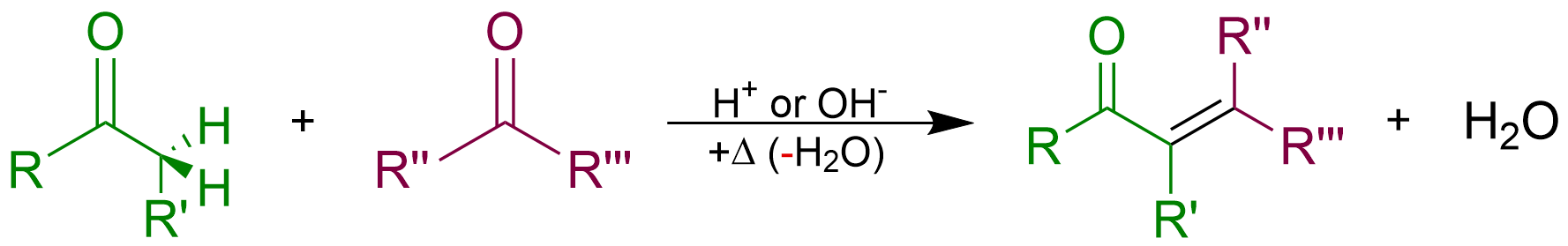|
Tartronic Semialdehyde
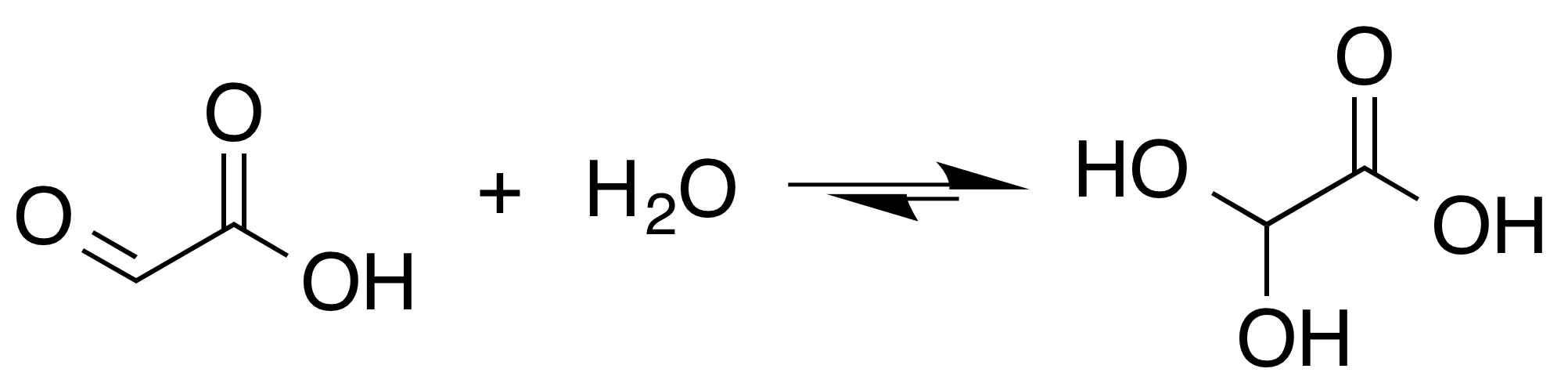
Tartronic acid semialdehyde is the organic compound with the formula OCHCH(OH)CO2H. The molecule has three functional groups, aldehyde, alcohol, and carboxylic acid. A white solid, it occurs naturally. At near neutral pH, it exists as the hydrated carboxylate (HO)2CHCH(OH)CO2−, which is referred to as tartronate semialdehyde. Tartronate semialdehyde is produced and consumed on a prodigious scale as an intermediate in photorespiration, an undesirable side reaction that competes with photosynthesis. It is produced biologically by the condensation Condensation is the change of the state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. The word most often refers to the water cycle. It can also be defined as the change in the state of water vapor ... of two equivalents of glyoxalate: :2{{nbspOC(H)CO2H → OC(H)CH(OH)CO2H + CO2 This condensation is catalyzed by tartronate-semialdehyde synthase. References Alpha hydroxy ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photorespiration
Photorespiration (also known as the oxidative photosynthetic carbon cycle or C2 cycle) refers to a process in plant physiology, plant metabolism where the enzyme RuBisCO oxygenates RuBP, wasting some of the energy produced by photosynthesis. The desired reaction is the addition of carbon dioxide to RuBP (carboxylation), a key step in the Calvin–Benson cycle, but approximately 25% of reactions by RuBisCO instead add oxygen to RuBP (Oxygenase, oxygenation), creating a product that cannot be used within the Calvin–Benson cycle. This process lowers the efficiency of photosynthesis, potentially lowering photosynthetic output by 25% in C3 carbon fixation, plants. Photorespiration involves a complex network of enzyme reactions that exchange metabolites between chloroplasts, leaf peroxisomes and mitochondria. The oxygenation reaction of RuBisCO is a wasteful process because 3-Phosphoglyceric acid, 3-phosphoglycerate is created at a lower rate and higher metabolic cost compared wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabolism. ''Photosynthesis'' usually refers to oxygenic photosynthesis, a process that produces oxygen. Photosynthetic organisms store the chemical energy so produced within intracellular organic compounds (compounds containing carbon) like sugars, glycogen, cellulose and starches. To use this stored chemical energy, an organism's cells metabolize the organic compounds through cellular respiration. Photosynthesis plays a critical role in producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, and it supplies most of the biological energy necessary for complex life on Earth. Some bacteria also perform anoxygenic photosynthesis, which uses bacteriochlorophyll to split hydrogen sulfide as a reductant instead of water, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensation Reaction
In organic chemistry, a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water. If water is lost, the reaction is also known as a dehydration synthesis. However other molecules can also be lost, such as ammonia, ethanol, acetic acid and hydrogen sulfide. The addition of the two molecules typically proceeds in a step-wise fashion to the addition product, usually in equilibrium, and with loss of a water molecule (hence the name condensation). The reaction may otherwise involve the functional groups of the molecule, and is a versatile class of reactions that can occur in acidic or basic conditions or in the presence of a catalyst. This class of reactions is a vital part of life as it is essential to the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids and to the biosynthesis of fatty acids. Many variations of condensation reactions exist. Common examples include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glyoxylic Acid
Glyoxylic acid or oxoacetic acid is an organic compound. Together with acetic acid, glycolic acid, and oxalic acid, glyoxylic acid is one of the C2 carboxylic acids. It is a colourless solid that occurs naturally and is useful industrially. Structure and nomenclature The structure of glyoxylic acid is shown as having an aldehyde functional group. The aldehyde is only a minor component of the form most prevalent in some situations. Instead, glyoxylic acid often exists as a hydrate or a cyclic dimer (chemistry), dimer. For example, in the presence of water, the carbonyl rapidly converts to a geminal diol (described as the "monohydrate"). The equilibrium constant (''K'') is 300 for the formation of dihydroxyacetic acid at room temperature: Dihydroxyacetic acid has been characterized by X-ray crystallography. : In aqueous solution, this monohydrate exists in equilibrium with a hemiacylal dimer form:Georges Mattioda and Yani Christidis “Glyoxylic Acid” Ullmann's Encyclopedia of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tartronate-semialdehyde Synthase
The enzyme tartronate-semialdehyde synthase () catalyzes the chemical reaction :2 glyoxylate \rightleftharpoons tartronate semialdehyde + CO2 This enzyme belongs to the family of lyases, specifically the carboxy-lyases, which cleave carbon-carbon bonds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is glyoxylate carboxy-lyase (dimerizing tartronate-semialdehyde-forming). Other names in common use include tartronate semialdehyde carboxylase, glyoxylate carbo-ligase, glyoxylic carbo-ligase, hydroxymalonic semialdehyde carboxylase, tartronic semialdehyde carboxylase, glyoxalate carboligase, and glyoxylate carboxy-lyase (dimerizing). This enzyme participates in glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism. It has 2 cofactors: FAD, and Thiamin diphosphate Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP or ThPP), or thiamine diphosphate (ThDP), or cocarboxylase is a thiamine (vitamin B1) derivative which is produced by the enzyme thiamine diphosphokinase. Thiamine pyrophosphate is a cofactor that is present ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Hydroxy Acids
Alpha hydroxy carboxylic acids, or α-hydroxy carboxylic acids (AHAs), are a group of carboxylic acids featuring a hydroxy group located ''one'' carbon atom away from the acid group. This structural aspect distinguishes them from beta hydroxy acids, where the functional groups are separated by ''two'' carbon atoms. Notable AHAs include glycolic acid, lactic acid, mandelic acid, and citric acid. α-Hydroxy acids are Strong acids, stronger acids compared to their non-alpha hydroxy counterparts, a property enhanced by internal hydrogen bonding. AHAs serve a dual purpose: industrially, they are utilized as additives in animal feed and as precursors for polymer synthesis. In cosmetics, they are commonly used for their ability to chemically exfoliate the skin. Occurrence Aldonic acids, a type of sugar acid, are a class of naturally occurring hydroxycarboxylic acids. They have the general chemical formula, HO2C(CHOH)''n''CH2OH. Gluconic acid, a particularly common aldonic acid, the oxidi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |