|
Subcutaneous Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis, an inflammatory disease, involves the skin in about 25% of patients. The most common lesions are erythema nodosum, plaques, maculopapular eruptions, subcutaneous nodules, and lupus pernio. Treatment is not required, since the lesions usually resolve spontaneously in two to four weeks. Although it may be disfiguring, cutaneous sarcoidosis rarely causes major problems.Harrison's Practice , Sarcoidosis. Classification Morphology Ulcerative sarcoidosis is a cutaneous condition affecting roughly 5% of people with . Annular sarcoidosis is a cutaneous condition characterized b ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcoidosis
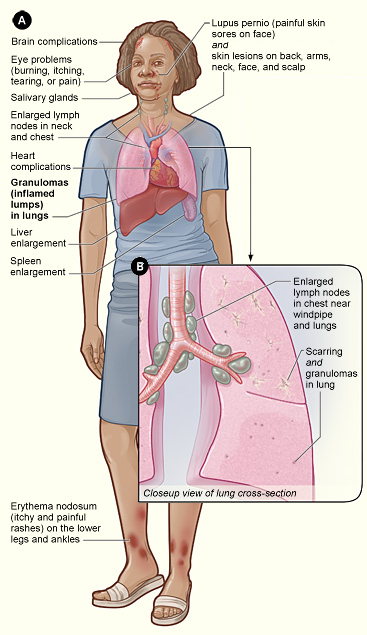
Sarcoidosis (; also known as Besnier–Boeck–Schaumann disease) is a disease involving abnormal collections of White blood cell, inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph nodes. Less commonly affected are the eyes, liver, heart, and Human brain, brain, though any Organ (anatomy), organ can be affected. The signs and symptoms depend on the organ involved. Often, no symptoms or only mild symptoms are seen. When it affects the lungs, wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, or chest pain may occur. Some may have Löfgren syndrome with fever, Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy, enlarged hilar lymph nodes, arthritis, and a rash known as erythema nodosum. The cause of sarcoidosis is unknown. Some believe it may be due to an immune reaction to a trigger such as an infection or chemicals in those who are genetically predisposed. Those with affected family members are at greater risk. Diagnosis is partly based on signs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin Ulcers
An ulcer is a sore on the skin or a mucous membrane, accompanied by the disintegration of tissue. Ulcers can result in complete loss of the epidermis and often portions of the dermis and even subcutaneous fat. Ulcers are most common on the skin of the lower extremities and in the gastrointestinal tract. An ulcer that appears on the skin is often visible as an inflamed tissue with an area of reddened skin. A skin ulcer is often visible in the event of exposure to heat or cold, irritation, or a problem with blood circulation. They can also be caused due to a lack of mobility, which causes prolonged pressure on the tissues. This stress in the blood circulation is transformed to a skin ulcer, commonly known as bedsores or decubitus ulcers. Ulcers often become infected, and pus forms. Signs and symptoms Skin ulcers appear as open craters, often round, with layers of skin that have eroded. The skin around the ulcer may be red, swollen, and tender. Patients may feel pain on the skin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (; also known as Besnier–Boeck–Schaumann disease) is a disease involving abnormal collections of White blood cell, inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph nodes. Less commonly affected are the eyes, liver, heart, and Human brain, brain, though any Organ (anatomy), organ can be affected. The signs and symptoms depend on the organ involved. Often, no symptoms or only mild symptoms are seen. When it affects the lungs, wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, or chest pain may occur. Some may have Löfgren syndrome with fever, Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy, enlarged hilar lymph nodes, arthritis, and a rash known as erythema nodosum. The cause of sarcoidosis is unknown. Some believe it may be due to an immune reaction to a trigger such as an infection or chemicals in those who are genetically predisposed. Those with affected family members are at greater risk. Diagnosis is partly based on signs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erythema Nodosum
Erythema nodosum (EN) is an inflammatory condition characterized by inflammation of subcutaneous fat tissue, resulting in painful red/blue lumps or nodules that are usually seen symmetrically on both shins, on the thighs, arms, and elsewhere. It can be caused by a variety of conditions but 20 to 50% of cases are idiopathic. It typically resolves spontaneously within 30 days. It is common in young people aged 12–20 years. Signs and symptoms Pre-eruptive phase The first signs of erythema nodosum are often flu-like symptoms such as a fever, cough, malaise, and aching joints. Some people also experience stiffness or swelling in the joints and weight loss. Eruptive phase Erythema nodosum is characterised by nodules (rounded lumps) below the skin surface, usually on the shins. These subcutaneous nodules can appear anywhere on the body, but the most common sites are the shins, arms, thighs, and torso. Each nodule typically disappears after around two weeks, though new ones may co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maculopapular
A maculopapular rash is a type of rash characterized by a flat, red area on the skin that is covered with small confluent bumps. It may only appear red in lighter-skinned people. The term "maculopapular" is a compound: '' macules'' are small, flat discolored spots on the surface of the skin; and ''papules'' are small, raised bumps. It is also described as erythematous, or red. This type of rash is common in several diseases and medical conditions, including scarlet fever, measles, Ebola virus disease, rubella, HIV, secondary syphilis (Congenital syphilis, which is asymptomatic, the newborn may present this type of rash), erythrovirus (parvovirus B19), chikungunya (alphavirus), zika, smallpox (which has been eradicated), varicella (when vaccinated persons exhibit symptoms from the modified form), heat rash, and sometimes in Dengue fever. It is also a common manifestation of a skin reaction to the antibiotic amoxicillin or chemotherapy drugs. Cutaneous infiltration of leukem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lupus Pernio
Lupus pernio is a chronic raised indurated (hardened) lesion of the skin, often purplish in color. It is seen on the nose, ears, cheeks, lips, and forehead. It is pathognomonic of sarcoidosis. The name "lupus pernio" is a misnomer, as microscopically this disease shows granulomatous infiltration and does not have features of either lupus nor pernio. Signs and symptoms The hallmarks of lupus pernio are violaceous or erythematous, indurated plaques that are mostly found on the cheeks and nose in the center of the face. Rarely, lesions may also affect the dorsum of the hands and feet and the ears. The symptoms of lupus pernio range from a few tiny nodules on the nose to vibrant plaques that cover both cheeks. Lupus pernio lesions begin slowly but eventually penetrate and indurate into the underlying bone and cartilage, resulting in deformity. There is a higher chance of extracutaneous involvement, especially in the respiratory tract, in lupus pernio. Causes The cause of cutane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papule
A papule is a small, well-defined bump in the skin lesion, skin. It may have a rounded, pointed or flat top, and may have a umbilication, dip. It can appear with a Peduncle (anatomy), stalk, be thread-like or look warty. It can be soft or firm and its surface may be rough or smooth. Some have Crust (dermatology), crusts or Scale (dermatology), scales. A papule can be flesh colored, yellow, white, brown, red, blue or purplish. There may be just one or many, and they may occur irregularly in different parts of the body or appear in clusters. It does not contain fluid but may progress to a pustule or vesicle (dermatology), vesicle. A papule is smaller than a Nodule (medicine), nodule; it can be as tiny as a pinhead and is typically less than 1 cm in width, according to some sources, and 0.5 cm according to others. When merged together, it appears as a plaque. A papule's colour might indicate its cause, such as white in Milium (dermatology), milia, red in eczema, yellowish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin Lesion
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. Conditions of the human integumentary system constitute a broad spectrum of diseases, also known as dermatoses, as well as many nonpathologic states (like, in certain circumstances, melanonychia and racquet nails). While only a small number of skin diseases account for most visits to the physician, thousands of skin conditions have been described. Classification of these conditions often presents many nosological challenges, since underlying causes and pathogenetics are often not known. Therefore, most current textbooks present a classification based on location (for example, conditions of the mucous membrane), morphology ( chronic blistering conditions), cause ( skin conditions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphea
Morphea is a form of scleroderma that mainly involves isolated patches of hardened skin on the face, hands, and feet, or anywhere else on the body, usually with no internal organ involvement. However, in Deep Morphea inflammation and sclerosis can be found in the deep dermis, panniculus, fascia, superficial muscle and bone. Signs and symptoms Morphea most often presents as macules or plaques a few centimeters in diameter, but also may occur as bands or in guttate lesions or nodules. Morphea is a thickening and hardening of the skin and subcutaneous tissues from excessive collagen deposition. Morphea includes specific conditions ranging from very small plaques only involving the skin to widespread disease causing functional and cosmetic deformities. Morphea discriminates from systemic sclerosis by its supposed lack of internal organ involvement. This classification scheme does not include the mixed form of morphea in which different morphologies of skin lesions are pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypopigmentation
Hypopigmentation is characterized specifically as an area of Human skin, skin becoming lighter than the baseline skin color, but not completely devoid of skin pigment, pigment. This is not to be confused with depigmentation, which is characterized as the absence of all pigment. It is caused by melanocyte or melanin depletion, or a decrease in the amino acid tyrosine, which is used by melanocytes to make melanin. Some common genetic causes include mutations in the tyrosinase gene or OCA2 gene. As melanin pigments tend to be in the skin, eye, and hair, these are the commonly affected areas in those with hypopigmentation. Hypopigmentation is common and approximately one in twenty have at least one hypopigmented macule. Hypopigmentation can be upsetting to some, especially those with darker skin whose hypopigmentation marks are seen more visibly. Most causes of hypopigmentation are not serious and can be easily treated. Presentation Associated conditions It is seen in: * Albinism * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation. Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different developmental origin, structure and chemical composition. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'' 'skin'). In mammals, the skin is an organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments, and internal organs. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibians, reptiles, and birds. Skin (including cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues) plays crucial roles in formation, structure, and function of extraskeletal apparatus such as horns of bovids (e.g., cattle) and rhinos, cervids' antlers, giraffids' ossicones, armadillos' osteoderm, and os penis/ os clitoris. All mammals have some hair on their skin, even marine mammals like whales, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyosis Vulgaris
Ichthyosis vulgaris (also known as "autosomal dominant ichthyosis" and "Ichthyosis simplex") is a skin disorder causing dry, scaly skin. It is the most common form, and one of the mildest forms, of ichthyosis,Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. . affecting around 1 in 250 people. For this reason it is known as common ichthyosis. It is usually an autosomal dominant inherited disease (often associated with filaggrin), although a rare non-heritable version called acquired ichthyosis exists. Presentation Ichthyosis vulgaris is the most common type within the ichthyoses, a diverse group of inherited skin disorders characterized by the way the skin produces keratin. These conditions all share the common trait of causing generalized skin scaling, which can range in its intensity. In comparison to the other forms of ichthyosis, IV is generally viewed as the least severe. The symptoms of the inherited form of ichthyosis vulg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |