|
Tangled Nature Model
The tangled nature model is a model of evolutionary ecology developed by Christensen, Di Collobiano, Hall and Jensen. It is an agent-based model where individual 'organisms' interact, reproduce, mutate and die across many generations. A notable feature of the model is punctuated equilibrium, abrupt and spontaneous transitions between long lived stable states. In addition to evolutionary ecology the model has been used to study sustainability, organizational ecology, the Gaia hypothesis opinion dynamics and cultural evolution among other topics. Model Description Individuals in the model are represented by binary 'genomes' a of some fixed length L. All individuals with the same genome are equivalent and combine into 'species' with populations N_a where N = \sum_a^D N_a is the total population and D the number of distinct species. The individuals interact through a coupling matrix J. Typically some fraction of the potential entries are set to zero, as well as the diagonals J_ = 0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Ecology
Evolutionary ecology lies at the intersection of ecology and evolutionary biology. It approaches the study of ecology in a way that explicitly considers the evolutionary histories of species and the interactions between them. Conversely, it can be seen as an approach to the study of evolution that incorporates an understanding of the interactions between the species under consideration. The main subfields of evolutionary ecology are life history evolution, sociobiology (the evolution of social behavior), the evolution of interspecific interactions (e.g. cooperation, predator–prey interactions, parasitism, mutualism) and the evolution of biodiversity and of ecological communities. Evolutionary ecology mostly considers two things: how interactions (both among species and between species and their physical environment) shape species through selection and adaptation, and the consequences of the resulting evolutionary change. Evolutionary models A large part of evolutionary ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agent-based Model
An agent-based model (ABM) is a computational model for simulating the actions and interactions of autonomous agents (both individual or collective entities such as organizations or groups) in order to understand the behavior of a system and what governs its outcomes. It combines elements of game theory, complex systems, emergence, computational sociology, multi-agent systems, and evolutionary programming. Monte Carlo methods are used to understand the stochasticity of these models. Particularly within ecology, ABMs are also called individual-based models (IBMs). A review of recent literature on individual-based models, agent-based models, and multiagent systems shows that ABMs are used in many scientific domains including biology, ecology and social science. Agent-based modeling is related to, but distinct from, the concept of multi-agent systems or multi-agent simulation in that the goal of ABM is to search for explanatory insight into the collective behavior of agents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punctuated Equilibrium
In evolutionary biology, punctuated equilibrium (also called punctuated equilibria) is a Scientific theory, theory that proposes that once a species appears in the fossil record, the population will become stable, showing little evolution, evolutionary change for most of its geological history. : ''Reprinted in'' * * This state of little or no morphological change is called ''stasis''. When significant evolutionary change occurs, the theory proposes that it is generally restricted to rare and geologic time scale, geologically rapid events of branching speciation called cladogenesis. Cladogenesis is the process by which a species splits into two distinct species, rather than one species gradually transforming into another. Punctuated equilibrium is commonly contrasted with phyletic gradualism, the idea that evolution generally occurs uniformly by the steady and gradual transformation of whole lineages (anagenesis). In 1972, paleontologists Niles Eldredge and Stephen Jay Goul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
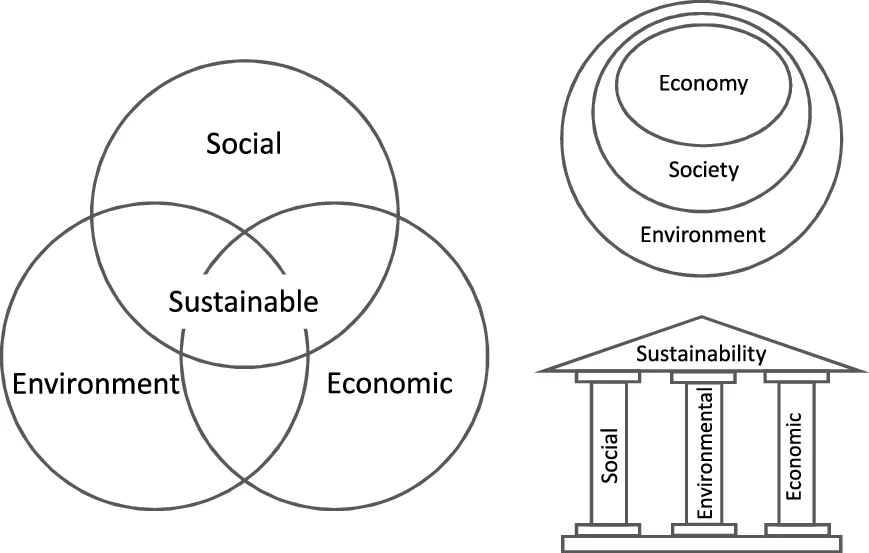
Sustainability
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions (or pillars): environmental, economic, and social. Many definitions emphasize the environmental dimension. This can include addressing key environmental problems, including climate change and biodiversity loss. The idea of sustainability can guide decisions at the global, national, organizational, and individual levels. A related concept is that of sustainable development, and the terms are often used to mean the same thing. UNESCO distinguishes the two like this: "''Sustainability'' is often thought of as a long-term goal (i.e. a more sustainable world), while ''sustainable development'' refers to the many processes and pathways to achieve it." Details around the economic dimension of sustainability are controversial. Scholars have discussed this under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organizational Ecology
Organizational ecology (also organizational demography and the population ecology of organizations) is a theoretical and empirical approach in the social sciences that is considered a sub-field of organizational studies. Organizational ecology utilizes insights from biology, economics,Douma, Sytse and Hein Schreuder, 2013. "Economic Approaches to Organizations". 5th edition. London: Pearso • and sociology, and employs statistical analysis to try to understand the conditions under which organizations emerge, grow, and die. The ecology of organizations is divided into three levels, the community, the population, and the organization. The community level is the functionally integrated system of interacting populations. The population level is the set of organizations engaged in similar activities. The organization level focuses on the individual organizations (some research further divides organizations into individual member and sub-unit levelsHannan, M., & Freeman, J. (1977). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaia Hypothesis
The Gaia hypothesis (), also known as the Gaia theory, Gaia paradigm, or the Gaia principle, proposes that living organisms interact with their Inorganic compound, inorganic surroundings on Earth to form a Synergy, synergistic and Homeostasis, self-regulating complex system that helps to maintain and perpetuate the conditions for life on the planet. The Gaia hypothesis was formulated by the chemist James Lovelock and co-developed by the microbiologist Lynn Margulis in the 1970s. Following the suggestion by his neighbour, novelist William Golding, Lovelock named the hypothesis after Gaia, the primordial deity who personified the Earth in Greek mythology. In 2006, the Geological Society of London awarded Lovelock the Wollaston Medal in part for his work on the Gaia hypothesis. Topics related to the hypothesis include how the biosphere and the evolution of organisms affect the stability of global temperature, salinity of seawater, atmospheric oxygen levels, the maintenance of a hyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigmoid Function
A sigmoid function is any mathematical function whose graph of a function, graph has a characteristic S-shaped or sigmoid curve. A common example of a sigmoid function is the logistic function, which is defined by the formula :\sigma(x) = \frac = \frac = 1 - \sigma(-x). Other sigmoid functions are given in the #Examples, Examples section. In some fields, most notably in the context of artificial neural networks, the term "sigmoid function" is used as a synonym for "logistic function". Special cases of the sigmoid function include the Gompertz curve (used in modeling systems that saturate at large values of ''x'') and the ogee curve (used in the spillway of some dams). Sigmoid functions have domain of all real numbers, with return (response) value commonly monotonically increasing but could be decreasing. Sigmoid functions most often show a return value (''y'' axis) in the range 0 to 1. Another commonly used range is from −1 to 1. A wide variety of sigmoid functions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of gametes or change in the number of chromosomes. The offspring that arise by asexual reproduction from either unicellular or multicellular organisms inherit the full set of genes of their single parent and thus the newly created individual is genetically and physically similar to the parent or an exact clone of the parent. Asexual reproduction is the primary form of reproduction for single-celled organisms such as archaea and eubacteria, bacteria. Many Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms including plants, animals, and Fungus, fungi can also reproduce asexually. In Vertebrate, vertebrates, the most common form of asexual reproduction is parthenogenesis, which is typically used as an alternative to sexual reproduction in times when reproductive opportunities are limited. Some Monitor lizard, monitor lizards, including Komodo dragons, can reproduce asexually. While all prokaryotes reproduce without the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tangled Nature Model Population
''Tangled'' is a 2010 American animated musical film, musical Adventure film, adventure fantasy comedy film produced by Walt Disney Animation Studios and released by Walt Disney Pictures. Loosely based on the German fairy tale "Rapunzel" in the Grimms' Fairy Tales, collection of folktales published by the Brothers Grimm, the film was directed by Nathan Greno and Byron Howard, and produced by Roy Conli, from a screenplay written by Dan Fogelman. Featuring the voices of Mandy Moore, Zachary Levi, and Donna Murphy, ''Tangled'' tells the story of Rapunzel (Tangled), Rapunzel, a lost young princess with magical long blonde hair who yearns to leave her secluded tower. She accepts the aid of an intruder, the outlaw Flynn Rider, to take her out into the world which she has never seen. Originally conceived and proposed by Disney animator Glen Keane in 2001, ''Tangled'' spent six years in production at a cost that has been estimated at $260 million, which, if accurate, would make it the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |