convex polyhedra, a tetrahedron can be folded from a single sheet of paper. It has two such nets. For any tetrahedron there exists a sphere (called the circumsphere) on which all four vertices lie, and another sphere (the insphere) tangent to the tetrahedron's faces. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometry
Geometry (; ) is a branch of mathematics concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. Geometry is, along with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a ''List of geometers, geometer''. Until the 19th century, geometry was almost exclusively devoted to Euclidean geometry, which includes the notions of point (geometry), point, line (geometry), line, plane (geometry), plane, distance, angle, surface (mathematics), surface, and curve, as fundamental concepts. Originally developed to model the physical world, geometry has applications in almost all sciences, and also in art, architecture, and other activities that are related to graphics. Geometry also has applications in areas of mathematics that are apparently unrelated. For example, methods of algebraic geometry are fundamental in Wiles's proof of Fermat's Last Theorem, Wiles's proof of Fermat's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platonic Solid
In geometry, a Platonic solid is a Convex polytope, convex, regular polyhedron in three-dimensional space, three-dimensional Euclidean space. Being a regular polyhedron means that the face (geometry), faces are congruence (geometry), congruent (identical in shape and size) regular polygons (all angles congruent and all edge (geometry), edges congruent), and the same number of faces meet at each Vertex (geometry), vertex. There are only five such polyhedra: Geometers have studied the Platonic solids for thousands of years. They are named for the ancient Greek philosopher Plato, who hypothesized in one of his dialogues, the ''Timaeus (dialogue), Timaeus'', that the classical elements were made of these regular solids. History The Platonic solids have been known since antiquity. It has been suggested that certain carved stone balls created by the late Neolithic people of Scotland represent these shapes; however, these balls have rounded knobs rather than being polyhedral, the num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
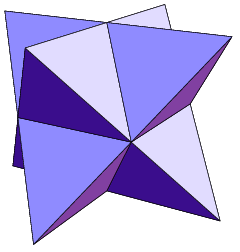
Stellated Octahedron
The stellated octahedron is the only stellation of the octahedron. It is also called the stella octangula (Latin for "eight-pointed star"), a name given to it by Johannes Kepler in 1609, though it was known to earlier geometers. It was depicted in Pacioli's ''Divina proportione, De Divina Proportione,'' 1509. It is the simplest of five regular polyhedral compounds, and the only regular polyhedral compound composed of only two polyhedra. It can be seen as a 3D extension of the hexagram: the hexagram is a two-dimensional shape formed from two overlapping equilateral triangles, central symmetry, centrally symmetric to each other, and in the same way the stellated octahedron can be formed from two centrally symmetric overlapping tetrahedra. This can be generalized to any desired amount of higher dimensions; the four-dimensional equivalent construction is the compound of two 5-cells. Construction and properties The stellated octahedron is constructed by a stellation of the regula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyhedral Compound
In geometry, a polyhedral compound is a figure that is composed of several polyhedra sharing a common Centroid, centre. They are the three-dimensional analogs of star polygon#Regular compounds, polygonal compounds such as the hexagram. The outer Vertex (geometry), vertices of a compound can be connected to form a convex polyhedron called its convex hull. A compound is a faceting of its convex hull. Another convex polyhedron is formed by the small central space common to all members of the compound. This polyhedron can be used as the core for a set of stellations. Regular compounds A regular polyhedral compound can be defined as a compound which, like a regular polyhedron, is vertex-transitive, edge-transitive, and face-transitive. Unlike the case of polyhedra, this is not equivalent to the symmetry group acting transitively on its flag (geometry), flags; the compound of two tetrahedra is the only regular compound with that property. There are five regular compounds of polyhe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual Polyhedron
In geometry, every polyhedron is associated with a second dual structure, where the vertices of one correspond to the faces of the other, and the edges between pairs of vertices of one correspond to the edges between pairs of faces of the other. Such dual figures remain combinatorial or abstract polyhedra, but not all can also be constructed as geometric polyhedra. Starting with any given polyhedron, the dual of its dual is the original polyhedron. Duality preserves the symmetries of a polyhedron. Therefore, for many classes of polyhedra defined by their symmetries, the duals belong to a corresponding symmetry class. For example, the regular polyhedrathe (convex) Platonic solids and (star) Kepler–Poinsot polyhedraform dual pairs, where the regular tetrahedron is self-dual. The dual of an isogonal polyhedron (one in which any two vertices are equivalent under symmetries of the polyhedron) is an isohedral polyhedron (one in which any two faces are equivalent .., and vice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire (classical Element)
Fire is one of the four classical elements along with earth, water and air in ancient Greek philosophy and science. Fire is considered to be both hot and dry and, according to Plato, is associated with the tetrahedron. Greek and Roman tradition Fire is one of the four classical elements in ancient Greek philosophy and science. It was commonly associated with the qualities of energy, assertiveness, and passion. In one Greek myth, Prometheus stole ''fire'' from the gods to protect the otherwise helpless humans, but was punished for this charity. Fire was one of many '' archai'' proposed by the pre-Socratics, most of whom sought to reduce the cosmos, or its creation, to a single substance. Heraclitus considered ''fire'' to be the most fundamental of all elements. He believed fire gave rise to the other three elements: "All things are an interchange for fire, and fire for all things, just like goods for gold and gold for goods." Diels-Kranz B90 (Freeman 9481970p. 45. He had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plato
Plato ( ; Greek language, Greek: , ; born BC, died 348/347 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical Greece, Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the written dialogue and dialectic forms. He influenced all the major areas of theoretical philosophy and practical philosophy, and was the founder of the Platonic Academy, a philosophical school in History of Athens, Athens where Plato taught the doctrines that would later become known as Platonism. Plato's most famous contribution is the theory of forms, theory of forms (or ideas), which aims to solve what is now known as the problem of universals. He was influenced by the pre-Socratic thinkers Pythagoras, Heraclitus, and Parmenides, although much of what is known about them is derived from Plato himself. Along with his teacher Socrates, and his student Aristotle, Plato is a central figure in the history of Western philosophy. Plato's complete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regular Polygons
In Euclidean geometry, a regular polygon is a polygon that is Equiangular polygon, direct equiangular (all angles are equal in measure) and Equilateral polygon, equilateral (all sides have the same length). Regular polygons may be either ''convex polygon, convex'' or ''star polygon, star''. In the limit (mathematics), limit, a sequence of regular polygons with an increasing number of sides approximates a circle, if the perimeter or area is fixed, or a regular apeirogon (effectively a Line (geometry), straight line), if the edge length is fixed. General properties These properties apply to all regular polygons, whether convex or star polygon, star: *A regular ''n''-sided polygon has rotational symmetry of order ''n''. *All vertices of a regular polygon lie on a common circle (the circumscribed circle); i.e., they are concyclic points. That is, a regular polygon is a cyclic polygon. *Together with the property of equal-length sides, this implies that every regular polygon also h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deltahedron
A deltahedron is a polyhedron whose faces are all equilateral triangles. The deltahedron was named by Martyn Cundy, after the Greek capital letter delta resembling a triangular shape Δ. Deltahedra can be categorized by the property of convexity. The simplest convex deltahedron is the regular tetrahedron, a pyramid with four equilateral triangles. There are eight convex deltahedra, which can be used in the applications of chemistry as in the polyhedral skeletal electron pair theory and chemical compounds. There are infinitely many concave deltahedra. Strictly convex deltahedron A polyhedron is said to be ''convex'' if a line between any two of its vertices lies either within its interior or on its boundary, and additionally, if no two faces are coplanar (lying in the same plane) and no two edges are collinear (segments of the same line), it can be considered as being strictly convex. Of the eight convex deltahedra, three are Platonic solids and five are Johnson solids. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convex Set
In geometry, a set of points is convex if it contains every line segment between two points in the set. For example, a solid cube (geometry), cube is a convex set, but anything that is hollow or has an indent, for example, a crescent shape, is not convex. The boundary (topology), boundary of a convex set in the plane is always a convex curve. The intersection of all the convex sets that contain a given subset of Euclidean space is called the convex hull of . It is the smallest convex set containing . A convex function is a real-valued function defined on an interval (mathematics), interval with the property that its epigraph (mathematics), epigraph (the set of points on or above the graph of a function, graph of the function) is a convex set. Convex minimization is a subfield of mathematical optimization, optimization that studies the problem of minimizing convex functions over convex sets. The branch of mathematics devoted to the study of properties of convex sets and convex f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides have the same length, and all three angles are equal. Because of these properties, the equilateral triangle is a regular polygon, occasionally known as the regular triangle. It is the special case of an isosceles triangle by modern definition, creating more special properties. The equilateral triangle can be found in various tilings, and in polyhedrons such as the deltahedron and antiprism. It appears in real life in popular culture, architecture, and the study of stereochemistry resembling the molecular known as the trigonal planar molecular geometry. Properties An equilateral triangle is a triangle that has three equal sides. It is a special case of an isosceles triangle in the modern definition, stating that an isosceles triangle is defined at least as having two equal sides. Based on the modern definition, this leads to an equilateral triangle in which one of the three sides may be considered its base. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Defect
In geometry, the angular defect or simply defect (also called deficit or deficiency) is the failure of some angles to add up to the expected amount of 360° or 180°, when such angles in the Euclidean plane would. The opposite notion is the ''excess''. Classically the defect arises in two contexts: in the Euclidean plane, angles about a point add up to 360°, while interior angles in a triangle add up to 180°. However, on a convex polyhedron, the angles of the faces meeting at a vertex add up to ''less'' than 360° (a defect), while the angles at some vertices of a nonconvex polyhedron may add up to ''more'' than 360° (an excess). Also the angles in a hyperbolic triangle add up to ''less'' than 180° (a defect), while those on a spherical triangle add up to ''more'' than 180° (an excess). In modern terms, the defect at a vertex is a discrete version of the curvature of the polyhedral surface concentrated at that point. Negative defect indicates that the vertex resembles a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |