|
Coracobrachialis Muscle
The coracobrachialis muscle muscle in the upper medial part of the arm. It is located within the anterior compartment of the arm. It originates from the coracoid process of the scapula; it inserts onto the middle of the medial aspect of the body of the humerus. It is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve. It acts to adduct and flex the arm. Structure Origin Coracobrachialis muscle arises from the (deep surface of the) apex of the coracoid process of the scapula (a common origin with the short head of the biceps brachii). It additionally also arises from the proximal portion of tendon of origin of the biceps brachii muscle. Insertion It is inserted (by means of a flat tendon) into an impression at the middle of the medial border of the body of the humerus (shaft of the humerus) between the attachments of the medial head of the triceps brachii and the brachialis. Innervation Coracobrachialis muscle is perforated by and innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve, which a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coracoid Process
The coracoid process (from Greek κόραξ, raven) is a small hook-like structure on the lateral edge of the superior anterior portion of the scapula (hence: coracoid, or "like a raven's beak"). Pointing laterally forward, it, together with the acromion, serves to stabilize the shoulder joint. It is palpable in the deltopectoral groove between the deltoid and pectoralis major muscles. Structure The coracoid process is a thick curved process attached by a broad base to the upper part of the neck of the scapula; it runs at first upward and medially; then, becoming smaller, it changes its direction, and projects forward and laterally. The component parts of the process are the base; angle; shaft; and apex of the coracoid process, respectively. The coracoglenoid notch is an indentation localized between the coracoid process and the glenoid. As the coracoid process projects laterally, it defines the subcoracoid space beneath. The ''ascending portion'', flattened from the fron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triceps Brachii
The triceps, or triceps brachii (Latin for "three-headed muscle of the arm"), is a large muscle on the back of the upper limb of many vertebrates. It consists of three parts: the medial, lateral, and long head. All three heads cross the elbow joint. However, the long head also crosses the shoulder joint. The triceps muscle contracts when the elbow is straightened and expands when the elbow is bent. The long head gets a further contraction when the arm is behind the torso due to how it crosses the shoulder joint. It is the muscle principally responsible for extension of the elbow joint (straightening of the arm). Structure * The long head arises from the infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula. It extends distally anterior to the teres minor and posterior to the teres major. * The medial head arises proximally in the humerus, just inferior to the groove of the radial nerve; from the dorsal (back) surface of the humerus; from the medial intermuscular septum; and its distal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avulsion Fracture
An avulsion fracture is a bone fracture which occurs when a fragment of bone tears away from the main mass of bone as a result of physical trauma. This can occur at the ligament by the application of forces external to the body (such as a fall or pull) or at the tendon by a muscular contraction that is stronger than the forces holding the bone together. Generally muscular avulsion is prevented by the neurological limitations placed on muscle contractions. Highly trained Athlete, athletes can overcome this neurological inhibition of strength and produce a much greater force output capable of breaking or avulsing a bone. Types Dental avulsion dental trauma, Traumatic complete displacement of a tooth from its socket in alveolar bone. It is a serious dental emergency in which Treatment of knocked-out (avulsed) teeth, prompt management (within 20–40 minutes of injury) affects the prognosis of the tooth. Tuberosity avulsion of the 5th metatarsal file:Proximal fractures of 5th me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strain (injury)
A strain is an acute or chronic soft tissue injury that occurs to a muscle, tendon, or both. The equivalent injury to a ligament is a sprain. Generally, the muscle or tendon overstretches and partially tears, under more physical stress than it can withstand, often from a sudden increase in duration, intensity, or frequency of an activity. Strains most commonly occur in the foot, leg, or back. Immediate treatment typically used to include four steps abbreviated as R.I.C.E. (rest, ice, compression, elevation) before the role of inflammation was found to be helpful. Signs and symptoms Typical signs and symptoms of a strain include pain, functional loss of the involved structure, muscle weakness, contusion, and localized inflammation. A strain can range from mild overstretching to severe tears, depending on the extent of injury. Cause A strain can occur as a result of improper body mechanics with any activity (e.g., contact sports, lifting heavy objects) that can induce m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Motion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
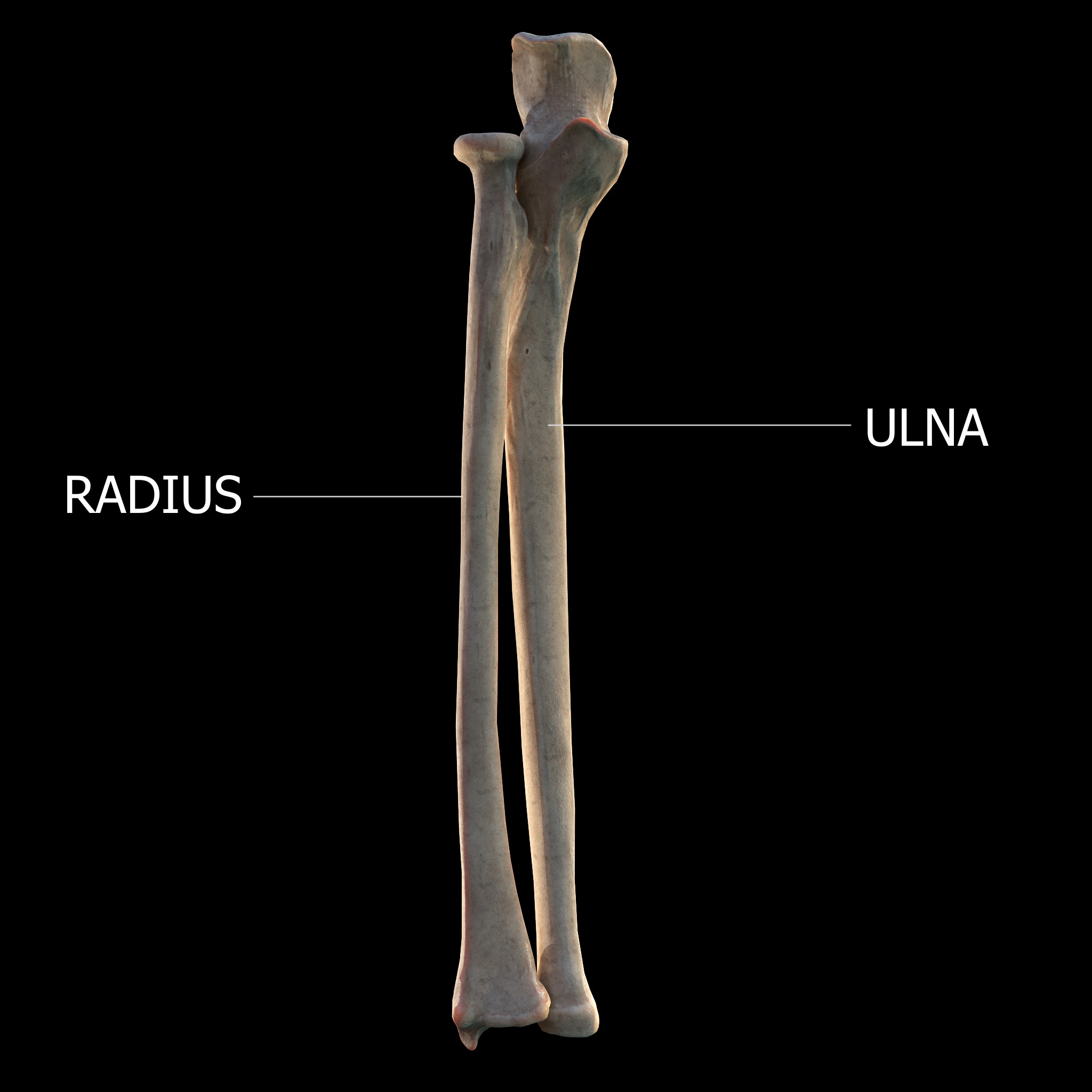
Forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus. The forearm contains two long bones, the radius and the ulna, forming the two radioulnar joints. The interosseous membrane connects these bones. Ultimately, the forearm is covered by skin, the anterior surface usually being less hairy than the posterior surface. The forearm contains many muscles, including the flexors and extensors of the wrist, flexors and extensors of the digits, a flexor of the elbow ( brachioradialis), and pronators and supinators that turn the hand to face down or upwards, respectively. In cross-section, the forearm can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Compression Syndrome
Nerve compression syndrome, or compression neuropathy, or nerve entrapment syndrome, is a medical condition caused by chronic, direct pressure on a peripheral nerve. It is known colloquially as a ''trapped nerve'', though this may also refer to nerve root compression (by a herniated disc, for example). Its symptoms include pain, tingling, numbness and muscle weakness. The symptoms affect just one particular part of the body, depending on which nerve is affected. The diagnosis is largely clinical and can be confirmed with diagnostic nerve blocks. Occasionally imaging and electrophysiology studies aid in the diagnosis. Timely diagnosis is important as untreated chronic nerve compression may cause permanent damage. A surgical nerve decompression can relieve pressure on the nerve but cannot always reverse the physiological changes that occurred before treatment. Nerve injury by a single episode of physical trauma is in one sense an acute compression neuropathy but is not usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachial Plexus
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves (nerve plexus) formed by the anterior rami of the lower four Spinal nerve#Cervical nerves, cervical nerves and first Spinal nerve#Thoracic nerves, thoracic nerve (cervical spinal nerve 5, C5, Cervical spinal nerve 6, C6, cervical spinal nerve 7, C7, cervical spinal nerve 8, C8, and thoracic spinal nerve 1, T1). This plexus extends from the spinal cord, through the cervicoaxillary canal in the neck, over the first rib, and into the axilla, armpit, it supplies Afferent nerve fiber, afferent and efferent nerve fibers to the chest, shoulder, arm, forearm, and hand. Structure The brachial plexus is divided into five ''roots'', three ''trunks'', six ''divisions'' (three anterior and three posterior), three ''cords'', and five ''branches''. There are five "terminal" branches and numerous other "pre-terminal" or "collateral" branches, such as the subscapular nerve, the thoracodorsal nerve, and the long thoracic nerve, that leave the plexus at vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Spinal Nerve 7
The cervical spinal nerve 7 (C7) is a spinal nerve A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries Motor neuron, motor, Sensory neuron, sensory, and Autonomic nervous system, autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each s ... of the cervical segment. Nervous System -- Groups of Nerves It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 7 (C7). It runs through the interspace between the C6 and C7 vertebrae. Additional images References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Spinal Nerve 6
The cervical spinal nerve 6 (C6) is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment. It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 6 (C6). The C6 nerve root shares a common branch from C5, and has a role in innervating many muscles of the rotator cuff and distal arm, including: * Subclavius *Supraspinatus * Infraspinatus *Biceps brachii * Brachialis *Deltoid * Teres minor *Brachioradialis *Serratus anterior *Subscapularis * Pectoralis major * Coracobrachialis * Teres major *Supinator * Extensor carpi radialis longus *Latissimus dorsi Damage to the C6 motor neuron, by way of impingement, ischemia, trauma, or degeneration of nerve tissue, can cause denervation Denervation is any loss of nerve supply regardless of the cause. If the nerves lost to denervation are part of neural communication to an organ system or for a specific tissue function, alterations to or compromise of physiological functioning ca ... of one or more of the associated muscles. Muscle atr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Spinal Nerve 5
The cervical spinal nerve 5 (C5) is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment. Nervous System -- Groups of Nerves It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 5 (C5). It contributes to the , , and before joining |
Upper Trunk
The upper (superior) trunk is part of the brachial plexus. It is formed by joining of the ventral rami of the fifth (C5) and sixth (C6) cervical nerves. The upper trunk divides into an anterior and posterior division. The branches of the upper trunk from proximal to distal are: * subclavian nerve (C5-C6) * suprascapular nerve (C5-C6) *anterior division of upper trunk (C5-C6, forms part of lateral cord) *posterior division of upper trunk (C5-C6, forms part of posterior cord) The axillary, radial, musculocutaneous and median nerve The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus. The median nerve originates from the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, and has cont ...s all contain axons derived from the upper trunk. Additional images File:Slide1cord.JPG, Brachial plexus. Deep dissection. File:Slide1ecc.JPG, Brachial plexus. Deep dissection. Anterolateral view {{ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |