|
Subacromial Space
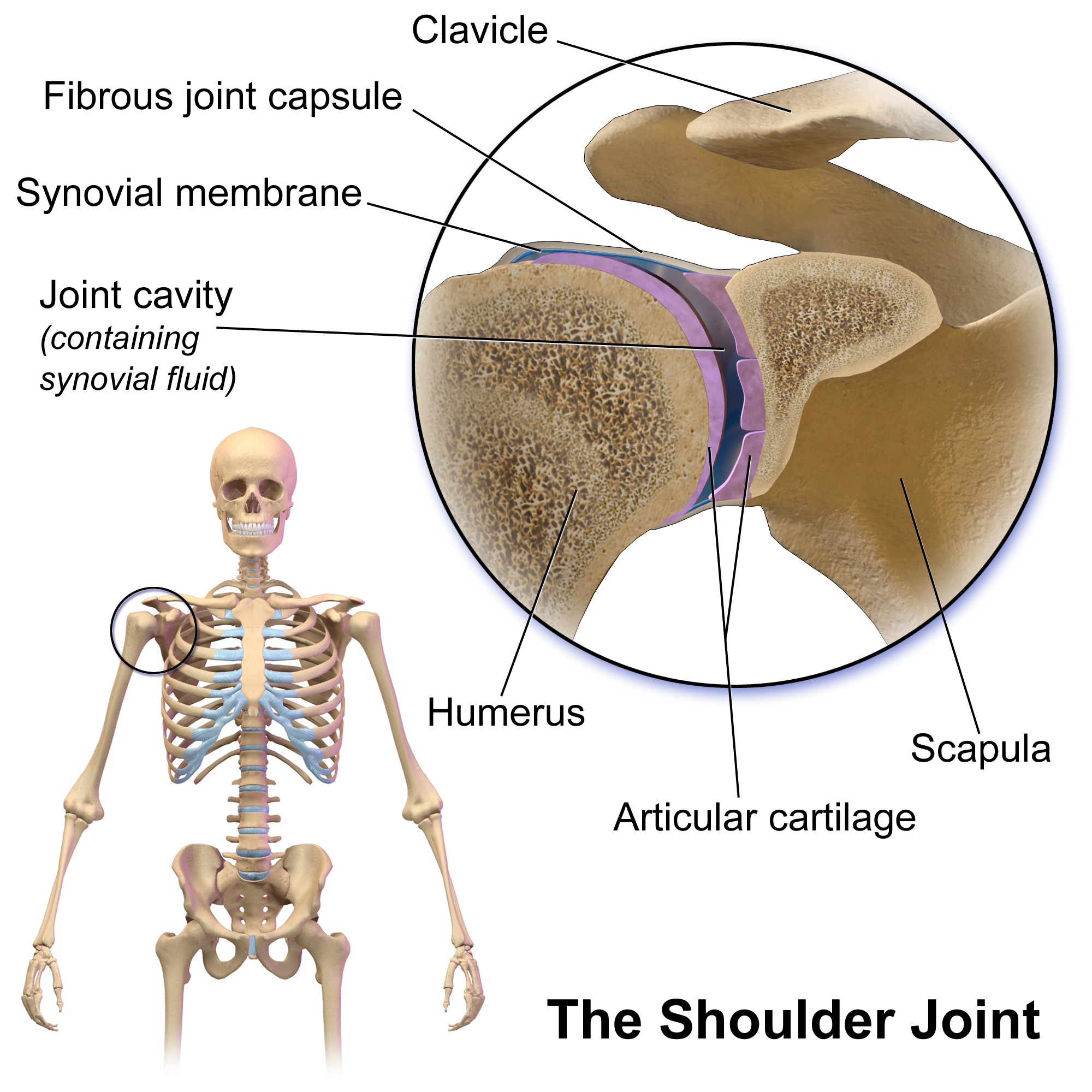
The shoulder joint (or glenohumeral joint from Greek ''glene'', eyeball, + -''oid'', 'form of', + Latin ''humerus'', shoulder) is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves an articulation between the glenoid fossa of the scapula (shoulder blade) and the head of the humerus (upper arm bone). Due to the very loose joint capsule, it gives a limited interface of the humerus and scapula, it is the most mobile joint of the human body. Structure The shoulder joint is a ball-and-socket joint between the scapula and the humerus. The socket of the glenoid fossa of the scapula is itself quite shallow, but it is made deeper by the addition of the glenoid labrum. The glenoid labrum is a ring of cartilaginous fibre attached to the circumference of the cavity. This ring is continuous with the tendon of the biceps brachii above. Spaces Significant joint spaces are: * The normal glenohumeral space is 4– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoulder
The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone) as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons. The articulations between the bones of the shoulder make up the shoulder joints. The shoulder joint, also known as the glenohumeral joint, is the major joint of the shoulder, but can more broadly include the acromioclavicular joint. In human anatomy, the shoulder joint comprises the part of the body where the humerus attaches to the scapula, and the head sits in the glenoid cavity. The shoulder is the group of structures in the region of the joint. The shoulder joint is the main joint of the shoulder. It is a ball and socket joint that allows the arm to rotate in a circular fashion or to hinge out and up away from the body. The joint capsule is a soft tissue envelope that encircles the glenohumeral joint and attaches to the scapula, humerus, and head of the biceps. It is lined by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Dislocation
A joint dislocation, also called luxation, occurs when there is an abnormal separation in the joint, where two or more bones meet. A partial dislocation is referred to as a subluxation. Dislocations are commonly caused by sudden Trauma (medicine), trauma to the joint like during a car accident or fall. A joint dislocation can damage the surrounding ligaments, tendons, muscles, and nerves. Dislocations can occur in any major joint (shoulder, knees, hips) or minor joint (toes, fingers). The most common joint dislocation is a shoulder dislocation. The treatment for joint dislocation is usually by closed reduction (orthopedic surgery), reduction, that is, skilled manipulation to return the bones to their normal position. Only trained medical professionals should perform reductions since the manipulation can cause injury to the surrounding soft tissue, nerves, or vascular structures. Signs and Symptoms The following symptoms are common with any type of dislocation. * Intense pain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
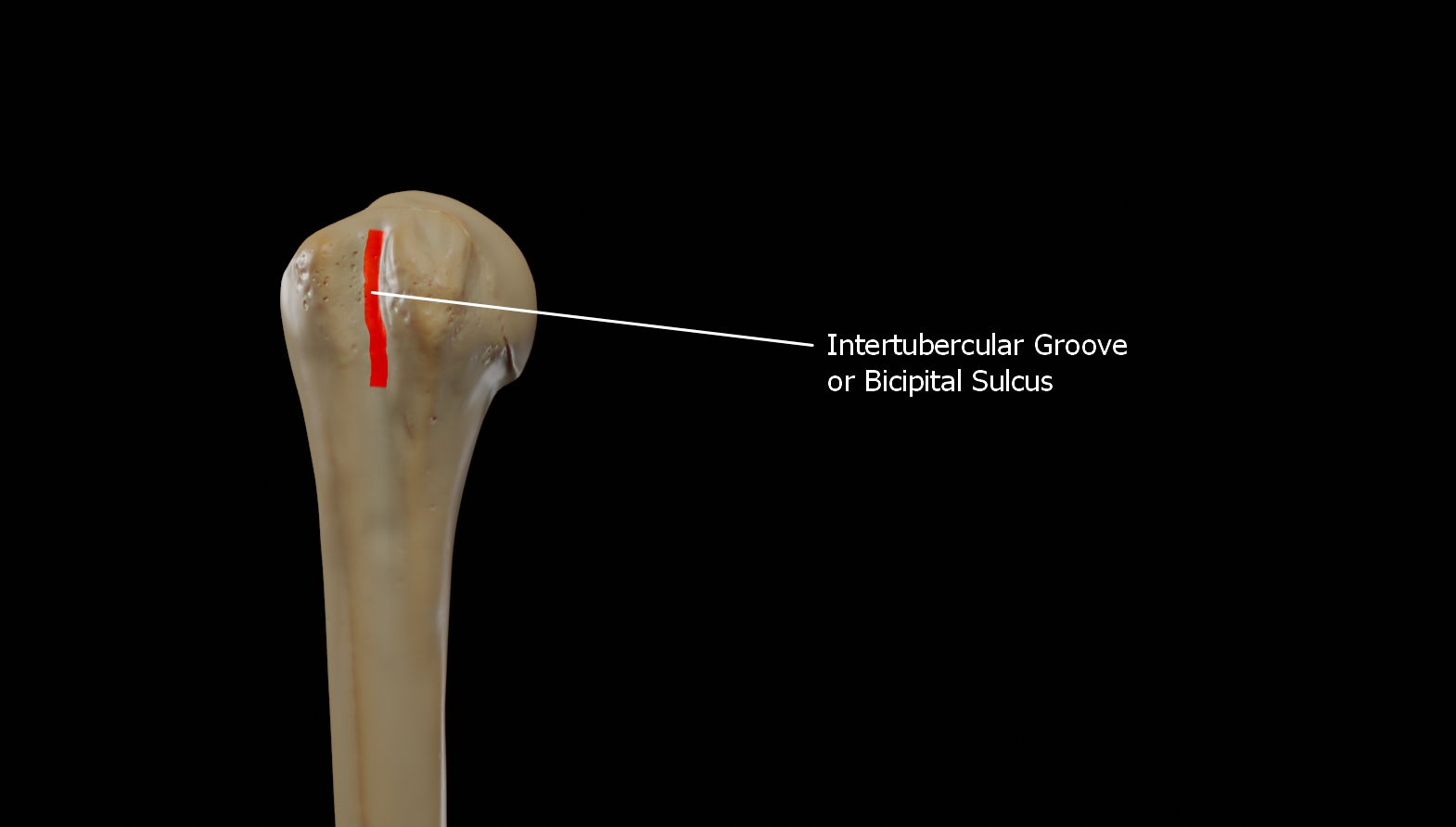
Bicipital Groove
The bicipital groove (intertubercular groove, sulcus intertubercularis) is a deep groove on the humerus that separates the greater tubercle from the lesser tubercle. It allows for the long tendon of the biceps brachii muscle to pass. Structure The bicipital groove separates the greater tubercle from the lesser tubercle. It is usually around 8 cm long and 1 cm wide in adults. The groove lodges the long tendon of the biceps brachii muscle, positioned between the tendon of the pectoralis major muscle on the lateral lip and the tendon of the teres major muscle on the medial lip. It also transmits a branch of the anterior humeral circumflex artery to the shoulder joint. The insertion of the latissimus dorsi muscle is found along the floor of the bicipital groove. The teres major muscle inserts on the medial lip of the groove. It runs obliquely downward, and ends near the junction of the upper with the middle third of the bone. It is the lateral wall of the axilla. Function The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotator Cuff
The rotator cuff (SITS muscles) is a group of muscles and their tendons that act to stabilize the human shoulder and allow for its extensive range of motion. Of the seven scapulohumeral muscles, four make up the rotator cuff. The four muscles are: * supraspinatus muscle * infraspinatus muscle * teres minor muscle * subscapularis muscle. Structure Muscles composing rotator cuff The supraspinatus muscle spreads out in a horizontal band to insert on the superior facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus. The greater tubercle projects as the most Lateral (anatomy), lateral structure of the humeral head. Medial (anatomy), Medial to this, in turn, is the lesser tubercle of the humeral head. The subscapularis muscle Origin (anatomy), origin is divided from the remainder of the rotator cuff origins as it is deep to the scapula. The four tendons of these muscles converge to form the rotator cuff tendon. These tendinous Insertion (anatomy), insertions along with the articular cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supra-acromial Bursa
The supra-acromial bursa is located on the superior aspect of the acromion and normally does not communicate with the glenohumeral joint.Resnick D. Diagnosis of bone and joint disorders. 3rd edition. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Company; 1995. Supra-acromial bursitis has not been receiving much attention from literature and remains described mainly as case reports of presumptive diagnosis with no histopathological correlation.Arend CF. Ultrasound of the Shoulder. Master Medical Books, 2013. Free chapter on ultrasound evaluation of the supra-acromial bursa available aShoulderUS.com Since the bursa is supra-acromial, not supraclavicular, fluid-filled masses located over the acromioclavicular joint or distal clavicle do not correspond to supra-acromial bursitis. See also * Subacromial bursa The subacromial bursa is the synovial cavity located just below the acromion, which communicates with the subdeltoid bursa in most individuals, forming the so-called subacromial-subdeltoid bursa (SSB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coracobrachialis Muscle
The coracobrachialis muscle muscle in the upper medial part of the arm. It is located within the anterior compartment of the arm. It originates from the coracoid process of the scapula; it inserts onto the middle of the medial aspect of the body of the humerus. It is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve. It acts to adduct and flex the arm. Structure Origin Coracobrachialis muscle arises from the (deep surface of the) apex of the coracoid process of the scapula (a common origin with the short head of the biceps brachii). It additionally also arises from the proximal portion of tendon of origin of the biceps brachii muscle. Insertion It is inserted (by means of a flat tendon) into an impression at the middle of the medial border of the body of the humerus (shaft of the humerus) between the attachments of the medial head of the triceps brachii and the brachialis. Innervation Coracobrachialis muscle is perforated by and innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve, which a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subscapularis Muscle
The subscapularis is a large triangular muscle which fills the subscapular fossa and inserts into the lesser tubercle of the humerus and the front of the capsule of the shoulder-joint. Structure The subscapularis is covered by a dense fascia which attaches to the scapula at the margins of the subscapularis' attachment (origin) on the scapula. The muscle's fibers pass laterally from its origin before coalescing into a tendon of insertion. The tendon intermingles with the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint capsule. A bursa (which communicates with the cavity of the shoulder jointMilano, Giuseppe and Grasso, AndreaShoulder Arthroscopy: Principles and Practice, Springer Science & Business Media, Dec 16, 2013. . Accessed 2016-11-07. via an aperture in the joint capsule) intervenes between the tendon and a bare area at the lateral angle of the scapula/the neck of the scapula. The subscapularis (supraserratus) bursa separates the subscapularis is from the serratus anterior. Origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coracoid Process
The coracoid process (from Greek κόραξ, raven) is a small hook-like structure on the lateral edge of the superior anterior portion of the scapula (hence: coracoid, or "like a raven's beak"). Pointing laterally forward, it, together with the acromion, serves to stabilize the shoulder joint. It is palpable in the deltopectoral groove between the deltoid and pectoralis major muscles. Structure The coracoid process is a thick curved process attached by a broad base to the upper part of the neck of the scapula; it runs at first upward and medially; then, becoming smaller, it changes its direction, and projects forward and laterally. The component parts of the process are the base; angle; shaft; and apex of the coracoid process, respectively. The coracoglenoid notch is an indentation localized between the coracoid process and the glenoid. As the coracoid process projects laterally, it defines the subcoracoid space beneath. The ''ascending portion'', flattened from the fron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcoracoid Bursa
The subcoracoid bursa or subcoracoid bursa of Collas is a synovial bursa located in the shoulder. It is located anterior to the subscapularis muscle and inferior to the coracoid process. Its function is to reduce friction between the coracobrachialis, subscapularis and short head of the biceps tendons, thus facilitating internal and external rotation of the shoulder. The subcoracoid bursa does not communicate with the glenohumeral joint under normal circumstances, but may communicate with the subacromial bursa. As such, contrast fluid injected into the glenohumeral joint during an arthrogram that extends into the subcoracoid bursa is abnormal, and indirectly implies a full thickness rotator cuff The rotator cuff (SITS muscles) is a group of muscles and their tendons that act to stabilize the human shoulder and allow for its extensive range of motion. Of the seven scapulohumeral muscles, four make up the rotator cuff. The four muscles a ... tear. References {{Bursae and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acromion
In human anatomy, the acromion (from Greek: ''akros'', "highest", ''ōmos'', "shoulder", : acromia) or summit of the shoulder is a bony process on the scapula (shoulder blade). Together with the coracoid process, it extends laterally over the shoulder joint. The acromion is a continuation of the scapular spine, and hooks over anteriorly. It articulates with the clavicle (collar bone) to form the acromioclavicular joint. Structure The acromion forms the summit of the shoulder and is a large, somewhat triangular or oblong process, flattened from behind forward. It projects laterally at first, then curves forward and upward to overhang the glenoid fossa.''Gray's Anatomy'' 1918, see infobox It starts from the base of acromion which marks its projecting point emerging from the spine of scapula. Surfaces Its superior surface, directed upward, backward, and lateralward, is convex, rough, and gives attachment to some fibers of the deltoideus, and in the rest of its extent is subc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subacromial Bursa
The subacromial bursa is the synovial cavity located just below the acromion, which communicates with the subdeltoid bursa in most individuals, forming the so-called subacromial-subdeltoid bursa (SSB). The SSB bursa is located deep to the deltoid muscle and the coracoacromial arch and extends laterally beyond the humeral attachment of the rotator cuff, anteriorly to overlie the intertubercular groove, medially to the acromioclavicular joint, and posteriorly over the rotator cuff. The SSB decreases friction, and allows free motion of the rotator cuff relative to the coracoacromial arch and the deltoid muscle. French anatomist and surgeon Jean-François Jarjavay is credited as the first to describe morbid processes of the SSB in 1867. Since then, histologic studies have documented that synovial membrane may undergo inflammatory and/or degenerative changes and many now believe that they correspond to different stages in the spectrum of disease, with long-lasting inflammation leadin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deltoid Muscle
The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the shoulder, human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle is made up of three distinct sets of muscle fibers, namely the # anterior or clavicular part (pars clavicularis) ( More commonly known as the front delt.) # posterior or scapular part (pars scapularis) ( More commonly known as the rear delt.) # intermediate or acromial part (pars acromialis) ( More commonly known as the side delt) The deltoid's fibres are pennate muscle. However, electromyography suggests that it consists of at least seven groups that can be independently coordinated by the nervous system. It was previously called the deltoideus (plural ''deltoidei'') and the name is still used by some anatomists. It is called so because it is in the shape of the Greek alphabet, Greek capital letter Delta (letter), delta (Δ). Deltoid is also further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |